Conceptualizing Family Influences on Children’s Energy Balance-Related Behaviors: Levels of Interacting Family Environmental Subsystems (The LIFES Framework)
Abstract
:1. Background
Family and EBRBs of Children
2. Levels of Interacting Family Environmental Systems (LIFES)
2.1. Theoretical Background
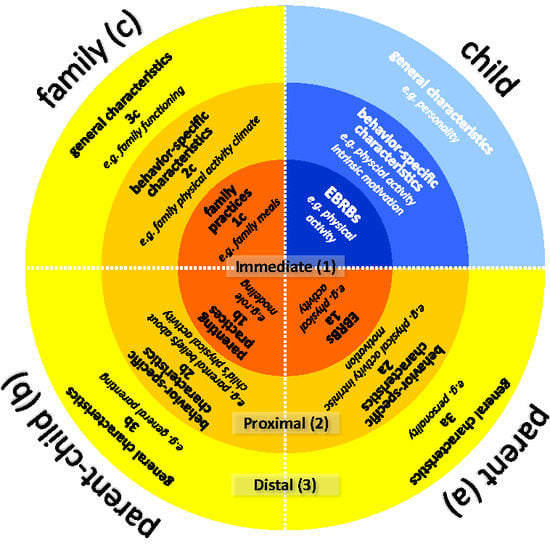
2.2. General Description
- three (sub)systems
- individual: influences related to individual family members (e.g., child, mother, father)
- parent-child: influences related to parent-child interactions (e.g., mother-child, father-child)
- family: influences related to the family as a whole
- and three levels of influences
- immediate: manifested behaviors
- proximal: behavior-specific factors
- distal: general factors
2.3. Description of Levels and Subsystems
2.3.1. Immediate Level
Individual—Parents’ Health Behavior (1a)
Parent-Child—Parenting Practices (1b)
Family—Family Practices (1c)
2.3.2. Proximal Level
Individual—Parents’ Behavior-Specific Characteristics (2a)
Parent-Child—Behavior-Specific Characteristics of the Parent-Child Subsystem (2b)
Family—Behavior-Specific Characteristics of the Family as a Whole (2c)
2.3.3. Distal Level
Individual—Parents’ General Factors (3a)
Parent-Child—General Parent-Child Characteristics (3b)
Family—General Characteristics of the Family as a Whole (3c)
2.4. Translation of LIFES’ Assumptions into Potential Mediated and Moderated Pathways
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization. Inequalities in Young People’s Health: HBSC International Report from the 2005/2006 Survey; World Health Organization: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Janssen, I. Physical Activity Epidemiology. In The Oxford Handbook of Exercise Psychology; Acevedo, E.O., Ed.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2012; pp. 9–34. [Google Scholar]
- Arundell, L.; Fletcher, E.; Salmon, J.; Veitch, J.; Hinkley, T. A systematic review of the prevalence of sedentary behavior during the after-school period among children aged 5–18 years. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2016, 13, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kremers, S.P.J.; Visscher, T.L.S.; Seidell, J.C.; van Mechelen, W.; Brug, J. Cognitive Determinants of Energy Balance-Related Behaviours. Sports Med. 2005, 35, 923–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacka, F.N.; Kremer, P.J.; Berk, M.; de Silva-Sanigorski, A.M.; Moodie, M.; Leslie, E.R.; Pasco, J.A.; Swinburn, B.A. A prospective study of diet quality and mental health in adolescents. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e24805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, L.; Mander, A.P.; Jones, L.R.; Emmett, P.M.; Jebb, S.A. Energy-dense, low-fiber, high-fat dietary pattern is associated with increased fatness in childhood. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2008, 87, 846–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Allen, M.S.; Vella, S.A. Screen-based sedentary behaviour and psychosocial well-being in childhood: Cross-sectional and longitudinal associations. Ment. Health Phys. Act. 2015, 9, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssen, I.; LeBlanc, A.G. Systematic review of the health benefits of physical activity and fitness in school-aged children and youth. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2010, 7, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Carson, V.; Hunter, S.; Kuzik, N.; Gray, C.E.; Poitras, V.J.; Chaput, J.-P.; Saunders, T.J.; Katzmarzyk, P.T.; Okely, A.D.; Connor Gorber, S.; et al. Systematic review of sedentary behaviour and health indicators in school-aged children and youth: An update. Appl. Physiol. Nutr. Metab. 2016, 41, 240–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tremblay, M.S.; LeBlanc, A.G.; Kho, M.E.; Saunders, T.J.; Larouche, R.; Colley, R.C.; Goldfield, G.; Gorber, S.C. Systematic review of sedentary behaviour and health indicators in school-aged children and youth. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2011, 8, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Telama, R.; Yang, X.; Leskinen, E.; Kankaanpää, A.; Hirvensalo, M.; Tammelin, T.; Viikari, J.S.A.; Raitakari, O.T. Tracking of physical activity from early childhood through youth into adulthood. Med. Sci. Sport Exerc. 2014, 46, 955–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sallis, J.F.; Nader, P.R. Family determinants of health behaviors. In Health Behavior: Emerging Research Perspectives; Gochman, D.S., Ed.; Plenum Press: New York, NY, USA, 1988; pp. 107–124. [Google Scholar]
- Sting, S. Gesundheit. In Handbuch Familie; Ecarius, J., Ed.; Vs. Verlag für Sozialwissenschaften: Wiesbaden, Germany, 2007; pp. 480–499. [Google Scholar]
- Campbell, T.L. Familien und Gesundheit: Zum Stand der Forschung. In Familie, System und Gesundheit. Systemische Konzepte für ein soziales Gesundheitswesen; Kröger, F., Hendrischke, A., McDaniel, S., Eds.; Auer: Heidelberg, Germany, 2000; pp. 225–241. [Google Scholar]
- Horn, T.S.; Horn, J.L. Family influences on children’s sport and physical activity participation, behavior, and psychosocial responses. In Handbook of Sport Psychology, 3rd ed.; Tenenbaum, G., Eklund, R.C., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2007; pp. 685–711. [Google Scholar]
- Schnabel, P.-E. Familie und Gesundheit: Bedingungen, Möglichkeiten und Konzepte der Gesundheitsförderung; Beltz Juventa: Weinheim, Germany, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Van der Horst, K.; Oenema, A.; Ferreira, I.; Wendel-Vos, W.; Giskes, K.; van Lenthe, F.; Brug, J. A systematic review of environmental correlates of obesity-related dietary behaviors in youth. Health Educ. Res. 2006, 22, 203–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lim, C.; Biddle, S. Longitudinal and prospective studies of parental correlates of physical activity in young people: A systematic review. Int. J. Sport Exerc. Psychol. 2012, 10, 211–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beets, M.W.; Cardinal, B.J.; Alderman, B.L. Parental Social Support and the Physical Activity-Related Behaviors of Youth: A Review. Health Educ. Behav. 2010, 37, 621–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brustad, R.J. Children’s Motivation for Involvement in Physical Activity. In The Oxford Handbook of Exercise Psychology; Acevedo, E.O., Ed.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2012; pp. 385–408. [Google Scholar]
- Gustafson, S.L.; Rhodes, R.E. Parental correlates of physical activity in children and early adolescents. Sports Med. 2006, 36, 79–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, L.; van Jaarsveld, C.; Wardle, J. Individual and family environment correlates differ for consumption of core and non-core foods in children. Br. J. Nutr. 2011, 105, 950–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edwardson, C.L.; Gorely, T. Parental influences on different types and intensities of physical activity in youth: A systematic review. Psychol. Sport Exerc. 2010, 11, 522–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kader, M.; Sundblom, E.; Elinder, L.S. Effectiveness of universal parental support interventions addressing children’s dietary habits, physical activity and bodyweight: A systematic review. Prev. Med. 2015, 77, 52–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaughn, A.E.; Ward, D.S.; Fisher, J.O.; Faith, M.S.; Hughes, S.O.; Kremers, S.P.J.; Musher-Eizenman, D.R.; O’Connor, T.M.; Patrick, H.; Power, T.G. Fundamental constructs in food parenting practices: A content map to guide future research. Nutr. Rev. 2016, 74, 98–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gevers, D.W.M.; Kremers, S.P.J.; de Vries, N.K.; van Assema, P. Clarifying concepts of food parenting practices. A Delphi study with an application to snacking behavior. Appetite 2014, 79, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kremers, S.P.J.; Brug, J.; de Vries, H.; Engels, R.C.M.E. Parenting style and adolescent fruit consumption. Appetite 2003, 41, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearson, N.; Atkin, A.J.; Biddle, S.J.; Gorely, T.; Edwardson, C. Parenting styles, family structure and adolescent dietary behaviour. Public Health Nutr. 2010, 13, 1245–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Horst, K.; Kremers, S.; Ferreira, I.; Singh, A.; Oenema, A.; Brug, J. Perceived parenting style and practices and the consumption of sugar-sweetened beverages by adolescents. Health Educ. Res. 2007, 22, 295–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sleddens, E.F.C.; Gerards, S.M.; Thijs, C.; VRIES, N.K.; Kremers, S.P.J. General Parenting, childhood overweight and obesity-inducing behaviors: A review. Pediatr. Obes. 2011, 6, 12–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Afonso, L.; Lopes, C.; Severo, M.; Santos, S.; Real, H.; Durão, C.; Moreira, P.; Oliveira, A. Bidirectional association between parental child-feeding practices and body mass index at 4 and 7 y of age. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2016, 103, 861–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jansen, P.W.; Tharner, A.; van der Ende, J.; Wake, M.; Raat, H.; Hofman, A.; Verhulst, F.C.; van Ijzendoorn, M.H.; Jaddoe, V.W.V.; Tiemeier, H. Feeding practices and child weight: Is the association bidirectional in preschool children? Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2014, 100, 1329–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rhee, K.E.; Coleman, S.M.; Appugliese, D.P.; Kaciroti, N.A.; Corwyn, R.F.; Davidson, N.S.; Bradley, R.H.; Lumeng, J.C. Maternal feeding practices become more controlling after and not before excessive rates of weight gain. Obesity 2009, 17, 1724–1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Webber, L.; Cooke, L.; Hill, C.; Wardle, J. Child adiposity and maternal feeding practices: A longitudinal analysis. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2010, 92, 1423–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sleddens, E.F.C.; Gubbels, J.S.; Kremers, S.P.J.; van der Plas, E.; Thijs, C. Bidirectional associations between activity-related parenting practices, and child physical activity, sedentary screen-based behavior and body mass index: A longitudinal analysis. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2017, 14, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berge, J.M. A Review of Familial Correlates of Child and Adolescent Obesity: What has the 21(st) Century Taught us so Far? Int. J. Adolesc. Med. Health 2009, 21, 457–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skelton, J.A.; Buehler, C.; Irby, M.B.; Grzywacz, J.G. Where are family theories in family-based obesity treatment? Conceptualizing the study of families in pediatric weight management. Int. J. Obes. 2012, 36, 891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McHale, J.P. When infants grow up in multiperson relationship systems. Infant Ment. Health J. 2007, 28, 370–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Berge, J.M.; Wall, M.; Larson, N.; Loth, K.A.; Neumark-Sztainer, D. Family functioning: Associations with weight status, eating behaviors, and physical activity in adolescents. J. Adolesc. Health 2013, 52, 351–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haines, J.; Rifas-Shiman, S.L.; Horton, N.J.; Kleinman, K.; Bauer, K.W.; Davison, K.K.; Walton, K.; Austin, S.B.; Field, A.E.; Gillman, M.W. Family functioning and quality of parent-adolescent relationship: Cross-sectional associations with adolescent weight-related behaviors and weight status. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2016, 13, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bronfenbrenner, U. The Ecology of Human Development; Harvard University Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Bronfenbrenner, U. Ecology of the family as a context for human development: Research perspectives. Dev. Psychol. 1986, 22, 723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Bertalanffy, L. General System Theory; Braziller: New York, NY, USA, 1968. [Google Scholar]
- Broderick, C.B. Understanding Family Process: Basics of Family Systems Theory; Sage Publications: Newbury Park, CA, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- White, J.M.; Klein, D.M. Family Theories; Sage Publications: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Cox, M.J.; Paley, B. Understanding families as systems. Curr. Dir. Psychol. Sci. 2003, 12, 193–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thelen, E.; Smith, L.B. Dynamic Systems Theories. In Handbook of Child Psychology; Damon, W., Lerner, R.M., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2007; pp. 258–312. [Google Scholar]
- Odum, H.T. Systems Ecology: An Introduction; John Wiley and Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Wachs, T.D. Necessary but Not Sufficient: The Respective Roles of Single and Multiple Influences on Individual Development; American Psychological Association: Worcester, MA, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Rutter, H.; Savona, N.; Glonti, K.; Bibby, J.; Cummins, S.; Finegood, D.T.; Greaves, F.; Harper, L.; Hawe, P.; Moore, L.; et al. The need for a complex systems model of evidence for public health. Lancet 2017, 390, 2602–2604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Park, S.H.; Cormier, E. Influence of Siblings on Child Health Behaviors and Obesity: A Systematic Review. J. Child Fam. Stud. 2018, 27, 2069–2081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McHale, S.M.; Updegraff, K.A.; Whiteman, S.D. Sibling relationships and influences in childhood and adolescence. J. Marriage Fam. 2012, 74, 913–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feinberg, M.; Solmeyer, A.; McHale, S. The Third Rail of Family Systems: Sibling Relationships, Mental and Behavioral Health, and Preventive Intervention in Childhood and Adolescence. Clin. Child Fam. Psychol. Rev. 2012, 15, 43–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandura, A. Human agency in social cognitive theory. Am. Psychol. 1989, 44, 1175–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baranowski, T. Families and health actions. In Handbook of Health Behavior Research 1: Personal and Social Determinants; Gochman, D.S., Ed.; Plenum Press: New York, NY, USA, 1997; pp. 179–206. [Google Scholar]
- Larsen, J.K.; Hermans, R.C.J.; Sleddens, E.F.C.; Engels, R.C.M.E.; Fisher, J.O.; Kremers, S.P.J. How parental dietary behavior and food parenting practices affect children’s dietary behavior. Interacting sources of influence? Appetite 2015, 89, 246–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasmussen, M.; Krølner, R.; Klepp, K.-I.; Lytle, L.; Brug, J.; Bere, E.; Due, P. Determinants of fruit and vegetable consumption among children and adolescents: A review of the literature. Part I: Quantitative studies. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2006, 3, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pearson, N.; Biddle, S.J.H.; Gorely, T. Family correlates of fruit and vegetable consumption in children and adolescents: A systematic review. Public Health Nutr. 2009, 12, 267–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verloigne, M.; van Lippevelde, W.; Maes, L.; Brug, J.; de Bourdeaudhuij, I. Family-and school-based correlates of energy balance-related behaviours in 10–12-year-old children: A systematic review within the ENERGY (EuropeaN Energy balance Research to prevent excessive weight Gain among Youth) project. Public Health Nutr. 2012, 15, 1380–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mutz, M.; Albrecht, P. Parents’ Social Status and Children’s Daily Physical Activity: The Role of Familial Socialization and Support. J. Child Fam. Stud. 2017, 26, 3026–3035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Biddle, S.J.H.; Atkin, A.J.; Cavill, N.; Foster, C. Correlates of physical activity in youth: A review of quantitative systematic reviews. Int. Rev. Sport Exerc. Psychol. 2011, 4, 25–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Wen, L.M.; Rissel, C. Associations of Parental Influences with Physical Activity and Screen Time among Young Children: A Systematic Review. J. Obes. 2015, 2015, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davison, K.K.; Francis, L.A.; Birch, L.L. Links between Parents’ and Girls’ Television Viewing Behaviors: A Longitudinal Examination. J. Pediatr. 2005, 147, 436–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Beydoun, M.A.; Li, J.; Liu, Y.; Moreno, L.A. Do children and their parents eat a similar diet? Resemblance in child and parental dietary intake: Systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Epidemiol. Commun. Health 2011, 65, 177–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darling, N.; Steinberg, L. Parenting style as context: An integrative model. Psychol. Bull. 1993, 113, 487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gevers, D.W.; Kremers, S.P.; de Vries, N.K.; van Assema, P. The Comprehensive Snack Parenting Questionnaire (CSPQ): Development and Test-Retest Reliability. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connor, T.M.; Mâsse, L.C.; Tu, A.W.; Watts, A.W.; Hughes, S.O.; Beauchamp, M.R.; Baranowski, T.; Pham, T.; Berge, J.M.; Fiese, B.; et al. Food parenting practices for 5 to 12 year old children: A concept map analysis of parenting and nutrition experts input. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2017, 14, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mâsse, L.C.; O’Connor, T.M.; Tu, A.W.; Hughes, S.O.; Beauchamp, M.R.; Baranowski, T. Conceptualizing physical activity parenting practices using expert informed concept mapping analysis. BMC Public Health 2017, 17, 574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Davison, K.K.; Blake, C.E.; Kachurak, A.; Lumeng, J.C.; Coffman, D.L.; Miller, A.L.; Hughes, S.O.; Power, T.G.; Vaughn, A.F.; Blaine, R.E.; et al. Development and preliminary validation of the Parenting around SNAcking Questionnaire (P-SNAQ). Appetite 2018, 125, 323–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaughn, A.E.; Tabak, R.G.; Bryant, M.J.; Ward, D.S. Measuring parent food practices: A systematic review of existing measures and examination of instruments. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2013, 10, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davison, K.K.; Jago, R. Change in parent and peer support across ages 9 to 15 yr and adolescent girls’ physical activity. Med. Sci. Sport Exerc. 2009, 41, 1816–1825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yee, A.Z.H.; Lwin, M.O.; Ho, S.S. The influence of parental practices on child promotive and preventive food consumption behaviors: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2017, 14, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerards, S.M.P.L.; Kremers, S.P.J. The Role of Food Parenting Skills and the Home Food Environment in Children’s Weight Gain and Obesity. Curr. Obes. Rep. 2015, 4, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kremers, S.P.J.; de Bruijn, G.-J.; Visscher, T.L.S.; van Mechelen, W.; de Vries, N.K.; Brug, J. Environmental influences on energy balance-related behaviors: A dual-process view. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2006, 3, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, J.K.; Hermans, R.C.J.; Sleddens, E.F.C.; Vink, J.M.; Kremers, S.P.J.; Ruiter, E.L.M.; Fisher, J.O. How to bridge the intention-behavior gap in food parenting: Automatic constructs and underlying techniques. Appetite 2018, 123, 191–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sleddens, E.F.C.; Kremers, S.P.J.; Hughes, S.O.; Cross, M.B.; Thijs, C.; de Vries, N.K.; O’Connor, T.M. Physical activity parenting: A systematic review of questionnaires and their associations with child activity levels. Obes. Rev. 2012, 13, 1015–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jago, R.; Edwards, M.J.; Urbanski, C.R.; Sebire, S.J. General and Specific Approaches to Media Parenting: A Systematic Review of Current Measures, Associations with Screen-Viewing, and Measurement Implications. Child. Obes. 2013, 9, S51–S72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trost, S.G.; McDonald, S.; Cohen, A. Measurement of General and Specific Approaches to Physical Activity Parenting: A Systematic Review. Child. Obes. 2013, 9, 40–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Timperio, A.F.; van Stralen, M.M.; Brug, J.; Bere, E.; Chinapaw, M.J.M.; de Bourdeaudhuij, I.; Jan, N.; Maes, L.; Manios, Y.; Moreno, L.A.; et al. Direct and indirect associations between the family physical activity environment and sports participation among 10–12 year-old European children: Testing the EnRG framework in the ENERGY project. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2013, 10, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- McHale, J.P.; Kuersten-Hogan, R.; Rao, N. Growing Points for Coparenting Theory and Research. J. Adult Dev. 2004, 11, 221–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Patrick, H.; Hennessy, E.; McSpadden, K.; Oh, A. Parenting Styles and Practices in Children’s Obesogenic Behaviors: Scientific Gaps and Future Research Directions. Child. Obes. 2013, 9, S73–S86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berge, J.M.; Wall, M.; Loth, K.; Neumark-Sztainer, D. Parenting Style as a Predictor of Adolescent Weight and Weight-Related Behaviors. J. Adolesc. Health 2010, 46, 331–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lloyd, A.B.; Lubans, D.R.; Plotnikoff, R.C.; Collins, C.E.; Morgan, P.J. Maternal and paternal parenting practices and their influence on children’s adiposity, screen-time, diet and physical activity. Appetite 2014, 79, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wake, M.; Nicholson, J.M.; Hardy, P.; Smith, K. Preschooler Obesity and Parenting Styles of Mothers and Fathers: Australian National Population Study. Pediatrics 2007, 120, e1520–e1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammons, A.J.; Fiese, B.H. Is frequency of shared family meals related to the nutritional health of children and adolescents? Pediatrics 2011, 127, e1565–e1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skeer, M.R.; Ballard, E.L. Are Family Meals as Good for Youth as We Think They Are? A Review of the Literature on Family Meals as They Pertain to Adolescent Risk Prevention. J. Youth Adolesc. 2013, 42, 943–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berge, J.M.; Rowley, S.; Trofholz, A.; Hanson, C.; Rueter, M.; MacLehose, R.F.; Neumark-Sztainer, D. Childhood obesity and interpersonal dynamics during family meals. Pediatrics 2014, 134, 923–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cleland, V.; Timperio, A.; Salmon, J.; Hume, C.; Telford, A.; Crawford, D. A Longitudinal Study of the Family Physical Activity Environment and Physical Activity among Youth. Am. J. Health Promot. 2011, 25, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Salmon, J.; Timperio, A.; Telford, A.; Carver, A.; Crawford, D. Association of Family Environment with Children’s Television Viewing and with Low Level of Physical Activity. Obes. Res. 2005, 13, 1939–1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naisseh, M.; Martinent, G.; Ferrand, C.; Hautier, C. Relationship between Parents’ Motivation for Physical Activity and Their Beliefs, and Support of Their Children’s Physical Activity: A Cluster Analysis. Pschol. Rep. 2015, 117, 230–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fredricks, J.A.; Eccles, J.S. Family Socialization, Gender, and Sport Motivation and Involvement. J. Sport Exerc. Psychol. 2005, 27, 3–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brustad, R.J. Attraction to Physical Activity in Urban Schoolchildren: Parental Socialization and Gender Influences. Res. Q. Exerc. Sport 1996, 67, 316–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zecevic, C.A.; Tremblay, L.; Lovsin, T.; Michel, L. Parental influence on young children’s physical activity. Int. J. Pediatr. 2010, 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fredricks, J.A.; Eccles, J.S. Parental influences on youth involvement in sports. In Developmental Sport and Exercise Psychology: A Lifespan Perspective; Weiss, M.R., Ed.; Fitness Information: Morgantown, WV, USA, 2004; pp. 145–164. [Google Scholar]
- Kimiecik, J.C.; Horn, T.S. Parental beliefs and children’s moderate-to-vigorous physical activity. Res. Q. Exerc. Sport 1998, 69, 163–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bois, J.E.; Sarrazin, P.G.; Brustad, R.J.; Trouilloud, D.O.; Cury, F. Mothers’ Expectancies and Young Adolescents’ Perceived Physical Competence: A Yearlong Study. J. Early Adolesc. 2002, 22, 384–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trost, S.G.; Sallis, J.F.; Pate, R.R.; Freedson, P.S.; Taylor, W.C.; Dowda, M. Evaluating a model of parental influence on youth physical activity. Am. J. Prev. Med. 2003, 25, 277–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews, K.R.; Silk, K.S.; Eneli, I.U. Parents as Health Promoters: A Theory of Planned Behavior Perspective on the Prevention of Childhood Obesity. J. Health Commun. 2010, 15, 95–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Webber, L.; Hill, C.; Cooke, L.; Carnell, S.; Wardle, J. Associations between child weight and maternal feeding styles are mediated by maternal perceptions and concerns. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2010, 64, 259–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Francis, L.A.; Hofer, S.M.; Birch, L.L. Predictors of maternal child-feeding style: Maternal and child characteristics. Appetite 2001, 37, 231–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gevers, D.W.M.; van Assema, P.; de Vries, N.K.; Kremers, S.P.J. Explaining use of food parenting practices: The importance of predisposing factors and parental cognitions. Public Health Nutr. 2017, 20, 2355–2363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baranowski, T.; Beltran, A.; Chen, T.-A.; Thompson, D.; O’Connor, T.; Hughes, S.; Diep, C.; Baranowski, J.C. Predicting use of ineffective vegetable parenting practices with the Model of Goal Directed Behavior. Public Health Nutr. 2015, 18, 1028–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bois, J.E.; Sarrazin, P.G.; Brustad, R.J.; Trouilloud, D.O.; Cury, F. Elementary schoolchildren’s perceived competence and physical activity involvement: The influence of parents’ role modelling behaviours and perceptions of their child’s competence. Psychol. Sport Exerc. 2005, 6, 381–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niermann, C.; Krapf, F.; Renner, B.; Reiner, M.; Woll, A. Family health climate scale (FHC-scale): Development and validation. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2014, 11, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerards, S.M.P.L.; Niermann, C.; Gevers, D.W.M.; Eussen, N.; Kremers, S.P.J. Context matters! The relationship between mother-reported family nutrition climate, general parenting, food parenting practices and children’s BMI. BMC Public Health 2016, 16, 1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niermann, C.Y.N.; Kremers, S.P.J.; Renner, B.; Woll, A. Family Health Climate and Adolescents’ Physical Activity and Healthy Eating: A Cross-Sectional Study with Mother-Father-Adolescent Triads. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0143599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flay, B.R.; Petraitis, J. The theory of triadic influence: A new theory of health behavior with implications for preventive interventions. Adv. Med. Sociol. 1994, 4, 19–44. [Google Scholar]
- Prinzie, P.; Stams, G.J.J.; Deković, M.; Reijntjes, A.H.A.; Belsky, J. The relations between parents’ Big Five personality factors and parenting: A meta-analytic review. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 2009, 97, 351–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanson, M.D.; Chen, E. Socioeconomic Status and Health Behaviors in Adolescence: A Review of the Literature. J. Behav. Med. 2007, 30, 263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Horst, K.; Paw, M.J.C.A.; Twisk, J.W.R.; van Mechelen, W. A brief review on correlates of physical activity and sedentariness in youth. Med. Sci. Sport Exerc. 2007, 39, 1241–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vereecken, C.A.; Keukelier, E.; Maes, L. Influence of mother’s educational level on food parenting practices and food habits of young children. Appetite 2004, 43, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maccoby, E.E.; Martin, J.A. Socialization in the context of the family: Parent-child interaction. In Handbook of Child Psychology: Vol. 4: Socialization, Personality and Social Development, 4th ed.; Mussen, P.H., Hetherington, E.M., Eds.; Wiley: New York, NY, USA; Chichester, UK, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Skinner, E.; Johnson, S.; Snyder, T. Six Dimensions of Parenting: A Motivational Model. Parenting 2005, 5, 175–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sleddens, E.F.C.; O’Connor, T.M.; Watson, K.B.; Hughes, S.O.; Power, T.G.; Thijs, C.; de Vries, N.K.; Kremers, S.P.J. Development of the Comprehensive General Parenting Questionnaire for caregivers of 5–13 year olds. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2014, 11, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinquart, M. Associations of general parenting and parent–child relationship with pediatric obesity: A meta-analysis. J. Pediatr. Psychol. 2014, 39, 381–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodenburg, G.; Kremers, S.P.J.; Oenema, A.; van de Mheen, D. Associations of parental feeding styles with child snacking behaviour and weight in the context of general parenting. Public Health Nutr. 2014, 17, 960–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sleddens, E.F.C.; Kremers, S.P.J.; Stafleu, A.; Dagnelie, P.C.; de Vries, N.K.; Thijs, C. Food parenting practices and child dietary behavior. Prospective relations and the moderating role of general parenting. Appetite 2014, 79, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez, N.V.; Schembre, S.; Belcher, B.R.; O’Connor, S.; Maher, J.P.; Arbel, R.; Margolin, G.; Dunton, G.F. Parenting styles, food-related parenting practices, and children’s healthy eating: A mediation analysis to examine relationships between parenting and child diet. Appetite 2018, 128, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epstein, N.B.; Bishop, D.S.; Levin, S. The McMaster Model of Family Functioning. J. Marital Fam. Ther. 1978, 4, 19–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moos, R.H.; Moos, B.S. A Typology of Family Social Environments. Fam. Process. 1976, 15, 357–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atkin, A.J.; Corder, K.; Goodyer, I.; Bamber, D.; Ekelund, U.; Brage, S.; Dunn, V.; van Sluijs, E.M.F. Perceived family functioning and friendship quality: Cross-sectional associations with physical activity and sedentary behaviours. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2015, 12, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Welsh, E.M.; French, S.A.; Wall, M. Examining the relationship between family meal frequency and individual dietary intake: Does family cohesion play a role? J. Nutr. Educ. Behav. 2011, 43, 229–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franko, D.L.; Thompson, D.; Bauserman, R.; Affenito, S.G.; Striegel-Moore, R.H. What’s love got to do with it? Family cohesion and healthy eating behaviors in adolescent girls. Int. J. Eat. Disord. 2008, 41, 360–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Bourdeaudhuij, I.; van Oost, P. Personal and family determinants of dietary behaviour in adolescents and their parents. Psychol. Health 2000, 15, 751–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimiecik, J.C.; Horn, T.S. Examining the relationship between family context and children’s physical activity beliefs: The role of parenting style. Psychol. Sport Exerc. 2012, 13, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hingle, M.D.; O’Connor, T.M.; Dave, J.M.; Baranowski, T. Parental involvement in interventions to improve child dietary intake: A systematic review. Prev. Med. 2010, 51, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- O’Connor, T.M.; Jago, R.; Baranowski, T. Engaging Parents to Increase Youth Physical Activity: A Systematic Review. Am. J. Prev. Med. 2009, 37, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, S.M.; Dawson, D. Purposive Leisure: Examining Parental Discourses on Family Activities. Leisure Sci. 2001, 23, 217–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baranowski, T.; O’Connor, T.; Hughes, S.; Sleddens, E.; Beltran, A.; Frankel, L.; Mendoza, J.A.; Baranowski, J. Houston … We Have a Problem! Measurement of Parenting. Child. Obes. 2013, 9, S1–S4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davison, K.K.; Gicevic, S.; Aftosmes-Tobio, A.; Ganter, C.; Simon, C.L.; Newlan, S.; Manganello, J.A. Fathers’ Representation in Observational Studies on Parenting and Childhood Obesity: A Systematic Review and Content Analysis. Am. J. Public Health 2016, 106, e14–e21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, P.J.; Young, M.D. The Influence of Fathers on Children’s Physical Activity and Dietary Behaviors: Insights, Recommendations and Future Directions. Curr. Obes. Rep. 2017, 6, 324–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brazendale, K.; Beets, M.W.; Weaver, R.G.; Pate, R.R.; Turner-McGrievy, G.M.; Kaczynski, A.T.; Chandler, J.L.; Bohnert, A.; von Hippel, P.T. Understanding differences between summer vs. school obesogenic behaviors of children: The structured days hypothesis. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2017, 14, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gubbels, J.S.; van Kann, D.H.H.; de Vries, N.K.; Thijs, C.; Kremers, S.P.J. The next step in health behavior research: The need for ecological moderation analyses—An application to diet and physical activity at childcare. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2014, 11, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Pathways Derived from LIFES | Potential Factors and Assumed Pathways |
|---|---|
| 2c-1c-1child | positive nutrition climate (2c) → more frequent family meals (1c) → child eats more regularly and has a higher intake of healthy foods (e.g., vegetables) (1child) |
| 2c-2child-1child | positive physical activity climate (2c) → child has more intrinsic motivation to be physically active (2child) → child is more physically active (1child) |
| 2a-2b-1b-1child | negative attitude regarding sugar sweetened beverages (2a) → more perceived importance that child does not drink sugar sweetened beverages (2b) → role modeling of drinking water instead of sugar sweetened beverages (1b) → child drinks more water instead of sugar sweetened beverages (1child) |
| 3c moderates 1b-1child | higher cohesion within the family (3c) stronger impact (moderation) of role modeling of reducing sedentary time (1b) → child reduces sedentary time (1child) |
| 3a-3b moderates 2b-2child-1child | higher level of agreeableness of a parent (3a) → more autonomy supportive parenting (3b) stronger impact (moderation) of more positive attitude towards child’s playing outside (2b) → more intrinsic motivation for playing outside in child (2child) → child plays more outside (1child) |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Niermann, C.Y.N.; Gerards, S.M.P.L.; Kremers, S.P.J. Conceptualizing Family Influences on Children’s Energy Balance-Related Behaviors: Levels of Interacting Family Environmental Subsystems (The LIFES Framework). Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 2714. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15122714
Niermann CYN, Gerards SMPL, Kremers SPJ. Conceptualizing Family Influences on Children’s Energy Balance-Related Behaviors: Levels of Interacting Family Environmental Subsystems (The LIFES Framework). International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2018; 15(12):2714. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15122714
Chicago/Turabian StyleNiermann, Christina Y.N., Sanne M.P.L. Gerards, and Stef P.J. Kremers. 2018. "Conceptualizing Family Influences on Children’s Energy Balance-Related Behaviors: Levels of Interacting Family Environmental Subsystems (The LIFES Framework)" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 15, no. 12: 2714. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15122714
APA StyleNiermann, C. Y. N., Gerards, S. M. P. L., & Kremers, S. P. J. (2018). Conceptualizing Family Influences on Children’s Energy Balance-Related Behaviors: Levels of Interacting Family Environmental Subsystems (The LIFES Framework). International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 15(12), 2714. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15122714