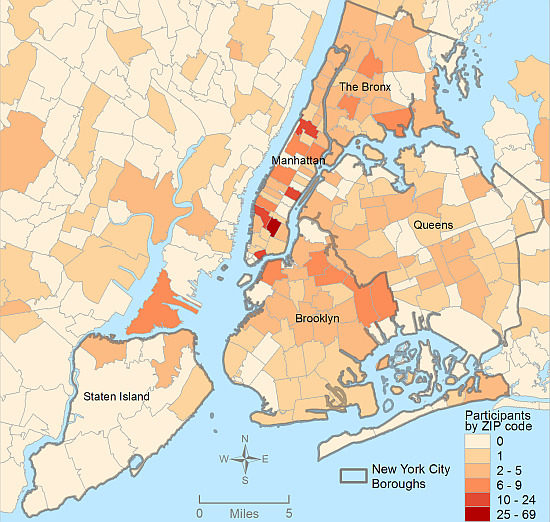
Examination of Spatial Polygamy among Young Gay, Bisexual, and Other Men Who Have Sex with Men in New York City: The P18 Cohort Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Study Design and Overview
2.1.1. Characterization of Neighborhood Environments
2.1.2. Individual-Level Characteristics
2.2. Statistical Analyses

3. Results
| Neighborhoods | % (N) |
|---|---|
| Residential boroughs | |
| Manhattan | 32 (194) |
| Brooklyn | 15 (91) |
| The Bronx | 10 (59) |
| Queens | 11 (66) |
| Staten Island | 1 (4) |
| New York (Non-metro NYC area) | 11 (67) |
| New Jersey | 9 (53) |
| Connecticut | 1 (7) |
| Other | 9 (52) |
| Socializing boroughs | |
| Manhattan | 47 (278) |
| Brooklyn | 14 (83) |
| The Bronx | 6 (37) |
| Queens | 8 (47) |
| Staten Island | 1 (3) |
| New York (Non-metro NYC area) | 10 (61) |
| New Jersey | 6 (37) |
| Connecticut | 1 (4) |
| Other | 7 (43) |
| Sex boroughs | |
| Manhattan | 32 (191) |
| Brooklyn | 14 (84) |
| The Bronx | 10 (59) |
| Queens | 9 (53) |
| Staten Island | 1 (3) |
| New York (Non-metro NYC area) | 10 (61) |
| New Jersey | 8 (49) |
| Connecticut | 1 (5) |
| Other | 8 (49) |
| Residential and social borough concordance | |
| Yes | 66 (395) |
| No | 34 (203) |
| Residential and sex borough concordance | |
| Yes | 68 (408) |
| No | 32 (190) |
| Social and sex borough concordance | |
| Yes | 63 (378) |
| No | 37 (220) |
| Residential, social, and sex borough concordance | |
| Yes | 25 (150) |
| No | 75 (448) |
4. Discussion
| Residential/Social Borough Concordance | Residential/Sex Borough Concordance | Social/Sex Borough Concordance | Residential/Social/Sex Borough Concordance | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No | Yes | No | Yes | No | Yes | No | Yes | |
| Sociodemographic characteristics | ||||||||
| Race/ethnicity | ||||||||
| Currently enrolled in school(yes) | 81 | 88 * | 84 | 87 | 85 | 86 | 84 | 89 |
| Perceived familial socioeconomic status | ||||||||
| Foreign-born (yes) | 10 | 11 | 12 | 11 | 10 | 12 | 12 | 9 |
| Household composition | ||||||||
| Sexual identity (exclusively homosexual) | 50 | 37 ** | 42 | 41 | 44 | 40 | 42 | 41 |
| Currently in male-male relationship (yes) | 27 | 26 | 31 | 25 | 28 | 26 | 27 | 25 |
| Current housing status (unstably housed) | 6 | 5 | 9 | 4 | 5 | 5 | 6 | 3 |
| Psychosocial factors | ||||||||
| Ethnic identity (high) | 38 | 38 | 35 | 40 | 40 | 37 | 40 | 33 |
| Experienced public gay-related stigma (high) | 54 | 45 * | 52 | 46 | 58 | 42 *** | 55 | 28 *** |
| Experienced personal gay-related stigma (high) | 47 | 49 | 44 | 50 | 47 | 48 | 49 | 45 |
| Has come out to peers (yes) | 71 | 67 | 59 | 74 *** | 64 | 72 * | 68 | 73 |
| Gay community affinity (high) | 51 | 38 ** | 41 | 43 | 45 | 41 | 42 | 43 |
| Internalized Homophobia (high) | 77 | 72 | 72 | 75 | 75 | 74 | 74 | 74 |
| Social support network characteristics | ||||||||
| Network size (>8 members) | 47 | 49 | 48 | 49 | 47 | 50 | 46 | 56 |
| Average duration of network relationships (≥2yrs) | 64 | 67 | 70 | 65 | 65 | 67 | 70 | 57 |
| Frequency of communication with network members (≥weekly) | 87 | 79 * | 82 | 82 | 84 | 81 | 84 | 78 |
| Emotional support (high) | 82 | 83 | 73 | 72 | 73 | 72 | 73 | 68 |
| Material support (high) | 72 | 72 | 70 | 73 | 73 | 72 | 72 | 74 |
| Health behaviors | ||||||||
| Alcohol use, last 30 days (yes) | 79 | 80 | 78 | 80 | 77 | 81 | 76 | 88 ** |
| Marijuana use. last 30 days (yes) | 45 | 47 | 41 | 49 | 40 | 50 * | 42 | 58 ** |
| Condomless oral sex, last 30 days (yes) | 48 | 58 * | 48 | 58 * | 43 | 61 *** | 52 | 63 * |
| Condomless anal sex, last 30 days (yes) | 19 | 21 | 20 | 21 | 20 | 21 | 21 | 17 |
5. Study Limitations
6. Future Research and Study Implications
7. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Frye, V.; Koblin, B.; Chin, J.; Beard, J.; Blaney, S.; Halkitis, P.; Vlahov, D.; Galea, S. Neighborhood-level correlates of consistent condom use among men who have sex with men: A multi-level analysis. AIDS Behav. 2010, 14, 974–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carpiano, R.M.; Kelly, B.C.; Easterbrook, A.; Parsons, J.T. Community and drug use among gay men: The role of neighborhoods and networks. J. Health Soc. Behav. 2011, 52, 74–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buttram, M.E.; Kurtz, S.P. Risk and protective factors associated with gay neighborhood residence. Amer. J. Mens Health 2013, 7, 110–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, B.C.; Carpiano, R.M.; Easterbrook, A.; Parsons, J.T. Sex and the community: The implications of neighbourhoods and social networks for sexual risk behaviours among urban gay men. Sociol. Health Ill. 2012, 34, 1085–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raymond, H.F.; Chen, Y.H.; Syme, S.L.; Catalano, R.; Hutson, M.A.; McFarland, W. The role of individual and neighborhood factors: HIV acquisition risk among high-risk populations in San Francisco. AIDS Behav. 2014, 18, 346–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matthews, S.A. Spatial polygamy and the heterogeneity of place: Studying people and place via egocentric methods. In Communities, Neighborhoods, and Health; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2011; pp. 35–55. [Google Scholar]
- Chaix, B.; Merlo, J.; Evans, D.; Leal, C.; Havard, S. Neighbourhoods in eco-epidemiologic research: Delimiting personal exposure areas. A response to Riva, Gauvin, Apparicio and Brodeur. Soc. Sci. Med. 2009, 69, 1306–1310. [Google Scholar]
- Dragowski, E.A.; Halkitis, P.N.; Moeller, R.W.; Siconolfi, D.E. Social and sexual contexts explain sexual risk taking in young gay, bisexual, and other young men who have sex with men, ages 13–29 years. J. HIV/AIDS Soc. Serv. 2013, 12, 236–255. [Google Scholar]
- Tobin, K.E.; Cutchin, M.; Latkin, C.A.; Takahashi, L.M. Social geographies of African American men who have sex with men (MSM): A qualitative exploration of the social, spatial and temporal context of HIV risk in Baltimore, Maryland. Health Place 2013, 22, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koblin, B.A.; Egan, J.E.; Rundle, A.; Quinn, J.; Tieu, H.V.; Cerda, M.; Ompad, D.C.; Greene, E.; Hoover, D.R.; Frye, V. Methods to measure the impact of home, social, and sexual neighborhoods of urban gay, bisexual, and other men who have sex with men. PLoS One 2013, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egan, J.E.; Frye, V.; Kurtz, S.P.; Latkin, C.; Chen, M.; Tobin, K.; Yang, C.; Koblin, B.A. Migration, neighborhoods, and networks: approaches to understanding how urban environmental conditions affect syndemic adverse health outcomes among gay, bisexual and other men who have sex with men. AIDS Behav. 2011, 15, S35–S50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sawatzky, R.; Liu-Ambrose, T.; Miller, W.C.; Marra, C.A. Physical activity as a mediator of the impact of chronic conditions on quality of life in older adults. Health Qual. Life Outcomes 2007, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motl, R.W.; McAuley, E. Physical activity, disability, and quality of life in older adults. Phys. Med. Rehabil. Clin. N. Am. 2010, 21, 299–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frye, V.; Latka, M.H.; Koblin, B.; Halkitis, P.N.; Putnam, S.; Galea, S.; Vlahov, D. The urban environment and sexual risk behavior among men who have sex with men. J. Urban. Health 2006, 83, 308–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Storholm, E.D.; Siconolfi, D.E.; Halkitis, P.N.; Moeller, R.W.; Eddy, J.A.; Bare, M.G. Sociodemographic factors contribute to mental health disparities and access to services among young men who have sex with men in New York City. J. Gay Lesbian Mental Health 2013, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapadia, F.; Siconolfi, D.E.; Barton, S.; Olivieri, B.; Lombardo, L.; Halkitis, P.N. Social support network characteristics and sexual risk taking among a racially/ethnically diverse sample of young, urban men who have sex with men. AIDS Behav. 2013, 17, 1819–1828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siconolfi, D.E.; Kapadia, F.; Halkitis, P.N.; Moeller, R.W.; Storholm, E.D.; Barton, S.C.; Solomon, T.M.; Jones, D. Sexual health screening among racially/ethnically diverse young gay, bisexual, and other men who have sex with men. J. Adolescent Health 2013, 52, 620–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halkitis, P.N.; Kapadia, F.; Siconolfi, D.E.; Moeller, R.W.; Figueroa, R.P.; Barton, S.C.; Blachman-Forshay, J. Individual, psychosocial, and social correlates of unprotected anal intercourse in a new generation of young men who have sex with men in New York City. Amer. J. Public Health 2013, 103, 889–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halkitis, P.N.; Moeller, R.W.; Siconolfi, D.E.; Storholm, E.D.; Solomon, T.M.; Bub, K.L. Measurement model exploring a syndemic in emerging adult gay and bisexual men. AIDS Behav. 2013, 17, 662–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halkitis, P.N.; Figueroa, R.P. Sociodemographic characteristics explain differences in unprotected sexual behavior among young HIV-negative gay, bisexual, and other YMSM in New York City. AIDS Patient Care Stds. 2013, 27, 181–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kapadia, F.; Halkitis, P.N.; Barton, S.; Siconolfi, D.E.; Figueroa, R.E.P. Associations between social support network-characteristics and receipt of emotional and material support among a sample of sexual minority youth. J. Gay Lesbian Soc. Serv. 2014, 26, 279–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duncan, D.T.; Castro, M.C.; Blossom, J.C.; Bennett, G.G.; Gortmaker, S.L. Evaluation of the positional difference between two common geocoding methods. Geospat. Health 2011, 5, 265–273. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Duncan, D.T.; Aldstadt, J.; Whalen, J.; Melly, S.J.; Gortmaker, S.L. Validation of walk score for estimating neighborhood walkability: an analysis of four U.S. metropolitan areas. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2011, 8, 4160–4179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phinney, J.S. The multigroup ethnic identity measure: A new scale for use with diverse groups. J. Adolescent Res. 1992, 7, 156–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frost, D.M.; Parsons, J.T.; Nanín, J.E. Stigma, concealment and symptoms of depression as explanations for sexually transmitted infections among gay men. J. Health Psychol. 2007, 12, 636–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Donnell, L.; Agronick, G.; San Doval, A.; Duran, R.; Myint-U, A.; Stueve, A. Ethnic and gay community attachments and sexual risk behaviors among urban Latino young men who have sex with men. AIDS Educ. Prev. 2002, 14, 457–471. [Google Scholar]
- Thiede, H.; Valleroy, L.A.; MacKellar, D.A.; Celentano, D.D.; Ford, W.L.; Hagan, H.; Koblin, B.A.; LaLota, M.; McFarland, W.; Shehan, D.A. Regional patterns and correlates of substance use among young men who have sex with men in 7 U.S. urban areas. Amer. J. Public Health 2003, 93, 1915–1921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobell, L.C.; Sobell, M.B. Alcohol Timeline Followback Users’ Manual; Addiction Research Foundation: Toronto, Canada, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Massey, D.S.; Denton, N. American Apartheid: Segregation and the Making of the Underclass; Harvard University Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Marsh, B.; Parnell, A.M.; Joyner, A.M. Institutionalization of racial inequality in local political geographies. Urban Geogr. 2010, 31, 691–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Logan, J.R.; Stults, B. The Persistence of Segregation in the Metropolis: New Findings from the 2010 Census. Census Brief. Prepared for Project US2010, 2011. Available online: http://www.s4.brown.edu/us2010/ (accessed on 15 May 2014).
- Duncan, D.T.; Kawachi, I.; White, K.; Williams, D.R. The geography of recreational open space: Influence of neighborhood racial composition and neighborhood poverty. J. Urban Health 2013, 90, 618–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duncan, D.T.; Hatzenbuehler, M.L.; Johnson, R.M. Neighborhood-level LGBT hate crimes and current illicit drug use among sexual minority youth. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2014, 135, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duncan, D.T.; Hatzenbuehler, M.L. Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender hate crimes and suicidality among a population-based sample of sexual-minority adolescents in Boston. Amer. J. Public Health 2014, 104, 272–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, M.M.; Quinn, J.W.; Jung, K.H.; Hoepner, L.; Diaz, D.; Perzanowski, M.; Rundle, A.; Kinney, P.L.; Perera, F.P.; Miller, R.L. Traffic density and stationary sources of air pollution associated with wheeze, asthma, and immunoglobulin E from birth to age 5 years among New York City children. Environ. Res. 2011, 111, 1222–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cornell, A.G.; Chillrud, S.N.; Mellins, R.B.; Acosta, L.M.; Miller, R.L.; Quinn, J.W.; Yan, B.; Divjan, A.; Olmedo, O.E.; Lopez-Pintado, S.; Kinney, P.L.; Perera, F.P.; Jacobson, J.S.; Goldstein, I.F.; Rundle, A.G.; Perzanowski, M.S. Domestic airborne black carbon and exhaled nitric oxide in children in NYC. J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2012, 22, 258–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rundle, A.; Neckerman, K.M.; Freeman, L.; Lovasi, G.S.; Purciel, M.; Quinn, J.; Richards, C.; Sircar, N.; Weiss, C. Neighborhood food environment and walkability predict obesity in New York City. Environ. Health Perspect. 2009, 117, 442–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lovasi, G.S.; Jacobson, J.S.; Quinn, J.W.; Neckerman, K.M.; Ashby-Thompson, M.N.; Rundle, A. Is the environment near home and school associated with physical activity and adiposity of urban preschool children? J. Urban Health 2011, 88, 1143–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.; Neckerman, K.; Quinn, J.; Weiss, C.; Jacobson, J.; Rundle, A. Neighbourhood immigrant acculturation and diet among Hispanic female residents of New York City. Public Health Nutr. 2011, 14, 1593–1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwate, N.O.; Loh, J.M.; White, K.; Saldana, N. Retail redlining in New York City: Racialized access to day-to-day retail resources. J. Urban Health 2013, 90, 632–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwate, N.O.; Yau, C.Y.; Loh, J.M.; Williams, D. Inequality in obesigenic environments: Fast food density in New York City. Health Place 2009, 15, 364–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwate, N.O.; Lee, T.H. Ghettoizing outdoor advertising: Disadvantage and ad panel density in black neighborhoods. J. Urban Health 2007, 84, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gordon, C.; Purciel-Hill, M.; Ghai, N.R.; Kaufman, L.; Graham, R.; van Wye, G. Measuring food deserts in New York City’s low-income neighborhoods. Health Place 2011, 17, 696–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barr, R.G.; Diez-Roux, A.V.; Knirsch, C.A.; Pablos-Mendez, A. Neighborhood poverty and the resurgence of tuberculosis in New York City, 1984–1992. Amer. J. Public Health 2001, 91, 1487–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janevic, T.; Borrell, L.N.; Savitz, D.A.; Herring, A.H.; Rundle, A. Neighbourhood food environment and gestational diabetes in New York City. Paediatr. Perinat. Epidemiol. 2010, 24, 249–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neckerman, K.M.; Lovasi, G.S.; Davies, S.; Purciel, M.; Quinn, J.; Feder, E.; Raghunath, N.; Wasserman, B.; Rundle, A. Disparities in urban neighborhood conditions: evidence from GIS measures and field observation in New York City. J. Public Health Policy 2009, 30, S264–S285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rundle, A.; Roux, A.V.D.; Free, L.M.; Miller, D.; Neckerman, K.M.; Weiss, C.C. The urban built environment and obesity in New York City: A multilevel analysis. Amer. J. Health Promot. 2007, 21, 326–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beard, J.R.; Cerda, M.; Blaney, S.; Ahern, J.; Vlahov, D.; Galea, S. Neighborhood characteristics and change in depressive symptoms among older residents of New York City. Amer. J. Public Health 2009, 99, 1308–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, C.C.; Purciel, M.; Bader, M.; Quinn, J.W.; Lovasi, G.; Neckerman, K.M.; Rundle, A.G. Reconsidering access: Park facilities and neighborhood disamenities in New York City. J. Urban Health 2011, 88, 297–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frank, J.W.; Hong, C.S.; Subramanian, S.V.; Wang, E.A. Neighborhood incarceration rate and asthma prevalence in New York City: A multilevel approach. Amer. J. Public Health 2013, 103, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Black, J.L.; Macinko, J. The changing distribution and determinants of obesity in the neighborhoods of New York City, 2003–2007. Amer. J. Epidemiol. 2010, 171, 765–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, K.; Borrell, L.N. Racial/ethnic residential segregation: Framing the context of health risk and health disparities. Health Place 2011, 17, 438–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Czarnecki, K.D.; Goranson, C.; Ellis, J.A.; Vichinsky, L.E.; Coady, M.H.; Perl, S.B. Using geographic information system analyses to monitor large-scale distribution of nicotine replacement therapy in New York City. Prev. Med. 2010, 50, 288–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooper, H.; des Jarlais, D.; Ross, Z.; Tempalski, B.; Bossak, B.H.; Friedman, S.R. Spatial access to sterile syringes and the odds of injecting with an unsterile syringe among injectors: A longitudinal multilevel study. J. Urban Health 2012, 89, 678–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galea, S.; Ahern, J.; Rudenstine, S.; Wallace, Z.; Vlahov, D. Urban built environment and depression: A multilevel analysis. J. Epidemiol. Community Health 2005, 59, 822–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karpati, A.M.; Bassett, M.T.; McCord, C. Neighbourhood mortality inequalities in New York City, 1989–1991 and 1999–2001. J. Epidemiol. Community Health 2006, 60, 1060–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahern, J.; Cerda, M.; Lippman, S.A.; Tardiff, K.J.; Vlahov, D.; Galea, S. Navigating non-positivity in neighbourhood studies: an analysis of collective efficacy and violence. J. Epidemiol. Community Health 2013, 67, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cerda, M.; Ransome, Y.; Keyes, K.M.; Koenen, K.C.; Tardiff, K.; Vlahov, D.; Galea, S. Revisiting the role of the urban environment in substance use: The case of analgesic overdose fatalities. Amer. J. Public Health 2013, 103, 2252–2260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huynh, M.; Maroko, A.R. Gentrification and preterm birth in New York City, 2008–2010. J. Urban Health 2014, 91, 211–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villanueva, C.; Aggarwal, B. The association between neighborhood socioeconomic status and clinical outcomes among patients 1 year after hospitalization for cardiovascular disease. J. Community Health 2013, 38, 690–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brouse, C.H.; Hillyer, G.C.; Basch, C.E.; Neugut, A.I. Geography, facilities, and promotional strategies used to encourage indoor tanning in New York City. J. Community Health 2011, 36, 635–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jack, D.; Neckerman, K.; Schwartz-Soicher, O.; Lovasi, G.S.; Quinn, J.; Richards, C.; Bader, M.; Weiss, C.; Konty, K.; Arno, P.; Viola, D.; Kerker, B.; Rundle, A. Socio-economic status, neighbourhood food environments and consumption of fruits and vegetables in New York City. Public Health Nutr. 2013, 16, 1197–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lovasi, G.S.; Schwartz-Soicher, O.; Neckerman, K.M.; Konty, K.; Kerker, B.; Quinn, J.; Rundle, A. Aesthetic amenities and safety hazards associated with walking and bicycling for transportation in New York City. Ann. Behav. Med. 2013, 45, S76–S85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, S.; Harris, T.G. Neighborhood contributions to racial and ethnic disparities in obesity among New York City adults. Amer. J. Public Health 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, H.P.; Torian, L.V.; Forgione, L.; Begier, E.M. Evaluation of HIV incidence surveillance in New York City, 2006. Public Health Rep. 2011, 126, 28–38. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Caravanos, J.; Weiss, A.L.; Blaise, M.J.; Jaeger, R.J. A survey of spatially distributed exterior dust lead loadings in New York City. Environ. Res. 2006, 100, 165–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frick, M.; Castro, M.C. Tobacco retail clustering around schools in New York City: Examining “place” and “space”. Health Place 2013, 19, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terzian, A.S.; Bodach, S.D.; Wiewel, E.W.; Sepkowitz, K.; Bernard, M.A.; Braunstein, S.L.; Shepard, C.W. Novel use of surveillance data to detect HIV-infected persons with sustained high viral load and durable virologic suppression in New York City. PLoS One 2012, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duncan, D.T.; Kawachi, I.; Subramanian, S.V.; Aldstadt, J.; Melly, S.J.; Williams, D.R. Examination of how neighborhood definition influences measurements of youths’ access to tobacco retailers: A methodological note on spatial misclassification. Amer. J. Epidemiol. 2014, 179, 373–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osypuk, T.L.; Galea, S. What level macro? Choosing appropriate levels to assess how place influences population health. In Macrosocial Determinants of Population Health; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2007; pp. 399–435. [Google Scholar]
- D’Agostino-McGowan, L.; Gennarelli, R.L.; Lyons, S.A.; Goodman, M.S. Using small-area analysis to estimate county-level racial disparities in obesity demonstrating the necessity of targeted interventions. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwyer-Lindgren, L.; Freedman, G.; Engell, R.E.; Fleming, T.D.; Lim, S.S.; Murray, C.J.; Mokdad, A.H. Prevalence of physical activity and obesity in U.S. counties, 2001–2011: A road map for action. Popul. Health Metrics 2013, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwyer-Lindgren, L.; Mokdad, A.H.; Srebotnjak, T.; Flaxman, A.D.; Hansen, G.M.; Murray, C.J. Cigarette smoking prevalence in U.S. counties: 1996–2012. Popul. Health Metrics 2014, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhang, L.; Penman, A.; May, W. Using small-area estimation method to calculate county-level prevalence of obesity in Mississippi, 2007–2009. In Prev. Chronic Dis.; 2011; 8, p. A85. Available online: http://www.cdc.gov/pcd/issues/2011/jul/10_0159.htm (accessed on 15 May 2014). [Google Scholar]
- Peterson, N.A.; Lowe, J.B.; Reid, R.J. Tobacco outlet density, cigarette smoking prevalence, and demographics at the county level of analysis. Subst. Use Misuse 2005, 40, 1627–1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reid, R.J.; Peterson, N.A.; Lowe, J.B.; Hughey, J. Tobacco outlet density and smoking prevalence: Does racial concentration matter? Drugs-Educ. Prev. Policy 2005, 12, 233–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boehmer, U.; Ozonoff, A.; Timm, A. County-level association of sexual minority density with breast cancer incidence: Results from an ecological study. Sex. Res. Soc. Policy 2011, 8, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boehmer, U.; Ozonoff, A.; Miao, X. An ecological approach to examine lung cancer disparities due to sexual orientation. Public Health 2012, 126, 605–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hatzenbuehler, M.L.; Keyes, K.M. Inclusive anti-bullying policies and reduced risk of suicide attempts in lesbian and gay youth. J. Adolesc. Health 2013, 53, S21–S26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hatzenbuehler, M.L.; Pachankis, J.E.; Wolff, J. Religious climate and health risk behaviors in sexual minority youths: A population-based study. Amer. J. Public Health 2012, 102, 657–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatzenbuehler, M.L.; Wieringa, N.F.; Keyes, K.M. Community-level determinants of tobacco use disparities in lesbian, gay, and bisexual youth: Results from a population-based study. Arch. Pediatr. Adolesc. Med. 2011, 165, 527–532. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hatzenbuehler, M.L. The social environment and suicide attempts in lesbian, gay, and bisexual youth. Pediatrics 2011, 127, 896–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loomis, B.R.; Kim, A.E.; Busey, A.H.; Farrelly, M.C.; Willett, J.G.; Juster, H.R. The density of tobacco retailers and its association with attitudes toward smoking, exposure to point-of-sale tobacco advertising, cigarette purchasing, and smoking among New York youth. Prev. Med. 2012, 55, 468–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, A.E.; Loomis, B.R.; Busey, A.H.; Farrelly, M.C.; Willett, J.G.; Juster, H.R. Influence of retail cigarette advertising, price promotions, and retailer compliance on youth smoking-related attitudes and behaviors. J. Public Health Manag. Pract. 2013, 19, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwan, M.-P. The uncertain geographic context problem. Ann. Assn. Amer. Geogr. 2012, 102, 958–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwan, M.-P. How GIS can help address the uncertain geographic context problem in social science research. Ann. GIS 2012, 18, 245–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delmelle, E. Spatial sampling. In The SAGE Handbook of Spatial Analysis; Fotheringham, A.S., Rogerson, P.A., Eds.; SAGE Publications: London, UK, 2009; pp. 183–206. [Google Scholar]
- Downs, T.J.; Ogneva-Himmelberger, Y.; Aupont, O.; Wang, Y.; Raj, A.; Zimmerman, P.; Goble, R.; Taylor, O.; Churchill, L.C.; Lemay, C.A. Vulnerability-based spatial sampling stratification for the National Children’s Study, Worcester County, Massachusetts: Capturing health-relevant environmental and sociodemographic variability. Environ. Health Perspect. 2010, 118, 1318–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.; Moudon, A.V.; Courbois, J.-Y.P. Built environment and behavior: Spatial sampling using parcel data. Ann. Epidemiol. 2006, 16, 387–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boruff, B.J.; Nathan, A.; Nijenstein, S. Using GPS technology to (re)-examine operational definitions of “neighbourhood” in place-based health research. Int. J. Health Geographics 2012, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chaix, B.; Meline, J.; Duncan, S.; Merrien, C.; Karusisi, N.; Perchoux, C.; Lewin, A.; Labadi, K.; Kestens, Y. GPS tracking in neighborhood and health studies: A step forward for environmental exposure assessment, a step backward for causal inference? Health Place 2013, 21, 46–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. HIV among Gay and Bisexual Men. Available online: http://www.cdc.gov/hiv/pdf/msm_fact_sheet_final_2014.pdf (accessed on 15 May 2014).
- New York City Department of Health and Mental Hygiene. HIV Epidemiology & Field Services Semiannual Report. 2012. Available online: http://www.nyc.gov/html/doh/downloads/pdf/dires/2012-1st-semi-rpt.pdf (accessed on 15 May 2014). [Google Scholar]
- New York City Department of Health and Mental Hygiene. New HIV Diagnoses Rising in New York City among Men Who Have Sex with Men. 2007. Available online: http://www.nyc.gov/html/doh/html/pr2007/pr079-07.shtml (accessed on 15 May 2014). [Google Scholar]
- El-Sadr, W.M.; Mayer, K.H.; Hodder, S.L. AIDS in America—Forgotten but not gone. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 362, 967–970. [Google Scholar]
- Wiewel, E.W.; Hanna, D.B.; Begier, E.M.; Torian, L.V. High HIV prevalence and diagnosis rates in New York City black men. J. Community Health 2011, 36, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shepard, C.W.; Gortakowski, H.W.; Nasrallah, H.; Cutler, B.H.; Begier, E.M. Using GIS-based density maps of HIV surveillance data to identify previously unrecognized geographic Foci of HIV burden in an urban epidemic. Public Health Rep. 2011, 126, 741–749. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nunn, A.; Yolken, A.; Cutler, B.; Trooskin, S.; Wilson, P.; Little, S.; Mayer, K. Geography should not be destiny: Focusing HIV/AIDS implementation research and programs on microepidemics in U.S. neighborhoods. Amer. J. Public Health 2014, 104, 775–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forney, J.C.; Miller, R.L.; City Project Study Team. Risk and protective factors related to HIV-risk behavior: A comparison between HIV-positive and HIV-negative young men who have sex with men. AIDS Care 2012, 24, 544–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Duncan, D.T.; Kapadia, F.; Halkitis, P.N. Examination of Spatial Polygamy among Young Gay, Bisexual, and Other Men Who Have Sex with Men in New York City: The P18 Cohort Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2014, 11, 8962-8983. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph110908962
Duncan DT, Kapadia F, Halkitis PN. Examination of Spatial Polygamy among Young Gay, Bisexual, and Other Men Who Have Sex with Men in New York City: The P18 Cohort Study. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2014; 11(9):8962-8983. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph110908962
Chicago/Turabian StyleDuncan, Dustin T., Farzana Kapadia, and Perry N. Halkitis. 2014. "Examination of Spatial Polygamy among Young Gay, Bisexual, and Other Men Who Have Sex with Men in New York City: The P18 Cohort Study" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 11, no. 9: 8962-8983. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph110908962
APA StyleDuncan, D. T., Kapadia, F., & Halkitis, P. N. (2014). Examination of Spatial Polygamy among Young Gay, Bisexual, and Other Men Who Have Sex with Men in New York City: The P18 Cohort Study. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 11(9), 8962-8983. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph110908962