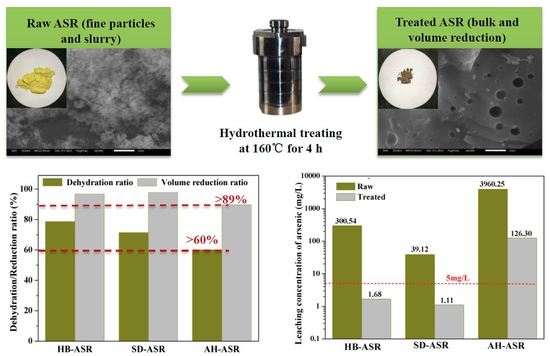
Hydrothermal Treatment of Arsenic Sulfide Residues from Arsenic-Bearing Acid Wastewater
Abstract
Share and Cite
Yao, L.; Min, X.; Xu, H.; Ke, Y.; Liang, Y.; Yang, K. Hydrothermal Treatment of Arsenic Sulfide Residues from Arsenic-Bearing Acid Wastewater. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 1863. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15091863
Yao L, Min X, Xu H, Ke Y, Liang Y, Yang K. Hydrothermal Treatment of Arsenic Sulfide Residues from Arsenic-Bearing Acid Wastewater. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2018; 15(9):1863. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15091863
Chicago/Turabian StyleYao, Liwei, Xiaobo Min, Hui Xu, Yong Ke, Yanjie Liang, and Kang Yang. 2018. "Hydrothermal Treatment of Arsenic Sulfide Residues from Arsenic-Bearing Acid Wastewater" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 15, no. 9: 1863. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15091863
APA StyleYao, L., Min, X., Xu, H., Ke, Y., Liang, Y., & Yang, K. (2018). Hydrothermal Treatment of Arsenic Sulfide Residues from Arsenic-Bearing Acid Wastewater. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 15(9), 1863. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15091863