Abstract
Aim: To examine the association of serum lipids, lipid ratios with Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) in a Chinese population. Methods: Data were drawn from a cross-sectional survey in China. CKD was defined as estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) < 60 mL/min/1.73m2 or albuminuria-to-creatinine ratio (ACR) > 30 mg/g. Multivariable logistic regressions and multivariate regression models were used. Serum lipids and lipid ratios included total cholesterol (TC), triglyceride (TG), low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C), high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C), TG/HDL-C ratio, TC/HDL-C ratio and LDL-C/HDL-C ratio. Results: In men, only logarithm-transformed (log) TG was associated with CKD. The odds ratio (every SD increment) was 1.39 (95% CI 1.03–1.87, P = 0.03). In women, none of the serum lipids and lipid ratios was associated with CKD. Using multivariate regression models, it was shown that log TG and log TG/HDL-C were negatively correlated with eGFR (P < 0.05) in men and LDL-C and log LDL-C/HDL-C ratio were correlated with ACR in men. In female subjects, serum TC, log TG, log TG/HDL-C and log TC/HDL-C were negatively correlated with eGFR (P < 0.05). All of serum lipid profiles and lipid related ratio were not correlated with ACR in women. Conclusion: Serum TG is the only suitable predictor for CKD in men. However, in women, none of serum lipids and lipid ratio can be used as a predictor for CKD. Log TG and log TG/HDL-C are negatively correlated with eGFR in both genders.
1. Introduction
It is well recognized that serum lipids are linked to atherosclerotic diseases [1]. Chronic kidney disease (CKD) shares some common risk factors, such as hypertension and diabetes, with cardiovascular diseases. Serum lipids might be independent risk factors for CKD. The results of previous studies are inconsistent [2,3,4,5,6]. A study by Kurella et al. [2] indicated that each component of metabolic syndrome including hypertriglyceridemia and low high density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C) is an independent risk factor of developing CKD. Previous studies based on Korean populations indicated that triglyceride (TG)/HDL-C ratio is independently associated with CKD [3,4]. However, in two previous studies based on Chinese populations, neither hypertriglyceridemia nor low HDL-C is associated with CKD [5,6].
As we know, there are limited data on the association of serum lipids with CKD in Chinese populations. Therefore, the association of serum lipids and CKD needs to be further explored in Chinese populations. The aim of the current study is to examine the association of serum lipid profiles, lipid ratios with CKD in a Chinese population.
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Study Population
This population-based, cross-sectional survey was conducted in Wanzai Town, Zhuhai City located in Southern China. The cross-sectional survey has been described in our previous paper [7]. In the current study, we briefly described the methods of the study again. We randomly selected three communities in Wanzai Town to perform the survey. This survey was conducted from June 2012 to October 2012. We invited all residents aged 18 years or older to participate in this survey. In total, 2142 study subjects (the mean age was 50 ± 13 years) participated in the survey and 308 subjects were excluded due to missing data. In the current study, 1834 subjects were included [7].
2.2. Ethics Statement
This study was approved by the ethics committee of the Third Affiliated Hospital of Southern Medical University. Written informed consents were given by all subjects.
2.3. Serum Lipid Profiles and Lipid-Related Ratios
Serum total cholesterol (TC), serum TG, and serum HDL-C were determined using colorimetric methods with the Roche assay (Roche cobas6000). Serum low density cholesterol (LDL-C) was indirectly calculated.
Lipid ratios are also used to predict cardiovascular risks and the ratios might be the stronger predictors of heart disease [8,9]. In the current study, we also used lipid ratios to predict the risk of CKD. TG/HDL-C was calculated as TG divided by HDL-C. The other two lipid ratios were TC/HDL-C ratio and LDL-C/HDL-C ratio.
According to the Chinese guideline, the optimal serum lipid profile is serum total TC level < 5.18 mmol/L, TG level < 1.7 mmol/L, LDL-C level < 3.37 mmol/L, and HDL-C level ≥ 1.04 mmol/L [10]. Dyslipidemia is defined by the presence of at least one of the following: serum total TC level ≥ 5.18 mmol/L, TG level ≥ 1.7 mmol/L, LDL-C level ≥ 3.37 mmol/L, and HDL-C- cholesterol level < 1.04 mmol/L, and/or having received treatment for dyslipidemia during the previous 2 weeks [10].
2.4. Determination of CKD
Both albuminuria and decreased glomerular filtration rate were used as markers of kidney damage. First morning void urine samples were collected. Women who were actively menstruating and subjects having urinary tract infection symptoms were excluded from the urine test. Urinary albumin was measured by an immune nephelometric method with the Orion assay. Serum creatinine and urinary creatinine were determined using colorimetric methods with the Roche assay [7].
Estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) was calculated as 175× (Scr)−1.234 × (Age)−0.179 × (if female, × 0.79). This is a modified MDRD equation which has been used as an alternative method to assess eGFR in the Chinese population [11]. Urinary albumin to creatinine ratio (ACR, mg/g) was calculated as urinary albumin divided by urinary creatinine. A decreased eGFR was defined as eGFR less than 60 mL/min/1.73m2. CKD was defined as a decreased eGFR and/or ACR ≥ 30 mg/g [12].
2.5. Data Collection
All members of trained medical staff, including physicians, general practitioners, medical students and nurses, performed physical examinations and data collection according to standardized procedures. Data on demographic status, personal and family history, education attainment, and lifestyle were obtained through questionnaires [7].
A full physical examination included anthropometric measurements and blood pressure measurement. According to the World Health Organization recommended procedures, height, weight, waist circumference and hip circumference were measured [13]. Waist circumference was accurate to 0.1 cm and weight was accurate to 0.1 kg. Systolic blood pressure (SBP) and diastolic blood pressure (DBP) were determined three times on the right arm in a seated position using a calibrated mercury sphygmomanometer. The average of the three consecutively reading was recorded [7].
Blood specimens were collected after an overnight fast for at least 10 hours and stored at 2 °C–8 °C until analysis. All samples were analyzed in the central laboratory of Third Affiliated Hospital of Southern Medical University [7].
Serum lipids, serum creatinine, serum fasting glucose, serum insulin and sensitivity C-reactive protein (CRP) was determined.
2.6. Data Analysis
All statistical analyses were conducted using Stata (version 11). Statistical significance was set at P value < 0.05. We used mean ± standard deviation to describe continuous variables with a normal distribution and medians and interquartile ranges for skewed distributed variables. Frequencies and percentages were used to indicate categorical variables.
Clinical characteristics of the study population were listed. We also compared the characteristics of male and female subjects. Student’s T test or rank-sum test were used for continuous variables and the chi-squared test for categorical variables.
In order to examine the associations of serum lipids, lipid ratios with CKD, logistic regression models were used for estimating the odds ratios (OR) and 95% confidence interval (CI). In the current study, the associations of serum lipids, and lipid ratios with CKD were explored in male and female subjects, respectively. The models were adjusted for socio-demographic status (age and educational attainment), comorbidities (history of hypertension, history of diabetes, and history of coronary heart disease and history of stroke), lifestyle factors (current smoking, current alcohol use, physical inactivity), systolic blood pressure (SBP), diastolic blood pressure (DBP), serum fasting glucose and waist circumference. Only eight subjects (five men and three women) were taking statins, so taking statin was not added as a covariate.
We also used multivariate regression models to examine the correlations of serum lipids and lipid ratios with eGFR or ACR in each gender, respectively. In the regression models, eGFR or logarithmically transformed ACR was used as a dependent variable, respectively. Multivariate regression models were also adjusted for variables which were used in the logistic regression models. These variables included age, educational attainment, history of hypertension, history of diabetes, history of coronary heart disease, history of stroke, current smoking, current alcohol use, physical inactivity, SBP, DBP, serum fasting glucose and waist circumference.
All logistic regression analyses and multivariate regression models were conducted separately in male and female subjects. All variables with a skewed distribution were logarithmically transformed before being analyzed. These variables included serum TG, TG/HDL-C ratio, TC/HDL-C ratio, LDL-C/HDL-C ratio and ACR.
3. Results
3.1. Clinical Characteristics of Study Population (Table 1)
A total of 1834 subjects (the mean age was 53 ± 15 years) were included in the analysis. Among 1834 subjects, only 37.02% (679) subjects were men and 12.81% (235) subjects had CKD.
Men had a significantly larger waist circumference, a higher SBP and a higher DBP than women. Women had a higher level of eGFR than men, but there was no significant difference on prevalence of CKD between men and women. In the past three months, no subjects used contrast agents or antibiotics. The proportions of current smokers and current alcohol use were significantly higher in men.
Men had a higher TG/HDL-C ratio, a higher TC/HDL-C ratio and a higher LDL-C/HDL-C ratio than women, and all of these differences were significant (P < 0.05). Men also had higher serum TGs and lower HDL-Cs than women.

Table 1.
Clinical characteristics of male and female subjects.
| Total | Male | Female | P value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| n = 1834 | n = 679 | n = 1155 | ||
| Clinical Characteristics | ||||
| Age (Years) | 53 ± 15 | 53 ± 15 | 53 ± 14 | 0.29 |
| Waist circumference(cm) | 83 ± 10 | 86 ± 10 | 81 ± 10 | <0.001 |
| History of Hypertension (%) | 372 (20.28) | 166 (24.45) | 206 (17.84) | 0.001 |
| History of Diabetes (%) | 115 (6.27) | 48 (7.07) | 67 (5.80) | 0.29 |
| History of Coronary heart disease (%) | 42 (2.29) | 23 (3.39) | 19 (1.65) | 0.27 |
| Current smoker (%) | 223 (12.16) | 214 (31.52) | 9 (0.78) | <0.001 |
| Current alcohol use (%) | 106 (5.78) | 94 (13.84) | 12 (1.04) | <0.001 |
| Education attainment High school or above (%) | 761 (41.49) | 344 (50.66) | 417 (36.10) | 0.92 |
| Physical inactivity (%) | 1013 (55.23) | 374 (55.08) | 639 (55.32) | <0.001 |
| Systolic blood pressure (mmHg) | 129 ± 20 | 130 ± 19 | 127 ± 21 | 0.003 |
| Diastolic blood pressure (mmHg) | 78 ± 11 | 80 ± 11 | 77 ± 11 | <0.001 |
| Serum lipids | ||||
| Cholesterol (mmol/L) | 5.39 ± 1.03 | 5.34 ± 0.99 | 5.42 ± 1.05 | 0.09 |
| LDL (mmol/L) | 3.18 ± 0.91 | 3.14 ± 0.92 | 3.20 ± 0.90 | 0.19 |
| HDL (mmol/L) | 1.54 ± 0.33 | 1.44 ± 0.31 | 1.60 ± 0.32 | <0.001 |
| Triglyceride (mmol/L) | 0.65 (0.32–1.98) | 1.37 (0.97–2.17) | 1.15 (0.83–1.61) | <0.001 |
| LDL/HDL ratio | 2.09 (1.67–2.59) | 2.22 (1.81–2.76) | 2.00 (1.60–2.48) | <0.001 |
| TG/HDL ratio | 0.83 (0.53–1.35) | 1.03 (0.63–1.68) | 0.73 (0.48–1.17) | <0.001 |
| TC/HDL ratio | 3.58 (3.01–4.15) | 3.83 (3.23–4.38) | 3.45 (2.92–3.99) | <0.001 |
| Other labratory | ||||
| Serum creatitine (umol/L) | 73 ± 17 | 87 ± 15 | 65 ± 11 | <0.001 |
| eGFR( mL/min/1.73m2) | 99 ± 22 | 92 ± 20 | 104 ± 22 | <0.001 |
| ACR (mg/g) | 8.49 (5.75–14.23) | 9.54 (6.63–15.56) | 6.81 (4.59–11.46) | <0.001 |
| Fasting glucose (mmo/L) | 5.01 ± 1.19 | 5.07 ± 1.26 | 4.98 ± 1.14 | 0.10 |
| Serum C-reactive protein (mg/L) | 0.99 (0.46–2.37) | 1.01 (0.49–2.63) | 0.98 (0.44–2.25) | 0.17 |
| CKD | 235 (12.81) | 83 (12.22) | 152 (13.16) | 0.56 |
| Dyslipidemia | 1474 (80.37) | 556 (81.89) | 918 (79.48) | 0.21 |
TC: total cholesterol; TG: triglyceride; LDL-C: low-density lipoprotein cholesterol; HDL-C: high-density lipoprotein cholesterol; eGFR: Estimated glomerular filtration rate; ACR: Urinary albumin to creatinine ratio; CKD: chronic kidney disease.
3.2. Association of Serum Lipids, Lipid Ratios with CKD in Male and Female Subjects (Table 2)
In unadjusted models, TC, logarithm-transformed (log) TG, and log TG/HDL-C ratio were significantly associated with CKD in male subjects. After adjusted for age, educational attainment, comorbidities, lifestyle factors, blood pressure, fasting glucose and waist circumference, only log TG was associated with CKD. The odds ratio (every SD increment) was 1.39 (95% CI 1.03–1.87, P = 0.03).
Table 2 showed that in the unadjusted model, TC, log TG, log LDL-C/HDL-C ratio, log TG/HDL-C ratio and log LDL-C/HDL-C ratio were associated with the risk of incident CKD in female subjects. However, further adjusted for potential confounders, none of the serum lipids and lipid ratios was associated with CKD.

Table 2.
Association of serum lipids and lipid ratios with Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) in male and female subjects.
| Men | Women | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unadjusted | Adjusted * | Unadjusted | Adjusted * | |||||
| OR (95% CI) | P value | OR (95% CI) | P value | OR (95% CI) | P value | OR (95% CI) | P value | |
| TC (one SD) | 1.29 (1.03–1.61) | 0.03 | 1.21 (0.91–1.62) | 0.19 | 1.27 (1.08–1.50) | 0.004 | 0.97 (0.79–1.20) | 0.79 |
| HDL (one SD) | 1.17 (0.94–1.44) | 0.16 | 1.20 (0.91–1.59) | 0.19 | 0.99 (0.84–1.18) | 0.94 | 1.12 (0.93–1.36) | 0.22 |
| LDL (one SD) | 0.97 (0.77–1.23) | 0.80 | 0.89 (0.67–1.18) | 0.40 | 1.18 (1.00–1.40) | 0.054 | 0.92 (0.75–1.13) | 0.44 |
| Log-triglyceride (one SD) | 1.53 (1.23–1.91) | <0.001 | 1.39 (1.03–1.87) | 0.03 | 1.44 (1.22–1.69) | <0.001 | 1.03 (0.83–1.28) | 0.82 |
| Log-TG/HDL (one SD) | 1.44 (1.14–1.82) | 0.002 | 1.30 (0.95–1.77) | 0.10 | 1.39 (1.17–1.64) | <0.001 | 0.98 (0.78–1.22) | 0.83 |
| Log-TC/HDL (one SD) | 1.13 (0.90–1.43) | 0.31 | 1.03 (0.76–1.40) | 0.84 | 1.29 (1.08–1.54) | 0.005 | 0.84 (0.67–1.06) | 0.14 |
| Log-LDL/HDL (one SD) | 0.93 (0.74–1.17) | 0.52 | 0.83 (0.64–1.09) | 0.18 | 1.22 (1.02–1.46) | 0.03 | 0.86 (0.69–1.07) | 0.18 |
Adjusted for age, educational attainment, history of hypertension, history of diabetes, history of coronary heart disease, history of stroke, current smoking, current alcohol use, physical inactivity, systolic blood pressure, diastolic blood pressure, fasting glucose and waist circumference. TC: total cholesterol; TG: triglyceride; HDL-C: high density lipoprotein cholesterol; LDL-C: low density lipoprotein cholesterol. Log: logarithm-transformed; SD: standard deviation.
3.3. Correlation of eGFR or ACR with Serum Lipids and Lipid Ratios
Correlations of eGFR/ACR with serum lipids and lipid ratios in each gender were shown in Table 3. In the adjusted models, log TG and log TG/HDL-C were negatively correlated with eGFR in male subjects (P < 0.05). The coefficient and 95% CI for log TG were −4.89 (95% CI: −7.61, −2.17, P < 0.001). And the coefficient and 95% CI for log TG/HDL-C were −4.04 (95% CI: −6.53, −1.65, P < 0.001). LDL-C and log LDL-C/HDL-C ratio were correlated with ACR. The co-efficient and 95% CI were −0.08 (95% CI: −0.15–−0.01, p = 0.02) for LDL and −0.25 (95% CI: −0.43–−0.07, p = 0.007) for log LDL-C/HDL-C, respectively.
In female subjects, serum TC, log TG, log TG/HDL-C ratio and log TC/HDL-C ratio were negatively correlated with eGFR (P < 0.05). The respective coefficient and 95% CI were −1.45 (95% CI: −2.76–−0.15, p = 0.03) for log TC, −1.78 (95% CI: −3.14–−0.43, p = 0.01) for log TG, −1.57 (95% CI: −2.92–−0.22, p = 0.03) for log TG/HDL-C ratio, and −1.53 (95% CI: −2.87–−0.18, p = 0.03) for log TC/HDL-C, respectively. All of serum lipid profiles and lipid related ratio were not correlated with ACR.
The associations of log TG with eGFR was shown in Figure 1 and Figure 2. The coefficient between log TG and eGFR in the unadjusted model were −2.76 (95% CI: −5.38, −0.14, P = 0.04) in men and −9.47 (95% CI: −11.84, −7.10, P < 0.001) in women, respectively.

Table 3.
Correlation of estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) and urinary albumin to creatinine ratio (ACR) with lipid profiles in male and female subjects.
| Men | Women | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| eGFR | ACR | eGFR | ACR | |||||
| Coefficient * (95% CI) | P value | Coefficient * (95% CI) | P value | Coefficient * (95% CI) | P value | Coefficient * (95% CI) | P value | |
| Total Cholesterol | −0.82 (−2.30–0.67) | 0.28 | −0.03 (−0.10–0.03) | 0.31 | −1.45 (−2.76–−0.15) | 0.03 | −0.02 (−0.07–0.03) | 0.43 |
| HDL | −0.01 (−4.84– 4.84) | 1.00 | 0.06 (−0.15–0.28) | 0.55 | 0.17 (−1.05–1.39) | 0.79 | 0.03 (−0.02–0.08) | 0.18 |
| LDL | 0.30 (−1.28–1.88) | 0.71 | −0.08 (−0.15–−0.01 | 0.02 | −0.74 (−2.03–0.55) | 0.26 | −0.03 (−0.08–0.02) | 0.25 |
| Log-triglyceride | −4.89 (−7.61–−2.17) | <0.001 | 0.003 (−0.12–0.12) | 0.96 | −1.78 (−3.14–−0.43) | 0.01 | 0.005 (−0.05–0.06) | 0.86 |
| Log-TG/HDL | −4.04 (−6.53–−1.65) | 0.001 | −0.005 (−0.11–0.10) | 0.94 | −1.57 (−2.92–−0.22) | 0.03 | −0.006 (−0.06–0.05) | 0.83 |
| Log-TC/HDL | −5.65 (−12.64–1.35) | 0.11 | −0.21 (−0.51–0.10) | 0.19 | −1.53 (−2.87–−0.18) | 0.03 | −0.05 (−0.10–0.005) | 0.08 |
| Log-LDL/HDL | 0.42 (−3.70–4.55) | 0.84 | −0.25 (−0.43–−0.07) | 0.007 | −0.64 (−1.93–0.65) | 0.33 | −0.03 (−0.08–0.02) | 0.22 |
Adjusted for age, educational attainment, history of hypertension, history of diabetes, history of coronary heart disease, history of stroke, current smoking, current alcohol use, physical inactivity, systolic blood pressure, diastolic blood pressure, fasting glucose and waist circumference. TC: total cholesterol; TG: triglyceride; HDL-C: high density lipoprotein cholesterol; LDL-C: low density lipoprotein cholesterol. Log: logarithm-transformed; eGFR: Estimated glomerular filtration rate; ACR: urinary albumin to creatinine ratio
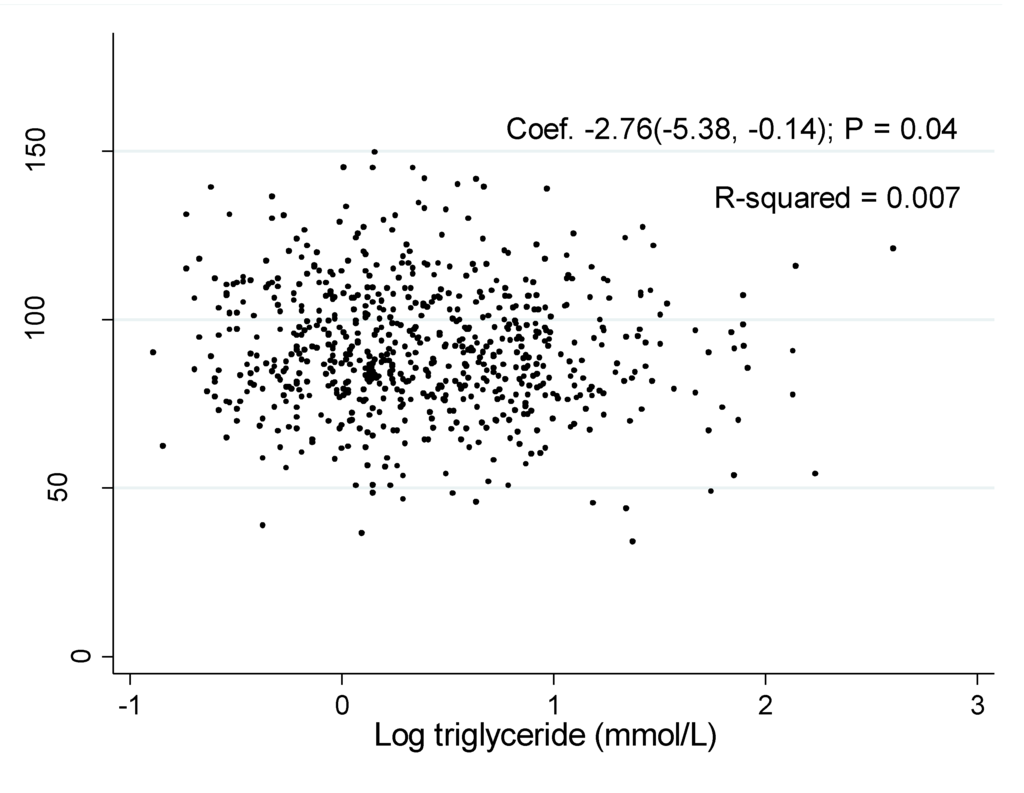
Figure 1.
Association of estimated glomerular filtration rate with log triglyceride in men.
Figure 1.
Association of estimated glomerular filtration rate with log triglyceride in men.
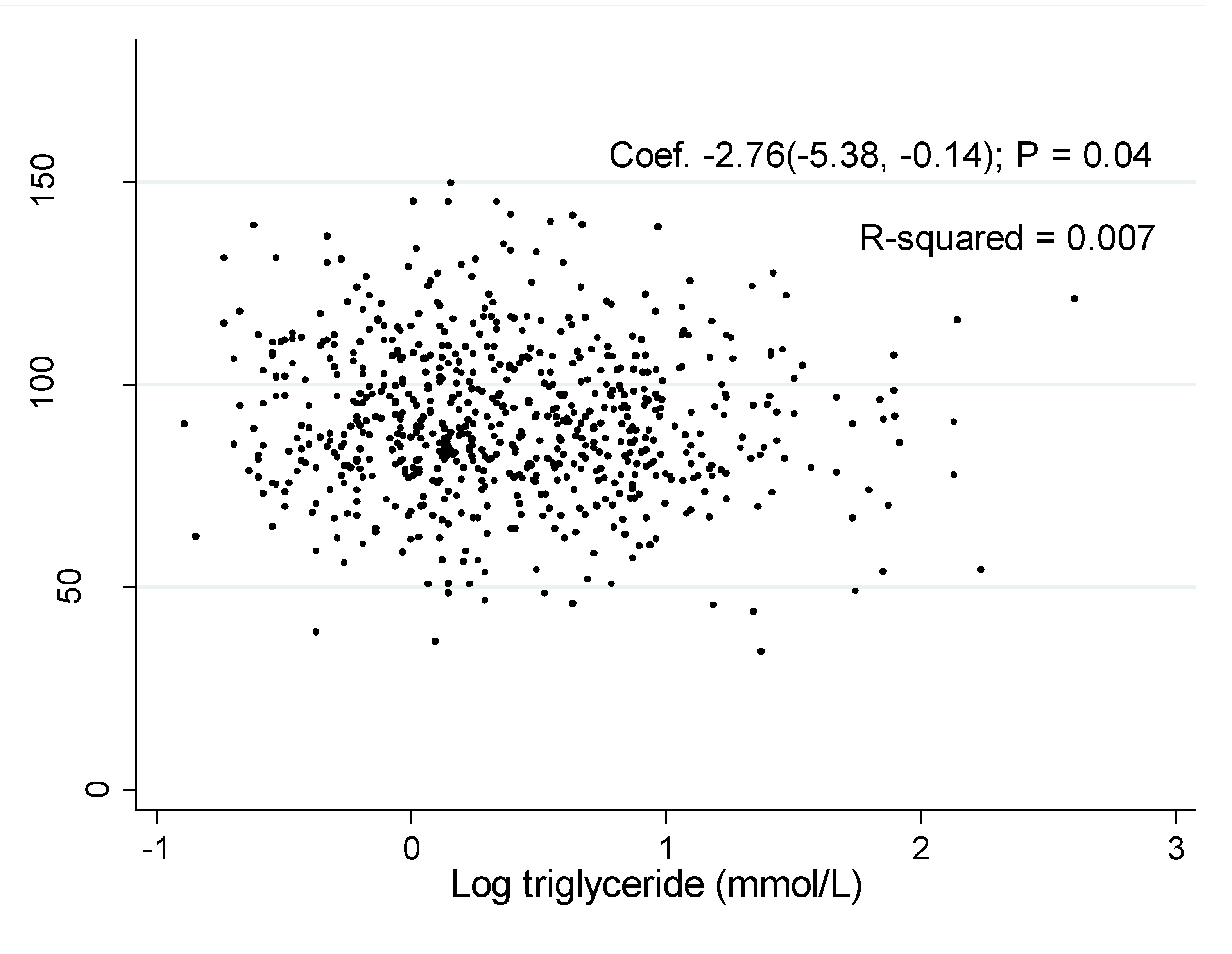
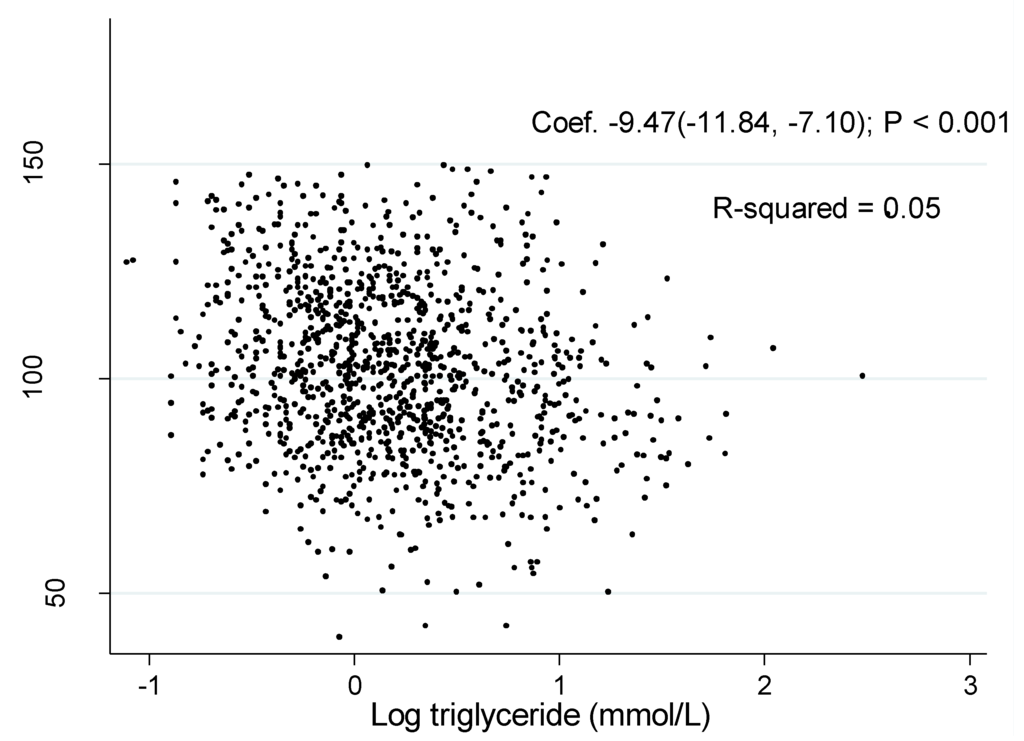
Figure 2.
Association of estimated glomerular filtration rate with log triglyceride in women.
Figure 2.
Association of estimated glomerular filtration rate with log triglyceride in women.
4. Discussion
The major finding of the current study was that the TG was associated with an increased risk of CKD in men. However, in women, none of the serum lipids and lipid ratios was associated with CKD. In both men and women, TG and TG/HDL-C ratio were negatively correlated with eGFR. In women, none of the serum lipids and lipid ratios was correlated with albuminuria.
Several previous studies showed that both a high level of cholesterol and triglyceride might play an important role in the pathogenesis and progression of kidney disease [14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22]. In rat models, it was found that hypercholesterolemia can induce a pro-inflammatory response and result macrophages recruitment [17]. Both hyperlipidemia and macrophage influx appear to precede in the genesis of glomerulosclerosis [17,18,19,20,21,22]. In rats with type 2 diabetes, lipoxidation stress was also related to glomerulosclerosis and tubulointerstitial disease [18]. It seemed that food restriction can prevent hypertriglyceridemia induced glomerular injury and macrophage influx in obese Zucker rat [20]. Both hypercholesterolemia and hypertriglyceridemia are associated with podocyte injury which might be accompanied by tubulointerstitial injury [21,22]. All of these studies indicated that dyslipidemia can contribute to kidney damage.
Dyslipidemia is an independent risk factor for progression of kidney disease in patients with diabetes [23]. In Samuelsson et al.’s study [24], 73 non-diabetic patients with CKD were followed for an average of 3.2 years. In the study, it is indicated that TC, LDL-C, and triglyceride-rich apoB-containing lipoproteins contributed to a more rapid decline in renal function. The results of the studies based on health persons were disparity [2,5,6]. After 9 years’ follow-up in the Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities study [2], it was shown that hypertriglycemia and low HDL-C were associated with the incident of CKD. However, the models were only adjusted for age, gender and race. Other potential confounders, such as blood pressure and serum glucose, were not added into the models [2]. One study based on 1456 elderly Chinese individuals indicated that low HDL-C and hypertriglyceridemia did not predict the risk of new onset of CKD [6]. In another cross-sectional study based on 4944 Chinese individuals, the association of low HDL-C and an elevated triglyceride level with CKD was abolished when adjusting for potential confounders [5]. In the current study, TG was associated with the incident CKD in men, but all of the serum lipids and lipid ratios were unlikely associated with CKD in women.
It has been recognized that small, density LDL-C phenotype is a risk factor of coronary heart disease [25]. The small, dense LDL-C phenotype is more commonly accompanied by the presence of hypertriglyceridemia, low HDL-C cholesterol levels, centrally obesity, and insulin resistance. The series of metabolic disorders might predict endothelial dysfunction that might lead to an increased susceptibility to thrombosis [26,27,28,29,30,31]. Reduction in fasting triglyceride levels will enlarge LDL-C particle size and reduce the risk of coronary heart disease [30]. However, a serum level of small density LDL-C particle is not a routine test in clinical practice. An alternation is using TG/LDL-C ratio which might be a surrogate for small, density LDL-C [32]. In one previous study, when using TG/HDL-C ratio to predict the existence of a small LDL-C particle size pattern, the sensitivity was 75.9% and the specificity 85.4% [33]. TG/HDL-C ratio can be used as a surrogate of insulin resistance and can be used to predict coronary heart disease independently [29,30,31,34]. Kim et al. used lipid ratios to predict CKD in Korean populations. The results indicated that TG/HDL-C ratio is the only lipid ratio associated with CKD in both men and women [3,4]. However, in the current study, we did not find significant association of lipid ratios with CKD in a Chinese population.
Although, hyperlipidemia and hypercholesterolemia are independent risk factors for progression of kidney disease, no conclusive evidences demonstrate that isolated hyperlipidemia can lead to CKD in healthy individuals [22]. Hyperlipidemia might be accompanied by coronary heart disease, diabetes and hypertension. Recently, studies have demonstrated that statin therapy can halt the progression of kidney failure in patients with CKD, diabetes or coronary heart disease [35,36,37,38]. An elevated level of TG and a low level of HDL-C are also components of metabolic syndrome [39]. According to the results of one study based on a Chinese population, an increased number of metabolic syndrome components is associated with CKD [5]. These results support lipid-lowering therapy in patients with CKD, diabetes and coronary heart disease. In the current study, it was also shown that both TG and TG/HDL-C ratio were negatively correlated with eGFR in men and women. LDL-C and LDL-C/HDL-C were associated with albuminuria in men.
Here, several limitations of the current study should be acknowledged. Firstly, this is only a cross-sectional study. Previous studies have shown that heavy proteinuria or end stage renal disease might be related with increased athrogenicity of LDL-C [40,41]. However, in the current study, only four subjects had macroalbuminuria (ACR > 300 mg/g) and no subjects had CKD 5 stage (eGFR < 15 mL/min). It was unlikely that dyslipidemia in this population was caused by CKD. Second, both albuminuria and eGFR were not measured repeatedly. Third, because we only included individuals who responded to an invitation, this might lead to a selection bias. Those individuals having more comorbidity might have a higher rate of participation willingness. In the current study, only 37.0% of subjects were men.
5. Conclusions
Among serum lipids profiles and lipid ratios, only serum TG is a suitable predictor for CKD in men and the association is independent of other potential confounders. In women, none of the serum lipids and lipid ratios can be used as a predictor for CKD. Log TG and log TG/HDL-C are negatively correlated with eGFR in both genders. In men, LDL-C and log LDL-C/HDL-C ratio are correlated with ACR. In female subjects, no serum lipid or lipid ratio is correlated with ACR.
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the following Science Foundation: (1) EU FP7 Program, UroSense, 2011; (2) ISN Research Committee grant, 2007; (3) ISN Research Committee grant, 2004; (4) Guangdong Provincial Science and Technique Program (No. 2011B031800386), 2011.
Authors Contributions
Liying Zhang and Hequn Zou designed and drafted the manuscript. Hequn Zou was the PI of this epidemiological study. Zhiyong Yuan, Wu Chen, Xinyu Liu, Yan Liang, and Xiaofei Shao performed this survey and collected the data. Shanying Chen analyzed the data.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Miller, M.; Stone, N.J.; Ballantyne, C.; Bittner, V.; Criqui, M.H.; Ginsberg, H.N.; Goldberg, A.C.; Howard, W.J.; Jacobson, M.S.; Kris-Etherton, P.M.; et al. Triglycerides and cardiovascular disease: A scientific statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2011, 123, 2292–2333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurella, M.; Lo, J.C.; Chertow, G.M. Metabolic syndrome and the risk for chronic kidney disease among nondiabetic adults. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2005, 16, 2134–2140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, H.T.; Shim, J.Y.; Lee, Y.J.; Lee, J.E.; Linton, J.A.; Kim, J.K.; Lee, H.R. Association between the ratio of triglycerides to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol and chronic kidney diseasein Korean adults: The 2005 Korean national hHealth and nutrition examination survey. Kidney Blood Press. Res. 2011, 34, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.Y.; Kang, H.T.; Lee, H.R.; Lee, Y.J.; Shim, J.Y. Comparison of lipid-related ratios for prediction of chronic kidney disease stage 3 or more in Korean adults. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2012, 27, 1524–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Liang, Y.; Qiu, B.; Wang, F.; Duan, X.; Yang, X.; Yang, J.; Huang, W.; Wang, N. Metabolic syndrome and chronic kidney disease in a rural Chinese population. Clin. Chim. Acta. 2011, 412, 1983–1988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.T.; Huang, J.W.; Chiang, C.K.; Yen, C.J.; Hung, K.Y.; Wu, K.D. Metabolic syndrome and insulin resistance as risk factors for development of chronic kidney disease and rapid decline in renal function in elderly. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2012, 97, 1268–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.Y.; Chen, Y.M.; Liu, X.Y.; Li, M.; Wu, B.D.; Li, Y.Q.; Liang, Y.; Shao, X.; Holthöfer, H.; Zou, H. Association of insulin resistance with chronic kidney disease in non-diabetic subjects with normal weight. Plos One 2013, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Sempos, R.; Donahue, J.; Dorn, J.; Trevisan, M.; Grundy, S.M. Non-high-density lipoprotein and very-low-density lipoprotein cholesterol and their risk predictive values in coronary heart disease. Am. J. Cardiol. 2006, 98, 1363–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eliasson, B.; Cederholm, J.; Eeg-Olofsson, K.; Svensson, A.M.; Zethelius, B.; Gudbjörnsdottir, S. Clinical usefulness of different lipid measures for prediction of coronary heart disease intype 2 diabetes: A report from the Swedish national diabetes register. Diabetes Care 2011, 34, 2095–2100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joint Committee for Developing Chinese guidelines on prevention and treatment of dyslipidemia in adults. Chinese guidelines on prevention and treatment of dyslipidemia in adults. (In Chinese)Chin. J. Cardiol. 2007, 35, 390–419. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Y.C.; Zuo, L.; Chen, J.H.; Luo, Q.; Yu, X.Q.; Li, Y.; Xu, J.; Huang, S.; Wang, L.; Huang, W. Modified glomerular filtration rate estimating equation for Chinese patients with chronic kidney disease. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2006, 17, 2937–2944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO). KDIGO 2012 clinical practice guideline for the evaluation and management of chronic kidney disease. KidneyInt. Suppl. 2013, 3, S1–S150. [Google Scholar]
- Molarius, A.; Seidell, J.C.; Sans, S.; Tuomilehto, J.; Kuulasmaa, K. Waist and hip circumferences, and waist-hip ratio in 19 populations of the WHO MONICA Project. Int. J. Obes. Relat. Metab. Disord. 1999, 23, 116–125. [Google Scholar]
- Wheeler, D.C.; Fernando, R.L.; Gillett, M.P.; Zaruba, J.; Persaud, J.; Kingstone, D.; Varghese, Z.; Moorhead, J.F. Characterisation of the binding of low-density lipoproteins to cultured rat mesangial cells. Nephrol. Dial. Transpl. 1991, 6, 701–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Shebeb, T.; Frohlich, J.; Magil, A.B. Glomerular disease in hypercholesterolemic guinea pigs: A pathogenetic study. Kidney Int. 1988, 33, 498–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neverov, N.I.; Kaysen, G.A.; Nuccitelli, R.; Weiss, R.H. HDL causes mesangial cell mitogenesis through a tyrosine kinase-dependent receptor mechanism. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 1997, 8, 1247–1256. [Google Scholar]
- Hattori, M.; Nikolic-Paterson, D.J.; Miyazaki, K.; Isbel, N.M.; Lan, H.Y.; Atkins, R.C.; Kawaguchi, H.; Ito, K. Mechanisms of glomerular macrophage infiltration in lipid-induced renal injury. Kidney Int. Suppl. 1999, 71, S47–S50. [Google Scholar]
- Dominguez, J.H.; Tang, N.; Xu, W.; Evan, A.P.; Siakotos, A.N.; Agarwal, R.; Walsh, J.; Deeg, M.; Pratt, H.J.; March, K.L.; et al. Studies of renal injury III: Lipid-induced nephropathy in type II diabetes. Kidney Int. 2000, 57, 92–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muntner, P.; Coresh, J.; Smith, J.C.; Eckfeldt, J.; Klag, M.J. Plasma lipids and risk of developing renal dysfunction: The atherosclerosis risk in communities study. Kidney Int. 2000, 58, 293–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maddox, D.A.; Alavi, F.K.; Santella, R.N.; Zawada, E.T., Jr. Prevention of obesity-linked renal disease: Age-dependent effects of dietary food restriction. Kidney Int. 2002, 62, 208–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrass, C.K. Cellular lipid metabolism and the role of lipids in progressive renal disease. Am. J. Nephrol. 2004, 24, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trevisan, R.; Dodesini, A.R.; Lepore, G. Lipids and renal disease. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2006, 17, S145–S147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravid, M.; Brosh, D.; Ravid-Safran, D.; Levy, Z.; Rachmani, R. Main risk factors for nephropathy in type 2 diabetes mellitus are plasma cholesterol levels, mean blood pressure, and hyperglycemia. Arch. Intern. Med. 1998, 158, 998–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samuelsson, O.; Attman, P.O.; Knight-Gibson, C.; Larsson, R.; Mulec, H.; Weiss, L.; Alaupovic, P. Complex apolipoprotein B-containing lipoprotein particles are associated with a higher rate of progression of human chronic renal insufficiency. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 1998, 9, 1482–1488. [Google Scholar]
- Austin, M.A.; Hokanson, J.E. Epidemiology of triglycerides, small dense low-density lipoprotein, and lipoprotein (a) as risk factors for coronary heart disease. Med. Clin. North Am. 1994, 78, 99–115. [Google Scholar]
- Austin, M.A.; Breslow, J.L.; Hennekens, C.H.; Buring, J.L.; Willett, W.C.; Krauss, R.M. Low density lipoprotein subclass pattern and risk of myocardial infarction. JAMA 1988, 260, 1917–1921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tornvall, P.; Karpe, F.; Carlson, L.A.; Hamsten, A. Relationships of low density lipoprotein subfractions to angiographically defined coronary heart disease in young survivors of myocardial infarction. Atherosclerosis 1991, 90, 67–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, H.; Genest, J.J., Jr; Blijlevens, E.; McNamara, J.R.; Jenner, J.L.; Ordovas, J.M.; Wilson, P.M.; Schaefer, E.J. Low density lipoprotein particle size and coronary artery disease. Arterioscler. Thromb. 1992, 12, 187–195. [Google Scholar]
- Coresh, J.; Kwiterovich, P.O., Jr; Smith, H.H.; Bachorik, P.S. Association of plasma triglyceride concentration and LDL particle diameter, density, and chemical composition with premature coronary artery disease in men and women. J. Lipid. Res. 1993, 34, 1687–1697. [Google Scholar]
- Lamarche, B.; Lemieux, I.; Després, J.P. The small, dense LDL phenotype and the risk of coronary heart disease: epidemiology, patho-physiology and therapeutic aspects. Diabetes Metab. 1999, 25, 199–211. [Google Scholar]
- Austin, M.A.; King, M.C.; Vranizan, K.M.; Krauss, R.M. Atherogenic lipoprotein phenotype. A proposed genetic marker for coronary heart disease risk. Circulation 1990, 82, 495–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhalodkar, N.C.; Blum, S.; Enas, E.A. Accuracy of the ratio of triglycerides to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol for predicting low-density lipoprotein cholesterol particle sizes, phenotype B, and particle concentrations among Asian Indians. Am. J. Cardiol. 2006, 97, 1007–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Liu, E.Y.; Hoffman, V.P.; Potts, A.J.; Sharma, B.; Henderson, D.C. Triglyceride/high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio: A surrogate to predict insulin resistance and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol particle size in nondiabetic patients with schizophrenia. J. Clin. Psychiatry 2011, 72, 806–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onat, A.; Can, G.; Kaya, H.; Hergenç, G. “Atherogenic index of plasma” (log10 triglyceride/high-density lipoprotein-cholesterol) predicts high blood pressure, diabetes, and vascular events. Clin. Lipidol. 2010, 4, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shepherd, J.; Kastelein, J.J.; Bittner, V.; Deedwania, P.; Breazna, A.; Dobson, S.; Zuckerman, A.; Wenger, N.K.; For the Treating to New Targets Investigators. Effect of intensive lipid lowering with atorvastatin on renal function in patients with coronary heart disease: the Treating to New Targets (TNT) study. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 1998, 32, S142–S156. [Google Scholar]
- Athyros, V.G.; Mikhailidis, D.P.; Papageorgiou, A.A.; Symeonidis, A.N.; Pehlivanidis, A.N.; Bouloukos, V.I.; Elisaf, M. The effect of statins versus untreated dyslipidaemia on renal function in patients with coronary heart disease. A subgroup analysis of the Greek atorvastatin and coronary heart disease evaluation (GREACE) study. J. Clin. Pathol. 2004, 57, 728–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianchi, S.; Bigazzi, R.; Caiazza, A.; Campese, V.M. A controlled, prospective study of the effects of atorvastatin on proteinuria and progression of kidney disease. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2007, 2, 1131–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koren, M.J.; Davidson, M.H.; Wilson, D.J.; Fayyad, R.S.; Zuckerman, A.; Reed, D.P.; ALLIANCE Investigators. Focused atorvastatin therapy in managed-care patients with coronary heart disease and CKD. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2009, 53, 741–750. [Google Scholar]
- National Cholesterol Education Program (NCEP) Expert Panel on Detection Ea, and Treatment of High Blood Cholesterol in Adults (Adult Treatment Panel III). Third report of the national cholesterol education program (NCEP) expert panel on detection, evaluation, and treatment of high blood cholesterol in adults (Adult Treatment Panel III) final report. Circulation 2002, 106, 3143–3421. [Google Scholar]
- Kasiske, B. Hyperlipidemia in patients with chronic renal disease. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 1998, 32, S142–S156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanner, C. Importance of hyperlipidaemia and therapy in renal patients. Nephrol. Dial. Transpl. 2000, 15, 92–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
