Role of High-Resolution Chest Computed Tomography in a Child with Persistent Tachypnoea and Intercostal Retractions: A Case Report of Neuroendocrine Cell Hyperplasia
Abstract
:1. Background
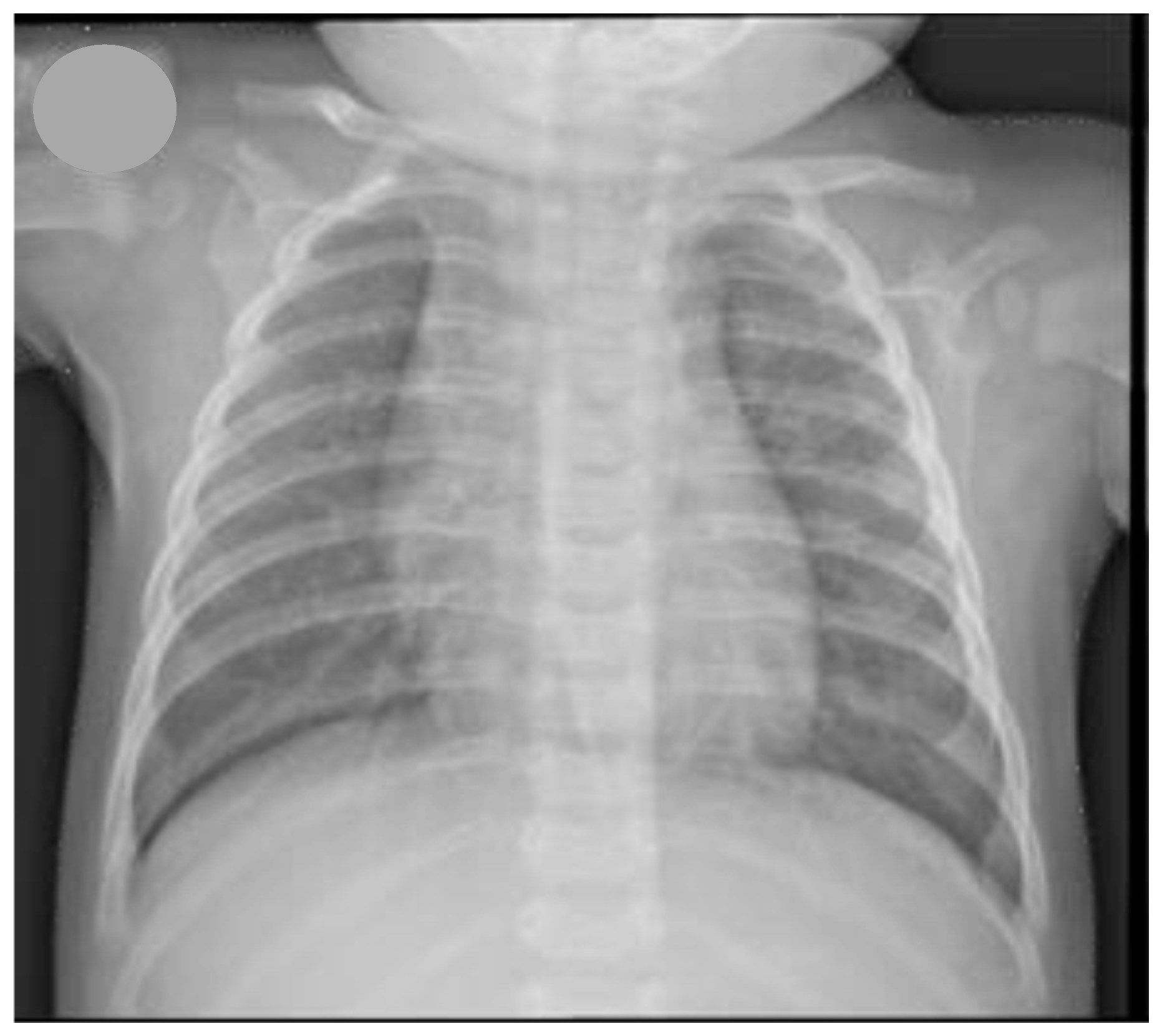
2. Case Presentation
Ethics, Approval and Consent to Participate
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Clement, A. ERS Task Force on chronic interstitial lung disease in immunocompetent children. Eur. Respir. J. 2004, 24, 686–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bush, A.; Nicholson, A.G. Chapter 17: Paediatric interstitial lung disease. Eur. Respir. Mon. 2009, 46, 319–354. [Google Scholar]
- Spagnolo, P.; Bush, A. Interstitial lung disease in children younger than 2 years. Pediatrics 2016, 137, e20152725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langston, C.; Fan, L.L. Diffuse interstitial lung disease in infants. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2001, S23, 74–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurland, G.; Deterding, R.R.; Hagood, J.S.; Young, L.R.; Brody, A.S.; Castile, R.G.; Dell, S.; Fan, L.L.; Hamvas, A.; Hilman, B.C.; et al. American Thoracic Society Committee on Childhood Interstitial Lung Disease (chILD), the chILD Research Network: An official American Thoracic Society clinical practice guideline: Classification, evaluation, and management of childhood interstitial lung disease in infancy. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2013, 188, 376–394. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Vece, T.J.; Young, L.R. Update on diffuse lung disease in children. Chest 2016, 149, 836–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deutsch, G.H.; Young, L.R.; Deterding, R.R.; Fan, L.L.; Dell, S.D.; Bean, J.A.; Brody, A.S.; Nogee, L.M.; Trapnell, B.C.; Langston, C.; et al. ChILD Research Co-operative. Diffuse lung disease in young children: Application of a novel classification scheme. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2007, 176, 1120–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuo, C.S.; Young, L.R. Interstitial lung disease in children. Curr. Opin. Pediatr. 2014, 26, 320–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caimmi, S.; Licari, A.; Caimmi, D.; Rispoli, A.; Baraldi, E.; Calabrese, F.; Marseglia, G.L. Neuroendocrine cell hyperplasia of infancy: An unusual cause of hypoxemia in children. Ital. J. Pediatr. 2016, 42, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thacker, P.G.; Vargas, S.O.; Fishman, M.P.; Casey, A.M.; Lee, E.Y. Current update on interstitial lung disease of infancy: New classification system, diagnostic evaluation, imaging algorithms, imaging findings, and prognosis. Radiol. Clin. N. Am. 2016, 54, 1065–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deterding, R.R.; Pye, C.; Fan, L.L.; Langston, C. Persistent tachypnea of infancy is associated with neuroendocrine cell hyperplasia. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2005, 40, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Popler, J.; Gower, W.A.; Mogayzel, P.J., Jr.; Nogee, L.M.; Langston, C.; Wilson, A.C.; Hay, T.C.; Deterding, R.R. Familial neuroendocrine cell hyperplasia of infancy. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2010, 45, 749–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, L.R.; Deutsch, G.H.; Bokulic, R.E.; Brody, A.S.; Nogee, L.M. A mutation in TTF1/NKX2.1 is associated with familial neuroendocrine cell hyperplasia of infancy. Chest 2013, 144, 1199–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lukkarinen, H.; Pelkonen, A.; Lohi, J.; Malmström, K.; Malmberg, L.P.; Kajosaari, M.; Lindahl, H.; Föhr, A.; Ruuskanen, O.; Mäkelä, M.J. Neuroendocrine cell hyperplasia of infancy: A prospective follow-up of nine children. Arch. Dis. Child. 2013, 98, 141–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carr, L.L.; Kern, J.A.; Deutsch, G.H. Diffuse idiopathic pulmonary neuroendocrine cell hyperplasia and neuroendocrine hyperplasia of infancy. Clin. Chest Med. 2016, 37, 579–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rauch, D.; Wetzke, M.; Reu, S.; Wesselak, W.; Schams, A.; Hengst, M.; Kammer, B.; Ley-Zaporozhan, J.; Kappler, M.; Proesmans, M.; et al. PTI (Persistent Tachypnea of Infancy) Study Group of the Kids Lung Register: Persistent tachypnea of infancy. Usual and aberrant. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2016, 193, 438–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bush, A.; Cunningham, S.; de Blic, J.; Barbato, A.; Clement, A.; Epaud, R.; Hengst, M.; Kiper, N.; Nicholson, A.G.; Wetzke, M.; et al. chILD-EU Collaboration: European protocols for the diagnosis and initial treatment of interstitial lung disease in children. Thorax 2015, 70, 1078–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomes, V.C.C.; Silva, M.C.C.; Maia Filho, J.H.; Daltro, P.; Ramos, S.G.; Brody, A.S.; Marchiori, E. Diagnostic criteria and follow-up in neuroendocrine cell hyperplasia of infancy: A case series. J. Bras. Pneumol. 2013, 39, 569–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kerby, G.S.; Wagner, B.D.; Popler, J.; Hay, T.C.; Kopecky, C.; Wilcox, S.L.; Quinones, R.R.; Giller, R.H.; Accurso, F.J.; Deterding, R.R. Abnormal infant pulmonary function in young children with neuroendocrine cell hyperplasia of infancy. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2013, 48, 1008–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brody, A.S.; Guillerman, R.P.; Hay, T.C.; Wagner, B.D.; Young, L.R.; Deutsch, G.H.; Fan, L.L.; Deterding, R.R. Neuroendocrine cell hyperplasia of infancy: Diagnosis with high-resolution CT. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2010, 194, 238–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yancheva, S.G.; Velani, A.; Rice, A.; Montero, A.; Hansell, D.M.; Koo, S.; Thia, L.; Bush, A.; Nicholson, A.G. Bombesin staining in neuroendocrine cell hyperplasia of infancy (NEHI) and other childhood interstitial lung diseases (chILD). Histopathology 2015, 67, 501–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, L.L.; Lung, M.C.; Wagener, J.S. The diagnostic value of bronchoalveolar lavage in immunocompetent children with chronic diffuse pulmonary infiltrates. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 1997, 23, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, L.L.; Deterding, R.R.; Langston, C. Pediatric interstitial lung disease revisited. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2004, 38, 369–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lelii, M.; Patria, M.F.; Pinzani, R.; Tenconi, R.; Mori, A.; Bonelli, N.; Principi, N.; Esposito, S. Role of High-Resolution Chest Computed Tomography in a Child with Persistent Tachypnoea and Intercostal Retractions: A Case Report of Neuroendocrine Cell Hyperplasia. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 1113. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph14101113
Lelii M, Patria MF, Pinzani R, Tenconi R, Mori A, Bonelli N, Principi N, Esposito S. Role of High-Resolution Chest Computed Tomography in a Child with Persistent Tachypnoea and Intercostal Retractions: A Case Report of Neuroendocrine Cell Hyperplasia. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2017; 14(10):1113. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph14101113
Chicago/Turabian StyleLelii, Mara, Maria Francesca Patria, Raffaella Pinzani, Rossana Tenconi, Alessandro Mori, Nicola Bonelli, Nicola Principi, and Susanna Esposito. 2017. "Role of High-Resolution Chest Computed Tomography in a Child with Persistent Tachypnoea and Intercostal Retractions: A Case Report of Neuroendocrine Cell Hyperplasia" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 14, no. 10: 1113. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph14101113
APA StyleLelii, M., Patria, M. F., Pinzani, R., Tenconi, R., Mori, A., Bonelli, N., Principi, N., & Esposito, S. (2017). Role of High-Resolution Chest Computed Tomography in a Child with Persistent Tachypnoea and Intercostal Retractions: A Case Report of Neuroendocrine Cell Hyperplasia. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 14(10), 1113. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph14101113





