Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis and Occupational Exposures: A Systematic Literature Review and Meta-Analyses
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Literature Search
2.2. Quality Classification
2.3. Statistical Analysis
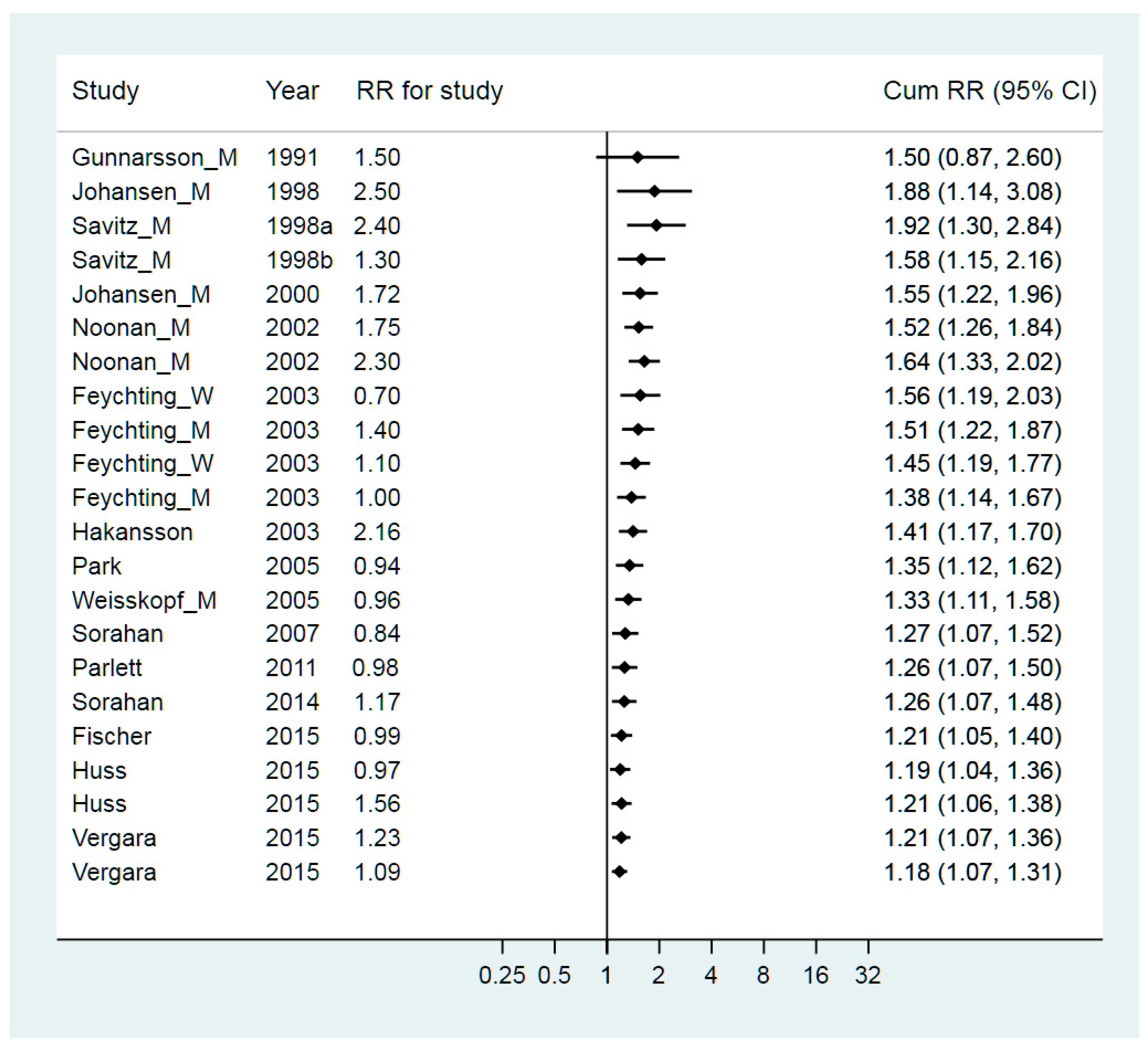
3. Results
3.1. Exposure to Heavy Physical Activities at Work
3.2. Exposure to Chemicals
3.3. Exposure to Metals
3.4. Exposure to Electromagnetic Fields and Work with Electricity
3.5. Nursing and Medical Treatment
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
Appendix A.1. Decision Protocol
Appendix A.2. Diagnosis
- Diagnosis of the studied disease made by applying uniform efforts and criteria to exposed and unexposed cohorts.
- Demonstration that ascertainment of patients is complete in the given population.
- Diagnosis of the studied disease made by applying established criteria.
Appendix A.3. Exposure
- Exposure, and hence assignment to the ‘exposed’ cohort, established before knowledge of diagnostic status, or without knowledge of diagnostic status, or confirmable independently of the knowledge of diagnostic status. Consideration of and accounting for possible misclassification.
- Unexposed cohort is appropriate to the risk factor in question, is well-matched to the exposed cohort on factors other than the exposure, and is otherwise representative of the general population.
- Exposure quantified, where possible, to permit assessment of dose-response relationships.
- Putative risk factor or exposure occurred before probable biologic onset of disease.
- Uniform effort to gather information equally from affected and unaffected individuals.
- Blinding of the information-gathering method to individuals’ disease status ideal; if not done—adequate justification as to why this does not affect the assessment of the risk factor in question.
- Blinding of subjects and individuals gathering the data as to the hypotheses being tested. If not done—adequate justification as to why this does not affect the assessment of the risk factor in question.
- Meticulous attention to avoiding recall bias or, if not possible, to evaluating its impact, estimating the magnitude of its impact and controlling for it.
- Exposure quantified, where possible, to permit assessment of dose-response.
Appendix A.4. Study Group
- Loss to follow-up low, and comparable in exposed and unexposed cohorts. Possible roles of competing causes of mortality accounted for. Preferably, all mortality data available for both cohorts.
- Appropriate choice of controls to assure they are matched to the patients and are also representative of the general population (assure adequate matching, avoid ‘overmatching’).
- High response rates from patients and controls.
Appendix A.5. Methods and Analysis
- Sources of biases and confounding identified and accounted for.
- Conclusion based on large numbers. Appropriate statistical analysis.
- Sources of biases and confounding identified and accounted for.
- Conclusions based on large numbers. Appropriate statistical analysis. Methods state if hypotheses were selected a priori for confirmatory analysis.
Appendix A.6. Criteria for Categorization into Armon Class
- Class I: All criteria were met within the respective design, i.e., a single score of 1 in every category.
- Class II: Single score of 1 or 2 in every category.
- Class III: Single score of 3 allowed for Diagnosis and 1 or 2 in the other categories (interval 2–3 is allowed).
- Class IV: Single score of 3 in categories other than Diagnosis.
- Class V: Single score of 4 in any category.
References
- Talbott, E.O.; Malek, A.M.; Lacomis, D. The epidemiology of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. In Handbook of Clinical Neurology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; pp. 225–238. [Google Scholar]
- Bidhendi, E.E.; Bergh, J.; Zetterstrom, P.; Andersen, P.M.; Marklund, S.L.; Brannstrom, T. Two superoxide dismutase prion strains transmit amyotrophic lateral sclerosis-like disease. J. Clin. Investig. 2016, 126, 2249–2253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breland, A.E.; Currier, R.D. Multiple sclerosis and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis in Mississippi. Neurology 1967, 17, 1011–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahlbom, I.C.; Cardis, E.; Green, A.; Linet, M.; Savitz, D.; Swerdlow, A. Review of the epidemiologic literature on EMF and Health. Environ. Health Perspect. 2001, 109, 911–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capozzella, A.; Sacco, C.; Chighine, A.; Loreti, B.; Scala, B.; Casale, T.; Sinibaldi, F.; Tomei, G.; Giubilati, R.; Tomei, F.; et al. Work related etiology of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS): A meta-analysis. Ann. Igiene 2014, 26, 456–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vergara, X.; Kheifets, L.; Greenland, S.; Oksuzyan, S.; Cho, Y.S.; Mezei, G. Occupational exposure to extremely low-frequency magnetic fields and neurodegenerative disease: A meta-analysis. J. Occup. Environ. Med. 2013, 55, 135–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, H.; Chen, G.; Chen, C.; Yu, Y.; Xu, Z. Association between extremely low-frequency electromagnetic fields occupations and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: A meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e48354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malek, A.M.; Barchowsky, A.; Bowser, R.; Youk, A.; Talbott, E.O. Pesticide exposure as a risk factor for amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: A meta-analysis of epidemiological studies: Pesticide exposure as a risk factor for ALS. Environ. Res. 2012, 117, 112–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamel, F.; Umbach, D.M.; Bedlack, R.S.; Richards, M.; Watson, M.; Alavanja, M.C.; Blair, A.; Hoppin, J.A.; Schmidt, S.; Sandler, D.P. Pesticide exposure and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Neurotoxicology 2012, 33, 457–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, M.D.; Gomes, J.; Cashman, N.R.; Little, J.; Krewski, D. A meta-analysis of observational studies of the association between chronic occupational exposure to lead and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. J. Occup. Environ. Med. 2014, 56, 1235–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lacorte, E.; Ferrigno, L.; Leoncini, E.; Corbo, M.; Boccia, S.; Vanacore, N. Physical activity, and physical activity related to sports, leisure and occupational activity as risk factors for ALS: A systematic review. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2016, 66, 61–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stroup, D.F.; Berlin, J.A.; Morton, S.C.; Olkin, I.; Williamson, G.D.; Rennie, D.; Moher, D.; Becker, B.J.; Sipe, T.A.; Thacker, S.B. Meta-analysis of observational studies in epidemiology: A proposal for reporting. Meta-analysis Of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (MOOSE) group. JAMA 2000, 283, 2008–2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guyatt, G.H.; Oxman, A.D.; Vist, G.; Kunz, R.; Brozek, J.; Alonso-Coello, P.; Montori, V.; Akl, E.A.; Djulbegovic, B.; Falck-Ytter, Y.; et al. GRADE guidelines: 4. Rating the quality of evidence—Study limitations (risk of bias). J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2011, 64, 407–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guyatt, G.H.; Oxman, A.D.; Sultan, S.; Glasziou, P.; Akl, E.A.; Alonso-Coello, P.; Atkins, D.; Kunz, R.; Brozek, J.; Montori, V.; et al. GRADE guidelines: 9. Rating up the quality of evidence. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2011, 64, 1311–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armon, C. An evidence-based medicine approach to the evaluation of the role of exogenous risk factors in sporadic amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Neuroepidemiology 2003, 22, 217–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gunnarsson, L.G.; Bodin, L. Parkinson’s disease and occupational exposures: A systematic literature review and meta-analyses. Scand. J. Work. Environ. Health 2017, 43, 197–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brooks, B.R.; Miller, R.G.; Swash, M.; Munsat, T.L. El Escorial revisited: Revised criteria for the diagnosis of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Amyotroph. Lateral Scler. Other Motor Neuron Disord. 2000, 1, 293–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beghi, E.; Logroscino, G.; Chio, A.; Hardiman, O.; Millul, A.; Mitchell, D.; Swingler, R.; Traynor, B.J. Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, physical exercise, trauma and sports: Results of a population-based pilot case-control study. Amyotroph. Lateral Scler. 2010, 11, 289–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bonvicini, F.; Marcello, N.; Mandrioli, J.; Pietrini, V.; Vinceti, M. Exposure to pesticides and risk of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: A population-based case-control study. Ann. Ist. Super. Sanita 2010, 46, 284–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chio, A.; Calvo, A.; Dossena, M.; Ghiglione, P.; Mutani, R.; Mora, G. ALS in Italian professional soccer players: The risk is still present and could be soccer-specific. Amyotroph. Lateral Scler. 2009, 10, 205–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, F.; Kwee, L.C.; Allen, K.D.; Umbach, D.M.; Ye, W.; Watson, M.; Keller, J.; Oddone, E.Z.; Sandler, D.P.; Schmidt, S.; et al. Association between blood lead and the risk of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2010, 171, 1126–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feychting, M.; Jonsson, F.; Pedersen, N.L.; Ahlbom, A. Occupational magnetic field exposure and neurodegenerative disease. Epidemiology 2003, 14, 413–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischer, H.; Kheifets, L.; Huss, A.; Peters, T.L.; Vermeulen, R.; Ye, W.; Fang, F.; Wiebert, P.; Vergara, X.P.; Feychting, M. Occupational Exposure to Electric Shocks and Magnetic Fields and Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis in Sweden. Epidemiology 2015, 26, 824–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gait, R.; Maginnis, C.; Lewis, S.; Pickering, N.; Antoniak, M.; Hubbard, R.; Lawson, I.; Britton, J. Occupational exposure to metals and solvents and the risk of motor neuron disease. A case-control study. Neuroepidemiology 2003, 22, 353–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallo, V.; Vanacore, N.; Bueno-de-Mesquita, H.B.; Vermeulen, R.; Brayne, C.; Pearce, N.; Wark, P.A.; Ward, H.A.; Ferrari, P.; Jenab, M.; et al. Physical activity and risk of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis in a prospective cohort study. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 2016, 31, 255–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gunnarsson, L.G.; Lindberg, G.; Soderfeldt, B.; Axelson, O. Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis in Sweden in relation to occupation. Acta Neurol. Scand. 1991, 83, 394–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gunnarsson, L.G.; Bodin, L.; Soderfeldt, B.; Axelson, O. A case-control study of motor neurone disease: Its relation to heritability, and occupational exposures, particularly to solvents. Br. J. Ind. Med. 1992, 49, 791–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harwood, C.A.; Westgate, K.; Gunstone, S.; Brage, S.; Wareham, N.J.; McDermott, C.J.; Shaw, P.J. Long-term physical activity: An exogenous risk factor for sporadic amyotrophic lateral sclerosis? Amyotroph. Lateral Scler. Front. Degener. 2016, 17, 377–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horner, R.D.; Grambow, S.C.; Coffman, C.J.; Lindquist, J.H.; Oddone, E.Z.; Allen, K.D.; Kasarskis, E.J. Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis among 1991 Gulf War veterans: Evidence for a time-limited outbreak. Neuroepidemiology 2008, 31, 28–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huisman, M.H.; Seelen, M.; de Jong, S.W.; Dorresteijn, K.R.; van Doormaal, P.T.; van der Kooi, A.J.; de Visser, M.; Schelhaas, H.J.; van den Berg, L.H.; Veldink, J.H. Lifetime physical activity and the risk of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2013, 84, 976–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huss, A.; Spoerri, A.; Egger, M.; Kromhout, H.; Vermeulen, R. Occupational exposure to magnetic fields and electric shocks and risk of ALS: The Swiss National Cohort. Amyotroph. Lateral Scler. Front. Degener. 2015, 16, 80–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hakansson, N.; Gustavsson, P.; Johansen, C.; Floderus, B. Neurodegenerative diseases in welders and other workers exposed to high levels of magnetic fields. Epidemiology 2003, 14, 420–426, discussion 427–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johansen, C.; Olsen, J.H. Mortality from amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, other chronic disorders, and electric shocks among utility workers. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1998, 148, 362–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johansen, C. Exposure to electromagnetic fields and risk of central nervous system disease in utility workers. Epidemiology 2000, 11, 539–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamel, F.; Umbach, D.M.; Munsat, T.L.; Shefner, J.M.; Hu, H.; Sandler, D.P. Lead exposure and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Epidemiology 2002, 13, 311–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lehman, E.J.; Hein, M.J.; Baron, S.L.; Gersic, C.M. Neurodegenerative causes of death among retired National Football League players. Neurology 2012, 79, 1970–1974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Longstreth, W.T.; McGuire, V.; Koepsell, T.D.; Wang, Y.; van Belle, G. Risk of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and history of physical activity: A population-based case-control study. Arch. Neurol. 1998, 55, 201–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGuire, V.; Longstreth, W.T., Jr.; Nelson, L.M.; Koepsell, T.D.; Checkoway, H.; Morgan, M.S.; van Belle, G. Occupational exposures and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. A population-based case-control study. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1997, 145, 1076–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noonan, C.W.; Reif, J.S.; Yost, M.; Touchstone, J. Occupational exposure to magnetic fields in case-referent studies of neurodegenerative diseases. Scand. J. Work. Environ. Health 2002, 28, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Park, R.M.; Schulte, P.A.; Bowman, J.D.; Walker, J.T.; Bondy, S.C.; Yost, M.G.; Touchstone, J.A.; Dosemeci, M. Potential occupational risks for neurodegenerative diseases. Am. J. Ind. Med. 2005, 48, 63–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parlett, L.E.; Bowman, J.D.; van Wijngaarden, E. Evaluation of occupational exposure to magnetic fields and motor neuron disease mortality in a population-based cohort. J. Occup. Environ. Med. 2011, 53, 1447–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peters, T.L.; Kamel, F.; Lundholm, C.; Feychting, M.; Weibull, C.E.; Sandler, D.P.; Wiebert, P.; Sparen, P.; Ye, W.; Fang, F. Occupational exposures and the risk of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Occup. Environ. Med. 2017, 74, 87–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruder, A.M.; Hein, M.J.; Hopf, N.B.; Waters, M.A. Mortality among 24,865 workers exposed to polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) in three electrical capacitor manufacturing plants: A ten-year update. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2014, 217, 176–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Savitz, D.A.; Checkoway, H.; Loomis, D.P. Magnetic field exposure and neurodegenerative disease mortality among electric utility workers. Epidemiology 1998, 9, 398–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savitz, D.A.; Loomis, D.P.; Tse, C.K. Electrical occupations and neurodegenerative disease: Analysis of U.S. mortality data. Arch. Environ. Health 1998, 53, 71–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sorahan, T.; Kheifets, L. Mortality from Alzheimer’s, motor neurone and Parkinson’s disease in relation to magnetic field exposure: Findings from the study of UK electricity generation and transmission workers, 1973–2004. Occup. Environ. Med. 2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sorahan, T.; Mohammed, N. Neurodegenerative disease and magnetic field exposure in UK electricity supply workers. Occup. Med. 2014, 64, 454–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stampfer, M.J. Welding occupations and mortality from Parkinson’s disease and other neurodegenerative diseases among United States men, 1985-1999. J. Occup. Environ. Hyg. 2009, 6, 267–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steenland, K.; Hein, M.J.; Cassinelli, R.T., 2nd; Prince, M.M.; Nilsen, N.B.; Whelan, E.A.; Waters, M.A.; Ruder, A.M.; Schnorr, T.M. Polychlorinated biphenyls and neurodegenerative disease mortality in an occupational cohort. Epidemiology 2006, 17, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanacore, N.; Cocco, P.; Fadda, D.; Dosemeci, M. Job strain, hypoxia and risk of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: Results from a death certificate study. Amyotroph. Lateral Scler. 2010, 11, 430–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weisskopf, M.G.; McCullough, M.L.; Morozova, N.; Calle, E.E.; Thun, M.J.; Ascherio, A. Prospective study of occupation and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis mortality. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2005, 162, 1146–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weisskopf, M.G.; Morozova, N.; O’Reilly, E.J.; McCullough, M.L.; Calle, E.E.; Thun, M.J.; Ascherio, A. Prospective study of chemical exposures and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2009, 80, 558–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Veldink, J.H.; Kalmijn, S.; Groeneveld, G.J.; Titulaer, M.J.; Wokke, J.H.; van den Berg, L.H. Physical activity and the association with sporadic ALS. Neurology 2005, 64, 241–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vergara, X.; Mezei, G.; Kheifets, L. Case-control study of occupational exposure to electric shocks and magnetic fields and mortality from amyotrophic lateral sclerosis in the US, 1991–1999. J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2015, 25, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrew, A.S.; Caller, T.A.; Tandan, R.; Duell, E.J.; Henegan, P.L.; Field, N.C.; Bradley, W.G.; Stommel, E.W. Environmental and Occupational Exposures and Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis in New England. Neurodegener. Dis. 2017, 17, 110–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Armon, C.; Kurland, L.T.; Daube, J.R.; O’Brien, P.C. Epidemiologic correlates of sporadic amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Neurology 1991, 41, 1077–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belli, S.; Vanacore, N. Proportionate mortality of Italian soccer players: Is amyotrophic lateral sclerosis an occupational disease? Eur. J. Epidemiol. 2005, 20, 237–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertke, S.J.; Lehman, E.J.; Wurzelbacher, S.J.; Hein, M.J. Mortality of lead smelter workers: A follow-up study with exposure assessment. Am. J. Ind. Med. 2016, 59, 979–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Binazzi, A.; Belli, S.; Uccelli, R.; Desiato, M.T.; Talamanca, I.F.; Antonini, G.; Corsi, F.M.; Scoppetta, C.; Inghilleri, M.; Pontieri, F.E.; et al. An exploratory case-control study on spinal and bulbar forms of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis in the province of Rome. Amyotroph. Lateral Scler. 2009, 10, 361–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buckley, J.; Warlow, C.; Smith, P.; Hilton-Jones, D.; Irvine, S.; Tew, J.R. Motor neuron disease in England and Wales, 1959–1979. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 1983, 46, 197–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burns, C.J.; Beard, K.K.; Cartmill, J.B. Mortality in chemical workers potentially exposed to 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid (2,4-D) 1945-94: An update. Occup. Environ. Med. 2001, 58, 24–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chancellor, A.M.; Slattery, J.M.; Fraser, H.; Warlow, C.P. Risk factors for motor neuron disease: A case-control study based on patients from the Scottish Motor Neuron Disease Register. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 1993, 56, 1200–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chio, A.; Meineri, P.; Tribolo, A.; Schiffer, D. Risk factors in motor neuron disease: A case-control study. Neuroepidemiology 1991, 10, 174–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, K.; Ghosh, M.; Nag, C.; Nandy, S.P.; Banerjee, M.; Datta, M.; Devi, G.; Chaterjee, G. Role of familial, environmental and occupational factors in the development of Parkinson’s disease. Neurodegener. Dis. 2011, 8, 345–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davanipour, Z.; Sobel, E.; Bowman, J.D.; Qian, Z.; Will, A.D. Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and occupational exposure to electromagnetic fields. Bioelectromagnetics 1997, 18, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deapen, D.M.; Henderson, B.E. A case-control study of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1986, 123, 790–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, F.; Quinlan, P.; Ye, W.; Barber, M.K.; Umbach, D.M.; Sandler, D.P.; Kamel, F. Workplace exposures and the risk of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Environ. Health Perspect. 2009, 117, 1387–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furby, A.; Beauvais, K.; Kolev, I.; Rivain, J.G.; Sebille, V. Rural environment and risk factors of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: A case-control study. J. Neurol. 2010, 257, 792–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallagher, J.P.; Sanders, M. Trauma and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: A report of 78 patients. Acta Neurol. Scand. 1987, 75, 145–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Govoni, V.; Granieri, E.; Fallica, E.; Casetta, I. Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, rural environment and agricultural work in the Local Health District of Ferrara, Italy, in the years 1964–1998. J. Neurol. 2005, 252, 1322–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graham, A.J.; Macdonald, A.M.; Hawkes, C.H. British motor neuron disease twin study. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 1997, 62, 562–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Granieri, E.; Carreras, M.; Tola, R.; Paolino, E.; Tralli, G.; Eleopra, R.; Serra, G. Motor neuron disease in the province of Ferrara, Italy, in 1964–1982. Neurology 1988, 38, 1604–1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gresham, L.S.; Molgaard, C.A.; Golbeck, A.L.; Smith, R. Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and occupational heavy metal exposure: A case-control study. Neuroepidemiology 1986, 5, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gunnarsson, L.G.; Lygner, P.E.; Veiga-Cabo, J.; de Pedro-Cuesta, J. An epidemic-like cluster of motor neuron disease in a Swedish county during the period 1973–1984. Neuroepidemiology 1996, 15, 142–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalfakis, N.; Vassilopoulos, D.; Voumvourakis, C.; Ndjeveleka, M.; Papageorgiou, C. Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis in southern Greece: An epidemiologic study. Neuroepidemiology 1991, 10, 170–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kondo, K.; Tsubaki, T. Case-control studies of motor neuron disease: Association with mechanical injuries. Arch. Neurol. 1981, 38, 220–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurtzke, J.F.; Beebe, G.W. Epidemiology of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: 1. A case-control comparison based on ALS deaths. Neurology 1980, 30, 453–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, R.J.; Schnatter, A.R.; Katz, A.M.; Thompson, F.S.; Murray, N.; Jorgensen, G.; Theriault, G. Updated mortality among diverse operating segments of a petroleum company. Occup. Environ. Med. 2000, 57, 595–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Malek, A.M.; Barchowsky, A.; Bowser, R.; Heiman-Patterson, T.; Lacomis, D.; Rana, S.; Youk, A.; Stickler, D.; Lackland, D.T.; Talbott, E.O. Environmental and occupational risk factors for amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: A case-control study. Neurodegener. Dis. 2014, 14, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitchell, J.D.; Davies, R.B.; al-Hamad, A.; Gatrell, A.C.; Batterby, G. MND risk factors: An epidemiological study in the north west of England. J. Neurol. Sci. 1995, 129, 61–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morahan, J.M.; Pamphlett, R. Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and exposure to environmental toxins: An Australian case-control study. Neuroepidemiology 2006, 27, 130–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pamphlett, R. Exposure to environmental toxins and the risk of sporadic motor neuron disease: An expanded Australian case-control study. Eur. J. Neurol. 2012, 19, 1343–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pamphlett, R.; Rikard-Bell, A. Different occupations associated with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: Is diesel exhaust the link? PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e80993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinkerton, L.E.; Hein, M.J.; Meyers, A.; Kamel, F. Assessment of ALS mortality in a cohort of formaldehyde-exposed garment workers. Amyotroph. Lateral Scler. Front. Degener. 2013, 14, 353–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pinkerton, L.E.; Hein, M.J.; Grajewski, B.; Kamel, F. Mortality from neurodegenerative diseases in a cohort of US flight attendants. Am. J. Ind. Med. 2016, 59, 532–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Provinciali, L.; Giovagnoli, A.R. Antecedent events in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: Do they influence clinical onset and progression? Neuroepidemiology 1990, 9, 255–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pupillo, E.; Messina, P.; Giussani, G.; Logroscino, G.; Zoccolella, S.; Chio, A.; Calvo, A.; Corbo, M.; Lunetta, C.; Marin, B.; et al. Physical activity and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: A European population-based case-control study. Ann. Neurol. 2014, 75, 708–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, A.L.; Johnson, N.J.; Cudkowicz, M.E.; Eum, K.D.; Weisskopf, M.G. Job-related formaldehyde exposure and ALS mortality in the USA. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roelofs-Iverson, R.A.; Mulder, D.W.; Elveback, L.R.; Kurland, L.T.; Molgaard, C.A. ALS and heavy metals: A pilot case-control study. Neurology 1984, 34, 393–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roosli, M.; Lortscher, M.; Egger, M.; Pfluger, D.; Schreier, N.; Lortscher, E.; Locher, P.; Spoerri, A.; Minder, C. Mortality from neurodegenerative disease and exposure to extremely low-frequency magnetic fields: 31 years of observations on Swiss railway employees. Neuroepidemiology 2007, 28, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savettieri, G.; Salemi, G.; Arcara, A.; Cassata, M.; Castiglione, M.G.; Fierro, B. A case-control study of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Neuroepidemiology 1991, 10, 242–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scarmeas, N.; Levy, G.; Tang, M.X.; Manly, J.; Stern, Y. Influence of leisure activity on the incidence of Alzheimer’s disease. Neurology 2001, 57, 2236–2242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schulte, P.A.; Burnett, C.A.; Boeniger, M.F.; Johnson, J. Neurodegenerative diseases: Occupational occurrence and potential risk factors, 1982 through 1991. Am. J. Public Health 1996, 86, 1281–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strickland, D.; Smith, S.A.; Dolliff, G.; Goldman, L.; Roelofs, R.I. Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and occupational history. A pilot case-control study. Arch. Neurol. 1996, 53, 730–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strickland, D.; Smith, S.A.; Dolliff, G.; Goldman, L.; Roelofs, R.I. Physical activity, trauma, and ALS: A case-control study. Acta Neurol. Scand. 1996, 94, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sutedja, N.A.; Veldink, J.H.; Fischer, K.; Kromhout, H.; Wokke, J.H.; Huisman, M.H.; Heederik, D.J.; Van den Berg, L.H. Lifetime occupation, education, smoking, and risk of ALS. Neurology 2007, 69, 1508–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valenti, M.; Pontieri, F.E.; Conti, F.; Altobelli, E.; Manzoni, T.; Frati, L. Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and sports: A case-control study. Eur. J. Neurol. 2005, 12, 223–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Y.; Su, F.C.; Callaghan, B.C.; Goutman, S.A.; Batterman, S.A.; Feldman, E.L. Environmental risk factors and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS): A case-control study of ALS in Michigan. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e101186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hill, A.B. The environment and disease: Association or causation? Proc. R. Soc. Med. 1965, 58, 295–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Begg, C.B.; Mazumdar, M. Operating characteristics of a rank correlation test for publication bias. Biometrics 1994, 50, 1088–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palmer, T.M.; Sterne, J.A.C.; Newton, H.J.; Cox, N.J. Meta-Analysis in Stata: An Updated Collection from the Stata Journal, 2nd ed.; Stata Press Publication: College Station, TX, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Horner, R.D.; Feussner, J.R.; Kasarskis, E.J. Prospective study of military service and mortality from ALS. Neurology 2005, 65, 180–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ioannides, Z.A.; Ngo, S.T.; Henderson, R.D.; McCombe, P.A.; Steyn, F.J. Altered Metabolic Homeostasis in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis: Mechanisms of Energy Imbalance and Contribution to Disease Progression. Neurodegener. Dis. 2016, 16, 382–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garzillo, E.M.; Lamberti, M.; Genovese, G.; Pedata, P.; Feola, D.; Sannolo, N.; Daniele, L.; Trojsi, F.; Monsurro, M.R.; Miraglia, N. Blood lead, manganese, and aluminum levels in a regional Italian cohort of ALS patients: Does aluminum have an influence? J. Occup. Environ. Med. 2014, 56, 1062–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






| Publication | Year | Diagnosis | Exposure | Study Group: Selection, Controls, Missing Data | Methods Analysis | Armon Global Class [15] | Funding: | Exposures | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Assessment | Grade | Number of Exposed Cases | Grade | |||||||
| Beghi [18] | 2010 | 1 | Q | 2 | 31 | 2–3 | 2–3 | III | PU | Hard physical work, physical trauma |
| Bonvicini [19] | 2010 | 1 | Q | 2 | 13 | 2 | 2 | II | PA | Chemicals (pesticides) |
| Chio [20] | 2009 | 2–3 | EC | 2 | 8 | 2 | 2–3 | III | PA, PU | Professional sports |
| Fang [21] | 2010 | 1 | EC | 2 | 151 | 1 | 1 | II | PA, PU | Lead |
| Feychting [22] | 2003 | 3 | JEM | 2–3 | 234 * | 1 | 1 | III | PU | Occupation (work with electricity, EMF, welding) |
| Fischer [23] | 2015 | 2–3 | JEM | 2 | 766 * | 1 | 1 | III | PU, I | Occupation (EMF, welding) |
| Gait [24] | 2003 | 3 | JEM | 2 | 13 * | 2–3 | 2 | III | ? | Metals and solvents |
| Gallo [25] | 2016 | 3 | Q | 2–3 | 17 | 2 | 2–3 | III | ? | Hard physical work |
| Gunnarsson [26] | 1991 | 3 | JEM | 2 | 32 * | 2 | 2 | III | PU | Occupation (electricians, chemicals, nurse) |
| Gunnarsson [27] | 1992 | 1 | Q | 2 | 10 * | 2 | 1 | II | PU | Metals, chemicals, welding |
| Harwood [28] | 2016 | 2 | Q | 2 | 175 | 2 | 2 | III | PU | Work related physical activity |
| Horner [29] | 2008 | 1 | EC | 2 | 48 | 2 | 2 | II | PU | Gulf War veterans |
| Huisman [30] | 2013 | 1 | Q | 1 | 103 | 2 | 1 | II | PU | Hard physical work |
| Huss [31] | 2015 | 3 | JEM | 2 | 46 * | 2 | 1 | III | PU | Occupation (work with electricity, EMF) |
| Håkansson [32] | 2003 | 3 | JEM | 2–3 | 13 | 2 | 1 | III | I | Occupation (EMF) |
| Johansen [33] | 1998 | 3 | JEM | 2–3 | 14 | 2 | 2 | III | PU, I | Occupation (EMF) |
| Johansen [34] | 2000 | 2 | JEM | 2 | 15 | 2 | 2 | II | PU, I | Occupation (work with electricity) |
| Kamel [35] | 2002 | 1 | Q | 1 | 11 | 2 | 1 | II | PU | Lead |
| Lehman [36] | 2012 | 3 | EC | 1 | 7 | 2 | 2 | III | PU | Professional sports |
| Longstreth [37] | 1998 | 1 | Q | 2 | 59 | 2–3 | 2 | III | PA | Hard physical work |
| McGuire [38] | 1997 | 1 | Q | 2 | 71 | 2–3 | 2 | III | PU | Chemicals, metals |
| Noonan [39] | 2002 | 3 | JEM | 2–3 | 19 * | 2 | 1–2 | III | ? | Occupation (work with electricity, EMF) |
| Park [40] | 2005 | 3 | JEM | 2–3 | 5965 * | 2 | 2 | III | PU | Occupation (EMF, pesticides and other chemicals, welding, nurse) |
| Parlett [41] | 2011 | 3 | JEM | 1 | 10 | 2–3 | 2–3 | III | none | Occupation (EMF) |
| Peters [42] | 2017 | 2–3 | JEM | 2–3 | 611 * | 1 | 1 | III | PA, PU | Occupation (chemicals, lead, nurse) |
| Ruder [43] | 2014 | 3 | EC | 1 | 20 | 2 | 2 | III | PU | Chemicals (PCB) |
| Savitz [44] | 1998a | 3 | JEM | 2–3 | 9 | 2 | 2 | III | I | Occupation (EMF) |
| Savitz [45] | 1998b | 3 | JEM | 2–3 | 114 | 2 | 2 | III | ? | Occupation (work with electricity) |
| Sorahan [46] | 2007 | 3 | JEM | 2 | 62 | 2 | 2 | III | I | Power station workers (work with electricity) |
| Sorahan [47] | 2014 | 3 | JEM | 2 | 11 | 2 | 2 | III | I | Power station workers (EMF) |
| Stampfer [48] | 2009 | 3 | JEM | 2–3 | 71 | 2 | 2 | III | I | Occupation (welding) |
| Steenland [49] | 2006 | 3 | JEM | 1 | 11 | 2 | 2 | III | ? | Chemicals (PCB) |
| Vanacore [50] | 2010 | 3 | JEM | 2–3 | 6 | 2–3 | 2–3 | III | ? | Hard physical work, professional sports |
| Weisskopf [51] | 2005 | 3 | Q | 2–3 | 30 * | 2 | 2 | III | ? | Occupation (work with electricity, nurse) |
| Weisskopf [52] | 2009 | 3 | Q | 2–3 | 142 | 2 | 2 | III | PU | Chemicals |
| Veldink [53] | 2005 | 1 | Q | 2 | 25 | 2–3 | 2–3 | III | PU | Strenuous physical work |
| Vergara [54] | 2015 | 3 | JEM | 2–3 | 503 * | 2–3 | 1–2 | III | PU | Occupation (EMF, work with electricity, welding) |
| Publication | Year | Diagnosis | Exposure | Study Group: Selection Controls Missing Data | Methods Analysis | Armon Global Class [15] | Funding | Exposures |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Andrew [55] | 2017 | 3 | 3–4 | 4 | 2–3 | V | PU, PA | Chemicals, metals, water-related activities |
| Armon [56] | 1991 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 2–3 | IV | PU | Physical work, trauma, metals |
| Belli [57] | 2005 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 3 | IV | ? | Professional soccer player |
| Bertke [58] | 2016 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 3–4 | IV | PU | Metals |
| Binazzi [59] | 2009 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 2–3 | IV | ? | All possible |
| Breland [3] | 1967 | 1–2 | 3 | 2–3 | 3 | IV | ? | Physical work |
| Buckley [60] | 1983 | 3–4 | 3 | 2–3 | 3 | IV | PU | Occupation |
| Burns [61] | 2001 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 3 | IV | I | 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid |
| Chancellor [62] | 1993 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 2–3 | IV | PA | Chemicals, manual work |
| Chiò [63] | 1991 | 1 | 3 | 3–4 | 3 | IV | I | Occupation |
| Das [64] | 2012 | 1 | 3 | 3 | 3 | IV | PU | Pesticides |
| Davanipour [65] | 1997 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 2–3 | IV | ? | EMF |
| Deapen [66] | 1986 | 2–3 | 2 | 3 | 3 | IV | PA | Physical trauma (electric shock) |
| Fang [67] | 2009 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 2–3 | IV | PU | Chemicals |
| Furby [68] | 2010 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 2–3 | IV | I | Agricultural work and chemicals |
| Gallagher [69] | 1987 | 1 | 2 | 4 | 4 | V | ? | Physical trauma |
| Govoni [70] | 2005 | 1 | 4 | 3 | 3 | V | PU | Living in an agricultural area |
| Graham [71] | 1997 | 3 | 2–3 | 3 | 2–3 | IV | PU | Chemicals |
| Granieri [72] | 1988 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 2–3 | IV | PU | Occupation (Physical work, farmer, forest work) |
| Gresham [73] | 1986 | 1 | 2–3 | 3 | 3 | IV | ? | Metals |
| Gunnarsson [74] | 1996 | 1 | 4 | 2 | 2–3 | V | PU | Living in an agricultural area |
| Kalfakis [75] | 1991 | 1 | 3 | 4 | 4 | V | ? | Occupation |
| Kamel [9] | 2012 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 2–3 | IV | PU | Pesticides |
| Kondo [76] | 1981 | 3 | 2–3 | 3 | 3 | IV | PU | Physical trauma |
| Kurtzke [77] | 1980 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 2–3 | IV | PU | All possible |
| Lewis [78] | 2000 | 3 | 3–4 | 2 | 2 | IV | I | Work at a petroleum company |
| Malek [79] | 2014 | 1 | 2–3 | 3–4 | 2–3 | IV | PA | Metals, pesticides |
| Mitchell [80] | 1995 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 3 | IV | PU | All possible |
| Morahan [81] | 2006 | 1 | 2–3 | 3–4 | 3 | IV | PA | Solvents, pesticides |
| Pamphlett [82] | 2012 | 1 | 2–3 | 3–4 | 3 | IV | PA | Solvents, pesticides (extension of Morahan 2006) |
| Pamhplett [83] | 2013 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 3 | V | PA | Diesel |
| Pinkerton [84] | 2013 | 3 | 3–4 | 2 | 3 | IV | PU | Chemicals (formaldehyde) |
| Pinkerton [85] | 2016 | 3 | 3–4 | 2 | 3–4 | IV | PU | Flight attendant |
| Provinciali [86] | 1990 | 1 | 3 | 3–4 | 3 | IV | ? | Metals, trauma, heavy manual labour |
| Pupillo [87] | 2014 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 1–2 | IV | PU, I | Physical work |
| Roberts [88] | 2015 | 3 | 3 | 2–3 | 3 | IV | PA | Formaldehyde |
| Roelofs-Iverson [89] | 1984 | 1 | 2–3 | 4 | 3 | V | PU | Heavy metals |
| Röösli [90] | 2007 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 3 | IV | PU | Occupation (EMF) |
| Savettieri [91] | 1991 | 3 | 2–3 | 4 | 2 | V | PU | All possible |
| Scarmeas [92] | 2002 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 2–3 | IV | ? | Athletic activity |
| Schulte [93] | 1996 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 3 | IV | ? | Occupation (farmers) |
| Strickland [94] | 1996 | 1 | 2–3 | 3 | 2–3 | IV | PU | Metals |
| Strickland [95] | 1996 | 1 | 2–3 | 3 | 2–3 | IV | PU | Physical work |
| Sutedja [96] | 2007 | 1 | 2–3 | 3 | 2 | IV | PU | Occupation (education) |
| Valenti [97] | 2005 | 1 | 3 | 3 | 3 | IV | ? | Athletic activity |
| Yu [98] | 2014 | 1 | 1–2 | 3–4 | 3 | IV | PU, I | Physical activity, metals, pesticides |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gunnarsson, L.-G.; Bodin, L. Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis and Occupational Exposures: A Systematic Literature Review and Meta-Analyses. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 2371. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15112371
Gunnarsson L-G, Bodin L. Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis and Occupational Exposures: A Systematic Literature Review and Meta-Analyses. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2018; 15(11):2371. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15112371
Chicago/Turabian StyleGunnarsson, Lars-Gunnar, and Lennart Bodin. 2018. "Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis and Occupational Exposures: A Systematic Literature Review and Meta-Analyses" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 15, no. 11: 2371. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15112371
APA StyleGunnarsson, L.-G., & Bodin, L. (2018). Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis and Occupational Exposures: A Systematic Literature Review and Meta-Analyses. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 15(11), 2371. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15112371





