Morphological, Toxicological, and Biochemical Characterization of Two Species of Gambierdiscus from Bahía de La Paz, Gulf of California
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
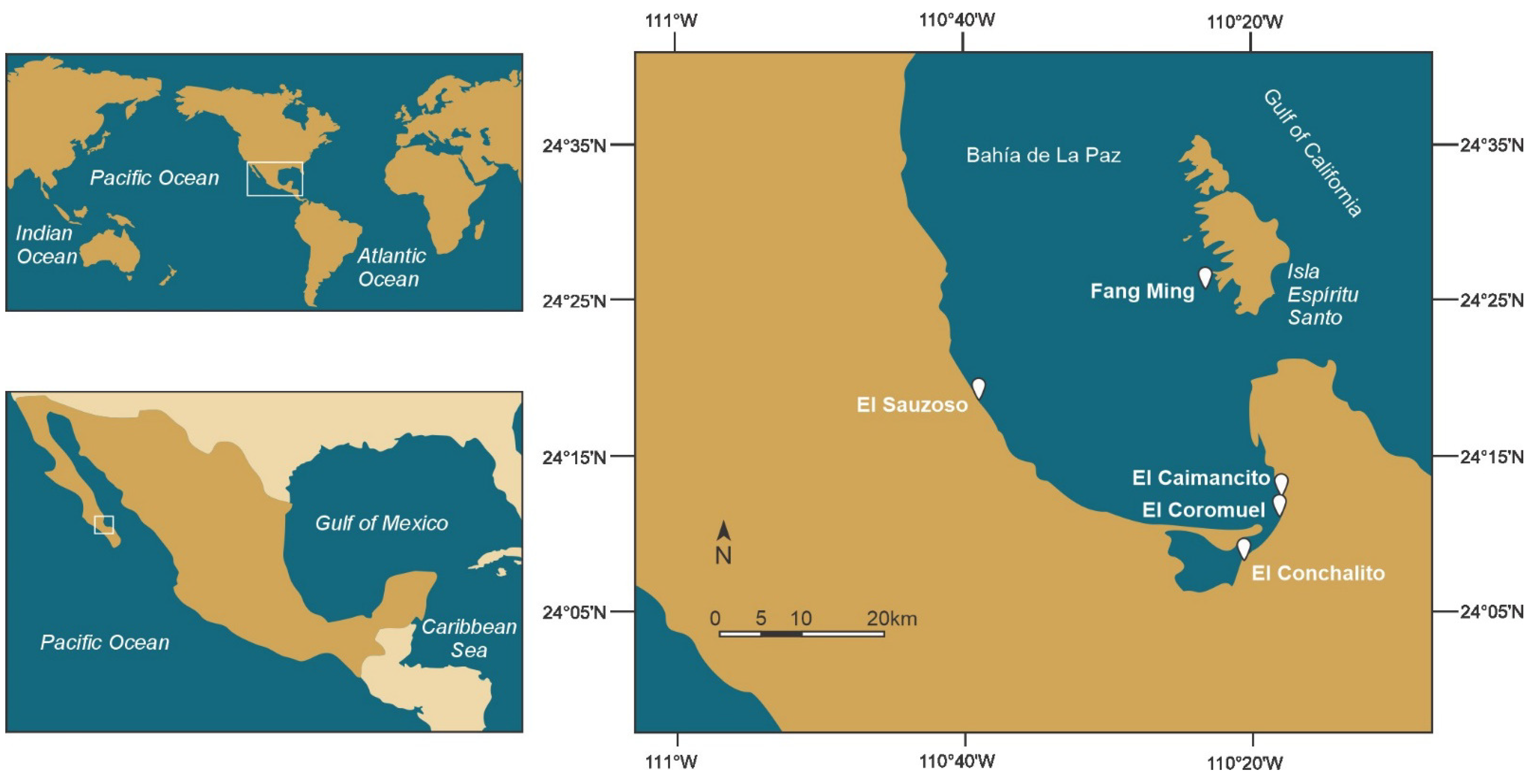
2.1. Isolation and Algal Cultures
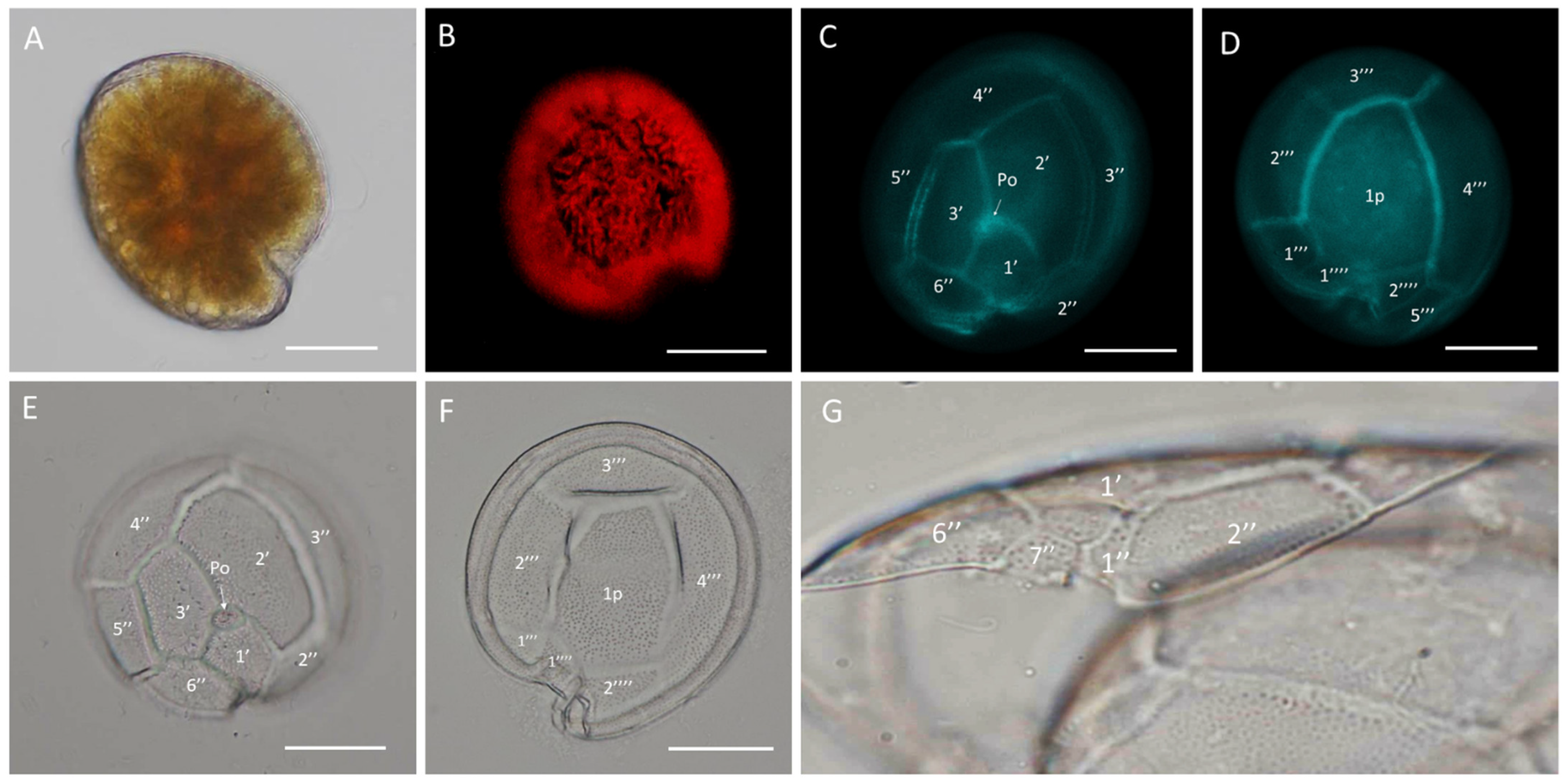
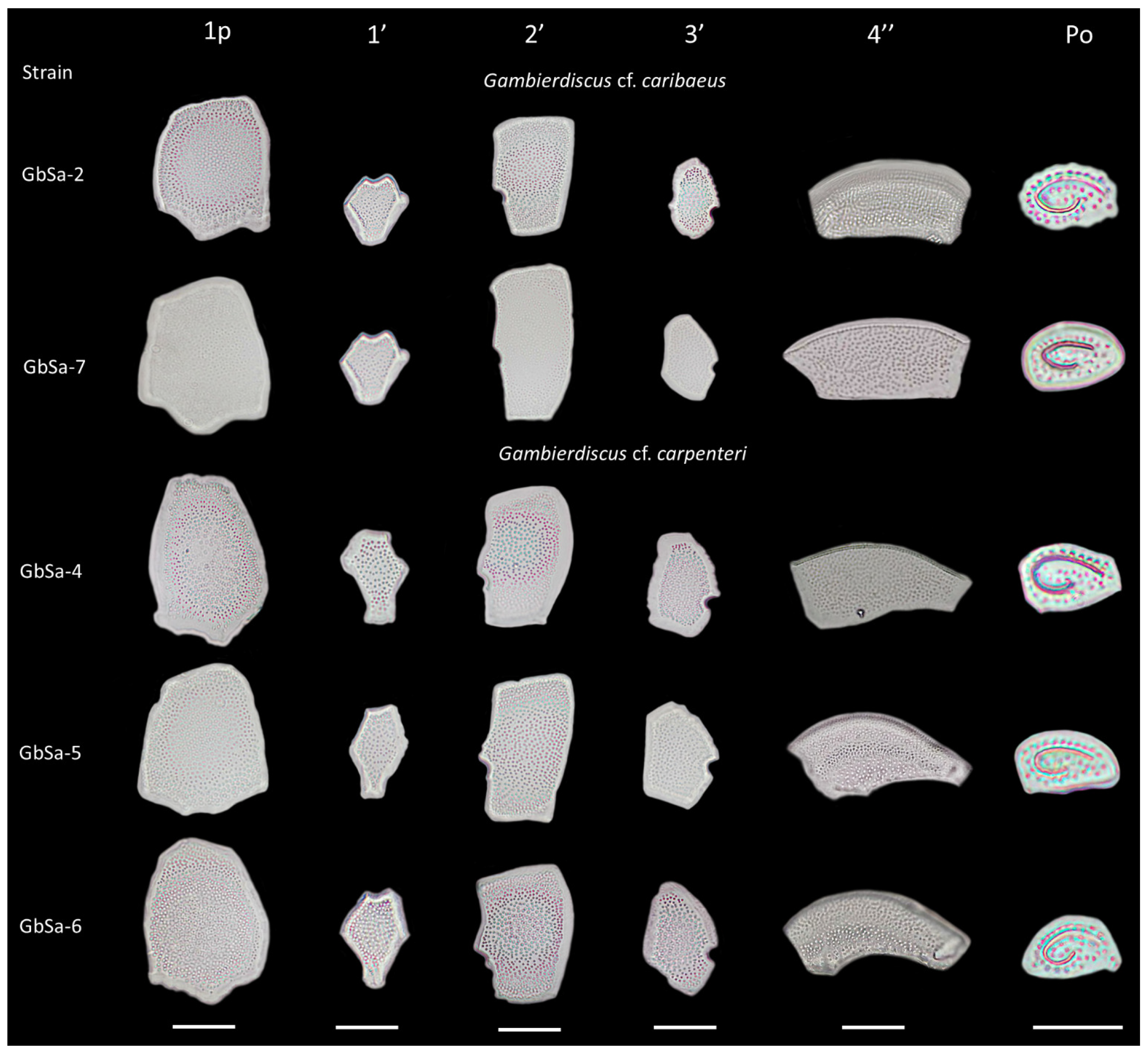
2.2. Morphological Identification
2.3. Biochemical Characterization
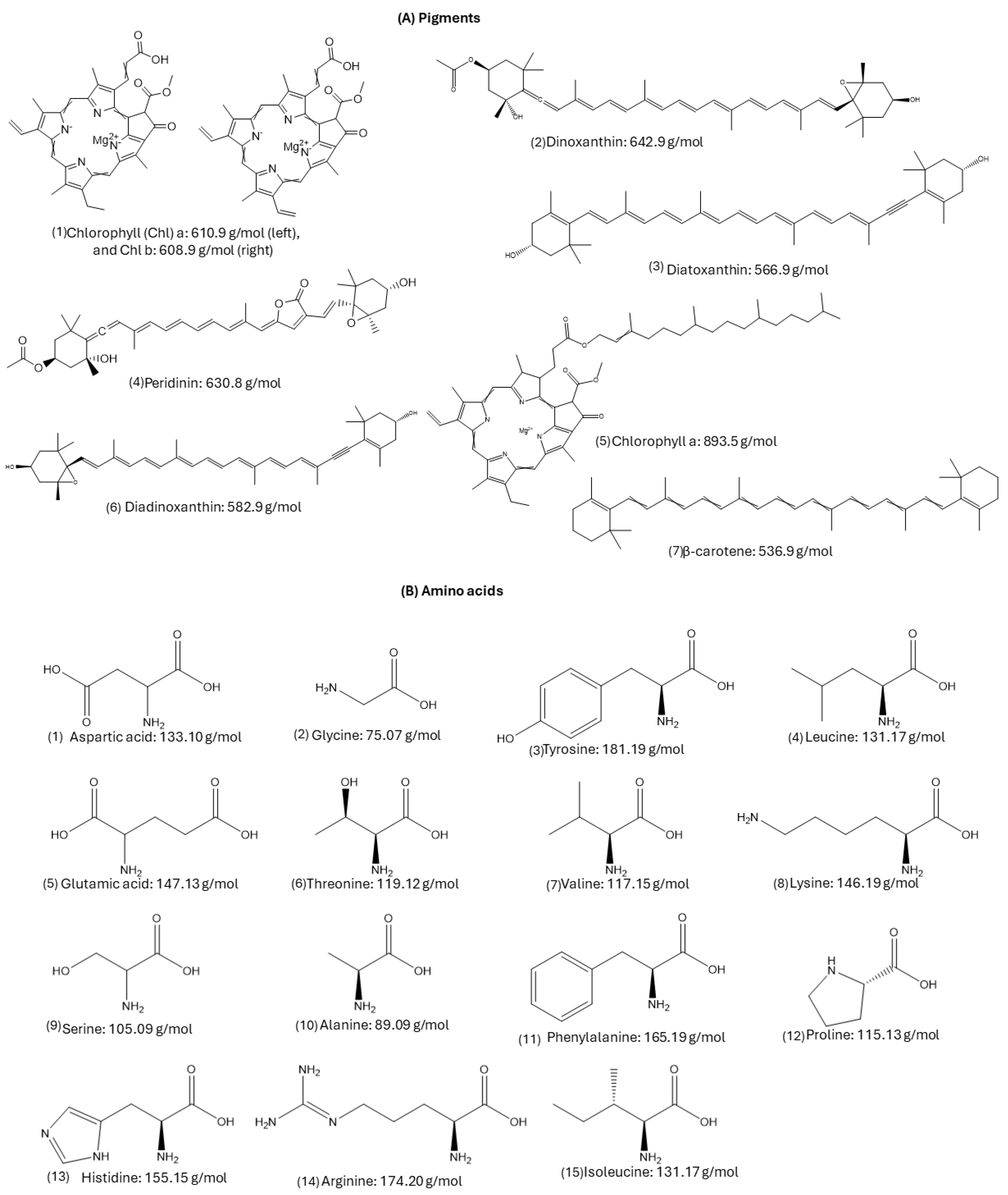
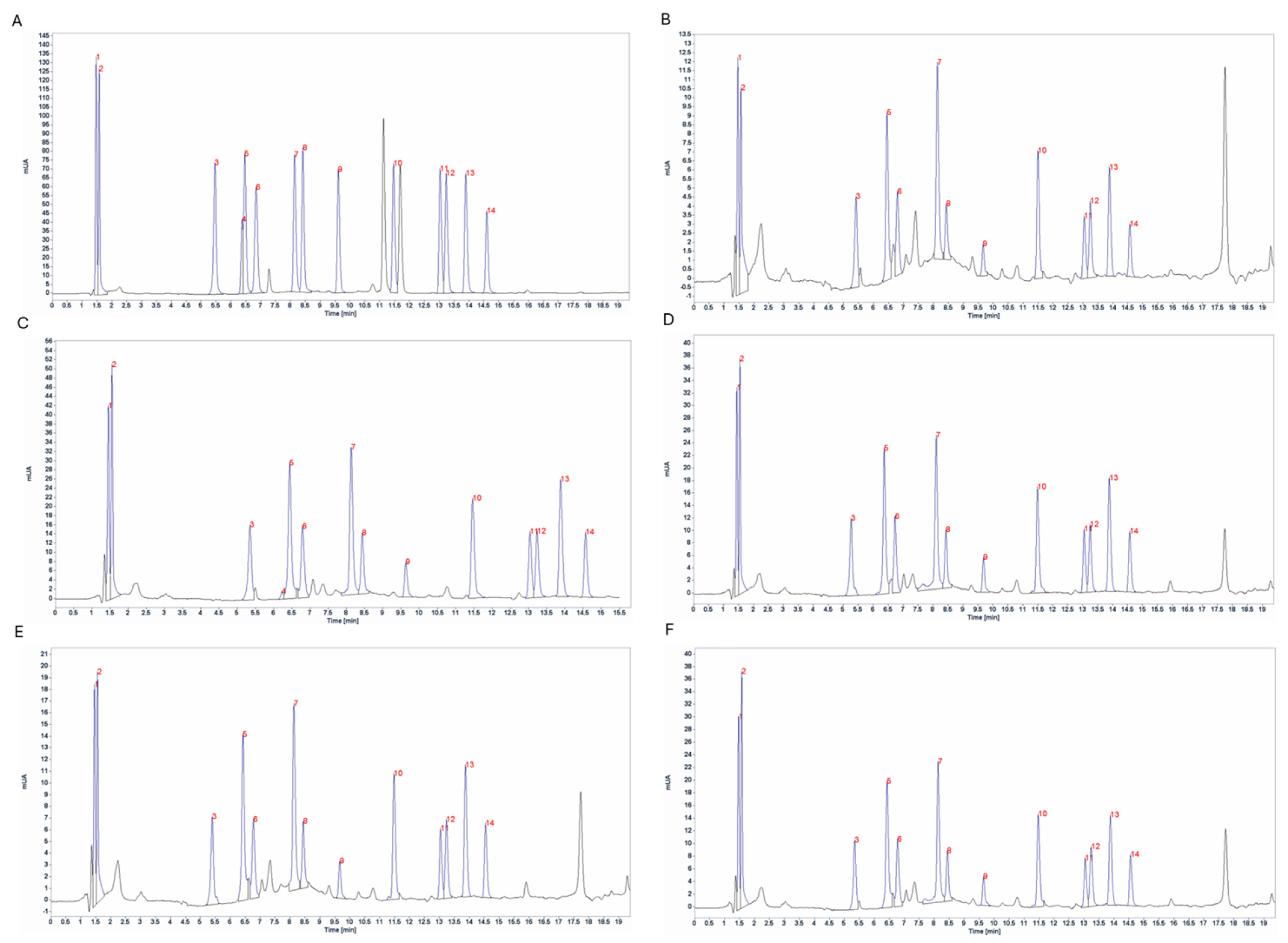
2.3.1. Pigments Composition
2.3.2. Amino Acid Composition
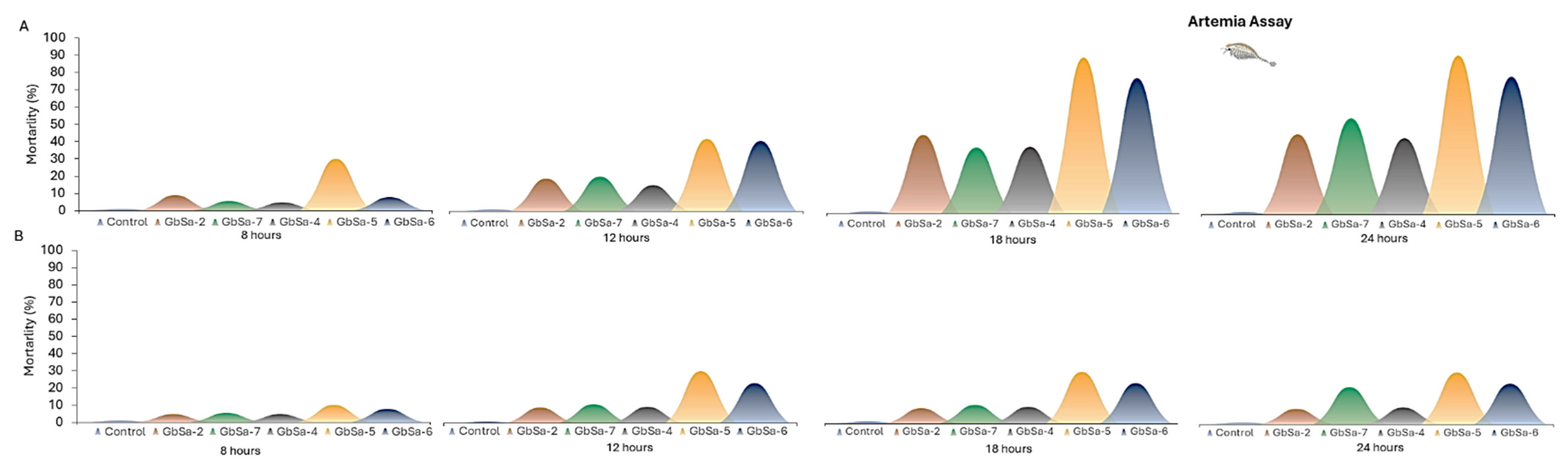
2.4. Toxicity Assay
2.4.1. Mouse Bioassay (MBA)
2.4.2. Artemia Assay (ARTOX)
2.4.3. Marine Fish Assay
2.5. Fluorescent Receptor Binding Assay (fRBA)
3. Discussion
3.1. Morphological Identification
3.2. Biochemical Characterization
3.2.1. Pigments Composition by HPLC-DAD
3.2.2. Amino acid Composition
3.3. Toxicity Assay
3.3.1. Mouse Bioassay (MBA)
3.3.2. Artemia Assay (ARTOX)
3.3.3. Marine Fish Assay
3.4. Fluorescent Receptor Binding Assay (fRBA)
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Isolated and Algal Cultures
4.2. Morphological Identification
4.2.1. Light Microscopy LM
4.2.2. Scanning Electron Microscopy SEM
4.3. Biochemical Characterization
4.3.1. High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC)
4.3.2. High-Performance Liquid Chromatography-Diode Array Detection (HPLC-DAD) for Amino Acid Composition
4.4. Toxicity Assay
4.4.1. Toxins Extraction
4.4.2. Mouse Bioassay (MBA)
4.4.3. Artemia salina Assay (ARTOX)
4.4.4. Marine Fish Assay
4.5. Fluorescent Receptor Binding Assay (fRBA)
5. Conclusions
- Gambierdiscus cf. carpenteri is the most abundant species in Bahía de La Paz and is associated with the production of toxins related to CFP. The presence of G. cf. caribeaus, G. cf. carolineanus, G. cf. toxicus, and F. cf. yasumotoi was also recorded.
- There are differences in pigment production and in the amino acid profiles between the strains G. cf. caribaeus and G. cf. carpenteri. These results suggest the presence of ecotypes, even among strains of the same species. The biochemical profiles could potentially establish chemotaxonomic criteria for the identification of Gambierdiscus species.
- Toxicity for CTX-like and MTX-like activity was confirmed in all strains of G. cf. caribeaus and G. cf. carpenteri. CTX-like and MTX-like toxicity produced a positive result in the MBA and caused the mortality of A. salina. In the marine fish assay, the CTXs-like extracts presented a low-to-medium toxicity through competition for VGSC site 5, as quantified by the fluorescent receptor binding assay.
- The differences in the responses across the various assays suggest that G. cf. caribeaus and G. cf. carpenteri from Bahía de La Paz may produce different metabolites associated with the genus Gambierdiscus.
- The Gulf of California is a potential hotspot of biodiversity and endemism for benthic dinoflagellate species and a key area for research on CTXs and MTXs, CFP-related compounds, other polyether toxins, and secondary metabolites.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chinain, M.; Gatti, C.M.I.; Darius, H.T.; Quod, J.P.; Tester, P.A. Ciguatera poisonings: A global review of occurrences and trends. Harmful Algae 2021, 102, 101873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- FAO; WHO. Report of the Expert Meeting on Ciguatera Poisoning: Rome, 19–23 November 2018; Food Safety and Quality No. 9; World Health Organization: Rome, Italy, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, D.M.; Glibert, P.M.; Burkholder, J.M. Harmful algal blooms and eutrophication: Nutrient sources, composition, and consequences. Estuaries 2002, 25, 704–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glibert, P.M.; Anderson, D.A.; Gentien, P.; Granéli, E.; Sellner, K.G. The global, complex phenomena of harmful algal blooms. Oceanography 2005, 18, 136–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallegraeff, G.M. Ocean climate change, phytoplankton community responses, and harmful algal blooms: A formidable predictive challenge. J. Phycol. 2010, 46, 220–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gobler, C.J.; Doherty, O.M.; Hattenrath-Lehmann, T.K.; Griffith, A.W.; Kang, Y.; Litaker, R.W. Ocean warming since 1982 has expanded the niche of toxic algal blooms in the North Atlantic and North Pacific oceans. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 4975–4980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heisler, J.; Glibert, P.M.; Burkholder, J.M.; Anderson, D.M.; Cochlan, W.; Dennison, W.C.; Dortch, Q.; Gobler, C.J.; Heil, C.A.; Humphries, E.; et al. Eutrophication and harmful algal blooms: A scientific consensus. Harmful Algae 2008, 8, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffith, A.W.; Gobler, C.J. Harmful algal blooms: A climate change co-stressor in marine and freshwater ecosystems. Harmful Algae 2020, 91, 101590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skinner, M.P.; Brewer, T.D.; Johnstone, R.; Fleming, L.E.; Lewis, R.J. Ciguatera fish poisoning in the Pacific Islands (1998 to 2008). PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2011, 5, e1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gingold, D.B.; Strickland, M.J.; Hess, J.J. Ciguatera fish poisoning and climate change: Analysis of National Poison Center data in the United States, 2001–2011. Environ. Health Perspect. 2014, 122, 580–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Núñez-Vázquez, E.J.; Almazán-Becerril, A.; López-Cortés, D.J.; Heredia-Tapia, A.; Hernández-Sandoval, F.E.; Band-Schmidt, C.J.; Bustillos-Guzmán, J.J.; Gárate-Lizárraga, I.; García-Mendoza, E.; Salinas-Zavala, C.A.; et al. Ciguatera in Mexico (1984–2013). Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parrilla-Cerrillo, M.C.; Vázquez-Castellanos, J.L.; Sáldate-Castañeda, E.O.; Nava-Fernández, L.M. Brotes de toxiinfecciones alimentarias de origen microbiano y parasitario. Salud Pública Mex. 1993, 35, 456–463. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Barton, E.D.; Tanner, P.; Turchen, S.G.; Tungen, C.L.; Manoguerra, A.; Clarck, R.F. Ciguatera fish poisoning: A Southern California epidemic. West. J. Med. 1995, 163, 31–35. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lechuga-Devéze, C.; Sierra-Beltrán, A. Documented case of ciguatera on the Mexican Pacific Coast. Nat. Toxins 1995, 3, 415–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Núñez-Vázquez, E.; Sierra-Beltrán, A.P.; Ochoa, J.L. Presencia de Biotoxinas Tipo Ciguatoxinas en Peces Carnívoros de Baja California Sur. In Proceedings of the XI Simposium Internacional de Biología Marina, La Paz, Mexico, 18–22 November 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Núñez-Vázquez, E.J.; Sierra-Beltrán, A.P.; and Ochoa, J.L. Fish Poisoning in Mexico. In Proceedings of the Abstracts of the VIII Conferencia Internacional sobre Algas Nocivas, Vigo, Spain, 25–29 June 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Núñez-Vázquez, E.J.; Bustillos-Guzmán, J.; Heredia-Tapia, A.; Yasumoto, T.; Cruz-Villacorta, A.; Band-Schmidt, C.J.; Gárate-Lizárraga, I.; López-Cortés, D.; Hernández-Sandoval, F.E.; Ochoa, J.L. Múltiples toxinas marinas en el hígado de Mycteroperca prionura, M. rosacea y Lutjanus colorado asociados a la ciguatera en la isla El Pardito, B.C.S. México. In Resúmenes del III Taller sobre Florecimientos Algales Nocivos: Integración del Conocimiento Sobre Eventos de FAN en México; Laboratorio Estatal de Salud Pública Dr. Galo Soberón y Parra; Secretaría de Salud México: Acapulco, Mexico, 2009; p. 52. [Google Scholar]
- Murray, J.S.; Passfield, E.M.F.; Rhodes, L.L.; Puddick, J.; Finch, S.C.; Smith, K.F.; van Ginkel, R.; Mudge, E.M.; Nishimura, T.; Funaki, H.; et al. Targeted Metabolite Fingerprints of Thirteen Gambierdiscus, Five Coolia and Two Fukuyoa Species. Mar. Drugs 2024, 22, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, M.J. Gambierdiscus yasumotoi, sp. nov. (Dinophyceae), a toxic benthic dinoflagellate from Southeastern Asia. J. Phycol. 1998, 34, 661–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez, F.; Qiu, D.; Lopes, R.M.; Lin, S. Fukuyoa paulensis gen. et sp. nov., a New Genus for the Globular Species of the Dinoflagellate Gambierdiscus (Dinophyceae). PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0119676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Park, J.S.; Kang, N.S.; Chomérat, N.; Mertens, K.N.; Gu, H.; Lee, K.-W.; Kim, K.H.; Baek, S.H.; Shin, K.; et al. A new potentially toxic dinoflagellate Fukuyoa koreansis sp. nov. (Gonyaulacales, Dinophyceae) from Korean coastal waters: Morphology, phylogeny, and effects of temperature and salinity on growth. Harmful Algae 2020, 109, 102107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.Z.; Xin, Y.H.; Wang, M.H. Gambierdiscus and Its Associated Toxins: A Minireview. Toxins 2022, 14, 485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Kohli, G.S.; Farrell, H.; Murray, S.A. Gambierdiscus, the cause of ciguatera fish poisoning: An increased human health threat influenced by climate change. In Climate Change and Marine and Freshwater Toxins; Botana, L.M., Louzao, C.M., Vilariño, N., Eds.; De Gruyter: Berlin, Germany, 2015; pp. 271–312. [Google Scholar]
- Mudge, E.M.; Miles, C.O.; Ivanova, L.; Uhlig, S.; James, K.S.; Erdner, D.L.; Fæste, C.K.; McCarron, P.; Robertson, A. Algal ciguatoxin identified as source of ciguatera poisoning in the Caribbean. Chemosphere 2023, 330, 138659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miles, C.O.; Burton, I.W.; Lewis, N.I.; Robertson, A.; Giddings, S.D.; McCarron, P.; Mudge, E.M. Isolation of Caribbean Ciguatoxin-5 (C-CTX5) and confirmation of its structure by NMR spectroscopy. Tetrahedron 2024, 162, 134115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores-Holguín, N.; Salas-Leiva, J.S.; Núñez-Vázquez, E.J.; Tovar-Ramírez, D.; Glossman-Mitnik, D. Exploring marine toxins: Comparative analysis of chemical reactivity properties and potential for drug discovery. Front. Chem. 2023, 11, 1286804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malto, Z.B.L.; Benico, G.A.; Batucan, J.D.; De la Cruz, J.; Romero, M.L.J.; Azanza, R.V.; Salvador-Reyes, L.A. Global mass spectrometric analysis reveals chemical diversity of secondary metabolites and 44-Methylgambierone production in Philippine Gambierdiscus strains. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 8, 767024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yon, T.; Réveillon, D.; Sibat, M.; Holland, C.R.; Litaker, W.; Nascimento, S.M.; Rossignoli, A.E.; Riobó, P.; Hess, P.; Bertrand, S. Targeted and non-targeted mass spectrometry to explore the chemical diversity of the genus Gambierdiscus in the Atlantic Ocean. Phytochemistry 2024, 222, 114095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sierra, B.A.; Cruz, A.; Núñez-Vázquez, E.J.; Del Villar, L.M.; Cerecero, J.; Ochoa, J.L. An overview of the marine food poisoning in Mexico. Toxicon 1998, 36, 1493–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Núñez-Vázquez, E.J.; Almazán-Becerril, A.; Heredia-Tapia, A.; Hernández-Becerril, D.U.; Troccoli-Ghinaglia, L.; Arredondo-Vega, B.O.; Herrera-Silveira, J.A.; Vázquez-Castellanos, J.L.; Ochoa, J.L. Incidencia del envenenamiento por Ciguatera en Mexico. In Proceedings of the 4th Reunión de Expertos en Envenenamientos por Animales Ponzoñosos, Cuernavaca, Mexico, 30–31 March 2000; pp. 56–57. [Google Scholar]
- Okolodkov, Y.B.; Gárate-Lizárraga, I. An annotated checklist of dinoflagellates (Dinophyceae) from the Mexican Pacific. Acta Botánica Mex. 2006, 74, 1–154. [Google Scholar]
- Gárate-Lizárraga, I.; Band-Schmidt, C.J.; Verdugo-Díaz, G.; Muñetón-Gómez, M.J.; Félix-Pico, E. Dinoflagelados (Dinophyceae) del sistema lagunar Magdalena-Almejas. In Estudios Ecológicos en Bahía Magdalena; Funes-Rodríguez, R., Gómez-Gutiérrez, J., Palomares-García, R., Eds.; Gobierno del Estado de B. C. S.: La Paz, Mexico; Secretaria de Turismo de B. C. S.: La Paz, Mexico; Fondo para la Protección de los Recursos Marinos de B. C. S.: La Paz, Mexico; Instituto Politécnico Nacional, Centro Interdisciplinario de Ciencias Marinas: La Paz, Mexico, 2007; pp. 145–174. [Google Scholar]
- Cortés-Altamirano, R. Two new localities for Gambierdiscus toxicus in the Mexican Pacific. Harmful Algae News 2012, 45, 10–11. [Google Scholar]
- Núñez-Vázquez, E.J.; Hernández-Sandoval, F.E.; Cordero-Tapia, A.; Almazán-Becerril, A.; Band-Schmidt, C.J.; Bustillos-Guzmán, J.; López-Cortés, D.; Salinas-Zavala, C.A.; Morales-Zárate, M.V.; Mejía-Rebollo, A.; et al. Presencia de microalgas bénticas potencialmente nocivas y mortandad de peces asociadas al Parque Marino de Cabo Pulmo, B.C.S. In Proceedings of the II Congreso Nacional de Sociedad Mexicana para el estudio de los Florecimientos Algales Nocivos, Manzanillo, Mexico, 30–31 October 2013; p. 41. [Google Scholar]
- Garate-Lizárraga, I.; Okolodkov, Y.B.; Cortés-Altamirano, R. Microalgas formadoras de florecimientos algales en el Golfo de California. In Florecimientos Algales Nocivos en Mexico; García-Mendoza, E., Quijano-Scheggia, S.I., Olivos-Ortíz, A., Núñez-Vázquez, E.J., Eds.; CICESE: Ensenada, Mexico, 2016; pp. 130–145. ISBN 978-607-95688-5-6. [Google Scholar]
- Okolodkov, Y.B.; Gárate-Lizárraga, I.; Martínez-Cruz, M.E.; Galicia-García, C. Epibenthic dinoflagellates of the southern Gulf of California: Species composition and abundance (2015–2019). In Proceedings of the 19th International Conference on Harmful Algae (ICHA 2021), La Paz, Mexico, 10–15 October 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Morquecho-Escamilla, L.; Reyes-Salinas, A.; Okolodkov, Y.B.; Gárate-Lizárraga, I.; Mazariegos-Villarreal, A.; Galicia-García, C. Aislamiento y caracterización taxonómica de dinoflagelados epífitos en Bahía de La Paz e Isla San José, Golfo de California. In Proceedings of the Memorias del IV Congreso Somefan y II Reunión Alen, Cancun, Mexico, 23–27 October 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Ramos-Santiago, A.E.; Band-Schmidt, C.J.; Leyva-Valencia, I.; Fernández-Herrera, L.J.; Núñez-Vázquez, E.J.; Okolodkov, Y.B. Gambierdiscus carpenteri (Dinophyceae) from Bahía de La Paz, Gulf of California: Morphology, genetic affinities, and mouse toxicity. Bot. Mar. 2024, 67, 309–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litaker, R.W.; Vandersea, M.W.; Faust, M.A.; Kibler, S.R.; Chinain, M.; Holmes, M.J.; Holland, W.C.; Tester, P.A. Taxonomy of Gambierdiscus including four new species, Gambierdiscus caribaeus, Gambierdiscus carolinianus, Gambierdiscus carpenteri and Gambierdiscus ruetzleri (Gonyaulacales, Dinophyceae). Phycologia 2009, 48, 344–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz-Asencio, L.; Rojas Abrahantes, G.; Pérez Avilleira, G.; Chamero, D.; Moreira González, A. Clave dicotómica para la identificación preliminar de las especies de Gambierdiscus y Fukuyoa reportadas en la región del Caribe. Rev. De Investig. Mar. 2023, 43, 25–35. Available online: https://hdl.handle.net/1834/43015 (accessed on 11 July 2024).
- Soler-Onís, E.; Fernández-Zabala, J.; Ojeda-Rodriguez, A.; Amorim, A. Bloom of Gambierdiscus caribaeus in the temperate-subtropical waters of El Hierro, Canary Islands (north East Atlantic). Harmful Algae News 2016, 55, 14–17. [Google Scholar]
- Díaz-Asencio, L.; Vandersea, M.; Chomérat, N.; Fraga, S.; Clausing, R.J.; Litaker, R.W.; Chamero-Lago, D.; Gómez-Batista, M.; Moreira-González, A.; Tester, P.; et al. Morphology, toxicity and molecular characterization of Gambierdiscus spp. towards risk assessment of ciguatera in south central Cuba. Harmful Algae 2019, 86, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, K.F.; Rhodes, L.; Verma, A.; Curley, B.G.; Harwood, D.; Kohli, G.S.; Solomona, D.; Rongo, T.; Munday, R.; Murray, S.A. A new Gambierdiscus species (Dinophyceae) from Rarotonga, Cook Islands: Gambierdiscus cheloniae sp. nov. Harmful Algae 2016, 60, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohli, G.S.; Murray, S.A.; Neilan, B.A.; Rhodes, L.L.; Harwood, D.T.; Smith, K.F.; Meyer, L.; Capper, A.; Brett, S.; Hallegraeff, G.M. High abundance of the potentially maitotoxic dinoflagellate Gambierdiscus carpenteri in temperate waters of New South Wales, Australia. Harmful Algae 2014, 39, 134–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vacarizas, J.; Benico, G.; Austero, N.; Azanza, R. Taxonomy and toxin production of Gambierdiscus carpenteri (Dinophyceae) in a tropical marine ecosystem: The first record from the Philippines. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 137, 430–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinain, M.; Gatti, C.M.; Roue, M.; Darius, H.T. Ciguatera-causing dinoflagellates in the genera Gambierdiscus and Fukuyoa: Distribution, ecophysiology and toxicology. In Dinoflagellates: Classification, Evolution, Physiology and Ecological Significance; Subba Rao, D.V., Ed.; Nova Science Publishers: Hauppauge, NY, USA, 2020; pp. 405–457. [Google Scholar]
- Litaker, R.W.; Holland, W.C.; Hardison, D.R.; Pisapia, F.; Hess, P.; Kibler, S.R.; Tester, P.A. Ciguatoxicity of Gambierdiscus and Fukuyoa species from the Caribbean and Gulf of Mexico. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0185776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tester, P.; Wickliffe, L.; Jossart, J.; Rhodes, L.; Enevoldsen, H.; Adachi, M.; Litaker, W. Global distribution of the genera Gambierdiscus and Fukuyoa. Harmful Algae 2018, 138, 138–143. [Google Scholar]
- Richlen, M.L.; Horn, K.; Uva, V.; Fachon, E.; Heidmann, S.L.; Smith, T.B.; Parsons, M.L.; Anderson, D.M. Gambierdiscus species diversity and community structure in St. Thomas, USVI and the Florida Keys, USA. Harmful Algae 2024, 131, 102562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Richlen, M.L.; Liefer, J.D.; Robertson, A.; Kulis, D.; Smith, T.B.; Parsons, M.L.; Anderson, D.M. Influence of environmental variables on Gambierdiscus spp. (Dinophyceae) growth and distribution. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0153197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loeffler, C.R.; Tartaglione, L.; Friedemann, M.; Spielmeyer, A.; Kappenstein, O.; Bodi, D. Ciguatera Mini Review: 21st Century Environmental Challenges and the Interdisciplinary Research Efforts Rising to Meet Them. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cementerio de Yates: Negligencia y Omisiones en la Bahía de La Paz Tras Paso de Norma. Available online: https://causanaturamedia.com/periodismo-cn/Cementerio-de-yates-negligencia-y-omisiones-en-la-bahia-de-La-Paz-tras-paso-de-Norma (accessed on 1 April 2024).
- Gobierno de BCS Sin Capacidad de Retirar Embarcaciones Varadas en La Paz: VCC. Available online: https://tribunademexico.com/gobierno-de-bcs-sin-capacidad/ (accessed on 11 July 2024).
- Parsons, M.L.; Settlemier, C.J.; Ballauer, J.M. An examination of the epiphytic nature of Gambierdiscus toxicus, a dinoflagellate involved in ciguatera fish poisoning. Harmful Algae 2011, 10, 598–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parsons, M.L.; Brandt, A.L.; Ellsworth, A.; Leynse, A.K.; Rains, L.K.; Anderson, D.M. Assessing the use of artificial substrates to monitor Gambierdiscus populations in the Florida Keys. Harmful Algae 2017, 68, 52–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tester, P.A.; Kibler, S.R.; Holland, W.C.; Usup, G.; Vandersea, M.W.; Leaw, C.P.; Teen, L.P.; Larsen, J.; Mohammad-Noor, N.; Faust, M.A.; et al. Sampling harmful benthic dinoflagellates: Comparison of artificial and natural substrate methods. Harmful Algae 2014, 39, 8–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islas y Áreas Protegidas del Golfo de California. Available online: https://www.gob.mx/semarnat/articulos/islas-y-areas-protegidas-del-golfo-de-california-269050 (accessed on 12 April 2021).
- Heredia-Tapia, A.; Arredondo-Vega, B.O.; NuñezVázquez, E.J.; Ochoa, J.L. Partial biochemical characterization and toxicological evaluation of the dinoflagellate Prorocentrum lima (=Exuviaella lima) isolated from El Pardito Island in Baja California Sur, México. In Proceedings of the Memorias 9th International Conference on Algal Blooms, Hobart, Australia, 7–11 February 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Nascimento, S.M.; Purdie, D.A.; and Morris, S. Morphology, toxin composition and pigment content of Prorocentrum lima strains isolated from a coastal lagoon in southern UK. Toxicon 2005, 45, 633–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- David, H.; Laza-Martínez, A.; Kromkamp, J.C.; Orive, E. Physiological response of Prorocentrum lima (Dinophyceae) to varying light intensities. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2018, 94, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Zhang, H.; Peng, J.; Zheng, G.; Lu, S.; Tan, Z. Adaptive responses of geographically distinct strains of the benthic dinoflagellate, Prorocentrum lima (Dinophyceae), to varying light intensity and photoperiod. Harmful Algae 2023, 127, 102479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zapata, M.; Freire, J.; Garrido, J.L. Pigment composition of several harmful algae as determined by HPLC using pyridine-containing mobile phase polymeric octadecylsilica column. In Harmful Algae; Reguera, B., Blanco, J., Fernández, M.L., Wyatt, T., Eds.; UNESCO—Xunta de Galicia: Santiago de Compostela, Spain, 1998; pp. 304–307. [Google Scholar]
- Zapata, M.; Fraga, S.; Rodríguez, F.; Garrido, J.L. Pigment-based chloroplast types in dinoflagellates. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2012, 465, 33–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carreto, J.I.; Carignan, M.O.; Montoya, N.G. Comparative studies on mycosporine-like amino acids, paralytic shellfish toxins and pigment profiles of the toxic dinoflagellates Alexandrium tamarense, Acatenella and A. minutum. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2001, 223, 49–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carreto, J.I.; Seguel, M.; Montoya, N.G.; Clément, A.; Carignan, M.O. Pigment profile of the ichthyotoxic dinoflagellate Gymnodinium sp. from a massive bloom in southern Chile. J. Plank. Res. 2001, 23, 1171–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bustillos-Guzmán, J.; Garate-Lizarraga, I.; López-Cortés, D.; Hernández-Sandoval, F.E. The use of pigment “fingerprints” in the study of harmful algal blooms. Rev. Biol. Trop. 2004, 52 (Suppl. S1), 17–26. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.; Peng, Y.; Yu, Z.; Dong, L.I.; Deng, C.; Yu, Z. HPLC pigment Profiles of 31 Harmful Algal Bloom Species Isolated from the Coastal Sea Areas of China. Ocean. Coast. Sea Res. 2014, 13, 941–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durand, M.; Berkaloff, C. Pigments composition and chloroplast organization of Gambierdiscus toxicus Adachi and Fukuyo (Dinophyceae). Phycologia 1985, 24, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Indelicato, S.R.; Watson, D.A. Identification of the Photosynthetic Pigments of the Tropical Benthic Dinoflagellate Gambierdiscus toxicus. Mar. Fish. Rev. 1986, 48, 44–47. [Google Scholar]
- Bomber, J.W.; Tindall, D.R.; Venable, C.W.; Miller, D.M. Pigment composition and low-ligth response of fourteen clones of Gambierdiscus toxicus. In Toxic Marine Phytoplankton; Graneli, E., Ed.; Elsevier Science Publishing Co., Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1990; pp. 263–268. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, D.M.; Tindall, D.R.; Venable, C.W. NMR Spectroscopy of Clorophyll(s)-a isolated from Gambierdiscus toxicus. In Toxic Marine Phytoplankton; Graneli, E., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1993; pp. 305–310. [Google Scholar]
- Bustillos-Guzmán, J.; Diogene, J. Pigment content and toxicity in three strains of Gambierdiscus toxicus: Implications of cell volume differences. In Harmful Algae; Reguera, B., Blanco, J., Fernández, M.L., Wyatt, T., Eds.; UNESCO—Xunta de Galicia: Santiago de Compostela, Spain, 1998; pp. 372–373. [Google Scholar]
- Fraga, S.; Rodríguez, F.; Caillaud, A.; Diogène, J.; Raho, N.; Zapata, M. Gambierdiscus excentricus sp. nov. (Dinophyceae), a benthic toxic dinoflagellate from the Canary Islands (NE Atlantic Ocean). Harmful Algae 2011, 11, 10–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flynn, K.; Flynn, K.J.; Jones, K.J. Changes in dinoflagellate intracellular amino acids in response to diurnal changes in light and N supply. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1993, 100, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flynn, K.J.; Jones, K.J.; Raine, R.; Richard, J.; Flynn, K. Use of intracellular amino acid analysis as an indicator of the physiological status of natural dinoflagellate populations. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1994, 103, 175–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okaichi, T. Significance of Amino Acid Composition of Phytoplankton and suspensoid in Marine Biological Production. Bull. Jap. Soc. Sc. Fish. 1974, 40, 471–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, T.; Suitani, Y.; Murakami, M.; Yamaguchi, K.; Konosu, S.; and Noda, H. Protein and Amino Acid Compositions of Five Species of Marine Phytoplankton. Bull. Japan Soc. Sc. Fish. 1986, 52, 337–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, A.S.; Jeong, H.J.; Kim, S.J.; Ok, J.E. Amino acids profiles of six dinoflagellate species belonging to diverse families: Possible use as animal feeds in aquaculture. Algae 2018, 33, 279–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, R.L. Detection of ciguatoxins and related benthic dinoflagellate toxins: In vivo and in vitro methods. In Manual on Harmful Marine Microalgae; Hallegraeff, G.M., Anderson, D.M., Cembella, A.D., Enevoldsen, H.O., Eds.; UNESCO-IOC: Paris, France, 1995; pp. 135–161. [Google Scholar]
- FAO. Marine Biotoxins; Food and Nutrition Paper 80; Food and Agriculture Organozation of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2004; 278p. [Google Scholar]
- Bienfang, P.; Oben, B.; DeFelice, S.; Moeller, P.; Huncik, K.; Oben, P.; Bowen, B. Ciguatera: The detection of neurotoxins in carnivorous reef fish from the coast of Cameroon, West Africa. Afr. J. Mar. Sci. 2008, 30, 533–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ley-Martínez, T.C.; Núñez-Vázquez, E.J.; Balart-Páez, E.F.; Poot-Delgado, C.A.; Band-Schmidt, C.J.; Almazán-Becerril, A. Identificación y cuantificación de ciguatoxinas en peces carnívoros de la Península de Yucatán. In Proceedings of the Memorias del IV Congreso Nacional de la SOMEFAN y II Congreso Latinoamericano de la ALEAN, Cancun, Mexico, 23–27 October 2017; p. 88. [Google Scholar]
- Neves, R.A.F.; Fernandes, T.; Santos, L.N.d.; Nascimento, S.M. Toxicity of benthic dinoflagellates on grazing, behavior and survival of the brine shrimp Artemia salina. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0175168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heredia-Tapia, A.; Arredondo-Vega, B.O.; Núñez-Vázquez, E.J.; Yasumoto, T.; Yasuda, M.; Ochoa, J.L. Isolation of Prorocentrum lima (Syn. Exuviaella lima) and diarrhetic shellfish poisoning (DSP) risk assessment in the Gulf of California, Mexico. Toxicon 2002, 40, 1121–1127. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ajuzie, C.C. Palatability and fatality of the dinoflagellate Prorocentrum lima to Artemia salina. J. Appl. Phycol. 2007, 19, 513–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faimali, M.; Giussani, V.; Piazza, V.; Garaventa, F.; Corrà, C.; Asnaghi, V.; Privitera, D.; Gallus, L.; Cattaneo-Vietti, R.; Mangialajo, L.; et al. Toxic effects of harmful benthic dinoflagellate Ostreopsis ovata on invertebrate and vertebrate marine organisms. Mar. Environ. Res. 2012, 76, 97–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, Y.; Zhang, K.; Geng, N.; Wu, M.; Yi, X.; Liu, R.; Challis, J.K.; Codling, G.; Xu, E.G.; Giesy, J.P. Molecular mechanisms of zooplanktonic toxicity in the okadaic acid-producing dinoflagellate Prorocentrum lima. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 279, 116942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, M.; Mak, M.Y.L.; Cheng, J.; Li, J.; Gu, J.R.; Leung, P.T.Y.; Lam, P.K.S. Effects of dietary exposure to ciguatoxin P-CTX-1 on the reproductive performance in marine medaka (Oryzias melastigma). Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 152, 110837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Chen, S.; Xu, S.Y.; Li, D.W.; Li, H.Y.; Yang, W.D. Toxicity and underlying mechanism of the toxic dinoflagellate Gambierdiscus caribaeus to the fish Oryzias melastigma. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 247, 114223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helfrich, P.; Bannerg, A. Experimental Induction of Ciguatera Toxicity in Fish through Diet. Nature 1963, 197, 1025–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davin, W.T., Jr.; Kohler, C.C.; Tindall, D.R. Effects of ciguatoxins on the bluehead. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 1986, 115, 908–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davin, W.T., Jr.; Kohler, C.C. Ciguatera toxins adversely affect piscivorous fishes. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 1988, 117, 374–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, R.J. Ciguatoxins are potent ichthyotoxins. Toxicon 1992, 30, 207–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magnelia, S.J.; Kohler, C.C. Acanthurids Do Not Avoid Consuming Cultured Toxic Dinoflagellates yet Do Not Become Ciguatoxic. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 1992, 121, 737–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quod, J. Action de la Ciguatoxine sur Léquilibrie de Distribution Hydroionique et sur la Perméabilité au Na+ du Muscle Blanc Dún Téléostéen, Chelon Labrosus; University of Bordeaux: Bordeaux, France, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Capra, M.F.; Cameron, J.; Flowers, A.E.; Coombe, I.F.; Blanton, C.G.; Hahn, S.T. The Effects of Ciguatoxin on Teleosts. In Proceedings of the 6th International Coral Reef Congress, Townsville, Australia, 8–12 August 1988; pp. 37–41. [Google Scholar]
- Durand-Clement, M.; Amade, P.; Puiseux-Dao, S. Induction of toxicity in fishes fed with cultures of the ciguateric dinoflagellate Gambierdiscus toxicus. In Proceedings of the 4th International Meeting of the SAA, Villeneuve d’Ascq, France, 15–17 September 1987; Stadier, T., Karamanos, Y., Verdus, M.C., Mollion, J., Christiaen, D., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1988; p. 19. [Google Scholar]
- Kohler, C.C.; Paleudis, G.A.; Tindall, D.R. Behavior abnormalities displayed by ocean surgeon following consumption of ciguatoxigenic dinoflagellates. Proc. Assn. Island Mar. Lab. Carib. 1989, 22, 34. [Google Scholar]
- Kelly, A.M.; Kohler, C.C.; Tindall, D.R. Are crustaceans linked to the ciguatera food chain? Environ. Biol. Fish. 1992, 33, 275–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohler, C.C.; Kholer, S. Ciguatera tropical fish poisoning: What’s happening in the food chain. In Proceedings of the 26th Meeting of the Association of Marine Laboratories of the Caribbean, San Salvador, The Bahamas, 11–16 June 1994; Gerace, D.T., Ed.; UNESCO; Paris, France, 1998; pp. 112–125. [Google Scholar]
- González, G.; Brusle, J.; Crespo, S. Ultrastructural alterations of cabrilla sea bass Serranus cabrilla liver related to experimental Gambierdiscus toxicus (dinoflagellate) ingestion. Dis. Aqua. Org. 1994, 18, 187–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edmunds, J.S.; McCarthy, R.A.; Ramsdell, J.S. Ciguatoxin reduces larval survivability in finfish. Toxicon 1999, 37, 1827–1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mak, L.Y.; Li, J.; Liu, C.N.; Cheng, S.H.; Lam, P.K.S.; Cheng, J.; Chan, L.L. Physiological and behavioural impacts of Pacific ciguatoxin-1 (P-CTX-1) on marine medaka (Oryzias melastigma). J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 321, 782–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clausing, R.J.; Ben Gharbia, H.; Sdiri, K.; Sibat, M.; Rañada-Mestizo, M.L.; Lavenu, L.; Hess, P.; Chinain, M.; Bottein, M.-Y.D. Tissue Distribution and Metabolization of Ciguatoxins in an Herbivorous Fish following Experimental Dietary Exposure to Gambierdiscus polynesiensis. Mar. Drugs 2024, 22, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, M.; Leung, P.T.; Ip, J.C.; Cheng, J.P.; Wu, J.J.; Gu, J.R.; Lam, P.K. Developmental toxicity and molecular responses of marine medaka (Oryzias melastigma) embryos to ciguatoxin P-CTX-1 exposure. Aquat. Toxicol. 2017, 185, 149–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leite, I.D.P.; Sdiri, K.; Taylor, A.; Viallon, J.; Gharbia, H.B.; Mafra Júnior, L.L.; Swarzenski, P.; Oberhaensli, F.; Darius, H.T.; Chinain, M.; et al. Experimental Evidence of Ciguatoxin Accumulation and Depuration in Carnivorous Lionfish. Toxins 2021, 13, 564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galarza, J.R.; Edwards, R.A.; Baden, D.G.; Tosteson, T.R. Effect of Barracuda Ciguatoxins on Pigment Granule Aggregation in Teleost Melanophores. Bull. De La Soc. De Pathol. Exot. 1993, 85, 528. [Google Scholar]
- Igarashi, T.; Aritake, S.; Yasumoto, T. Mechanisms underlying the hemolytic and ichthyotoxic activities of maitotoxin. Nat. Toxins 1999, 7, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murata, M.; Naoki, H.; Iwashita, T.; Matsunaga, S.; Sasaki, M.; Yokoyama, A.; Takeshi, Y. Structure of Maitotoxin. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1993, 115, 2060–2062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolaou, K.C.; Frederick, M.O.; Aversa, R.J. The continuing saga of the marine polyether biotoxins. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2008, 47, 7182–7225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohli, G.S.; Papiol, G.G.; Rhodes, L.L.; Harwood, D.T.; Selwood, A.; Jerrett, A.; Murray, S.A.; Neilan, B.A. A feeding study to probe the uptake of Maitotoxin by snapper (Pagrus auratus). Harmful Algae 2014, 37, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasumoto, T.; Bagnis, R.; Vernoux, J.P. Toxicity of the surgeonfishes. II. Properties of the principal water-soluble toxin. Bull. Jpn. Soc. Fish. 1976, 42, 359–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahishi, M.; Tatsumi, M.; Ohizumi, Y.; Yasumoto, T. Ca2+ channel activation function of maitotoxin the most potent marine toxin known, in clonal rat pheochromocytoma cells. J. Biol. Chem. 1983, 258, 10944–10949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murata, M.; Yasumoto, T. The structure elucidation and biological activities of high molecular weight algal toxins: Maitotoxin, prymnesins and zooxanthellatoxins. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2000, 17, 293–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terao, K.; Ito, E.; Igarashi, T.; Aritake, S.; Seki, T.; Satake, M.; Yasumoto, T. Effects of Prymnesin, Maitotoxin and Gymnomidine on the structure of Gills of small fish Akahire, Tanichtys albonubes. Lin. In Harmful and Toxic Algal Blooms; Yasumoto, T., Oshima, Y., Fukuyo, Y., Eds.; IOC-UNESCO: Paris, France, 1996; pp. 479–481. [Google Scholar]
- Landsberg, J.H. Tropical reef fish disease outbreaks and mass mortalities in Florida: What is the role of dietary biological toxins? Dis. Aquat. Org. 1995, 22, 83–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCall, J.R.; Jacocks, H.M.; Niven, S.C.; Poli, M.A.; Baden, D.G.; Bourdelais, A.J. Development and utilization of a fluorescence-based receptor-binding assay for the site 5 voltage-sensitive sodium channel ligands brevetoxin and ciguatoxin. J. AOAC Int. 2014, 97, 307–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pisapia, F.; Holland, W.C.; Hardison, D.R.; Litaker, R.W.; Fraga, S.; Nishimura, T.; Adachi, M.; Nguyen-Ngoc, L.; Séchet, V.; Amzil, Z.; et al. Toxicity screening of 13 Gambierdiscus strains using neuro-2a and erythrocyte lysis bioassays. Harmful Algae 2017, 63, 173–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holland, W.C.; Litaker, R.W.; Tomas, C.R.; Kibler, S.R.; Place, A.R.; Davenport, E.D.; Tester, P.A. Differences in the toxicity of six Gambierdiscus (Dinophyceae) species measured using an in vitro human erythrocyte lysis assay. Toxicon 2013, 65, 15–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossignoli, A.E.; Tudó, A.; Bravo, I.; Díaz, P.A.; Diogène, J.; Riobó, P. Toxicity Characterisation of Gambierdiscus Species from the Canary Islands. Toxins 2020, 12, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murray, J.S.; Nishimura, T.; Finch, S.C.; Rhodes, L.L.; Puddick, J.; Harwood, D.T.; Larsson, M.E.; Doblin, M.A.; Leung, P.; Yan, M.; et al. The role of 44-methylgambierone in ciguatera fish poisoning: Acute toxicity, production by marine microalgae and its potential as a biomarker for Gambierdiscus spp. Harmful Algae 2020, 97, 101853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; He, X.; Lee, W.H.; Chan, L.L.; Lu, D.; Wang, P.; Tao, X.; Li, H.; Yu, K. Ciguatoxin-Producing Dinoflagellate Gambierdiscus in the Beibu Gulf: First Report of Toxic Gambierdiscus in Chinese Waters. Toxins 2021, 13, 643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munday, R.; Murray, S.; Rhodes, L.; Larsson, M.; Harwood, D. Ciguatoxins and Maitotoxins in extracts of sixteen Gambierdiscus isolates and one Fukuyoa isolate from the South Pacific and their toxicity to mice by intraperitoneal and oral administration. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsson, M.; Laczka, O.; Harwood, D.; Lewis, R.; Himaya, S.; Murray, S.; Doblin, M. Toxicology of Gambierdiscus spp. (Dinophyceae) from tropical and temperate Australian waters. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darius, H.T.; Roué, M.; Sibat, M.; Viallon, J.; Gatti, C.M., II; Vandersea, M.W.; Tester, P.A.; Litaker, R.W.; Amzil, Z.; Hess, P.; et al. Toxicological Investigations on the Sea Urchin Tripneustes gratilla (Toxopneustidae, Echinoid) from Anaho Bay (Nuku Hiva, French Polynesia): Evidence for the Presence of Pacific Ciguatoxins. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darius, H.T.; Revel, T.; Viallon, J.; Sibat, M.; Cruchet, P.; Longo, S.; Hardison, D.R.; Holland, W.C.; Tester, P.A.; Litaker, R.W.; et al. Comparative Study on the Performance of Three Detection Methods for the Quantification of Pacific Ciguatoxins in French Polynesian Strains of Gambierdiscus polynesiensis. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Estevez, P.; Oses-Prieto, J.; Castro, D.; Penin, A.; Burlingame, A.; Gago-Martinez, A. First Detection of Algal Caribbean Ciguatoxin in Amberjack Causing Ciguatera Poisoning in the Canary Islands (Spain). Toxins 2024, 16, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lluch-Cota, S.; Aragón-Noriega, E.A.; Arreguín-Sánchez, F.; Aurioles-Gamboa, D.; Bautista-Romero, J.J.; Brusca, R.C.; Cervantes-Duarte, R.; Cortés-Altamirano, R.; Del-Monte-Luna, P.; Esquivel-Herrera, A.; et al. The Gulf of California: Review of ecosystem status and sustainability challenges. Prog. Oceanogr. 2007, 73, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brusca, R.C.; Findley, L.T.; Hastings, P.A.; Hendrickx, M.E.; Torre, J.; van der Heiden, A.M. Macrofaunal diversity in the Gulf of California. In Biodiversity, Ecosystems, and Conservation in Northern Mexico; Cartron, J.L.E., Ceballos, G., Felger, R.S., Eds.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2005; pp. 179–203. [Google Scholar]
- Brusca, R.C. The Gulf of California: Biodiversity and Conservation. Arizona-Sonora Desert Museum Studies in Natural History; University of Arizona Press: Tucson, AZ, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Gómez-Cabrera, I. Pesca Deportiva y Pesca Ribereña en Baja California Sur, México: Comparación del Valor Económico. Ph.D. Thesis, Universidad Autónoma de Baja California Sur, La Paz, Mexico, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Gómez-Cabrera, I.D.; Ivanova-Boncheva, A. Valor económico de la pesca deportiva como fuente principal de atracción turística en Los Cabos, Baja California Sur, México. TURYDES Tur. Y Desarro. Local Sosten. 2013, 6, 25. [Google Scholar]
- Keller, M.D.; Selvin, R.C.; Claus, W.; Guillard, R.R.L. Media for the culture of oceanic ultraphytoplankton. J. Phycol. 1987, 23, 633–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillard, R.R.L.; Ryther, J.H. Studies of marine planktonic diatoms. I. Cyclotella nana Hustedt, and Detonula confervacea (Cleve) Gran. Can. J. Microbiol. 1962, 8, 229–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guillard, R.R. Culture of phytoplankton for feeding marine invertebrates. In Culture of Marine Invertebrate Animals; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1975; pp. 29–60. [Google Scholar]
- Fritz, L.; Triemer, R.E. A rapid simple technique utilizing Calcofluor White M28 for the visualization of dinoflagellate thecal plates. J. Phycol. 1985, 21, 662–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidussi, F.; Claustre, H.; Bustillos-Guzmán, J.; Cailleau, C.; Marty, J.C. Rapid HPLC method for determination of phytoplankton chemotaxinomic pigments: Separation of chlorophyll a from divinyl-chlorophyll a and zeaxanthin from lutein. J. Plankton Res. 1996, 18, 2377–2382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montoura, R.F.C.; Repeta, D. Calibration methods for HPLC. In Phytoplankton Pigments in Oceanography: Guidelines to Modern Methods; Jeffrey, S.W., Mantoura, R.F.C., Wright, S.W., Eds.; UNESCO: Paris, France, 1997; pp. 407–428. [Google Scholar]
- Gratzfeld-Huesgen, A. Sensitive and Reliable Amino Acid Analysis in Protein Hydrolysates Using the Agilent 1100 Series HPLC. Agilent Technologies. Publication Number 5968–5658E. 1999. Available online: https://channel.gimitec.com/sites/default/files/59685658.pdf (accessed on 12 July 2024).
- AOAC. AOAC Official Method 994.12 Amino Acids in Feeds; Association of Official Analytical Collaboration (AOAC International): Rockville, ML, USA, 2000; 1p. [Google Scholar]
- Chinain, M.; Darius, H.T.; Ung, A.; Cruchet, P.; Wang, Z.; Ponton, D.; Laurent, D.; Pauillac, S. Growth and toxin production in the ciguatera-causing dinoflagellate Gambierdiscus polynesiensis (Dinophyceae) in culture. Toxicon 2010, 56, 739–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satake, M.; Murata, M.; Yasumoto, T. The structure of CTX3C, a ciguatoxin congener isolated from cultured Gambierdiscus toxicus. Tetrahedr. Lett. 1993, 34, 1975–1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, M.J.; Lewis, R.J. Purification and characterisation of large and small maitotoxins from cultured Gambierdiscus toxicus. Nat. Toxins 1994, 2, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Cell Size (µm) | Apical Pore Plate Po (µm) | Po Apical Pore (µm) | 1p Plate (µm) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Specie/Strain | D | W | D/W | L | W | L/W | Number | Diameter | L | W | L/W |
| G. cf. caribaeus/ GbSa-2 | 87.15 ± 4.73 | 83.32 ± 4.90 | 1.05 ± 0.56 | 10.04 ± 0.35 | 6.21 ± 0.31 | 1.62 ± 0.07 | 37.16 ± 2.32 | 0.48 ± 0.05 | 49.88 ± 4.24 | 37.55 ± 3.09 | 1.29 ± 0.13 |
| G. cf. caribaeus/ GbSa-7 | 79.32 ± 8.75 | 70.29 ± 5.98 | 1.13 ± 0.63 | 9.91 ± 1.22 | 6.23 ± 0.89 | 1.59 ± 1.38 | 37.50 ± 5.23 | 0.41 ± 0.05 | 45.55 ± 3.31 | 36.19 ± 1.99 | 1.28 ± 0.10 |
| G. cf. carpenteri/ GbSa-4 | 77.67 ± 7.12 | 71.31 ± 5.74 | 1.09 ± 1.24 | 10.35 ± 0.49 | 6.17 ± 0.37 | 1.68 ± 1.32 | 40.50 ± 3.24 | 0.41 ± 0.09 | 55.59 ± 2.95 | 35.99 ± 3.72 | 1.62 ± 0.19 |
| G. cf. carpenteri/ GbSa-5 | 79.44 ± 6.73 | 71.32 ± 6.55 | 1.11 ± 1.03 | 11.03± 0.95 | 7.28 ± 1.71 | 1.52 ± 0.56 | 41.50 ± 1.58 | 0.42 ± 0.10 | 46.99 ± 2.26 | 30.90 ± 5.23 | 1.55 ± 0.29 |
| G. cf. carpenteri/ GbSa-6 | 79.59 ± 8.63 | 71.34 ± 9.25 | 1.12 ± 0.93 | 10.47± 1.49 | 6.67 ± 1.29 | 1.57 ± 1.16 | 40.00 ± 2.49 | 0.42 ± 0.07 | 47.61 ± 4.33 | 29.86 ± 4.15 | 1.61 ± 0.24 |
| Species | Strain Code | Chl a | Chl c2 | Diadino | Dino | Diato | Peri | ββ-Car |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gambierdiscus cf. caribeus | GbSa-2 | 149.38 | 57.79 | 26.41 | 2.05 | 26.41 | 81.26 | 6.02 |
| GbSa-7 | 203.79 | 37.08 | 25.77 | 4.71 | 3.67 | 55.73 | 6.45 | |
| Gambierdiscus cf. carpenteri | GbSa-4 | 152.41 | 34.24 | 21.10 | 0.00 | 3.90 | 49.47 | 3.99 |
| GbSa-5 | 124.95 | 22.88 | 15.70 | 3.28 | 3.26 | 34.42 | 4.10 | |
| GbSa-6 | 278.69 | 30.96 | 15.99 | 4.74 | 5.67 | 23.89 | 12.85 |
| Species | Strain Code | Glu | Asp | Ser | His | Gly | Thr | Ala | Arg | Tyr | Val | Phe | Iso | Leu | Lys | Pro |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gambierdiscus cf. caribeus | Gbsa-2 | 17.41 | 15.85 | 13.52 | Nd | 8.31 | 14.95 | 12.84 | 17.70 | 18.71 | 15.20 | 17.36 | 16.53 | 16.24 | 15.22 | 17.78 |
| Gbsa-7 | 32.74 | 28.15 | 22.68 | 13.04 | 16.69 | 24.79 | 22.33 | 25.69 | 24.26 | 24.44 | 27.11 | 23.06 | 29.33 | 23.24 | 52.30 | |
| Gambierdiscus cf. carpenteri | Gbsa-4 | 36.39 | 30.93 | 26.31 | Nd | 18.66 | 28.91 | 27.53 | 30.63 | 29.47 | 28.48 | 30.68 | 27.27 | 32.20 | 26.58 | 18.10 |
| Gbsa-5 | 14.80 | 12.74 | 11.45 | Nd | 7.72 | 12.52 | 11.26 | 14.51 | 14.52 | 12.78 | 14.20 | 13.08 | 14.35 | 12.86 | 12.52 | |
| Gbsa-6 | 30.94 | 27.14 | 21.12 | Nd | 15.04 | 23.83 | 22.13 | 25.23 | 24.93 | 23.26 | 24.86 | 23.13 | 25.26 | 21.99 | 24.14 |
| Specie/Strain | Pigments | Method | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gambierdiscus toxicus Gambier Island | Chl c1, Chl c2, and Peri | TLC | [68] |
| Gambierdiscus toxicus Southern coast Florida | Chl a, Chl c1, Chl c2, Diadino, Dino, Peri, and ββ-car | TLC | [69] |
| Gambierdiscus toxicus Fourteen clones: Bermuda Great Issacs Light, Bahamas; Drifth Algae, Gulf Stream; Gingerbreads, Bahamas; Hawaii; Marathon key, Fl; Martnique, Caribbean; Virgin Gorda, V.I. | Chl a, Chl c2, Peri, Diadino, and Dino | TLC, HPLC | [70] |
| Gambierdiscus toxicus Caribean clone | Chl a | NMR | [71] |
| Gambierdiscus toxicus Three clones: | Chl a | HPLC-DAD | [72] |
| Gambierdiscus excentricus Canary Islands (NE Atlantic Ocean) | Chl a, Chl a allomer, Chl c1, Chl c2, Diadchr, Diadino, Dino, Diato, (MgDVP), Peri, Perid-ol, Peri-like, Pyrrho, and ββ-car | HPLC-DAD | [73] |
| Gambierdiscus sp. | Chl a, Chl c1, Chl c2, Diadino, Dino, and Peri | HPLC-DAD | [63] |
| Gambierdiscus cf. caribaeus Gambierdiscus cf. carpenteri Five clones: Bahía de La Paz, Gulf of California | Chl a, Chl c2, Diadino, Dino, Diato, Peri; and ββ-car Chl a, Chl c2, Diadino, Dino, Diato, Peri; and ββ-car | HPLC-DAD HPLC-DAD | This study This study |
| Dinoflagellate/Strain | Amino Acids | Method | Family | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Prorocentrum triestinum | Asp, Ser, Thr, Glu, Pro, Gly, Ala, Cys, Val, Met, Iso, Leu, Tyr, Phe, Lys, His, Arg, Try | Prorocentraceae | [76] | |
| Prorocentrum minimum, Noctiluca scintillans | His, Thr, Arg, Val, Phe, Iso; Leu, Lys, Asp, Glu, Ser, Gly, Ala, Tyr, Cys, Met, Try, and Pro | HSAA | Prorocentraceae, Noctilucaceae | [77] |
| Aureodinium pigmentosum, Prorocentrum micans, Glenodinium foliaceum, Heterocapsa triquetra, Scrippsiella trochoidea, Alexandrium tamarense y Gymnodinium catenatum | Glu, Gln, Arg, Tau, Gin/Glu | HPLC | [74] | |
| Heterocapsa rotundata Shiwa Bay, Korea | His, Thr, Arg, Val, Phe, Iso; Leu, Lys, Asp, Glu, Ser, Gly, Ala, Tau, GABA, Tyr, and Pro | HPLC-FLD | Heterocapsaceae | [78] |
| Ansanella granifera Shiwa Bay, Korea | His, Thr, Arg, Val, Met, Phe, Iso; Leu, Lys, Asp, Glu, Ser, Gly, Ala, Tau, GABA, Tyr, and Pro | Suessiaceae | ||
| Alexandrium andersonii Jinhae Bay, Korea | His, Thr, Arg, Val, Met, Phe, Iso; Leu, Lys, Asp, Glu, Ser, Gly, Ala, Tau, GABA, Tyr, and Pro | Ostreopsidaceae | ||
| Takayama tasmanica Glenhaven, New Zeland | His, Thr, Arg, Val, Met, Phe, Iso; Leu, Lys, Asp, Glu, Ser, Gly, Ala, Tyr, and Pro | Brachidiniaceae | ||
| Tanayama helix Tasman Sea, Australia | His, Thr, Arg, Val, Met, Phe, Iso; Leu, Lys, Asp, Glu, Ser, Gly, Ala, Tyr, and Pro | Brachidiniaceae | ||
| Gymnodnium smaydae Shiwa Bay, Korea | His, Thr, Arg, Val, Met, Phe, Iso; Leu, Lys, Asp, Glu, Ser, Gly, Ala, Tau, GABA, Tyr, and Pro | Gymnodinaceae | ||
| Gambierdiscus cf. caribaeus Gambierdiscus cf. carpenteri Five clones: Bahía de La Paz, Gulf of California | His, Thr, Arg, Val, Phe, Iso; Leu, Lys, Asp, Glu, Ser, Gly, Ala, Tyr, and Pro His, Thr, Arg, Val, Phe, Iso; Leu, Lys, Asp, Glu, Ser, Gly, Ala, Tyr, and Pro | HPLC-DAD HPLC-DAD | Ostreopsidaceae Ostreopsidaceae | This study This study |
| Specie/Strain | Origin | Assays Toxicity | Toxins Detected | Method | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gambierdiscus caribaeus | |||||
| Gam19, Jar 17 gam 20, Gam 4, SW gam 1, NCMA 1733, TC tow Gam 3, Norval Cay, SW gam 5, CBC gam1 NCMA 1651 Mexico Algae 1 gam 1 Jamaica Algae 1 gam 1 ETB Gam 6, Outfish 7-1, Outhfish 7-3 Jar 2 Tow 3, Keys jar 7 gam 7 ST1 C5 SJ3 07 BB gam 4 BRP gam 4, Coral cove gam 1 Dive 1 fa gam 1 WBHR 21 gam 2, WBHR 26 gam 1 | Belize Gran Cayman) Cancun, Mexico Ocho ríos, Jamaica DryTortugas (Long key, Florida); St. Thomas St. Jhons Bathtub Beach, Florida Jupiter, Florida Ft. Pierce, Florida Flower Garden | HA | --- | --- | [119] |
| CBCGam1 CCMP1651 Dive1TA KeysJar7 MexicoAlgae1 SWGam5 | Carrie Bow Cay Belize Gran Cayman Island, Caribbean Carrie Bow Cay, Belize Florida Keys, USA Cancún, Mexico Southwater Cay, Belize | CBA-N2a Average, within species toxicity (fg CTX3C eq cell−1 (0.66 ± 0.34, 51%)) | --- | --- | [47] |
| BillHiGam8 | Waikiki Beach, Honolulu, Hawaii | CBA-N2a and ELA (DSF: 1.6–1.0 fg CTX3C eq cell−1) MSF: 5.3–1.0 pg MTX eq cell−1 | --- | --- | [119] |
| CUB4A5 | Cienfuegos, Cuba | RBA | --- | --- | [42] |
| 10 strains Culture Collection of Harmful Microalgae of the Spanish Institute of Oceanography (CCVIEO) | Canary Islands | Neuro-2a Cell Assay, ELA (<LOD to 90.37 ± 15.89 fg CTX1B eq cell−1) | --- | --- | [120] |
| 1 strain GCBG01 | Micronesia Weizhou Island, Beibu Gulf of China | MBA Neuro-2a cells (0.54 fg CTX3C eq cell−1) | 44-methylgambierone --- | LC-MS/MS --- | [121] [122] |
| BPAug08 and USVI-08 | St. Thomas, US Virgin Islands | N2a–MTT Gambierone (0.6 ± 0.2 pg cell−1 and 9.8 ± 0.6 pg cell−1 44-methylgambierone: 7.1 ± 4.2 pg cell−1) | Gambierone, 44-methylgambierone C-CTX-5 | LC–HRMS | [24] |
| DiveIFM4 NOAA STIC5 NOAA | Atlantic Ocean | --- | Gambierone, 44-methylgambierone | LC-MS/MS | [28] |
| CAWD301 | Pohnpei | --- | Gambieric acid A, methylgambierone, MTX-7 trace | LC-MS/MS | [18] |
| BPAug08 and USVI-08 | St. Thomas, US Virgin Islands | --- | C-CTX-5 | NMR spectroscopy | [25] |
| G. cf. caribaeus/ GbSa-2 and GbSa-7 | El Sauzoso, Gulf of California, Mexico | MBA, ARTOX, MFA (CTXs and MTXs-like activity) fRBA | --- | --- | This study |
| Gambierdiscus carpenteri | |||||
| Mixed PR gam 4NCMA 1654 GT4 PatH1jar 5 gam 3 WBHR21 ETB Exp 24 gam 1 Jamaica Algae 2 gam 1 | Puerto Rico Guam Belize Oahu, Hawaii Flower Gardens Dry Tortugas Ocho Rios | Hemolytic assay | --- | --- | [119] |
| 4 isolates | Cook islands, French Polynesia and Australia | MBA (LD50 20– 38 mg kg−1) | 44-methylgambierone in Cook island and French Polynesia strains; Australia island negative strains | LC-MS/MS | [123] |
| CAWD237 CAWD364 | Australia | --- | MTX-6 trace Gambierone, 44-methylgambierone, Gambieric acid A | LC-MS/MS | [18] |
| Bill Aruba Gam15 GT4 Jamaica Algae2Gam1 Mexico Algae2Gam1 WBHR21 | Aruba, Caribbean Carrie Bow Cay Belize Ocho Rios, Jamaica, Caribbean Cancun, Mexico Flower Garden Banks Nat. Mar. Sanctuary (West Bank) Gulf of Mexico, USA | CBA-N2a Average, within species toxicity (fg CTX3C eq cell−1) (0.89 ± 0.41, 47%) | --- | --- | [48] |
| AWD237 | New South Wales, Australia | MBA (LD50 5.1–14.4 mg/Kg) | CTXs and MTXs no detected | LC-MS/MS | [123] |
| Tropical UTSH12C4 UTSH16C3 UTSH16A1 UTSH16D2 | Heron Island Lagoon, Australia | Ca2+ Influx SH-SY5Y Cell FLIPR Bioassay MTX-like activity (3–4) | MTX-3 | LC-MS/MS | [124] |
| Gam1BOL_080513 | Bolinao, Pangasinan, Luzon Island Phillipnes | RBA (7.48 ± 0.49 pg PbTx eq cell−1) | --- | --- | [45] |
| NHA19 and NAH20 | Anaho Bay (Nuku Hiva Island, Marquesas archipelago) | CBA-N2a Were nontoxic | --- | --- | [125] |
| Gam1BOL080513 | Bolinao, Pangasinan | RBA | 44-methylgambierone | UPLC-MS/MS | [27] |
| GCARBAPAZ3 | Isla Gaviota, Gulf of California, Mexico | MBA (CTXs and MTXs-like activity) 5.9 mg kg−1 CTXs-like and 0.06 mg kg−1 MTX-like | --- | --- | [38] |
| G. c.f. carpenteri/ GbSa-4, GbSa-5, and GbSa-6 | El Sauzoso, Gulf of California, Mexico | MBA, ARTOX, MFA (CTXs and MTXs-like activity) f -RBA | --- | --- | This study |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fernández-Herrera, L.J.; Núñez-Vázquez, E.J.; Hernández-Sandoval, F.E.; Ceseña-Ojeda, D.O.; García-Davis, S.; Teles, A.; Virgen-Félix, M.; Tovar-Ramírez, D. Morphological, Toxicological, and Biochemical Characterization of Two Species of Gambierdiscus from Bahía de La Paz, Gulf of California. Mar. Drugs 2024, 22, 422. https://doi.org/10.3390/md22090422
Fernández-Herrera LJ, Núñez-Vázquez EJ, Hernández-Sandoval FE, Ceseña-Ojeda DO, García-Davis S, Teles A, Virgen-Félix M, Tovar-Ramírez D. Morphological, Toxicological, and Biochemical Characterization of Two Species of Gambierdiscus from Bahía de La Paz, Gulf of California. Marine Drugs. 2024; 22(9):422. https://doi.org/10.3390/md22090422
Chicago/Turabian StyleFernández-Herrera, Leyberth José, Erick Julián Núñez-Vázquez, Francisco E. Hernández-Sandoval, Daniel Octavio Ceseña-Ojeda, Sara García-Davis, Andressa Teles, Marte Virgen-Félix, and Dariel Tovar-Ramírez. 2024. "Morphological, Toxicological, and Biochemical Characterization of Two Species of Gambierdiscus from Bahía de La Paz, Gulf of California" Marine Drugs 22, no. 9: 422. https://doi.org/10.3390/md22090422
APA StyleFernández-Herrera, L. J., Núñez-Vázquez, E. J., Hernández-Sandoval, F. E., Ceseña-Ojeda, D. O., García-Davis, S., Teles, A., Virgen-Félix, M., & Tovar-Ramírez, D. (2024). Morphological, Toxicological, and Biochemical Characterization of Two Species of Gambierdiscus from Bahía de La Paz, Gulf of California. Marine Drugs, 22(9), 422. https://doi.org/10.3390/md22090422










