In Vitro Anti-Inflammatory Activity and Structural Characteristics of Polysaccharides Extracted from Lobonema smithii Jellyfish
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Chemical Composition of Polysaccharides Isolated from L. smithii
2.2. Molecular Weight (Mw) Analysis
2.3. Effects of L. smithii Polysaccharides on the Cell Viability and NO Production
2.4. JF3 Inhibits LPS-Induced Cell Viability and NO Production
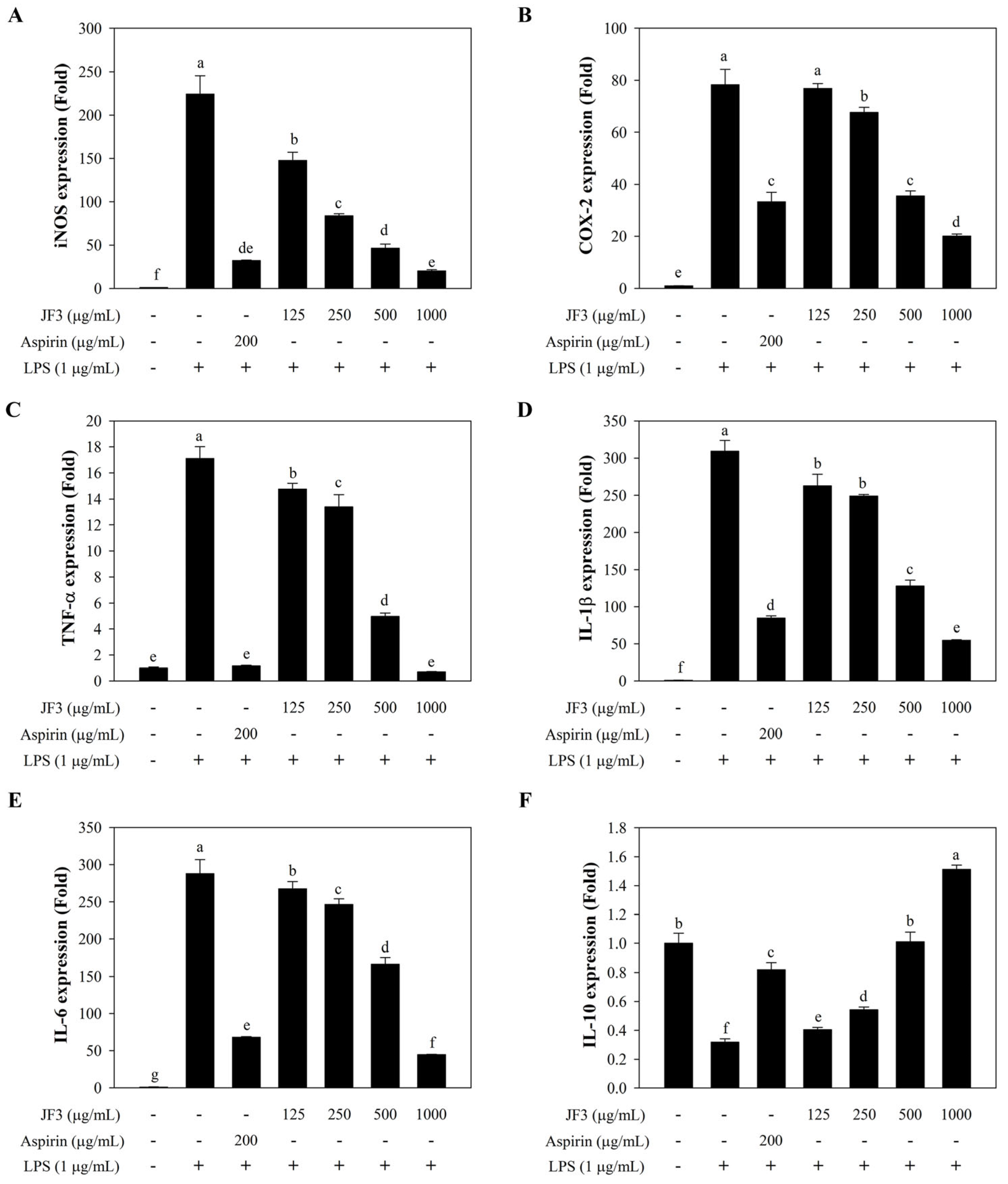
2.5. JF3 Inhibits LPS-Induced Expression of iNOS, COX-2, and Cytokines
2.6. JF3 Suppresses LPS-Induced Nuclear Factor-κB (NF-κB) Activation
2.7. JF3 Suppresses LPS-Induced Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase (MAPK) Activation
2.8. JF3 Inhibits LPS-Induced Cell Surface Expression
2.9. Methylation Analysis of JF3
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials and Chemicals
4.2. Polysaccharide Extraction and Fractionation
4.3. Chemical Composition
4.4. Monosaccharide Characterisation
4.5. Measurement of Mw
4.6. Measurement of the Anti-Inflammatory Activity of L. smithii Polysaccharides
4.6.1. Cell Culture and Treatment
4.6.2. Cell Viability Analysis
4.6.3. Determination of NO Release
4.6.4. Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) Analysis
4.6.5. Western Blotting Analysis
4.6.6. Flow Cytometry Analysis
4.7. Desulphation of Polysaccharide
4.8. Methylation Analysis of JF3
4.9. Statistical Analyses
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fedorov, S.N.; Ermakova, S.P.; Zvyagintseva, T.N.; Stonik, V.A. Anticancer and cancer preventive properties of marine polysaccharides: Some results and prospects. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 4876–4901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Wang, S.-X.; Guan, H.-S. The antiviral activities and mechanisms of marine polysaccharides: An overview. Mar. Drugs 2012, 10, 2795–2816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheong, K.-L.; Yu, B.; Chen, J.; Zhong, S. A comprehensive review of the cardioprotective effect of marine algae polysaccharide on the gut microbiota. Foods 2022, 11, 3550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, X.; Tao, N.; Wang, X.; Xiao, J.; Wang, M. Marine-derived bioactive compounds with anti-obesity effect: A review. J. Funct. Foods 2016, 21, 372–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, L.S.E.P.W.; Pinheiro, T.S.; Castro, A.J.G.; Dore, C.M.P.G.; da Silva, N.B.; Faustino Alves, M.G.d.C.; Santos, M.S.N.; Leite, E.L. Fucose-containing sulfated polysaccharides from brown macroalgae Lobophora variegata with antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and antitumoral effects. J. Appl. Phycol. 2014, 26, 1783–1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.J.; Shiu, S.M.; Hsieh, M.C.; Tsai, G.J. Anti-inflammatory activity of a sulfated polysaccharide from the brown alga Sargassum cristaefolium. Food Hydrocoll. 2016, 53, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.-M.; Wang, J.-F.; Zha, X.-Q.; Pan, L.-H.; Zhang, H.-L.; Luo, J.-P. Structural characterization and immunomodulatory activity of a new polysaccharide from jellyfish. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 159, 188–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Ayala, G.G.; Malinconico, M.; Laurienzo, P. Marine derived polysaccharides for biomedical applications: Chemical modification approaches. Molecules 2008, 13, 2069–2106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Sun, J.; Liu, J.; Gou, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wu, X.; Sun, R.; Tang, S.; Kan, J.; Qian, C.; et al. Structural characterization and anti-inflammatory activity of alkali-soluble polysaccharides from purple sweet potato. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 131, 484–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, H.; Tang, Q.; Huang, H.; Hao, W.; Wei, X. Grape-seed proanthocyanidins inhibit the lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory mediator expression in RAW264.7 macrophages by suppressing MAPK and NF-κB signal pathways. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2016, 41, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, P.A.; Chien, S.Y.; Chan, Y.L.; Lu, M.K.; Wu, C.H.; Kong, Z.L.; Wu, C.J. Inhibition of lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced inflammatory responses by Sargassum hemiphyllum sulfated polysaccharide extract in RAW 264.7 macrophage cells. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 2062–2068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.-T.; Dai, Q.; Zhang, S.-X.; Liu, Y.-J.; Yu, Q.-Q.; Tan, F.; Lu, S.-H.; Wang, Q.; Chen, J.-W.; Huang, H.-Q.; et al. Ulinastatin attenuates LPS-induced inflammation in mouse macrophage RAW264.7 cells by inhibiting the JNK/NF-κB signaling pathway and activating the PI3K/Akt/Nrf2 pathway. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2018, 39, 1294–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.H.; Han, M.H.; Hwang, H.J.; Kim, G.Y.; Moon, S.K.; Hyun, J.W.; Kim, W.J.; Choi, Y.H. Diallyl trisulfide exerts anti-inflammatory effects in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated RAW264.7 macrophages by suppressing the Toll-like receptor 4/nuclear factor-kB pathway. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2015, 35, 487–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.Y.; Sun, L.; Niu, X.T.; Chen, X.M.; Tian, J.X.; Kong, Y.D.; Wang, G.Q. Astaxanthin protects lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory response in Channa argus through inhibiting NF-kB and MAPKs signaling pathways. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019, 86, 280–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Q.; Qi, C.; Peng, G.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Meng, Z. Immune-enhancing effects of a polysaccharide PRG1-1 from Russula griseocarnosa on RAW264.7 macrophage cells via the MAPK and NF-kB signalling pathways. Food Agric. Immunol. 2018, 29, 833–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Meng, T.; Hao, N.; Tao, H.; Zou, S.; Li, M.; Ming, P.; Ding, H.; Dong, J.; Feng, S.; et al. Immune regulation mechanism of Astragaloside IV on RAW264.7 cells through activating the NF-κB/MAPK signaling pathway. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2017, 49, 38–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishimoto, S.; Goto, Y.; Morishige, H.; Shiraishi, R.; Doi, M.; Akiyama, K.; Yamauchi, S.; Sugahara, T. Mode of action of the immunostimulatory effect of collagen from jellyfish. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2008, 72, 2806–2814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugahara, T.; Ueno, M.; Goto, Y.; Shiraishi, R.; Doi, M.; Akiyama, K.; Yamauchi, S. Immunostimulation effect of jellyfish collagen. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2006, 70, 2131–2137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Gao, J.; Zhang, L.; Qin, N.; Zhu, B.; Xia, X. Jellyfish skin polysaccharides enhance intestinal barrier function and modulate the gut microbiota in mice with DSS-induced colitis. Food Funct. 2021, 12, 10121–10135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.-L.; Cui, S.-H.; Zha, X.-Q.; Bansal, V.; Xue, L.; Li, X.-L.; Hao, R.; Pan, L.-H.; Luo, J.-P. Jellyfish skin polysaccharides: Extraction and inhibitory activity on macrophage-derived foam cell formation. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 106, 393–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, S.J.; Ahn, E.-Y.; Park, Y.; Lee, H.-J. An aqueous extract of Nomura’s jellyfish ameliorates inflammatory responses in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated RAW264.7 cells and a zebrafish model of inflammation. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 100, 583–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Omori, M.; Nakano, E. Jellyfish fisheries in southeast Asia. Hydrobiologia 2001, 451, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assaw, S.; Ahmad, A.S.; Abd Wahid, M.E. Potential of Malaysian white type edible jellyfish, Lobonema smithii as antioxidant and collagen promoter in dermal wound of Sprague Dawley rats. Middle East J. Sci. Res. 2016, 24, 2137–2144. [Google Scholar]
- Rodsuwan, U.; Thumthanaruk, B.; Kerdchoechuen, O.; Laohakunjit, N. Functional properties of type A gelatin from jellyfish (Lobonema smithii). Int. Food Res. J. 2016, 23, 507–514. [Google Scholar]
- Upata, M.; Siriwoharn, T.; Makkhun, S.; Yarnpakdee, S.; Regenstein, J.M.; Wangtueai, S. Tyrosinase inhibitory and antioxidant activity of enzymatic protein hydrolysate from jellyfish (Lobonema smithii). Foods 2022, 11, 615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muangrod, P.; Charoenchokpanich, W.; Roytrakul, S.; Rungsardthong, V.; Vatanyoopaisarn, S.; Charoenlappanit, S.; Wonganu, B.; Thumthanaruk, B. Effect of pepsin on antioxidant and antibacterial activity of protein hydrolysate from salted jellyfish (Lobonema smithii and Rhopilema hispidum) by-products. E3S Web Conf. 2022, 355, 02013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Migone, C.; Scacciati, N.; Grassiri, B.; De Leo, M.; Braca, A.; Puppi, D.; Zambito, Y.; Piras, A.M. Jellyfish polysaccharides for wound healing applications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 11491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- You, S.; Lim, S.-T. Molecular characterization of corn starch using an aqueous HPSEC-MALLS-RI system under various dissolution and analytical conditions. Cereal Chem. 2000, 77, 303–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.; Zhu, W.; Wang, M.; Hu, M.; Chen, W.; Xu, X.; Lu, C. Polysaccharides from Smilax glabra inhibit the pro-inflammatory mediators via ERK1/2 and JNK pathways in LPS-induced RAW264.7 cells. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 122, 428–436. [Google Scholar]
- Himaya, S.W.A.; Ryu, B.; Qian, Z.-J.; Kim, S.-K. Sea cucumber, Stichopus japonicus ethyl acetate fraction modulates the lipopolysaccharide induced iNOS and COX-2 via MAPK signaling pathway in murine macrophages. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2010, 30, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bezerra, I.L.; Caillot, A.R.C.; Palhares, L.; Santana-Filho, A.P.; Chavante, S.F.; Sassaki, G.L. Structural characterization of polysaccharides from Cabernet Franc, Cabernet Sauvignon and Sauvignon Blanc wines: Anti-inflammatory activity in LPS stimulated RAW264.7 cells. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 186, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Y.; Wan, X.; Niu, F.; Xie, S.; Guo, H.; Yang, Y.; Guo, L.; Zhou, C. Salvia plebeia R. Br.: An overview about its traditional uses, chemical constituents, pharmacology and modern applications. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 121, 109589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baker, E.J.; Valenzuela, C.A.; De Souza, C.O.; Yaqoob, P.; Miles, E.A.; Calder, P.C. Comparative anti-inflammatory effects of plant- and marine-derived omega-3 fatty acids explored in an endothelial cell line. BBA-Mol. Cell Biol. 2020, 1865, 158662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; Feng, X.; Guo, J.; Wang, L.; Guo, X.; Zhu, X. A review of extraction, purification, structural properties and biological activities of legumes polysaccharides. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 1021448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Yu, X.; Yang, X.; Li, Y.; Yao, Y.; Lui, E.M.K.; Ren, G. Structural and anti-inflammatory characterization of a novel neutral polysaccharide from North American ginseng (Panax quinquefolius). Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2015, 74, 12–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.N.; Heo, S.J.; Yoon, W.J.; Kang, S.M.; Ahn, G.; Yi, T.H.; Jeon, Y.J. Fucoxanthin inhibits the inflammatory response by suppressing the activation of NF-kB and MAPKs in lipopolysaccharide-induced RAW264.7 macrophages. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2010, 649, 369–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Yan, J.; Wu, L.; Yu, Y.; Ye, R.D.; Zhang, Y.; Liang, X. In vitro immunomodulatory effects of human milk oligosaccharides on murine macrophage RAW264.7 cells. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 207, 230–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, H.; Zhang, J.; Chen, F.; Chen, X.; Zhou, Z.; Wang, H. Activation of RAW264.7 macrophages by the polysaccharide from the roots of Actinidia eriantha and its molecular mechanisms. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 121, 388–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.; Wang, Y.; Huang, J.; Qian, N.; Shen, G.; Chen, L. Anti-inflammatory activity of polysaccharides from Phellinus linteus by regulating the NF-κB translocation in LPS-stimulated RAW264.7 macrophages. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 129, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Z.S.; Xiang, X.W.; Jin, H.X.; Guo, X.Y.; Liu, L.J.; Huang, Y.N.; OuYang, X.K.; Qu, Y.L. Composition and anti-inflammatory effect of polysaccharides from Sargassum horneri in RAW264.7 macrophages. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 88, 403–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thalhamer, T.; McGrath, M.A.; Harnett, M.M. MAPKs and their relevance to arthritis and inflammation. Rheumatology 2008, 47, 409–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.A.; Moon, S.-M.; Choi, Y.H.; Han, S.H.; Park, B.-R.; Choi, M.S.; Kim, J.-S.; Kim, Y.H.; Kim, D.K.; Kim, C.S. Aqueous extract of Codium fragile suppressed inflammatory responses in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated RAW264.7 cells and carrageenan-induced rats. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 93, 1055–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zailan, N.F.Z.; Jaganathan, N.; Sandramuti, T.; Sarchio, S.N.E.; Hassan, M. Inhibition of GSK-3 by Tideglusib suppresses activated macrophages and inflammatory responses in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated RAW264.7 cell line. Malays. J. Med. Health Sci. 2020, 16, 2–8. [Google Scholar]
- Rhule, A.; Navarro, S.; Smith, J.R.; Shepherd, D.M. Panax notoginseng attenuates LPS-induced pro-inflammatory mediators in RAW264.7 cells. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2006, 106, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.A.-O.; Lu, S.A.-O.; Xi, L. Murine macrophage requires CD11b to recognize Talaromyces marneffei. Infect. Drug Resist. 2020, 13, 911–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, C.; Chen, L.; Yang, L.; Ji, X. An insight into anti-inflammatory effects of natural polysaccharides. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 153, 248–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lake, A.C.; Vassy, R.; Di Benedetto, M.; Lavigne, D.; Le Visage, C.; Perret, G.Y.; Letourneur, D. Low molecular weight fucoidan increases VEGF165-induced endothelial cell migration by enhancing VEGF165 binding to VEGFR-2 and NRP1. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 37844–37852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Y.; Xiong, Q.; Wang, X.; Li, X.; Yu, C.; Wu, J.; Yi, J.; Zhao, X.; Xu, Y.; Cui, H. Characterization of a novel purified polysaccharide from the flesh of Cipangopaludina chinensis. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 136, 875–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, Q.; Hao, H.; He, L.; Jing, Y.; Xu, T.; Chen, J.; Zhang, H.; Hu, T.; Zhang, Q.; Yang, X.; et al. Anti-inflammatory and anti-angiogenic activities of a purified polysaccharide from flesh of Cipangopaludina chinensis. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 176, 152–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Gao, Y.; Xu, D.; Gao, Q. A polysaccharide from cultured mycelium of Hericium erinaceus and its anti-chronic atrophic gastritis activity. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2015, 81, 656–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, S.; Zhao, D.; Wang, M. A polysaccharide from cultured mycelium of Hericium erinaceus relieves ulcerative colitis by counteracting oxidative stress and improving mitochondrial function. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 125, 572–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.-H.; Ko, C.-I.; Jee, Y.; Jeong, Y.; Kim, M.; Kim, J.-S.; Jeon, Y.-J. Anti-inflammatory effect of fucoidan extracted from Ecklonia cava in zebrafish model. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 92, 84–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obluchinskaya, E.D.; Pozharitskaya, O.N.; Shikov, A.N. In vitro anti-inflammatory activities of fucoidans from five species of brown seaweeds. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ni, L.; Wang, L.; Fu, X.; Duan, D.; Jeon, Y.-J.; Xu, J.; Gao, X. In vitro and in vivo anti-inflammatory activities of a fucose-rich fucoidan isolated from Saccharina japonica. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 156, 717–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DuBois, M.; Gilles, K.A.; Hamilton, J.K.; Rebers, P.A.; Smith, F. Colorimetric method for determination of sugars and related substances. Anal. Chem. 1956, 28, 350–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowry, O.; Rosebrough, N.; Farr, A.L.; Randall, R. Protein measurement with the folin phenol reagent. J. Biol. Chem. 1951, 193, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodgson, K.; Price, R.G. A note on the determination of the ester sulphate content of sulphated polysaccharides. Biochem. J. 1962, 84, 106–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filisetti-Cozzi, T.M.C.C.; Carpita, N.C. Measurement of uronic acids without interference from neutral sugars. Anal. Chem. 1991, 197, 157–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tabarsa, M.; Lee, S.-J.; You, S. Structural analysis of immunostimulating sulfated polysaccharides from Ulva pertusa. Carbohydr. Res. 2012, 361, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciucanu, I.; Kerek, F. A simple and rapid method for the permethylation of carbohydrates. Carbohydr. Res. 1984, 131, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Components | L. smithii Polysaccharides | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Crude | JF1 | JF2 | JF3 | |
| Yield (%) | 1.30 ± 0.10 x | 77.2 ± 0.61 y | 13.2 ± 0.22 y | 9.70 ± 0.05 y |
| Total carbohydrate (%) | 62.5 ± 0.12 a | 72.2 ± 0.06 a | 66.0 ± 0.06 a | 67.6 ± 0.06 a |
| Protein (%) | 24.1 ± 0.06 b | 18.1 ± 0.00 b | 13.6 ± 0.04 c | 7.12 ± 0.13 c |
| Sulphate (%) | 10.2 ± 0.88 c | 8.27 ± 0.21 c | 17.3 ± 0.21 b | 22.7 ± 0.21 b |
| Uronic acid (%) | 3.17 ± 0.06 d | 1.47 ± 0.03 d | 2.97 ± 0.02 d | 3.40 ± 0.10 d |
| Monosaccharide content (%) | ||||
| D-galactose | 26.2 ± 0.20 b | 41.0 ± 1.00 a | 12.5 ± 0.02 c | 28.4 ± 0.00 b |
| D-glucose | 33.1 ± 0.10 a | 40.2 ± 0.21 b | 52.4 ± 0.36 a | 56.7 ± 0.05 a |
| L-arabinose | 15.0 ± 0.00 c | 11.7 ± 0.07 c | 15.4 ± 0.15 b | 0.60 ± 0.15 d |
| D-mannose | 15.2 ± 0.10 c | 3.83 ± 0.06 d | 10.6 ± 0.11 d | 13.7 ± 0.06 c |
| L-rhamnose | 8.30 ± 0.20 d | 1.80 ± 0.03 e | 6.36 ± 0.15 e | 0.54 ± 0.03 d |
| L-fucose | 2.23± 0.25 e | 1.30 ± 0.06 e | 2.53 ± 0.06 f | 0.10 ± 0.10 e |
| L. smithii Polysaccharides | Mw (kDa) | Rg (nm) | SVg (cm3/g) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Crude | 865.0 ± 8.71 a | 124.0 ± 3.90 a | 5.57 ± 0.57 a |
| JF1 | 477.6 ± 7.94 c | 77.7 ± 3.61 c | 2.49 ± 0.39 c |
| JF2 | 524.1 ± 7.55 b | 94.4 ± 2.53 b | 4.05 ± 0.26 b |
| JF3 | 293.0 ± 6.63 d | 56.3 ± 7.20 d | 1.59 ± 0.66 d |
| Characteristic Fragment Ions (m/z) | Methylation Product | Glycosidic Linkage | JF3 (%) | D-JF3 (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 84, 102, 118, 129, 162, 207 | 1,5-di-O-acetyl-2,3,4,6-tetra-O-methyl-Man | Manp-(1→ | 9.1 | 10.5 |
| 87, 101, 118, 129, 161, 206, 234 | 1,3,5-tri-O-acetyl-2,4,6-tri-O-methyl-Glc | →3)-Glcp-(1→ | 16.4 | 48.4 |
| 87, 101, 118, 129, 162, 189, 234 | 1,5,6-tri-O-acetyl-2,3,4-tri-O-methyl-Gal | →6)-Galp-(1→ | 1.00 | 1.30 |
| 87, 101, 118, 129, 189, 234 | 1,3,5,6-tetra-O-acetyl-2,4-di-O-methyl-Glc | →3,6)-Glcp-(1→ | 45.2 | 13.5 |
| 87, 101, 118, 129, 189, 234 | 1,3,5,6-tri-O-acetyl-2,4-di-O-methyl-Gal | →3,6)-Galp-(1→ | 28.3 | 26.3 |
| Target Genes | Sequences of the Primers (5′ to 3′) | |
|---|---|---|
| Forward | Reverse | |
| IL-1β | GGGCCTCAAAGGAAAGAATC | TACCAGTTGGGGAACTCTGC |
| IL-6 | AGTTGCCTTCTTGGGACTGA | CAGAATTGCCATTGCACAAC |
| IL-10 | TACCTGGTAGAAGTGATGCC | CATCATGTATGCTTCTATGC |
| TNF-α | ATGAGCACAGAAAGCATGATC | TACAGGCTTGTCACTCGAATT |
| iNOS | TTCCAGAATCCCTGGACAAG | TGGTCAAACTCTTGGGGTTC |
| COX-2 | AGAAGGAAATGGCTGCAGAA | GCTCGGCTTCCAGTATTGAG |
| β-actin | CCACAGCTGAGAGGGAAATC | AAGGAAGGCTGGAAAAGAGC |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Summat, T.; Wangtueai, S.; You, S.; Rod-in, W.; Park, W.J.; Karnjanapratum, S.; Seesuriyachan, P.; Surayot, U. In Vitro Anti-Inflammatory Activity and Structural Characteristics of Polysaccharides Extracted from Lobonema smithii Jellyfish. Mar. Drugs 2023, 21, 559. https://doi.org/10.3390/md21110559
Summat T, Wangtueai S, You S, Rod-in W, Park WJ, Karnjanapratum S, Seesuriyachan P, Surayot U. In Vitro Anti-Inflammatory Activity and Structural Characteristics of Polysaccharides Extracted from Lobonema smithii Jellyfish. Marine Drugs. 2023; 21(11):559. https://doi.org/10.3390/md21110559
Chicago/Turabian StyleSummat, Thitikan, Sutee Wangtueai, SangGuan You, Weerawan Rod-in, Woo Jung Park, Supatra Karnjanapratum, Phisit Seesuriyachan, and Utoomporn Surayot. 2023. "In Vitro Anti-Inflammatory Activity and Structural Characteristics of Polysaccharides Extracted from Lobonema smithii Jellyfish" Marine Drugs 21, no. 11: 559. https://doi.org/10.3390/md21110559
APA StyleSummat, T., Wangtueai, S., You, S., Rod-in, W., Park, W. J., Karnjanapratum, S., Seesuriyachan, P., & Surayot, U. (2023). In Vitro Anti-Inflammatory Activity and Structural Characteristics of Polysaccharides Extracted from Lobonema smithii Jellyfish. Marine Drugs, 21(11), 559. https://doi.org/10.3390/md21110559