A Hadal Streptomyces-Derived Echinocandin Acylase Discovered through the Prioritization of Protein Families
Abstract
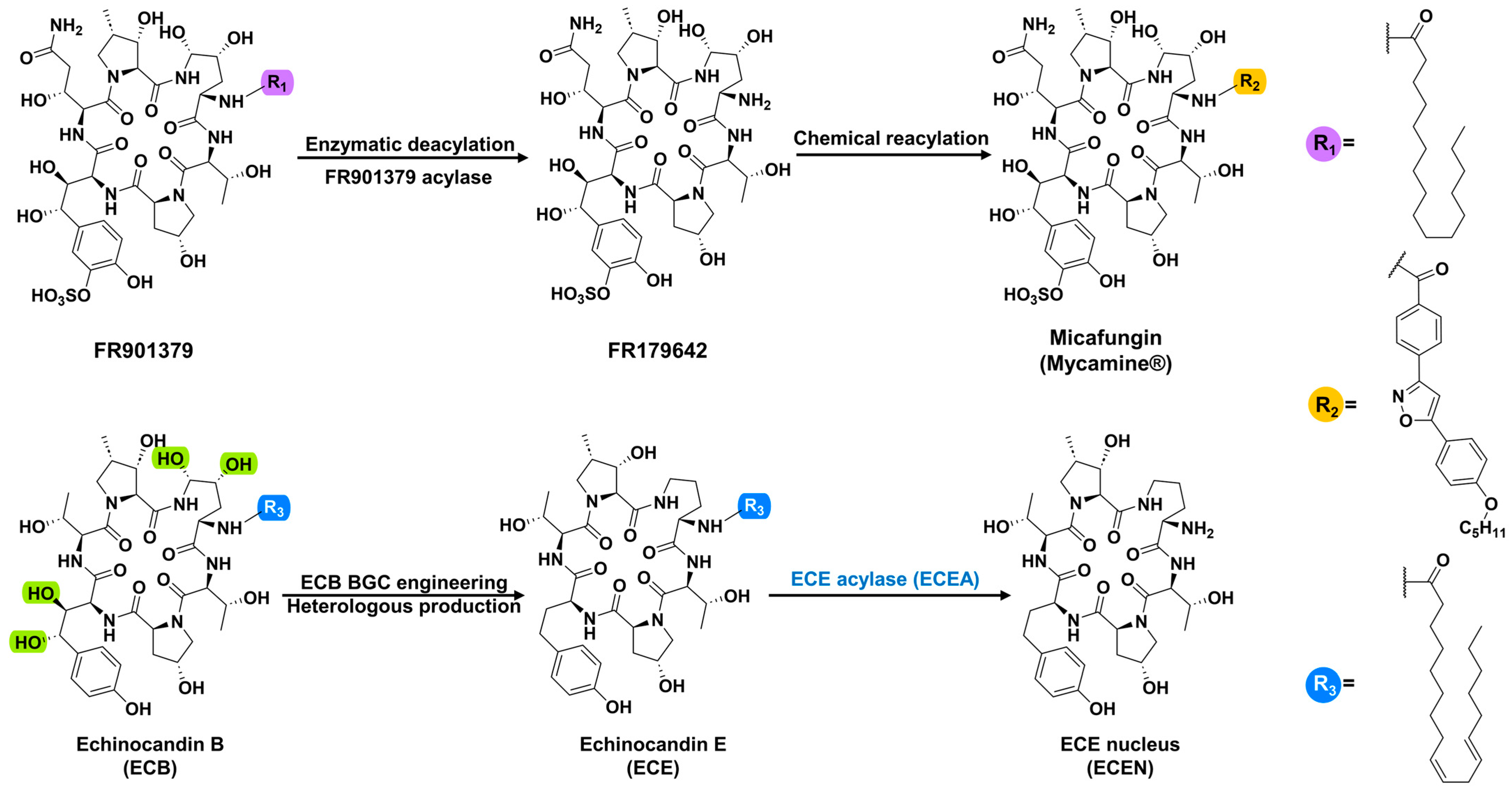
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
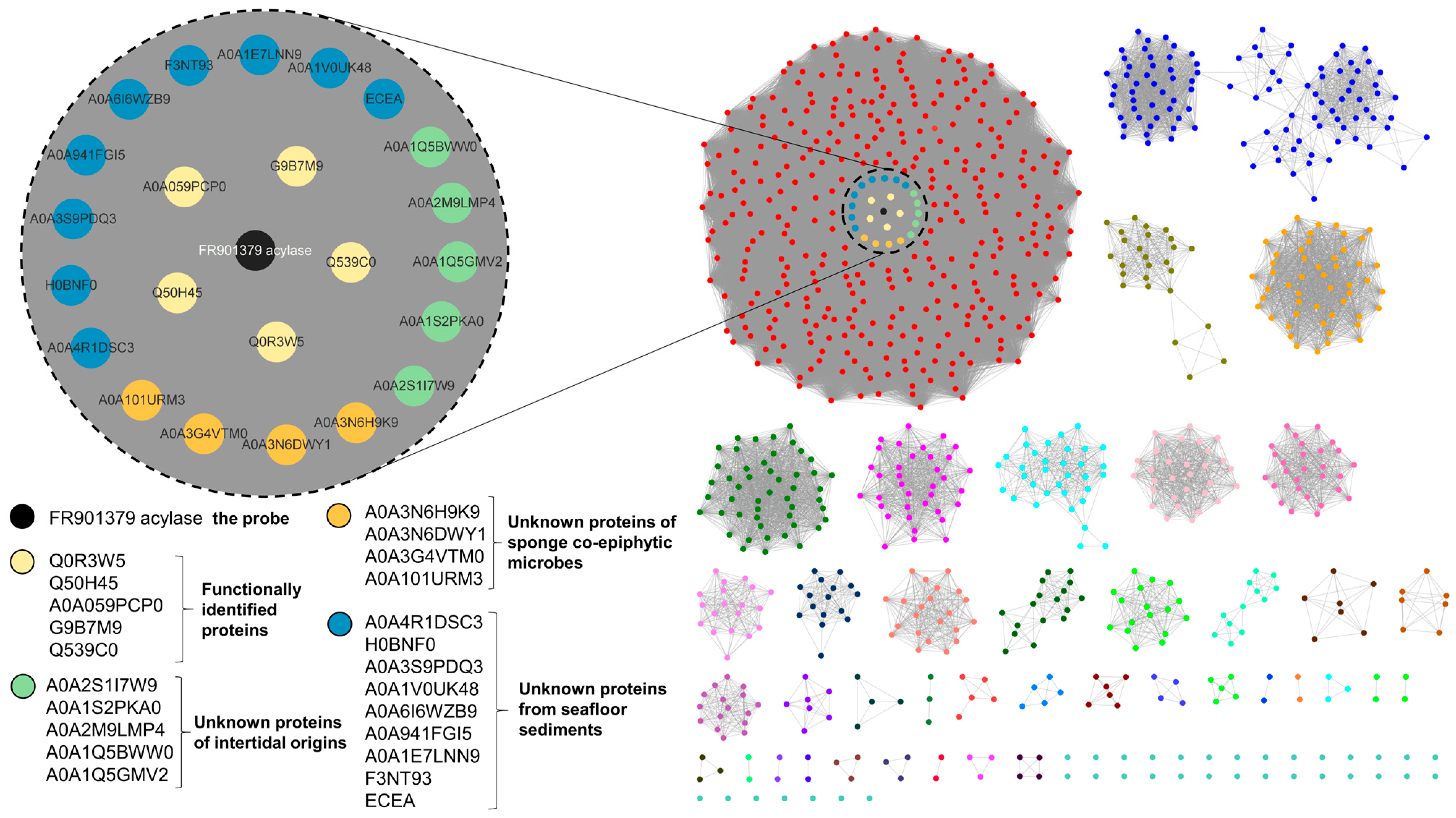
2.1. Hypothetic Echinocandin Acylases Prioritized by EFT-EST
2.2. Deacylation Activity of the Hadal Bacterium Streptomyces sp. SY1965
2.3. Engineering of Streptomyces Lividans TK24 for the Heterologous Production of Recombinant ECEA
2.4. Deacylation of Echinocandin E using the Recombinant Strain TKecea66
2.5. Deacylation of FR901379 using the Recombinant Strain TKecea66
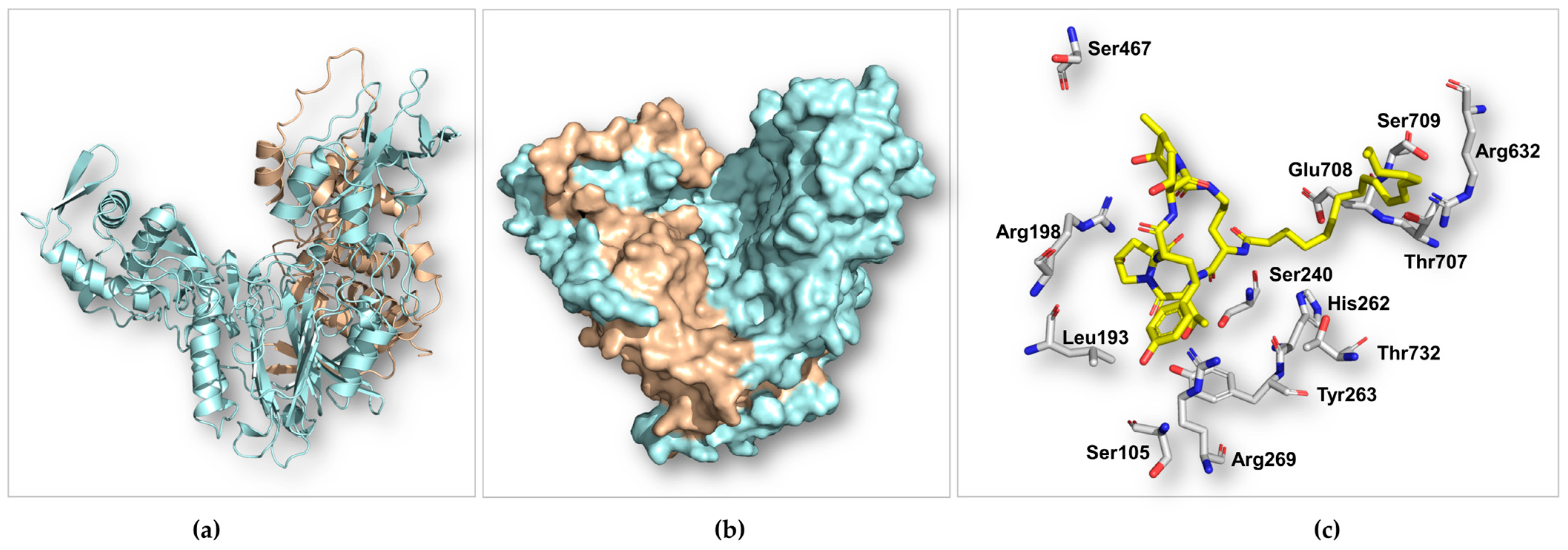
2.6. Analysis of the Predicted Structure of ECEA
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Bioinformatic Analysis
3.2. Strains and Reagents
3.3. HPLC and LC-MS Analyses
3.4. Heterologous Expression of the ECE Acylase Gene in S. lividans TK24
3.5. Protein Production and Purification
3.6. Preparation of ECE and the ECEN
3.7. Biotransformation Assay
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Denning, D.W. Echinocandin antifungal drugs. Lancet 2003, 362, 1142–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perlin, D.S. Mechanisms of echinocandin antifungal drug resistance. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2015, 1354, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antinori, S.; Milazzo, L.; Sollima, S.; Galli, M.; Corbellino, M. Candidemia and invasive candidiasis in adults: A narrative review. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2016, 34, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szymański, M.; Chmielewska, S.; Czyżewska, U.; Malinowska, M.; Tylicki, A. Echinocandins—Structure, mechanism of action and use in antifungal therapy. J. Enzyme Inhib. Med. Chem. 2022, 37, 876–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syed, Y.Y. Rezafungin: First Approval. Drugs 2023, 83, 833–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, L.; Li, J.; Liu, A.; Chang, Q.; Lin, H.; Chen, D. Efficient Bioconversion of Echinocandin B to Its Nucleus by Overexpression of Deacylase Genes in Different Host Strains. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 79, 1126–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, S.-P.; Han, X.; Zhu, H.-Y.; Sheng, Q.; Tang, H.; Liu, Z.-Q.; Zheng, Y.-G. Functional expression of an echinocandin B deacylase from Actinoplanes utahensis in Escherichia coli. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 187, 850–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kreuzman, A.J.; Hodges, R.L.; Swartling, J.R.; Pohl, T.E.; Ghag, S.K.; Baker, P.J.; McGilvray, D.; Yeh, W.K. Membrane-associated echinocandin B deacylase of Actinoplanes utahensis: Purification, characterization, heterologous cloning and enzymatic deacylation reaction. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2000, 24, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueda, S.; Shibata, T.; Ito, K.; Oohata, N.; Yamashita, M.; Hino, M.; Yamada, M.; Isogai, Y.; Hashimoto, S. Cloning and expression of the FR901379 acylase gene from Streptomyces sp. no. 6907. J. Antibiot. 2011, 64, 169–175. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, X.; Jiang, Q.; Chen, X.; Shu, H.; Xu, Y.; Sheng, H.; Yu, Y.; Wang, W.; Keller, N.P.; Xu, J.; et al. Unnatural tetradeoxy echinocandins produced by gene cluster design and heterologous expression. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2023, 21, 3552–3556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polderman-Tijmes, J.J.; Jekel, P.A.; de Vries, E.J.; van Merode, A.E.; Floris, R.; van der Laan, J.M.; Sonke, T.; Janssen, D.B. Cloning, sequence analysis, and expression in Escherichia coli of the gene encoding an alpha-amino acid ester hydrolase from Acetobacter turbidans. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2002, 68, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zallot, R.; Oberg, N.; Gerlt, J.A. The EFI Web Resource for Genomic Enzymology Tools: Leveraging Protein, Genome, and Metagenome Databases to Discover Novel Enzymes and Metabolic Pathways. Biochemistry 2019, 58, 4169–4182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oberg, N.; Zallot, R.; Gerlt, J.A. EFI-EST, EFI-GNT, and EFI-CGFP: Enzyme Function Initiative (EFI) Web Resource for Genomic Enzymology Tools. J. Mol. Biol. 2023, 435, 168018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerlt, J.A.; Bouvier, J.T.; Davidson, D.B.; Imker, H.J.; Sadkhin, B.; Slater, D.R.; Whalen, K.L. Enzyme Function Initiative-Enzyme Similarity Tool (EFI-EST): A web tool for generating protein sequence similarity networks. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2015, 1854, 1019–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saito, R.; Smoot, M.E.; Ono, K.; Ruscheinski, J.; Wang, P.-L.; Lotia, S.; Pico, A.R.; Bader, G.D.; Ideker, T. A travel guide to Cytoscape plugins. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 1069–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, W.; Qin, L.; Lian, X.-Y.; Zhang, Z. New Antifungal Metabolites from the Mariana Trench Sediment-Associated Actinomycete Streptomyces sp. SY1965. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bryant, P.; Pozzati, G.; Elofsson, A. Improved prediction of protein-protein interactions using AlphaFold2. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oinonen, C.; Rouvinen, J. Structural comparison of Ntn-hydrolases. Protein Sci. 2001, 9, 2329–2337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linhorst, A.; Lübke, T. The Human Ntn-Hydrolase Superfamily: Structure, Functions and Perspectives. Cells 2022, 11, 1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Yoon, K.-H.; Khang, Y.; Turley, S.; Hol, W.G.J. The 2.0 Å Crystal Structure of Cephalosporin Acylase. Structure 2000, 8, 1059–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, H.; Maurer, K.H.; Hutchinson, C.R. Transformation of Streptomyces erythraeus. J. Antibiot. 1986, 39, 1304–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elbing, K.L.; Brent, R. Recipes and Tools for Culture of Escherichia coli. Curr. Protoc. Mol. Biol. 2019, 125, e83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazodier, P.; Petter, R.; Thompson, C. Intergeneric conjugation between Escherichia coli and Streptomyces species. J. Bacteriol. 1989, 171, 3583–3585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jiang, X.; Shu, H.; Feng, S.; Wang, P.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, N. A Hadal Streptomyces-Derived Echinocandin Acylase Discovered through the Prioritization of Protein Families. Mar. Drugs 2024, 22, 212. https://doi.org/10.3390/md22050212
Jiang X, Shu H, Feng S, Wang P, Zhang Z, Wang N. A Hadal Streptomyces-Derived Echinocandin Acylase Discovered through the Prioritization of Protein Families. Marine Drugs. 2024; 22(5):212. https://doi.org/10.3390/md22050212
Chicago/Turabian StyleJiang, Xuejian, Hongjun Shu, Shuting Feng, Pinmei Wang, Zhizhen Zhang, and Nan Wang. 2024. "A Hadal Streptomyces-Derived Echinocandin Acylase Discovered through the Prioritization of Protein Families" Marine Drugs 22, no. 5: 212. https://doi.org/10.3390/md22050212
APA StyleJiang, X., Shu, H., Feng, S., Wang, P., Zhang, Z., & Wang, N. (2024). A Hadal Streptomyces-Derived Echinocandin Acylase Discovered through the Prioritization of Protein Families. Marine Drugs, 22(5), 212. https://doi.org/10.3390/md22050212






