Biomethanation of Harmful Macroalgal Biomass in Leach-Bed Reactor Coupled to Anaerobic Filter: Effect of Water Regime and Filter Media
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Inoculum and Ulva Biomass
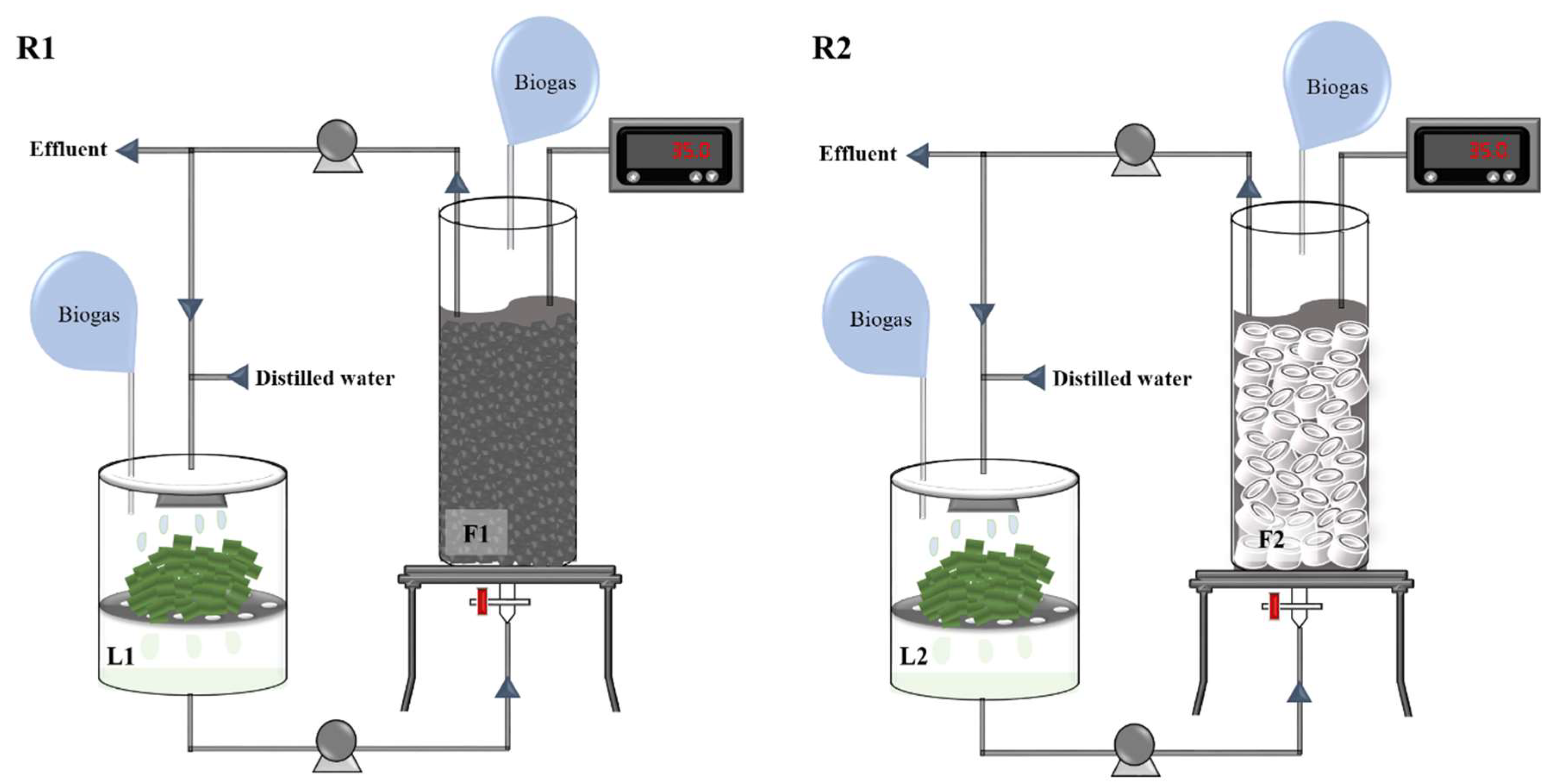
2.2. Reactor Setup and Operation
2.3. DNA Extraction
2.4. Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction
2.5. High-Resolution Melting Analysis
2.6. Analytical Methods
3. Results
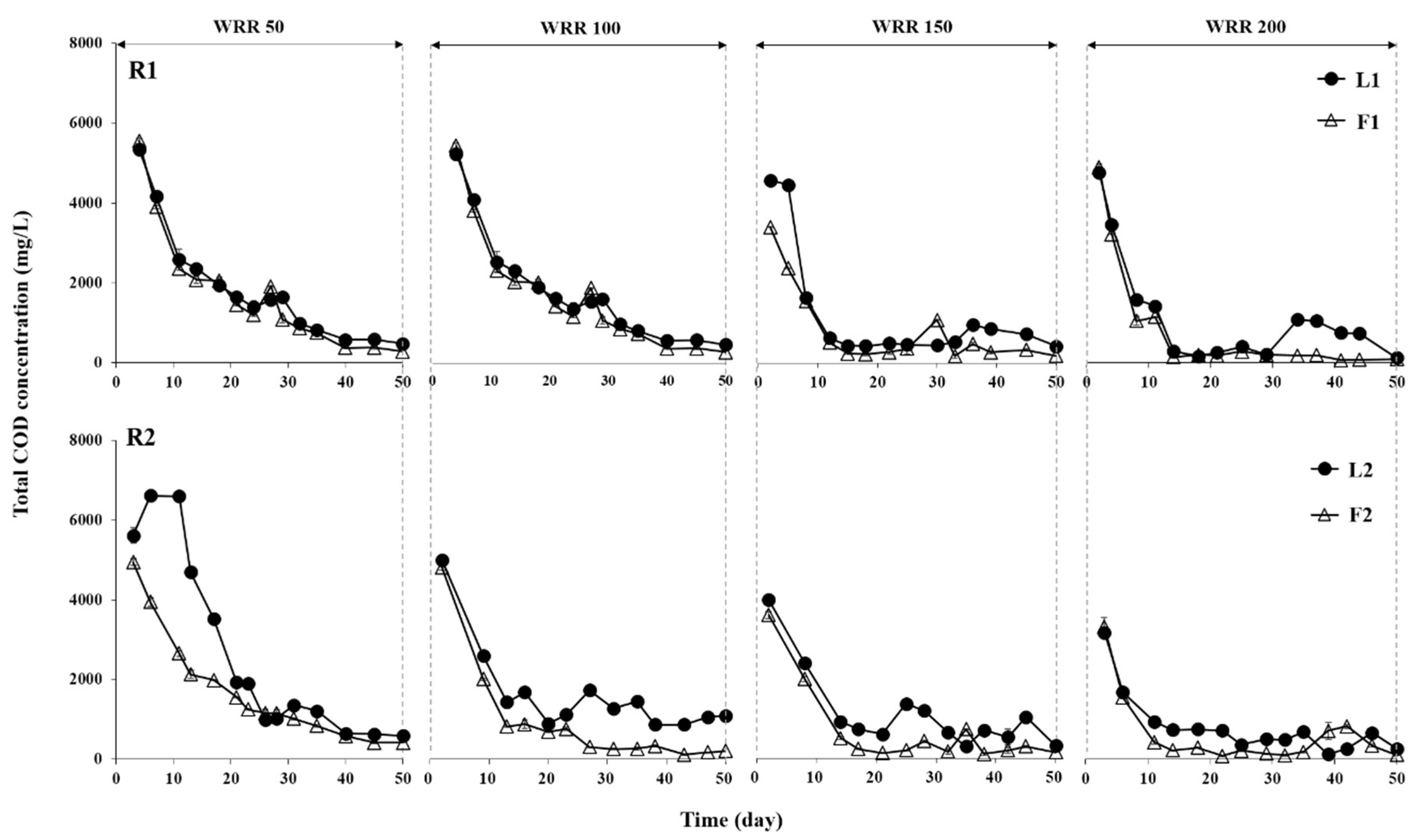
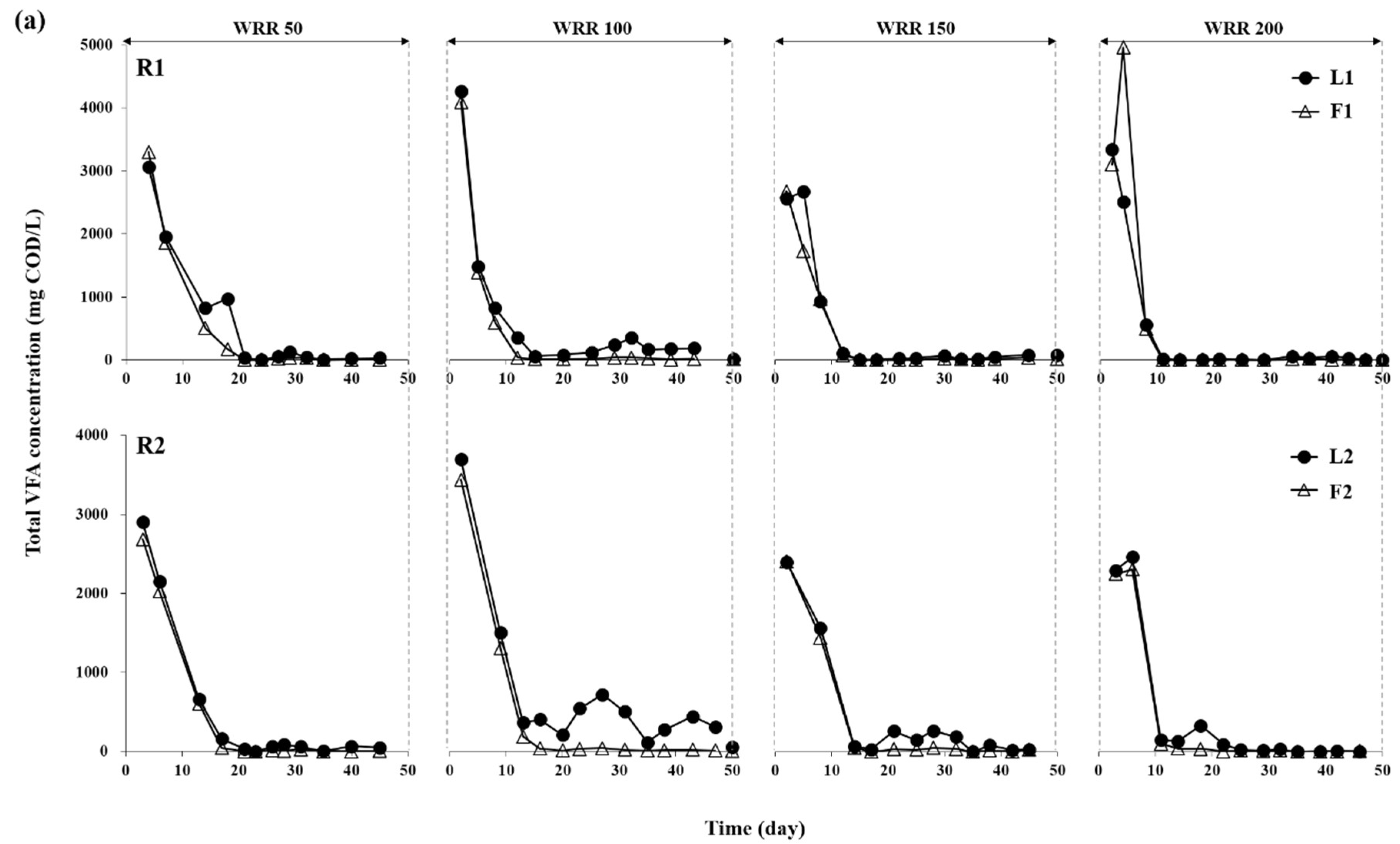
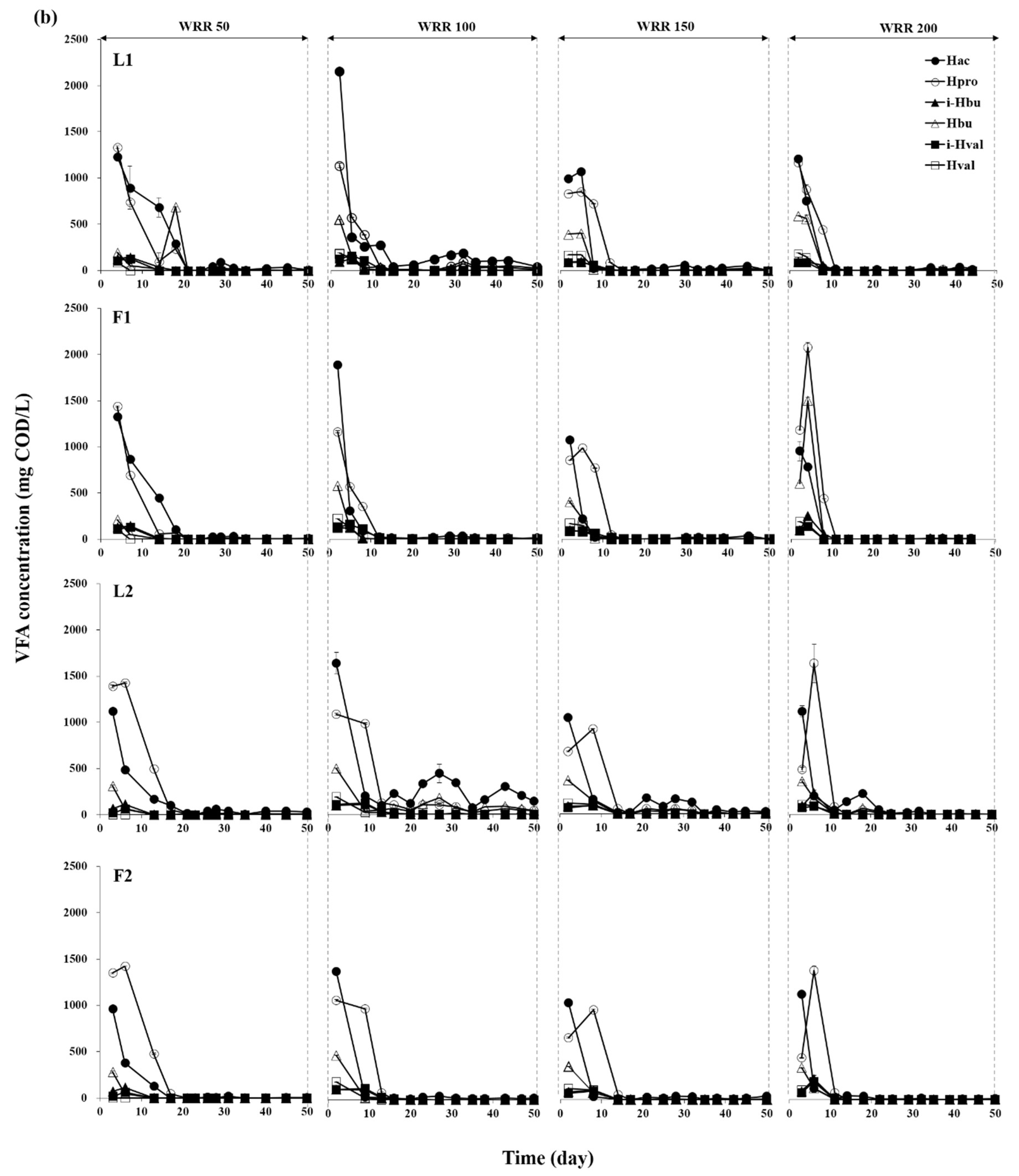
3.1. Degradation of Ulva Biomass
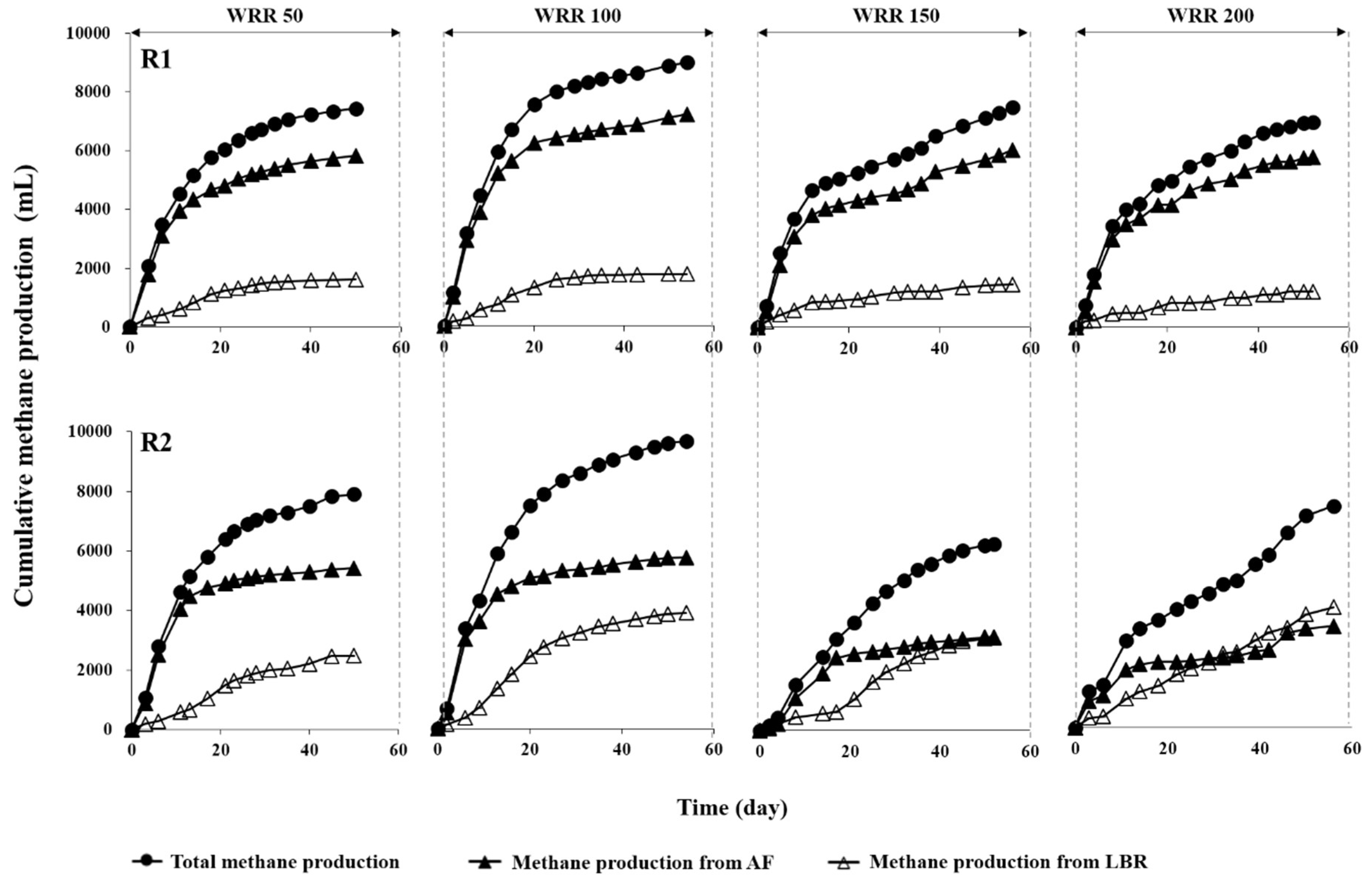
3.2. Methane Production Performance
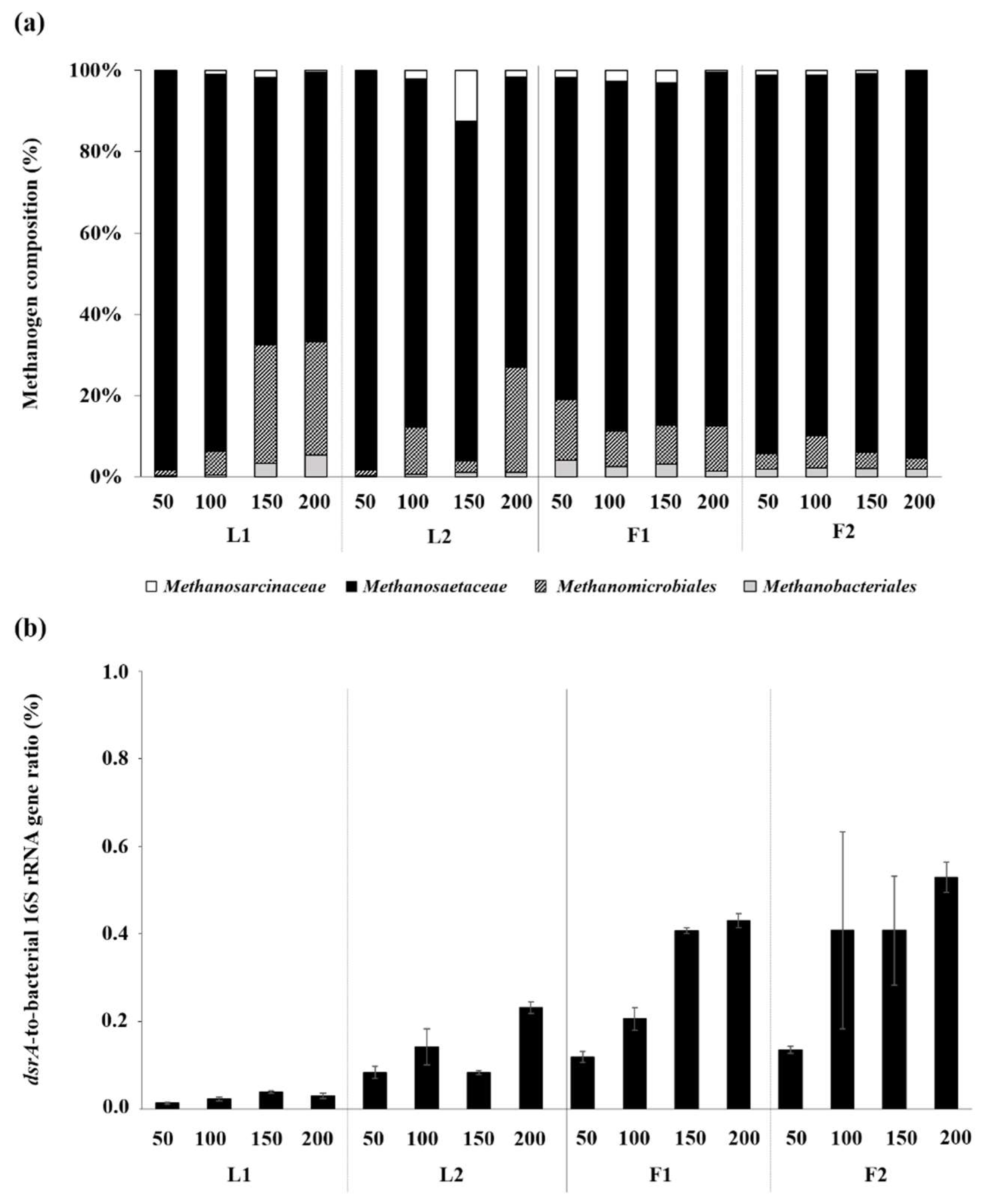
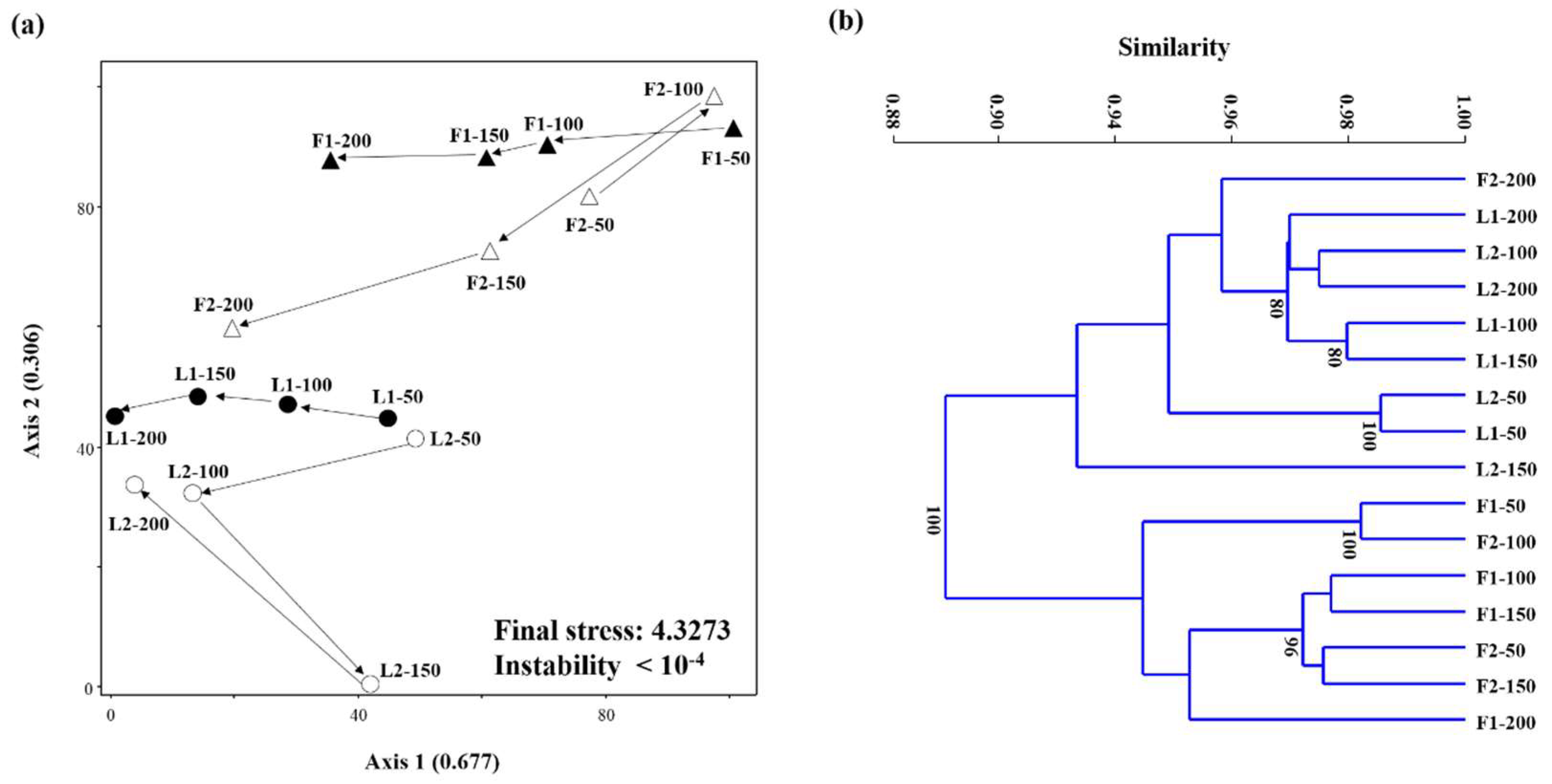
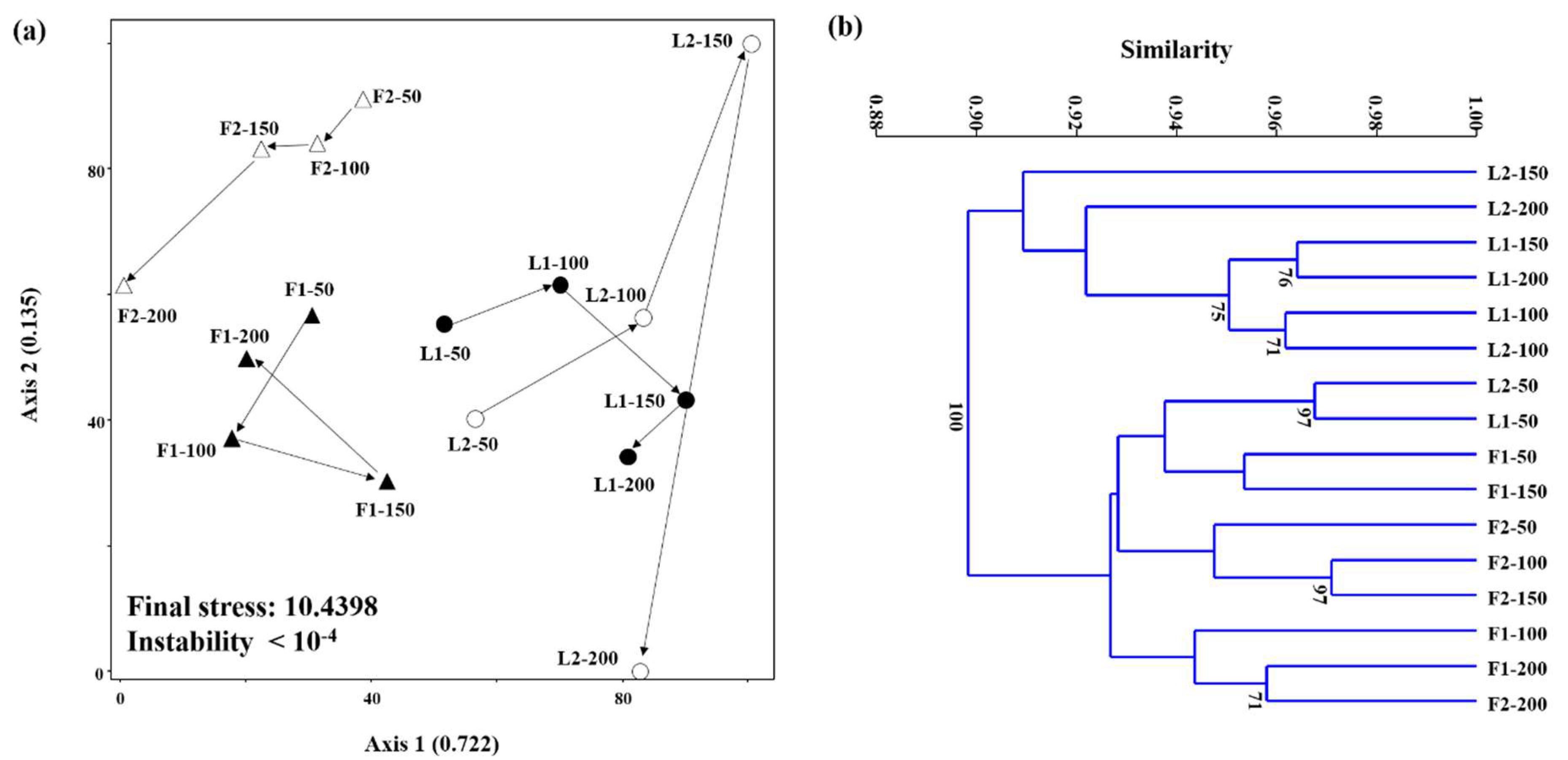
3.3. Microbial Community Structures
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Charlier, R.H.; Morand, P.; Finkl, C.W. How Brittany and Florida coasts cope with green tides. Int. J. Environ. Stud. 2008, 65, 191–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, N.H.; Zhang, X.W.; Mao, Y.Z.; Liang, C.W.; Xu, D.; Zou, J.; Zhuang, Z.M.; Wang, Q.Y. ‘Green tides’ are overwhelming the coastline of our blue planet: Taking the world’s largest example. Ecol. Res. 2011, 26, 477–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, L.; Bao, X.; Zhao, L. Economic cost of an algae bloom cleanup in China’s 2008 Olympic sailing venue. Eos Trans. Am. Geophys. Union 2009, 90, 238–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruhn, A.; Dahl, J.; Nielsen, H.B.; Nikolaisen, L.; Rasmussen, M.B.; Markager, S.; Olesen, B.; Arias, C.; Jensen, P.D. Bioenergy potential of Ulva lactuca: Biomass yield, methane production and combustion. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 2595–2604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, J.C.; Gonçalves, P.R.; Nobre, A.; Alves, M.M. Biomethanation potential of macroalgae Ulva spp. and Gracilaria spp. and in co-digestion with waste activated sludge. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 114, 320–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, H.; Kim, J.; Lee, J.; Hwang, S.; Lee, C. Biomethanation potential of marine macroalgal Ulva biomass in sequencing batch mode: Changes in process performance and microbial community structure over five cycles. Biomass Bioenergy 2016, 91, 143–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.Y.; Karthikeyan, O.P.; Selvam, A.; Wong, J.W.C. Microbial community distribution and extracellular enzyme activities in leach bed reactor treating food waste: Effect of different leachate recirculation practices. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 168, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riggio, S.; Torrijos, M.; Vives, G.; Esposito, G.; van Hullebusch, E.D.; Steyer, J.P.; Escudié, R. Leachate flush strategies for managing volatile fatty acids accumulation in leach-bed reactors. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 232, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lehtomäki, A.; Huttunen, S.; Lehtinen, T.M.; Rintala, J.A. Anaerobic digestion of grass silage in batch leach bed processes for methane production. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 3267–3278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linke, B.; Rodríguez-Abalde, Á.; Jost, C.; Krieg, A. Performance of a novel two-phase continuously fed leach bed reactor for demand-based biogas production from maize silage. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 177, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, S.; Selvam, A.; Karthikeyan, O.P.; Wong, J.W.C. Responses of microbial community and acidogenic intermediates to different water regimes in a hybrid solid anaerobic digestion system treating food waste. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 168, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karadag, D.; Köroğlu, O.E.; Ozkaya, B.; Cakmakci, M. A review on anaerobic biofilm reactors for the treatment of dairy industry wastewater. Process Biochem. 2015, 50, 262–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.P.; Prerna, P. Review of recent advances in anaerobic packed-bed biogas reactors. Renew. Sust. Energy Rev. 2009, 13, 1569–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, G.K.; Kasapgil, B.; Ince, O. Comparison of porous and non-porous media in upflow anaerobic filters when treating dairy wastewater. Water Res. 1994, 28, 1619–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loupasaki, E.; Diamadopoulos, E. Attached growth systems for wastewater treatment in small and rural communities: A review. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2013, 88, 190–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanphoti, N.; Towprayoon, S.; Chaiprasert, P.; Nopharatana, A. The effects of leachate recirculation with supplemental water addition on methane production and waste decomposition in a simulated tropical landfill. J. Environ. Manag. 2006, 81, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bohutskyi, P.; Bouwer, E. Biogas production from algae and cyanobacteria through anaerobic digestion: A review, analysis, and research needs. In Advanced Biofuels and Bioproducts; Lee, J.W., Ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2013; pp. 873–975. [Google Scholar]
- Jo, Y.; Kim, J.; Hwang, S.; Lee, C. Anaerobic treatment of rice winery wastewater in an upflow filter packed with steel slag under different hydraulic loading conditions. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 193, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Jung, H.; Lee, C. Shifts in bacterial and archaeal community structures during the batch biomethanation of Ulva biomass under mesophilic conditions. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 169, 502–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Lee, C. Response of a continuous anaerobic digester to temperature transitions: A critical range for restructuring the microbial community structure and function. Water Res. 2016, 89, 241–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ben-Dov, E.; Brenner, A.; Kushmaro, A. Quantification of sulfate-reducing bacteria in industrial wastewater, by real-time polymerase chain reaction (PCR) using dsrA and apsA Genes. Microb. Ecol. 2007, 54, 439–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baek, G.; Kim, J.; Cho, K.; Bae, H.; Lee, C. The biostimulation of anaerobic digestion with (semi) conductive ferric oxides: Their potential for enhanced biomethanation. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 99, 10355–10366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Lee, S.; Lee, C. Comparative study of changes in reaction profile and microbial community structure in two anaerobic repeated-batch reactors started up with different seed sludges. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 129, 495–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCune, B.; Grace, J.B.; Urban, D.L. Analysis of Ecological Communities; MjM Software Design: Gleneden Beach, OR, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- APHA-AWWA-WEF. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater; American Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.Z.; Ban, Q.Y.; Zhang, L.G.; Ajar Kumar, J. Syntrophic propionate degradation in anaerobic digestion: A review. Int. J. Agric. Biol. 2012, 14, 163–170. [Google Scholar]
- Lehtomäki, A.; Björnsson, L. Two-Stage anaerobic digestion of energy crops: Methane production, nitrogen mineralisation and heavy metal mobilization. Environ. Technol. 2006, 27, 209–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.W.; Samani, Z.; Hanson, A.; Smith, G. Energy recovery from grass using two-phase anaerobic digestion. Waste Manag. 2002, 22, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nkemka, V.N.; Rivera, J.A.; Murto, M. Two-stage dry anaerobic digestion of beach cast seaweed and its co digestion with cow manure. J. Waste Manag. 2014, 2014, 325341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, E.; Wall, D.M.; Herrmann, C.; Xia, A.; Murphy, J.D. What is the gross energy yield of third generation gaseous biofuel sourced from seaweed? Energy 2015, 81, 352–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Zhou, D.; Luo, G.; Zhang, S.; Chen, J. Macroalgae for biofuels production: Progress and perspectives. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 47, 427–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, B.H.; Selvam, A.; Wong, J.W.C. Application of rumen microbes to enhance food waste hydrolysis in acidogenic leach-bed reactors. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 168, 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nkemka, V.N.; Murto, M. Evaluation of biogas production from seaweed in batch tests and in UASB reactors combined with the removal of heavy metals. J. Environ. Manag. 2010, 91, 1573–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuo, Z.; Wu, S.; Zhang, W.; Dong, R. Effects of organic loading rate and effluent recirculation on the performance of two-stage anaerobic digestion of vegetable waste. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 146, 556–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jo, Y.; Kim, J.; Lee, C. Continuous treatment of dairy effluent in a downflow anaerobic filter packed with slag grains: Reactor performance and kinetics. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2016, 68, 147–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wellinger, A.; Lindberg, A. Biogas Upgrading and Utilisation, Task 24-Energy from Biological Conversion of Organic Waste; IEA Bioenergy: Paris, France, 2001; pp. 1–19. [Google Scholar]
| Parameters | Units | Anaerobic Sludge | Ulva Biomass |
|---|---|---|---|
| Total COD | g/L | 27.5 (0.1) a | - b |
| Soluble COD | g/L | 2.7 (0.0) | - |
| TS | g/L or g/kg wet c | 38.2 (0.1) | 153.9 (8.4) |
| TVS | g/L or g/kg wet | 22.6 (0.1) | 126.1 (7.8) |
| TSS | g/L | 30.8 (0.3) | - |
| VSS | g/L | 20.5 (0.3) | - |
| Carbon | % | 27.8 (0.5) | 37.8 (0.5) |
| Hydrogen | % | 4.4 (0.1) | 7.2 (0.3) |
| Nitrogen | % | 5.4 (0.1) | 5.4 (0.0) |
| Sulfur | % | 1.0 (0.2) | 1.9 (0.2) |
| Oxygen | % | 22.2 (0.6) | 35.7 (0.3) |
| Parameter a | Unit | R1 | R2 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WRR 50 b | WRR 100 | WRR 150 | WRR 200 | WRR 50 | WRR 100 | WRR 150 | WRR 200 | ||
| TS reduction | % | 85.0 (0.1) c | 75.4 (0.6) | 75.9 (0.8) | 69.3 (3.3) | 78.4 (0.7) | 76.3 (1.0) | 73.1 (0.8) | 73.3 (2.2) |
| VS reduction | % | 87.1 (0.8) | 78.0 (0.8) | 75.4 (1.1) | 68.4 (2.1) | 82.3 (0.0) | 78.4 (1.0) | 72.9 (0.5) | 71.7 (2.0) |
| Total CH4 | mL | 7437 (28) | 8808 (16) | 7415 (26) | 6878 (14) | 7905 (56) | 9613 (43) | 6165 (70) | 7381 (35) |
| CH4 from LBR | mL | 1614 (1) | 1736 (8) | 1438 (25) | 1190 (6) | 2482 (5) | 3881 (10) | 3066 (66) | 4007 (1) |
| CH4 from AF | mL | 5823 (28) | 7072 (14) | 5977 (8) | 5688 (13) | 5423 (55) | 5732 (42) | 3099 (22) | 3374 (35) |
| Ymaf | mL/g VS fed | 203 (0.01) | 285 (0.02) | 210 (0.0) | 238 (0.0) | 216 (0.02) | 309 (0.02) | 148 (0.02) | 218 (0.02) |
| Ymat | mL/g VS fed | 225 (0.07) | 317 (0.09) | 231 (0.08) | 280 (0.08) | 236 (0.07) | 344 (0.18) | 161 (0.01) | 251 (0.1) |
| Total H2S | mL | 84.3 (0.0) | 93.1 (0.0) | 53.6 (0.0) | 48.0 (0.0) | 87.0 (0.0) | 43.3 (0.0) | 27.2 (0.0) | 26.5 (0.0) |
| H2S from LBR | mL | 16.7 (0.0) | 10.8 (0.0) | 10.0 (0.0) | 8.9 (0.0) | 23.2 (0.0) | 21.8 (0.0) | 13.3 (0.0) | 13.7 (0.0) |
| H2S from AF | mL | 67.6 (0.0) | 82.3 (0.0) | 43.6 (0.0) | 39.1 (0.0) | 63.8 (0.0) | 21.5 (0.0) | 13.9 (0.0) | 12.8 (0.0) |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jung, H.; Kim, J.; Lee, C. Biomethanation of Harmful Macroalgal Biomass in Leach-Bed Reactor Coupled to Anaerobic Filter: Effect of Water Regime and Filter Media. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 866. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15050866
Jung H, Kim J, Lee C. Biomethanation of Harmful Macroalgal Biomass in Leach-Bed Reactor Coupled to Anaerobic Filter: Effect of Water Regime and Filter Media. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2018; 15(5):866. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15050866
Chicago/Turabian StyleJung, Heejung, Jaai Kim, and Changsoo Lee. 2018. "Biomethanation of Harmful Macroalgal Biomass in Leach-Bed Reactor Coupled to Anaerobic Filter: Effect of Water Regime and Filter Media" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 15, no. 5: 866. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15050866
APA StyleJung, H., Kim, J., & Lee, C. (2018). Biomethanation of Harmful Macroalgal Biomass in Leach-Bed Reactor Coupled to Anaerobic Filter: Effect of Water Regime and Filter Media. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 15(5), 866. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15050866





