Association between Problematic Internet Use and Sleep Disturbance among Adolescents: The Role of the Child’s Sex
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Participants
2.2. Questionnaire
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion and Implication
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lin, M.P.; Wu, J.Y.; Chen, C.J.; You, J. Positive outcome expectancy mediates the relationship between social influence and Internet addiction among senior high-school students. J. Behav. Addict. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beard, K.W.; Wolf, E.M. Modification in the proposed diagnostic criteria for Internet addiction. Cyberpsychol. Behav. 2001, 4, 377–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuss, D.J.; Lopez-Fernandez, O. Internet addiction and problematic Internet use: A systematic review of clinical research. World J. Psychiatry 2016, 6, 143–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peter, B. Adolescence: A Psychoanalytic Interpretation; Reissue Edition: New York, NY, USA, 1966. [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton, K.R.; Felton, J.W.; Risco, C.M.; Lejuez, C.W.; MacPherson, L. Brief report: The interaction of impulsivity with risk-taking is associated with early alcohol use initiation. J. Adolesc. 2014, 37, 1253–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Public Health Implications of Excessive Use of the Internet, Computers, Smartphones and Similar Electronic Devices Meeting report. In Main Meeting Hall, Foundation for Promotion of Cancer Research National Cancer Research Centre; WHO: Tokyo, Japan, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, K.; Son, H.; Park, M.; Han, J.; Kim, K.; Lee, B.; Gwak, H. Internet overuse and excessive daytime sleepiness in adolescents. Psychiat. Clin. Neuros. 2009, 63, 455–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carskadon, M.A. Patterns of sleep and sleepiness in adolescents. Pediatrician 1990, 17, 5–12. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Eaton, D.K.; McKnight-Eily, L.R.; Lowry, R.; Perry, G.S.; Presley-Cantrell, L.; Croft, J.B. Prevalence of insufficient, borderline, and optimal hours of sleep among high school students—United States, 2007. J. Adolesc. Health. 2010, 46, 399–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meldrum, R.C.; Barnes, J.C.; Hay, C. Sleep Deprivation, Low Self-Control, and Delinquency: A Test of the Strength Model of Self-Control. J. Youth Adolesc. 2015, 44, 465–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Twenge, J.M. iGen: Why Today’s Super-Connected Kids Are Growing Up Less Rebellious, More Tolerant, Less Happy; Atria Books: New York, NY, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Billari, F.C.; Giuntella, O.; Stella, L. Broadband internet, digital temptations, and sleep. J. Econ. Behav. Organ. 2018, 153, 58–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van den Bulck, J. Television viewing, computer game playing, and Internet use and self-reported time to bed and time out of bed in secondary-school children. Sleep 2004, 27, 101–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Islamie, F.S.; Allahbakhshi, K.; Valipour, A.A.; Mohammadian-Hafshejani, A. Some Facts on Problematic Internet Use and Sleep Disturbance among Adolescents. Iran. J. Public Health 2016, 45, 1531–1532. [Google Scholar]
- Ekinci, O.; Celik, T.; Savas, N.; Toros, F. Association Between Internet Use and Sleep Problems in Adolescents. Noro Psikiyatr. Ars. 2014, 51, 122–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ha, L.; Fang, L. Internet experience and time displacement of traditional news media use: An application of the theory of the niche. Telematics Inf. 2012, 29, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.L.; Gau, S.S. Sleep problems and internet addiction among children and adolescents: A longitudinal study. J. Sleep Res. 2016, 25, 458–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seybert, H. Internet Use in Households and by Individuals in 2011; Eurostat: Brussels, Belgium, 2011; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Karacic, S.; Oreskovic, S. Internet Addiction Through the Phase of Adolescence: A Questionnaire Study. JMIR Ment. Health 2017, 4, e11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lam, L.T.; Peng, Z.W.; Mai, J.C.; Jing, J. Factors associated with Internet addiction among adolescents. Cyberpsychol. Behav. 2009, 12, 551–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaib, F.; Attarian, H. Sex and Gender Differences in Sleep Disorders: An Overview. In Principles of Gender-Specific Medicine, 3rd ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2017; pp. 585–601. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Ji, C.Y.; Zong, X.N.; Zhang, Y.Q. Body mass index growth curves for Chinese children and adolescents aged 0 to 18 years. Chin. J. Pediatr. 2009, 47, 493–498. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Mei, Z.; Ogden, C.L.; Flegal, K.M.; Grummer-Strawn, L.M. Comparison of the prevalence of shortness, underweight, and overweight among US children aged 0 to 59 months by using the CDC 2000 and the WHO 2006 growth charts. J. Pediatr. 2008, 153, 622–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, K.S. Caught in the Net: How to Recognize the Signs of Internet Addiction and a Winning Strategy for Recovery; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Lai, C.M.; Mak, K.K.; Watanabe, H.; Ang, R.P.; Pang, J.S.; Ho, R.C. Psychometric properties of the internet addiction test in Chinese adolescents. J. Pediatr. Psychol. 2013, 38, 794–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Zhou, X.; Lu, C.; Wu, J.; Deng, X.; Hong, L. Problematic Internet Use in high school students in Guangdong Province, China. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e19660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khazaal, Y.; Billieux, J.; Thorens, G.; Khan, R.; Louati, Y.; Scarlatti, E.; Theintz, F.; Lederrey, J.; Van Der Linden, M.; Zullino, D. French validation of the internet addiction test. Cyberpsychol. Behav. 2008, 11, 703–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buysse, D.J.; Reynolds, C.R.; Monk, T.H.; Berman, S.R.; Kupfer, D.J. The Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index: A new instrument for psychiatric practice and research. Psychiatry Res. 1989, 28, 193–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, P.S.; Wang, S.Y.; Wang, M.Y.; Su, C.T.; Yang, T.T.; Huang, C.J.; Fang, S.C. Psychometric evaluation of the Chinese version of the Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index (CPSQI) in primary insomnia and control subjects. Qual. Life Res. 2005, 14, 1943–1952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeMaris, A. Regression with Social Data: Modeling Continuous and Limited Response Variables; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Xin, M.; Xing, J.; Pengfei, W.; Houru, L.; Mengcheng, W.; Hong, Z. Online activities, prevalence of Internet addiction and risk factors related to family and school among adolescents in China. Addict. Behav. Rep. 2018, 7, 14–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, L.; Deng, J.; He, Y.; Deng, X.; Huang, J.; Huang, G.; Gao, X.; Lu, C. Prevalence and correlates of sleep disturbance and depressive symptoms among Chinese adolescents: A cross-sectional survey study. BMJ Open. 2014, 4, e5517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medeiros, A.L.D.; Mendes, D.B.F.; Lima, P.F.; Araujo, J.F. The Relationships between Sleep-Wake Cycle and Academic Performance in Medical Students. Biol. Rhythm. Res. 2001, 32, 263–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leproult, R.; Van Cauter, E. Role of sleep and sleep loss in hormonal release and metabolism. Endocr. Dev. 2010, 17, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ashare, R.L.; Lerman, C.; Tyndale, R.F.; Hawk, L.W.; George, T.P.; Cinciripini, P.; Schnoll, R.A. Sleep Disturbance During Smoking Cessation: Withdrawal or Side Effect of Treatment? J. Smok Cessat. 2017, 12, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schlarb, A.A.; Friedrich, A.; Classen, M. Sleep problems in university students—An intervention. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2017, 13, 1989–2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lemola, S.; Perkinson-Gloor, N.; Brand, S.; Dewald-Kaufmann, J.F.; Grob, A. Adolescents’ electronic media use at night, sleep disturbance, and depressive symptoms in the smartphone age. J. Youth Adolesc. 2015, 44, 405–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, Y.; Chen, Y.; Lu, Y.; Li, L. Exploring Associations between Problematic Internet Use, Depressive Symptoms and Sleep Disturbance among Southern Chinese Adolescents. Int J. Environ. Res. Public Health. 2016, 13, 313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.Y.; Kim, M.S.; Park, B.; Kim, J.H.; Choi, H.G. Lack of sleep is associated with internet use for leisure. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e191713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cajochen, C.; Frey, S.; Anders, D.; Spati, J.; Bues, M.; Pross, A.; Mager, R.; Wirz-Justice, A.; Stefani, O. Evening exposure to a light-emitting diodes (LED)—Backlit computer screen affects circadian physiology and cognitive performance. J. Appl Physiol. 2011, 110, 1432–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lagus, M. Molecular Mechanisms of Sleep and Mood; National Institute for Health and Welfare: Helsiinki, Finland, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Seney, M.L.; Sibille, E. Sex differences in mood disorders: Perspectives from humans and rodent models. Biol. Sex. Differ. 2014, 5, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Sleep Foundation, Do Women Need More Sleep than Men? Available online: https://www.sleepfoundation.org/sleep-news/do-women-need-more-sleep-men (accessed on 27 November 2018).
- Ebarhim, A.; Babak, G.; Alimohammad, A.; Shabnam, J.; Alireza, A.; Forough, F. High Prevalence of Sleep Problems in School- and Preschool-aged Children in Tehran: A Population Based Study. Iran. J. Pediatr. 2013, 23, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sommet, N.; Morselli, D. Keep Calm and Learn Multilevel Logistic Modeling: A Simplified Three-Step Procedure Using Stata, R., Mplus, and SPSS. Int. Rev. Soc. Psychol. 2017, 30, 203–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Variable | Total (%) | Boys (%) | Girls (%) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | 4750 (100) | 2335 (49.2) | 2415 (50.8) | 0.151 |
| Age, mean (SD) | 16.0 (1.5) | 15.99 (1.5) | 16.1 (1.5) | |
| Ethnicity | 0.492 | |||
| Han | 4361 (91.8) | 2137 (91.5) | 2224 (92.1) | |
| Other ethnic groups | 389 (8.2) | 198 (8.5) | 191 (7.9) | |
| HSS | <0.001 | |||
| Above average | 1583 (33.3) | 764 (32.7) | 819 (33.9) | |
| Average | 2802 (59.0) | 1340 (57.4) | 1462 (60.5) | |
| Below average | 306 (6.4) | 205 (8.8) | 101 (4.2) | |
| Missing data | 59 (1.2) | 26 (1.1) | 33 (1.4) | |
| Academic pressure | <0.001 | |||
| Above average | 2424 (51.0) | 1225 (52.5) | 1199(49.6) | |
| Average | 2073 (43.6) | 955 (40.9) | 1118 (46.3) | |
| Below average | 229 (4.8) | 141 (6.0) | 88 (3.6) | |
| Missing data | 24 (0.5) | 14 (0.6) | 10 (0.4) | |
| Weight status | <0.001 | |||
| Normal | 4027 (84.8) | 1850 (79.2) | 2177 (90.1) | |
| Overweight or obese | 723 (15.2) | 485 (20.8) | 238 (9.9) | |
| Daily hours of outdoor activity | <0.001 | |||
| Less than 2 h | 3315 (69.8) | 1463 (62.7) | 1852 (76.7) | |
| 2–3 h | 731 (15.4) | 428 (18.3) | 303 (12.5) | |
| More than 3 h | 536 (11.3) | 347 (14.9) | 189 (7.8) | |
| Missing data | 168 (3.5) | 97 (4.2) | 71 (2.9) | |
| IAT scores, mean (SD) | 37.2 (13.2) | 38.5 (13.9) | 35.9 (12.4) | <0.001 |
| Problem Internet use | <0.001 | |||
| No | 4014 (84.5) | 1906 (81.6) | 2108 (87.3) | |
| Yes | 736 (15.5) | 429 (18.4) | 307 (12.7) | |
| Total PSQI scores, mean (SD) | 6.8 (3.5) | 6.6 (3.7) | 7.0 (3.2) | |
| Sleep disturbance | <0.001 | |||
| No | 2892 (60.9) | 1494 (64.0) | 1398 (57.9) | |
| Yes | 1858 (39.1) | 841 (36.0) | 1017 (42.1) |
| Variable | Sleep Disturbance | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total, OR (95% CI) | p-Value | Boys, OR (95% CI) | p-Value | Girls, OR (95% CI) | p-Value | |
| PIU (Ref. = No) | ||||||
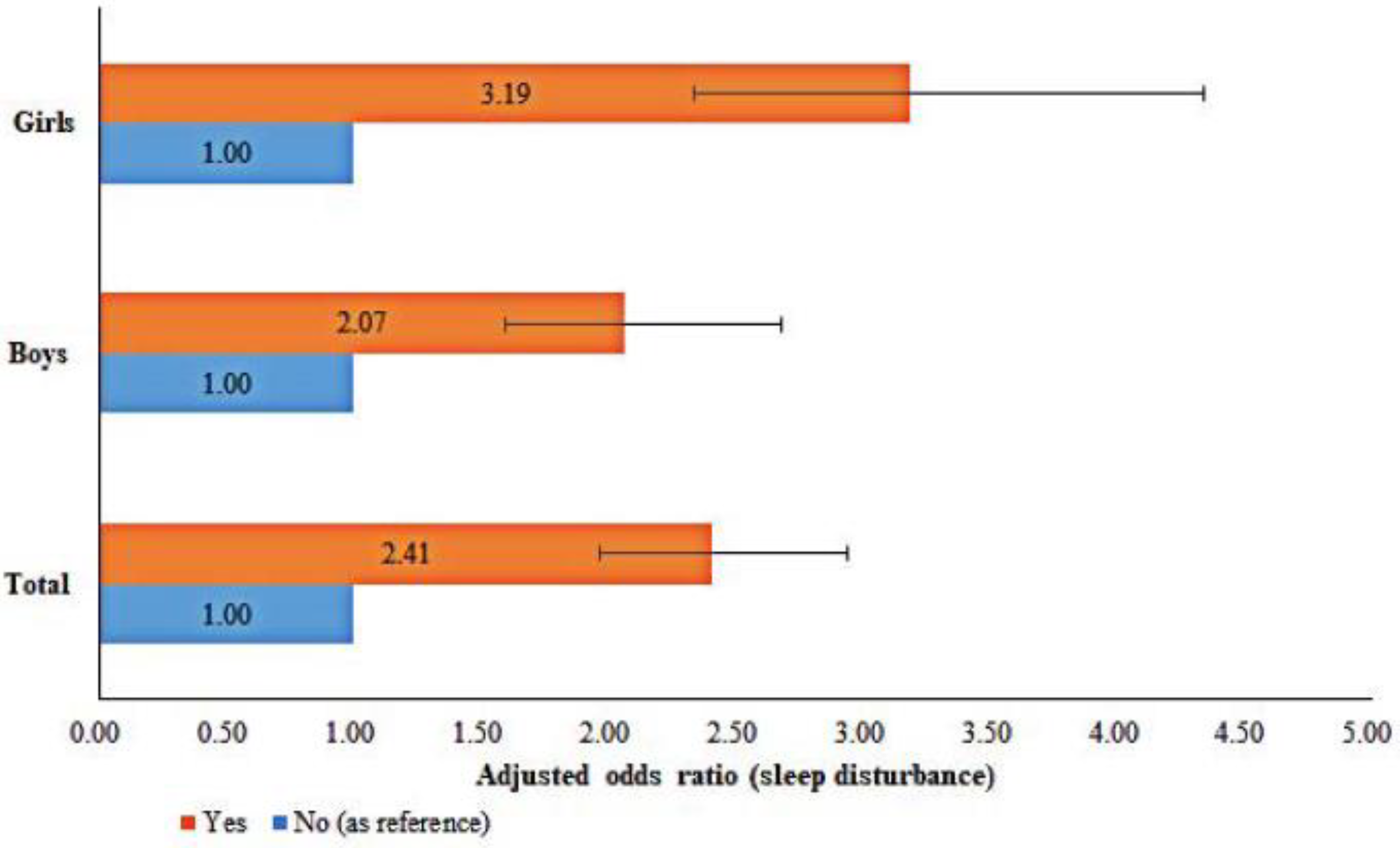
| Yes | 2.57 (2.13–3.09) | <0.001 | 2.36 (1.85–3.02) | <0.001 | 3.15 (2.34–4.24) | <0.001 |
| Age (1-year increase) | 1.42 (1.35–1.48) | <0.001 | 1.48 (1.39–1.59) | <0.001 | 1.36 (1.28–1.44) | <0.001 |
| Ethnicity (Ref. = Other ethnic groups) | 1.29 (1.02–1.63) | 0.038 | 1.30 (0.92–1.83) | 0.139 | 1.28 (0.92–1.77) | 0.146 |
| HSS (Ref. = Above average) | ||||||
| Average | 1.63 (1.42–1.87) | <0.001 | 1.81 (1.48–2.21) | <0.001 | 1.48 (0.94–2.34) | 0.091 |
| Below average | 2.35 (1.78–3.12) | <0.001 | 3.41 (2.37–4.91) | <0.001 | 1.48 (1.23–1.79) | <0.001 |
| Academic pressure (Ref. = Above average) | ||||||
| Average | 0.52 (0.46–0.59) | <0.001 | 0.47 (0.38–0.57) | <0.001 | 0.56 (0.47–0.67) | <0.001 |
| Below average | 0.56 (0.41–0.76) | <0.001 | 0.59 (0.39–0.87) | 0.008 | 0.55 (0.34–0.89) | 0.015 |
| Weight status (Ref. = Normal) | ||||||
| Overweight or Obese | 0.86 (0.72–1.02) | 0.081 | 0.93 (0.74–1.16) | 0.504 | 0.86 (0.64–1.15) | 0.294 |
| Daily hours of outdoor activity (Ref. = Less than 2 h) | ||||||
| 2–3 h | 0.95 (0.79–1.13) | 0.545 | 0.98 (0.78–1.25) | 0.897 | 0.97 (0.75–1.27) | 0.826 |
| More than 3 h | 0.91 (0.74–1.12) | 0.380 | 0.87 (0.67–1.14) | 0.309 | 1.13 (0.81–1.57) | 0.484 |
| Variable | Sleep Disturbance | |
|---|---|---|
| OR (95% CI) | p-Value | |
| Sex * PIU (Interaction item) | 1.48 (1.12–2.20) | 0.031 |
| PIU (Ref. = No) | ||
| Yes | 2.14 (1.67–2.75) | <0.001 |
| Sex (Ref. = Boys) | 1.32 (1.14–1.52) | <0.001 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, J.; Guo, Y.; Du, X.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, W.; Xiao, D.; Wang, T.; Lu, C.; Guo, L. Association between Problematic Internet Use and Sleep Disturbance among Adolescents: The Role of the Child’s Sex. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 2682. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15122682
Yang J, Guo Y, Du X, Jiang Y, Wang W, Xiao D, Wang T, Lu C, Guo L. Association between Problematic Internet Use and Sleep Disturbance among Adolescents: The Role of the Child’s Sex. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2018; 15(12):2682. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15122682
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Jiewen, Yangfeng Guo, Xueying Du, Yi Jiang, Wanxin Wang, Di Xiao, Tian Wang, Ciyong Lu, and Lan Guo. 2018. "Association between Problematic Internet Use and Sleep Disturbance among Adolescents: The Role of the Child’s Sex" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 15, no. 12: 2682. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15122682
APA StyleYang, J., Guo, Y., Du, X., Jiang, Y., Wang, W., Xiao, D., Wang, T., Lu, C., & Guo, L. (2018). Association between Problematic Internet Use and Sleep Disturbance among Adolescents: The Role of the Child’s Sex. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 15(12), 2682. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15122682




