Vascular Hyperactivity in the Rat Renal Aorta Participates in the Association between Immune Complex-Mediated Glomerulonephritis and Systemic Hypertension
Abstract
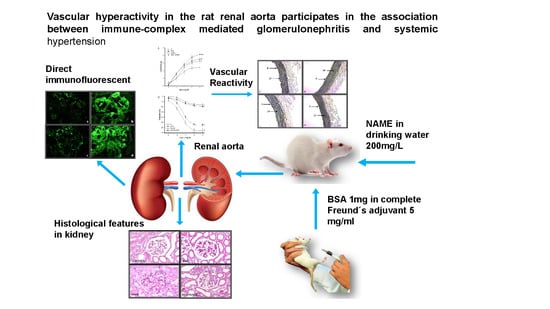
:1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Animal Treatment
2.2. Systolic Blood Pressure
2.3. Proteinuria and Glomerular Filtration
2.4. Histological Preparation
2.5. Vascular Reactivity
2.6. L-NAME
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Blood Pressure
3.2. Proteinuria and Glomerular Filtration
3.3. Vascular Reactivity
3.3.1. Vasoconstriction
3.3.2. Vasodilatation
3.3.3. Effect of L-NAME
3.3.4. Histological Characteristics (Elastic Fibers) in Renal Artery
3.3.5. Histological Features in Kidney
4. Discussion
5. Endothelium
6. Endothelial and Inducible Nitric Oxide Synthases
7. Elastic Fibers in Renal Aorta
8. Hypertension and Glomerulonephritis
9. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Stevens, P.E.; Levin, A. Evaluation and management of chronic kidney disease: Synopsis of the kidney disease: Improving global outcomes 2012 clinical practice guideline. Ann. Intern. Med. 2013, 158, 825–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.J.; Jennette, J.C.; Falk, R.J. Immune complex glomerulonephritis is induced in rats immunized with heterologous myeloperoxidase. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 1994, 97, 466–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, W.S.; Jeong, K.H.; Moon, J.Y.; Lee, S.H.; Cho, J.H.; Lee, T.W.; Park, Y.K.; Cho, B.S.; Ihm, C.G. Relationship between glomerulomegaly and clinicopathologic findings in IgA nephropathy. Clin. Nephrol. 2012, 78, 470–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gadau, J.; Peters, H.; Kastner, C.; Kühn, H.; Nieminen-Kelhä, M.; Khadzhynov, D.; Krämer, S.; Castrop, H.; Bachmann, S.; Theilig, F. Mechanisms of tubular volume retention in immune-mediated glomerulonephritis. Kidney. Int. 2009, 75, 699–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Okuda, S.; Onoyama, K.; Fujimi, S.; Oh, Y.; Nomoto, K.; Omae, T. Influence of hypertension on the progression of experimental autologous immune complex nephritis. J. Lab. Clin. Med. 1983, 101, 461–471. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dixon, F.J.; Wilson, C.B.; Marquardt, H. Experimental immunologic glomerulonephritis. Adv. Nephrol. Necker. Hosp. 1971, 1, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, K.; Oite, T.; Kihara, I.; Shimizu, F. Experimental glomerulonephritis induced by human IgG in rats. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 1984, 57, 575–582. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Woitas, R.P.; Morioka, T. Influence of isoelectric point on glomerular deposition of antibodies and immune complexes. Nephron 1996, 74, 713–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pirkle, J.L.; Freedman, B.I. Hypertension and chronic kidney disease: Controversies in pathogenesis and treatment. Minerva. Urol. Nefrol. 2013, 65, 37–50. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sánchez, T.G.; Baños, G. Hipertensión Arterial: Fisiopatología; Gustavo Sánchez Torres y Guadalupe Baños de MacCarthy: México City, México, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Iversen, B.M.; Amann, K.; Kvam, F.I.; Wang, X.; Ofstad, J. Increased glomerular capillary pressure and size mediate glomerulosclerosis in SHR juxtamedullary cortex. Am. J. Physiol. 1998, 274, F365–F373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Tang, Z.; Yang, G.; Shen, S.; Yu, Y.; Zeng, C.; Chen, H.; Liu, Z.H.; Li, L.S. Malignant hypertension in patients with idiopathic IgA nephropathy. Kidney Blood Press. Res. 2005, 28, 251–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ihm, C.G. Hypertension in Chronic Glomerulonephritis. Electr. Blood Press. 2015, 13, 41–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez-Torres, I.; Roque, P.; El Hafidi, M.; Diaz-Diaz, E.; Baños, G. Association of renal damage and oxidative stress in a rat model of metabolic syndrome. Influence of gender. Free. Radic. Res. 2009, 43, 761–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- BenGershom, E. Screening for albuminuria: A case for estimation of albumin in urine. Clin. Chem. 1975, 21, 1795–1798. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Perrone, R.D.; Madias, N.E.; Levey, A.S. Serum creatinine as an index of renal function: New insights into old concepts. Clin. Chem. 1992, 38, 1933–1953. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Luna, G.L. Histopathology Laboratories, 3a Edition, Armed Forces Institute of Pathology Washington, D.C. Eds; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1967; pp. 72–99. [Google Scholar]
- Perez-Torres, I.; El Hafidi, M.; Carvajal, K.; Baños, G. Castration modifies aortic vasoreactivity and serum fatty acids in a sucrose-fed rat model of metabolic syndrome. Heart Vessel. 2009, 24, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puar, T.H.; Mok, Y.; Debajyoti, R.; Khoo, J.; How, C.H.; Ng, A.K. Secondary hypertension in adults. Singap. Med. J. 2016, 57, 228–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freedman, B.I.; Sedor, J.R. Hypertension-associated kidney disease: Perhaps no more. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2008, 19, 2047–2051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anjum, S.; Muzaale, A.D.; Massie, A.B.; Bae, S.; Luo, X.; Grams, M.E.; Lentine, K.L.; Garg, A.X.; Segev, D.L. Patterns of End-Stage Renal Disease Caused by Diabetes, Hypertension, and Glomerulonephritis in Live Kidney Donors. Am. J. Trans. 2016, 16, 3540–3547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stein, H.D.; Sterzel, R.B.; Hunt, J.D.; Pabst, R.; Kashgarian, M. No aggravation of the course of experimental glomerulonephritis in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Am. J. Pathol. 1986, 122, 520–530. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Luke, R.G. Hypertensive nephrosclerosis. Kidney Int. 2006, 70, 1383–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hill, G.S.; Heudes, D.; Jacquot, C.; Gauthier, E.; Bariéty, J. Morphometric evidence for impairment of renal autoregulation in advanced essential hypertension. Kidney Int. 2006, 69, 823–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heeringa, P.; van Goor, H.; Itoh-Lindstrom, Y.; Maeda, N.; Falk, R.J.; Assmann, K.J.; Kallenberg, C.G.; Jennette, J.C. Lack of endothelial nitric oxide synthase aggravates murine accelerated anti-glomerular basement membrane glomerulonephritis. Am. J. Pathol. 2000, 156, 879–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meenakshi, S.R.; Agarwal, R. Nitric oxide levels in patients with chronic renal disease. J. Clin. Diagn. Res. 2013, 7, 1288–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez-Torres, I.; El Hafidi, M.; Infante, O.; Baños, G. Effects of sex hormone levels on aortic vascular reactivity and variables associated with the metabolic syndrome in sucrose-fed female rats. Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2008, 86, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soto, M.E.; Iturriaga, H.V.; Guarner-Lans, V.; Zuñiga-Muñoz, A.; Aranda, F.A.; Velázquez, E.R.; Pérez-Torres, I. Participation of oleic acid in the formation of the aortic aneurysm in Marfan syndrome patients. Prostaglandins. Other Lipid Med. 2016, 123, 46–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cook, H.T.; Sullivan, R. Glomerular nitrite synthesis in in situ immune complex glomerulonephritis in the rat. Am. J. Pathol. 1991, 139, 1047–1052. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Furusu, A.; Miyazaki, M.; Abe, K.; Tsukasaki, S.; Shioshita, K.; Sasaki, O.; Miyazaki, K.; Ozono, Y.; Koji, T.; Harada, T.; et al. Expression of endothelial and inducible nitric oxide synthase in human glomerulonephritis. Kidney Int. 1998, 53, 1760–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakagawa, T.; Tanabe, K.; Croker, B.P.; Johnson, R.J.; Grant, M.B.; Kosugi, T.; Li, Q. Endothelial dysfunction as a potential contributor in diabetic nephropathy. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2011, 7, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forbes, M.S.; Thornhill, B.A.; Park, M.H.; Chevalier, R.L. Lack of endothelial nitric-oxide synthase leads to progressive focal renal injury. Am. J. Pathol. 2007, 170, 87–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kashem, A.; Endoh., M.; Yano, N.; Yamauchi, F.; Nomoto, Y.; Sakai, H. Expression of inducible-NOS in human glomerulonephritis: The possible source is infiltrating monocytes/macrophages. Kidney Int. 1996, 50, 392–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jansen, A.; Cook, T.; Taylor, G.M.; Largen, P.; Riveros-Moreno, V.; Moncada, S.; Cattell, V. Induction of nitric oxide synthase in rat immune complex glomerulonephritis. Kidney Int. 1994, 45, 1215–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez-Maldonado, M. Hypertension in end-stage renal disease. Kidney Int. Suppl. 1998, 68, S67–S72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scarpelli, P.T.; Gallo, M.; De Cesaris, F.; Chiari, G.; Dedola, G.; Cappeli, S.; Becucci, A.; Becherelli, P.; Tosi, B.; Fanetti, C.; et al. Continuing follow-up of malignant hypertension. J. Nephrol. 2002, 15, 431–437. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kuijpers, M.H.; Gruys, E. Spontaneous hypertension and hypertensive renal disease in the fawn-hooded rat. Br. J. Exp. Pathol. 1984, 65, 181–190. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ofstad, J.; Iversen, B.M. Glomerular and tubular damage in normotensive and hypertensive rats. Am. J. Physiol. Renal. Physiol. 2005, 288, F665–F672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soto, M.E.; Guarner-Lans, V.; Herrera-Morales, K.Y.; Pérez-Torres, I. Participation of arachidonic acid metabolism in the aortic aneurysm formation in patients with marfan syndrome. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakayama, T.; Sato, W.; Kosugi, T.; Zhang, L.; Campbell-Thompson, M.; Yoshimura, A.; Croker, B.P.; Johnson, R.J.; Nakagawa, T. Endothelial injury due to eNOS deficiency accelerates the progression of chronic renal disease in the mouse. Am. J. Phys. Ren. Physiol. 2009, 296, F317–F327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Scarpelli, P.T.; Gallo, M.; De Cesaris, F.; Chiari, G.; Dedola, G.; Cappeli, S.; Becucci, A.; Becherelli, P.; Tosi, B.; Fanetti, C.; et al. Intrinsic proinflammatory signaling in podocytes contributes to podocyte damage and prolonged proteinuria. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol. 2012, 303, F1473–F1485. [Google Scholar]










| Variables | C | BSA | NAME | BSA + NAME |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BP (mmHg) | 97.32 ± 2.91 | 126.90 ± 2.24 ** | 147.07 ± 1.07 *** | 173.41 ± 5.36 *** |
| Proteinuria (mg protein/24 h) | 29.89 ± 3.71 | 50.98 ± 10.06 * | 162.66 ± 31.32 *** | 178.64 ± 23.90 *** |
| SCr (µg/dL) | 0.68 ± 0.05 | 0.95 ± 0.10 ** | 1.18 ± 0.12 ** | 1.35 ± 0.09 ** |
| UCr (mg/dL) | 1.06 ± 0.08 | 0.52 ± 0.19 * | 0.76 ± 0.06 * | 0.67 ± 0.36 |
| CrCl (mL/min) | 0.0114 ± 0.0015 | 0.0073 ± 0.0006 * | 0.0066 ± 0.0006 *** | 0.0051 ± 0.0004 ** |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pérez-Torres, I.; Moguel-González, B.; Soria-Castro, E.; Guarner-Lans, V.; Avila-Casado, M.D.C.; Goes, T.I.F.V. Vascular Hyperactivity in the Rat Renal Aorta Participates in the Association between Immune Complex-Mediated Glomerulonephritis and Systemic Hypertension. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 1164. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15061164
Pérez-Torres I, Moguel-González B, Soria-Castro E, Guarner-Lans V, Avila-Casado MDC, Goes TIFV. Vascular Hyperactivity in the Rat Renal Aorta Participates in the Association between Immune Complex-Mediated Glomerulonephritis and Systemic Hypertension. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2018; 15(6):1164. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15061164
Chicago/Turabian StylePérez-Torres, Israel, Bernardo Moguel-González, Elizabeth Soria-Castro, Verónica Guarner-Lans, María Del Carmen Avila-Casado, and Teresa Imelda Fortoul Vander Goes. 2018. "Vascular Hyperactivity in the Rat Renal Aorta Participates in the Association between Immune Complex-Mediated Glomerulonephritis and Systemic Hypertension" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 15, no. 6: 1164. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15061164
APA StylePérez-Torres, I., Moguel-González, B., Soria-Castro, E., Guarner-Lans, V., Avila-Casado, M. D. C., & Goes, T. I. F. V. (2018). Vascular Hyperactivity in the Rat Renal Aorta Participates in the Association between Immune Complex-Mediated Glomerulonephritis and Systemic Hypertension. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 15(6), 1164. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15061164