Oleaginous Heterotrophic Dinoflagellates—Crypthecodiniaceae
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
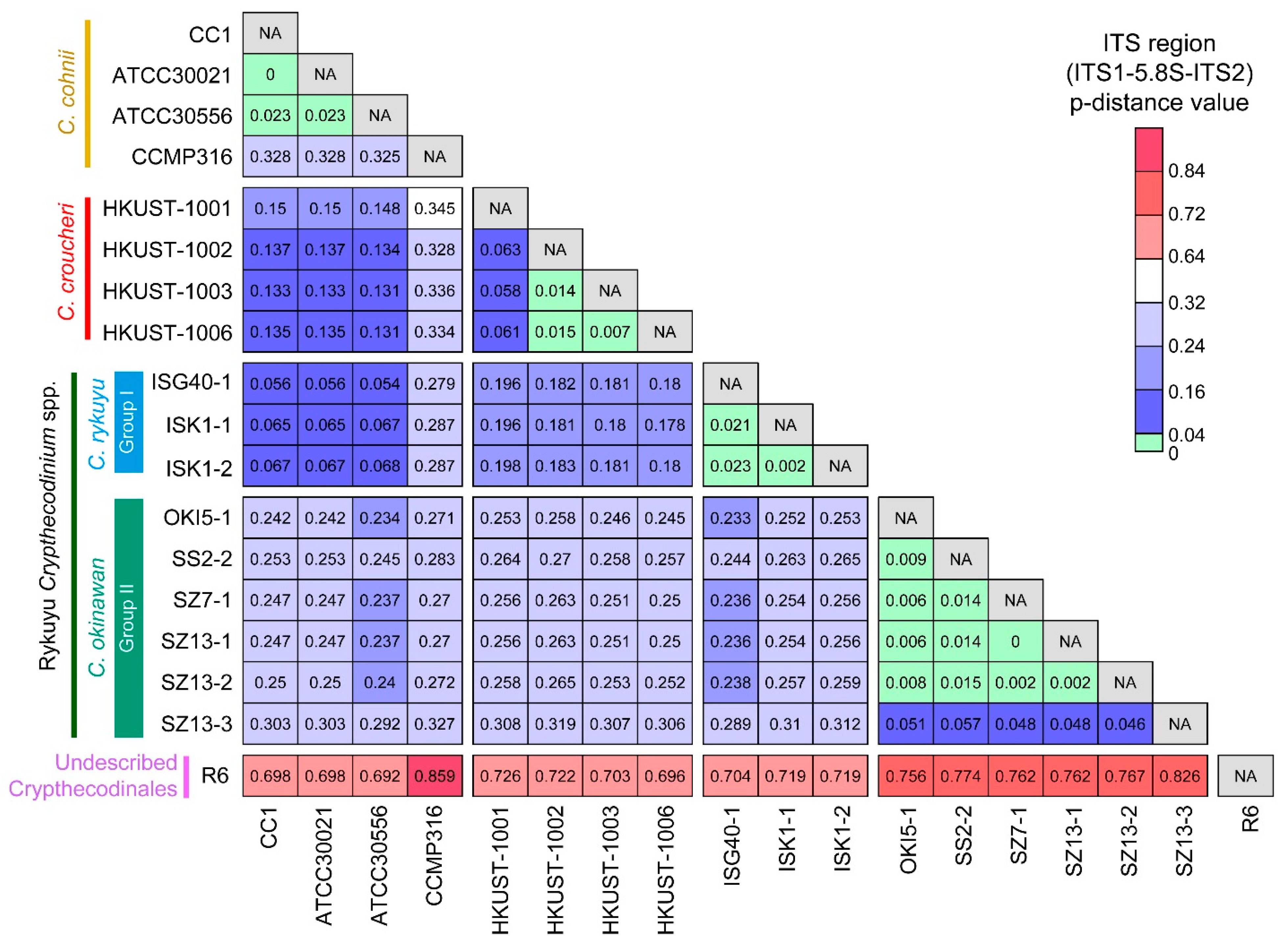
2.1. Genetic Distances Suggest Interspecific Demarcations within Crypthecodiniaceae
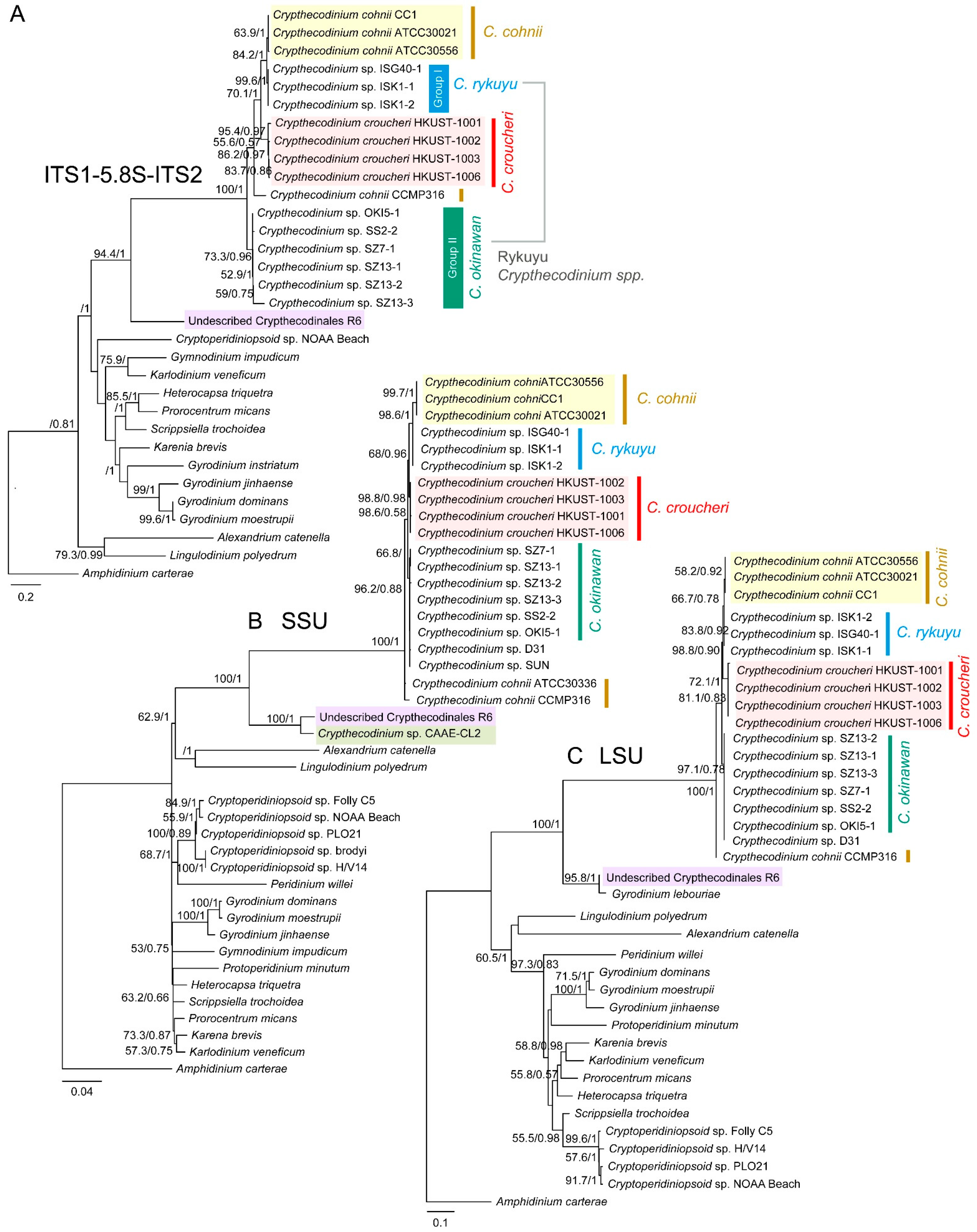
2.2. Phylogenetic Analyses Suggested Multiple Clades within Crypthecodiniaceae
2.3. Crypthecodinium croucheri: Species Novel Kwok, Law and Wong 2023
2.3.1. General Description
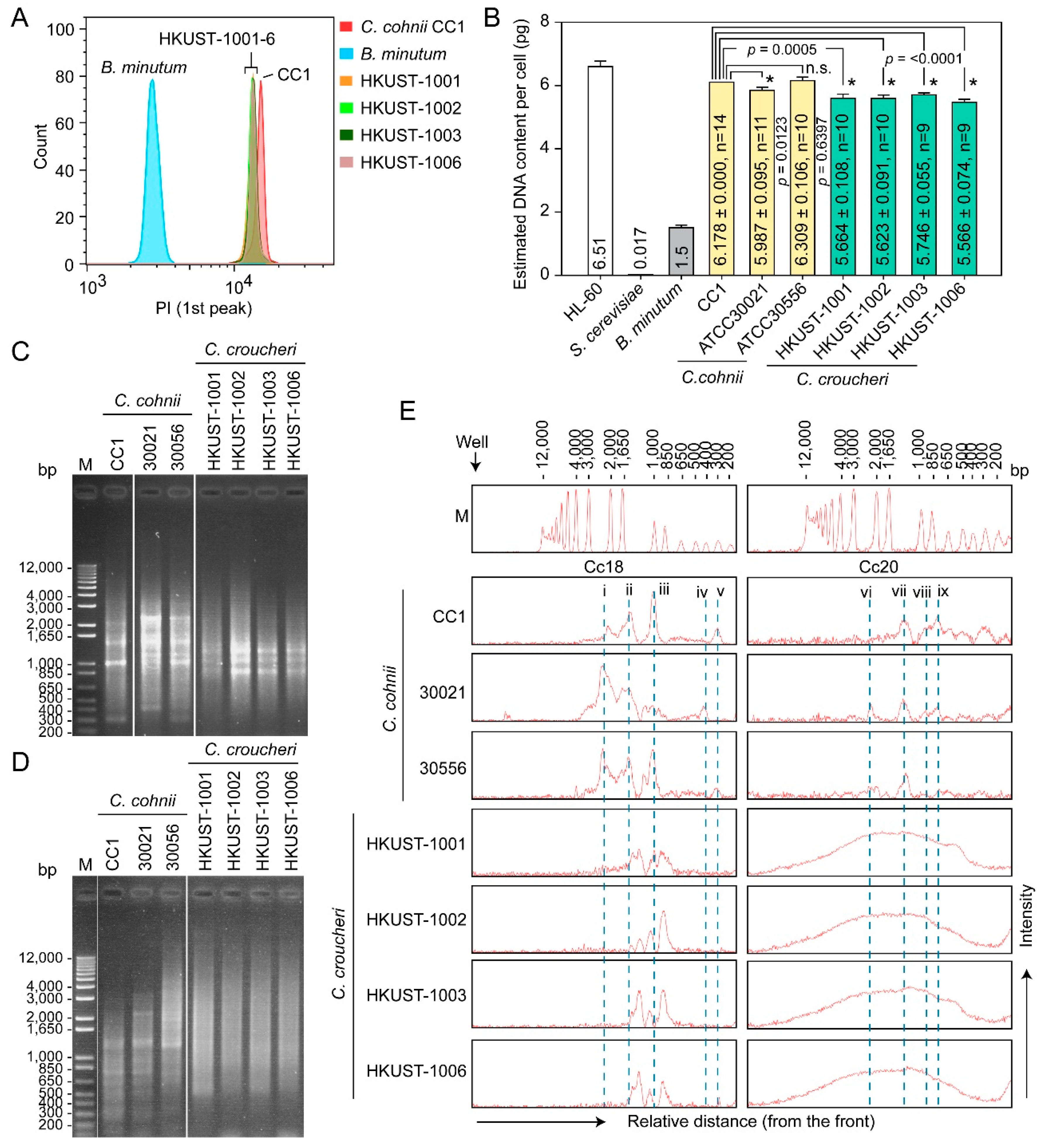
2.3.2. Genome Sizes and Amplification Fragment Length Polymorphism (AFLP)
2.3.3. Lipid Content
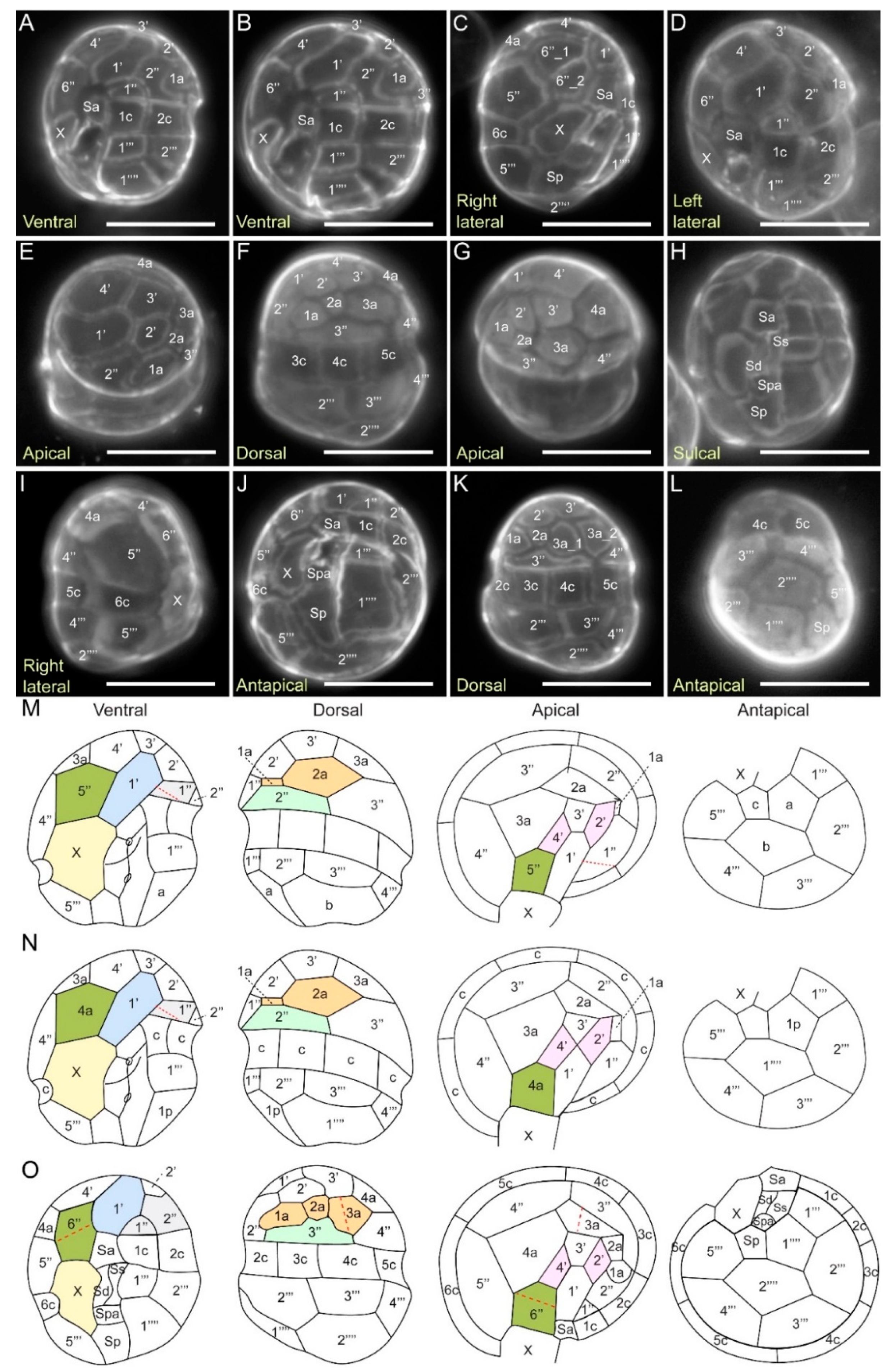
2.3.4. Kofoidian Plate Pattern
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Establishment of Clonal Cultures
4.2. Fluorescence Microscopy and Thecal Plate Formulation
4.3. DNA Extraction, Amplification Fragments Length Polymorphism (AFLP), Genetic Distances and Phylogenetic Analyses
4.4. Flow Cytometric Analyses of Cellular Lipid Content and Nuclear Genome Size
4.5. Biochemical Quantification of Lipid Content
4.6. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lauritzen, L.; Brambilla, P.; Mazzocchi, A.; Harslof, L.B.; Ciappolino, V.; Agostoni, C. DHA Effects in Brain Development and Function. Nutrients 2016, 8, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratledge, C. Fatty acid biosynthesis in microorganisms being used for Single Cell Oil production. Biochimie 2004, 86, 807–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Swaaf, M.E.; Pronk, J.T.; Sijtsma, L. Fed-batch cultivation of the docosahexaenoic-acid-producing marine alga Crypthecodinium cohnii on ethanol. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2003, 61, 40–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Tian, W.; Fu, Z.; Ye, W.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Z.; Sun, D. Mechanisms of Sodium-Acetate-Induced DHA Accumulation in a DHA-Producing Microalga, Crypthecodinium sp. SUN. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendes, A.; Reis, A.; Vasconcelos, R.; Guerra, P.; Lopes da Silva, T. Crypthecodinium cohnii with emphasis on DHA production: A review. J. Appl. Phycol. 2008, 21, 199–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biecheler, B. Sur un Péridinien cuirasse incolore nouveau Crypthecodinium n.g. setense n. sp. et la famille nouvelle des Crypthecodiniacées. Bull. Soc. Zool Fr. 1938, 63, 9–13. [Google Scholar]
- Pringsheim, E.G. Micro-organisms from decaying seaweed. Nature 1956, 178, 480–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beam, C.A.; Himes, M. Distribution of members of the Crypthecodinium cohnii (Dinophyceae) species complex. J. Protozool. 1982, 29, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parrow, M.W.; Elbrachter, M.; Krause, M.K.; Burkholder, J.M.; Deamer, N.J.; Htyte, N.; Allen, E.H. The taxonomy and growth of a Crypthecodinium species (Dinophyceae) isolated from a brackish-water fish aquarium. Afr. J. Mar. Sci. 2006, 28, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preparata, R.M.; Beam, C.A.; Himes, M.; Nanney, D.L.; Meyer, E.B.; Simon, E.M. Crypthecodinium and Tetrahymena: An exercise in comparative evolution. J. Mol. Evol. 1992, 34, 209–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beam, C.A.; Himes, M. Sexual isolation and genetic diversification among some strains of Crypthecodinium cohnii-like dinoflagellates evidence of speciation. J. Protozool. 1977, 24, 532–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabowo, D.A.; Hiraishi, O.; Suda, S. Diversity Crypthecodinium spp. (Dinophyceae) from Okinawa prefecture, Japan. J. Mar. Sci. Tech. 2013, 21, 181–191. [Google Scholar]
- Ucko, M.; Elbrachter, M.; Schnepf, E. A Crypthecodinium cohnii-like dinoflagellate feeding myzocytotically on the unicellular red alga Porphyridium sp. Eur. J. Phycol. 1997, 32, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakobsen, H.H.; Thoisen, C.; Hansen, B.W. Crypthecodinium cohnii: A promising prey toward large-scale intensive rearing of the live feed copepod Acartia tonsa (Dana). Aquac. Int. 2018, 26, 237–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atalah, E.; Cruz, C.M.H.; Izquierdo, M.S.; Rosenlund, G.; Caballero, M.J.; Valencia, A.; Robaina, L. Two microalgae Crypthecodinium cohnii and Phaeodactylum tricornutum as alternative source of essential fatty acids in starter feeds for seabream (Sparus aurata). Aquaculture 2007, 270, 178–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasso, S.; Pohnert, G.; Lohr, M.; Mittag, M.; Hertweck, C. Microalgae in the postgenomic era: A blooming reservoir for new natural products. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2012, 36, 761–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honda, M. Nutraceutical and Pharmaceutical Applications of Carotenoids. In Pigments from Microalgae Handbook; Jacob-Lopes, E., Queiroz, M.I., Zepka, L.Q., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 449–469. [Google Scholar]
- Molino, A.; Mehariya, S.; Iovine, A.; Casella, P.; Marino, T.; Karatza, D.; Chianese, S.; Musmarra, D. Enhancing Biomass and Lutein Production From Scenedesmus almeriensis: Effect of Carbon Dioxide Concentration and Culture Medium Reuse. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M.; Nakano, S.-i. New insights into the stoichiometric regulation of carotenoid production in Chlorella vulgaris. Bioresour. Technol. Rep. 2022, 20, 101227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.-H.; Kato, Y.; Matsuda, M.; Chen, C.-Y.; Nagarajan, D.; Hasunuma, T.; Kondo, A.; Chang, J.-S. Lutein production with Chlorella sorokiniana MB-1-M12 using novel two-stage cultivation strategies—Metabolic analysis and process improvement. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 334, 125200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, N.; Tanaka, A.; Horiguchi, T. Pigment compositions are linked to the habitat types in dinoflagellates. J. Plant Res. 2015, 128, 923–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Cheng, K.-W.; Chen, F. Light induces carotenoids accumulation in a heterotrophic docosahexaenoic acid producing microalga, Crypthecodinium sp. SUN. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 276, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Withers, N.W.; Tuttle, R.C. Carotenes from Mutants of the Dinoflagellate, Crypthecodinium cohnii. J. Protozool. 1979, 26, 135–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turck, D.; Bohn, T.; Castenmiller, J.; De Henauw, S.; Hirsch-Ernst, K.I.; Maciuk, A.; Mangelsdorf, I.; McArdle, H.J.; Naska, A.; Pelaez, C.; et al. Safety of oil from Schizochytrium sp. (strain ATCC 20889) for use in infant and follow-on formula as a novel food pursuant to Regulation (EU) 2015/2283. EFSA J. 2022, 20, e07083. [Google Scholar]
- Litaker, R.W.; Tester, P.A.; Colorni, A.; Levy, M.G.; Noga, E.J. The Phylogenetic Relationship of Pfiesteria Piscicida, Cryptoperidiniopsoid Sp. Amyloodinoum Ocellatum and a Pfiesteria-Like Dinoflagellate to Other Dinoflagellates and Apicomplexans. J. Phycol. 1999, 35, 1379–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, F.J.R. On dinoflagellate evolution. Biosystems 1980, 13, 65–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diao, J.; Song, X.; Zhang, X.; Chen, L.; Zhang, W. Genetic Engineering of Crypthecodinium cohnii to Increase Growth and Lipid Accumulation. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, C.M.C.; Chong, C.; Wong, J.T.Y. A dinoflagellate mutant with higher frequency of multiple fission. Protoplasma 2001, 216, 75–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, M.; Wang, F.; Zeng, L.; Bi, Y.; Cui, J.; Liu, L.; Bi, Y.; Chen, L.; Zhang, W. Identification and metabolomic analysis of a starch-deficient Crypthecodinium cohnii mutant reveals multiple mechanisms relevant to enhanced growth and lipid accumulation. Algal Res. 2020, 50, 102001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dauvillee, D.; Deschamps, P.; Ral, J.P.; Plancke, C.; Putaux, J.L.; Devassine, J.; Durand-Terrasson, A.; Devin, A.; Ball, S.G. Genetic dissection of floridean starch synthesis in the cytosol of the model dinoflagellate Crypthecodinium cohnii. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 21126–21130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuttle, R.C.; Loeblich, A.R., 3rd. N-methyl-N’-nitro-N-nitrosoguanidine and UV induced mutants of the dinoflagellate Crypthecodinium cohnii. J. Protozool. 1977, 24, 313–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuttle, R.C.; Loeblich, A.R., 3rd. Genetic recombination in the dinoflagellate Crypthecodinium cohnii. Science 1974, 185, 1061–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deschamps, P.; Guillebeault, D.; Devassine, J.; Dauvillee, D.; Haebel, S.; Steup, M.; Buleon, A.; Putaux, J.L.; Slomianny, M.C.; Colleoni, C.; et al. The heterotrophic dinoflagellate Crypthecodinium cohnii defines a model genetic system to investigate cytoplasmic starch synthesis. Eukaryot. Cell 2008, 7, 872–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuttle, R.C.; Loeblich, A.R., 3rd. An optimal growth medium for the dinoflagellate Crypthecodinium cohnii. Phycologia 1975, 14, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, J.T.Y.; Whiteley, A. An improved method of cell cycle synchronisation for the heterotrophic dinoflagellate Crypthecodinium cohnii Biecheler analyzed by flow cytometry. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 1996, 197, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, W.S.; Kwok, A.C.M.; Wong, J.T.Y. Knockdown of Dinoflagellate Cellulose Synthase CesA1 Resulted in Malformed Intracellular Cellulosic Thecal Plates and Severely Impeded Cyst-to-Swarmer Transition. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwok, A.C.M.; Zhang, F.; Ma, Z.; Chan, W.S.; Yu, V.C.; Tsang, J.S.H.; Wong, J.T.Y. Functional responses between PMP3 small membrane proteins and membrane potential. Environ. Microbiol 2020, 22, 3066–3080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, T.H.K.; Wu, Z.; Kwok, A.C.M.; Wong, J.T.Y. Knockdown of Dinoflagellate Condensin CcSMC4 Subunit Leads to S-Phase Impediment and Decompaction of Liquid Crystalline Chromosomes. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steele, R.E.; Rae, P.M.M. Comparison of DNAs of Crypthecodinium cohnii-like dinoflagellates from widespread geographic locations. J. Protozool. 1980, 27, 479–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ott, B.M.; Litaker, R.W.; Holland, W.C.; Delwiche, C.F. Using RDNA sequences to define dinoflagellate species. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0264143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ki, J.S.; Park, M.H.; Han, M.S. Discriminative power of nuclear rDNA sequences for the DNA taxonomy of the dinoflagellate genus Peridinium (DINOPHYCEAE) 1. J. Phycol. 2011, 47, 426–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wayne Litaker, R.; Vandersea, M.W.; Kibler, S.R.; Reece, K.S.; Stokes, N.A.; Lutzoni, F.M.; Yonish, B.A.; West, M.A.; Black, M.N.D.; Tester, P.A. Recognizing dinoflagellate species using ITS rDNA sequences. J. Phycol. 2007, 43, 344–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stern, R.F.; Andersen, R.A.; Jameson, I.; Kupper, F.C.; Coffroth, M.A.; Vaulot, D.; Le Gall, F.; Veron, B.; Brand, J.J.; Skelton, H.; et al. Evaluating the ribosomal internal transcribed spacer (ITS) as a candidate dinoflagellate barcode marker. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e42780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yelland, J.N.; Bravo, J.P.K.; Black, J.J.; Taylor, D.W.; Johnson, A.W. A single 2′-O-methylation of ribosomal RNA gates assembly of a functional ribosome. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2022, 30, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, R.E. Saprophytic and phagocytic isolates of the colourless heterotrophic dinoflagellate Gyrodinium lebouriae Herdman. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. UK 1977, 57, 303–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantell, C.L. The Water-Soluble Gums: Their Botany, Sources and Utilization. Econ. Bot. 1949, 3, 3–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreau, H.; Géraud, M.L.; Bhaud, Y.; Soyer-Gobillard, M.O. Cloning, characterization and chromosomal localization of a repeated sequence in Crypthecodinium cohnii, a marine dinoflagellate. Int. Microbiol. 1998, 1, 35–43. [Google Scholar]
- Piovesan, A.; Pelleri, M.C.; Antonaros, F.; Strippoli, P.; Caracausi, M.; Vitale, L. On the length, weight and GC content of the human genome. BMC Res. Notes 2019, 12, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoguchi, E.; Shinzato, C.; Kawashima, T.; Gyoja, F.; Mungpakdee, S.; Koyanagi, R.; Takeuchi, T.; Hisata, K.; Tanaka, M.; Fujiwara, M.; et al. Draft assembly of the Symbiodinium minutum nuclear genome reveals dinoflagellate gene structure. Curr. Biol. 2013, 23, 1399–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherman, F. Getting started with yeast. Methods Enzymol. 2002, 350, 3–41. [Google Scholar]
- Greenspan, P.; Fowler, S.D. Spectrofluorometric studies of the lipid probe, nile red. J. Lipid Res. 1985, 26, 781–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Chen, F.; Liang, S.Z. Production potential of docosahexaenoic acid by the heterotrophic marine dinoflagellate Crypthecodinium cohnii. Process. Biochem. 1999, 34, 633–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwok, A.C.M.; Wong, J.T.Y. Lipid biosynthesis and its coordination with cell cycle progression. Plant Cell Physiol. 2005, 46, 1973–1986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de la Jara, A.; Mendoza, H.; Martel, A.; Molina, C.; Nordströn, L.; de la Rosa, V.; Díaz, R. Flow cytometric determination of lipid content in a marine dinoflagellate, Crypthecodinium cohnii. J. Appl. Phycol. 2003, 15, 433–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Diao, J.; Bi, Y.; Zeng, L.; Wang, F.; Chen, L.; Zhang, W. Rewiring the Metabolic Network to Increase Docosahexaenoic Acid Productivity in Crypthecodinium cohnii by Fermentation Supernatant-Based Adaptive Laboratory Evolution. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 824189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Wang, F.; Pei, G.; Cui, J.; Diao, J.; Lv, M.; Chen, L.; Zhang, W. Repeated fed-batch strategy and metabolomic analysis to achieve high docosahexaenoic acid productivity in Crypthecodinium cohnii. Microb. Cell Fact. 2020, 19, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pei, G.S.; Li, X.R.; Liu, L.S.; Liu, J.; Wang, F.Z.; Chen, L.; Zhang, W.W. De novo transcriptomic and metabolomic analysis of docosahexaenoic acid (DHA)-producing Crypthecodinium cohnii during fed-batch fermentation. Algal Res. 2017, 26 (Suppl. C), 380–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lizuka, T.; Uehara, K.; Takeuchi, D. Marine Micro-Algae Food Material Containing Docosahexaenoic Acid, Food Containing the Same and Manufacturing Method Therefor. US Patent 5,547,699, 20 August 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Nakajima, T.; Kondo, A. Method for Extracting Fat-Soluble Components from Microbial Cells. European Patent Office EP0990694A1, 10 June 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Zhan, G.; Wu, Y.; Fu, Z. Method of Extracting DHA Unsaturated Fatty Acid from Dino Flagellate Fermentation Liquor. China Patent CN101585759A, 25 November 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, H.; Ren, L.; Li, S.; Hu, N.; Jin, M. Technique for Extracting and Refining DHA Enriched Fatty Acid from Crypthecodinium cohnii. China Patent CN101168501B, 7 April 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Park, J.; Jeong, H.J.; Yoon, E.Y.; Moon, S.J. Easy and Rapid Quantification of Lipid Contents of Marine Dinoflagellates Using the Sulpho-Phospho-Vanillin Method. ALGAE 2016, 31, 391–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inouye, L.S.; Lotufo, G.R. Comparison of macro-gravimetric and micro-colorimetric lipid determination methods. Talanta 2006, 70, 584–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byreddy, A.R.; Gupta, A.; Barrow, C.J.; Puri, M. A quick colorimetric method for total lipid quantification in microalgae. J. Microbiol. Methods 2016, 125 (Suppl. C), 28–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratledge, C.; Kanagachandran, K.; Anderson, A.J.; Grantham, D.J.; Stephenson, J.C. Production of docosahexaenoic acid by Crypthecodinium cohnii grown in a pH-auxostat culture with acetic acid as principal carbon source. Lipids 2001, 36, 1241–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fensome, R.A.; Taylor, F.J.R.; Norris, G.; Sarjeant, W.A.S.; Wharton, D.I.; Williams, G.L. A classification of living and fossil dinoflagellates. Micropaleontol. Spec. Publ. 1993, 7, 351. [Google Scholar]
- Chatton, É. Classe des dinoflagellés ou péridiniens. In Traité de Zoologie. Anatomie, Systématique, Biologie; Grassé, P.P., Ed.; Masson: Paris, France, 1952; Volume 1, pp. 309–406. [Google Scholar]
- Biecheler, B. Recherches sur les Péridiniens. Bull. Biol. Fr. Belg. Supplément 1952, 36, 1–149. [Google Scholar]
- Jilan, S. Overview of the South China Sea circulation and its influence on the coastal physical oceanography outside the Pearl River Estuary. Cont. Shelf Res. 2004, 24, 1745–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, D.M.; Anderson, P.; Bricelij, V.M.; Cullen, J.J.; Hodgkiss, I.J.; Ho, K.C.; Rensel, J.E.; Wong, J.T.Y.; Wu, R.S.S. Study of Red Tide Monitoring and Management in Hong Kong: Final Report; Agriculture, Fisheries and Conservation Department, Government of the Hong Kong Special Administrative Region: Hong Kong, China, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Law, S. Red Tide Species in Hong Kong; Agriculture, Fisheries and Conservation Department, The Government of the Hong Kong S.A.R.: Hong Kong, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Shears, N.T.; Ross, P.M. Blooms of benthic dinoflagellates of the genus Ostreopsis; an increasing and ecologically important phenomenon on temperate reefs in New Zealand and worldwide. Harmful Algae 2009, 8, 916–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavaux, A.-S.; Berdalet, E.; Lemée, R. Chemical Ecology of the Benthic Dinoflagellate Genus Ostreopsis: Review of Progress and Future Directions. Front. Mar. Sci. 2020, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longo, G.O.; Hay, M.E. Does seaweed–coral competition make seaweeds more palatable? Coral Reefs 2014, 34, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwok, A.C.M.; Chan, W.S.; Wong, J.T.Y. Dinoflagellate Amphiesmal Dynamics: Cell Wall Deposition with Ecdysis and Cellular Growth. Mar. Drugs 2023, 21, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larsson, M.E.; Bramucci, A.R.; Collins, S.; Hallegraeff, G.; Kahlke, T.; Raina, J.-B.; Seymour, J.R.; Doblin, M.A. Mucospheres produced by a mixotrophic protist impact ocean carbon cycling. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decho, A.W.; Gutierrez, T. Microbial Extracellular Polymeric Substances (EPSs) in Ocean Systems. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LaJeunesse, T.C.; Parkinson, J.E.; Gabrielson, P.W.; Jeong, H.J.; Reimer, J.D.; Voolstra, C.R.; Santos, S.R. Systematic Revision of Symbiodiniaceae Highlights the Antiquity and Diversity of Coral Endosymbionts. Curr. Biol. 2018, 28, 2570–2580.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seligo, A. Untersuchungen uber Flagellaten. Beitr. Biol. Pflanzen 1885, 4, 145–180. [Google Scholar]
- Schiller, J. Dinoflagellatae (Peridineae) in monographischer Behandlung. In Rabenhorst’s Kryptogamen-flora von Deutschland, Österreich und der Schweiz, 2nd ed.; Kolkwitz, R., Ed.; Akademische Verlagsgesellschaft: Leipzig, Germany, 1933; Volume 10, pp. 433–617. [Google Scholar]
- Shcherbik, N.; Pestov, D.G. The Impact of Oxidative Stress on Ribosomes: From Injury to Regulation. Cells 2019, 8, 1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fabritius, D.; Neumann, D. Production and Use of an Antioxidant Extract from Crypthecodinium Sp. US 2008/0206379 A1, 28 August 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Caruana, A.M.N.; Steinke, M.; Turner, S.M.; Malin, G. Concentrations of dimethylsulphoniopropionate and activities of dimethylsulphide-producing enzymes in batch cultures of nine dinoflagellate species. Biogeochemistry 2012, 110, 87–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Q.; Shang, L.; Wang, X.; Hu, Z.; Du, H.; Wang, H. Different dimethylsulphoniopropionate-producing ability of dinoflagellates could affect the structure of their associated bacterial community. Algal Research 2021, 57, 102359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bullock, H.A.; Luo, H.; Whitman, W.B. Evolution of Dimethylsulfoniopropionate Metabolism in Marine Phytoplankton and Bacteria. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Accoroni, S.; Romagnoli, T.; Penna, A.; Capellacci, S.; Ciminiello, P.; Dell’Aversano, C.; Tartaglione, L.; Abboud-Abi Saab, M.; Giussani, V.; Asnaghi, V.; et al. Ostreopsis fattorussoi sp. nov. (Dinophyceae), a new benthic toxic Ostreopsis species from the eastern Mediterranean Sea. J. Phycol. 2016, 52, 1064–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes da Silva, T.; Moniz, P.; Silva, C.; Reis, A. The Role of Heterotrophic Microalgae in Waste Conversion to Biofuels and Bioproducts. Processes 2021, 9, 1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, M.; Marotta, B.; Xu, H.; Geraert, P.-A.; Kaushik, S.; Montero, D.; Izquierdo, M. Complete replacement of fish oil by three microalgal products rich in n-3 long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids in early weaning microdiets for gilthead sea bream (Sparus aurata). Aquaculture 2022, 558, 738354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.A.; Al-Adul-Elah, K.; Azad, I.S.; Alzalzalah, A.; Alnuiami, S. High DHA algae meal as cost-effective alternative to high DHA fish oil in finisher feed for sobaity sea bream (Sparidentex hasta). Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2022, 284, 115209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyd, C.E.; D’Abramo, L.R.; Glencross, B.D.; Huyben, D.C.; Juarez, L.M.; Lockwood, G.S.; McNevin, A.A.; Tacon, A.G.J.; Teletchea, F.; Tomasso, J.R.; et al. Achieving sustainable aquaculture: Historical and current perspectives and future needs and challenges. J. World Aquac. Soc. 2020, 51, 578–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haapala, O.K.; Soyer, M.O. Structure of dinoflagellate chromosomes. Nat. New Biol. 1973, 244, 195–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guillard, R.R.; Ryther, J.H. Studies of marine planktonic diatoms. I. Cyclotella nana Hustedt, and Detonula confervacea (cleve) Gran. Can. J. Microbiol. 1962, 8, 229–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fritz, L.; Triemer, R.E. A Rapid Simple Technique Utilizing Calcofluor White M2r for the Visualization of Dinoflagellate Thecal Plates. J. Phycol. 1985, 21, 662–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeung, P.K.K.; Kong, K.F.; Wong, F.T.W.; Wong, J.T.Y. Sequence data for two large-subunit rRNA genes from an Asian strain of Alexandrium catenella. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1996, 62, 4199–4201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeung, P.K.; Wong, F.T.; Wong, J.T. Large subunit rDNA sequences from Alexandrium catenella strains isolated during harmful algal blooms in Hong Kong. J. Appl. Phycol. 2002, 14, 147–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puchooa, D. A simple, rapid and efficient method for the extraction of genomic DNA from lychee (Litchi chinensis Sonn.). Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2004, 3, 253–255. [Google Scholar]
- Tamura, K.; Peterson, D.; Peterson, N.; Stecher, G.; Nei, M.; Kumar, S. MEGA5: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2011, 28, 2731–2739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronquist, F.; Huelsenbeck, J.P. MrBayes 3: Bayesian phylogenetic inference under mixed models. Bioinformatics 2003, 19, 1572–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenspan, P.; Mayer, E.P.; Fowler, S.D. Nile red: A selective fluorescent stain for intracellular lipid droplets. J. Cell Biol. 1985, 100, 965–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwok, A.C.M.; Wong, J.T.Y. Cellulose synthesis is coupled to cell cycle progression at G1 in the dinoflagellate Crypthecodinium cohnii. Plant Physiol. 2003, 131, 1681–1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soyer-Gobillard, M.-O.; Gillet, B.; Géraud, M.; Bhaud, Y. Dinof lagellate chromosome behaviour during stages of replication. Int. Microbiol. 1999, 2, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]



| C. cohnii ATCC30556 (n = 24) | C. croucheri HKUST-1002 (n = 31) | C. rykuyu (Rykuyu Isolate Group I) (n = 3) * | C. okinawan (Rykuyu Isolate Group II) (n = 6) * | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Length (μm) | Mean | 16.9 ± 2.1 | 15.0 ± 2.8 | 10.3 ± 0.7 | 9.9 ± 0.6 |
| Minimum | 13.9 | 10.7 | 9.5 | 8.9 | |
| Maximum | 21.3 | 21.1 | 11.0 | 10.4 | |
| Width (μm) | Mean | 14.1 ± 2.0 | 12.6 ± 2.6 | 8.7 ± 0.0 | 8.4 ± 0.6 |
| Minimum | 11.2 | 7.9 | 8.7 | 7.4 | |
| Maximum | 18.2 | 18.6 | 8.8 | 9.0 | |
| Mean length/width ratio | 1.20 | 1.22 | 1.19 | 1.18 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kwok, A.C.M.; Law, S.P.C.; Wong, J.T.Y. Oleaginous Heterotrophic Dinoflagellates—Crypthecodiniaceae. Mar. Drugs 2023, 21, 162. https://doi.org/10.3390/md21030162
Kwok ACM, Law SPC, Wong JTY. Oleaginous Heterotrophic Dinoflagellates—Crypthecodiniaceae. Marine Drugs. 2023; 21(3):162. https://doi.org/10.3390/md21030162
Chicago/Turabian StyleKwok, Alvin Chun Man, Stanley Ping Chuen Law, and Joseph Tin Yum Wong. 2023. "Oleaginous Heterotrophic Dinoflagellates—Crypthecodiniaceae" Marine Drugs 21, no. 3: 162. https://doi.org/10.3390/md21030162
APA StyleKwok, A. C. M., Law, S. P. C., & Wong, J. T. Y. (2023). Oleaginous Heterotrophic Dinoflagellates—Crypthecodiniaceae. Marine Drugs, 21(3), 162. https://doi.org/10.3390/md21030162






