Abstract
Identification of the sources of soil mercury (Hg) on the provincial scale is helpful for enacting effective policies to prevent further contamination and take reclamation measurements. The natural and anthropogenic sources and their contributions of Hg in Chinese farmland soil were identified based on a decision tree method. The results showed that the concentrations of Hg in parent materials were most strongly associated with the general spatial distribution pattern of Hg concentration on a provincial scale. The decision tree analysis gained an 89.70% total accuracy in simulating the influence of human activities on the additions of Hg in farmland soil. Human activities—for example, the production of coke, application of fertilizers, discharge of wastewater, discharge of solid waste, and the production of non-ferrous metals—were the main external sources of a large amount of Hg in the farmland soil.
1. Introduction
Mercury (Hg) is considered a global pollutant, and the effects of Hg on ecosystems and human health are well documented [1,2,3]. The concentrations of Hg in farmland soil are greatly influenced by parent material and soil properties, including organic matter, soil microbes, and soil pH [4,5,6], as well as human activities, such as non-ferrous mining, petroleum refining and fossil fuel combustion, discharge of wastes from industry production, and applications of fertilizers [7,8,9]. Some studies suggested that anthropogenic sources are leading to a general increase in Hg on local, regional, and global scales [10,11,12].
Efforts to identify the sources of Hg in farmland soil are of great significance for contamination prevention and control in the soil-crop system [13]. To search for possible Hg sources of heavy metal concentrations in soil, a number of methods have been proposed, including statistical and geochemical, regulatory reference value, and GIS-based methods [14,15,16,17,18]. Since soil Hg concentration is the result of multiple source interactions, the analysis should consider all of these sources and their interactions. The present study aims to develop a method to estimate the potential sources for Hg in farmland soil, based on a decision tree analysis (DTA). Compared to other statistical tools, DTA offers the following advantages: (a) it is able to handle different types of variables including numeric, categorical, ratings, and survival data; (b) it is able to identify nonlinear relationship and high-order interactions; and (c) results from DTA can be interpreted relatively easily [19,20].
However, there have only been a few studies using DTA in assessing soil pollution by heavy metals [19,21,22,23]. A classification and regression tree (CART) method was used to simulate soil Cu concentration and concluded that low soil Cu accumulation was driven by terrain characteristic, agriculture land uses, and soil properties, while high Cu resulted from industrial and agricultural activities [21]. CART was used to investigate the sorption and retention of heavy metals by soil [22]. Hu and Cheng used a conditional inference tree (CIT) to study the sources of heavy metals and concluded that Cd, Zn, Cu, Pb, and Cr in surface soils were largely by anthropogenic sources, whereas As, Ni, and Hg mostly originated from the soil parent materials [19]. In the above studies, the DTA methods were used under the cases in which the data pairs were at point scale, where the soil Hg addition was mainly from a single source.
On a provincial scale, the sources of soil Hg accumulation from high Hg concentrations in parent materials and human activities are interactive and complicated. Moreover, the identification of Hg sources on the provincial scale is helpful to provide a scientific basis for the government to enact effective policy to prevent further Hg pollution and carry out remediation methods. This study aims to: (a) identify the natural and anthropogenic sources of Hg accumulations in farmland soils on the provincial scale in China; and (b) evaluate the influencing magnitudes of these factors on Hg present in the soil, based on a decision tree method.
2. Data Collection and Methods
2.1. Hg Concentrations in Farmland Soil in China
The data on Hg concentration in farmland topsoil (0–20 or 0–15 cm) were collected from the studies published during 2005–2013 throughout China. The process of selecting relevant papers and the data records have been described in the work of Zhang et al. [24,25]. In total, 388 peer-reviewed articles on Hg concentrations are collected. The selected Hg concentrations in farmland soil are then grouped on the provincial scale as an area-weighted mean, based on the following equation:
where Cm is Hg concentration in farmland soil in province m, n is the number of the published papers in province m, and Ai is the investigated area in the ith data record.
2.2. Backgrounds of Soil Hg Concentrations and Statistic Data on Provincial Scale
The magnitude of Hg background depends on the composition of the parent rock material from which the soil was derived. Mercury is an extremely rare element in Earth’s crust, having an average crustal abundance by mass of only 0.08 parts per million [26]. Hg is found either as a native metal (rare) or in cinnabar, living stonite and other minerals, with cinnabar (HgS) being the most common ore [27]. The Hg backgrounds on the provincial scale were collected from the book of Soil Backgrounds in China [28], which collected soils from A, B, and C horizons of 4095 soil profiles and analyzed for concentrations of 13 elements involved of Hg [29]. These soil samples were developed from 19 kinds of parent materials in China, on which the Hg concentration ranged from 0.03 mg/kg on sedimentary red sandstone to 0.177 mg/kg on marine sedimentary parent material [28].
The reasons for selecting human actives on influencing Hg concentrations in soil are followed the previous studies and whether these data are accessible. The continuous application of wastewater and solid wastes into the farmland would lead to the high Hg concentrations in soil [30,31]. The long-term application of excessive fertilizers, organic manures, and pesticides to the farmland have been approved to introduce additional Hg concentration into soils [9,32,33]. The production procedures of coke, paper, steel, and glass could emit Hg into the environment, and eventually lead to high concentrations of Hg in soils [7,34,35]. Particularly, the mining and smelting activities on non-ferrous metals could emit a large amount of Hg into the atmosphere, water, and soil [36,37], and Hg could be accumulated in the soil through atmospheric depositions and wastewater irrigations. The anthropogenic attributes are from the Statistic Book of China [38]; including discharge of wastewater per farmland land (DWW); discharge of solid waste per farmland land (DSW); pesticide application rate (PAR); fertilizer application rate (FAR); irrigation rate (RR); production of coke (PFC); the total production of paper, steel, and glass (PI); non-ferrous metal reserves (NFMR); and combustion of fossil fuel (CFF).
2.3. Decision Tree Method to Drive Potential Hg Sources in Soil on Provincial Scale
The decision tree method is used to identify the potential sources of Hg present in the soil. Understanding the impact of soil and landscape properties and human activities on Hg content could be used to estimate the Hg addition in the soil. The detail information on the decision tree model, C5, is described in the papers of [39,40].
The input to the model of C5.0 is a training set of records, each of which is a set of attribute values tagged with a decision label. In this study, the data pairs of Hg addition and the potential sources of soil Hg were used as inputs. Hg accumulation was calculated as follows:
where ACm is the Hg addition in province m, Cm, and Bm are the Hg concentration and background value in province m [28,41,42]. The unit for ACm, Cm, and Bm is mg/kg.
ACm = Cm − Bm
To construct the decision tree to simulate the human activities on Hg concentration in soil, nine attributes are selected. The C5.0 can pre-selected a subset of the attributes that will be used to construct the decision tree by the function of “winnowing”. The remaining attributes are then listed in order of importance, where the numerical importance shown for each attribute is the estimated percentage increase in error rate or misclassification cost that would result from removal of that attribute.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Statistic Information of Hg Concentration in Farmland Soil
The statistic information of Hg concentration in farmland soil on the provincial scale is described in Table 1. The investigated areas were spatially distributed in 30 provinces, municipalities, or districts, covering all of the mainland area of China except the Tibet Autonomous Region and Taiwan Province. The number of studies within a province ranged from 2 to 27, and the number of investigated samples ranged from 31 to 31,211.

Table 1.
Statistic information of Hg concentration in farmland soil on provincial scale.
The range of area-weighted Hg concentration in farmland soil was from 0.017 mg/kg to 0.554 mg/kg. Some of the provinces had higher Hg concentrations than the reference II of 0.300 mg/kg under soil pH < 7.5, indicating that these areas faced high Hg pollution risk. The high Hg concentrations occurred in Tianjin, Xinjiang, Hunan, Guangxi, Guizhou, and Fujian, with the value higher than 0.200 mg/kg. The Hg concentration in the farmland soil of Guangdong, Hubei, Jiangxi, Liaoning, Shanghai, Sichuan, Yunnan, and Zhejiang ranged from 0.100 mg/kg to 0.200 mg/kg. The remaining provinces had Hg concentrations under the value of 0.100 mg/kg.
3.2. The Influence of Initial Hg Concentration in Parent Materials on Hg Concentration in Farmland Soil
To illustrate the contribution of physical initial concentration in parent materials on current Hg concentrations in farmland soil, the spatial distribution of background of soil Hg, and the area-weighted mean of Hg in farmland soil are illustrated in Figure 1. The background concentration of Hg in soil showed an obvious spatial trend of soil Hg concentrations decreasing from the south to the north. The area-weighted average of Hg concentration in farmland soil had a similar spatial trend, but Hg concentrations in some provinces disrupted such spatial variations.
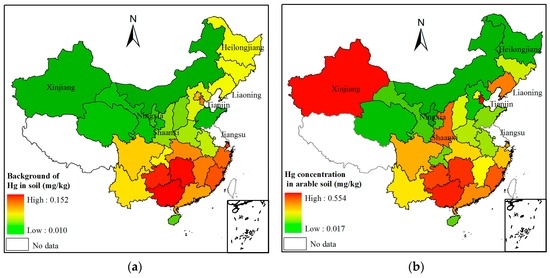
Figure 1.
Spatial distribution of (a) background of Hg concentration in soil [28,41,42]; and (b) area-weighted average of Hg concentration in arable soils in the mainland of China. Note: in this section, Jiangsu Province was not involved since the background value of Hg is 0.287 mg/kg, which much different from those in other provinces. The area-weighted Hg concentration in the arable soil in Jiangsu Province is 0.1148 mg/kg.
The relationship between the background concentrations of Hg in soil and the area-weighted Hg concentration in farmland soil on a provincial scale were examined (Figure 2). From Figure 2a, it was evident that several data deviated from the primary trend, indicating the Hg concentrations in these provinces were greatly influenced by external sources. If these provinces were removed from the data set (Figure 2b), the background concentrations of Hg dominated in farmland soils of the remaining provinces in farmland soil in the remaining provinces.
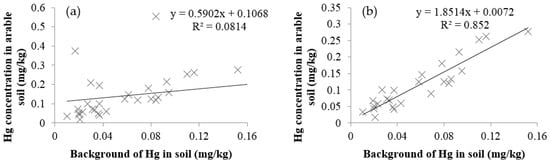
Figure 2.
Scatter plots of background of Hg in soil and Hg concentration in arable soil (a) the whole data set; and (b) after removing four data pairs.
The excluded four provinces were Liaoning, Shaanxi, Tianjin, and Xinjiang, which had relatively low backgrounds yet high Hg contents in farmland soil. Liaoning Province had a lot of non-ferrous mining and smelting activities, high farmland irrigation rates with wastewater, and well developed heavy industries [30,43,44]. In Xinjiang and Tianjin, the high Hg contents in farmland soil were mainly introduced by the sewage irrigation [45,46,47]. The high Hg concentration in Shaanxi Province might be due to non-ferrous mining and smelting activities and sewage irrigation [37,48].
3.3. The Influence of Human Activities on Hg Accumulation in Farmland Soil
3.3.1. Description of the Decision Tree
To assess the importance of potential human sources on Hg accumulation in farmland soil on a provincial scale, the decision tree method of C5.0 was used. From Figure 2, Hg concentrations in most provinces were higher than the according backgrounds except for in Ningxia (−0.0035 mg/kg) and Heilongjiang (−0.0016 mg/kg), indicating these areas were influenced by exterior factors. Hg concentrations were seldom influenced by the human activities in these two provinces since the averaged concentrations of Hg from 2006–2013 were even lower than their corresponding background values. Certainly, the limited collected samples in these two provinces might introduce some uncertainty on the Hg concentration, and led to the negative values. The accumulations of Hg in the remaining provinces ranged from 0.0040 mg/kg (in Hebei Province) to 0.4702 mg/kg (in Tianjin). The higher Hg accumulations represented stronger influences from external sources.
According to the ranges of Hg accumulations (ACm) in farmland soil, the 29 provincial cases were grouped into five grades (G1–G5). Hg accumulation in the five grade ranges were 0.004–0.050 mg/kg, 0.051–0.100 mg/kg, 0.101–0.150 mg/kg, 0.151–0.2000 mg/kg, and 0.201–0.470 mg/kg. The simulated tree included eight nodes (Figure 3). In the decision tree, 2, 2, 1, 1, 1 branches were for the grades from G1 to G5. The accuracy of the C5.0 training process correctly matching to their respective classes was 89.70%. Among the 13 samples in G1, 12 provinces were correctly simulated for G1, and 1 for G3. Among the six provinces in G2, five were correctly simulated into G2, while one was for G4. Among the six provinces in G3, five were correctly classified in G3, and one for G2. The four provinces in G4 and G5 were correctly simulated into their according grades.
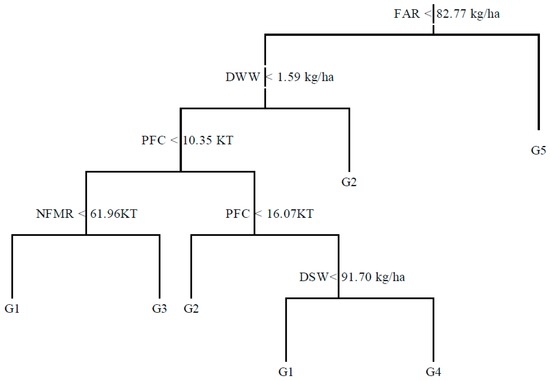
Figure 3.
Decision tree on Hg concentration in farmland soil in China.
3.3.2. Evaluation of the Relative Importance of Factors on Hg Accumulation
The method C5.0 provides the relative importance of independent variables on the soil Hg concentration. The decision tree finally selected five attributes of fertilizer application rate (FAR), discharge of wastewater (DWW), production of coke (PFC), non-ferrous metal reserves (NFMR), and discharge of solid waste (DSW), from the nine initially selected attributes. This selection does not mean that the unselected parameters had little contribution to the Hg accumulation in arable soil. The reason for these parameters not being selected in the decision tree might be that they had a non-essential effect on Hg accumulation.
The misclassification error showed that PFC was most important to classify soil Hg accumulation (omitting PFC increased misclassification error to 24.1%), followed by the parameters of FAR, DSW, and DWW (misclassification error to 17.2%), and NFMR (misclassification error increased to 13.8%). The high Hg concentration in the arable soil in the mining area of non-ferrous metals or fossil fuels is mainly due to mineral excavation, ore transportation, smelting, and refining in these areas, as well as disposal of the tailings and wastewater around mines [49,50,51]. Although the activities of non-ferrous metal mining—such as copper, lead, and zinc—could introduce larger amounts of Hg into the environment than the fossil mining [37,51,52], the contribution of fossil mining was higher than non-ferrous metals on the accumulation of Hg in farmland soil because the production of fossils were much higher than the non-ferrous metals. For example, coal production was 36.8 × 108 T, and the total production of non-ferrous metals was 4.05 × 107 T in 2013 in China [53].
The effect of fertilizer applications showed high contribution on Hg accumulations in farmland soil. Hg concentrations detected in fertilizers commonly used in agricultural activities ranged from 0 to 5.1 mg/kg [33]. Particularly, the content of Hg in calcium superphosphate was 5–10 times higher than the limit of grade II soil in Environmental Quality Standard for soils in China (GB 15618-1995). The other study showed that the phosphorous fertilizers could influence soil Hg concentrations to some extent where has a low Hg background value in soil [9]. Thus the application of liquid and soil manure or inorganic fertilizers could introduce a large amount of Hg into farmland soil since fertilizer application is a common agricultural practice [32].
The discharge of solid wastes or wastewater had great effect on the Hg accumulation in farmland soil. The wastes from the pharmaceutical, paper, electric, and chemical industry plants often contained a large amount of Hg [54]. In China, most of the irrigated water was untreated sewage or effluents of primary treatments, and the municipal wastewater and industrial wastewater were not separated in many cases. Thus, Hg could enter into the soil through direct sewage irrigation or atmospheric diffusion or surface runoff flushing or weathering from the solid wastes [55]. In China, irrigation with sewage was becoming a common practice due to shortage of fresh water. This situation was especially common in the urban and suburban areas [47,56] and the arid or semiarid areas [45]. The total area of sewage area in China was about 40,000 km2.
3.3.3. Decision Rules for Hg Accumulation in Farmland Soil
FAR had the determinant effect on whether Hg accumulation reached a level of G5.0. When FAR was higher than 82.77 kg/ha, the soil would accumulate to a great amount of Hg in farmland soil. In fact, the two regions also had high irrigation rates (higher than 75%) [38], and the sewage irrigation might introduce a considerable amount of Hg into farmland soil.
When FAR was lower than 82.77 kg/ha, and DWW was higher than 1597 T, such as the megacity of Beijing and Shanghai, Hg would be introduced into farmland soil since sewage might be used for irrigating farmland soil. As a result, Hg pollution problems were broadly noticed in soil irrigated with the reclaimed water. Under the conditions of FAR lower than 82.77 kg/ha, DWW lower than 1597 T, PFF lower than 1035 KT, and NFMR lower than 6196 KT, Hg accumulations would be in G1. While under the same condition of FAR, DWW, EP, but with NFME greater than 6196 KT, Hg accumulations would reach G3. This also indicates that mining and smelting activities introduced large Hg concentrations into farmland soils.
When FAR was lower than 82.77 kg/ha, DWW was less than 1.57 KT, and the EP was between 1036 KT and 1607 KT, Hg accumulation would be in G2; while under the same condition of FAR, DWW, EP, if the DSW were lower than 91.70 kg/ha, Hg accumulation would be in G1; otherwise Hg would be in G4. The solid wastes from industry development, such as battery production, contained high Hg contents. If these wastes were not properly disposed, they would pollute the peripheral farmland soils.
3.4. Limitations and Uncertainties
The method of decision tree C5.0 identified the sources of soil Hg concentrations on the provincial scale and found the complicated relationship between the Hg concentrations and the sources from parent materials and human activates. However, there were some limitations when using C5.0 to simulate the sources of Hg concentration in soil. First, the simulation results showed instability [57]. Even a small change in the input data would cause large variations in the simulated tree. Second, C5.0 has the inadequacy in applying regression for predicting continuous values. Although the decision tree method has been used to assess soil Cu content (divided into six grades) considering the human activities and gained a better estimation result than Kriging, it still can only simulate the scalar data [21].
4. Conclusions
This study identified the potential sources of Hg in the farmland soil on a provincial scale in China based on the soil Hg concentrations from published papers, the background Hg concentrations from parent materials, and the statistical data relevant to Hg sources. The decision tree gained a reliable result on simulating the interactive effects of the multiple sources of Hg in soil. The natural factors showed a strong influence on Hg concentration in farmland soil on the province scale, while the human activities changed such spatial trends. The human activities of production of coke, application of fertilizers, discharge of wastewater, discharge of solid waste, and production of non-ferrous metals, led to the high accumulation of Hg in farmland soil in China.
Acknowledgments
This study is supported by the public science and technology research funds projects of the Ministry of Land and Resources of China (201411006-02).
Author Contributions
Taiyang Zhong wrote this manuscript, Dongmei Chen gave some suggestions on the manuscript and polished the languages, and Xiuying Zhang designed the framework of this study and collected the data used in this study.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare not conflicts of interest.
References
- Valenti, T.W.; Cherry, D.S.; Neves, R.J.; Schmerfeld, J. Acute and chronic toxicity of mercury to early life stages of the rainbow mussel, Villosa iris (Bivalvia: Unionidae). Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2005, 24, 1242–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gray, J.E.; Theodorakos, P.M.; Fey, D.L.; Krabbenhoft, D.P. Mercury concentrations and distribution in soil, water, mine waste leachates, and air in and around mercury mines in the Big Bend region, Texas, USA. Environ. Geochem. Health 2015, 37, 35–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, J.; Huang, Z.; Pan, X.D. Exposure assessment of heavy metals (Cd, Hg, and Pb) by the intake of local foods from Zhejiang, China. Environ. Geochem. Health 2014, 36, 765–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigues, S.; Pereira, M.E.; Duarte, A.C.; Ajmone-Marsan, F.; Davidson, C.M.; Grcman, H.; Hossack, I.; Hursthouse, A.S.; Ljung, K.; Martini, C.; et al. Mercury in urban soils: A comparison of local spatial variability in six European cities. Sci. Total Environ. 2006, 368, 926–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barkay, T.; Wagner-Dobler, I. Microbial transformations of mercury: Potentials, challenges, and achievements in controlling mercury toxicity in the environment. In Advances in Applied Microbiology; Laskin, A.I., Bennett, J.W., Gadd, G.M., Eds.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 2005; Volume 57, pp. 1–52. [Google Scholar]
- Randall, P.; Chattopadhyay, S. Influence of ph and oxidation-reduction potential (Eh) on the dissolution of mercury-containing mine wastes from the sulphur bank mercury mine. Miner. Metallur. Process. 2004, 21, 93–98. [Google Scholar]
- Shai, N.N. The Heavy Metals Distribution Characteristics and Risky Evaluations of Farmland Soils-Crops around Different Types of Chemical Industrial Park. Master’s Thesis, Nanjing Agriculture University, Nanjing, China, 9 June 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Bavec, S.; Biester, H.; Gosar, M. Urban sediment contamination in a former Hg mining district, Idrija, Slovenia. Environ. Geochem. Health 2014, 36, 427–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirlean, N.; Baisch, P.; Machado, I.; Shumilin, E. Mercury contamination of soil as the result of long-term phosphate fertilizer production. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2008, 81, 305–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hagan, N.; Robins, N.; Hsu-Kim, H.; Halabi, S.; Gonzales, R.D.E.; Ecos, E.; Richter, D.; Vandenberg, J. Mercury hair levels and factors that influence exposure for residents of Huancavelica, Peru. Environ. Geochem. Health 2015, 37, 507–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henriques, B.; Rodrigues, S.M.; Coelho, C.; Cruz, N.; Duarte, A.C.; Romkens, P.F.A.M.; Pereira, E. Risks associated with the transfer of toxic organo-metallic mercury from soils into the terrestrial feed chain. Environ. Int. 2013, 59, 408–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seigneur, C.; Vijayaraghavan, K.; Lohman, K.; Karamchandani, P.; Scott, C. Global source attribution for mercury deposition in the United States. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2004, 38, 555–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shan, Y.; Tysklind, M.; Hao, F.; Ouyang, W.; Chen, S.; Lin, C. Identification of sources of heavy metals in agricultural soils using multivariate analysis and GIS. J. Soils Sediments 2013, 13, 720–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Z.H.; Feng, X.B.; Zhang, C.; Wang, J.F.; Jiang, T.M.; Xiao, H.J.; Li, Y.; Wang, X.; Qiu, G.L. Assessing anthropogenic sources of mercury in soil in Wanshan Hg mining area, Guizhou, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2013, 20, 7560–7569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.Y.; Lin, F.F.; Wong, M.T.; Feng, X.L.; Wang, K. Identification of soil heavy metal sources from anthropogenic activities and pollution assessment of Fuyang county, China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2009, 154, 439–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, M.; Wu, L.; Bi, X.; Ren, L.; Wang, L.; Ma, Z.; Bao, Z.; Li, Z. Assessing heavy-metal contamination and sources by GIS-based approach and multivariate analysis of urban-rural topsoils in Wuhan, Central China. Environ. Geochem. Health 2010, 32, 59–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, Y.G.; Li, Q.S.; Fang, J.H.; He, B.Y.; Fu, H.B.; Tong, Z.J. Identification of heavy metal sources in the reclaimed farmland soils of the pearl river estuary in China using a multivariate geostatistical approach. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2014, 105, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Zhao, Y.; Zhao, X.; Wang, Y.; Deng, W. Sources of heavy metal pollution in agricultural soils of a rapidly industrializing area in the Yangtze Delta of China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2014, 108, 161–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.; Cheng, H. Application of stochastic models in identification and apportionment of heavy metal pollution sources in the surface soils of a large-scale region. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 3752–3760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De’ath, G.; Fabricius, K.E. Classification and regression trees: A powerful yet simple technique for ecological data analysis. Ecology 2000, 81, 3178–3192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.Y.; Lin, F.F.; Jiang, Y.G.; Wang, K.; Wong, M.T.F. Assessing soil Cu content and anthropogenic influences using decision tree analysis. Environ. Pollut. 2008, 156, 1260–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vega, F.A.; Matias, J.M.; Andrade, M.L.; Reigosa, M.J.; Covelo, E.F. Classification and regression trees (CARTS) for modelling the sorption and retention of heavy metals by soil. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 167, 615–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartman, J.S.; Weisberg, P.J.; Pillai, R.; Ericksen, J.A.; Kuiken, T.; Lindberg, S.E.; Zhang, H.; Rytuba, J.J.; Gustin, M.S. Application of a rule-based model to estimate mercury exchange for three background biomes in the continental United States. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 4989–4994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.Y.; Chen, D.M.; Zhong, T.Y.; Zhang, X.M.; Cheng, M.; Li, X.H. Assessment of cadmium (Cd) concentration in arable soil in China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 4932–4941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Zhong, T.; Chen, D.; Zhang, X. Spatial dsitrbution of mercury (Hg) concentration in agricultural soil and its risk assessment on food safety in China. Sustainbility 2016, 8, 12. [Google Scholar]
- Ehrlich, H.L.; Newman, D.K. Geomicrobiology, 5th ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2008; p. 265. [Google Scholar]
- Rytuba, J.J. Mercury from mineral deposits and potential environmental impact. Environ. Geol. 2003, 43, 13. [Google Scholar]
- China Environmental Monitoring Center. Chinese Soil Element Background Concentent; Chinese Environment Science Press: Beijing, China, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Li, M.; Xi, X.; Xiao, G.; Cheng, H.; Yang, Z.; Zhou, G.; Ye, J.; Li, Z. National multi-purpose regional geochemical survey in China. J. Geochem. Explor. 2014, 139, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Wang, X.; Allinson, G.; Li, X.; Xiong, Z. Risk assessment of heavy metals in soil previously irrigated with industrial wastewater in Shenyang, China. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 161, 516–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.F.; Wang, Z.W.; Meng, Q.W.; Hu, P.P.; Hou, Y.Y.; Wang, Z.L.; Zhang, H. Contents and health risk assessment of heavy metals in wheat and rice grown in Tianjin sewage irrigation area, China. J. Agro-Environ. Sci. 2015, 34, 7. [Google Scholar]
- Zahra, A.; Alireza, M.; Jafar, N.; Mehdi, H.; Masoud, Y.; Mehdi, A.; AmirHossein, M. Effect of fertilizer application on soil heavy metal concentration. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2010, 160, 83–89. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, X.L.; Wang, D.Y. Mercury in some chemical fertilizers and the effect of calcium superphosphate on mercury uptake by cron seedlings (Zea mays L.). J. Environ. Sci. (China) 2010, 22, 1184–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Liu, G.J.; Kang, Y.; Wu, B.; Sun, R.Y.; Zhou, C.C.; Wu, D. Coal utilization in China: Environmental impacts and human health. Environ. Geochem. Health 2014, 36, 735–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navarro, M.; López, H.; Sánchez, M.; López, M.C. The effect of industrial pollution on mercury levels in water, soil, and sludge in the coastal area of Motril, Southeast Spain. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 1993, 24, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; He, M.; Xie, J.; Xi, J.; Lu, X. Heavy metal pollution of the world largest antimony mine-affected agricultural soils in Hunan province (China). J. Soils Sediments 2010, 10, 827–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.N.; Ke, H.L.; Zhao, A.N.; Liu, R.P.; Zhang, J.H. Assessment of heavy metals contamination of farmland soils in some gold mining area of Xiao Qinling. Chin. J. Soil Sci. 2007, 4, 024. [Google Scholar]
- National Bureau of Statistics of China. China Statistical Yearbook; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2013.
- Zhang, X.Y.; Jiang, H.; Jin, J.X.; Xu, X.H.; Zhang, Q.X. Analysis of acid rain patterns in Northeastern China using a decision tree method. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 46, 590–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeFries, R.S.; Chan, J.C.W. Multiple criteria for evaluating machine learning algorithms for land cover classification from satellite data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2000, 74, 503–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, J.; Wang, W.; Wen, C.; Yi, Z.; Tang, S. Concentrations and distributions of selenium and heavy metals in Hainan paddy soil and assessment of ecological security. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2012, 32, 3477–3486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, N.; Lai, W.P.; Xu, M.; Zheng, C. The data process and results of 11 kinds of element in soil of Chongqing. Environ. Protect. Chongqing 1982, 18–37. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, X.Y.; Li, P.J.; Sun, H.Y. Status and cause of heavy metal pollution of the soils in typical industrial and mining areas and wastewater irrigation zones in Liaoning. Soil 2006, 38, 192–195. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, N.; Wang, Q.; Liu, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Z. Spatial variation of heavy metals contamination in the soil and vegetables of Huludao city. Environ. Sci. 2009, 30, 2071–2076. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.Y.; Liu, H.F. Heavy metal pollution and prohibition in the irrigated area by wastewater in Miquan, Xinjiang. J. Changji Univ. 2007, 7, 45–48. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.J. Distribution of Several Soil Heavy Metal Elements Content and Pollution Evaluation in Changji Typical Model Region, Xinjiang. Master’s Thesis, Xinjiang Agricultural University, Ürümqi, China, 10 June 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, T.; Wang, J.; Sun, H.W.; Zhang, Y.F. Contamniation of cadmium and mercury in farmland of Tianjin and extration methods for predicting their bioavailability. J. Agro-Environ. Sci. 2012, 31, 119–124. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, M. Distribution characteristics and pollution assessment of heavy metals in agricultural soil of eastern guanzhong—A case study of Fuping county. J. Gansu Agric. Univ. 2013, 48, 99–104. [Google Scholar]
- Shao, X.; Cheng, H.; Duan, X.; Lin, C. Concentrations and chemical forms of heavy metals in agricultural soil near the world’s largest and oldest tungsten mine located in China. Chem. Spec. Bioavailab. 2013, 25, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salomons, W. Environmental impact of metals derived from mining activities: Processes, predictions, prevention. J. Geochem. Explor. 1995, 52, 5–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Wang, S.X.; Streets, D.G.; Hao, J.M.; Chan, M.; Jiang, J.K. Trends in anthropogenic mercury emissions in China from 1995 to 2003. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 5312–5318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, M.; Liao, B.; Shu, W.; Yang, B.; Lan, C. Pollution assessment and potential sources of heavy metals in agricultural soils around four Pb/Zn mines of Shaoguan city, China. Soil Sediment Contam. 2015, 24, 76–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Bureau of Statistics of the People’s Republic of China. Statistical Bulletin of the National Economic and Social Development in 2013. Available online: http://www.stats.gov.cn/tjsj/zxfb/201402/t20140224_514970.html (accessed on 4 September 2016).
- Zhang, L.; Wong, M.H. Environmental mercury contamination in China: Sources and impacts. Environ. Int. 2007, 33, 108–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, Y.; Tang, W.; Deng, H.; Li, M.; Yu, M.; Li, Y. Fuzzy synthetic assessment of heavy metal contamination in crop-reclaimed Mn minelands. J. Guangxi Norm. Univ. 2009, 27, 5. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.Y.; Xie, S.Y.; Wei, X.G.; Hao, X.D. Evaluation on the mercury pollution of main vegetable producing areas in Guangzhou city. Hubei Agric. Sci. 2011, 50, 3069–3070. [Google Scholar]
- Patel, B.R.; Rana, K.K. A survey on decision tree algorithm for classification. Int. J. Eng. Dev. Res. 2014, 2, 5. [Google Scholar]
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).