Diversity of Bacterial Communities of Fitness Center Surfaces in a U.S. Metropolitan Area
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Sample Collection
2.2. DNA Extraction and Pyrosequencing
2.3. Computational and Statistical Analyses
3. Results
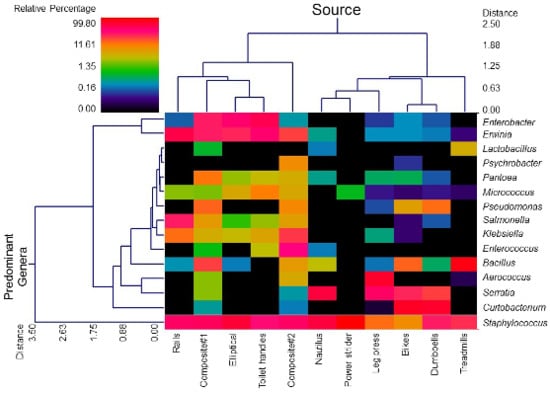
3.1. Diversity and Relative Abundance of Bacterial Genera in Surface Swab Sample of Fitness Center




3.2. Probable Source of Bacteria in Surface Swab Sample of Fitness Center


4. Discussion and Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Walsh, K. Global Health Club Industry Proves Resilient. Available online: http://download.ihrsa.org/press/2013_IHRSA_Global_Report_Feature.pdf (accessed on 23 August 2014).
- 58.5 Million Americans Utilize Health Clubs. Available online: http://www.ihrsa.org/media-center/2013/5/8/585-million-americans-utilize-health-clubs.html (accessed on 23 August 2014).
- Ayliffe, G.A.; Collins, B.J.; Lowbury, E.J.; Babb, J.R.; Lilly, H.A. Ward floors and other surfaces as reservoirs of hospital infection. J. Hyg. 1967, 65, 515–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Oliveira, A.B.A.; da Cunha, D.T.; Stedefeldt, E.; Capalonga, R.; Tondo, E.C.; Cardoso, M.R.I. Hygiene and good practices in school meal services: Organic matter on surfaces, microorganisms and health risks. Food Control 2014, 40, 120–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Microbes in pool filter backwash as evidence of the need for improved swimmer hygiene-metro-Atlanta, Georgia, 2012. MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2013, 62, 385–388. [Google Scholar]
- Cooper, R.A. Surgical site infections: Epidemiology and microbiological aspects in trauma and orthopaedic surgery. Int. Wound J. 2013, 10, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliver, S.P.; Jayarao, B.M.; Almeida, R.A. Foodborne pathogens in milk and the dairy farm environment: Food safety and public health implications. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2005, 2, 115–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- David, M.Z.; Mennella, C.; Mansour, M.; Boyle-Vavra, S.; Daum, R.S. Predominance of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus among pathogens causing skin and soft tissue infections in a large urban jail: Risk factors and recurrence rates. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2008, 46, 3222–3227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorwitz, R.J. A review of community-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus skin and soft tissue infections. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2008, 27, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montgomery, K.; Ryan, T.J.; Krause, A.; Starkey, C. Assessment of athletic health care facility surfaces for MRSA in the secondary school setting. J. Environ. Health 2010, 72, 8–11. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Newsome, A.; DuBois, J.; Tenney, J. Disinfection of football protective equipment using chlorine dioxide produced by the ICA TriNova system. BMC Public Health 2009, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rackham, D.M.; Ray, S.M.; Franks, A.S.; Bielak, K.M.; Pinn, T.M. Community-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus nasal carriage in a college student athlete population. Clin. J. Sport Med. 2010, 20, 185–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stanforth, B.; Krause, A.; Starkey, C.; Ryan, T.J. Prevalence of community-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in high school wrestling environments. J. Environ. Health 2010, 72, 12–16. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ryan, K.A.; Ifantides, C.; Bucciarelli, C.; Saliba, H.; Tuli, S.; Black, E.; Thompson, L.A. Are gymnasium equipment surfaces a source of staphylococcal infections in the community? Am. J. Infect. Control. 2011, 39, 148–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldhammer, K.A.; Dooley, D.P.; Ayala, E.; Zera, W.; Hill, B.L. Prospective study of bacterial and viral contamination of exercise equipment. Clin. J. Sport Med. 2006, 16, 34–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pace, N.R. A molecular view of microbial diversity and the biosphere. Science 1997, 276, 734–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kembel, S.W.; Jones, E.; Kline, J.; Northcutt, D.; Stenson, J.; Womack, A.M.; Bohannan, B.J.; Brown, G.Z.; Green, J.L. Architectural design influences the diversity and structure of the built environment microbiome. ISME J. 2012, 6, 1469–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hewitt, K.M.; Gerba, C.P.; Maxwell, S.L.; Kelley, S.T. Office space bacterial abundance and diversity in three metropolitan areas. PLoS One 2012, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flores, G.E.; Bates, S.T.; Caporaso, J.G.; Lauber, C.L.; Leff, J.W.; Knight, R.; Fierer, N. Diversity, distribution and sources of bacteria in residential kitchens. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 15, 588–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flores, G.E.; Bates, S.T.; Knights, D.; Lauber, C.L.; Stombaugh, J.; Knight, R.; Fierer, N. Microbial biogeography of public restroom surfaces. PLoS One 2011, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feazel, L.M.; Baumgartner, L.K.; Peterson, K.L.; Frank, D.N.; Harris, J.K.; Pace, N.R. Opportunistic pathogens enriched in showerhead biofilms. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2009, 106, 16393–16399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barker, J.; Bloomfield, S.F. Survival of Salmonella in bathrooms and toilets in domestic homes following salmonellosis. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2000, 89, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desai, R.; Pannaraj, P.S.; Agopian, J.; Sugar, C.A.; Liu, G.Y.; Miller, L.G. Survival and transmission of community-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus from fomites. Am. J. Infect. Control. 2011, 39, 219–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, R.; Mehta, S.; Weed, D.; Price, C.S. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus survival on hospital fomites. Infect. Control. Hosp. Epidemiol. 2006, 27, 1267–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanford, M.D.; Widmer, A.F.; Bale, M.J.; Jones, R.N.; Wenzel, R.P. Efficient detection and long-term persistence of the carriage of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Clin. Infect. Dis. 1994, 19, 1123–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bures, S.; Fishbain, J.T.; Uyehara, C.F.; Parker, J.M.; Berg, B.W. Computer keyboards and faucet handles as reservoirs of nosocomial pathogens in the intensive care unit. Am. J. Infect. Control. 2000, 28, 465–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekanem, E.E.; DuPont, H.L.; Pickering, L.K.; Selwyn, B.J.; Hawkins, C.M. Transmission dynamics of enteric bacteria in day-care centers. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1983, 118, 562–572. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Manning, M.L.; Archibald, L.K.; Bell, L.M.; Banerjee, S.N.; Jarvis, W.R. Serratia marcescens transmission in a pediatric intensive care unit: A multifactorial occurrence. Am. J. Infect. Control. 2001, 29, 115–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abad, F.X.; Pinto, R.M.; Bosch, A. Survival of enteric viruses on environmental fomites. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1994, 60, 3704–3710. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Brooke, J.S.; Annand, J.W.; Hammer, A.; Dembkowski, K.; Shulman, S.T. Investigation of bacterial pathogens on 70 frequently used environmental surfaces in a large urban U.S. university. J. Environ. Health 2009, 71, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Reynolds, K.A.; Watt, P.M.; Boone, S.A.; Gerba, C.P. Occurrence of bacteria and biochemical markers on public surfaces. Int. J. Environ. Health Res. 2005, 15, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; O’dononghue, M.; Boost, M.V. Characterization of staphylococci contaminating automated teller machines in Hong Kong. Epidemiol. Infect. 2012, 140, 1366–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dowd, S.E.; Callaway, T.R.; Wolcott, R.D.; Sun, Y.; McKeehan, T.; Hagevoort, R.G.; Edrington, T.S. Evaluation of the bacterial diversity in the feces of cattle using 16S rDNA bacterial tag-encoded FLX amplicon pyrosequencing (bTEFAP). BMC Microbiol. 2008, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dowd, S.E.; Sun, Y.; Wolcott, R.D.; Domingo, A.; Carroll, J.A. Bacterial tag-encoded FLX amplicon pyrosequencing (bTEFAP) for microbiome studies: bacterial diversity in the ileum of newly weaned Salmonella-infected pigs. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2008, 5, 459–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Callaway, T.R.; Dowd, S.E.; Edrington, T.S.; Anderson, R.C.; Krueger, N.; Bauer, N.; Kononoff, P.J.; Nisbet, D.J. Evaluation of bacterial diversity in the rumen and feces of cattle fed different levels of dried distillers grains plus solubles using bacterial tag-encoded FLX amplicon pyrosequencing. J. Anim. Sci. 2010, 88, 3977–3983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edgar, R.C. Search and clustering orders of magnitude faster than BLAST. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 2460–2461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eren, A.M.; Zozaya, M.; Taylor, C.M.; Dowd, S.E.; Martin, D.H.; Ferris, M.J. Exploring the diversity of Gardnerella vaginalis in the genitourinary tract microbiota of monogamous couples through subtle nucleotide variation. PLoS One 2011, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swanson, K.S.; Dowd, S.E.; Suchodolski, J.S.; Middelbos, I.S.; Vester, B.M.; Barry, K.A.; Nelson, K.E.; Torralba, M.; Henrissat, B.; Coutinho, P.M.; et al. Phylogenetic and gene-centric metagenomics of the canine intestinal microbiome reveals similarities with humans and mice. ISME J. 2011, 5, 639–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeSantis, T.Z.; Hugenholtz, P.; Larsen, N.; Rojas, M.; Brodie, E.L.; Keller, K.; Huber, T.; Dalevi, D.; Hu, P.; Andersen, G.L. Greengenes, a chimera-checked 16S rRNA gene database and workbench compatible with ARB. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 72, 5069–5072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Knights, D.; Kuczynski, J.; Charlson, E.S.; Zaneveld, J.; Mozer, M.C.; Collman, R.G.; Bushman, F.D.; Knight, R.; Kelley, S.T. Bayesian community-wide culture-independent microbial source tracking. Nat. Methods 2011, 8, 761–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costello, E.K.; Lauber, C.L.; Hamady, M.; Fierer, N.; Gordon, J.I.; Knight, R. Bacterial community variation in human body habitats across space and time. Science 2009, 326, 1694–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capone, K.A.; Dowd, S.E.; Stamatas, G.N.; Nikolovski, J. Diversity of the human skin microbiome early in life. J. Invest. Dermatol. 2011, 131, 2026–2032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, L.; Tin, S.; Kelley, S. Culture-independent analysis of bacterial diversity in a child-care facility. BMC Microbiol. 2007, 7, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McManus, C.J.; Kelley, S.T. Molecular survey of aeroplane bacterial contamination. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2005, 99, 502–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rintala, H.; Pitkaranta, M.; Toivola, M.; Paulin, L.; Nevalainen, A. Diversity and seasonal dynamics of bacterial community in indoor environment. BMC Microbiol. 2008, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coton, E.; Desmonts, M.H.; Leroy, S.; Coton, M.; Jamet, E.; Christieans, S.; Donnio, P.Y.; Lebert, I.; Talon, R. Biodiversity of coagulase-negative staphylococci in French cheeses, dry fermented sausages, processing environments and clinical samples. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2010, 137, 221–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gillespie, B.E.; Headrick, S.I.; Boonyayatra, S.; Oliver, S.P. Prevalence and persistence of coagulase-negative Staphylococcus species in three dairy research herds. Vet. Microbiol. 2009, 134, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hedman, P.; Ringertz, O.; Eriksson, B.; Kvarnfors, P.; Andersson, M.; Bengtsson, L.; Olsson, K. Staphylococcus saprophyticus found to be a common contaminant of food. J. Infect. 1990, 21, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leroy, S.; Giammarinaro, P.; Chacornac, J.P.; Lebert, I.; Talon, R. Biodiversity of indigenous staphylococci of naturally fermented dry sausages and manufacturing environments of small-scale processing units. Food Microbiol. 2010, 27, 294–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raz, R.; Colodner, R.; Kunin, C.M. Who are you—Staphylococcus saprophyticus? Clin. Infect. Dis. 2005, 40, 896–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soge, O.O.; Meschke, J.S.; No, D.B.; Roberts, M.C. Characterization of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus and methicillin-resistant coagulase-negative Staphylococcus spp. isolated from US West Coast public marine beaches. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2009, 64, 1148–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hedman, P.; Ringertz, O. Urinary tract infections caused by Staphylococcus saprophyticus. A matched case control study. J. Infect. 1991, 23, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huebner, J.; Goldmann, D.A. Coagulase-negative staphylococci: Role as pathogens. Annu. Rev. Med. 1999, 50, 223–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heikens, E.; Fleer, A.; Paauw, A.; Florijn, A.; Fluit, A.C. Comparison of genotypic and phenotypic methods for species-level identification of clinical isolates of coagulase-negative staphylococci. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2005, 43, 2286–2290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vuong, C.; Otto, M. Staphylococcus epidermidis infections. Microbes Infect. 2002, 4, 481–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raad, I.; Alrahwan, A.; Rolston, K. Staphylococcus epidermidis: Emerging resistance and need for alternative agents. Clin. Infect. Dis. 1998, 26, 1182–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- von Eiff, C.; Peters, G.; Heilmann, C. Pathogenesis of infections due to coagulasenegative staphylococci. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2002, 2, 677–685. [Google Scholar]
- Rupp, M.E.; Archer, G.L. Coagulase-negative staphylococci: Pathogens associated with medical progress. Clin. Infect. Dis. 1994, 19, 231–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eady, E.A.; Cove, J.H. Staphylococcal resistance revisited: Community-acquired methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus—An emerging problem for the management of skin and soft tissue infections. Curr. Opin. Infect. Dis. 2003, 16, 103–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, L.G.; Diep, B.A. Colonization, fomites, and virulence: Rethinking the pathogenesis of community-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infection. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2008, 46, 752–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scott, E.; Duty, S.; McCue, K. A critical evaluation of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus and other bacteria of medical interest on commonly touched household surfaces in relation to household demographics. Am. J. Infect. Control. 2009, 37, 447–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zetola, N.; Francis, J.S.; Nuermberger, E.L.; Bishai, W.R. Community-acquired meticillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus: An emerging threat. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2005, 5, 275–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hersh, A.L.; Chambers, H.F.; Maselli, J.H.; Gonzales, R. NAtional trends in ambulatory visits and antibiotic prescribing for skin and soft-tissue infections. Arch. Int. Med. 2008, 168, 1585–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Initial National Priorities for Comparative Effectiveness Research. Available online: http://www.iom.edu/Reports/2009/ComparativeEffectivenessResearchPriorities.aspx (accessed on 23 August 2014).
- Scallan, E.; Hoekstra, R.M.; Angulo, F.J.; Tauxe, R.V.; Widdowson, M.A.; Roy, S.L.; Jones, J.L.; Griffin, P.M. Foodborne illness acquired in the United States—Major pathogens. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2011, 17, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, W.H.; Kao, C.Y.; Yang, D.C.; Tseng, C.C.; Wu, A.B.; Teng, C.H.; Wang, M.C.; Wu, J.J. Clinical and microbiological characteristics of Klebsiella pneumoniae from community-acquired recurrent urinary tract infections. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2014, 33, 1533–1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.H.; Liu, Y.C.; Lee, S.S.; Yen, M.Y.; Chen, Y.S.; Wang, J.H.; Wann, S.R.; Lin, H.H. Primary liver abscess due to Klebsiella pneumoniae in Taiwan. Clin. Infect. Dis. 1998, 26, 1434–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorny, R.L.; Dutkiewicz, J. Bacterial and fungal aerosols in indoor environment in Central and eastern European countries. Ann. Agric. Environ. Med. 2002, 9, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gorny, R.L.; Dutkiewicz, J.; Krysińska-Traczyk, E. Size distribution of bacterial and fungal bioaerosols in indoor air. Ann. Agric. Environ. Med. 1999, 6, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bonetta, S.; Bonetta, S.; Mosso, S.; Sampo, S.; Carraro, E. Assessment of microbiological indoor air quality in an Italian office building equipped with an HVAC system. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2010, 161, 473–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andersson, A.M.; Weiss, N.; Rainey, F.; Salkinoja-Salonen, M.S. Dust-borne bacteria in animal sheds, schools and children’s day care centres. J. Appl. Microbiol. 1999, 86, 622–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aliabadi, A.A.; Rogak, S.N.; Bartlett, K.H.; Green, S.I. Preventing airborne disease transmission: Review of methods for ventilation design in health care facilities. Adv. Prev. Med. 2011, 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marthi, B.; Fieland, V.P.; Walter, M.; Seidler, R.J. Survival of bacteria during aerosolization. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1990, 56, 3463–3467. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Walter, M.V.; Marthi, B.; Fieland, V.P.; Ganio, L.M. Effect of aerosolization on subsequent bacterial survival. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1990, 56, 3468–3472. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Won, W.D.; Ross, H. Effect of diluent and relative humidity on apparent viability of airborne Pasteurella pestis. Appl. Microbiol. 1966, 14, 742–745. [Google Scholar]
- Bolister, N.J.; Johnson, H.E.; Wathes, C.M. The ability of airborne Klebsiella pneumoniae to colonize mouse lungs. Epidemiol. Infect. 1992, 109, 121–131. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
Appendix
| Group | Description | Number of Samples (n) * |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Stair rail (Rails) | 2 |
| 2 | Nautilus machine | 4 |
| 3 | Stationary bike | 4 |
| 4 | Dumb bell | 4 |
| 5 | Treadmill | 4 |
| 6 | Power Stride | 4 |
| 7 | Elliptical | 4 |
| 8 | Leg press | 4 |
| 9 | Toilet handle | 2 |
| 10 | Composite sample, week 1 ** | |
| 11 | Composite sample, week 2 ** | |
| Total | 32 | |
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mukherjee, N.; Dowd, S.E.; Wise, A.; Kedia, S.; Vohra, V.; Banerjee, P. Diversity of Bacterial Communities of Fitness Center Surfaces in a U.S. Metropolitan Area. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2014, 11, 12544-12561. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph111212544
Mukherjee N, Dowd SE, Wise A, Kedia S, Vohra V, Banerjee P. Diversity of Bacterial Communities of Fitness Center Surfaces in a U.S. Metropolitan Area. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2014; 11(12):12544-12561. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph111212544
Chicago/Turabian StyleMukherjee, Nabanita, Scot E. Dowd, Andy Wise, Sapna Kedia, Varun Vohra, and Pratik Banerjee. 2014. "Diversity of Bacterial Communities of Fitness Center Surfaces in a U.S. Metropolitan Area" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 11, no. 12: 12544-12561. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph111212544
APA StyleMukherjee, N., Dowd, S. E., Wise, A., Kedia, S., Vohra, V., & Banerjee, P. (2014). Diversity of Bacterial Communities of Fitness Center Surfaces in a U.S. Metropolitan Area. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 11(12), 12544-12561. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph111212544