Analysis of Heavy Metal Sources in the Soil of Riverbanks Across an Urbanization Gradient
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Sample Collection and Measurement
2.3. Statistical Data Analysis
2.4. Multiple Source Data Integration and Geographical Detector Method
2.4.1. Multiple Source Data Integration
2.4.2. Geographical Detector Method
3. Results
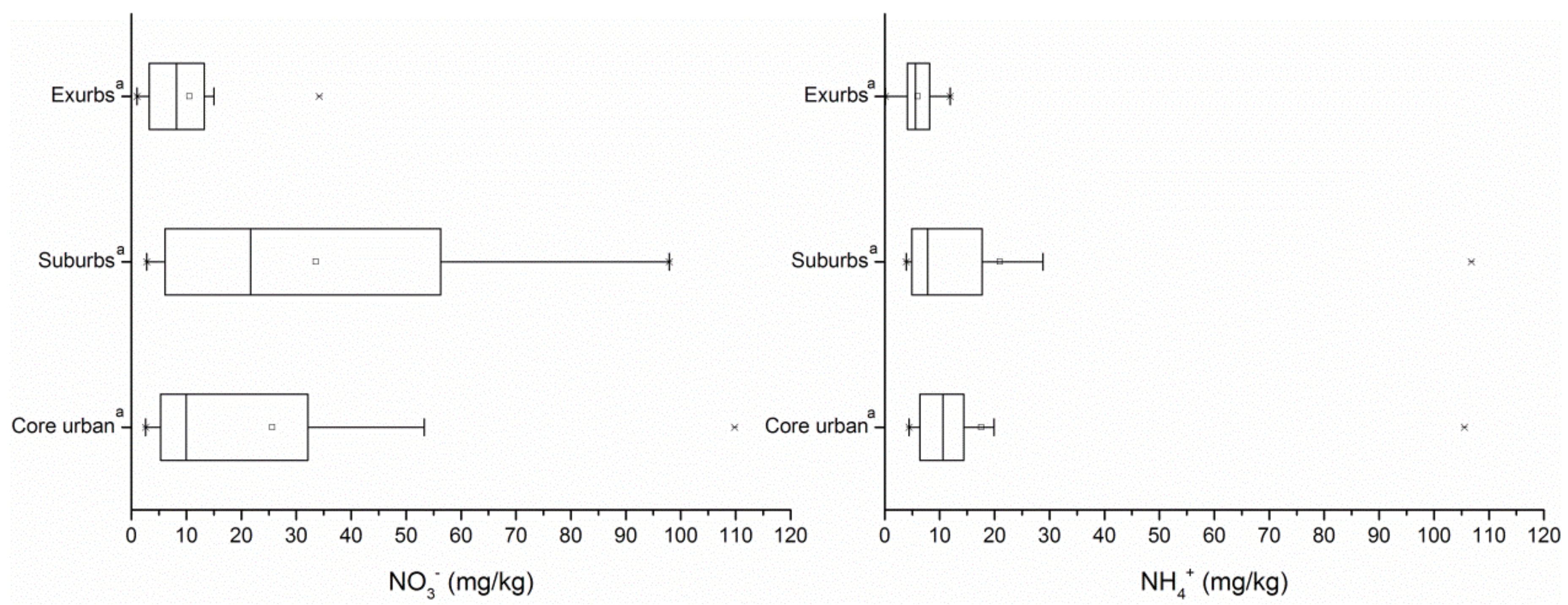
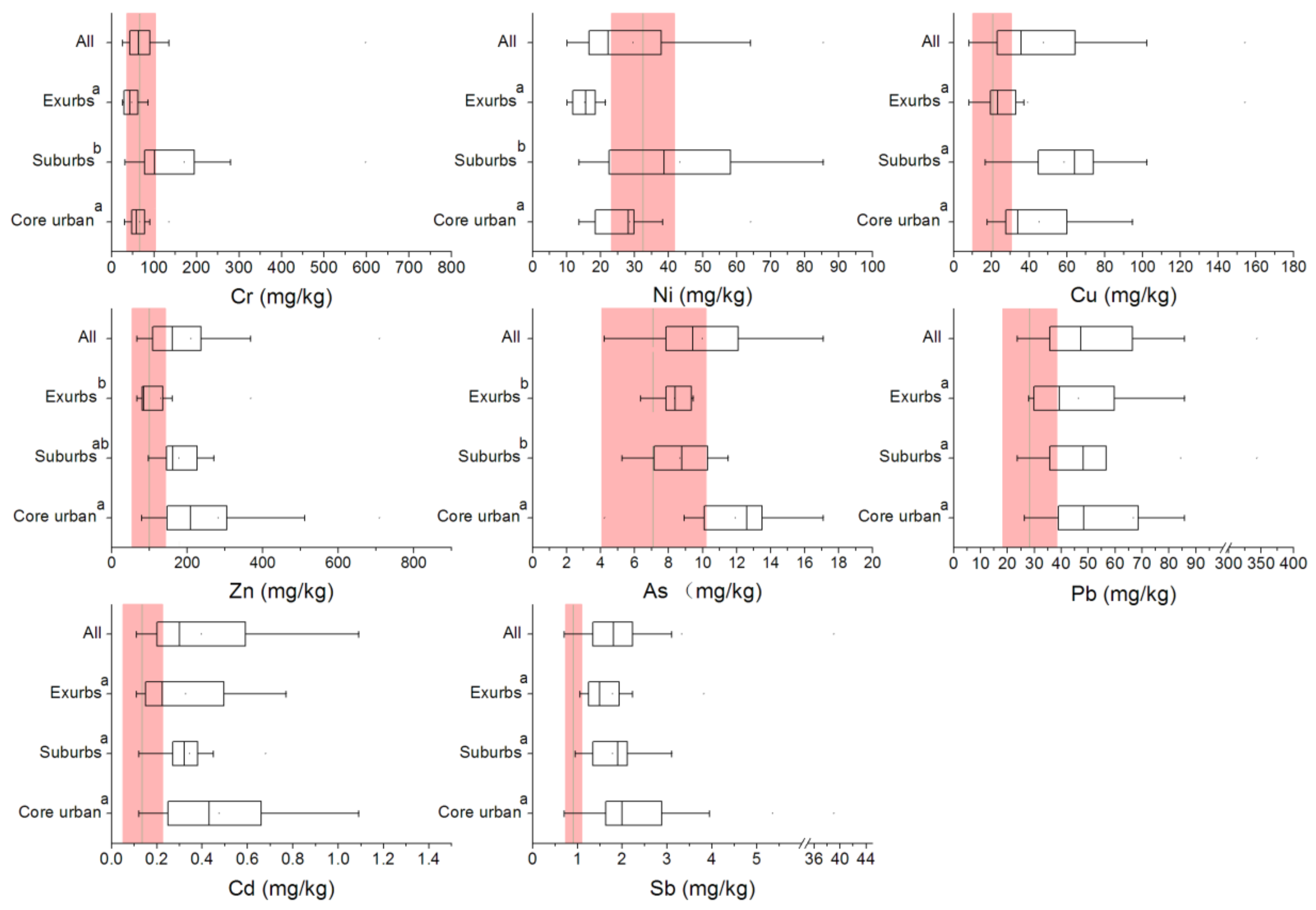
3.1. Descriptive Statistics of Heavy Metal Concentrations in the Different Urban Gradients and Background Values
3.2. The Spatial Distribution of the Heavy Metals during the Urbanization Gradients
3.3. Source Apportionment for Heavy Metals
3.3.1. Correlation Analysis
3.3.2. PCA Analysis
3.3.3. Cluster Analysis
3.3.4. Geodetector Model
4. Discussion
4.1. PAC-MLR Methods and Geodetector Model for Source Apportionment of Soil Heavy Metal
4.2. Analysis of Pollution Sources
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wong, C.S.; Li, X.; Thornton, I. Urban environmental geochemistry of trace metals. Environ. Pollut. 2006, 142, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hu, B.; Jia, X.; Hu, J.; Xu, D.; Xia, F.; Li, Y. Assessment of heavy metal pollution and health risks in the soil-plant-human system in the Yangtze river delta, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, R.; Wang, M.; Chen, W.; Peng, C. Spatial pattern of heavy metals accumulation risk in urban soils of Beijing and its influencing factors. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 210, 174–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Trujillo-González, J.M.; Torres-Mora, M.A.; Keesstra, S.; Brevik, E.C.; Jiménez-Ballesta, R. Heavy metal accumulation related to population density in road dust samples taken from urban sites under different land uses. Sci. Total. Environ. 2016, 553, 636–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, D.; O’Connor, D.; Nathanail, P.; Tian, L.; Ma, Y. Integrated gis and multivariate statistical analysis for regional scale assessment of heavy metal soil contamination: A critical review. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 231, 1188–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Christakos, G.; Guo, M.; Xiao, L.; Huang, W. Space-time quantitative source apportionment of soil heavy metal concentration increments. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 223, 560–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, T.; Chang, Q.; Liu, J.; Clevers, J.; Kooistra, L. Identification of soil heavy metal sources and improvement in spatial mapping based on soil spectral information: A case study in northwest China. Sci. Total. Environ. 2016, 565, 155–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yesilonis, I.D.; Pouyat, R.V.; Neerchal, N.K. Spatial distribution of metals in soils in Baltimore, maryland: Role of native parent material, proximity to major roads, housing age and screening guidelines. Environ. Pollut. 2008, 156, 723–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, A.; Wang, J.; Qin, X.; Wang, K.; Han, P.; Zhang, S. Multivariate and geostatistical analyses of the spatial distribution and origin of heavy metals in the agricultural soils in Shunyi, Beijing, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 425, 66–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, J.F.; Li, X.H.; Christakos, G.; Liao, Y.L.; Zhang, T.; Gu, X.; Zheng, X.Y. Geographical detectors-based health risk assessment and its application in the neural tube defects study of the Heshun region, China. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2010, 24, 107–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.F.; Zhang, T.L.; Fu, B.J. A measure of spatial stratified heterogeneity. Ecolog. Indic. 2016, 67, 250–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, B.; Zhao, R.; Chen, S.; Zhou, Y.; Jin, B.; Li, Y.; Shi, Z. Heavy metal pollution delineation based on uncertainty in a coastal industrial city in the Yangtze river delta, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.; Yang, S. Heavy metal enrichments in the Changjiang (Yangtze river) catchment and on the inner shelf of the east China sea over the last 150 years. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 543, 105–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Han, T.; Ding, Y.; Sun, J.; Wang, F.; Zhu, C. Heavy metal pollution in a soil-rice system in the Yangtze river region of China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2015, 13, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The Chinese state council. The report of environmental protection work of the 23rd Meeting of the 11th Standing Committee of the National People’s Congress. 2011. Available online: http://www.npc.gov.cn/huiyi/ztbg/gwygyhjbhgzqkbg/2011-10/26/content_1677000.htm (accessed on 12 September 2018).
- Yin, S.; Wu, Y.; Xu, W.; Li, Y.; Shen, Z.; Feng, C. Contribution of the upper river, the estuarine region, and the adjacent sea to the heavy metal pollution in the Yangtze estuary. Chemosphere 2016, 155, 564–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ministry of Environmental Protection and Ministry of Land and Resources. China’s Soil Pollution Status Bulletin. 2014. Available online: http://www.gov.cn/foot/2014-04/17/content_2661768.htm (accessed on 12 September 2018).
- Wang, S.L.; Xu, X.R.; Sun, Y.X.; Liu, J.L.; Li, H.B. Heavy metal pollution in coastal areas of south China: A review. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2013, 76, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, Y.; Li, D.; Zhang, N. Comparison of interpolation models for estimating heavy metals in soils under various spatial characteristics and sampling methods. Trans. GIS 2018, 22, 409–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Lee, S.L.; Wong, S.C.; Shi, W.; Thornton, I. The study of metal contamination in urban soils of Hong Kong using a gis-based approach. Environ. Pollut. 2004, 129, 113–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, C.S.; Li, X.; Shi, W.; Cheung, S.C.; Thornton, I. Metal contamination in urban, suburban, and country park soils of Hong Kong: A study based on gis and multivariate statistics. Sci. Total Environ. 2006, 356, 45–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bai, J.; Jia, J.; Zhang, G.; Zhao, Q.; Lu, Q.; Cui, B.; Liu, X. Spatial and temporal dynamics of heavy metal pollution and source identification in sediment cores from the short-term flooding riparian wetlands in a Chinese delta. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 219, 379–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.; Cheng, H. A method for apportionment of natural and anthropogenic contributions to heavy metal loadings in the surface soils across large-scale regions. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 214, 400–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Wang, D.; Wang, Q.; Liu, S.; Zhu, Y.; Wu, W. Impacts from land use pattern on spatial distribution of cultivated soil heavy metal pollution in typical rural-urban fringe of northeast China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Q.; Li, Z.; Lu, X.; Duan, Q.; Huang, L.; Bi, J. A review of soil heavy metal pollution from industrial and agricultural regions in China: Pollution and risk assessment. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 642, 690–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, X.D.; Tang, M.P.; Lu, Y.C.; Hong, L.X.; Tian, D.L. Forest inventory in China: Status and challenges. Int. For. Rev. 2009, 11, 52–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaral, S.; Monteiro, A.M.V.; Camara, G.; Quintanilha, J.A. Dmsp/ols night-time light imagery for urban population estimates in the Brazilian amazon. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2006, 27, 855–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Lin, Q.; Shi, P. Spatial pattern and influencing factors of landslide casualty events. J. Geol. Sci. 2018, 28, 259–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Deng, L.; Zuo, S.; Luo, Y.; Shao, G.; Wei, X.; Hua, L.; Yang, Y. Geographical modeling of spatial interaction between human activity and forest connectivity in an urban landscape of southeast China. Landsc. Ecol. 2014, 29, 1741–1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Wang, X.; Xu, J.; Xu, C.; Lu, D.; Ye, C.; Wang, Z.; Bai, L. Quantifying the influence of natural and socioeconomic factors and their interactive impact on PM2.5 pollution in China. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 241, 475–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- China National Environmental Monitoring Centre. The Soil Element Background Values in China; China Environmental Science Press: Beijing, China, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Environmental Protection Bureau and Quality and Technology Supervision Bureau. Environmental Quality Standard for Soils. 1995. Available online: http://bz.mep.gov.cn/bzwb/trhj/trhjzlbz/199603/W020070313485587994018.pdf (accessed on 12 September 2019).
- Huang, Y.; Deng, M.; Wu, S.; Japenga, J.; Li, T.; Yang, X.; He, Z. A modified receptor model for source apportionment of heavy metal pollution in soil. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 354, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahodaran, N.K.; Ray, J.G. Heavy metal contamination in “chemicalized’ green revolution banana fields in southern India. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mugosa, B.; Durovic, D.; Nedovic-Vukovic, M.; Barjaktarovic-Labovic, S.; Vrvic, M. Assessment of ecological risk of heavy metal contamination in coastal municipalities of Montenegro. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2016, 13, 393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, L.; Yang, Z.; Li, L.; Wang, L. Source identification and risk assessment of heavy metal contaminations in urban soils of Changsha, a mine-impacted city in southern China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2016, 23, 17058–17066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, F.; Qu, L.; Wang, T.; Luo, L.; Chen, H.; Dahlgren, R.A.; Zhang, M.; Mei, K.; Huang, H. Distribution and source analysis of heavy metal pollutants in sediments of a rapid developing urban river system. Chemosphere 2018, 207, 218–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Omwene, P.I.; Oncel, M.S.; Celen, M.; Kobya, M. Heavy metal pollution and spatial distribution in surface sediments of Mustafakemalpasa stream located in the world’s largest Borate basin (Turkey). Chemosphere 2018, 208, 782–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiao, P.; Lei, M.; Guo, G.; Yang, J.; Zhou, X.; Chen, T. Quantitative analysis of the factors influencing soil heavy metal lateral migration in rainfalls based on Geographical detector software: A case study in Huanjiang county, China. Sustainability 2017, 9, 1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, B.; Jiang, X.; Duan, X.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, J.; Tang, J.; Sun, G. An integrated h-g scheme identifying areas for soil remediation and primary heavy metal contributors: A risk perspective. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fei, X.; Lou, Z.; Christakos, G.; Ren, Z.; Liu, Q.; Lv, X. The association between heavy metal soil pollution and stomach cancer: A case study in Hangzhou city, China. Environ. Geochem. Health 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, T.; Hu, Z.; Shi, Z.; Guo, L.; Chen, Y.; Li, Q.; Wu, G. Geo-detection of factors controlling spatial patterns of heavy metals in urban topsoil using multi-source data. Sci. Total. Environ. 2018, 643, 451–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, Y.; Deng, L.Y.; Zuo, S.D.; Song, X.D.; Liao, Y.L.; Xu, C.D.; Chen, Q.; Hua, L.Z.; Li, Z.W. Quantifying the influences of various ecological factors on land surface temperature of urban forests. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 216, 519–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, X.; Feng, L. Spatial distribution of hazardous elements in urban topsoils surrounding Xi’an industrial areas, (China): Controlling factors and contamination assessments. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 174, 662–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Y.; Cao, J.; Posmentier, E.S.; Fung, K.; Tian, H.; An, Z. Particulate-associated potentially harmful elements in urban road dusts in Xi’an, China. Appl. Geochem. 2008, 23, 835–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Lu, X.; Yang, G. Sources identification of heavy metals in urban topsoil from inside the Xi’an second ringroad, China using multivariate statistical methods. CATENA 2012, 98, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Liao, Q.; Shao, S.; Zhang, N.; Shen, Q.; Liu, C. Heavy metal pollution, fractionation, and potential ecological risks in sediments from lake Chaohu (eastern China) and the surrounding rivers. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2015, 12, 14115–14131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yizhi, H. Background value and its differentiation characteristics of soil environment in Ningbo city. Environ. Pollut. Control 1991, 13, 25–27. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Chu, Z.; Yang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Sun, L.; Yang, W.; Yang, L.; Gao, Y. Assessment of heavy metal contamination from penguins and anthropogenic activities on fildes peninsula and ardley island, antarctic. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 646, 951–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Velzen, D.; Langenkamp, H.; Herb, G. Antimony, its sources, applications and flow paths into urban and industrial waste: A review. Waste Manag. Res. 1998, 16, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Zhu, T.; Li, M.; He, J.; Huang, R. Heavy metal contamination in soil and brown rice and human health risk assessment near three mining areas in central China. J. Healthc Eng. 2017, 2017, 4124302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, C.; Guo, X.; Yin, S.; Tian, C.; Li, Y.; Shen, Z. Heavy metal partitioning of suspended particulate matter-water and sediment-water in the Yangtze estuary. Chemosphere 2017, 185, 717–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rastmanesh, F.; Safaie, S.; Zarasvandi, A.R.; Edraki, M. Heavy metal enrichment and ecological risk assessment of surface sediments in Khorramabad river, west Iran. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2018, 190, 273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yaylalı-Abanuz, G. Heavy metal contamination of surface soil around Gebze industrial area, Turkey. Microchem. J. 2011, 99, 82–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, A.; Gunawardana, C.; Gunawardena, J.; Egodawatta, P.; Ayoko, G.A.; Goonetilleke, A. Taxonomy of factors which influence heavy metal build-up on urban road surfaces. J. Hazard. Mater. 2016, 310, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- El Zrelli, R.; Courjault-Rade, P.; Rabaoui, L.; Castet, S.; Michel, S.; Bejaoui, N. Heavy metal contamination and ecological risk assessment in the surface sediments of the coastal area surrounding the industrial complex of Gabes city, Gulf of gabes, SE Tunisia. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 101, 922–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhatia, A.; Singh, S.; Kumar, A. Heavy metal contamination of soil, irrigation water and vegetables in peri-urban agricultural areas and markets of Delhi. Water Environ. Res. 2015, 87, 2027–2034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Heavy Metal | Class I | Class II | Class III | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cr≤ | 90 | 150 | 200 | 250 | 300 |
| Ni≤ | 40 | 40 | 50 | 60 | 200 |
| Cu≤ | 35 | 50 | 100 | 100 | 400 |
| Zn≤ | 100 | 200 | 250 | 300 | 500 |
| As≤ | 15 | 20 | 25 | 30 | 30 |
| Cd≤ | 0.20 | 0.30 | 0.30 | 0.60 | 1.0 |
| Pb≤ | 35 | 250 | 300 | 350 | 500 |
| Cr | Ni | Cu | Zn | As | Cd | Sb | Pb | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean Prediction Errors | −2.3668 | −0.1954 | 0.1942 | 1.0176 | 0.1171 | 0.0022 | −0.0927 | −1.1284 |
| RMSE | 72.9 | 14.8 | 27.4 | 14.6 | 3 | 0.3 | 5.5 | 54.3 |
| Factors | pH | OM | NH4+ | NO3−-N | Cr | Ni | Cu | Zn | As | Cd | Sb | Pb | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Core urban region | pH | 1.000 | 0.092 | 0.313 | −0.292 | 0.025 | 0.082 | 0.072 | 0.115 | −0.091 | 0.321 | −0.133 | −0.138 |
| OM | 1.000 | 0.008 | 0.099 | 0.285 | 0.255 | 0.606 * | 0.477 | 0.442 | 0.535 | 0.154 | 0.265 | ||
| NH4+ | 1.000 | −0.082 | 0.768 ** | 0.835 ** | 0.306 | −0.101 | 0.168 | −0.232 | −0.075 | −0.197 | |||
| NO3−-N | 1.000 | −0.070 | −0.094 | −0.208 | −0.191 | −0.150 | −0.184 | −0.162 | 0.008 | ||||
| Cr | 1.000 | 0.967 ** | 0.697 ** | 0.186 | 0.517 | 0.127 | 0.286 | 0.145 | |||||
| Ni | 1.000 | 0.651 * | 0.203 | 0.534 | 0.093 | 0.230 | 0.109 | ||||||
| Cu | 1.000 | 0.695 ** | 0.645 * | 0.470 | 0.637 * | 0.370 | |||||||
| Zn | 1.000 | 0.680 * | 0.534 | 0.446 | 0.487 | ||||||||
| As | 1.000 | 0.414 | 0.499 | 0.221 | |||||||||
| Cd | 1.000 | 0.240 | 0.184 | ||||||||||
| Sb | 1.000 | 0.004 | |||||||||||
| Pb | 1.000 | ||||||||||||
| Suburb | pH | 1.000 | −0.145 | −0.152 | 0.364 | −0.145 | −0.348 | −0.393 | −0.305 | −0.178 | −0.420 | −0.333 | −0.346 |
| OM | 1.000 | 0.103 | 0.600 | 0.340 | 0.427 | 0.461 | 0.479 | −0.200 | 0.052 | 0.035 | 0.231 | ||
| NH4+ | 1.000 | 0.055 | −0.207 | −0.094 | −0.106 | −0.045 | −0.568 | 0.741 * | −0.026 | −0.059 | |||
| NO3−-N | 1.000 | −0.015 | 0.218 | 0.108 | 0.152 | −0.276 | −0.166 | −0.594 | 0.174 | ||||
| Cr | 1.000 | 0.746 * | 0.735 * | 0.731 * | 0.158 | 0.225 | 0.539 | −0.198 | |||||
| Ni | 1.000 | 0.921 ** | 0.954 ** | 0.226 | 0.287 | −0.009 | −0.230 | ||||||
| Cu | 1.000 | 0.972 ** | 0.439 | 0.116 | 0.164 | −0.012 | |||||||
| Zn | 1.000 | 0.284 | 0.211 | 0.071 | −0.218 | ||||||||
| As | 1.000 | −0.558 | 0.110 | 0.336 | |||||||||
| Cd | 1.000 | 0.185 | −0.360 | ||||||||||
| Sb | 1.000 | 0.164 | |||||||||||
| Pb | 1.000 | ||||||||||||
| Exurb | pH | 1.000 | −0.292 | −0.664 | 0.367 | 0.700 | 0.738* | 0.591 | 0.618 | 0.641 | 0.598 | 0.711 * | 0.617 |
| OM | 1.000 | 0.220 | −0.545 | 0.073 | −0.045 | 0.459 | 0.460 | −0.471 | 0.478 | 0.381 | 0.341 | ||
| NH4+ | 1.000 | 0.160 | −0.562 | −0.511 | −0.717 * | −0.689 | −0.831* | −0.405 | −0.695 | −0.641 | |||
| NO3−-N | 1.000 | 0.356 | 0.383 | −0.323 | −0.342 | 0.051 | −0.352 | −0.240 | −0.426 | ||||
| Cr | 1.000 | 0.956 ** | 0.704 | 0.647 | 0.565 | 0.384 | 0.667 | 0.350 | |||||
| Ni | 1.000 | 0.610 | 0.571 | 0.651 | 0.382 | 0.599 | 0.301 | ||||||
| Cu | 1.000 | 0.988 ** | 0.456 | 0.809 * | 0.970 ** | 0.855 ** | |||||||
| Zn | 1.000 | 0.415 | 0.869 ** | 0.990 ** | 0.908 ** | ||||||||
| As | 1.000 | 0.207 | 0.433 | 0.340 | |||||||||
| Cd | 1.000 | 0.889 ** | 0.928 ** | ||||||||||
| Sb | 1.000 | 0.925 ** | |||||||||||
| Pb | 1.000 | ||||||||||||
| Whole study area | pH | 1 | −0.352 | 0.194 | 0.207 | 0.173 | 0.293 | 0.297 | 0.358 | 0.239 | 0.331 | 0.061 | 0.075 |
| OM | 1 | −0.054 | −0.017 | 0.011 | −0.028 | 0.372 * | 0.238 | −0.002 | 0.331 | 0.06 | 0.094 | ||
| NH4+ | 1 | 0.061 | 0.043 | 0.326 | 0.077 | −0.02 | −0.033 | 0.044 | −0.034 | −0.056 | |||
| NO3−-N | 1 | 0.117 | 0.245 | −0.014 | −0.05 | −0.098 | −0.142 | −0.117 | 0.149 | ||||
| Cr | 1 | 0.773 ** | 0.504 ** | 0.132 | 0.018 | 0.047 | 0.017 | −0.026 | |||||
| Ni | 1 | 0.604 ** | 0.275 | 0.237 | 0.115 | 0.09 | 0.022 | ||||||
| Cu | 1 | 0.588 ** | 0.324 | 0.444 * | 0.322 | 0.228 | |||||||
| Zn | 1 | 0.678 ** | 0.600 ** | 0.480 ** | 0.233 | ||||||||
| As | 1 | 0.328 | 0.492 ** | 0.205 | |||||||||
| Cd | 1 | 0.281 | 0.052 | ||||||||||
| Sb | 1 | 0.019 | |||||||||||
| Pb | 1 |
| Elements | Core Urban | Whole Region | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Factor 1 | Factor 2 | Factor 3 | Factor 1 | Factor 2 | Factor 3 | |
| Cr | 0.739 | −0.638 | 0.136 | 0.473 | 0.800 | −0.038 |
| Ni | 0.718 | −0.656 | 0.146 | 0.622 | 0.688 | −0.014 |
| Cu | 0.940 | −0.002 | −0.020 | 0.827 | 0.253 | 0.096 |
| Zn | 0.748 | 0.543 | 0.057 | 0.844 | −0.335 | 0.002 |
| As | 0.830 | 0.068 | −0.124 | 0.684 | −0.406 | 0.002 |
| Cd | 0.522 | 0.500 | −0.122 | 0.611 | −0.306 | −0.183 |
| Sb | 0.616 | 0.117 | −0.589 | 0.561 | −0.397 | −0.322 |
| Pb | 0.393 | 0.379 | 0.764 | 0.255 | −0.179 | −0.927 |
| Initial Eigenvalues | 4.002 | 1.545 | 1.005 | 3.228 | 1.738 | 1.009 |
| Variance % | 50.021 | 19.310 | 12.559 | 40.347 | 21.727 | 12.607 |
| Cumulative % | 50.021 | 69.331 | 81.890 | 40.347 | 62.074 | 74.680 |
| Urban Gradient | Element | SDi | SPo | SDe | Ele | pH | NH4+ | NO3−-N | OM | ST | HD | SI | GLAr | DS | Ag | 1CLU | 2CLU | AAr | Iar | Tar | RRL | NTL |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Core urban region | Cr | 0.095 | 0.095 | 0.101 | 0.002 | 0.043 | 0.555 | 0.213 | 0.193 | 0.272 | 0.115 | 0.037 | 0.022 | 0.015 | 0.027 | 0.018 | 0.194 | 0.065 | 0.001 | 0.038 | 0.024 | 0.162 |
| Ni | 0.087 | 0.087 | 0.094 | 0.000 | 0.018 | 0.657 | 0.162 | 0.134 | 0.220 | 0.100 | 0.021 | 0.025 | 0.013 | 0.026 | 0.033 | 0.173 | 0.084 | 0.001 | 0.040 | 0.009 | 0.114 | |
| Cu | 0.002 | 0.002 | 0.001 | 0.002 | 0.094 | 0.078 | 0.036 | 0.221 | 0.033 | 0.006 | 0.014 | 0.006 | 0.016 | 0.021 | 0.015 | 0.102 | 0.035 | 0.002 | 0.018 | 0.012 | 0.263 | |
| Zn | 0.156 | 0.156 | 0.151 | 0.000 | 0.435 | 0.378 | 0.144 | 0.376 | 0.298 | 0.168 | 0.040 | 0.015 | 0.026 | 0.023 | 0.010 | 0.075 | 0.006 | 0.002 | 0.010 | 0.002 | 0.095 | |
| As | 0.072 | 0.072 | 0.070 | 0.000 | 0.079 | 0.169 | 0.147 | 0.396 | 0.180 | 0.077 | 0.035 | 0.011 | 0.028 | 0.022 | 0.084 | 0.150 | 0.090 | 0.001 | 0.005 | 0.003 | 0.025 | |
| Cd | 0.042 | 0.042 | 0.047 | 0.000 | 0.030 | 0.032 | 0.124 | 0.088 | 0.056 | 0.057 | 0.006 | 0.004 | 0.026 | 0.012 | 0.013 | 0.046 | 0.021 | 0.001 | 0.003 | 0.007 | 0.106 | |
| Sb | 0.156 | 0.156 | 0.150 | 0.000 | 0.373 | 0.038 | 0.095 | 0.161 | 0.157 | 0.156 | 0.006 | 0.006 | 0.014 | 0.014 | 0.002 | 0.091 | 0.001 | 0.002 | 0.011 | 0.005 | 0.333 | |
| Pb | 0.013 | 0.013 | 0.012 | 0.001 | 0.156 | 0.085 | 0.085 | 0.182 | 0.101 | 0.013 | 0.022 | 0.004 | 0.020 | 0.010 | 0.002 | 0.026 | 0.001 | 0.004 | 0.015 | 0.035 | 0.015 | |
| Suburb | Cr | 0.163 | 0.179 | 0.163 | NA | 0.008 | 0.383 | 0.164 | 0.124 | 0.188 | 0.162 | 0.032 | 0.001 | 0.026 | 0.015 | 0.010 | 0.107 | 0.023 | 0.001 | 0.003 | 0.018 | 0.075 |
| Ni | 0.079 | 0.110 | 0.079 | NA | 0.050 | 0.445 | 0.150 | 0.190 | 0.117 | 0.085 | 0.035 | 0.001 | 0.039 | 0.019 | 0.010 | 0.073 | 0.004 | 0.002 | 0.006 | 0.015 | 0.069 | |
| Cu | 0.060 | 0.113 | 0.060 | NA | 0.052 | 0.361 | 0.140 | 0.289 | 0.131 | 0.082 | 0.048 | 0.002 | 0.056 | 0.015 | 0.008 | 0.073 | 0.014 | 0.000 | 0.004 | 0.018 | 0.017 | |
| Zn | 0.058 | 0.096 | 0.058 | NA | 0.036 | 0.343 | 0.164 | 0.284 | 0.121 | 0.079 | 0.035 | 0.002 | 0.052 | 0.013 | 0.007 | 0.062 | 0.010 | 0.000 | 0.008 | 0.019 | 0.023 | |
| As | 0.004 | 0.065 | 0.004 | NA | 0.003 | 0.600 | 0.169 | 0.041 | 0.115 | 0.026 | 0.052 | 0.000 | 0.073 | 0.011 | 0.000 | 0.061 | 0.050 | 0.001 | 0.004 | 0.016 | 0.104 | |
| Cd | 0.015 | 0.029 | 0.015 | NA | 0.072 | 0.699 | 0.350 | 0.122 | 0.097 | 0.018 | 0.016 | 0.000 | 0.065 | 0.013 | 0.010 | 0.054 | 0.101 | 0.003 | 0.005 | 0.022 | 0.017 | |
| Sb | 0.086 | 0.102 | 0.086 | NA | 0.030 | 0.072 | 0.202 | 0.251 | 0.102 | 0.088 | 0.016 | 0.003 | 0.030 | 0.007 | 0.005 | 0.103 | 0.026 | 0.002 | 0.003 | 0.004 | 0.268 | |
| Pb | 0.015 | 0.036 | 0.015 | NA | 0.022 | 0.425 | 0.219 | 0.198 | 0.031 | 0.022 | 0.016 | 0.001 | 0.025 | 0.009 | 0.003 | 0.047 | 0.213 | 0.000 | 0.005 | 0.010 | 0.407 | |
| Exurb | Cr | 0.043 | 0.048 | 0.057 | 0.191 | 0.583 | 0.217 | 0.337 | 0.143 | 0.006 | 0.020 | 0.042 | 0.082 | 0.136 | 0.055 | 0.123 | 0.200 | 0.090 | NA | NA | 0.046 | 0.075 |
| Ni | 0.059 | 0.064 | 0.076 | 0.225 | 0.519 | 0.416 | 0.420 | 0.174 | 0.004 | 0.027 | 0.049 | 0.106 | 0.157 | 0.055 | 0.156 | 0.242 | 0.192 | NA | NA | 0.046 | 0.103 | |
| Cu | 0.010 | 0.063 | 0.014 | 0.054 | 0.314 | 0.114 | 0.036 | 0.092 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.004 | 0.016 | 0.076 | 0.055 | 0.066 | 0.111 | 0.017 | NA | NA | 0.206 | 0.008 | |
| Zn | 0.010 | 0.054 | 0.012 | 0.054 | 0.361 | 0.122 | 0.041 | 0.070 | 0.001 | 0.002 | 0.013 | 0.012 | 0.084 | 0.052 | 0.058 | 0.108 | 0.025 | NA | NA | 0.187 | 0.008 | |
| As | 0.013 | 0.085 | 0.073 | 0.069 | 0.608 | 0.391 | 0.025 | 0.353 | 0.000 | 0.005 | 0.031 | 0.018 | 0.087 | 0.033 | 0.177 | 0.193 | 0.030 | NA | NA | 0.111 | 0.003 | |
| Cd | 0.023 | 0.025 | 0.056 | 0.142 | 0.563 | 0.077 | 0.066 | 0.111 | 0.001 | 0.002 | 0.098 | 0.030 | 0.130 | 0.044 | 0.051 | 0.135 | 0.047 | NA | NA | 0.097 | 0.002 | |
| Sb | 0.014 | 0.043 | 0.018 | 0.088 | 0.513 | 0.134 | 0.007 | 0.055 | 0.000 | 0.001 | 0.049 | 0.012 | 0.113 | 0.056 | 0.064 | 0.115 | 0.023 | NA | NA | 0.170 | 0.006 | |
| Pb | 0.012 | 0.033 | 0.020 | 0.084 | 0.467 | 0.158 | 0.055 | 0.076 | 0.003 | 0.004 | 0.072 | 0.015 | 0.125 | 0.050 | 0.058 | 0.124 | 0.049 | NA | NA | 0.173 | 0.001 |
| Study Area | Heavy Metal | Interactive Effect Combinations |
|---|---|---|
| Core urban | Cu | SDe∩SDi; SDe∩SPo; NH4+∩SDi; NH4+∩SPo; NH4∩SDe; NH4+∩pH; NH4+∩ST; NH4+∩HD; NH4+∩NO3−-N; GLAr∩SDi; GLAr∩SPo; GLAr∩SDe; GLAr∩NO3−-N; GLAr∩HD; NO3−-N∩LU1 |
| Sb | Ele∩AAr; | |
| Suburb | Cr | pH∩NO3−-N; |
| Ni | pH∩NO3−-N; | |
| Cu | pH∩NO3−-N; AAr∩Ag; | |
| Zn | pH∩NO3−-N; LU1∩Ag; AAr∩Ag; | |
| As | pH∩NO3−-N; pH∩OM; pH∩LU1; LU1∩IAr; | |
| Pb | pH∩NO3−-N; pH∩OM; LU1∩Ag; SD∩Ag; | |
| Exurb | Cr | HD∩SI; SI∩Ag; RRL∩OM; |
| Ni | HD∩SI; SI∩Ag; | |
| Cu | SDi∩SPo; SDi∩SDe; SDi∩HD; SDi∩SD; SDe∩SI; Ele∩OM; pH∩OM; LU1∩OM; | |
| Zn | SDi∩SPo; SDi∩SDe; SDi∩HD; SDe∩OM; LU1∩OM; LU2∩OM; GLAr∩OM; | |
| Cd | SDi∩SPo; SDi∩HD; Ag∩SPo; | |
| Sb | SDi∩SPo; SDi∩SDe; SDi∩HD; SDe∩NO3−-N; SDe∩OM; Ele∩OM; GLAr∩NO3−-N; OM∩NO3−-N; LU1∩NO3−-N; | |
| Pb | SDi∩SPo; SDi∩SDe; SDi∩HD; SDe∩OM; Ele∩NO3−-N; Ele∩OM; |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zuo, S.; Dai, S.; Li, Y.; Tang, J.; Ren, Y. Analysis of Heavy Metal Sources in the Soil of Riverbanks Across an Urbanization Gradient. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 2175. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15102175
Zuo S, Dai S, Li Y, Tang J, Ren Y. Analysis of Heavy Metal Sources in the Soil of Riverbanks Across an Urbanization Gradient. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2018; 15(10):2175. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15102175
Chicago/Turabian StyleZuo, Shudi, Shaoqing Dai, Yaying Li, Jianfeng Tang, and Yin Ren. 2018. "Analysis of Heavy Metal Sources in the Soil of Riverbanks Across an Urbanization Gradient" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 15, no. 10: 2175. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15102175
APA StyleZuo, S., Dai, S., Li, Y., Tang, J., & Ren, Y. (2018). Analysis of Heavy Metal Sources in the Soil of Riverbanks Across an Urbanization Gradient. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 15(10), 2175. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15102175





