Microbial Community Structure in the Sediments and Its Relation to Environmental Factors in Eutrophicated Sancha Lake
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
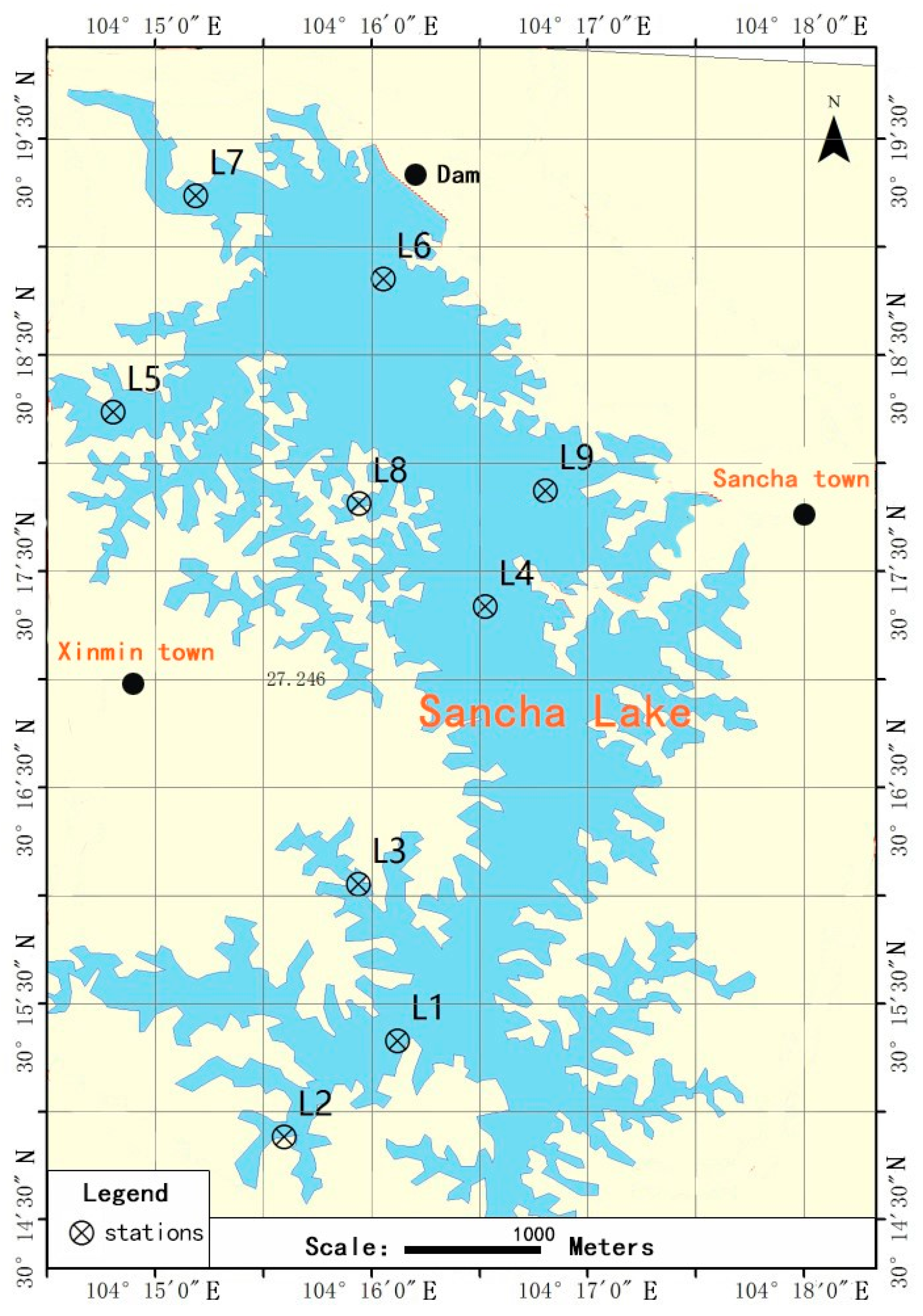
2.1. Site Description and Sample Collection
2.2. Determination of Physicochemical Factors of the Sediments and Overlying Water
2.3. DNA Extraction and PCR Amplification
2.4. Illumina Miseq Sequencing and Data Processing and Analysis
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Physicochemical Properties of the Sediments and Overlying Water
3.2. Analysis of Diversity and Richness of Microbial Communities
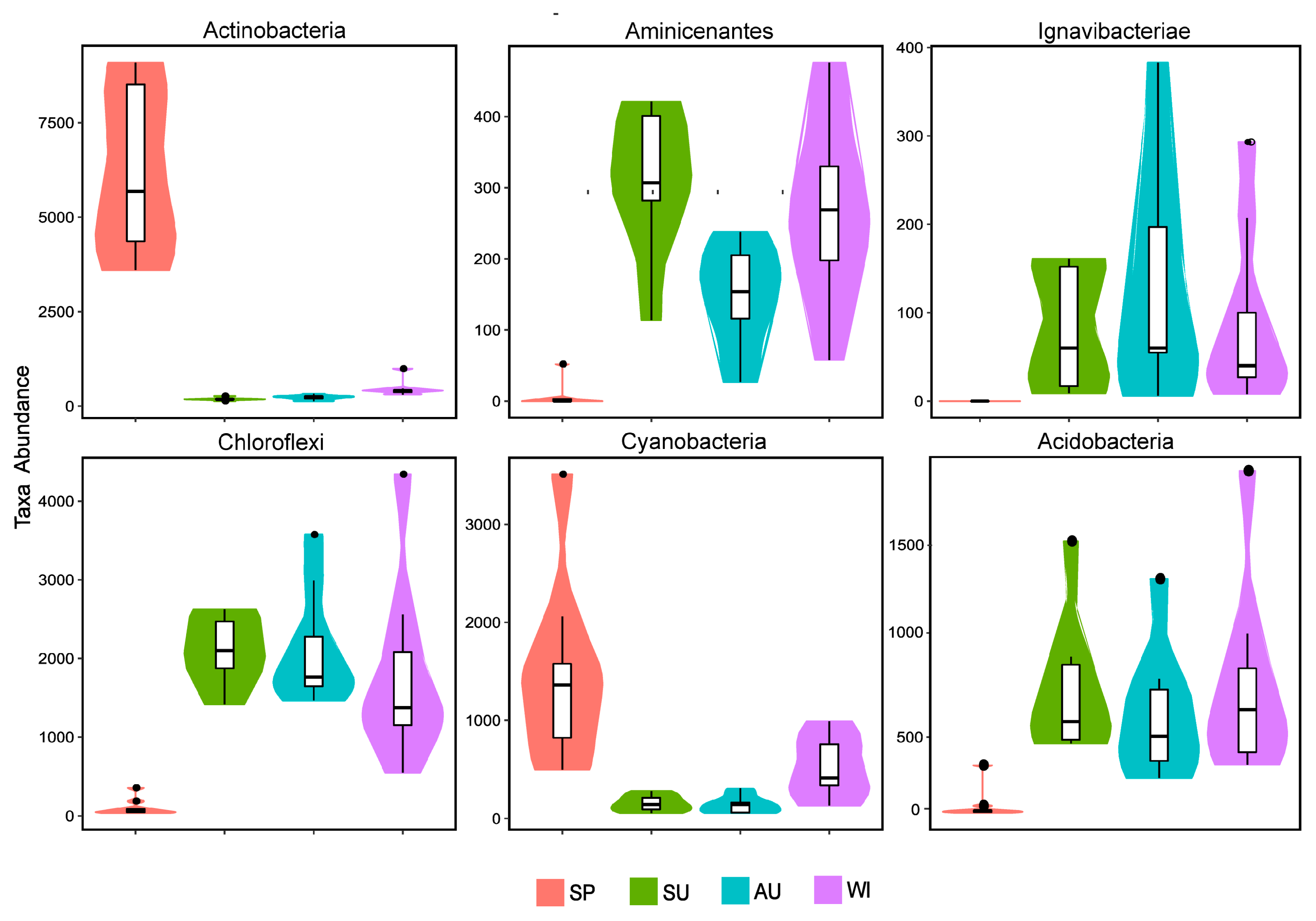
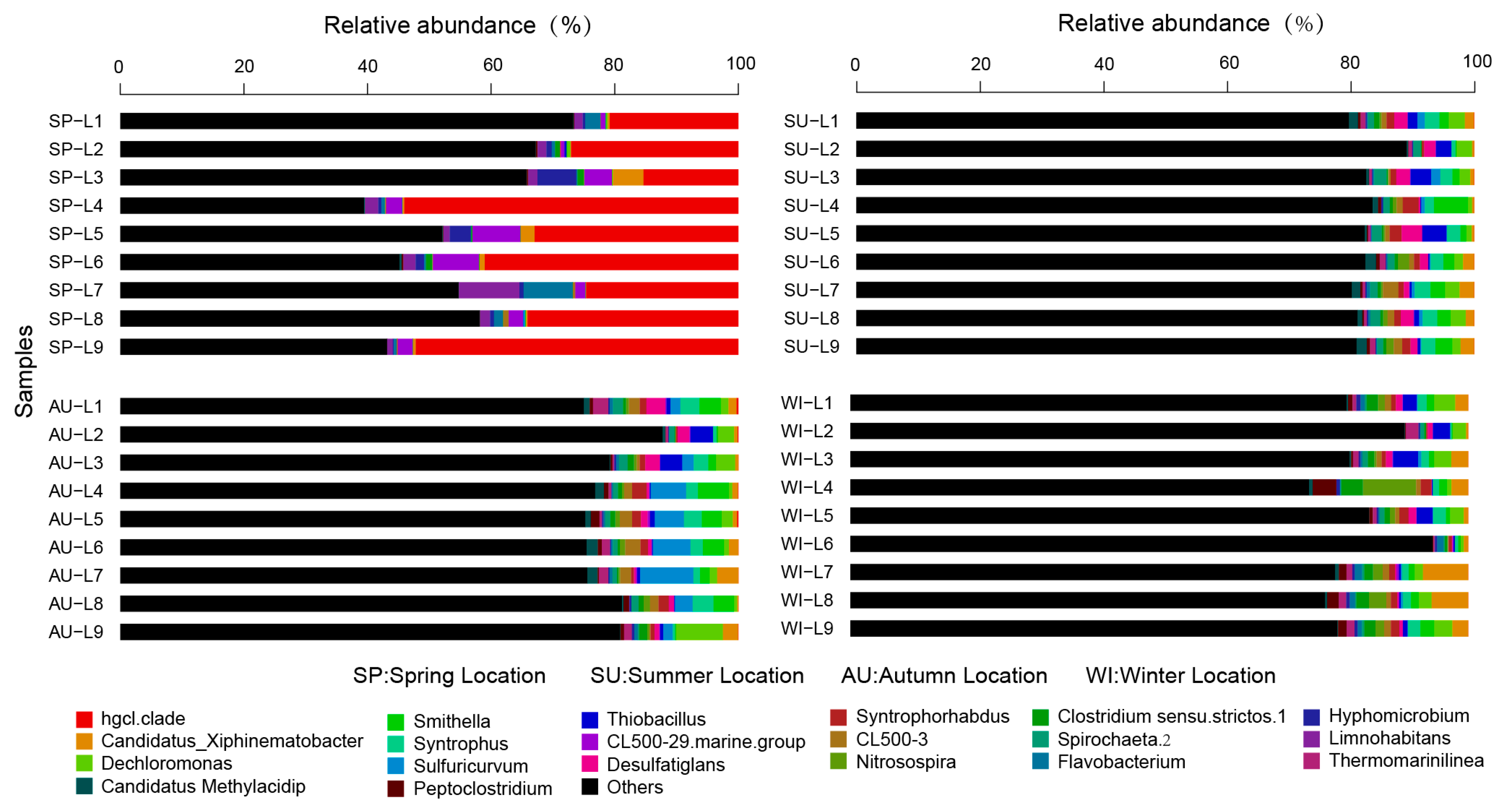
3.3. Analysis of the Taxonomic Composition and Spatiotemporal Changes of Microbial Communities
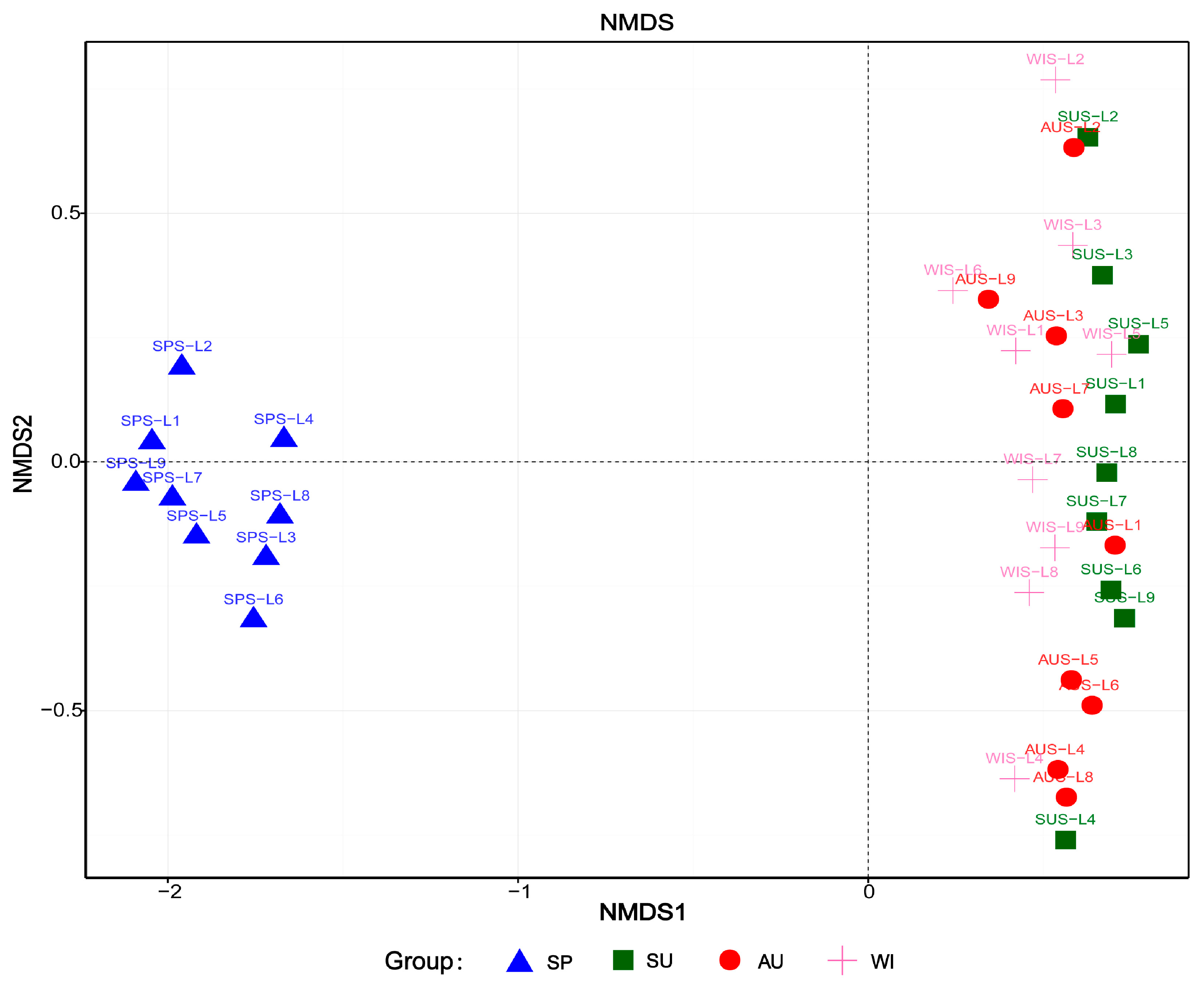
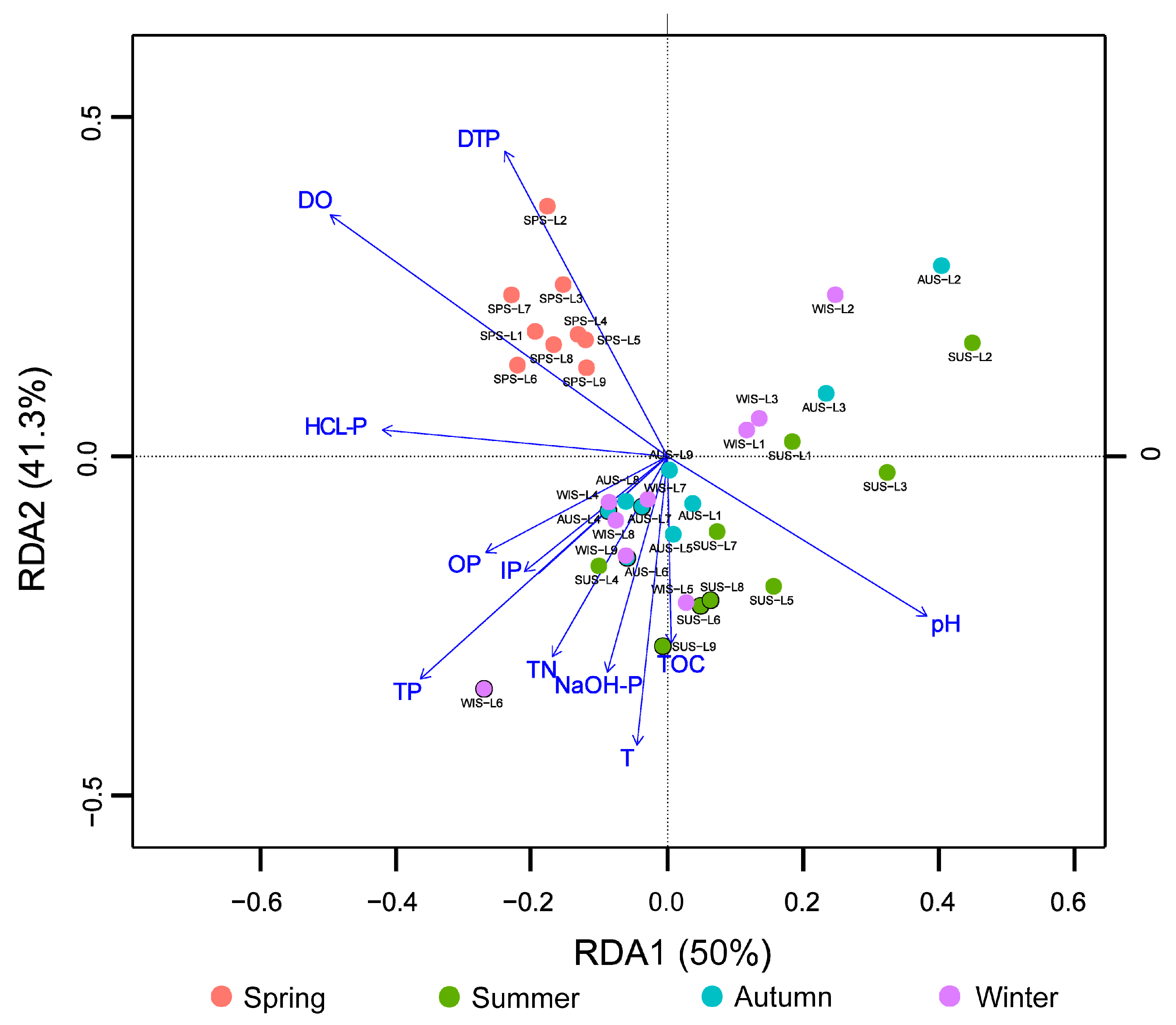
3.4. Analysis of Microbial Community Structure Differences
3.5. Correlation Analysis of Microbial Populations and Environmental Physicochemical Factors
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Peng, L.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, Y.; Hua, Y. Seasonal variation of bacterial community in sediments of urban eutrophic lakes. Chin. J. Appl. Environ. Biol. 2015, 21, 1012–1018. [Google Scholar]
- Nealson, K.H. SEDIMENT BACTERIA: Who’s There, What Are They Doing, and What’s New? Annu. Earth Planet. Sci. 1997, 25, 403–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, F.; Lin, G.; Gao, G.; Qin, B.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, G.; Zhou, Z.; Shen, J.; Liu, F. Bacterial and archaeal assemblages in sediments of a large shallow freshwater lake, Lake Taihu, as revealed by denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2009, 106, 1022–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Xi, W.; Ye, W.; Yang, H. Bacterial community composition of a shallow hypertrophic freshwater lake in China, revealed by 16S rRNA gene sequences. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2007, 61, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamaki, H.; Sekiguchi, Y.; Hanada, S. Comparative analysis of bacteria diversity in freshwater sediment of a shallow eutrophic lake by molecular and improved cultivation-based techniques. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 71, 2162–2169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.N.; Zhao, J.R.; Zhang, X.J. Planktonic bacterial community structure and its response to eutrophic factors in Lake ULanSuHai. Microbiol. China 2014, 41, 1082–1093. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, X.; Kou, W.B.; Yu, H. Environmental factors influencing the spatial distribution of sediment bacterial communitv structure and function in poyang Lake. Res. Environ. Sci. 2017, 30, 529–536. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, X.; Xing, P. The vertical distribution of sediment archaeal community in the “black bloom” disturbing Zhushan Bay of Lake Taihu. Archaea 2016, 2016, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.M.; Wu, Y.Q.; Wang, Y.L. Microbial community structure characteristics and its key driving factors in surface sediments along Nanfei River. China Environ. Sci. 2018, 38, 3552–3561. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, P.Y.; CHen, Q.C.; Hu, X.K. Structure characteristics of core bacterial communities in surface sediments and analysis on their responses to environmental factors in the inlet of Bohai Bay. Microbiol. China 2018, 45, 1940–1955. [Google Scholar]
- SAI·Bayartu; Huang, J.; Xie, G.J. Response of planktonic bacterial abundance to eutrophication and salinization in Lake Bo-sten, Xinjiang. J. Lake Sci. 2011, 23, 934–941. [Google Scholar]
- Qu, J.H.; Yuan, H.L.; Huang, H.Z. The vertical distribution of sediment bacterial community in the Guanting Reservoir. Sci. China Ser. D 2005, 35, 233–240. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, Z.J.; Cheng, H.Y.; Li, Y.Y. Community structure and influencing factors of bacterioplankton in the Main Cancel of the Mid-line Project of South-to-North Water Division in sections of Henan Province. China Environ. Sci. 2017, 37, 1505–1513. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, J.Q.; Gong, Z.L. Gcd Gene diversity of quinoprotein glucose dehydrogenase in the sediment of Sancha Lake and its response to the environment. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.W.; Yang, H.Z.; Zhao, M.X. Spatial distribution patterns of benthic microbial communities along the Pearl Estuary, China. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 2014, 37, 578–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, N.; Tan, G.; Wang, H.; Gai, X. Effect of biochar additions to soil on nitrogen leaching, microbial biomass and bacterial community structure. Eur. J. Soil Boil. 2016, 74, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quast, C.; Pruesse, E.; Yilmaz, P.; Gerken, J.; Schweer, T.; Yarza, P.; Peplies, J.; Glöckner, F.O. The SILVA ribosomal RNA gene database project: improved data processing and web-based tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, D590–D596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, B.; Teh, B.-S.; Sun, C.; Hu, S.; Lu, X.; Boland, W.; Shao, Y. Biodiversity and Activity of the Gut Microbiota across the Life History of the Insect Herbivore Spodoptera littoralis. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 29505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, J.R.; Nagarajan, N.; Pop, M. Statistical methods for detecting differentially abundant features in clinical metagenomic samples. PLoS Comput. Boil. 2009, 5, e1000352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.-J.; Li, J.-H.; Friedman, C.R.; Wang, H.-F. Variation of soil bacterial communities in a chronosequence of rubber tree (Hevea brasiliensis) plantations. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.W.; Guan, G.L.; Liao, C. Phosphorus existing forms and its spatial distribution characteristic in Yaohu Lake sediments. Chin. J. Environ. Eng. 2016, 10, 2756–2760. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, L.; Xie, P.; Li, S.; Tang, H.; Liu, H. The low TN:TP ratio, a cause or a result of Microcystis blooms? Water Res. 2003, 37, 2073–2080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United States Environmental Protection Agency. Nutrient Criteria Technical Guidance Manual: Lakes and Reservoirs; Office of Water, Office of Science and Technology: Washington, DC, USA, 2000.
- Zhang, X.J.; Zhao, Y.L.; Jin, Y.D. Diversity and phylogenetic analysis of bacteria in sediments of Xiaokou sites in Lake Wuliangsuhai. J. Mongolia Agric. Univ. 2011, 32, 206–212. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, W.; Liu, X.; Lin, S.; Tan, J.; Pan, J.; Li, D.; Yang, H. The vertical distribution of bacterial and archaeal communities in the water and sediment of Lake Taihu. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2009, 70, 263–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Cheng, B.; Li, C.Q. Bacterial communities in Nanchang section of the Ganjiang River in wet seaon. China Environ. Sci. 2016, 36, 2453–2462. [Google Scholar]
- Keshri, J.; Pradeep, A.S.; Sime-Ngando, T. Distinctive patterns in the taxonomical resolution of bacterioplankton in the sediment and pore waters of contrasted Freshwater Lakes. Microb. Ecol. 2018, 75, 662–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Y.; Ruan, X.; Zhang, Y.; Li, R. Illumina sequencing-based analysis of sediment bacteria community in different trophic status freshwater lakes. MicrobiologyOpen 2017, 6, e00450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Li, G.; Wang, C.; Jing, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, S.; Liu, Y. Community dynamics of prokaryotic and eukaryotic microbes in an estuary reservoir. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 6966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winters, A.D.; Marsh, T.L.; Brenden, T.O.; Faisal, M. Molecular characterization of bacterial communities associated with sediments in the Laurentian Great Lakes. J. Great Lakes 2014, 40, 640–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, W.; Yi, L.; Wang, P.F. Response of bacterial community compositions to different sources of pollutants in sediments of a tributary of Taihu Lake, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2016, 23, 13886–13894. [Google Scholar]
- Seymour, J.; Seuront, L.; Mitchell, J.; Seymour, J. Microscale gradients of planktonic microbial communities above the sediment surface in a mangrove estuary. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2007, 73, 651–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yandigeri, M.S.; Meena, K.K.; Srinivasan, R.; Pabbi, S. Effect of mineral phosphate solubilization on biological nitrogen fixation by diazotrophic cyanobacteria. Indian J. Microbiol. 2011, 51, 48–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Season | Spring | Summer | Autumn | Winter |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | 6.36 ± 0.17 b | 7.49 ± 0.088 a | 7.26 ± 0.30 a | 6.96 ± 0.17 a |
| T (°C) | 13.16 ± 0.80 c | 17.93 ± 1.28 a | 15.45 ± 1.31 b | 12.10 ± 0.17 c |
| DO (mg·L−1) | 8.25 ± 0.82 a | 6.27 ± 1.04 b | 5.11 ± 0.65 c | 5.44 ± 0.74 c |
| DTP (mg·L−1) | 0.12 ± 0.150 a | 0.016 ± 0.007 b | 0.024 ± 0.008 b | 0.027 ± 0.012 b |
| TOC (mg·g−1) | 21.28 ± 4.55 b | 27.03 ± 5.14 a | 22.43 ± 3.82 ab | 21.45 ± 5.24 b |
| TN (mg·g−1) | 1.92 ± 0.42 b | 2.56 ± 0.43 a | 1.97 ± 0.49 b | 1.73 ± 0.63 b |
| TP (mg·kg−1) | 1247.60 ± 716.26 b | 2266.55 ± 2.04 a | 2090.56 ± 1.57 a | 1306.93 ± 1.00 b |
| IP (mg·kg−1) | 862.37 ± 552.21 b | 1116.74 ± 1.30 a | 1616.00 ± 1.29 a | 991.21 ± 662.21 b |
| NaOH-P (mg·kg−1) | 172.46 ± 110.88 b | 377.54 ± 239.05 a | 378.46 ± 312.10 a | 167.21 ± 77.35 b |
| HCl-P (mg·kg−1) | 773.25 ± 563.11 b | 999.24 ± 1.10 a | 1237.74 ± 1.14 a | 827.92 ± 1.06 b |
| OP (mg·kg−1) | 268.86 ± 121.24 b | 314.78 ± 123.09 a | 319.61 ± 124.60 a | 289.25 ± 164.85 b |
| Bacteria Group | pH | T | DO | DTP | TOC | TN | TP | IP | NaOH-P | HCl-P | OP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Proteobacteria | 0.28 | −0.026 | −0.27 | −0.226 | 0.158 | 0.178 | −0.273 | −0.23 | −0.322 | −0.234 | −0.25 |
| Actinobacteria | −0.761 ** | −0.212 | 0.639 ** | 0.540 ** | −0.127 | −0.071 | −0.344 * | −0.089 | −0.194 | −0.341 * | −0.048 |
| Bacteroidetes | −0.052 | −0.284 | 0.362 | 0.32 | −0.068 | 0.053 | 0.106 | 0.108 | 0.005 | 0.203 | 0.064 |
| Firmicutes | −0.052 | −0.284 | 0.362 | 0.32 | −0.068 | 0.053 | 0.106 | 0.108 | 0.005 | 0.203 | 0.064 |
| Cyanobacteria | −0.674 ** | −0.226 | 0.544 ** | 0.33 * | −0.321 | −0.177 | −0.281 * | −0.114 | −0.277 | −0.102 | −0.330 * |
| Verrucomicrobia | 0.296 | 0.021 | −0.362 | −0.117 | −0.195 | 0.260 | 0.218 | 0.157 | 0.259 | 0.103 | −0.101 |
| Chloroflexi | 0.685 ** | 0.277 | −0.555 | −0.437 ** | 0.239 | 0.549 ** | −0.043 | −0.092 | 0.071 | −0.139 | −0.086 |
| Acidobacteria | 0.463 ** | 0.179 | 0.544 ** | −0.349 * | 0.165 | 0.311 | −0.091 | −0.051 | −0.06 | −0.095 | −0.077 |
| Planctomycetes | 0.474 ** | 0.293 | −0.438 ** | −0.169 | 0.074 | 0.044 | 0.330 * | 0.229 | 0.159 | 0.408 * | 0.124 |
| Spirochaetae | 0.243 | 0.221 | −0.236 | −0.2047 | −0.06 | −0.319 | −0.153 | −0.302 | 0.243 | 0.201 | 0.104 |
| Nitrospirae | 0.330 ** | 0.085 | −0.233 | −0.322 | 0.145 | 0.056 * | −0.129 | −0.307 | −0.288 | −0.048 | 0.026 |
| Aminicenantes | 0.538 ** | 0.234 | −0.466 ** | −0.397 * | 0.142 | 0.265 | 0.232 | 0.105 | 0.275 | 0.09 | 0.029 |
| Ignavibacteriae | 0.635 ** | 0.261 | −0.438 ** | −4.3 ** | 0.277 | 0.10 | −0.188 | −0.221 | −0.036 | −0.236 | −0.125 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, J.; Xu, W.; Mou, Z. Microbial Community Structure in the Sediments and Its Relation to Environmental Factors in Eutrophicated Sancha Lake. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 1931. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16111931
Li Y, Zhang J, Zhang J, Xu W, Mou Z. Microbial Community Structure in the Sediments and Its Relation to Environmental Factors in Eutrophicated Sancha Lake. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2019; 16(11):1931. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16111931
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Yong, Jiejie Zhang, Jianqiang Zhang, Wenlai Xu, and Zishen Mou. 2019. "Microbial Community Structure in the Sediments and Its Relation to Environmental Factors in Eutrophicated Sancha Lake" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 16, no. 11: 1931. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16111931
APA StyleLi, Y., Zhang, J., Zhang, J., Xu, W., & Mou, Z. (2019). Microbial Community Structure in the Sediments and Its Relation to Environmental Factors in Eutrophicated Sancha Lake. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 16(11), 1931. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16111931




