Marine-Derived Yaequinolone Derivative CHNQD-02792 Suppresses Colorectal Cancer Cell Proliferation and Induces Apoptosis via MAPK Pathway Modulation
Abstract
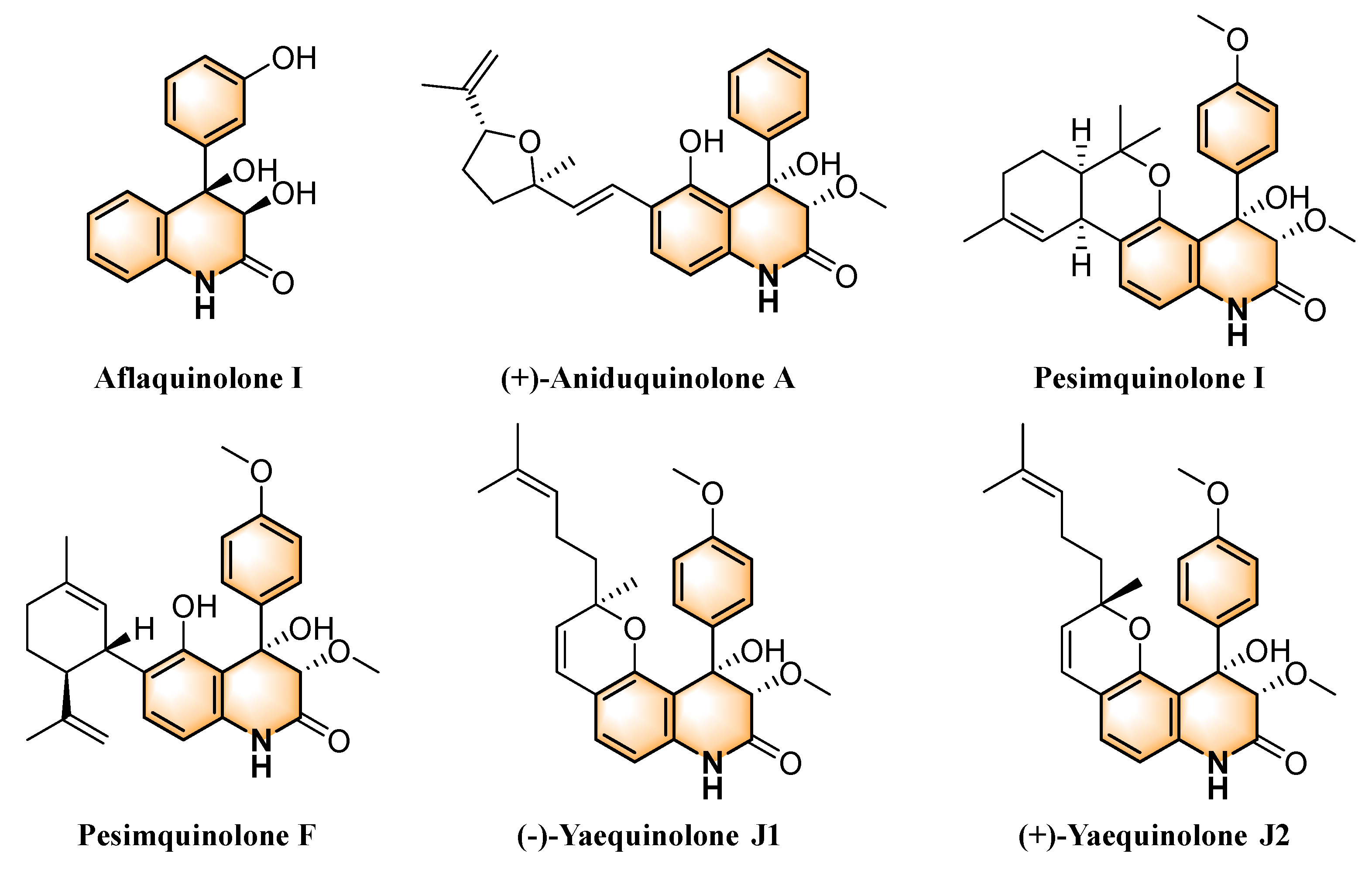
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
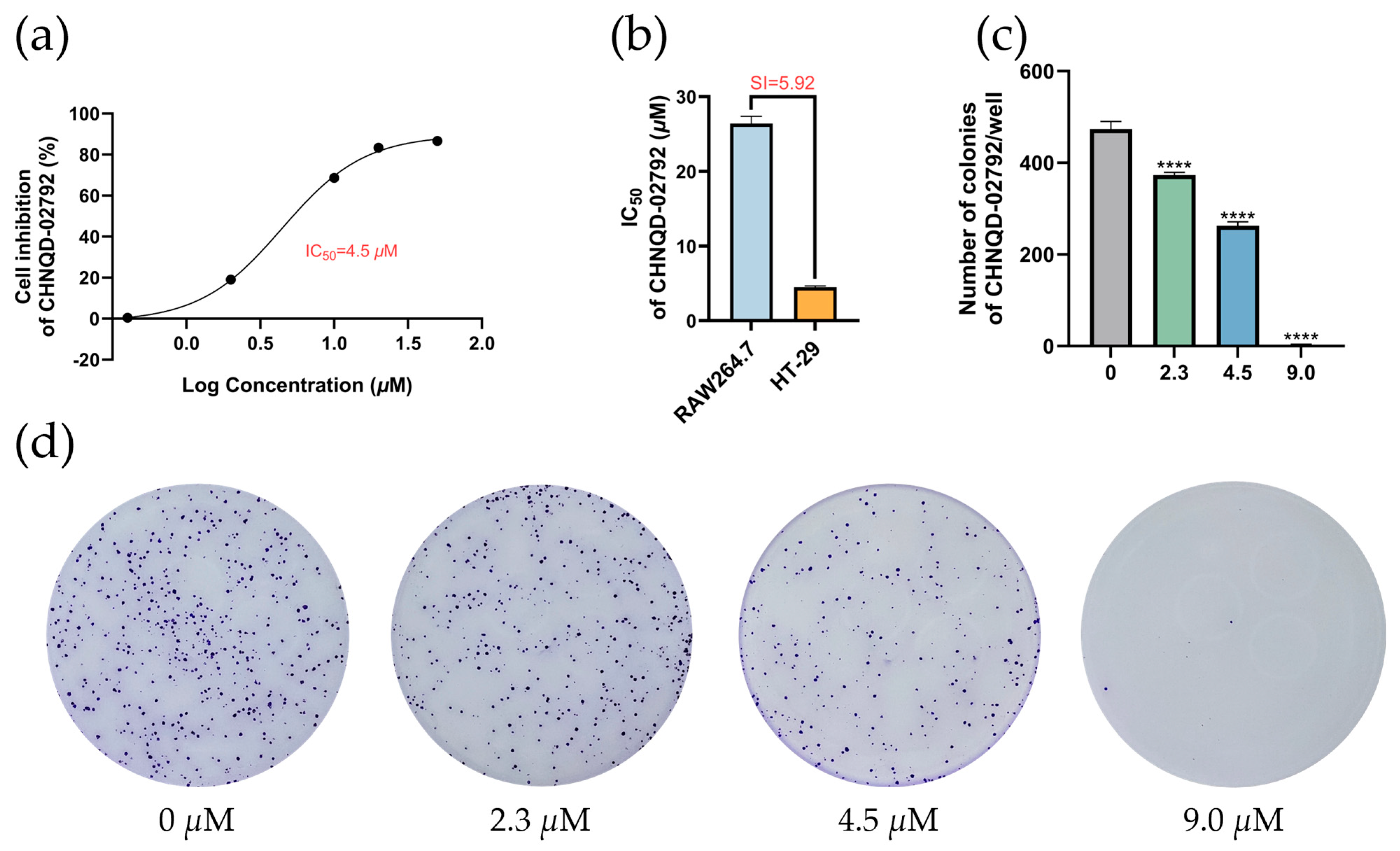
2.1. Selectivity of Quinolone Derivatives for Various Colorectal Cancer Cell Lines
2.2. CHNQD-02792 Induces HT-29 Cell Cycle Block in G2/M Phase
2.3. CHNQD-02792 Induces Apoptosis in HT-29 Cells
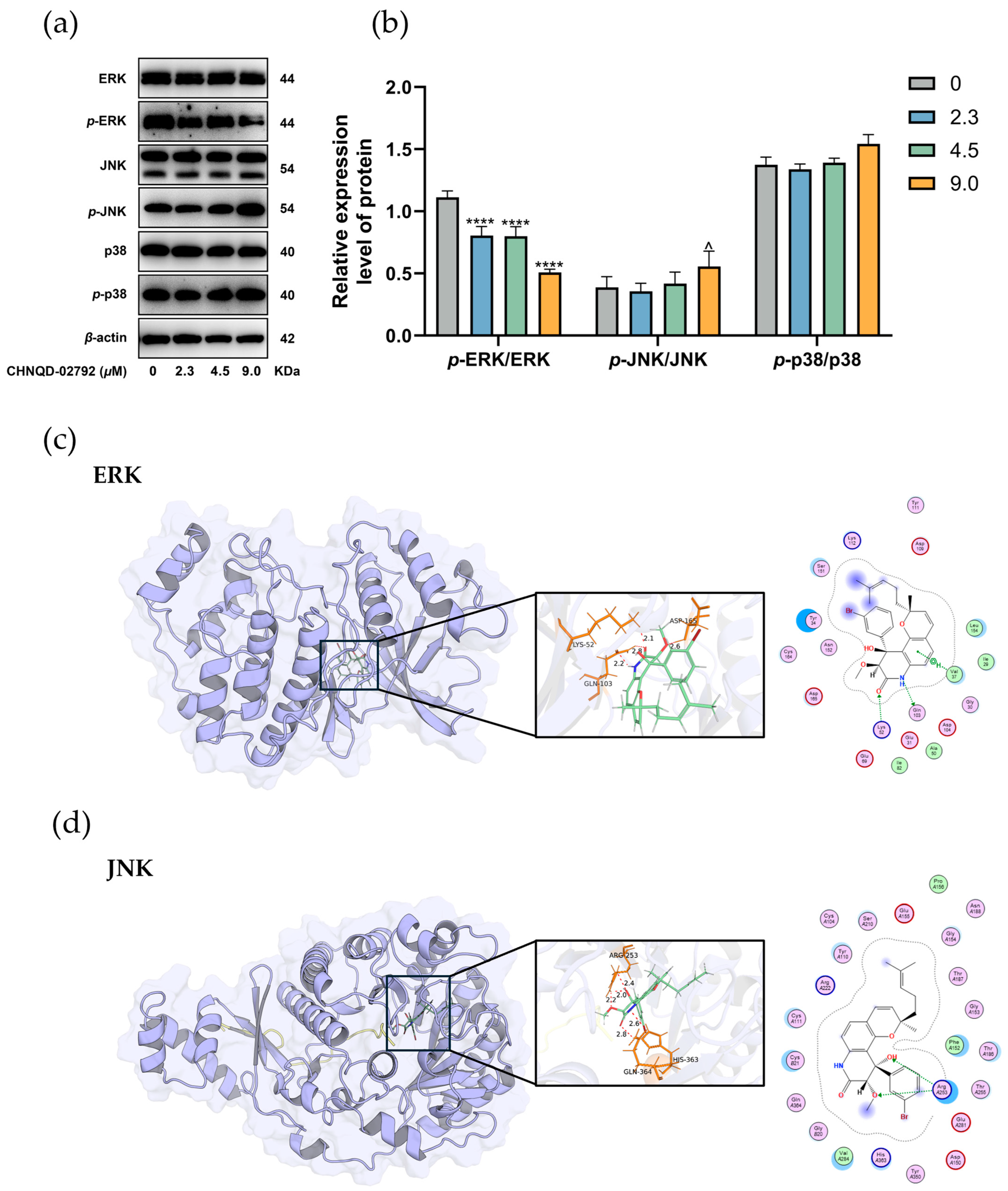
2.4. Effect of CHNQD-02792 on MAPK Signaling Pathway
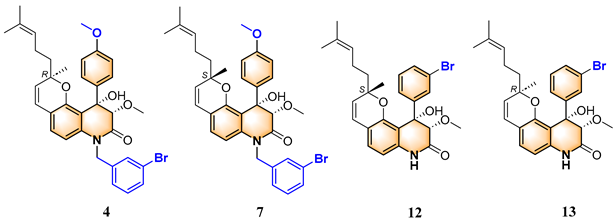
2.5. Structure-Activity Relationship
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Main Instruments and Reagents
3.2. Sample Information
3.3. Cell Lines
3.4. Cell Culture
3.5. MTT Assay
3.6. Colony Formation Assay
3.7. Cell Cycle Assay
3.8. Apoptosis Assay
3.9. Western Blot Assay
3.10. Molecular Docking
3.11. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| MAPK | mitogen-activated protein kinase |
| ERK | extracellular signal-regulated kinase |
| JNK | c-Jun N-terminal kinase |
| ASMR | age-standardized mortality rate |
| G2/M phase | G2 phase to M phase transition |
| CDK1 | Cyclin-dependent kinase 1 |
| Bcl-2 | B-cell lymphoma 2 |
| Bax | Bcl-2 associated X-protein |
References
- Bray, F.; Laversanne, M.; Weiderpass, E.; Soerjomataram, I. The ever-increasing importance of cancer as a leading cause of premature death worldwide. Cancer 2021, 127, 3029–3030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferlay, J.; Colombet, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Parkin, D.M.; Piñeros, M.; Znaor, A.; Bray, F. Cancer statistics for the year 2020: An overview. Int. J. Cancer 2021, 149, 778–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.Y.; Jiang, Y.Y.; Li, P.J.; Yao, B.; Song, Y.J.; Gao, J.X.; Said, G.; Gao, Y.; Lai, J.Y.; Shao, C.L. Discovery of a potential bladder cancer inhibitor CHNQD-01281 by regulating EGFR and promoting infiltration of cytotoxic T cells. Mar. Life Sci. Technol. 2024, 6, 502–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, M.; Abnet, C.C.; Neale, R.E.; Vignat, J.; Giovannucci, E.L.; McGlynn, K.A.; Bray, F. Global burden of 5 major types of gastrointestinal cancer. Gastroenterology 2020, 159, 335–349.e315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Yang, Q.; Zhao, S.; Sun, L.; Li, R.; Wang, J.; Wang, D. Evolving landscape of colorectal cancer: Global and regional burden, risk factor dynamics, and future scenarios (the global burden of disease 1990–2050). Ageing Res. Rev. 2025, 104, 102666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.K.; Liles, E.G.; Bent, S.; Levin, T.R.; Corley, D.A. Accuracy of fecal immunochemical tests for colorectal cancer: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann. Intern. Med. 2014, 160, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allemani, C.; Matsuda, T.; Di Carlo, V.; Harewood, R.; Matz, M.; Nikšić, M.; Bonaventure, A.; Valkov, M.; Johnson, C.J.; Estève, J.; et al. Global surveillance of trends in cancer survival 2000-14 (CONCORD-3): Analysis of individual records for 37,513,025 patients diagnosed with one of 18 cancers from 322 population-based registries in 71 countries. Lancet 2018, 391, 1023–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keum, N.; Giovannucci, E. Global burden of colorectal cancer: Emerging trends, risk factors and prevention strategies. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 16, 713–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Goding Sauer, A.; Fedewa, S.A.; Butterly, L.F.; Anderson, J.C.; Cercek, A.; Smith, R.A.; Jemal, A. Colorectal cancer statistics, 2020. CA Cancer J Clin 2020, 70, 145–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro, M.; Nicolas, A.; Ferrandez, A.; Lanas, A. Colorectal cancer population screening programs worldwide in 2016: An update. World J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 23, 3632–3642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, H.; Ran, X.; An, L.; Zheng, R.; Zhang, S.; Ji, J.S.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, W.; Wei, W.; He, J. Disparities in stage at diagnosis for five common cancers in China: A multicentre, hospital-based, observational study. Lancet Public Health 2021, 6, e877–e887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bando, H.; Ohtsu, A.; Yoshino, T. Therapeutic landscape and future direction of metastatic colorectal cancer. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2023, 20, 306–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seymour, M.T.; Morton, D.; International FOxTROT Trial Investigators. FOxTROT: An international randomised controlled trial in 1052 patients (pts) evaluating neoadjuvant chemotherapy (NAC) for colon cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37, 3504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Liu, P.; Zhou, M.; Yin, L.; Wang, M.; Liu, T.; Jiang, X.; Gao, H. Small-molecule drugs of colorectal cancer: Current status and future directions. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2024, 1870, 166880. [Google Scholar]
- Aprile, G.; Rihawi, K.; De Carlo, E.; Sonis, S.T. Treatment-related gastrointestinal toxicities and advanced colorectal or pancreatic cancer: A critical update. World J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 21, 11793–11803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.Y.; Tang, M.L.; Ning, J.F.; Hao, Y.P.; Zhou, L.; Sun, X. Novel octapeptide-DTX prodrugs targeting MMP-7 as effective agents for the treatment of colorectal cancer with lower systemic toxicity. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 193, 112194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fakih, M.; Vincent, M. Adverse events associated with anti-EGFR therapies for the treatment of metastatic colorectal cancer. Curr. Oncol. 2010, 17, S18–S30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pala, L.; Conforti, F.; Pagan, E.; Bagnardi, V.; De Pas, T.M.; Mazzarol, G.; Barberis, M.; Pennacchioli, E.; Orsolini, G.; Prestianni, P.; et al. Different response to immunotherapy according to melanoma histologic subtype. J. Immunother. 2022, 45, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yule, M.S.; Brown, L.R.; Waller, R.; Wigmore, S.J. Cancer cachexia. BMJ 2024, 387, e080040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Chen, J.; Hu, G.; Yu, J.; Zhu, X.; Lin, Y.; Chen, S.; Yuan, J. Statistical research on the bioactivity of new marine natural products discovered during the 28 years from 1985 to 2012. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 202–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scherlach, K.; Hertweck, C. Discovery of aspoquinolones A-D, prenylated quinoline-2-one alkaloids from Aspergillus nidulans, motivated by genome mining. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2006, 4, 3517–3520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, J.; Lion, U.; Sattler, I.; Gollmick, F.A.; Grabley, S.; Cai, J.; Meiners, M.; Schünke, H.; Schaumann, K.; Dechert, U.; et al. Diastereomeric quinolinone alkaloids from the marine-derived fungus Penicillium janczewskii. J. Nat. Prod. 2005, 68, 1397–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, C.; Li, X.; Zhang, K.; Li, X.N.; Wang, W.; Zang, Y.; Chen, X.; Li, Q.; Wei, M.; Chen, C.; et al. Pesimquinolones I-S, eleven new quinolone alkaloids produced by Penicillium simplicissimum and their inhibitory activity on NO production. Bioorg. Chem. 2021, 108, 104635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Shao, C.L.; Meng, H.; She, Z.G.; Wang, C.Y. Anti-respiratory syncytial virus prenylated dihydroquinolone derivatives from the gorgonian-derived fungus Aspergillus sp. XS-20090B15. J. Nat. Prod. 2014, 77, 2720–2724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, C.L.; Xu, R.F.; Wang, C.Y.; Qian, P.Y.; Wang, K.L.; Wei, M.Y. Potent Antifouling Marine Dihydroquinolin-2(1H)-one-Containing Alkaloids from the Gorgonian Coral-Derived Fungus Scopulariopsis sp. Mar. Biotechnol. 2015, 17, 408–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebada, S.S.; Ebrahim, W. A new antibacterial quinolone derivative from the endophytic fungus Aspergillus versicolor strain Eich.5.2.2. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2020, 134, 151–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mou, X.F.; Liu, X.; Xu, R.F.; Wei, M.Y.; Fang, Y.W.; Shao, C.L. Scopuquinolone B, a new monoterpenoid dihydroquinolin-2(1H)-one isolated from the coral-derived Scopulariopsis sp. fungus. Nat. Prod. Res. 2018, 32, 773–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Lv, L.X.; Wang, W.W.; Wei, M.Y.; Gu, Y.C.; Shao, C.L. Recent advances of bioactive marine natural products in drug discovery. J. Ocean. Univ. China 2024, 23, 1297–1318. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, F.W.; Gao, Y.; Gu, Y.C.; Shao, C.L. Scalable total synthesis of aflaquinolone I and confirmation of the absolute configuration. Tetrahedron 2023, 134, 7. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, F.W.; Mou, X.F.; Qu, Y.; Wei, M.Y.; Chen, G.Y.; Wang, C.Y.; Gu, Y.C.; Shao, C.L. Scalable total synthesis of (+)-aniduquinolone A and its acid-catalyzed rearrangement to aflaquinolones. Commun. Chem. 2022, 5, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamie, P.F.; Philoppes, J.N. Design and synthesis of three series of novel antitumor–azo derivatives. Med. Chem. Res. 2017, 26, 1228–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Zhou, L.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, M.; Dong, Y.; Wang, Y.; Pei, R.; He, E.; Liang, Y.; Shen, Y.; et al. Targeting MAPK14 by Lobeline Upregulates Slurp1-Mediated Inhibition of Alternative Activation of TAM and Retards Colorectal Cancer Growth. Adv. Sci. 2025, 12, 2407900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeed, A.; Su, J.; Ouyang, S. Marine-derived drugs: Recent advances in cancer therapy and immune signaling. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 134, 111091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Y.; Zhou, T.Y.; Guo, F.W.; Wei, M.Y.; Chen, G.Y.; Gu, Y.C.; Wang, C.Y.; Shao, C.L. Analogues of natural products yaequinolones as potential inflammatory inhibitors: Design, synthesis and biological evaluation. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2023, 250, 115183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Wu, L.; Yan, G.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, M.; Wu, Y.; Li, Y. Inflammation and tumor progression: Signaling pathways and targeted intervention. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2021, 6, 263. [Google Scholar]
- Park, M.D.; Le Berichel, J.; Hamon, P.; Wilk, C.M.; Belabed, M.; Yatim, N.; Saffon, A.; Boumelha, J.; Falcomatà, C.; Tepper, A.; et al. Hematopoietic aging promotes cancer by fueling IL-1α-driven emergency myelopoiesis. Science 2024, 386, eadn0327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; He, L.; Jiang, Q.; Zhu, H.; Kong, D.; Zhang, H.; Cheng, Z.; Deng, H.; Zheng, Y.; Ying, X. Systems Pharmacology-Based Dissection of Anti-Cancer Mechanism of Traditional Chinese Herb Saussurea involucrata. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 678203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Compounds | 3″R/S | R1 | R2 | R3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | R | H | H | H |
| 2 | S | H | H | H |
| 3 | R | OCH3 | H | 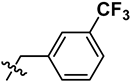 |
| 4 | R | OCH3 | H | 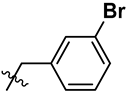 |
| 5 | R | OCH3 | H |  |
| 6 | S | OCH3 | H | 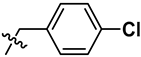 |
| 7 | S | OCH3 | H | 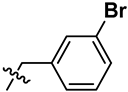 |
| 8 | S | OCH3 | H | 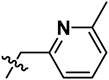 |
| 9 | S | OCH3 | H | H |
| 10 | R | H | NO2 | H |
| 11 | S | H | NO2 | H |
| 12 | S | Br | H | H |
| 13 | R | Br | H | H |
| Compounds | CT-26 | RKO | LoVo | HT-29 | HCT-116 | DLD-1 | LS-174T |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4 | >50.0 | 48.3 | >50.0 | >50.0 | >50.0 | >50.0 | >50.0 |
| 7 | >50.0 | 22.0 | 25.0 | >50.0 | >50.0 | >50.0 | >50.0 |
| 12 | 26.3 | 37.3 | >50.0 | 42.8 | 25.8 | 11.6 | 7.7 |
| 13 | >50.0 | 28.0 | 28.29 | 4.5 | 50.0 | >50.0 | 24.3 |
 | |||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kang, J.-Q.; Zhou, T.-Y.; Wang, W.-H.; Wei, M.-Y.; Shao, C.-L. Marine-Derived Yaequinolone Derivative CHNQD-02792 Suppresses Colorectal Cancer Cell Proliferation and Induces Apoptosis via MAPK Pathway Modulation. Mar. Drugs 2025, 23, 136. https://doi.org/10.3390/md23040136
Kang J-Q, Zhou T-Y, Wang W-H, Wei M-Y, Shao C-L. Marine-Derived Yaequinolone Derivative CHNQD-02792 Suppresses Colorectal Cancer Cell Proliferation and Induces Apoptosis via MAPK Pathway Modulation. Marine Drugs. 2025; 23(4):136. https://doi.org/10.3390/md23040136
Chicago/Turabian StyleKang, Jia-Qi, Tian-Yi Zhou, Wen-Hui Wang, Mei-Yan Wei, and Chang-Lun Shao. 2025. "Marine-Derived Yaequinolone Derivative CHNQD-02792 Suppresses Colorectal Cancer Cell Proliferation and Induces Apoptosis via MAPK Pathway Modulation" Marine Drugs 23, no. 4: 136. https://doi.org/10.3390/md23040136
APA StyleKang, J.-Q., Zhou, T.-Y., Wang, W.-H., Wei, M.-Y., & Shao, C.-L. (2025). Marine-Derived Yaequinolone Derivative CHNQD-02792 Suppresses Colorectal Cancer Cell Proliferation and Induces Apoptosis via MAPK Pathway Modulation. Marine Drugs, 23(4), 136. https://doi.org/10.3390/md23040136








