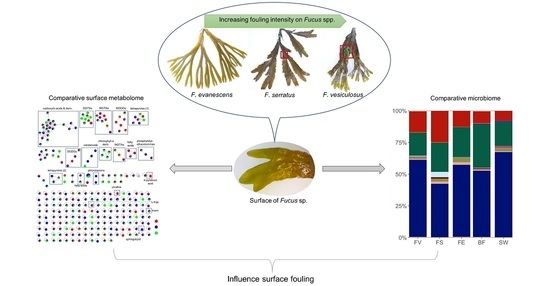
Metabolomics and Microbiomics Insights into Differential Surface Fouling of Three Macroalgal Species of Fucus (Fucales, Phaeophyceae) That Co-Exist in the German Baltic Sea
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
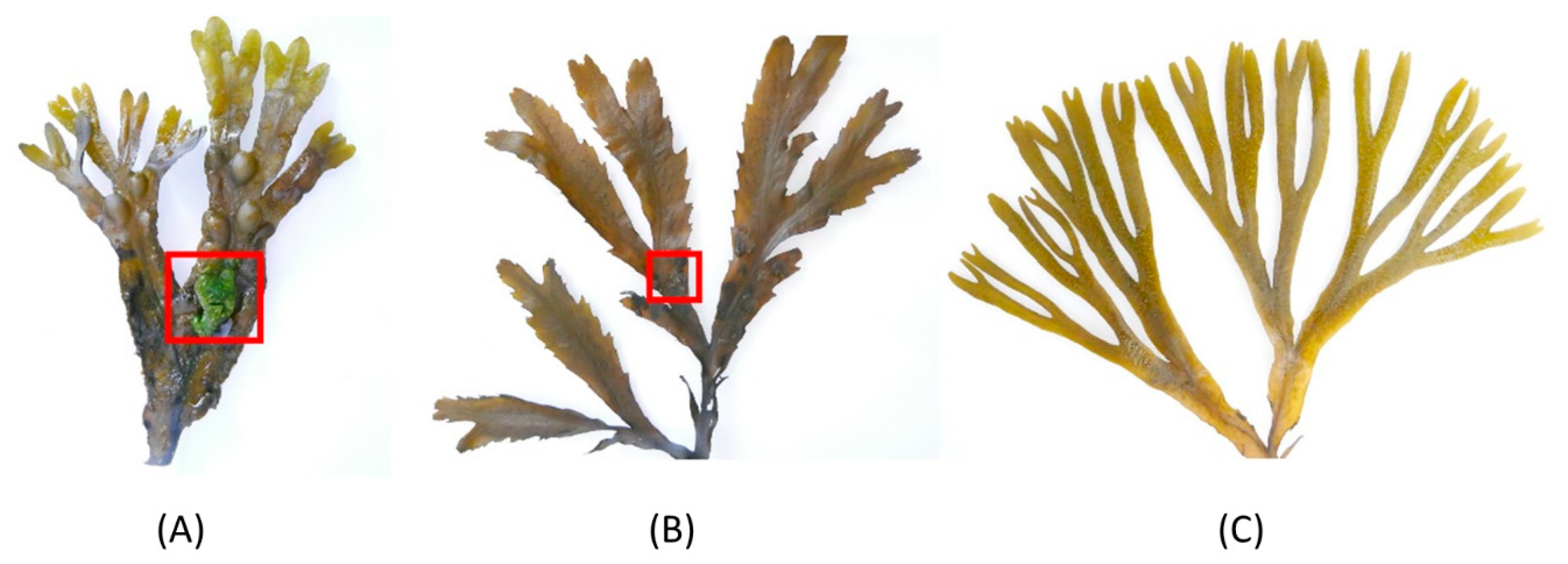
2.1. Macroscopic Fouling Intensity
2.2. Comparative Untargeted Metabolomics of Crude Extracts
Comparison of the Surface Metabolomes of SA and SD
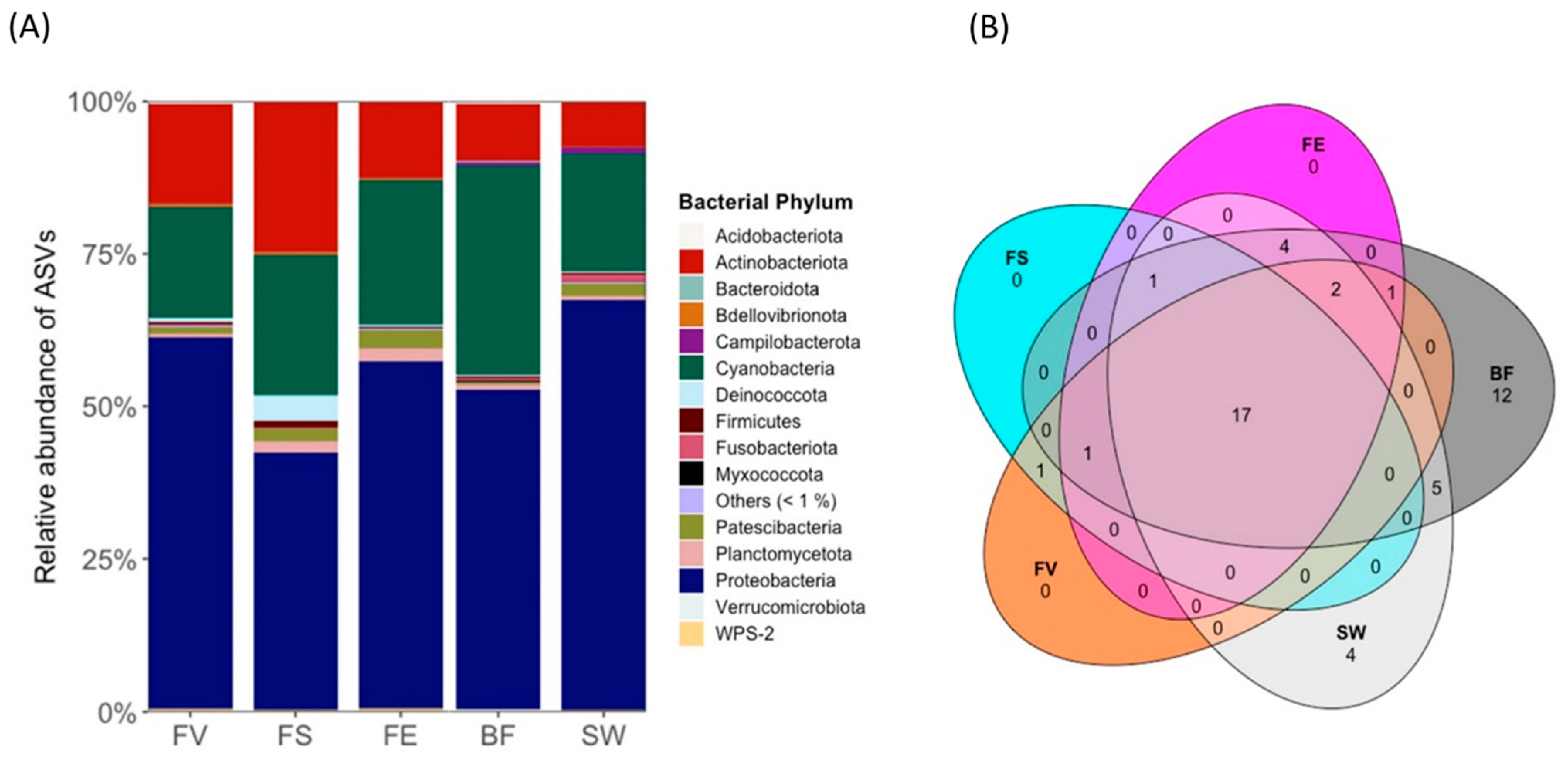
2.3. Microbiome Analysis
2.3.1. Epiphytic Bacterial Microbiome
2.3.2. Comparative Analysis of Eukaryotic Epiphytes
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Sampling and Sample Processing
4.2. Algal Extractions
4.3. UPLC-QToF -MS/MS Metabolomics
4.4. Molecular Networking
4.5. DNA Extraction
4.6. Amplicon Sequencing and Bioinformatic Processing
4.7. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Capistrant-Fossa, K.A.; Morrison, H.G.; Engelen, A.H.; Quigley, C.T.C.; Morozov, A.; Serrão, E.A.; Brodie, J.; Gachon, C.M.M.; Badis, Y.; Johnson, L.E.; et al. The microbiome of the habitat-forming brown alga Fucus vesiculosus (Phaeophyceae) has similar cross-Atlantic structure that reflects past and present drivers1. J. Phycol. 2021, 57, 1681–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Manaway, I.M.; Rashedy, S.H. The ecology and physiology of seaweeds: An overview. In Sustainable Global Resources of Seaweeds Volume 1: Bioresources, Cultivation, Trade and Multifarious Applications; Ranga Rao, A., Ravishankar, G.A., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; Volume 1, pp. 3–16. [Google Scholar]
- Rinne, H.; Salovius-Laurén, S. The status of brown macroalgae Fucus spp. and its relation to environmental variation in the Finnish marine area, northern Baltic Sea. Ambio 2020, 49, 118–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wikström, S.A.; von Wachenfeldt, T.; Kautsky, L. Establishment of the exotic species Fucus evanescens C. Ag. (Phaeophyceae) in Öresund, southern Sweden. Bot. Mar. 2002, 45, 510–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coyer, J.; Peters, A.; Hoarau, G.; Stam, W.; Olsen, J. Hybridization of the marine seaweeds, Fucus serratus and Fucus evanescens (Heterokontophyta: Phaeophyceae) in a 100-year-old zone of secondary contact. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. B Biol. Sci. 2002, 269, 1829–1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grinberg, M.; Orevi, T.; Kashtan, N. Bacterial surface colonization, preferential attachment and fitness under periodic stress. PLoS Comp. Biol. 2019, 15, e1006815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egan, S.; Harder, T.; Burke, C.; Steinberg, P.; Kjelleberg, S.; Thomas, T. The seaweed holobiont: Understanding seaweed-bacteria interactions. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2013, 37, 462–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zammuto, V.; Rizzo, M.G.; Spanò, A.; Spagnuolo, D.; Di Martino, A.; Morabito, M.; Manghisi, A.; Genovese, G.; Guglielmino, S.; Calabrese, G.; et al. Effects of crude polysaccharides from marine macroalgae on the adhesion and biofilm formation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Staphylococcus aureus. Algal Res. 2022, 63, 102646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busetti, A.; Maggs, C.A.; Gilmore, B.F. Marine macroalgae and their associated microbiomes as a source of antimicrobial chemical diversity. Eur. J. Phycol. 2017, 52, 452–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meichssner, R.; Stegmann, N.; Cosin, A.-S.; Sachs, D.; Bressan, M.; Marx, H.; Krost, P.; Schulz, R. Control of fouling in the aquaculture of Fucus vesiculosus and Fucus serratus by regular desiccation. J. Appl. Phycol. 2020, 32, 4145–4158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, R.C.; da Gama Bahia, R. Rhodoliths: Can its importance on a large scale be promoted by a microscale and invisible phenomenon? Front. Mar. Sci. 2021, 8, 630517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizuta, H.; Uji, T.; Yasui, H. Extracellular silicate uptake and deposition induced by oxidative burst in Saccharina japonica sporophytes (Phaeophyceae). Algal Res. 2021, 58, 102369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plouguerné, E.; Ioannou, E.; Georgantea, P.; Vagias, C.; Roussis, V.; Hellio, C.; Kraffe, E.; Stiger-Pouvreau, V. Anti-microfouling activity of lipidic metabolites from the invasive brown alga Sargassum muticum (Yendo) Fensholt. Mar. Biotechnol. 2010, 12, 52–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ternon, E.; Paix, B.; Thomas, O.P.; Briand, J.-F.; Culioli, G. Exploring the role of macroalgal surface metabolites on the settlement of the benthic dinoflagellate Ostreopsis cf. ovata. Front. Mar. Sci. 2020, 7, 683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nylund, G.M.; Cervin, G.; Persson, F.; Hermansson, M.; Steinberg, P.D.; Pavia, H. Seaweed defence against bacteria: A poly-brominated 2-heptanone from the red alga Bonnemaisonia hamifera inhibits bacterial colonisation. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2008, 369, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Gama, B.A.P.; Plouguerné, E.; Pereira, R.C. The antifouling defence mechanisms of marine macroalgae. Adv. Bot. Res. 2014, 71, 413–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harder, T. Marine epibiosis: Concepts, ecological consequences and host defence. In Marine and Industrial Biofouling; Flemming, H., Murthy, P.S., Venkatesan, R., Cooksey, K., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; pp. 219–231. [Google Scholar]
- Croft, M.T.; Lawrence, A.D.; Raux-Deery, E.; Warren, M.J.; Smith, A.G. Algae acquire vitamin B12 through a symbiotic relationship with bacteria. Nature 2005, 438, 90–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grant, M.A.A.; Kazamia, E.; Cicuta, P.; Smith, A.G. Direct exchange of vitamin B12 is demonstrated by modelling the growth dynamics of algal–bacterial cocultures. ISME J. 2014, 8, 1418–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noorjahan, A.; Mahesh, S.; Aiyamperumal, B.; Anantharaman, P. Exploring Marine Fungal Diversity and Their Applications in Agriculture. In Fungal Diversity, Ecology and Control Management; Rajpal, V.R., Singh, I., Navi, S.S., Eds.; Springer Nature: Singapore, 2022; pp. 293–310. [Google Scholar]
- Egan, S.; Thomas, T.; Kjelleberg, S. Unlocking the diversity and biotechnological potential of marine surface associated microbial communities. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2008, 11, 219–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corrigan, S.; Brown, A.R.; Tyler, C.R.; Wilding, C.; Daniels, C.; Ashton, I.G.C.; Smale, D.A. Development and diversity of epibiont assemblages on cultivated sugar Kelp (Saccharina latissima) in relation to farming schedules and harvesting techniques. Life 2023, 13, 209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wheeler, G.L.; Tait, K.; Taylor, A.; Brownlee, C.; Joint, I. Acyl-homoserine lactones modulate the settlement rate of zoospores of the marine alga Ulva intestinalis via a novel chemokinetic mechanism. Plant Cell Environ. 2006, 29, 608–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, M.; Rempt, M.; Grosser, K.; Pohnert, G.; Weinberger, F. Surface-associated fucoxanthin mediates settlement of bacterial epiphytes on the rockweed Fucus vesiculosus. Biofouling 2011, 27, 423–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, H.; Zhao, Y.; Guo, L. A bioactive substance derived from brown seaweeds: Phlorotannins. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Carver, J.J.; Phelan, V.V.; Sanchez, L.M.; Garg, N.; Peng, Y.; Nguyen, D.D.; Watrous, J.; Kapono, C.A.; Luzzatto-Knaan, T.; et al. Sharing and community curation of mass spectrometry data with Global Natural Products Social Molecular Networking. Nat. Biotechnol. 2016, 34, 828–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, J.C.; Lombardi, A.T. Chlorophylls in microalgae: Occurrence, distribution, and biosynthesis. In Pigments from Microalgae Handbook; Jacob-Lopes, E., Queiroz, M.I., Zepka, L.Q., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 1–18. [Google Scholar]
- Pantos, O.; Bongaerts, P.; Dennis, P.G.; Tyson, G.W.; Hoegh-Guldberg, O. Habitat-specific environmental conditions primarily control the microbiomes of the coral Seriatopora hystrix. ISME J. 2015, 9, 1916–1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wahl, M.; Shahnaz, L.; Dobretsov, S.; Saha, M.; Symanowski, F.; David, K.; Lachnit, T.; Vasel, M.; Weinberger, F. Ecology of antifouling resistance in the bladder wrack Fucus vesiculosus: Patterns of microfouling and antimicrobial protection. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2010, 411, 33–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lachnit, T.; Fischer, M.; Künzel, S.; Baines, J.F.; Harder, T. Compounds associated with algal surfaces mediate epiphytic colonization of the marine macroalga Fucus vesiculosus. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2013, 84, 411–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parrot, D.; Blümel, M.; Utermann, C.; Chianese, G.; Krause, S.; Kovalev, A.; Gorb, S.N.; Tasdemir, D. Mapping the surface microbiome and metabolome of brown seaweed Fucus vesiculosus by amplicon sequencing, integrated metabolomics and imaging techniques. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papazian, S.; Parrot, D.; Burýšková, B.; Weinberger, F.; Tasdemir, D. Surface chemical defence of the eelgrass Zostera marina against microbial foulers. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 3323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cirri, E.; Grosser, K.; Pohnert, G. A solid phase extraction based non-disruptive sampling technique to investigate the surface chemistry of macroalgae. Biofouling 2016, 32, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rickert, E.; Lenz, M.; Barboza, F.R.; Gorb, S.N.; Wahl, M. Seasonally fluctuating chemical microfouling control in Fucus vesiculosus and Fucus serratus from the Baltic Sea. Mar. Biol. 2016, 163, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pendyala, M.; Parvataneni, R.; Krishna, N.; Rao, D.; Rao, C. Sphingolipids from marine organisms: A review. Nat. Prod. Sci. 2003, 9, 117–142. [Google Scholar]
- Wilson, M.P.; Footitt, E.J.; Papandreou, A.; Uudelepp, M.-L.; Pressler, R.; Stevenson, D.C.; Gabriel, C.; McSweeney, M.; Baggot, M.; Burke, D.; et al. An LC–MS/MS-based method for the quantification of pyridox(am)ine 5′-phosphate oxidase activity in dried blood spots from patients with epilepsy. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 8892–8900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Latorre, N.; Castañeda, F.; Meynard, A.; Rivas, J.; Contreras-Porcia, L. First approach of characterization of bioactive compound in Pyropia orbicularis during the daily tidal cycle. Lat. Am. J. Aquat. Res. 2019, 47, 826–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rickert, E.; Wahl, M.; Link, H.; Richter, H.; Pohnert, G. Seasonal variations in surface metabolite composition of Fucus vesiculosus and Fucus serratus from the Baltic Sea. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0168196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lachnit, T.; Wahl, M.; Harder, T. Isolated thallus-associated compounds from the macroalga Fucus vesiculosus mediate bacterial surface colonization in the field similar to that on the natural alga. Biofouling 2010, 26, 247–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menshova, R.V.; Shevchenko, N.M.; Imbs, T.I.; Zvyagintseva, T.N.; Malyarenko, O.S.; Zaporoshets, T.S.; Besednova, N.N.; Ermakova, S.P. Fucoidans from brown alga Fucus evanescens: Structure and biological activity. Front. Mar. Sci. 2016, 3, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groisillier, A.; Shao, Z.; Michel, G.; Goulitquer, S.; Bonin, P.; Krahulec, S.; Nidetzky, B.; Duan, D.; Boyen, C.; Tonon, T. Mannitol metabolism in brown algae involves a new phosphatase family. J. Exp. Bot. 2013, 65, 559–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rickert, E.; Karsten, U.; Pohnert, G.; Wahl, M. Seasonal fluctuations in chemical defenses against macrofouling in Fucus vesiculosus and Fucus serratus from the Baltic Sea. Biofouling 2015, 31, 363–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dittami, S.M.; Gravot, A.; Renault, D.; Goulitquer, S.; Eggert, A.; Bouchereau, A.; Boyen, C.; Tonon, T. Integrative analysis of metabolite and transcript abundance during the short-term response to saline and oxidative stress in the brown alga Ectocarpus siliculosus. Plant Cell Environ. 2011, 34, 629–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, B. Antibacterial activity of glycerol, lactose, maltose, mannitol, raffinose and xylose. Noto-are Med. 2014, 17223318. [Google Scholar]
- Buedenbender, L.; Astone, F.A.; Tasdemir, D. Bioactive molecular networking for mapping the antimicrobial constituents of the Baltic brown alga Fucus vesiculosus. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heavisides, E.; Rouger, C.; Reichel, A.; Ulrich, C.; Wenzel-Storjohann, A.; Sebens, S.; Tasdemir, D. Seasonal variations in the metabolome and bioactivity profile of Fucus vesiculosus extracted by an optimised, pressurised liquid extraction protocol. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plouguerné, E.; Souza, L.; Sassaki, G.; Hellio, C.; Trepos, R.; Da Gama, B.; Pereira, R.; Barreto-Bergter, E. Glycoglycerolipids from Sargassum vulgare as potential antifouling agents. Front. Mar. Sci. 2020, 7, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alagawany, M.; Elnesr, S.S.; Farag, M.R.; El-Naggar, K.; Taha, A.E.; Khafaga, A.F.; Madkour, M.; Salem, H.M.; El-Tahan, A.M.; El-Saadony, M.T. Betaine and related compounds: Chemistry, metabolism and role in mitigating heat stress in poultry. J. Therm. Biol. 2022, 104, 103168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe, S.; Kaneda, T. Studies on the effect of marine products on cholesterol metabolism in rat-XI, isolation of a new betaine, ulvaline, from a green laver Monostroma nitidum and Its depressing effect on plasma cholesterol levels. Bull. Jpn. Soc. Sci. Fish 1975, 41, 567–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llewellyn, C.A.; Sommer, U.; Dupont, C.L.; Allen, A.E.; Viant, M.R. Using community metabolomics as a new approach to discriminate marine microbial particulate organic matter in the western English Channel. Prog. Oceanogr. 2015, 137, 421–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sofy, A.R.; Dawoud, R.A.; Sofy, M.R.; Mohamed, H.I.; Hmed, A.A.; El-Dougdoug, N.K. Improving regulation of enzymatic and non-enzymatic antioxidants and stress-related gene stimulation in cucumber mosaic cucumovirus-infected cucumber plants treated with glycine betaine, chitosan and combination. Molecules 2020, 25, 2341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okeke, E.S.; Nweze, E.J.; Chibuogwu, C.C.; Anaduaka, E.G.; Chukwudozie, K.I.; Ezeorba, T.P.C. Aquatic phlorotannins and human health: Bioavailability, toxicity, and future prospects. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2021, 16, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negara, B.F.S.P.; Sohn, J.-H.; Kim, J.-S.; Choi, J.-S. Antifungal and larvicidal activities of phlorotannins from brown seaweeds. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lemesheva, V.; Islamova, R.; Stepchenkova, E.; Shenfeld, A.; Birkemeyer, C.; Tarakhovskaya, E. Antibacterial, antifungal and algicidal activity of phlorotannins, as principal biologically active components of ten species of brown algae. Plants 2023, 12, 821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sachindra, N.M.; Sato, E.; Maeda, H.; Hosokawa, M.; Niwano, Y.; Kohno, M.; Miyashita, K. Radical scavenging and singlet oxygen quenching activity of marine carotenoid fucoxanthin and its metabolites. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 55, 8516–8522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, D.Y.; Shachar-Hill, Y. Do betaine lipids replace phosphatidylcholine as fatty acid editing hubs in microalgae? Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1077347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonilla-Rosso, G.; Peimbert, M.; Alcaraz, L.D.; Hernández, I.; Eguiarte, L.E.; Olmedo-Alvarez, G.; Souza, V. Comparative metagenomics of two microbial mats at Cuatro Ciénegas Basin II: Community structure and composition in oligotrophic environments. Astrobiology 2012, 12, 659–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selvarajan, R.; Sibanda, T.; Tekere, M. Thermophilic bacterial communities inhabiting the microbial mats of “indifferent” and chalybeate (iron-rich) thermal springs: Diversity and biotechnological analysis. MicrobiologyOpen 2018, 7, e00560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lachnit, T.; Meske, D.; Wahl, M.; Harder, T.; Schmitz, R. Epibacterial community patterns on marine macroalgae are host-specific but temporally variable. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 13, 655–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvarajan, R.; Sibanda, T.; Venkatachalam, S.; Ogola, H.J.O.; Christopher Obieze, C.; Msagati, T.A. Distribution, interaction and functional profiles of epiphytic bacterial communities from the rocky intertidal seaweeds, South Africa. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 19835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bondoso, J.; Balagué, V.; Gasol, J.M.; Lage, O.M. Community composition of the Planctomycetes associated with different macroalgae. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2014, 88, 445–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díez-Vives, C.; Gasol, J.M.; Acinas, S.G. Spatial and temporal variability among marine Bacteroidetes populations in the NW Mediterranean sea. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 2014, 37, 68–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suh, S.-S.; Park, M.; Hwang, J.; Kil, E.-J.; Jung, S.W.; Lee, S.; Lee, T.-K. Seasonal dynamics of marine microbial community in the South Sea of Korea. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0131633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zulkifly, S.; Hanshew, A.; Young, E.B.; Lee, P.; Graham, M.E.; Graham, M.E.; Piotrowski, M.; Graham, L.E. The epiphytic microbiota of the globally widespread macroalga Cladophora glomerata (Chlorophyta, Cladophorales). Am. J. Bot. 2012, 99, 1541–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, P.; Aslam, M.; Du, H.; Liang, H.; Wang, H.; Liu, X.; Chen, W. Environmental factors shape the epiphytic bacterial communities of Gracilariopsis lemaneiformis. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 8671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.-X.; Fang, F.; Chen, Y.-P.; Guo, J.-S.; Li, K.; Wang, H. N2O micro-profiles in biofilm from a one-stage autotrophic nitrogen removal system by microelectrode. Chemosphere 2017, 175, 482–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, J.; Yang, H.; Liu, Y.; Qi, H.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Q. The study of natural biofilm formation and microbial community structure for recirculating aquaculture system. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2021, 742, 012018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhu, H.; Lei, X.; Zhang, H.; Guan, C.; Chen, Z.; Zheng, W.; Xu, H.; Tian, Y.; Yu, Z.; et al. The first evidence of deinoxanthin from Deinococcus sp. Y35 with strong algicidal effect on the toxic dinoflagellate Alexandrium tamarense. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 290, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stock, W.; Willems, A.; Mangelinckx, S.; Vyverman, W.; Sabbe, K. Selection constrains lottery assembly in the microbiomes of closely related diatom species. ISME Commun. 2022, 2, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, N.; Sun, L.; Ding, N.; Li, C.; Fu, B.; Wang, C.; Gao, P.; Wang, R. Diversity of algicidal bacteria associated with harmful microalgae and the algicidal mechanisms. Microbiol. China 2019, 46, 1204–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moran, M.A.; Belas, R.; Schell, M.A.; González, J.M.; Sun, F.; Sun, S.; Binder, B.J.; Edmonds, J.; Ye, W.; Orcutt, B.; et al. Ecological genomics of marine roseobacters. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 4559–4569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rohde, S.; Hiebenthal, C.; Wahl, M.; Karez, R.; Bischof, K. Decreased depth distribution of Fucus vesiculosus (Phaeophyceae) in the Western Baltic: Effects of light deficiency and epibionts on growth and photosynthesis. Eur. J. Phycol. 2008, 43, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bengtsson, M.M.; Bühler, A.; Brauer, A.; Dahlke, S.; Schubert, H.; Blindow, I. Eelgrass leaf surface microbiomes are locally variable and highly correlated with epibiotic eukaryotes. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.-L.; Chiang, K.-P.; Tsai, S.-F. Neglect of presence of bacteria leads to inaccurate growth parameters of the oligotrich ciliate Strombidium sp. during grazing experiments on nanoflagellates. Front. Mar. Sci. 2020, 7, 569309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinn, A.P.; Mühlhölzl, A.P.; Coates, C.J.; Metochis, C.; Freeman, M.A. Zoothamnium duplicatum infestation of cultured horseshoe crabs (Limulus polyphemus). J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2015, 125, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jøstensen, J.-P.; Sperstad, S.; Johansen, S.; Landfald, B. Molecular-phylogenetic, structural and biochemical features of a cold-adapted, marine ichthyosporean near the animal-fungal divergence, described from in vitro cultures. Eur. J. Protistol. 2002, 38, 93–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.-Z.; Miao, F.-P.; Fang, S.-T.; Liu, X.-H.; Yin, X.-L.; Ji, N.-Y. Sesteralterin and tricycloalterfurenes A–D: Terpenes with rarely occurring frameworks from the marine-alga-epiphytic fungus Alternaria alternata k21-1. J. Nat. Prod. 2017, 80, 2524–2529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhanasekaran, S.; Yang, Q.; Godana, E.A.; Liu, J.; Li, J.; Zhang, H. Trehalose supplementation enhanced the biocontrol efficiency of Sporidiobolus pararoseus Y16 through increased oxidative stress tolerance and altered transcriptome. Pest Manag. Sci. 2021, 77, 4425–4436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dewapriya, P.; Li, Y.-X.; Himaya, S.W.A.; Kim, S.-K. Isolation and characterization of marine-derived Mucor sp. for the fermentative production of tyrosol. Process Biochem. 2014, 49, 1402–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arias, L.S.; Delbem, A.C.; Fernandes, R.A.; Barbosa, D.B.; Monteiro, D.R. Activity of tyrosol against single and mixed-species oral biofilms. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2016, 120, 1240–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Othmani, A.; Briand, J.-F.; Ayé, M.; Molmeret, M.; Culioli, G. Surface metabolites of the brown alga Taonia atomaria have the ability to regulate epibiosis. Biofouling 2016, 32, 801–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, M.; Wahl, M. Seasonal variation in the antifouling defence of the temperate brown alga Fucus vesiculosus. Biofouling 2013, 29, 661–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paix, B.; Othmani, A.; Debroas, D.; Culioli, G.; Briand, J.-F. Temporal covariation of epibacterial community and surface metabolome in the Mediterranean seaweed holobiont Taonia atomaria. Environ. Microbiol. 2019, 21, 3346–3363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roleda, M.Y.; Hurd, C.L. Seaweed nutrient physiology: Application of concepts to aquaculture and bioremediation. Phycologia 2019, 58, 552–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visch, W.; Nylund, G.M.; Pavia, H. Growth and biofouling in kelp aquaculture (Saccharina latissima): The effect of location and wave exposure. J. Appl. Phycol. 2020, 32, 3199–3209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stratil, S.B.; Neulinger, S.C.; Knecht, H.; Friedrichs, A.K.; Wahl, M. Temperature-driven shifts in the epibiotic bacterial community composition of the brown macroalga Fucus vesiculosus. MicrobiologyOpen 2013, 2, 338–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catarino, M.D.; Silva, A.M.S.; Cardoso, S.M. Phycochemical constituents and biological activities of Fucus spp. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wikström, S.A.; Kautsky, L. Invasion of a habitat-forming seaweed: Effects on associated biota. Biol. Invasions 2004, 6, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chambers, M.C.; Maclean, B.; Burke, R.; Amodei, D.; Ruderman, D.L.; Neumann, S.; Gatto, L.; Fischer, B.; Pratt, B.; Egertson, J. A cross-platform toolkit for mass spectrometry and proteomics. Nat. Biotechnol. 2012, 30, 918–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pluskal, T.; Castillo, S.; Villar-Briones, A.; Oresic, M. MZmine 2: Modular framework for processing, visualizing, and analyzing mass spectrometry-based molecular profile data. BMC Bioinform. 2010, 11, 395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nothias, L.-F.; Petras, D.; Schmid, R.; Dührkop, K.; Rainer, J.; Sarvepalli, A.; Protsyuk, I.; Ernst, M.; Tsugawa, H.; Fleischauer, M.; et al. Feature-based molecular networking in the GNPS analysis environment. Nat. Methods 2020, 17, 905–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horai, H.; Arita, M.; Kanaya, S.; Nihei, Y.; Ikeda, T.; Suwa, K.; Ojima, Y.; Tanaka, K.; Tanaka, S.; Aoshima, K.; et al. MassBank: A public repository for sharing mass spectral data for life sciences. J. Mass Spectrom. 2010, 45, 703–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Da Silva, R.R.; Wang, M.; Nothias, L.-F.; van der Hooft, J.J.J.; Caraballo-Rodríguez, A.M.; Fox, E.; Balunas, M.J.; Klassen, J.L.; Lopes, N.P.; Dorrestein, P.C. Propagating annotations of molecular networks using in silico fragmentation. PLoS Comp. Biol. 2018, 14, e1006089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohimani, H.; Gurevich, A.; Shlemov, A.; Mikheenko, A.; Korobeynikov, A.; Cao, L.; Shcherbin, E.; Nothias, L.-F.; Dorrestein, P.C.; Pevzner, P.A. Dereplication of microbial metabolites through database search of mass spectra. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 4035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ernst, M.; Kang, K.B.; Caraballo-Rodríguez, A.M.; Nothias, L.-F.; Wandy, J.; Chen, C.; Wang, M.; Rogers, S.; Medema, M.H.; Dorrestein, P.C.; et al. MolNetEnhancer: Enhanced molecular networks by integrating metabolome mining and annotation tools. Metabolites 2019, 9, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feunang, Y.D.; Eisner, R.; Knox, C.; Chepelev, L.; Hastings, J.; Owen, G.; Fahy, E.; Steinbeck, C.; Subramanian, S.; Bolton, E.; et al. ClassyFire: Automated chemical classification with a comprehensive, computable taxonomy. J. Cheminform. 2016, 8, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, P.; Markiel, A.; Ozier, O.; Baliga, N.S.; Wang, J.T.; Ramage, D.; Amin, N.; Schwikowski, B.; Ideker, T. Cytoscape: A software environment for integrated models of biomolecular interaction networks. Genome Res. 2003, 13, 2498–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magoč, T.; Salzberg, S.L. FLASH: Fast length adjustment of short reads to improve genome assemblies. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 2957–2963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callahan, B.J.; McMurdie, P.J.; Rosen, M.J.; Han, A.W.; Johnson, A.J.A.; Holmes, S.P. DADA2: High-resolution sample inference from Illumina amplicon data. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 581–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murali, A.; Bhargava, A.; Wright, E.S. IDTAXA: A novel approach for accurate taxonomic classification of microbiome sequences. Microbiome 2018, 6, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMurdie, P.J.; Holmes, S. phyloseq: An R package for reproducible interactive analysis and graphics of microbiome census data. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e61217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Cui, Y.; Li, X.; Yao, M. microeco: An R package for data mining in microbial community ecology. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2021, 97, fiaa255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pang, Z.; Chong, J.; Zhou, G.; de Lima Morais, D.A.; Chang, L.; Barrette, M.; Gauthier, C.; Jacques, P.-É.; Li, S.; Xia, J. MetaboAnalyst 5.0: Narrowing the gap between raw spectra and functional insights. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, W388–W396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Oppong-Danquah, E.; Blümel, M.; Tasdemir, D. Metabolomics and Microbiomics Insights into Differential Surface Fouling of Three Macroalgal Species of Fucus (Fucales, Phaeophyceae) That Co-Exist in the German Baltic Sea. Mar. Drugs 2023, 21, 595. https://doi.org/10.3390/md21110595
Oppong-Danquah E, Blümel M, Tasdemir D. Metabolomics and Microbiomics Insights into Differential Surface Fouling of Three Macroalgal Species of Fucus (Fucales, Phaeophyceae) That Co-Exist in the German Baltic Sea. Marine Drugs. 2023; 21(11):595. https://doi.org/10.3390/md21110595
Chicago/Turabian StyleOppong-Danquah, Ernest, Martina Blümel, and Deniz Tasdemir. 2023. "Metabolomics and Microbiomics Insights into Differential Surface Fouling of Three Macroalgal Species of Fucus (Fucales, Phaeophyceae) That Co-Exist in the German Baltic Sea" Marine Drugs 21, no. 11: 595. https://doi.org/10.3390/md21110595
APA StyleOppong-Danquah, E., Blümel, M., & Tasdemir, D. (2023). Metabolomics and Microbiomics Insights into Differential Surface Fouling of Three Macroalgal Species of Fucus (Fucales, Phaeophyceae) That Co-Exist in the German Baltic Sea. Marine Drugs, 21(11), 595. https://doi.org/10.3390/md21110595