The Effects of Locus of Control, Agents of Socialization and Sport Socialization Situations on the Sports Participation of Women in Taiwan
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Research Hypotheses
2.1. The Relationship between Locus of Control and Sports Participation
2.2. The Relationship between Agents of Socialization and Sports Participation
2.3. The Relationship between Sport Socialization Situations and Sports Participation
3. Methods
Participants
4. Measurements
4.1. Locus of Control Scale
4.2. Agents of Socialization Scale
4.3. Sport Socialization Situations Scale
4.4. Level of Exercise Participation
4.5. Data Analysis
5. Results
5.1. Descriptive Statistics
5.2. The Structural Model and Hypothesis Testing
6. Discussion
7. Recommendations
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| If I set a reasonable goal, I am likely to achieve it with hard work and commitment. |
| The things that happen in peoples’ lives are of their own doing. |
| Using good interpersonal skills can help get people to like me. |
| How I treat people determines how they treat me. |
Appendix B
| Construct | Item |
|---|---|
| Family | The members of my family always encouraged me to participate in sports activities. |
| I always received compliment on doing exercises from my family members. | |
| My family members were always very supportive of my sport activities. | |
| My family and I always participate in sports together. | |
| Friend | Friends always encouraged me to participate in sports. |
| Friends and I always participate in sports together. | |
| Associations with friends in sports made me feel good. | |
| Community | There are enough sports fields for me to do sports nearby my place. |
| There are many sports-related events nearby my place. | |
| I enjoyed doing sports with my neighbors. | |
| Mass media | Ads related to sports on media always increased my desire for sports participation. |
| Seeing famous athletes on media always increased my desire for sports participation. | |
| I am very interested in sports-related news. | |
| I acquired sports skills through media. |
Appendix C
| Very safe |
| Very comfortable |
| Easy to approach |
| Great exercise atmosphere |
Appendix D
| Frequency: On average, how many times you do exercise in a week? 1: None 2: 1–2 times 3: 3–4 times 4: 5–6 times 5: more than 7 times |
| Intensity: On average, how did you feel after workout? Not tired at all 2. Not tired 3. Somewhat tired 4. Tired 5. Very tired. |
| Duration: On average, how many minutes did you exercise each time? 1: less than 30 min 2. 31–60 min 3. 61–90 min 4. 91–120 min 5. More than 121 min. |
References
- Hsieh, H.H.; Chang, C.M.; Liu, L.W.; Huang, H.C. The Relative Contribution of Dietary Habits, Leisure-Time Exercise, Exercise Attitude, and Body Mass Index to Self-Rated Health among College Students in Taiwan. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Humphreys, B.R.; McLeod, L.; Ruseski, J.E. Physical activity and health outcomes: Evidence from Canada. Health Econ. 2014, 23, 33–54. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Y.; Shi, H.; Yu, D.; Qiu, P. Health benefits of traditional Chinese sports and physical activity for older adults: A systematic review of evidence. J. Sport Health Sci. 2016, 5, 270–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oja, P.; Titze, S.; Kokko, S.; Kujala, U.M.; Heinonen, A.; Kelly, P.; Koski, P.; Foster, C. Health benefits of different sport disciplines for adults: Systematic review of observational and intervention studies with meta-analysis. Br. J. Sports Med. 2015, 49, 434–440. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Woelfel, J.; Haller, H.O. Significant others, the self-reflexive act, and the attitude formation process. Am. Sociol. Rev. 1971, 36, 74–87. [Google Scholar]
- Coakley, J. Sport and Socialization. Exerc. Sport Sci. Rev. 1993, 21, 169–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coakley, J. Sports in Society: Issues and Controversies; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Kuo, P.-K.; Li, F.-E. The Research of the motivation, level of involvement and recreational benefits of the super triathlon participants. Sports Tour. Res. 2015, 4, 11–28. [Google Scholar]
- Boyle, R.; Haynes, R. Power Play: Sport, the Media and Popular Culture; Edinburgh University Press: Edinburgh, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Trolan, E.J. The impact of the media on gender inequality within sport. Soc. Behav. Sci. 2013, 91, 215–227. [Google Scholar]
- Senne, J.A. Examination of Gender Equity and Female Participation in Sport. Sport J. 2016, 19, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Spaaij, R.; Anderson, A. Parents or peers: Which is it? Sport socialization and team identification in Australia: A rejoinder to Melnick and Wann. Int. Rev. Sociol. Sport 2012, 47, 526–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whisenant, W.A.; Pederson, P.M.; Obenour, B.L. Success and gender: Determining the rate of advancement for intercollegiate athletic directors. Sex Roles 2002, 47, 485–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colley, R.C.; Garriguet, D.; Janssen, I.; Craig, C.L.; Clarke, J.; Tremblay, M.S. Physical activity of Canadian children and youth: Accelerometer results from the 2007 to 2009 Canadian health measures survey. Health Rep. 2011, 22, 15–23. [Google Scholar]
- Troiano, R.P.; Berrigan, D.; Dodd, K.W.; Mâsse, L.C.; Tilert, T.; McDowell, M. Physical activity in the United States measured by accelerometer. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2008, 40, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rotter, J. Generalized expectancies for internal versus external control of reinforcement. Psychol. Monogr. 1966, 80, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arslan, C.; Dilmaç, B.; Hamarta, E. Coping with stress and trait anxiety in terms of locus of control: A study with Turkish university students. Soc. Behav. Personal. Int. J. 2009, 37, 791–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.Y.; Tsai, Y.M. Aerobic dance intervention on body image and exercise self- efficacy of college students in internal-external locus of control. J. Phys. Educ. Sports 2006, 16, 19–30. [Google Scholar]
- Furnham, A.; Greaves, N. Gender and locus of control correlates of body image dissatisfaction. Eur. J. Personal. 1994, 8, 183–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adame, D.D.; Johnson, T.C.; Cole, S.P.; Matthiasson, H.; Abbas, M.A. Physical fitness in relation to amount of physical exercise, body image, and locus of control among college men and women. Percept. Mot. Ski. 1990, 70, 1347–1350. [Google Scholar]
- Leonard, W.M., II. A Sociology Perspective of Sport; Macmillan: New York, NY, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Snyder, E.E.; Spreitzer, E.A. Social Aspect of Sport; Prentice-Hall: Englewood Cliffs, NJ, USA, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Popenoe, D. Sociology; Prentice Hall: Englewood Cliffs, NJ, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Allender, S.; Cowburn, G.; Foster, C. Understanding participation in sport and physical activity among children and adults: A review of qualitative studies. Health Educ. Res. 2006, 21, 826–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seabral, A.F.; Mendonca, D.M.; Thomis, M.A.; Peters, T.J.; Maia, J.A. Associations between sport participation, demographic and socio-cultural factors in Portuguese children and adolescents. Eur. J. Public Health 2007, 18, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.E.; Liu, C.C.; Lee, C.H.; Tsai, F.H.; Chen, Z.M.; Lee, S.Y. A study of socialization into sport and motivations of athletes’ participation sport. Natl. Pingtung Univ. Educ. Phys. Educ. 2012, 15, 394–406. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.H.; Chang, C.M.; Yang, M.H. The impact of sports socializing on sports participation behavior of junior high school students. NCYU J. Phys. Educ. Health Recreat. 2011, 10, 60–68. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, H.L.; Huang, C.C.; Lee, C.Y. Empirical interpretation of female teacher participating in table-tennis experience. Natl. Taipei Univ. Educ. Phys. Educ. 2014, 9, 24–32. [Google Scholar]
- Hung, C.W. The relationship between socialization and sports. Q. Chin. Phys. Educ. 2000, 14, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, S.M. An exploration of sports and socialization. Q. Chin. Phys. Educ. 1996, 10, 34–41. [Google Scholar]
- Higginson, D.C. The influence of socializing agents in the female sport-participation process. Adolescence 1985, 20, 73–82. [Google Scholar]
- Chien, Y.C. The application of IPA to examine the needs on exercise environment among the middle-aged and elder residents. Master’s Thesis, National Pingtung University of Science and Technology, Pingtung, Taiwan, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.C.; Huang, Y.H.; Lee, T.H.; Chen, H.C.; Chang, C.J. Factors predicting the exercise participation in community-dwelling population. Taiwan Fam. Med. Res. 2005, 3, 29–41. [Google Scholar]
- Sallis, J.F.; Kerr, J. Physical activity and the built environment. J. Phys. Act. Health 2007, 4, 228–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, K.R. Physical Self-Perception and Exercise Involvement. Ph.D. Thesis, Arizona State University, Phoenix, AZ, USA, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Chin, W.W. The partial least squares approach for structural equation modeling. In Modern Methods for Business Research; Marcoulides, G.A., Ed.; Lawrence Erlbaum Associates: Mahwah, NJ, USA, 1998; pp. 295–336. [Google Scholar]
- Kock, N. Warp PLS 5.0 User Manual; Script Warp Systems: Laredo, TX, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Crothers, L.M.; Kanyongo, G.Y.; Kolbert, J.B.; Lipinski, J.; Kachmar, S.P.; Koch, G.D. Job stress and locus of control in teachers: Comparisons between samples from the United States and Zimbabwe. Int. Rev. Educ. 2010, 56, 651–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.M. Prediction of coach’s locus of control and players’ goal orientation to coach’s leadership behavior. Sports Exerc. Res. 2011, 13, 257–266. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, C.F. A Study of the Effects of Internal-External Control Orientation and the Size of the Practice Target on the Performance of Table Tennis Forehand Stroke. Natl. Taiwan Univ. Phys. Educ. J. 1997, 1, 95–120. [Google Scholar]
- Coleman, L.; Cox, L.; Roker, D. Girls and young women’s participation in physical activity: Psychological and social influences. Health Educ. Res. 2007, 23, 633–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, D.R.; Gittelsohn, J.; Charleston, J.; Felix-Aaron, K.; Appel, L.J. Motivation for exercise and weight loss among African-American women: Focus group results and their contribution towards program development. Ethn. Health 2001, 6, 227–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, M.; Sargent, L.; Stacy, R. Predictors of leisure-time physical activity among African American women. Am. J. Health Behav. 2005, 29, 352–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, S.W.; Hsieh, J.S. Residents’ usage of neighborhood parks: A case study on Jingfeng Park, First Wanyo Park and Shinfeng Park in Taipei City. J. Agric. For. 2009, 6, 29–41. [Google Scholar]
- Vojnovic, I. Building communities to promote physical activity: A multi-scale geographical analysis. Geografiska Annaler: Series B. Hum. Geogr. 2006, 88, 67–90. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.M.; Chao, K.Y.; Chou, C.C.; Lin, J.C. Active community environmental factors affecting residents’ participation in physical activity. J. Phys. Educ. Sport Sci. 2010, 11, 11–22. [Google Scholar]
- Duncan, M.J.; Spence, J.C.; Mummery, W.K. Perceived environment and physical activity: A meta-analysis of selected environmental characteristics. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2005, 2, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, C.T.L. Media systems and their effects on women’s sport participation in Taiwan. Sport Educ. Soc. 2009, 14, 37–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.C.; Liaw, Y.H.; Barnd, S. Cultural and Social Factors Affecting Women’s Physical Activity Participation in Taiwan. Sport Educ. Soc. 2004, 9, 379–393. [Google Scholar]
| Variables | Groups | N | % | Variables | Groups | N | % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Education Level | Elementary school | 5 | 1.2 | Marital status | Married | 289 | 71.9 |
| Junior high school | 9 | 2.2 | Unmarried | 113 | 28.1 | ||
| Senior high school | 57 | 14.2 | Monthly income (USD) | No income | 15 | 3.7 | |
| Junior college | 75 | 18.7 | Between $1 and $650 | 25 | 6.2 | ||
| College | 185 | 46.0 | Between $650 and $1300 | 184 | 45.8 | ||
| Graduate school | 71 | 17.7 | Between $1300 and $2600 | 166 | 41.3 | ||
| Age | Between 20 and 30 years old | 77 | 19.2 | Exceeded $2600 | 12 | 3.0 | |
| Between 31 and 40 years old | 139 | 34.6 | Number of children | No children | 131 | 32.6 | |
| Between 41 and 50 years old | 130 | 32.3 | One | 62 | 15.4 | ||
| Between 51 and 60 years old | 44 | 10.9 | Two | 141 | 35.1 | ||
| Exceeded 61 years old | 12 | 3.0 | Three or more than three | 68 | 16.9 | ||
| Full time job | Yes | 374 | 93.0 | Participate in sport clubs | Yes | 84 | 20.9 |
| No | 28 | 7.0 | No | 318 | 79.1 | ||
| Participation in school sports teams in past years of study | Yes | 90 | 22.4 | ||||
| No | 312 | 77.6 |
| Variables | Mean | Standard Deviation | Score Range |
|---|---|---|---|
| LC | 4.11 | 0.57 | 1–5 |
| FA | 3.8 | 0.65 | 1–5 |
| FR | 3.53 | 0.66 | 1–5 |
| COM | 3.04 | 0.78 | 1–5 |
| MM | 3.07 | 0.69 | 1–5 |
| SSS | 3.79 | 0.65 | 1–5 |
| SP | 9.63 | 4.76 | 2–50 |
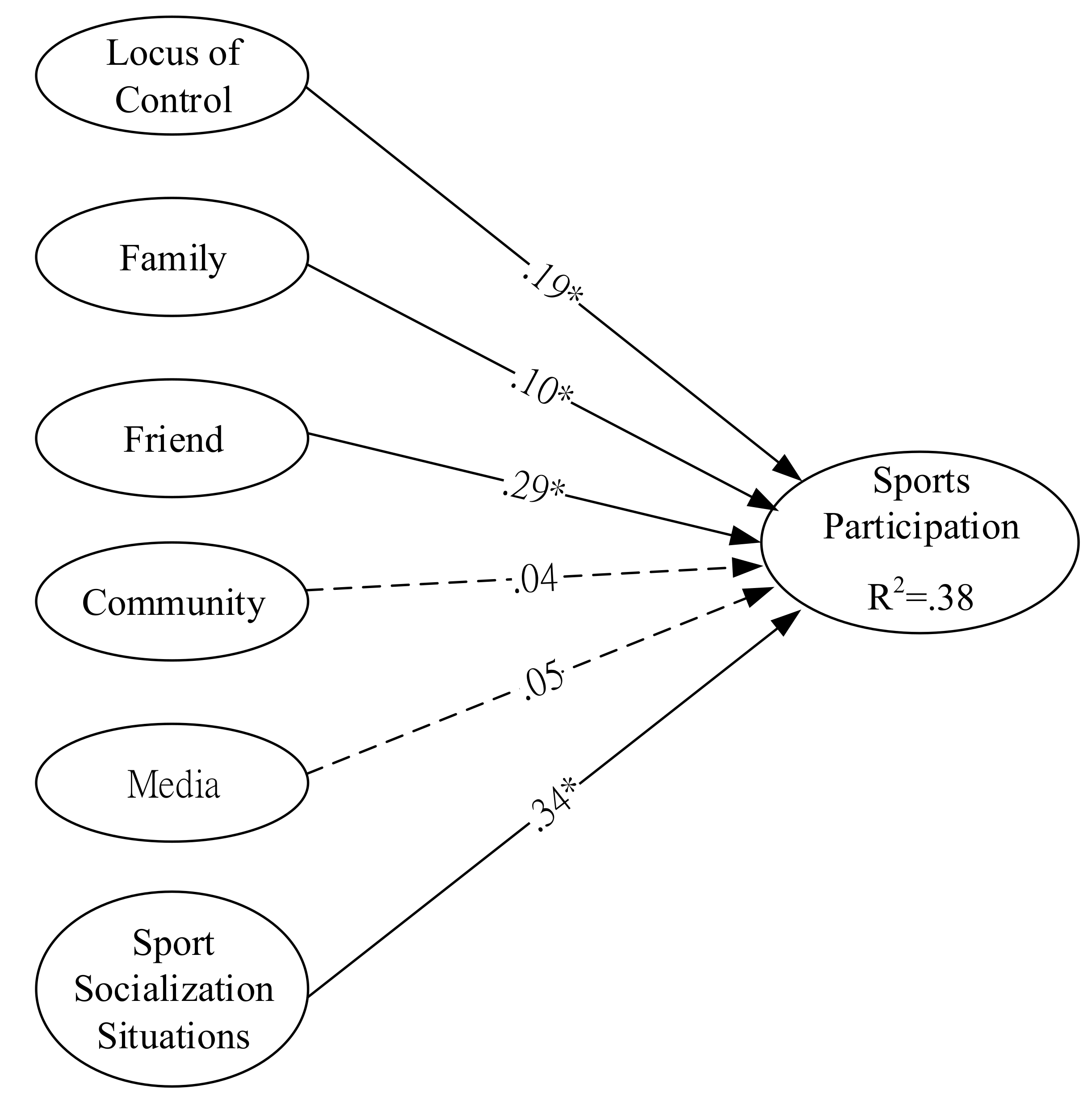
| Hypothesis | Path | Path Coefficient | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| H1 | LC → SP | 0.19 (β1) | <0.05 * |
| H2 | FA → SP | 0.10 (β2) | <0.05 * |
| H3 | FR → SP | 0.29 (β3) | <0.05 * |
| H4 | COM → SP | 0.04 (β4) | >0.05 |
| H5 | MM → SP | 0.05 (β5) | >0.05 |
| H6 | SSS → SP | 0.34 (β6) | <0.05 * |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, H.-C.; Liu, L.-W.; Chang, C.-M.; Hsieh, H.-H.; Lu, H.-C. The Effects of Locus of Control, Agents of Socialization and Sport Socialization Situations on the Sports Participation of Women in Taiwan. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 1841. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16101841
Huang H-C, Liu L-W, Chang C-M, Hsieh H-H, Lu H-C. The Effects of Locus of Control, Agents of Socialization and Sport Socialization Situations on the Sports Participation of Women in Taiwan. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2019; 16(10):1841. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16101841
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Hsiu-Chin, Li-Wei Liu, Chia-Ming Chang, Huey-Hong Hsieh, and Hsin-Chi Lu. 2019. "The Effects of Locus of Control, Agents of Socialization and Sport Socialization Situations on the Sports Participation of Women in Taiwan" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 16, no. 10: 1841. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16101841
APA StyleHuang, H.-C., Liu, L.-W., Chang, C.-M., Hsieh, H.-H., & Lu, H.-C. (2019). The Effects of Locus of Control, Agents of Socialization and Sport Socialization Situations on the Sports Participation of Women in Taiwan. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 16(10), 1841. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16101841






