Marine Staurosporine Analogues: Activity and Target Identification in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Structure of Compound 4
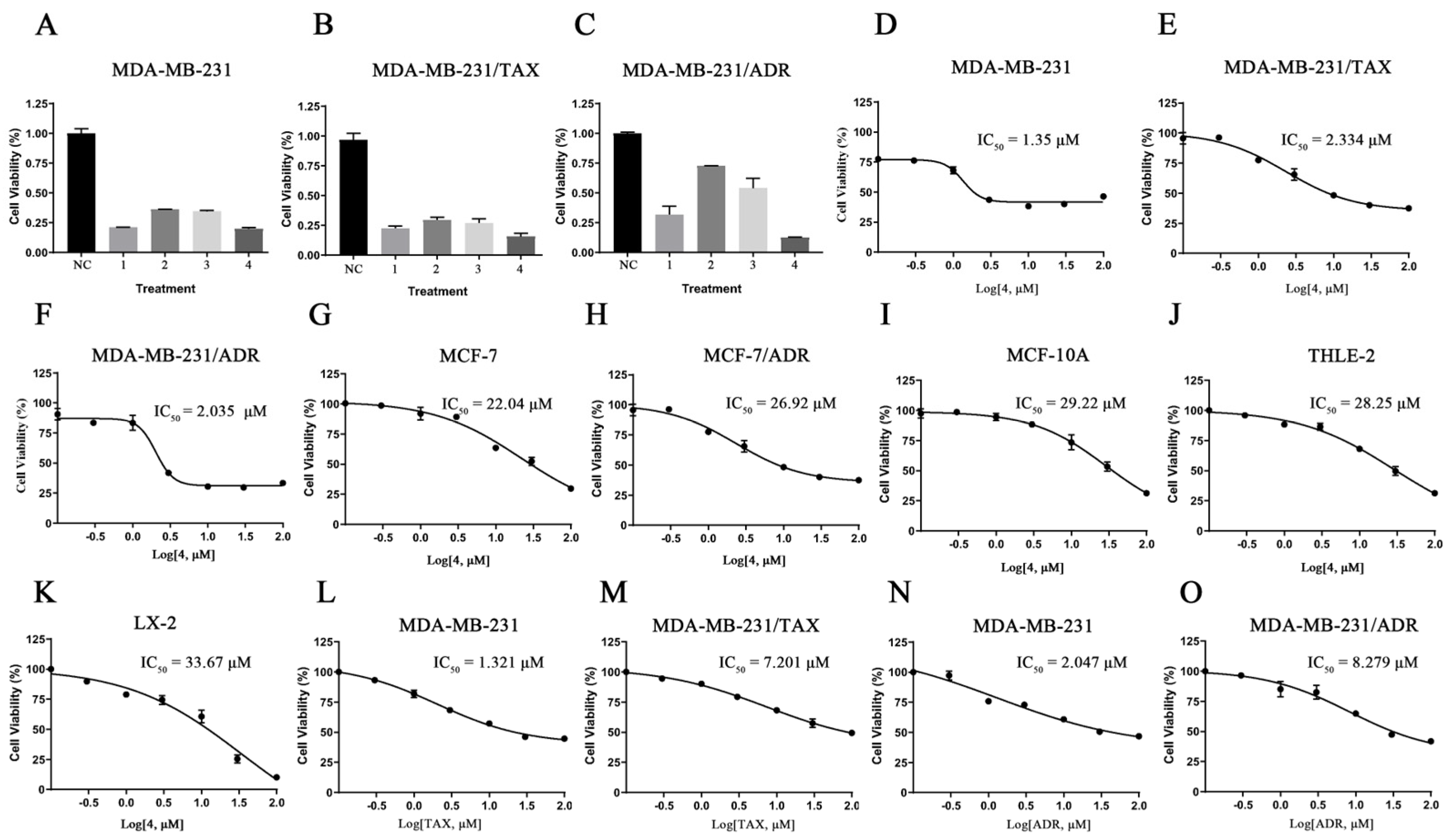
2.2. Compound 4 Exhibited the Best Inhibitory Activity against TNBC Cell Lines
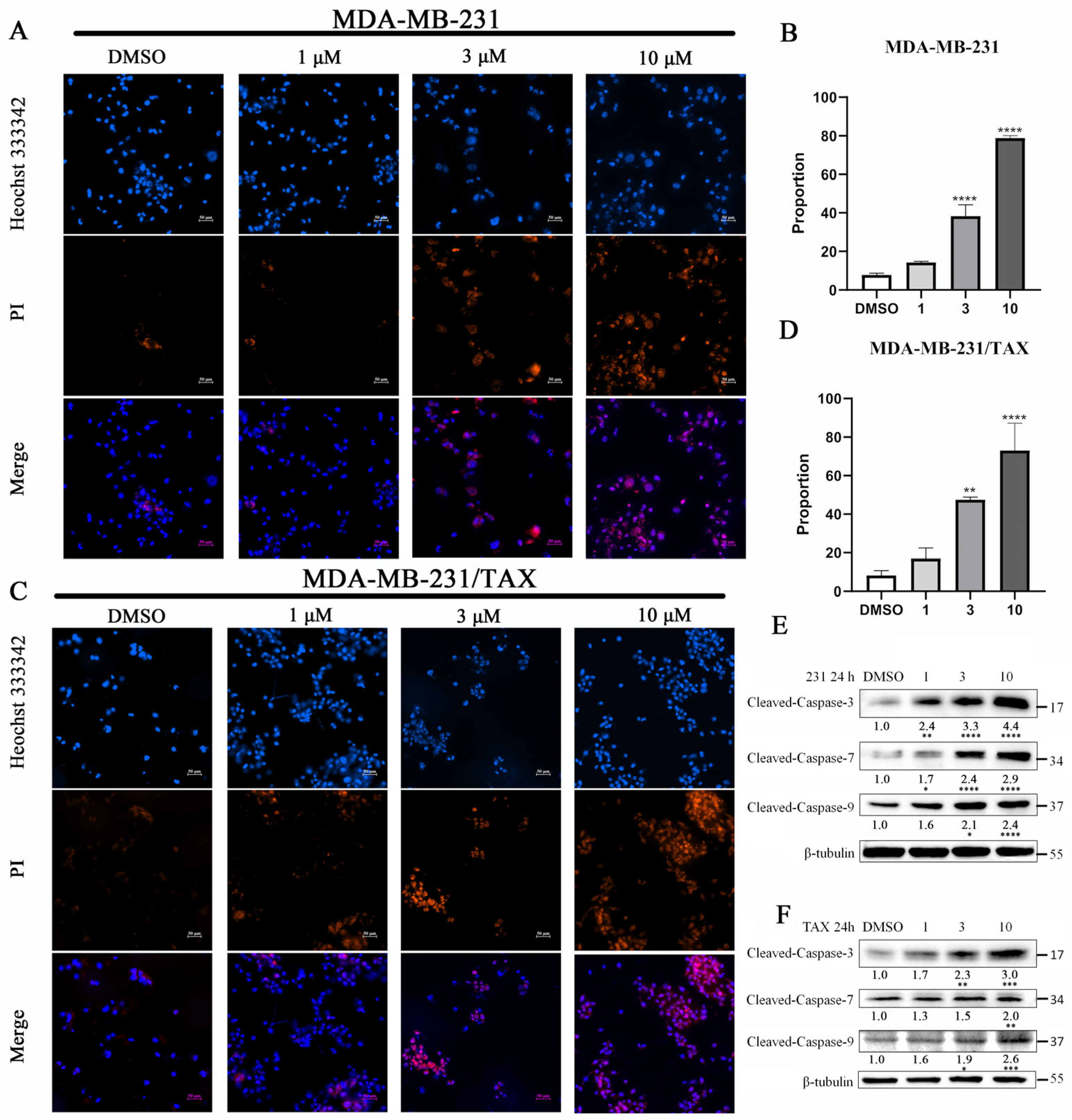
2.3. The Effects of Compound 4 on the Apoptosis of TNBC Cell Lines
2.4. The Effects of Compound 4 on the Cell Cycle of TNBC Cells
2.5. The Effects of Compound 4 on the Stemness of TNBC Cells
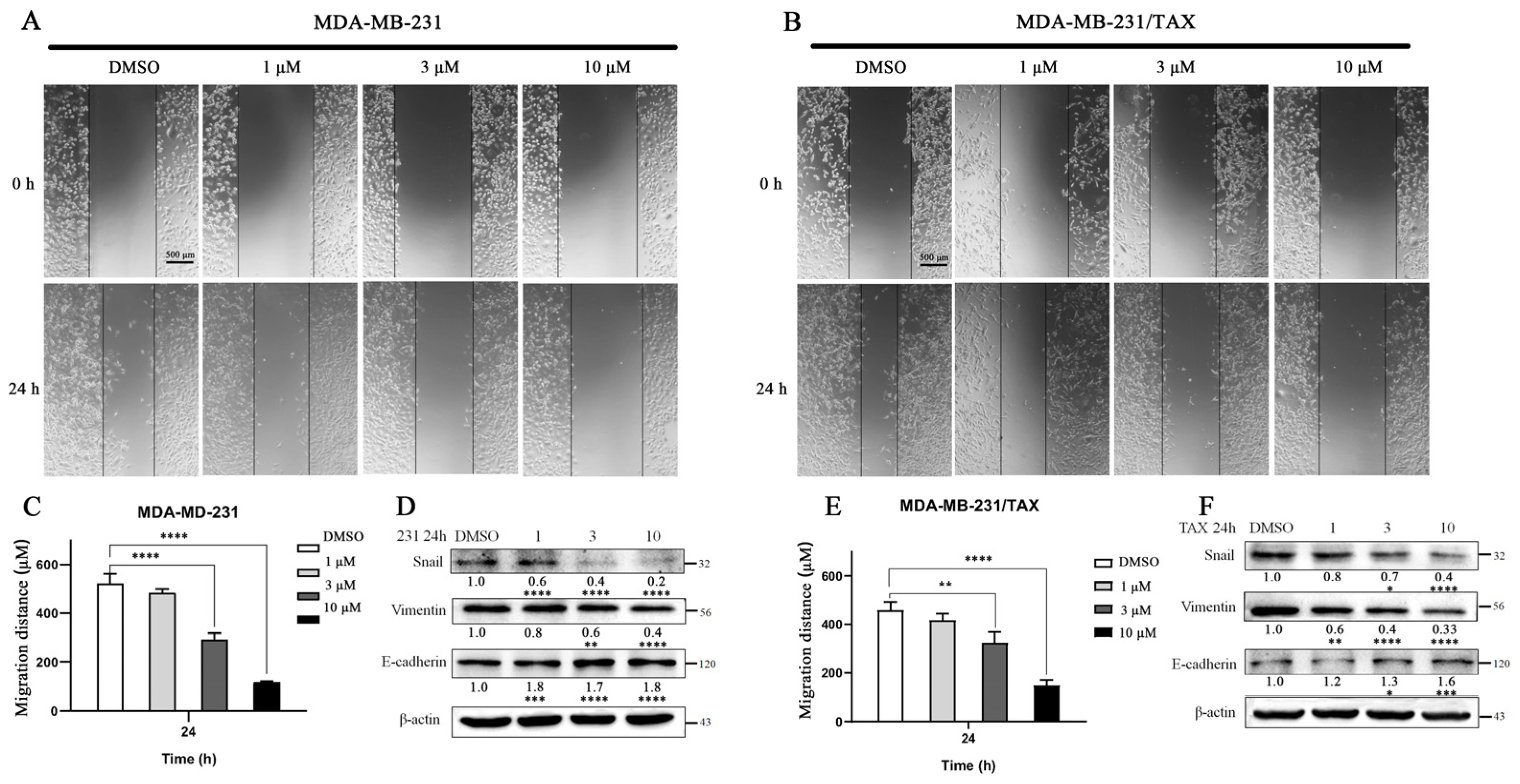
2.6. The Effects of Compound 4 on the Cell Migration of TNBC Cells
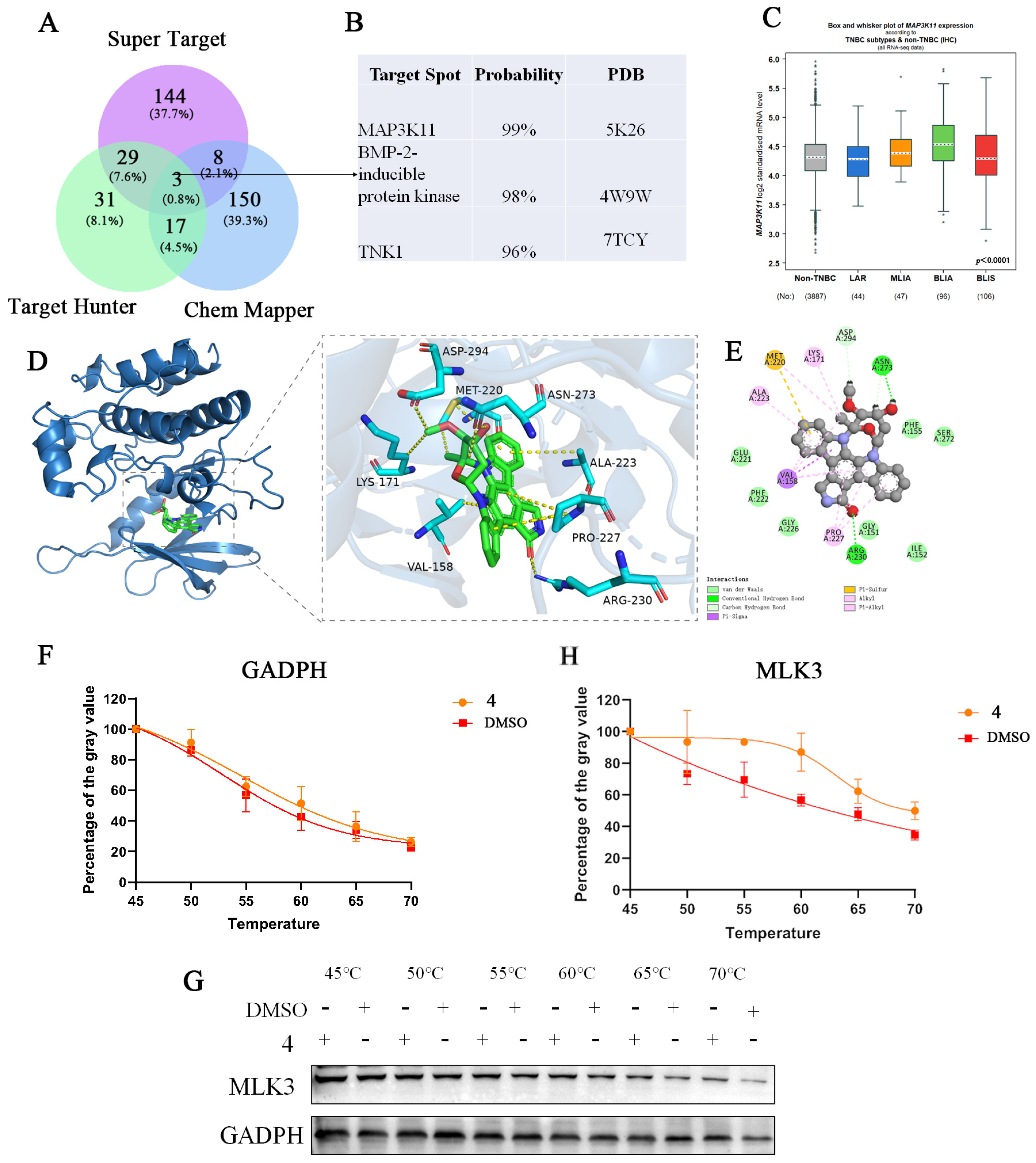
2.7. Target Identification and Binding Mode Analysis of Compound 4
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.1.1. Cell Lines and Cell Culture
4.1.2. Reagents and Antibodies
4.2. Experimental Methods
4.2.1. Compound Screening Sources
4.2.2. CCK8 Toxicity Assay
4.2.3. Apoptosis Analysis
4.2.4. Cellular Senescence Assay
4.2.5. Cancer Cell Stemness Assay
4.2.6. Cell Cycle Analysis
4.2.7. Wound-Healing Assay
4.2.8. Western Blotting
4.2.9. Molecular Docking and Virtual Screening
4.2.10. Cellular Thermal Shift Assay
4.2.11. Statistical Analyses
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhong, X.D.; Chen, L.J.; Xu, X.Y.; Liu, Y.J.; Tao, F.; Zhu, M.H.; Li, C.Y.; Zhao, D.; Yang, G.J.; Chen, J. Berberine as a potential agent for breast cancer therapy. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 993775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.Y.; Wang, W.; Leung, C.H.; Yang, G.J.; Chen, J. KDM5 family as therapeutic targets in breast cancer: Pathogenesis and therapeutic opportunities and challenges. Mol. Cancer 2024, 23, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, G.J.; Liu, Y.J.; Ding, L.J.; Tao, F.; Zhu, M.H.; Shi, Z.Y.; Wen, J.M.; Niu, M.Y.; Li, X.; Xu, Z.S.; et al. A state-of-the-art review on LSD1 and its inhibitors in breast cancer: Molecular mechanisms and therapeutic significance. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 989575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, G.J.; Wang, W.; Mok, S.W.F.; Wu, C.; Law, B.Y.K.; Miao, X.M.; Wu, K.J.; Zhong, H.J.; Wong, C.Y.; Wong, V.K.W.; et al. Selective inhibition of lysine-specific demethylase 5a (kdm5a) using a rhodium(iii) complex for triple-negative breast cancer therapy. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2018, 57, 13091–13095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.J.; Zhong, H.J.; Ko, C.N.; Wong, S.Y.; Vellaisamy, K.; Ye, M.; Ma, D.L.; Leung, C.H. Identification of a rhodium(iii) complex as a wee1 inhibitor against tp53-mutated triple-negative breast cancer cells. Chem. Commun. 2018, 54, 2463–2466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Won, K.A.; Spruck, C. Triple-negative breast cancer therapy: Current and future perspectives (review). Int. J. Oncol. 2020, 57, 1245–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derakhshan, F.; Reis-Filho, J.S. Pathogenesis of triple-negative breast cancer. Annu. Rev. Pathol. 2022, 17, 181–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, L.; Duan, J.J.; Bian, X.W.; Yu, S.C. Triple-negative breast cancer molecular subtyping and treatment progress. Breast Cancer Res. 2020, 22, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Q.; Shi, Y.; Wen, H.; Zhang, D.; Yan, X.; He, S.; Ding, L. Asepterpenedol A, a novel indole sesquiterpene with a rare 7/6/5/5/6/6-hexacyclic scaffold from a marine-derived fungus Chloridium sp. NBU3282. J. Mol. Struct. 2024, 1296, 136723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, L.; Talwar, A.; Chauhan, P.M. Bis and tris indole alkaloids from marine organisms: New leads for drug discovery. Curr. Med. Chem. 2007, 14, 1789–1803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.Y.; Chen, L.Y.; Chen, P.J.; El-Shazly, M.; Peng, B.R.; Chen, Y.C.; Su, C.H.; Su, J.H.; Sung, P.J.; Yen, P.T.; et al. Probing anti-leukemic metabolites from marine-derived Streptomyces sp. Ly1209. Metabolites 2022, 12, 320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Jin, W.; Zhou, X.; Li, J.; Xu, C.; Ma, Z.; Wang, J.; Qin, L.; Zhou, B.; Ding, W.; et al. Identification, structure-activity relationships of marine-derived indolocarbazoles, and a dual pkcθ/δ inhibitor with potent antipancreatic cancer efficacy. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 63, 12978–12991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, L.; Li, W.; Zhong, X.; Feng, F.; Xin, Y.; Yan, X.; Lazaro, J.E.H.; Zhang, B.; Shi, Y.; Yang, G.-J.; et al. Bresmycins A and B, potent anti-breast cancer indolocarbazole alkaloids from the sponge-associated Streptomyces sp. NBU3142. J. Mol. Struct. 2023, 1290, 135809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, Y.O.; Hitron, J.A.; Wang, X.; Chang, Q.; Pan, J.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, J.; Wang, S.; Lee, J.C.; Shi, X. Cr(VI) induces mitochondrial-mediated and caspase-dependent apoptosis through reactive oxygen species-mediated p53 activation in JB6 Cl41 cells. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2010, 245, 226–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Ma, X.; Fu, X.; Yan, R. Phytochemical content, cellular antioxidant activity and antiproliferative activity of Adinandra nitida tea (Shiyacha) infusion subjected to in vitro gastrointestinal digestion. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 50430–50440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Zhu, J.; Guo, L.; Shi, X.; Liu, Y.; Yang, X. Differential effects of polyphenols-enriched extracts from hawthorn fruit peels and fleshes on cell cycle and apoptosis in human MCF-7 breast carcinoma cells. Food Chem. 2013, 141, 1008–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsamman, K.; El-Masry, O.S. Staurosporine alleviates cisplatin chemoresistance in human cancer cell models by suppressing the induction of SQSTM1/p62. Oncol. Rep. 2018, 40, 2157–2162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reya, T.; Morrison, S.J.; Clarke, M.F.; Weissman, I.L. Stem cells, cancer, and cancer stem cells. Nature 2001, 414, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schatton, T.; Frank, N.Y.; Frank, M.H. Identification and targeting of cancer stem cells. Bioessays 2009, 31, 1038–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dean, M.; Fojo, T.; Bates, S. Tumour stem cells and drug resistance. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2005, 5, 275–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez Molina, D.; Jafari, R.; Ignatushchenko, M.; Seki, T.; Larsson, E.A.; Dan, C.; Sreekumar, L.; Cao, Y.; Nordlund, P. Monitoring drug target engagement in cells and tissues using the cellular thermal shift assay. Science 2013, 341, 84–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, J.; Xie, N.; Yang, J.; Guan, H.; Chen, W.; Wu, H.; Yuan, Z.; Wang, K.; Li, G.; Sun, J.; et al. Sirna-mediated suppression of synuclein γ inhibits mda-mb-231 cell migration and proliferation by downregulating the phosphorylation of akt and erk. J. Breast Cancer 2014, 17, 200–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerwick, W.H.; Moore, B.S. Lessons from the past and charting the future of marine natural products drug discovery and chemical biology. Chem. Biol. 2012, 19, 85–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; Zhao, J.; Luo, L.; Gao, Y.; Bao, H.; Li, P.; Zhang, H. Research progress of indole compounds with potential antidiabetic activity. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 223, 113665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, M.; Saxena, A.; Saha, B. An insight in anti-malarial potential of indole scaffold: A review. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 218, 113400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kochanowska-Karamyan, A.J.; Hamann, M.T. Marine indole alkaloids: Potential new drug leads for the control of depression and anxiety. Chem. Rev. 2010, 110, 4489–4497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiore, A.; Murray, P.J. Tryptophan and indole metabolism in immune regulation. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2021, 70, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Dong, W.; Guo, Q.; Li, X.; Huang, L. The importance of indole and azaindole scaffold in the development of antitumor agents. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 203, 112506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.; Wen, X.; Gong, Y.; Wang, X. Current scenario of indole derivatives with potential anti-drug-resistant cancer activity. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 200, 112359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehbub, M.F.; Lei, J.; Franco, C.; Zhang, W. Marine sponge derived natural products between 2001 and 2010: Trends and opportunities for discovery of bioactives. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 4539–4577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Soest, R.W.; Boury-Esnault, N.; Vacelet, J.; Dohrmann, M.; Erpenbeck, D.; De Voogd, N.J.; Santodomingo, N.; Vanhoorne, B.; Kelly, M.; Hooper, J.N. Global diversity of sponges (porifera). PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e35105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaffney, E.V. A cell line (HBL-100) established from human breast milk. Cell Tissue Res. 1982, 227, 563–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, L.Y.; Chiu, S.M.; Oleinick, N.L. Staurosporine-induced death of mcf-7 human breast cancer cells: A distinction between caspase-3-dependent steps of apoptosis and the critical lethal lesions. Exp. Cell Res. 2003, 283, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keydar, I.; Chen, L.; Karby, S.; Weiss, F.R.; Delarea, J.; Radu, M.; Chaitcik, S.; Brenner, H.J. Establishment and characterization of a cell line of human breast carcinoma origin. Eur. J. Cancer 1979, 15, 659–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, C.B. Apoptosis in the pathogenesis and treatment of disease. Science 1995, 267, 1456–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cryns, V.; Yuan, J. Proteases to die for. Genes. Dev. 1998, 12, 1551–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, M.; Hakem, R.; Soengas, M.S.; Duncan, G.S.; Shahinian, A.; Kägi, D.; Hakem, A.; McCurrach, M.; Khoo, W.; Kaufman, S.A.; et al. Essential contribution of caspase 3/CPP32 to apoptosis and its associated nuclear changes. Genes. Dev. 1998, 12, 806–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jänicke, R.U.; Sprengart, M.L.; Wati, M.R.; Porter, A.G. Caspase-3 is required for DNA fragmentation and morphological changes associated with apoptosis. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 9357–9360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Nijhawan, D.; Budihardjo, I.; Srinivasula, S.M.; Ahmad, M.; Alnemri, E.S.; Wang, X. Cytochrome c and datp-dependent formation of apaf-1/caspase-9 complex initiates an apoptotic protease cascade. Cell 1997, 91, 479–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, G.M. Caspases: The executioners of apoptosis. Biochem. J. 1997, 326 Pt 1, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milanovic, M.; Fan, D.N.Y.; Belenki, D.; Däbritz, J.H.M.; Zhao, Z.; Yu, Y.; Dörr, J.R.; Dimitrova, L.; Lenze, D.; Monteiro Barbosa, I.A.; et al. Senescence-associated reprogramming promotes cancer stemness. Nature 2018, 553, 96–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milczarek, M. The Premature Senescence in Breast Cancer Treatment Strategy. Cancers 2020, 12, 1815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mosieniak, G.; Sliwinska, M.A.; Alster, O.; Strzeszewska, A.; Sunderland, P.; Piechota, M.; Was, H.; Sikora, E. Polyploidy formation in doxorubicin-treated cancer cells can favor escape from senescence. Neoplasia 2015, 17, 882–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campisi, J. Suppressing cancer: The importance of being senescent. Science 2005, 309, 886–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, M.; Sexl, V.; Sherr, C.J.; Roussel, M.F. Assembly of cyclin d-dependent kinase and titration of p27kip1 regulated by mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase (Mek1). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 1091–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimri, G.P.; Lee, X.; Basile, G.; Acosta, M.; Scott, G.; Roskelley, C.; Medrano, E.E.; Linskens, M.; Rubelj, I.; Pereira-Smith, O.; et al. A biomarker that identifies senescent human cells in culture and in aging skin in vivo. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1995, 92, 9363–9367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gescher, A. Staurosporine analogues-pharmacological toys or useful antitumour agents? Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2000, 34, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, L.N.; De Moliner, E.; Brown, N.R.; Song, H.; Barford, D.; Endicott, J.A.; Noble, M.E. Structural studies with inhibitors of the cell cycle regulatory kinase cyclin-dependent protein kinase 2. Pharmacol. Ther. 2002, 93, 113–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Hajj, M.; Wicha, M.S.; Benito-Hernandez, A.; Morrison, S.J.; Clarke, M.F. Prospective identification of tumorigenic breast cancer cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 3983–3988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ginestier, C.; Hur, M.H.; Charafe-Jauffret, E.; Monville, F.; Dutcher, J.; Brown, M.; Jacquemier, J.; Viens, P.; Kleer, C.G.; Liu, S.; et al. ALDH1 is a marker of normal and malignant human mammary stem cells and a predictor of poor clinical outcome. Cell Stem Cell 2007, 1, 555–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, S.Q.; Alexandrou, A.T.; Li, J.J. Breast cancer stem cells: Multiple capacities in tumor metastasis. Cancer Lett. 2014, 349, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duester, G. Families of retinoid dehydrogenases regulating vitamin A function: Production of visual pigment and retinoic acid. Eur. J. Biochem. 2000, 267, 4315–4324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magni, M.; Shammah, S.; Schiró, R.; Mellado, W.; Dalla-Favera, R.; Gianni, A.M. Induction of cyclophosphamide-resistance by aldehyde-dehydrogenase gene transfer. Blood 1996, 87, 1097–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Li, J.G.; Zheng, X.Y.; Jin, F.; Dong, H.T. Expression of CD133, PAX2, ESA, and GPR30 in invasive ductal breast carcinomas. Chin. Med J. (Engl.) 2009, 122, 2763–2769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.; Tang, H.; Zhao, S.; Gao, X.; Yang, L.; Xu, J. Circ-e-cad encodes a protein that promotes the proliferation and migration of gastric cancer via the tgf-β/smad/c-e-cad/pi3k/akt pathway. Mol. Carcinog. 2023, 62, 360–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, A.; Ashary, N.; Singh, N.; Sharma, S.; Modi, D. Modulation of e-cadherin and n-cadherin by ovarian steroids and embryonic stimuli. Tissue Cell 2021, 73, 101670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peinado, H.; Olmeda, D.; Cano, A. Snail, zeb and bhlh factors in tumour progression: An alliance against the epithelial phenotype? Nat. Rev. Cancer 2007, 7, 415–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moody, S.E.; Perez, D.; Pan, T.C.; Sarkisian, C.J.; Portocarrero, C.P.; Sterner, C.J.; Notorfrancesco, K.L.; Cardiff, R.D.; Chodosh, L.A. The transcriptional repressor snail promotes mammary tumor recurrence. Cancer Cell 2005, 8, 197–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.; Dong, C.; Zhou, B.P. Epigenetic regulation of emt: The snail story. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2014, 20, 1698–1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savagner, P. Leaving the neighborhood: Molecular mechanisms involved during epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Bioessays 2001, 23, 912–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Liu, Y.; Feng, Y.; Gao, S. Snail gene inhibited by hypoxia-inducible factor 1α (hif-1α) in epithelial ovarian cancer. Int. J. Immunopathol. Pharmacol. 2016, 29, 364–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Wu, W.; Du, Y.; Santos, S.J.; Conrad, S.E.; Watson, J.T.; Grammatikakis, N.; Gallo, K.A. Hsp90/p50cdc37 is required for mixed-lineage kinase (mlk) 3 signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 19457–19563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ke, R.; Viswakarma, N.; Menhart, M.; Singh, S.K.; Kumar, S.; Srivastava, P.; Vishnoi, K.; Kashyap, T.; Srivastava, D.; Nair, R.S.; et al. MLK3 promotes prooncogenic signaling in hepatocellular carcinoma via TGF-β pathway. Oncogene 2024, 43, 2307–2324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chadee, D.N.; Xu, D.; Hung, G.; Andalibi, A.; Lim, D.J.; Luo, Z.; Gutmann, D.H.; Kyriakis, J.M. Mixed-lineage kinase 3 regulates b-raf through maintenance of the b-raf/raf-1 complex and inhibition by the nf2 tumor suppressor protein. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 4463–4468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhan, Y.; Modi, N.; Stewart, A.M.; Hieronimus, R.I.; Liu, J.; Gutmann, D.H.; Chadee, D.N. Regulation of mixed lineage kinase 3 is required for neurofibromatosis-2-mediated growth suppression in human cancer. Oncogene 2011, 30, 781–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Miller, E.M.; Gallo, K.A. MLK3 is critical for breast cancer cell migration and promotes a malignant phenotype in mammary epithelial cells. Oncogene 2010, 29, 4399–4411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, P.; Senthivinayagam, S.; Rangasamy, V.; Sondarva, G.; Rana, B. Mixed lineage kinase-3/jnk1 axis promotes migration of human gastric cancer cells following gastrin stimulation. Mol. Endocrinol. 2010, 24, 598–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swenson, K.I.; Winkler, K.E.; Means, A.R. A new identity for MLK3 as an NIMA-related, cell cycle-regulated kinase that is localized near centrosomes and influences microtubule organization. Mol. Biol. Cell 2003, 14, 156–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cha, H.; Dangi, S.; Machamer, C.E.; Shapiro, P. Inhibition of mixed-lineage kinase (MLK) activity during G2-phase disrupts microtubule formation and mitotic progression in HeLa cells. Cell. Signal. 2006, 18, 93–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cedeno-Rosario, L.; Honda, D.; Sunderland, A.M.; Lewandowski, M.D.; Taylor, W.R.; Chadee, D.N. Phosphorylation of mixed lineage kinase MLK3 by cyclin-dependent kinases CDK1 and CDK2 controls ovarian cancer cell division. J. Biol. Chem. 2022, 298, 102263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohn, E.J.; Jung, D.B.; Lee, H.; Han, I.; Lee, J.; Lee, H.; Kim, S.H. Cnot2 promotes proliferation and angiogenesis via vegf signaling in mda-mb-231 breast cancer cells. Cancer Lett. 2018, 412, 88–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adriá-Cebrián, J.; Guaita-Esteruelas, S.; Lam, E.W.; Rodríguez-Balada, M.; Capellades, J.; Girona, J.; Jimenez-Santamaria, A.M.; Yanes, O.; Masana, L.; Gumà, J. Mcf-7 drug resistant cell lines switch their lipid metabolism to triple negative breast cancer signature. Cancers 2021, 13, 5871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, T.; Liu, P.; Li, Q.; Shi, C.; Wang, X. Inhibitory effects of everolimus in combination with paclitaxel on adriamycin-resistant breast cancer cell line mda-mb-231. Taiwan. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2020, 59, 828–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, J.; Fei, C.J.; Hu, Y.; Wu, X.Y.; Nie, L.; Chen, J. Current understanding of the cGAS-STING signaling pathway: Structure, regulatory mechanisms, and related diseases. Zool. Res. 2023, 44, 183–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiu, H.T.; Lin, Y.C.; Lee, M.N.; Chen, Y.L.; Wang, M.S.; Lai, C.C. Biochemical characterization and substrate specificity of the gene cluster for biosyntheses of K-252a and its analogs by in vitro heterologous expression system of Escherichia coli. Mol. Biosyst. 2009, 5, 1192–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.K.; Su, L.D.; Feng, L.L.; Li, J.L.; Pan, L.; Danzeng, Q.; Li, Y.; Shang, T.; Zhan, X.L.; Chen, S.Y.; et al. TFPI from erythroblasts drives heme production in central macrophages promoting erythropoiesis in polycythemia. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 3976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, L.; Sung, J.; Stacey, G.; Masters, J.R. Detection of mycoplasma in cell cultures. Nat. Protoc. 2010, 5, 929–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.W.; Ma, J.K.; Jiang, R.; Zhan, X.L.; Chen, S.Y.; Feng, L.L.; Zhang, Q.; Liang, T.B.; Lv, K.; Yang, G.J.; et al. Meteorin links the bone marrow hypoxic state to hematopoietic stem/progenitor cell mobilization. Cell Rep. 2022, 40, 111361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.J.; Wang, W.; Lei, P.M.; Leung, C.H.; Ma, D.L. A 7-methoxybicoumarin derivative selectively inhibits brd4 bd2 for anti-melanoma therapy. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 164, 3204–3220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.J.; Ko, C.N.; Zhong, H.J.; Leung, C.H.; Ma, D.L. Structure-based discovery of a selective kdm5a inhibitor that exhibits anti-cancer activity via inducing cell cycle arrest and senescence in breast cancer cell lines. Cancers 2019, 11, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Qiu, T.X.; Hu, Y.; Liu, L.; Chen, J. Antiviral effects of natural small molecules on aquatic rhabdovirus by interfering with early viral replication. Zool. Res. 2022, 43, 966–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, G.J.; Song, Y.Q.; Wang, W.; Han, Q.B.; Ma, D.L.; Leung, C.H. An optimized brd4 inhibitor effectively eliminates nf-κb-driven triple-negative breast cancer cells. Bioorg Chem. 2021, 114, 105158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, S.S.; Yang, G.J.; Wang, W.H.; Song, Y.Q.; Ko, C.N.; Han, Q.B.; Ma, D.L.; Leung, C.H. Identification of a cytisine-based EED-EZH2 protein-protein interaction inhibitor preventing metastasis in triple-negative breast cancer cells. Acta Mater. Med. 2022, 1, 197–211. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Chen, R.Y.; Shi, J.J.; Li, C.Y.; Liu, Y.J.; Gao, C.; Gao, M.R.; Zhang, S.; Lu, J.F.; Cao, J.F.; et al. Emerging role of Jumonji domain-containing protein D3 in inflammatory diseases. J. Pharm. Anal. 2024, 14, 100978. [Google Scholar]
- Perrin, J.; Werner, T.; Kurzawa, N.; Rutkowska, A.; Childs, D.D.; Kalxdorf, M.; Poeckel, D.; Stonehouse, E.; Strohmer, K.; Heller, B.; et al. Identifying drug targets in tissues and whole blood with thermal-shift profiling. Nat. Biotechnol. 2020, 38, 303–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, R.-Y.; Ding, L.-J.; Liu, Y.-J.; Shi, J.-J.; Yu, J.; Li, C.-Y.; Lu, J.-F.; Yang, G.-J.; Chen, J. Marine Staurosporine Analogues: Activity and Target Identification in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Mar. Drugs 2024, 22, 459. https://doi.org/10.3390/md22100459
Chen R-Y, Ding L-J, Liu Y-J, Shi J-J, Yu J, Li C-Y, Lu J-F, Yang G-J, Chen J. Marine Staurosporine Analogues: Activity and Target Identification in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Marine Drugs. 2024; 22(10):459. https://doi.org/10.3390/md22100459
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Ru-Yi, Li-Jian Ding, Yan-Jun Liu, Jin-Jin Shi, Jing Yu, Chang-Yun Li, Jian-Fei Lu, Guan-Jun Yang, and Jiong Chen. 2024. "Marine Staurosporine Analogues: Activity and Target Identification in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer" Marine Drugs 22, no. 10: 459. https://doi.org/10.3390/md22100459
APA StyleChen, R.-Y., Ding, L.-J., Liu, Y.-J., Shi, J.-J., Yu, J., Li, C.-Y., Lu, J.-F., Yang, G.-J., & Chen, J. (2024). Marine Staurosporine Analogues: Activity and Target Identification in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Marine Drugs, 22(10), 459. https://doi.org/10.3390/md22100459






