The Epidemiological Influence of Climatic Factors on Shigellosis Incidence Rates in Korea
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Collection
2.2. Statistical Analysis
- Equation (1). GAM for evaluating the effect of temperature
- Equation (2). GAM for evaluating the effect of precipitation
- Equation (3). GAM for smoothing plots
- Equation (4). GAM for seasonality stratification
3. Results
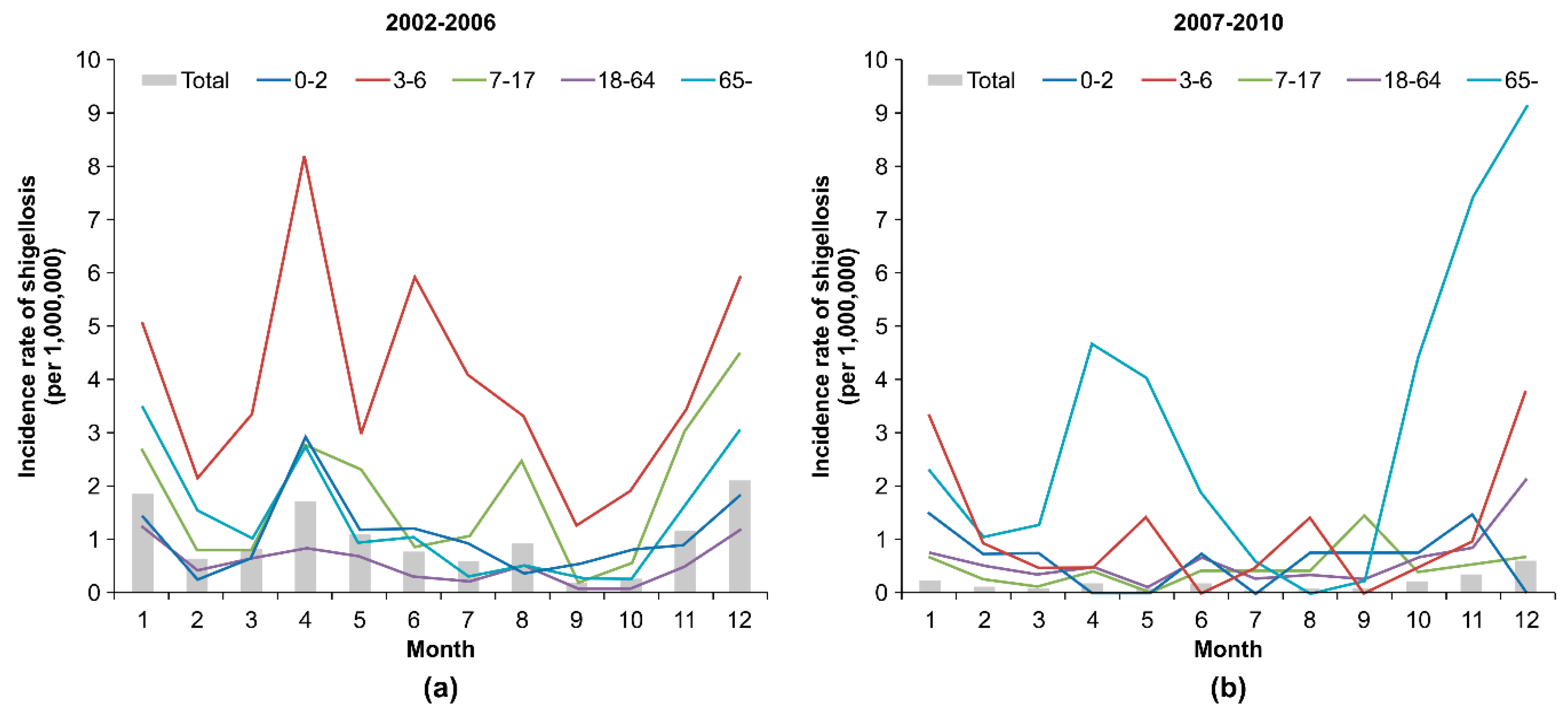
3.1. Distribution of Shigellosis Incidence across the Seasons according to Age
3.2. Association between Climatic Factors and the Incidence of Shigellosis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kotloff, K.L.; Winickoff, J.P.; Ivanoff, B.; Clemens, J.D.; Swerdlow, D.L.; Sansonetti, P.J.; Adak, G.K.; Levine, M.M. Global burden of Shigella infections: Implications for vaccine development and implementation of control strategies. Bull. World Health Organ. 1999, 77, 651–666. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sack, R.B.; Rahman, M.; Yunus, M.; Khan, E.H. Antimicrobial resistance in organisms causing diarrheal disease. Clin. Infect. Dis. 1997, 24, S102–S105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heymann, D.L. Control of Communicable Diseases Manual; American Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.C.; Jeong, Y.S.; Oh, J.Y.; Kang, H.Y.; Kim, K.H.; Kim, J.; Lee, Y.C.; Cho, D.T.; Seol, S.Y. Epidemiology of shigellosis in Korea. J. Bacteriol. Virol. 2006, 36, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.C.; Oh, J.Y.; Kim, K.S.; Jeong, Y.W.; Cho, J.W.; Park, J.C.; Seol, S.Y.; Cho, D.T. Antimicrobial resistance of Shigella sonnei in Korea during the last two decades. Apmis 2001, 109, 228–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seol, S.Y.; Kim, Y.T.; Jeong, Y.S.; Oh, J.Y.; Kang, H.Y.; Moon, D.C.; Kim, J.; Lee, Y.C.; Cho, D.T.; Lee, J.C. Molecular characterization of antimicrobial resistance in Shigella sonnei isolates in Korea. J. Med. Microbiol. 2006, 55, 871–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.-J.; Lin, C.-Y.; Wu, Y.-T.; Wu, P.-C.; Lung, S.-C.; Su, H.-J. Effects of extreme precipitation to the distribution of infectious diseases in Taiwan, 1994–2008. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e34651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, L.; Zhang, Y.; Ding, G.; Liu, Q.; Zhou, M.; Li, X.; Jiang, B. Meteorological variables and bacillary dysentery cases in Changsha City, China. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2014, 90, 697–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, P.; Huang, D.; Guo, J.; Wang, P.; Zhou, B. Bacillary dysentery and meteorological factors in northeastern China: A historical review based on classification and regression trees. Jpn. J. Infect. Dis. 2008, 61, 356–360. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Huang, D.; Guan, P.; Guo, J.; Wang, P.; Zhou, B. Investigating the effects of climate variations on bacillary dysentery incidence in northeast China using ridge regression and hierarchical cluster analysis. BMC Infect. Dis. 2008, 8, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelly-Hope, L.A.; Alonso, W.J.; Thiem, V.D.; Canh, D.G.; Anh, D.D.; Lee, H.; Miller, M.A. Temporal trends and climatic factors associated with bacterial enteric diseases in Vietnam, 1991–2001. Environ. Health Perspect. 2008, 116, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.S.; Hoang, T.H.; Pham-Duc, P.; Lee, M.; Grace, D.; Phung, D.C.; Thuc, V.M.; Nguyen-Viet, H. Seasonal and geographical distribution of bacillary dysentery (shigellosis) and associated climate risk factors in Kon Tum Province in Vietnam from 1999 to 2013. Infect. Dis. Poverty 2017, 6, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Wang, L.; Sun, W.; Hou, X.; Yang, H.; Sun, L.; Xu, S.; Sun, Q.; Zhang, J.; Song, H. Identifying high-risk areas of bacillary dysentery and associated meteorological factors in Wuhan, China. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 3239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, W.; Sun, X.; Song, Y.; Tao, F.; Feng, W.; He, Y.; Zhao, N.; Yuan, Z. Applied mixed generalized additive model to assess the effect of temperature on the incidence of bacillary dysentery and its forecast. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e62122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Bi, P.; Hiller, J.E. Weather and the transmission of bacillary dysentery in Jinan, northern China: A time-series analysis. Public Health Rep. 2008, 123, 61–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Bi, P.; Hiller, J.E.; Sun, Y.; Ryan, P. Climate variations and bacillary dysentery in northern and southern cities of China. J. Infect. 2007, 55, 194–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pai, H. Bacillary dysentery. J. Korean Med. Assoc. 2003, 46, 527–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, N.-O.; Jung, S.-M.; Na, H.-Y.; Chung, G.T.; Yoo, C.-K.; Seong, W.K.; Hong, S. Enteric bacteria isolated from diarrheal patients in Korea in 2014. Osong Public Health Res. Perspect. 2015, 6, 233–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.; Cho, E. National Infectious Diseases Surveillance data of South Korea. Epidemiol. Health 2014, 36, e2014030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.; Lee, D.; Kim, J. Production and validation of daily grid data with 1 km resolution in South Korea. J. Clim. Res. 2013, 8, 13–25. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, M.-K.; Han, M.-S.; Jang, D.-H.; Baek, S.-G.; Lee, W.-S.; Kim, Y.-H.; Kim, S. Production technique of observation grid data of 1 km resolution. J. Clim. Res. 2012, 7, 55–68. [Google Scholar]
- Bogin, B.; Smith, B.H. Evolution of the Human Life Cycle; Wiley-Liss: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Unkel, S.; Farrington, C.; Garthwaite, P.H.; Robertson, C.; Andrews, N. Statistical methods for the prospective detection of infectious disease outbreaks: A review. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. A Stat. Soc. 2012, 175, 49–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jajosky, R.A.; Groseclose, S.L. Evaluation of reporting timeliness of public health surveillance systems for infectious diseases. BMC Public Health 2004, 4, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Neimann, J.; Engberg, J.; Mølbak, K.; Wegener, H.C. A case–control study of risk factors for sporadic Campylobacter infections in Denmark. Epidemiol. Infect. 2003, 130, 353–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, M.O.; Seo, S.H. School dietitians’ perceptions of potentially hazardous food and inspection of food safety and sanitation. J. Korean Diet. Assoc. 2008, 14, 176–185. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, G.M.; Lee, S.Y. A study on the sanitation management status and barriers to HACCP system implementation of school foodservice institutions in Seoul metropolitan area. Korean J. Commun. Nutr. 2008, 13, 405–417. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J. Studies on the knowledge, attitudes, and behavior of mothers toward food hygiene and safety of school food-service programs-Part 1. J. Food Hyg. Saf. 2004, 19, 38–48. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, Y. The importance of hygiene condition and HACCP system application at school food service. Food Sci. Ind. 2003, 36, 92–98. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, Y.S.; Park, J.W.; Bang, K.S.; Jung, S.R.; Woo, H.S.; Lee, H.J.; Jang, H.S. A study on the evaluation of maternal child health services in public health centers. J. Korean Commun. Nurs. 2002, 13, 280–291. [Google Scholar]
- Koh, M.; Jung, L.; Lee, J. Performance status of sanitary management of school food service in the Jeonnam area. Korean J. Hum. Ecol. 2004, 7, 51–67. [Google Scholar]
- Park, S.H.; Lim, Y.H. A study on the sanitary management of school foodservice operations in Daejeon and Chungnam. Korean J. Commun. Nutr. 2005, 10, 234–242. [Google Scholar]
- Eriksen, H.; Koch, A.; Elstrøm, P.; Nilsen, R.; Harthug, S.; Aavitsland, P. Healthcare-associated infection among residents of long-term care facilities: A cohort and nested case–control study. J. Hosp. Infect. 2007, 65, 334–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gray, J. Infection control: Beyond the horizon. J. Hosp. Infect. 2015, 89, 237–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, M.H.; Kim, M.H. A Proposal of Policy on the Long-term Care System for the Elderly. J. Public Welf. Adm. 2007, 17, 105–152. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, E. Current Situation and Policy Implication for the Elderly Long-Term Care Insurance; Health-Welfare Policy Forum: Seoul, Korea, 2009; pp. 23–31. [Google Scholar]
- Calderon-Margalit, R.; Navon-Venezia, S.; Gefen, D.; Amitai, Z.; Barda, R.; Vulikh, I.; Sompolinsky, D. Biennial hyperepidemic shigellosis in an observant Jewish community. Epidemiol. Infect. 2010, 138, 244–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gradus, M.; Nichamin, H. Shigellosis winter trends in Milwaukee. Wis. Med. J. 1989, 88, 17–18. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Han, G.H.; Kim, J.H. The ecological characteristics of the communities and social interactions of the elderly in rural Korea. Korean J. Commun. Living Sci. 2005, 16, 73–88. [Google Scholar]
- Stine, S.W.; Song, I.; Choi, C.Y.; Gerba, C.P. Effect of relative humidity on preharvest survival of bacterial and viral pathogens on the surface of cantaloupe, lettuce, and bell peppers. J. Food Prot. 2005, 68, 1352–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Year | 2002 | 2003 | 2004 | 2005 | 2006 | 2007 | 2008 | 2009 | 2010 | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | 15.73 | 23.00 | 9.57 | 5.61 | 7.55 | 1.83 | 2.98 | 2.92 | 2.49 | 7.90 |
| Sex | ||||||||||
| Men | 13.46 | 22.36 | 9.54 | 5.00 | 6.94 | 1.50 | 2.67 | 1.77 | 1.92 | 7.18 |
| Women | 18.02 | 23.64 | 9.60 | 6.22 | 8.16 | 2.16 | 3.29 | 4.08 | 3.05 | 8.62 |
| Age (years) | ||||||||||
| 0–2 | 15.04 | 26.99 | 5.42 | 7.11 | 8.87 | 0.00 | 3.66 | 2.17 | 1.46 | 8.37 |
| 3–6 | 56.59 | 113.55 | 12.72 | 13.83 | 36.90 | 3.80 | 4.09 | 3.21 | 3.79 | 30.84 |
| 7–17 | 24.36 | 45.10 | 28.44 | 4.83 | 8.18 | 0.94 | 2.56 | 1.51 | 0.85 | 13.02 |
| 18–64 | 9.52 | 10.11 | 5.11 | 3.97 | 5.24 | 1.52 | 1.72 | 2.18 | 1.93 | 4.55 |
| ≥65 | 24.56 | 28.09 | 10.96 | 14.68 | 8.56 | 5.10 | 11.48 | 9.87 | 8.04 | 12.78 |
| Climatic Factors | Time-Point | Relative Risk | 95% Confidence Interval | Change (%) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Maximum temperature | Present | 1.100 | 1.060 | 1.140 | 10.0 | <0.001 |
| Lag 1 | 1.128 | 1.085 | 1.171 | 12.8 | <0.001 | |
| Lag 2 | 1.136 | 1.092 | 1.180 | 13.6 | <0.001 | |
| Lag 3 | 1.106 | 1.063 | 1.149 | 10.6 | <0.001 | |
| Lag 4 | 1.098 | 1.057 | 1.139 | 9.8 | <0.001 | |
| Lag 5 | 1.076 | 1.033 | 1.119 | 7.6 | <0.001 | |
| Lag 6 | 1.080 | 1.038 | 1.122 | 8.0 | <0.001 | |
| Daily precipitation | Present | 1.025 | 1.003 | 1.047 | 2.5 | 0.030 |
| Lag 1 | 1.021 | 0.997 | 1.045 | 2.1 | 0.094 | |
| Lag 2 | 1.020 | 0.996 | 1.045 | 2.0 | 0.110 | |
| Lag 3 | 1.012 | 0.987 | 1.038 | 1.2 | 0.342 | |
| Lag 4 | 1.026 | 1.003 | 1.049 | 2.6 | 0.026 | |
| Lag 5 | 1.029 | 1.005 | 1.052 | 2.9 | 0.018 | |
| Lag 6 | 1.029 | 1.004 | 1.054 | 2.9 | 0.026 | |
| Season | Time-Point | Maximum Temperature | Mean Precipitation | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RR | 95% CI | Change (%) | p-Value | RR | 95% CI | Change (%) | p-Value | ||||
| Spring | Present | 1.047 | 0.968 | 1.126 | 4.7 | 0.252 | 1.049 | 1.017 | 1.081 | 4.9 | 0.003 |
| Lag 1 | 1.044 | 0.969 | 1.119 | 4.4 | 0.259 | 1.046 | 1.010 | 1.083 | 4.6 | 0.016 | |
| Lag 2 | 1.161 | 1.078 | 1.245 | 16.1 | <0.001 | 1.084 | 1.047 | 1.121 | 8.4 | <0.001 | |
| Lag 3 | 1.122 | 1.050 | 1.194 | 12.2 | 0.002 | 1.082 | 1.032 | 1.133 | 8.2 | 0.002 | |
| Lag 4 | 1.070 | 0.999 | 1.141 | 7.0 | 0.063 | 1.037 | 0.975 | 1.099 | 3.7 | 0.252 | |
| Lag 5 | 1.023 | 0.949 | 1.098 | 2.3 | 0.544 | 1.041 | 0.979 | 1.103 | 4.1 | 0.206 | |
| Lag 6 | 1.048 | 0.973 | 1.123 | 4.8 | 0.224 | 1.066 | 0.996 | 1.135 | 6.6 | 0.072 | |
| Summer | Present | 0.997 | 0.877 | 1.116 | −0.3 | 0.955 | 1.000 | 0.978 | 1.022 | 0.0 | 0.989 |
| Lag 1 | 1.175 | 1.032 | 1.317 | 17.5 | 0.027 | 0.999 | 0.971 | 1.027 | −0.1 | 0.939 | |
| Lag 2 | 1.040 | 0.904 | 1.175 | 4.0 | 0.574 | 0.971 | 0.943 | 0.999 | −2.9 | 0.039 | |
| Lag 3 | 0.968 | 0.848 | 1.088 | −3.2 | 0.592 | 0.981 | 0.956 | 1.005 | −1.9 | 0.116 | |
| Lag 4 | 1.009 | 0.900 | 1.117 | 0.9 | 0.875 | 1.015 | 0.995 | 1.035 | 1.5 | 0.149 | |
| Lag 5 | 0.887 | 0.780 | 0.995 | −11.3 | 0.029 | 1.001 | 0.981 | 1.021 | 0.1 | 0.905 | |
| Lag 6 | 0.967 | 0.857 | 1.077 | −3.3 | 0.554 | 1.011 | 0.988 | 1.035 | 1.1 | 0.354 | |
| Autumn | Present | 1.067 | 0.974 | 1.160 | 6.7 | 0.174 | 1.118 | 1.031 | 1.204 | 11.8 | 0.012 |
| Lag 1 | 1.186 | 1.073 | 1.300 | 18.6 | 0.003 | 1.066 | 0.982 | 1.149 | 6.6 | 0.134 | |
| Lag 2 | 1.200 | 1.080 | 1.320 | 20.0 | 0.003 | 1.027 | 0.935 | 1.118 | 2.7 | 0.573 | |
| Lag 3 | 1.179 | 1.061 | 1.297 | 17.9 | 0.006 | 0.994 | 0.906 | 1.082 | −0.6 | 0.892 | |
| Lag 4 | 1.177 | 1.048 | 1.306 | 17.7 | 0.013 | 1.069 | 1.011 | 1.126 | 6.9 | 0.024 | |
| Lag 5 | 1.183 | 1.041 | 1.324 | 18.3 | 0.020 | 1.030 | 0.974 | 1.087 | 3.0 | 0.301 | |
| Lag 6 | 1.149 | 1.006 | 1.292 | 14.9 | 0.058 | 1.007 | 0.956 | 1.058 | 0.7 | 0.785 | |
| Winter | Present | 1.098 | 1.051 | 1.145 | 9.8 | <0.001 | 1.071 | 0.977 | 1.165 | 7.1 | 0.152 |
| Lag 1 | 1.156 | 1.108 | 1.205 | 15.6 | <0.001 | 1.074 | 0.974 | 1.175 | 7.4 | 0.163 | |
| Lag 2 | 1.167 | 1.120 | 1.214 | 16.7 | <0.001 | 1.018 | 0.917 | 1.119 | 1.8 | 0.727 | |
| Lag 3 | 1.122 | 1.075 | 1.169 | 12.2 | <0.001 | 1.039 | 0.939 | 1.140 | 3.9 | 0.453 | |
| Lag 4 | 1.174 | 1.126 | 1.222 | 17.4 | <0.001 | 0.847 | 0.736 | 0.958 | −15.3 | 0.003 | |
| Lag 5 | 1.138 | 1.085 | 1.191 | 13.8 | <0.001 | 0.982 | 0.880 | 1.085 | −1.8 | 0.735 | |
| Lag 6 | 1.108 | 1.059 | 1.157 | 10.8 | <0.001 | 0.991 | 0.888 | 1.093 | −0.9 | 0.856 | |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Song, Y.-J.; Cheong, H.-K.; Ki, M.; Shin, J.-Y.; Hwang, S.-s.; Park, M.; Ki, M.; Lim, J. The Epidemiological Influence of Climatic Factors on Shigellosis Incidence Rates in Korea. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 2209. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15102209
Song Y-J, Cheong H-K, Ki M, Shin J-Y, Hwang S-s, Park M, Ki M, Lim J. The Epidemiological Influence of Climatic Factors on Shigellosis Incidence Rates in Korea. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2018; 15(10):2209. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15102209
Chicago/Turabian StyleSong, Yeong-Jun, Hae-Kwan Cheong, Myung Ki, Ji-Yeon Shin, Seung-sik Hwang, Mira Park, Moran Ki, and Jiseun Lim. 2018. "The Epidemiological Influence of Climatic Factors on Shigellosis Incidence Rates in Korea" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 15, no. 10: 2209. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15102209
APA StyleSong, Y.-J., Cheong, H.-K., Ki, M., Shin, J.-Y., Hwang, S.-s., Park, M., Ki, M., & Lim, J. (2018). The Epidemiological Influence of Climatic Factors on Shigellosis Incidence Rates in Korea. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 15(10), 2209. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15102209






