ESI FTICR-MS Analysis of Larvae from the Marine Sponge Luffariella variabilis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
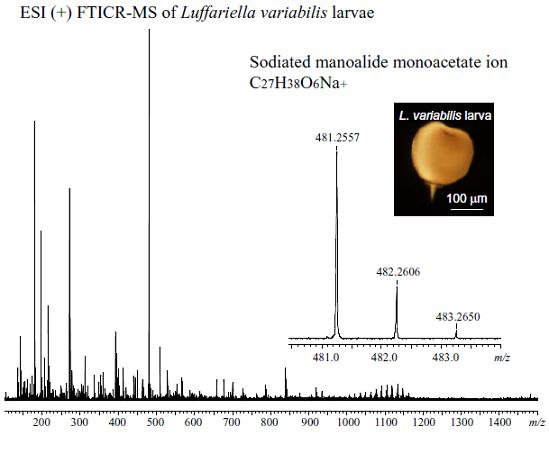
2. Results and Discussion
4. Experimental Section
4.1. Animal material
4.2. Larval collection
4.3. Standards
4.4. Sample preparation
4.5. ESI FTICR-MS
Acknowledgements
References
- Caley, MJ; Carr, MH; Hixon, MA; Hughes, TP; Jones, GP; Menge, BA. Recruitment and the local dynamics of open marine populations. Annu Rev Ecol Syst 1996, 27, 477–500. [Google Scholar]
- Paul, VJ. Ecological roles of marine natural products; Comstock Publishing Associates: New York, NY, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Pawlik, JR. Marine invertebrate chemical defences. Chem Rev 1993, 93, 1911–1922. [Google Scholar]
- Burns, E; Ifrach, I; Carmeli, S; Pawlik, JR; Han, M. Comparison of anti-predatory defences of Red Sea and Caribbean sponges. I. Chemical defence. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 2003, 252, 105–114. [Google Scholar]
- Metaxas, A; Scheibling, RE; Robinson, MC; Young, CM. Larval development, settlement, and early post-settlement behavior of the tropical sea star Oreaster reticulatus. Bull Mar Sci 2008, 83, 471–480. [Google Scholar]
- McClintock, JB; Vernon, JD. Chemical defence in the eggs and embryos of antarctic sea stars (Echinodermata). Mar Biol 1990, 105, 491–495. [Google Scholar]
- Lindquist, N; Hay, ME; Fenical, W. Defence of ascidians and their conspicuous larvae: Adult vs. larval chemical defences. Ecol Monogr 1992, 62, 547–568. [Google Scholar]
- Cowart, JD; Fielman, KT; Woodin, SA; Lincoln, DE. Halogenated metabolites in two marine polychaetes and their planktotrophic and lecithotrophic larvae. Mar Biol 2000, 136, 993–1002. [Google Scholar]
- Lopanik, N; Lindquist, N; Targett, N. Potent cytotoxins produced by a microbial symbiont protect host larvae from predation. Oecologia 2004, 139, 131–139. [Google Scholar]
- Pawlik, JR; Kernan, MR; Molinski, TF; Harper, MK; Faulkner, DJ. Defensive chemicals of the Spanish Dancer nudibranch, Hexabranchus sanguineus, and its egg ribbons: Macrolides derived from a sponge diet. J Exp Mar Bio Ecol 1988, 119, 99–109. [Google Scholar]
- Lindquist, N; Hay, ME. Palatability and chemical defence of marine invertebrate larvae. Ecol Monogr 1996, 62, 547–568. [Google Scholar]
- Ettinger-Epstein, P; Whalan, SW; Battershill, CN; de Nys, R. Temperature cues gametogenesis and larval release in a tropical sponge. Mar Biol 2007, 153, 171–178. [Google Scholar]
- De Silva, ED; Scheuer, PJ. Manoalide, an antibiotic sesterterpenoid from the marine sponge Luffariella variabilis (Polejaffe). Tetrahedron Lett 1980, 21, 1611–1614. [Google Scholar]
- De Silva, ED; Scheuer, PJ. Three new sesterterpenoid antibiotics from the marine sponge Luffariella variabilis (Polejaff). Tetrahedron Lett 1981, 22, 3147–3150. [Google Scholar]
- Cambie, RC; Craw, PA; Berquist, PR; Karuso, P. Chemistry of sponges. III. Manoalide monoacetate & thorectolide monoacetate, two new sesterterpenoids from Thorectandra excavatus. J Nat Prod 1988, 51, 331–334. [Google Scholar]
- Kernan, MR; Faulkner, DJ; Jacobs, RS. Luffariellins, antiinflammatory sesterterpenes of chemotaxonomic importance from sponge Luffariella variabilis. J Org Chem 1987, 52, 3081–3083. [Google Scholar]
- Tsuda, M; Shigemori, H; Ishibashi, M; Sasaki, T; Kobayashi, J. Luffariolides A-E, new cytotoxic sesterterpenes from the Okinawan marine sponge Luffariella sp. J Org Chem 1992, 57, 3503–3507. [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi, J; Zeng, CM; Ishibashi, M; Sasaki, T. Luffariolides F and G, new manoalide derivatives from the Okinawan marine sponge Luffariella sp. J Nat Prod 1993, 56, 436–439. [Google Scholar]
- Tsuda, M; Endo, T; Mikami, Y; Fromont, J; Kobayashi, J. Luffariolides H and J, new sesterterpenes from a marine sponge Luffariella species. J Nat Prod 2002, 65, 1507–1508. [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson, PB; Marshall, LA; Sung, A; Jacobs, RS. Inactivation of human synovial fluid phospholipase A2 by the natural product, manoalide. Biochem Pharmacol 1990, 39, 1557–1564. [Google Scholar]
- Glaser, KB; Jacobs, RS. Inactivation of bee venom phospholipase A2 by manoalide: A model based on the reactivity of manoalide with amino acids and peptide sequences. Biochem Pharmacol 1987, 36, 2079–2086. [Google Scholar]
- Lombardo, D; Dennis, EA. Cobra venom phospholipase A2 inhibition by manoalide. A novel type of phospholipase inhibitor. J Biol Chem 1985, 260, 7234–7240. [Google Scholar]
- Wheeler, L. Treatment of cutaneous hyperproliferative dermatoses with manoalide US Patent 4786651. 1988.
- Rodgers, KE; diZerega, GS. Method for reducing or preventing post-surgical adhesion formation using manoalide and analogs thereof US Patent 5639468. 1997.
- Ettinger-Epstein, P; Tapiolas, DM; Motti, CA; Wright, AD; Battershill, CN; de Nys, R. Production of manoalide and its analogues by the sponge Luffariella variabilis is hardwired. Mar Biotechnol 2008, 10, 64–74. [Google Scholar]
- Ettinger-Epstein, P; Motti, CA; de Nys, R; Wright, AD; Battershill, CN; Tapiolas, DM. Acetylated sesterterpenes from the Great Barrier Reef sponge Luffariella variabilis. J Nat Prod 2007, 70, 648–651. [Google Scholar]
- Duffy, JE; Paul, VJ. Prey nutritional quality and the effectiveness of chemical defences against tropical reef fishes. Oecologia 1992, 90, 333–339. [Google Scholar]
- Namikoshi, M; Suzuki, S; Meguro, S; Nagai, H; Koike, Y; Kitazawa, A; Kobayashi, H; Oda, T; Yamada, J. Manoalide derivatives from a marine sponge Luffariella sp. collected in Palau. Fish Sci 2004, 70, 152–158. [Google Scholar]
- Skindersoe, ME; Ettinger-Epstein, P; Rasmussen, TB; Bjarnsholt, T; De Nys, R; Givskov, M. Quorum sensing antagonism from marine organisms. Mar Biotechnol 2008, 10, 56–63. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, X; Siegel, M. M. FTICR-MS applications for the structure determination of natural products. Anal Bioanal Chem 2007, 389, 1341–1363. [Google Scholar]
- Thoms, C; Ebel, R; Proksch, P. Activated chemical defence in Aplysina sponges revisited. J Chem Ecol 2006, 32, 97–123. [Google Scholar]
- Webster, NS; Xavier, JR; Freckelton, ML; Motti, CA; Cobb, R. Shifts in microbial and chemical patterns within the marine sponge Aplysina aerophoba during a disease outbreak. Environ Microbiol 2008, 10, 3366–3376. [Google Scholar]
- Kelman, D; Kashman, Y; Rosenberg, E; Ilan, M; Ifrach, I; Loya, Y. Antimicrobial activity of the reef sponge Amphimedon viridis from the Red Sea: Evidence for selective toxicity. Aquat Microb Ecol 2001, 24, 9–16. [Google Scholar]
- Schmitt, S; Weisz, JB; Lindquist, N; Hentschell, U. Vertical transmission of a phylogenetically complex microbial consortium in the viviparous sponge Ircinia felix. Appl Environ Microbiol 2007, 73, 2067–2078. [Google Scholar]
- Motti, CA; Tapiolas, DM; Willis, RH; Freckelton, ML. FTICR-MS and LC-UV/MS-SPE-NMR applications for the rapid dereplication of a crude extract from the sponge Ianthella flabelliformis. J Nat Prod 2009, 72, 290–294. [Google Scholar]



| No. | mode | Formula | Corresponding ion | m/z calculated | m/z observed | Δ ppm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | + | C25H35O4+ | [M + H]+ | 399.2530 | not obs | - |
| C25H34O4Na+ | [M + Na]+ | 421.2349 | 421.2343 | 1.4 | ||
| C25H36O5Na+ | [M + H2O + Na]+ | 439.2455 | 439.2448 | 1.6 | ||
| C50H70O10Na+ | [2M + 2H2O + Na]+ | 855.5018 | 855.5015 | 0.4 | ||
| 1 | − | C25H33O4− | [M − H]− | 397.2384 | 397.2388 | 1.0 |
| C50H71O10− | [2M + 2H2O − H]− | 831.5053 | 831.5055 | 0.2 | ||
| 3 | + | C27H39O6+ | [M + H]+ | 459.2741 | not obs | - |
| C27H38O6Na+ | [M + Na]+ | 481.2561 | 481.2567 | 1.2 | ||
| C54H76O12Na+ | [2M + Na]+ | 939.5229 | 939.5216 | 1.4 | ||
| C81H114O18Na+ | [3M + Na]+ | 1397.7897 | 1397.7821 | 5.4 | ||
| 3 | − | C27H37O6− | [M − H]− | 457.2596 | not obs | - |
| C25H33O4− | [M − H2O − C2H3O]− | 397.2384 | 397.2384 | 0 | ||
© 2010 by the authors; licensee Molecular Diversity Preservation International, Basel, Switzerland This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Motti, C.A.; Ettinger-Epstein, P.; Willis, R.H.; Tapiolas, D.M. ESI FTICR-MS Analysis of Larvae from the Marine Sponge Luffariella variabilis. Mar. Drugs 2010, 8, 190-199. https://doi.org/10.3390/md8010190
Motti CA, Ettinger-Epstein P, Willis RH, Tapiolas DM. ESI FTICR-MS Analysis of Larvae from the Marine Sponge Luffariella variabilis. Marine Drugs. 2010; 8(1):190-199. https://doi.org/10.3390/md8010190
Chicago/Turabian StyleMotti, Cherie A., Piers Ettinger-Epstein, Richard H. Willis, and Dianne M. Tapiolas. 2010. "ESI FTICR-MS Analysis of Larvae from the Marine Sponge Luffariella variabilis" Marine Drugs 8, no. 1: 190-199. https://doi.org/10.3390/md8010190
APA StyleMotti, C. A., Ettinger-Epstein, P., Willis, R. H., & Tapiolas, D. M. (2010). ESI FTICR-MS Analysis of Larvae from the Marine Sponge Luffariella variabilis. Marine Drugs, 8(1), 190-199. https://doi.org/10.3390/md8010190