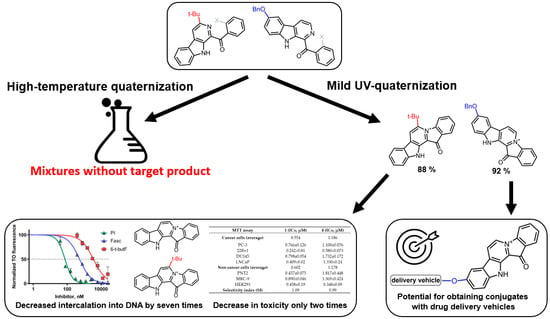
A New Mild Method for Synthesis of Marine Alkaloid Fascaplysin and Its Therapeutically Promising Derivatives
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
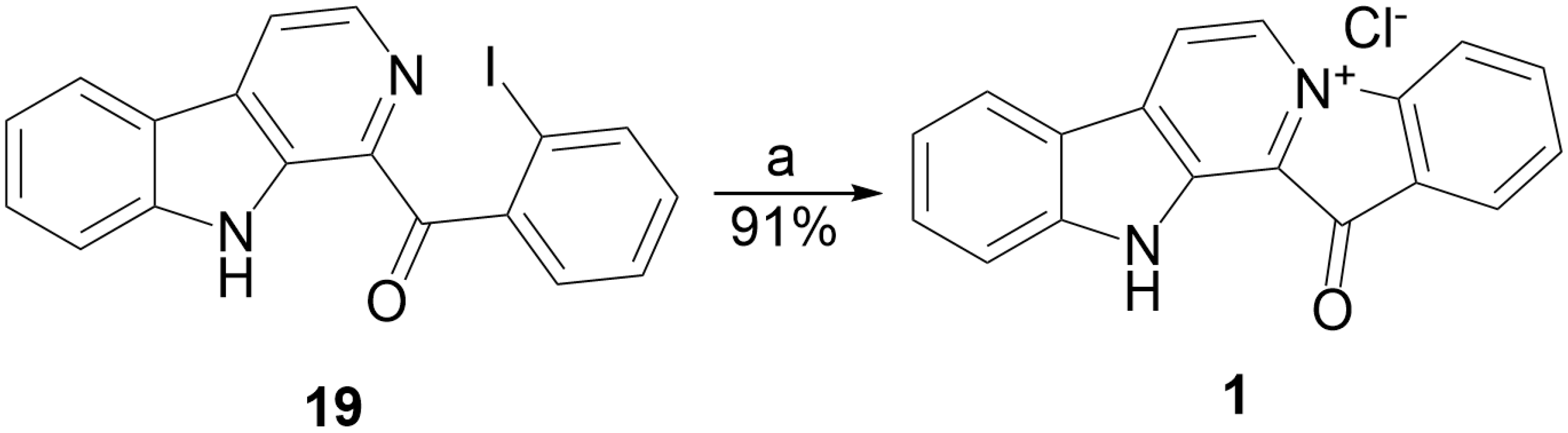
2.1. Development of the UV Quaternization Protocol
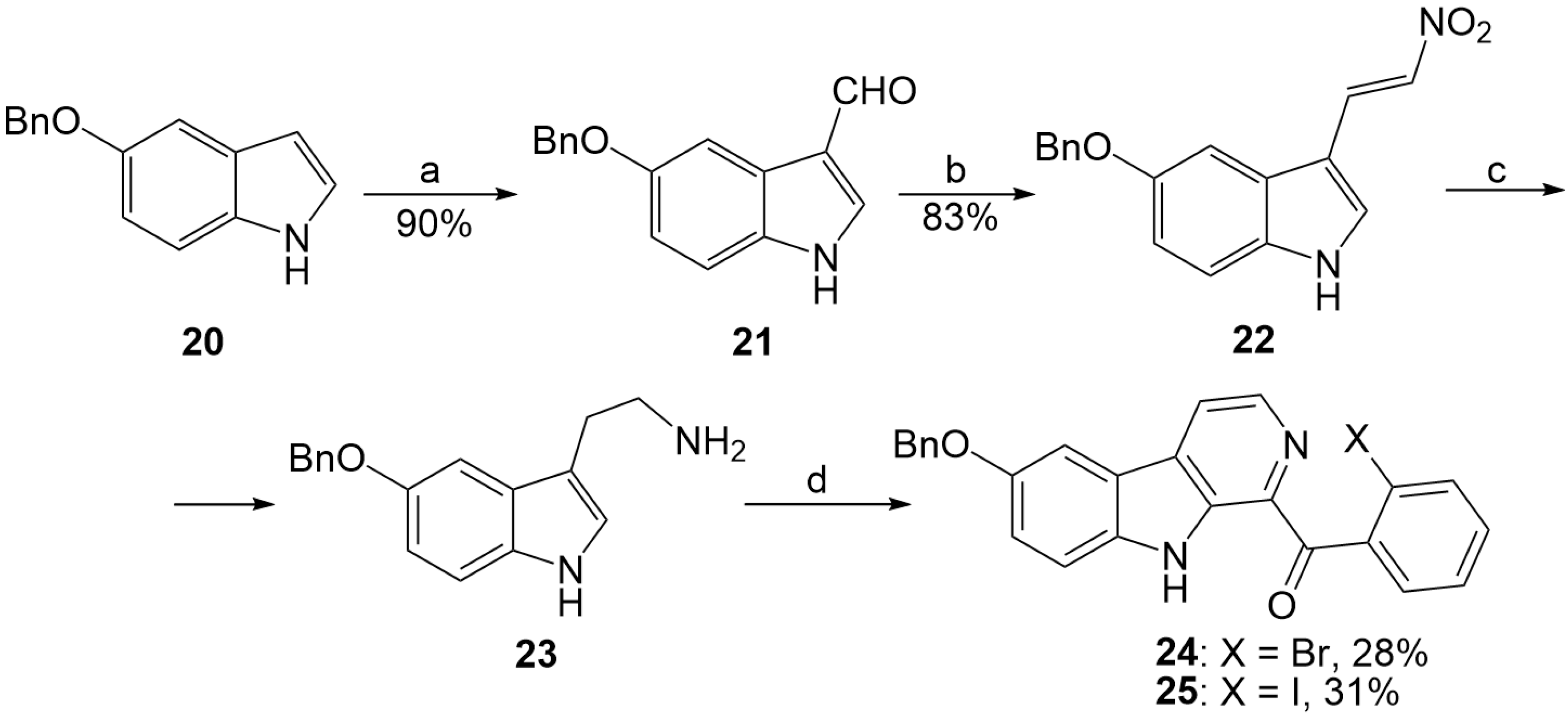
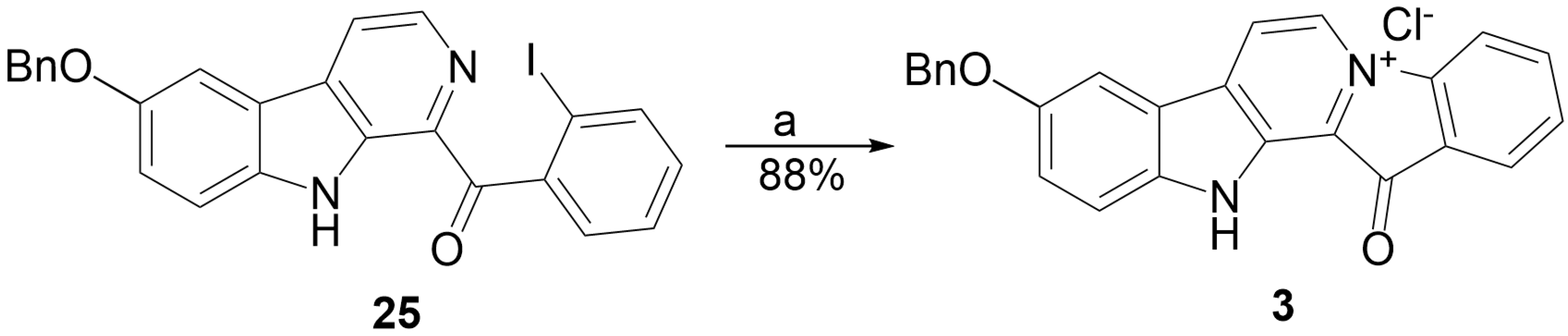
2.2. Synthesis of 9-Benzyloxyfascaplysin
2.3. Study of 6-tert-Butylfascaplysin
2.3.1. Chemistry
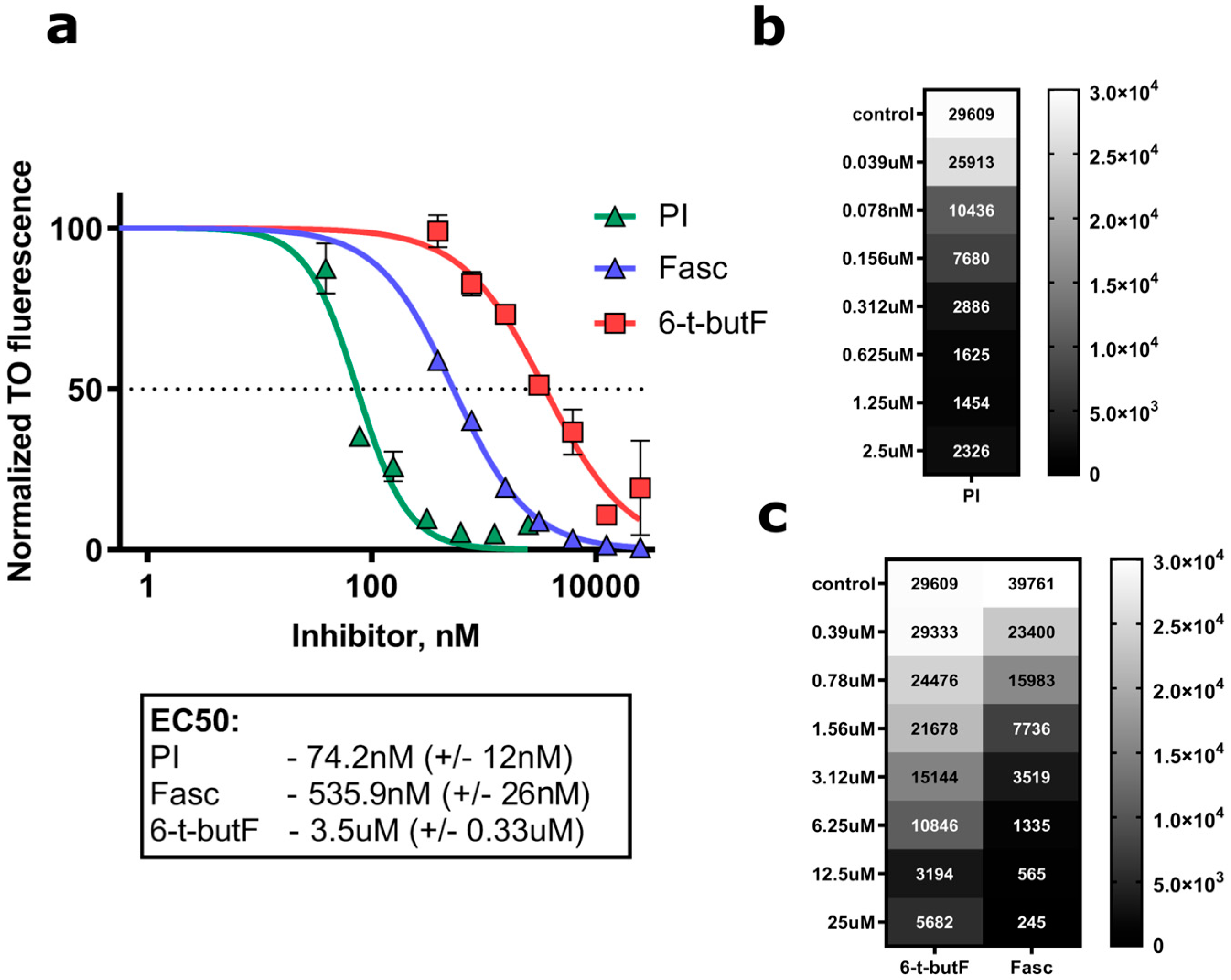
2.3.2. Biological Studies
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemistry
3.1.1. Synthesis of Compound 21
3.1.2. Synthesis of Compound 22
3.1.3. Synthesis of Compound 23
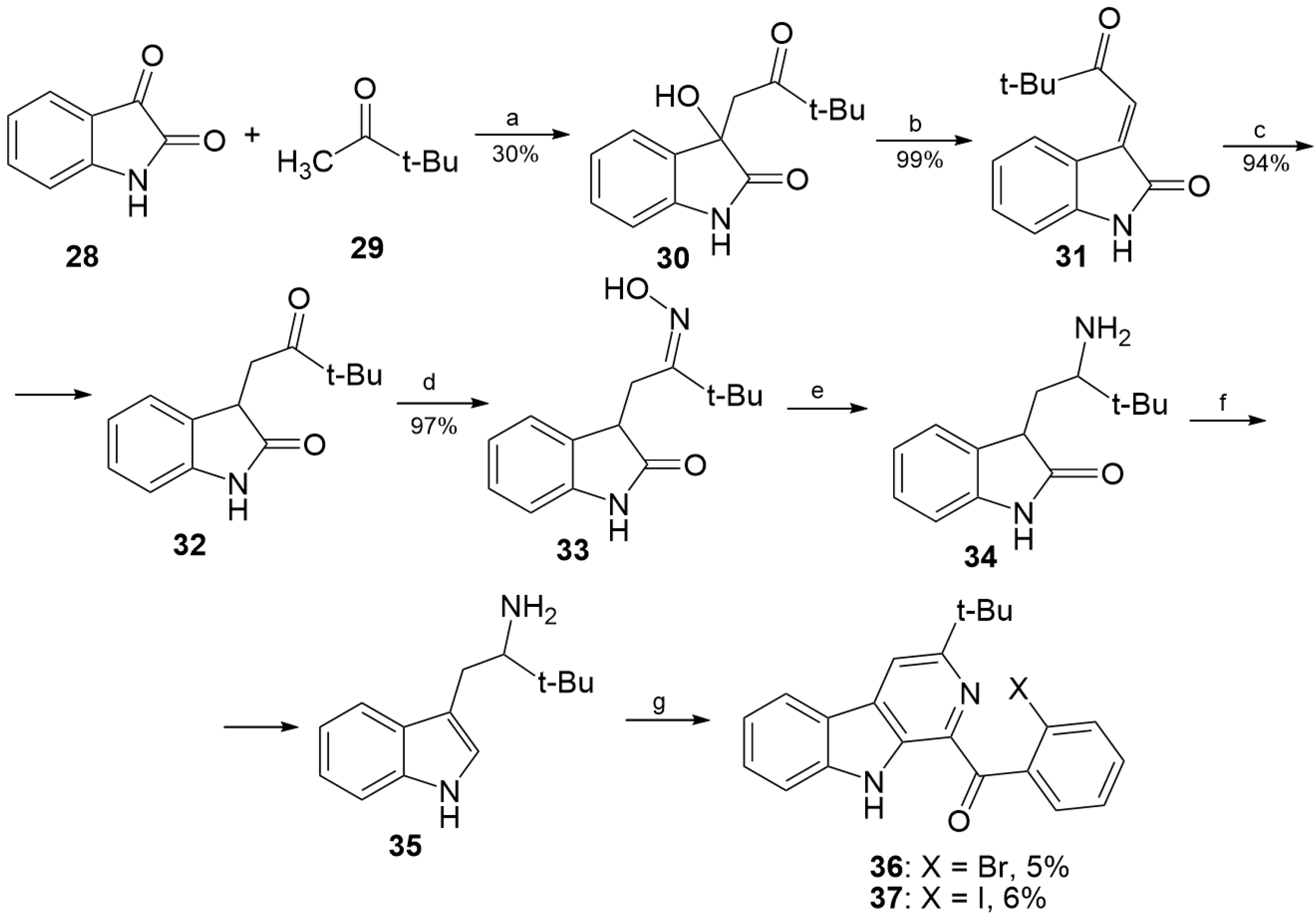
3.1.4. Preparation of Compound 30
3.1.5. Preparation of Compound 31
3.1.6. Preparation of Compound 32
3.1.7. Preparation of Compound 33
3.1.8. Synthesis of Compound 35
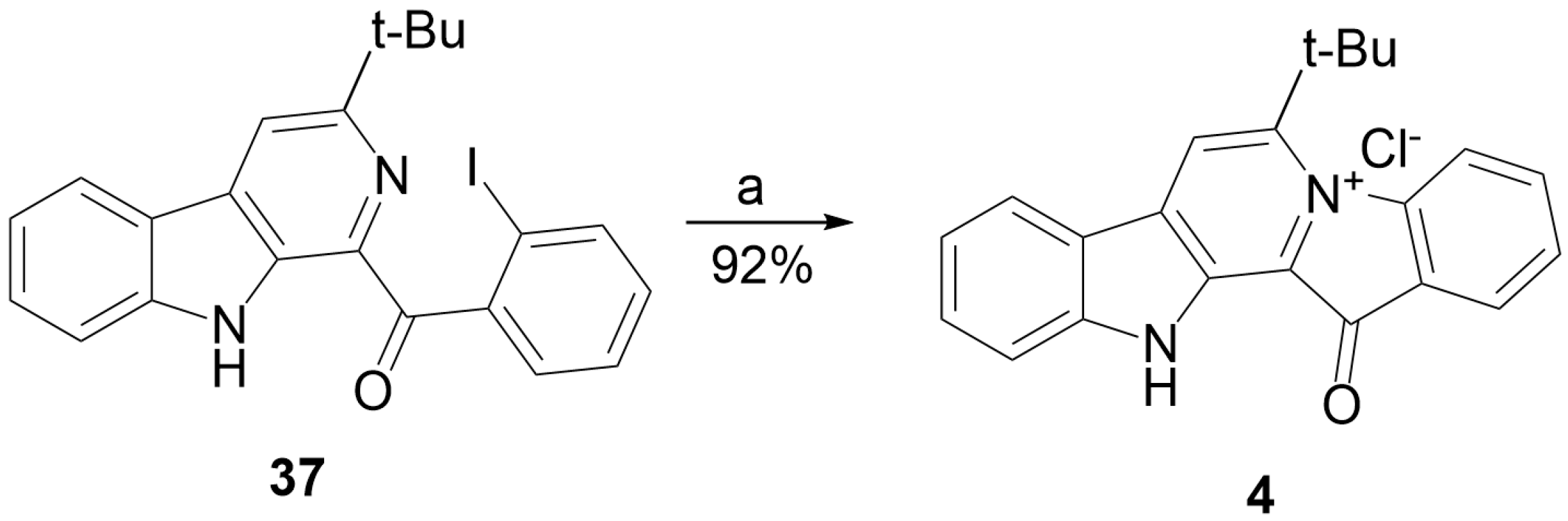
3.1.9. Preparation of Substituted 1-Benzoyl-β-Carbolines 14–19, 24–25, 36–37
3.1.10. Preparation of Fascaplysins 1, 3, 4
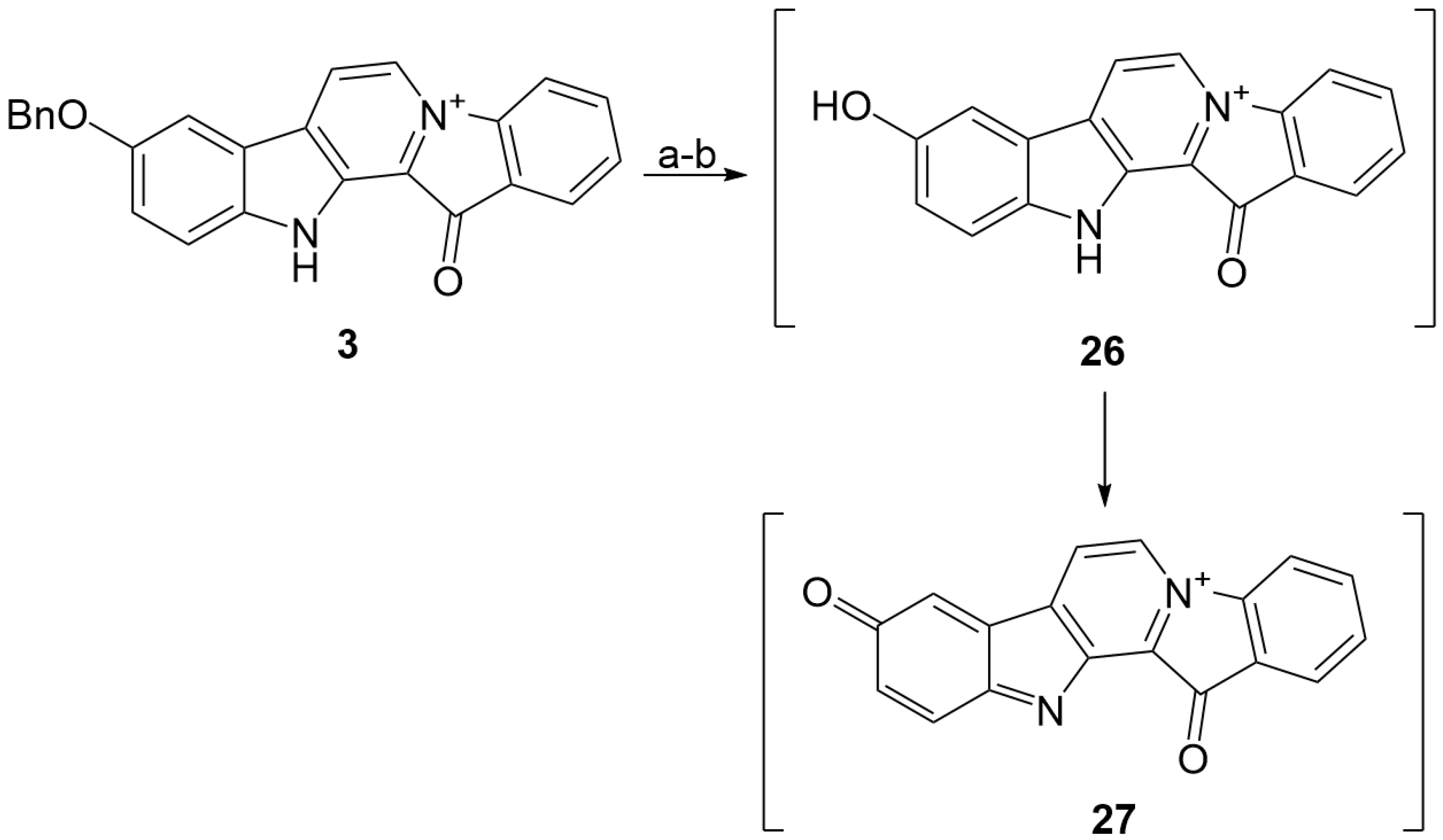
3.1.11. An Attempt to Remove the Benzyl Protection from 3
3.2. Biological Assay
3.2.1. Reagents
3.2.2. Cell Lines and Culture Conditions
3.2.3. MTT Assay
3.2.4. Thiazole Orange Displacement (DNA Intercalation Assay)
3.2.5. Data and Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bharate, S.B.; Manda, S.; Mupparapu, N.; Battini, N.; Vishwakarma, R.A. Chemistry and Biology of Fascaplysin, a Potent Marine-Derived CDK-4 Inhibitor. Mini Rev. Med. Chem. 2012, 12, 650–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roll, D.M.; Ireland, C.M.; Lu, H.S.M.; Clardy, J. Fascaplysin, an Unusual Antimicrobial Pigment from the Marine Sponge Fascaplysinopsis sp. J. Org. Chem. 1988, 53, 3276–3278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimenez, C.; Quinoa, E.; Adamczeski, M.; Hunter, L.M.; Crews, P. Novel Sponge-Derived Amino Acids. 12. Tryptophan-Derived Pigments and Accompanying Sesterterpenes from Fascaplysinopsis reticulata. J. Org. Chem. 1991, 56, 3403–3410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirsch, G.; König, G.M.; Wright, A.D.; Kaminsky, R. A New Bioactive Sesterterpene and Antiplasmodial Alkaloids from the Marine Sponge Hyrtios cf. erecta. J. Nat. Prod. 2000, 63, 825–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Duyne, R.; Guendel, I.; Kehn-Hall, K.; Easley, R.; Klase, Z.; Liu, C.; Young, M.; Kashanchi, F. The Identification of Unique Serum Proteins of HIV-1 Latently Infected Long-Term Non-Progressor Patients. AIDS Res. Ther. 2010, 7, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munakata, T.; Inada, M.; Tokunaga, Y.; Wakita, T.; Kohara, M.; Nomoto, A. Suppression of Hepatitis C Virus Replication by Cyclin-Dependent Kinase Inhibitors. Antivir. Res. 2014, 108, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charan, R.D.; McKee, T.C.; Gustafson, K.R.; Pannell, L.K.; Boyd, M.R. Thorectandramine, a Novel β-Carboline Alkaloid from the Marine Sponge Thorectandra sp. Tetrahedron Lett. 2002, 43, 5201–5204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhidkov, M.E.; Baranova, O.V.; Balaneva, N.N.; Fedorov, S.N.; Radchenko, O.S.; Dubovitskii, S.V. The First Syntheses of 3-Bromofascaplysin, 10-Bromofascaplysin and 3,10-Dibromofascaplysin—Marine Alkaloids from Fascaplysinopsis reticulata and Didemnum Sp. by Application of a Simple and Effective Approach to the Pyrido[1,2-a:3,4-B′]Diindole System. Tetrahedron Lett. 2007, 48, 7998–8000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.-L.; Zheng, Y.-L.; Chen, H.-M.; Yan, X.-J.; Wang, F.; Xu, W.-F. Anti-proliferation of human cervical cancer HeLa cell line by fascaplysin through apoptosis induction. Acta Pharm. Sin. 2009, 44, 980–986. [Google Scholar]
- Lyakhova, I.A.; Bryukhovetsky, I.S.; Kudryavtsev, I.V.; Khotimchenko, Y.S.; Zhidkov, M.E.; Kantemirov, A.V. Antitumor Activity of Fascaplysin Derivatives on Glioblastoma Model In Vitro. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 2018, 164, 666–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhidkov, M.E.; Smirnova, P.A.; Tryapkin, O.A.; Kantemirov, A.V.; Khudyakova, Y.V.; Malyarenko, O.S.; Ermakova, S.P.; Grigorchuk, V.P.; Kaune, M.; von Amsberg, G.; et al. Total Syntheses and Preliminary Biological Evaluation of Brominated Fascaplysin and Reticulatine Alkaloids and Their Analogues. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Chen, H.; Lu, X.; Wang, F.; Xu, W.; Jin, H.; Zhu, P. Fascaplysin Exert Anti-Tumor Effects through Apoptotic and Anti-Angiogenesis Pathways in Sarcoma Mice Model. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2011, 43, 251–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soni, R.; Muller, L.; Furet, P.; Schoepfer, J.; Stephan, C.; Zumstein-Mecker, S.; Fretz, H.; Chaudhuri, B. Inhibition of Cyclin-Dependent Kinase 4 (Cdk4) by Fascaplysin, a Marine Natural Product. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2000, 275, 877–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahgoub, T.; Eustace, A.J.; Collins, D.M.; Walsh, N.; O’Donovan, N.; Crown, J. Kinase Inhibitor Screening Identifies CDK4 as a Potential Therapeutic Target for Melanoma. Int. J. Oncol. 2015, 47, 900–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Guan, X.; Wang, L.-L.; Li, B.; Sang, X.-B.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, Y. Fascaplysin Inhibit Ovarian Cancer Cell Proliferation and Metastasis through Inhibiting CDK4. Gene 2017, 635, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hörmann, A.; Chaudhuri, B.; Fretz, H. DNA Binding Properties of the Marine Sponge Pigment Fascaplysin. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2001, 9, 917–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahale, S.; Aubry, C.; James Wilson, A.; Jenkins, P.R.; Maréchal, J.-D.; Sutcliffe, M.J.; Chaudhuri, B. CA224, a Non-Planar Analogue of Fascaplysin, Inhibits Cdk4 but Not Cdk2 and Arrests Cells at G0/G1 Inhibiting PRB Phosphorylation. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2006, 16, 4272–4278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahale, S.; Bharate, S.B.; Manda, S.; Joshi, P.; Bharate, S.S.; Jenkins, P.R.; Vishwakarma, R.A.; Chaudhuri, B. Biphenyl-4-Carboxylic Acid [2-(1 H -Indol-3-Yl)-Ethyl]-Methylamide (CA224), a Nonplanar Analogue of Fascaplysin, Inhibits Cdk4 and Tubulin Polymerization: Evaluation of in Vitro and in Vivo Anticancer Activity. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 57, 9658–9672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahale, S.; Bharate, S.B.; Manda, S.; Joshi, P.; Jenkins, P.R.; Vishwakarma, R.A.; Chaudhuri, B. Antitumour Potential of BPT: A Dual Inhibitor of Cdk4 and Tubulin Polymerization. Cell Death Dis. 2015, 6, e1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aubry, C.; Jenkins, P.R.; Mahale, S.; Chaudhuri, B.; Maréchal, J.-D.; Sutcliffe, M.J. New Fascaplysin-Based CDK4-Specific Inhibitors: Design, Synthesis and Biological Activity. Chem. Commun. 2004, 15, 1696–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, M.D.; Wilson, A.J.; Emmerson, D.P.G.; Jenkins, P.R.; Mahale, S.; Chaudhuri, B. Synthesis, Crystal Structure and Biological Activity of β-Carboline Based Selective CDK4-Cyclin D1 Inhibitors. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2006, 4, 4478–4484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahale, S.; Aubry, C.; Jenkins, P.R.; Maréchal, J.-D.; Sutcliffe, M.J.; Chaudhuri, B. Inhibition of Cancer Cell Growth by Cyclin Dependent Kinase 4 Inhibitors Synthesized Based on the Structure of Fascaplysin. Bioorg. Chem. 2006, 34, 287–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aubry, C.; Wilson, A.J.; Jenkins, P.R.; Mahale, S.; Chaudhuri, B.; Maréchal, J.-D.; Sutcliffe, M.J. Design, Synthesis and Biological Activity of New CDK4-Specific Inhibitors, Based on Fascaplysin. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2006, 4, 787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jenkins, P.R.; Wilson, J.; Emmerson, D.; Garcia, M.D.; Smith, M.R.; Gray, S.J.; Britton, R.G.; Mahale, S.; Chaudhuri, B. Design, Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of New Tryptamine and Tetrahydro-β-Carboline-Based Selective Inhibitors of CDK4. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2008, 16, 7728–7739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aubry, C.; Wilson, A.J.; Emmerson, D.; Murphy, E.; Chan, Y.Y.; Dickens, M.P.; García, M.D.; Jenkins, P.R.; Mahale, S.; Chaudhuri, B. Fascaplysin-Inspired Diindolyls as Selective Inhibitors of CDK4/Cyclin D1. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2009, 17, 6073–6084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, S.; Foster, C.; Lazo, J.S.; Kingston, D.G.I. Sesterterpenoids and an Alkaloid from a Thorectandra Sp. as Inhibitors of the Phosphatase Cdc25B. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2005, 13, 5094–5098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Yan, X.-J.; Chen, H.-M. Fascaplysin, a Selective CDK4 Inhibitor, Exhibit Anti-Angiogenic Activity In Vitro and In Vivo. Cancer Chemother. Pharm. 2007, 59, 439–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.L.; Lu, X.L.; Lin, J.; Chen, H.M.; Yan, X.J.; Wang, F.; Xu, W.F. Direct Effects of Fascaplysin on Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells Attributing the Anti-Angiogenesis Activity. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2010, 64, 527–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Chen, H.; Yan, X.; Zheng, Y. Fascaplysin Sensitizes Cells to TRAIL-Induced Apoptosis through Upregulating DR5 Expression. Chin. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2013, 31, 560–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Guru, S.K.; Pathania, A.S.; Manda, S.; Kumar, A.; Bharate, S.B.; Vishwakarma, R.A.; Malik, F.; Bhushan, S. Fascaplysin Induces Caspase Mediated Crosstalk Between Apoptosis and Autophagy Through the Inhibition of PI3K/AKT/MTOR Signaling Cascade in Human Leukemia HL-60 Cells. J. Cell. Biochem. 2015, 116, 985–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, N.; Mu, X.; Lv, X.; Wang, L.; Li, N.; Gong, Y. Autophagy Represses Fascaplysin-Induced Apoptosis and Angiogenesis Inhibition via ROS and P8 in Vascular Endothelia Cells. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 114, 108866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, T.-I.; Lee, Y.-M.; Nam, T.-J.; Ko, Y.-S.; Mah, S.; Kim, J.; Kim, Y.; Reddy, R.; Kim, Y.; Hong, S.; et al. Fascaplysin Exerts Anti-Cancer Effects through the Downregulation of Survivin and HIF-1α and Inhibition of VEGFR2 and TRKA. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, T.-I.; Lee, J.; Kim, S.; Nam, T.-J.; Kim, Y.-S.; Kim, B.; Yim, W.; Lim, J.-H. Fascaplysin Sensitizes Anti-Cancer Effects of Drugs Targeting AKT and AMPK. Molecules 2017, 23, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamilton, G. Cytotoxic Effects of Fascaplysin against Small Cell Lung Cancer Cell Lines. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 1377–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rath, B.; Hochmair, M.; Plangger, A.; Hamilton, G. Anticancer Activity of Fascaplysin against Lung Cancer Cell and Small Cell Lung Cancer Circulating Tumor Cell Lines. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plangger, A.; Rath, B.; Hochmair, M.; Funovics, M.; Neumayer, C.; Zeillinger, R.; Hamilton, G. Synergistic Cytotoxicity of the CDK4 Inhibitor Fascaplysin in Combination with EGFR Inhibitor Afatinib against Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Investig. New Drugs 2022, 40, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.; Xu, G. Fascaplysin Induces Apoptosis and Ferroptosis, and Enhances Anti-PD-1 Immunotherapy in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) by Promoting PD-L1 Expression. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 13774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharate, S.B.; Manda, S.; Joshi, P.; Singh, B.; Vishwakarma, R.A. Total Synthesis and Anti-Cholinesterase Activity of Marine-Derived Bis-Indole Alkaloid Fascaplysin. MedChemComm 2012, 3, 1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, T.A.; Milan-Lobo, L.; Che, T.; Ferwerda, M.; Lambu, E.; McIntosh, N.L.; Li, F.; He, L.; Lorig-Roach, N.; Crews, P.; et al. Identification of the First Marine-Derived Opioid Receptor “Balanced” Agonist with a Signaling Profile That Resembles the Endorphins. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2017, 8, 473–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuzmich, A.S.; Fedorov, S.N.; Shastina, V.V.; Shubina, L.K.; Radchenko, O.S.; Balaneva, N.N.; Zhidkov, M.E.; Park, J.-I.; Kwak, J.Y.; Stonik, V.A. The Anticancer Activity of 3- and 10-Bromofascaplysins Is Mediated by Caspase-8, -9, -3-Dependent Apoptosis. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2010, 18, 3834–3840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyshlovoy, S.A.; Kaune, M.; Hauschild, J.; Kriegs, M.; Hoffer, K.; Busenbender, T.; Smirnova, P.A.; Zhidkov, M.E.; Poverennaya, E.V.; Oh-Hohenhorst, S.J.; et al. Efficacy and Mechanism of Action of Marine Alkaloid 3,10-Dibromofascaplysin in Drug-Resistant Prostate Cancer Cells. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyakhova, I.; Piatkova, M.; Khotimchenko, Y.; Zhidkov, M.; Kantemirov, A.; Khotimchenko, R.; Bryukhovetskiy, A.; Sharma, A.; Sharma, H.S.; Bryukhovetskiy, I. 3-Bromofascaplysin Is a Prospective Chemical Compound for Developing New Chemotherapy Agents in Glioblastoma Treatment. In International Review of Neurobiology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; Volume 151, pp. 325–343. ISBN 978-0-12-821114-4. [Google Scholar]
- Zhidkov, M.E.; Kaune, M.; Kantemirov, A.V.; Smirnova, P.A.; Spirin, P.V.; Sidorova, M.A.; Stadnik, S.A.; Shyrokova, E.Y.; Kaluzhny, D.N.; Tryapkin, O.A.; et al. Study of Structure–Activity Relationships of the Marine Alkaloid Fascaplysin and Its Derivatives as Potent Anticancer Agents. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spirin, P.; Shyrokova, E.; Lebedev, T.; Vagapova, E.; Smirnova, P.; Kantemirov, A.; Dyshlovoy, S.A.; von Amsberg, G.; Zhidkov, M.; Prassolov, V. Cytotoxic Marine Alkaloid 3,10-Dibromofascaplysin Induces Apoptosis and Synergizes with Cytarabine Resulting in Leukemia Cell Death. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, S.; Guru, S.K.; Manda, S.; Kumar, A.; Mintoo, M.J.; Prasad, V.D.; Sharma, P.R.; Mondhe, D.M.; Bharate, S.B.; Bhushan, S. A Marine Sponge Alkaloid Derivative 4-Chloro Fascaplysin Inhibits Tumor Growth and VEGF Mediated Angiogenesis by Disrupting PI3K/Akt/MTOR Signaling Cascade. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2017, 275, 47–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manda, S.; Sharma, S.; Wani, A.; Joshi, P.; Kumar, V.; Guru, S.K.; Bharate, S.S.; Bhushan, S.; Vishwakarma, R.A.; Kumar, A.; et al. Discovery of a Marine-Derived Bis-Indole Alkaloid Fascaplysin, as a New Class of Potent P-Glycoprotein Inducer and Establishment of Its Structure–Activity Relationship. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 107, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, H.; Qiu, H.; Zhang, K.; Zhang, P.; Liang, W.; Yang, M.; Mou, C.; Lin, M.; He, M.; Xiao, X.; et al. Fascaplysin Derivatives Are Potent Multitarget Agents against Alzheimer’s Disease: In Vitro and in Vivo Evidence. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2019, 10, 4741–4756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Liu, F.; Sang, J.; Lin, M.; Ma, J.; Xiao, X.; Yan, S.; Naman, C.; Wang, N.; He, S.; et al. 9-Methylfascaplysin Is a More Potent Aβ Aggregation Inhibitor than the Marine-Derived Alkaloid, Fascaplysin, and Produces Nanomolar Neuroprotective Effects in SH-SY5Y Cells. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Qiu, H.; Yang, N.; Xie, H.; Liang, W.; Lin, J.; Zhu, H.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, N.; Tan, X.; et al. Fascaplysin Derivatives Binding to DNA via Unique Cationic Five-Ring Coplanar Backbone Showed Potent Antimicrobial/Antibiofilm Activity against MRSA in Vitro and in Vivo. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2022, 230, 114099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Qiu, H.; Liang, W.; Lin, J.; Lin, J.; Liu, W.; Wang, X.; Cui, W.; Chen, X.; Wang, H.; et al. Derivatization of Marine-Derived Fascaplysin via Highly Regioselective Suzuki-Miyaura Coupling Contributing to the Enhanced Antibacterial Activity. ChemistrySelect 2022, 7, e202201441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelcman, B.; Gribble, G.W. Total Synthesis of the Marine Sponge Pigment Fascaplysin. Tetrahedron Lett. 1990, 31, 2381–2384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocca, P.; Marsais, F.; Godard, A.; Quéguiner, G. A Short Synthesis of the Antimicrobial Marine Sponge Pigment Fascaplysin. Tetrahedron Lett. 1993, 34, 7917–7918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhidkov, M.E.; Baranova, O.V.; Kravchenko, N.S.; Dubovitskii, S.V. A New Method for the Synthesis of the Marine Alkaloid Fascaplysin. Tetrahedron Lett. 2010, 51, 6498–6499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waldmann, H.; Eberhardt, L.; Wittstein, K.; Kumar, K. Silver Catalyzed Cascade Synthesis of Alkaloid Ring Systems: Concise Total Synthesis of Fascaplysin, Homofascaplysin C and Analogues. Chem. Commun. 2010, 46, 4622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakoori, A.; Bremner, J.B.; Willis, A.C.; Haritakun, R.; Keller, P.A. Rapid Cascade Synthesis of Poly-Heterocyclic Architectures from Indigo. J. Org. Chem. 2013, 78, 7639–7647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhidkov, M.E.; Kantemirov, A.V.; Koisevnikov, A.V.; Andin, A.N.; Kuzmich, A.S. Syntheses of the Marine Alkaloids 6-Oxofascaplysin, Fascaplysin and Their Derivatives. Tetrahedron Lett. 2018, 59, 708–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina, P.; Fresneda, P.M.; García-Zafra, S.; Almendros, P. Iminophosphorane-Mediated Syntheses of the Fascaplysin Alkaloid of Marine Origin and Nitramarine. Tetrahedron Lett. 1994, 35, 8851–8854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radchenko, O.S.; Novikov, V.L.; Elyakov, G.B. A Simple and Practical Approach to the Synthesis of the Marine Sponge Pigment Fascaplysin and Related Compounds. Tetrahedron Lett. 1997, 38, 5339–5342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhidkov, M.E.; Kaminskii, V.A. A New Method for the Synthesis of the Marine Alkaloid Fascaplysin Based on the Microwave-Assisted Minisci Reaction. Tetrahedron Lett. 2013, 54, 3530–3532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.-P.; Liu, M.-C.; Cai, Q.; Jia, F.-C.; Wu, A.-X. A Cascade Coupling Strategy for One-Pot Total Synthesis of β-Carboline and Isoquinoline-Containing Natural Products and Derivatives. Chem. Eur. J. 2013, 19, 10132–10137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battini, N.; Padala, A.K.; Mupparapu, N.; Vishwakarma, R.A.; Ahmed, Q.N. Unexplored Reactivity of 2-Oxoaldehydes towards Pictet–Spengler Conditions: Concise Approach to β-Carboline Based Marine Natural Products. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 26258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dighe, S.U.; Samanta, S.K.; Kolle, S.; Batra, S. Iodine-Mediated Oxidative Pictet-Spengler Reaction Using Terminal Alkyne as the 2-Oxoaldehyde Surrogate for the Synthesis of 1-Aroyl-β-Carbolines and Fused-Nitrogen Heterocycles. Tetrahedron 2017, 73, 2455–2467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girreser, U.; Hermann, T.W.; Piotrowska, K. Oxidation and Degradation Products of Papaverine, Part II[1]: Investigations on the Photochemical Degradation of Papaverine Solutions. Int. J. Pharm. Med. Chem. 2003, 336, 401–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Girreser, U.; Czyrski, A.; Hermann, T.W. Synthesis and Structure Elucidation of a New Isoquinolinium Inner Salt. Tetrahedron Lett. 2009, 50, 4610–4612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Y.; Ahmad, M.; Chen, S.; Gillespie, P.; Le, N.; Mennona, F.; Mischke, S.; So, S.-S.; Wang, H.; Burghardt, C.; et al. Discovery of 1-Arylcarbonyl-6,7-Dimethoxyisoquinoline Derivatives as Glutamine Fructose-6-Phosphate Amidotransferase (GFAT) Inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2011, 21, 6264–6269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franklin, C.S.; White, A.C. A Novel Preparation of Alpha-Substituted Tryptamines from Isatins. J. Chem. Soc. 1963, 196, 1335–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ash, A.S.F.; Wragg, W.R. 790. Synthesis of the 3-2′-Aminopropyl- and 3-2′-Aminobutyl-Derivatives of 5-Hydroxyindole, and an Alternative Synthesis of 5-Hydroxytryptamine. J. Chem. Soc. 1958, 3887–3892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyshlovoy, S.A.; Pelageev, D.N.; Hauschild, J.; Borisova, K.L.; Kaune, M.; Krisp, C.; Venz, S.; Sabutskii, Y.E.; Khmelevskaya, E.A.; Busenbender, T.; et al. Successful Targeting of the Warburg Effect in Prostate Cancer by Glucose-Conjugated 1,4-Naphthoquinones. Cancers 2019, 11, 1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
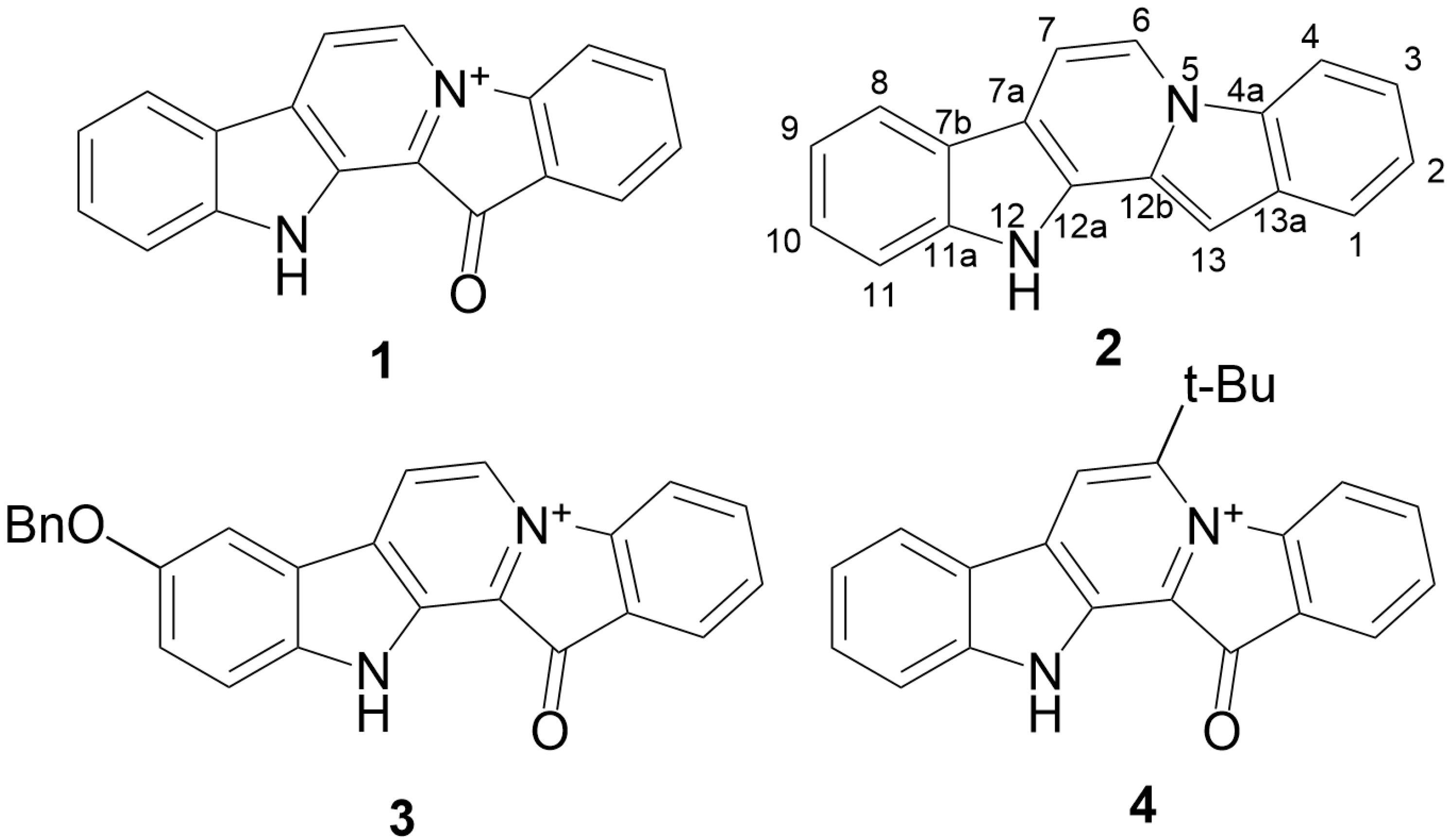

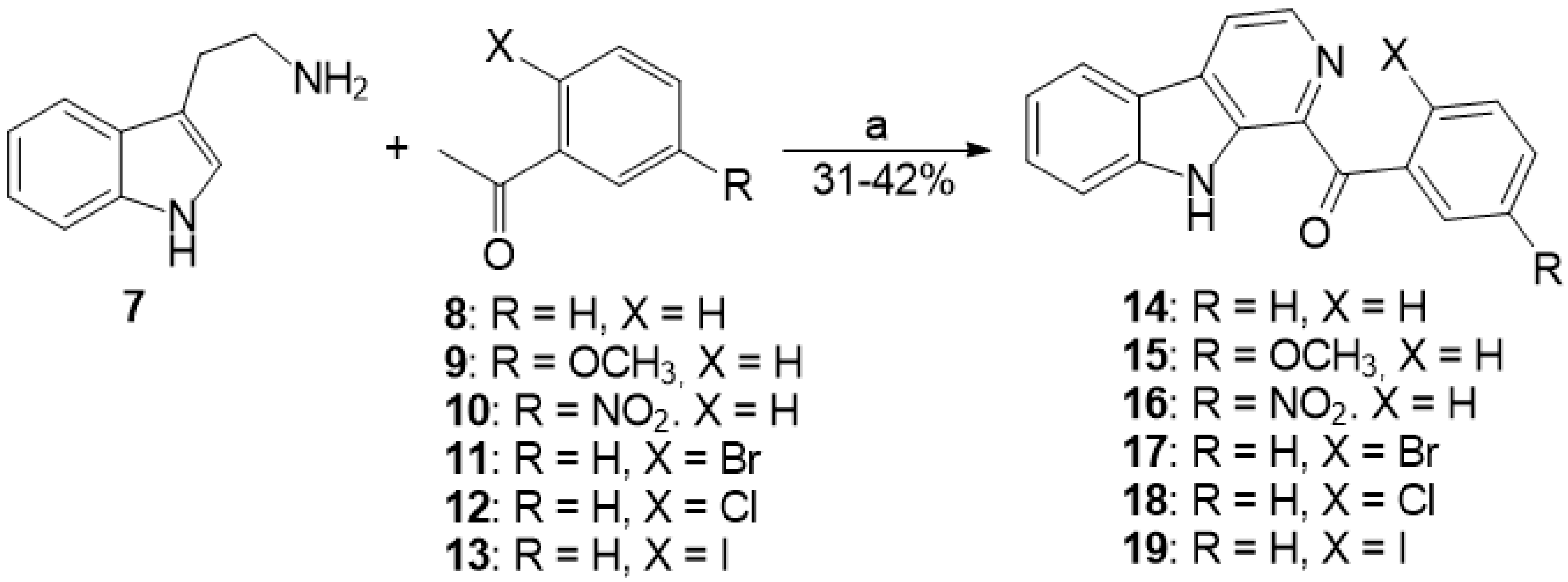
| Compound | R | X | Solvent | T, °C | Time, h | Special Condition | Result |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 14 | H | H | DMSO | 35 | 20 | — | — |
| 14 | H | H | DMSO | 35 | 12 | DBU | — |
| 14 | H | H | DMSO | 35 | 12 | TsOH | — |
| 15 | OCH3 | H | DMSO | 35 | 12 | — | Trace a |
| 16 | NO2 | H | DMSO | 35 | 12 | — | Trace a |
| 17 | H | Br | DMSO | 35 | 5 | — | 10% |
| 17 | H | Br | DMSO | 35 | 16 | — | 10% |
| 17 | H | Br | DMSO | 70 | 5 | AIBN | Mixture |
| 17 | H | Br | DMSO | 90 | 5 | BPO | Mixture |
| 17 | H | Br | EtOAc | 35 | 11 | — | — |
| 17 | H | Br | EtOH | 35 | 12 | — | — |
| 17 | H | Br | CHCl3 | 35 | 12 | — | — |
| 17 | H | Br | Dioxane | 35 | 12 | — | — |
| 17 | H | Br | Acetone | 35 | 12 | — | — |
| 17 | H | Br | CH3COOH | 35 | 12 | — | — |
| 17 | H | Br | Acetonitrile | 35 | 5 | — | Trace a |
| 17 | H | Br | DMSO | 80 | 5 | — | Mixture a |
| 18 | H | Cl | DMSO | 35 | 12 | — | — |
| 19 | H | I | DMSO | 35 | 5 | — | 50% |
| 19 | H | I | Acetonitrile | −5 | 5 | — | 50% |
| 19 | H | I | Acetonitrile | −5 | 3 × 1.5 b | — | 91% |
| Compound | X | Solvent | T, °C | Time, h | Special Condition | Result |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 24 | Br | — | 200 | 0.25 | — | Starting material |
| 24 | Br | — | 220 | 0.25 | — | Mixture, no target |
| 24 | Br | — | 240 | 0.10 | — | Mixture, no target |
| 25 | I | Acetonitrile | −5 | 3 × 1.5 a | UV irradiation | 88% |
| Compound | X | T, °C | Time, h | Special Condition | Result |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 36 | Br | 225 | 0.5 | — | no 4 |
| 36 | Br | 225 | 1 | — | no 4 |
| 36 | Br | 235 | 0.5 | — | no 4 |
| 37 | I | −5 | 0.5 × 3 a | UV, acetonitrile | 92% of 4 |
| MTT Assay | 1 (IC50, μM) | 4 (IC50, μM) |
|---|---|---|
| Cancer cells (average) | 0.554 | 1.186 |
| PC-3 | 0.766 ± 0.126 | 1.100 ± 0.076 |
| 22Rv1 | 0.242 ± 0.81 | 0.580 ± 0.073 |
| DU145 | 0.798 ± 0.054 | 1.732 ± 0.172 |
| LNCaP | 0.409 ± 0.02 | 1.330 ± 0.24 |
| Non-cancer cells (average) | 0.602 | 1.178 |
| PNT2 | 0.457 ± 0.075 | 1.817 ± 0.448 |
| MRC-9 | 0.890 ± 0.046 | 1.369 ± 0.424 |
| HEK293 | 0.458 ± 0.19 | 0.348 ± 0.09 |
| Selectivity index (SI) | 1.09 | 0.99 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tryapkin, O.A.; Kantemirov, A.V.; Dyshlovoy, S.A.; Prassolov, V.S.; Spirin, P.V.; von Amsberg, G.; Sidorova, M.A.; Zhidkov, M.E. A New Mild Method for Synthesis of Marine Alkaloid Fascaplysin and Its Therapeutically Promising Derivatives. Mar. Drugs 2023, 21, 424. https://doi.org/10.3390/md21080424
Tryapkin OA, Kantemirov AV, Dyshlovoy SA, Prassolov VS, Spirin PV, von Amsberg G, Sidorova MA, Zhidkov ME. A New Mild Method for Synthesis of Marine Alkaloid Fascaplysin and Its Therapeutically Promising Derivatives. Marine Drugs. 2023; 21(8):424. https://doi.org/10.3390/md21080424
Chicago/Turabian StyleTryapkin, Oleg A., Alexey V. Kantemirov, Sergey A. Dyshlovoy, Vladimir S. Prassolov, Pavel V. Spirin, Gunhild von Amsberg, Maria A. Sidorova, and Maxim E. Zhidkov. 2023. "A New Mild Method for Synthesis of Marine Alkaloid Fascaplysin and Its Therapeutically Promising Derivatives" Marine Drugs 21, no. 8: 424. https://doi.org/10.3390/md21080424
APA StyleTryapkin, O. A., Kantemirov, A. V., Dyshlovoy, S. A., Prassolov, V. S., Spirin, P. V., von Amsberg, G., Sidorova, M. A., & Zhidkov, M. E. (2023). A New Mild Method for Synthesis of Marine Alkaloid Fascaplysin and Its Therapeutically Promising Derivatives. Marine Drugs, 21(8), 424. https://doi.org/10.3390/md21080424