Effects of PM2.5 on Cardio-Pulmonary Function Injury in Open Manganese Mine Workers
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Subjects
2.2. Occupational Health Examination
2.3. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. General Characteristics of the Participants
3.2. Lung Function Test Indicators between Exposed Group and Control Group
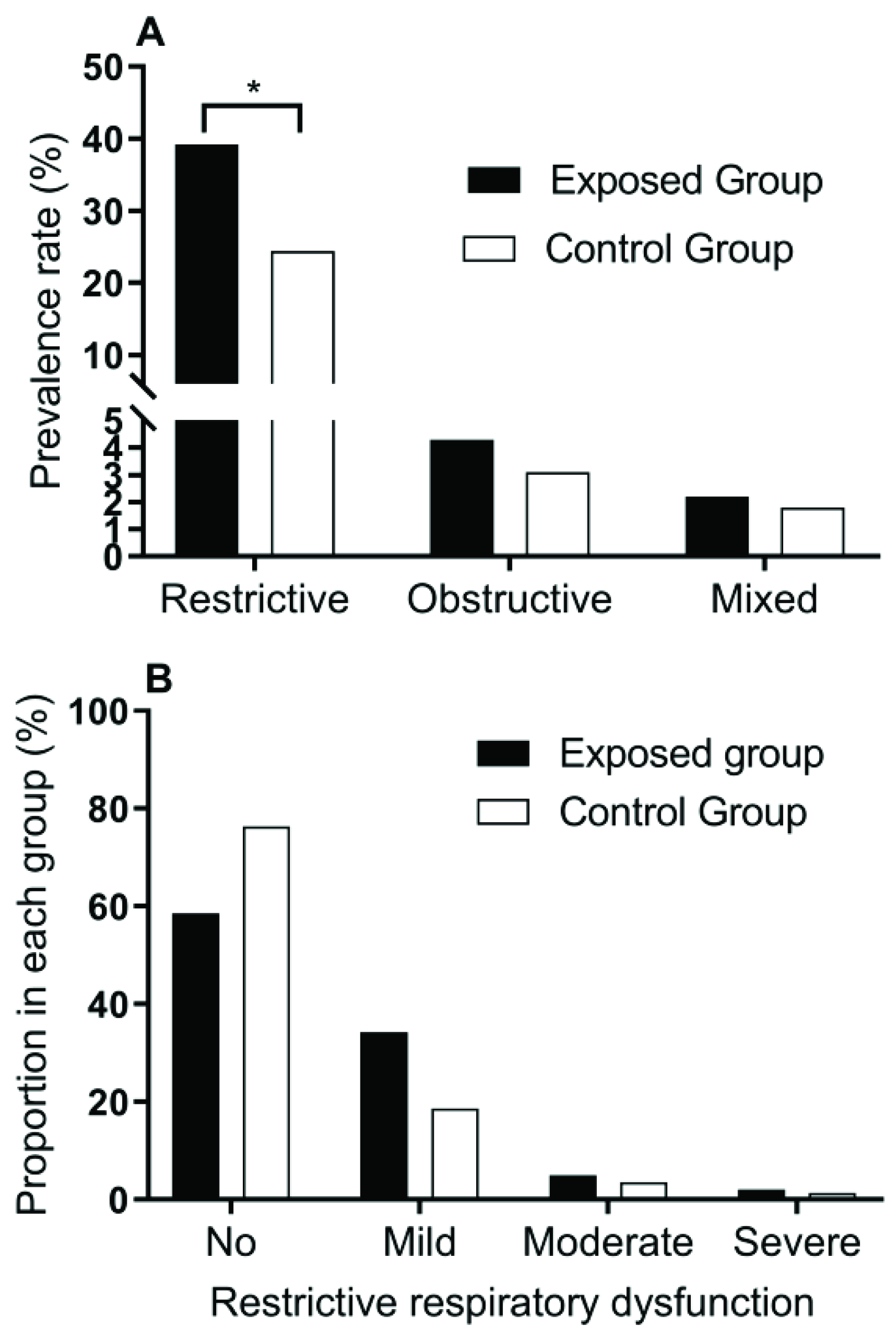
3.3. Lung Function Damage in the Exposed Group and the Control Group
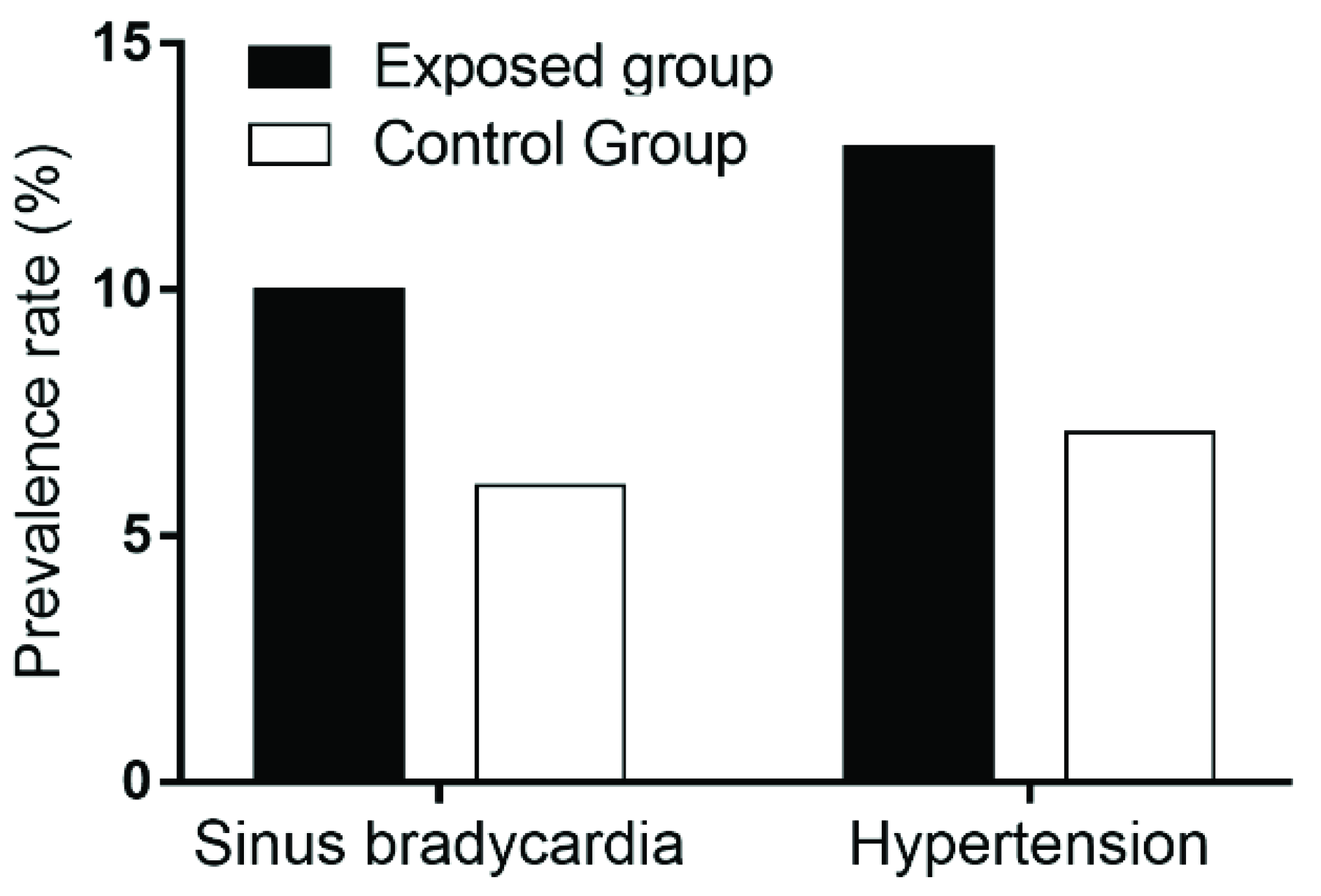
3.4. ECG Abnormalities in the Exposed Group and the Control Group
3.5. Hypertension in the Exposed Group and the Control Group
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kim, Y.; Seo, J.; Kim, J.Y.; Lee, J.Y.; Kim, H.; Kim, B.M. Characterization of PM2.5 and identification of transported secondary and biomass burning contribution in Seoul, Korea. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2018, 25, 4330–4343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bell, M.L.; Francesca, D.; Keita, E.; Zeger, S.L.; Samet, J.M. Spatial and Temporal Variation in PM2.5Chemical Composition in the United States for Health Effects Studies. Environ. Health Perspect. 2007, 115, 989–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, C.C.; Hsieh, W.Y.; Tsai, C.H.; Chen, C.Y.; Chang, H.F.; Lin, C.S. In Vitro and In Vivo Experimental Studies of PM2.5 on Disease Progression. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, S.; Gao, D.; Liao, F.; Zhou, F.; Wang, X. The health effects of ambient PM2.5 and potential mechanisms. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2016, 128, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, T.; Tang, M. Biological effects of airborne fine particulate matter (PM2.5) exposure on pulmonary immune system. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2018, 60, 195–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maji, K.J.; Dikshit, A.K.; Arora, M.; Deshpande, A. Estimating premature mortality attributable to PM2.5 exposure and benefit of air pollution control policies in China for 2020. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 612, 683–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vahedian, M.; Khanjani, N.; Mirzaee, M.; Koolivand, A. Ambient air pollution and daily hospital admissions for cardiovascular diseases in Arak, Iran. ARYA Atheroscler. 2017, 13, 117–134. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, P.; Xin, J.; Wang, Y.; Wang, S.; Li, G.; Pan, X.; Liu, Z.; Wang, L. The acute effects of fine particles on respiratory mortality and morbidity in Beijing, 2004–2009. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2013, 20, 6433–6444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.; He, J.; Wu, L.; Jin, T.; Chen, X.; Li, R.; Ren, P.; Zhang, L.; Mao, H. Health burden attributable to ambient PM2.5 in China. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 223, 575–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kloog, I. Fine particulate matter (PM2.5) association with peripheral artery disease admissions in northeastern United States. Int. J. Environ. Health Res. 2016, 26, 572–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Li, X.; Wang, S.; Wang, C.; Huang, F.; Gao, Q.; Wu, L.; Tao, L.; Guo, J.; Wang, W.; et al. Fine Particulate Air Pollution and Hospital Emergency Room Visits for Respiratory Disease in Urban Areas in Beijing, China, in 2013. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0153099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leon-Kabamba, N.; Ngatu, N.R.; Kakoma, S.J.; Nyembo, C.; Mbelambela, E.P.; Moribe, R.J.; Wembonyama, S.; Danuser, B.; Oscar-Luboya, N. Respiratory health of dust-exposed Congolese coltan miners. Int. Arch. Occup. Environ. Health 2018, 91, 859–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bell, M.L. Assessment of the Health Impacts of Particulate Matter Characteristics; Research Report 161; Health Effects Institute: Boston, MA, USA, 2012; pp. 5–38. [Google Scholar]
- Rice, M.B.; Ljungman, P.L.; Wilker, E.H.; Dorans, K.S.; Gold, D.R.; Schwartz, J.; Koutrakis, P.; Washko, G.R.; O’Connor, G.T.; Mittleman, M.A. Long-Term Exposure to Traffic Emissions and Fine Particulate Matter and Lung Function Decline in the Framingham Heart Study. Am. J. Resp. Crit. Care 2015, 191, 656–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, H.; Wang, Q.G.; Yang, M.; Li, F.; Wang, J.; Sun, Y.; Wang, C.; Wu, H.; Qian, X. Chemical characterization and source apportionment of PM2.5 aerosols in a megacity of Southeast China. Atmos. Res. 2016, 181, 288–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, W.H.; Li, W.Y.; Li, M. Harm of Productive Dust on the Workers’ Health in a Tire Producing Factory. Occup. Health 2007, 23, 2250–2251. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, Y.J.; Li, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Roberts, A.M.; Cai, L.; Myers, S.R.; Wang, L.; Schuchke, D.A. Elevation of serum endothelins and cardiotoxicity induced by particulate matter (PM2.5) in rats with acute myocardial infarction. Cardiovasc. Toxicol. 2002, 2, 253–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaufman, J.D.; Adar, S.D.; Barr, R.G.; Budoff, M.; Burke, G.L.; Curl, C.L.; Daviglus, M.L.; Diez Roux, A.V.; Gassett, A.J.; Jacobs, D.R., Jr.; et al. Association between air pollution and coronary artery calcification within six metropolitan areas in the USA (the Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis and Air Pollution): A longitudinal cohort study. Lancet 2016, 388, 696–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfaro-Moreno, E.; Torres, V.; Miranda, J.; Martinez, L.; Garcia-Cuellar, C.; Nawrot, T.S.; Vanaudenaerde, B.; Hoet, P.; Ramirez-Lopez, P.; Rosas, I.; et al. Induction of IL-6 and inhibition of IL-8 secretion in the human airway cell line Calu-3 by urban particulate matter collected with a modified method of PM sampling. Environ. Res. 2009, 109, 528–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.; Huang, S.; Du, L.; Sun, W.; Yu, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, J.; Li, X.; Li, X.; Yu, B.; et al. Expression of HMGB1 in maternal exposure to fine particulate air pollution induces lung injury in rat offspring assessed with micro-CT. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2018, 280, 64–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Chitano, P.; Murphy, T.M. Length oscillation induces force potentiation in infant guinea pig airway smooth muscle. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2005, 289, L909–L915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandevanter, D.R.; Pasta, D.J. Evidence of diminished FEV1 and FVC in 6-year-olds followed in the European Cystic Fibrosis Patient Registry, 2007–2009. J. Cyst. Fibros. 2013, 12, 786–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chao, T.P.; Sperandio, E.F.; Ostolin, T.; Almeida, V.R.; Romiti, M.; Gagliardi, A.R.T.; Arantes, R.L.; Dourado, V.Z. Use of cardiopulmonary exercise testing to assess early ventilatory changes related to occupational particulate matter. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 2018, 51, e6486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Geng, H.; Meng, Z.; Zhang, Q. Effects of blowing sand fine particles on plasma membrane permeability and fluidity, and intracellular calcium levels of rat alveolar macrophages. Toxicol. Lett. 2005, 157, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeidler-Erdely, P.C.; Meighan, T.G.; Erdely, A.; Fedan, J.S.; Thompson, J.A.; Bilgesu, S.; Waugh, S.; Anderson, S.; Marshall, N.B.; Afshari, A.; et al. Effects of acute inhalation of aerosols generated during resistance spot welding with mild-steel on pulmonary, vascular and immune responses in rats. Inhal. Toxicol. 2014, 26, 697–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, J.; Wan, L.; Sheng, C.J.; Xie, X.L. The correlative study on pulmonary function changes and Th1/Th2 cells & regulatory T cells in adjuvant arthritis rats. Xi BaoYuFenZiMian YiXueZaZhi 2011, 27, 56–60. [Google Scholar]
- Atkinson, R.W.; Kang, S.; Anderson, H.R.; Mills, I.C.; Walton, H.A. Epidemiological time series studies of PM2.5 and daily mortality and hospital admissions: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2015, 25, 208–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, Q.M.; Liu, T.; Korantzopoulos, P.; Zhang, Z.W.; Zhao, J.P.; Li, G.P. Association between air pollution and development of atrial fibrillation: A meta-analysis of observational studies. Heart Lung 2016, 45, 557–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunch, T.J.; Horne, B.D.; Asirvatham, S.J.; Day, J.D.; Crandall, B.G.; Weiss, J.P.; Osborn, J.S.; Anderson, J.L.; Muhlestein, J.B.; Lappe, D.L.; et al. Atrial fibrillation hospitalization is not increased with short-term elevations in exposure to fine particulate air pollution. Pacing Clin. Electrophysiol. 2011, 34, 1475–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burrello, J.; Monticone, S.; Buffolo, F.; Tetti, M.; Veglio, F.; Williams, T.A.; Mulatero, P. Is There a Role for Genomics in the Management of Hypertension? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, Y.; Qi, C.; Tao, N.; Han, R.; Jiang, Y.; Guan, S.; Ge, H.; Ning, L.; Xiao, J.; Liu, J. Changing work stressors and coping resources influence blood pressure and hypertension incidence in a large OHSPIW cohort. J. Hum. Hypertens. 2017, 31, 313–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mucci, N.; Giorgi, G.; De Pasquale Ceratti, S.; Fiz-Perez, J.; Mucci, F.; Arcangeli, G. Anxiety, Stress-Related Factors, and Blood Pressure in Young Adults. Front. Psychol. 2016, 7, 1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
| Characteristics | Exposed Group (n = 140) | Control Group (n = 140) | t or χ2 | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 32.40 ± 7.53 | 31.21 ± 6.83 | 1.385 | 0.167 |
| Working age (years) | 2.28 ± 0.50 | 2.18 ± 0.96 | 1.093 | 0.275 |
| Sex (n, %) | ||||
| Male | 121 (86.4) | 110 (78.6) | 2.993 | 0.084 |
| Female | 19 (13.6) | 30 (21.4) | 1.088 | 0.278 |
| Weight (kg) | 66.65 ± 6.42 | 65.83 ± 6.19 | 1.723 | 0.086 |
| Height (cm) | 168.35 ± 7.29 | 166.74 ± 8.31 | 0.988 | 0.324 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 24.04 ± 3.39 | 23.63 ± 3.55 | 3.527 | 0.060 |
| Smoking (n, %) | 68 (48.6) | 52 (37.1) | 25.35 | <0.001 |
| PM2.5 concentration of 8-h TWA in the working places (mg/m3) | 1.28 ± 0.36 | 0.46 ± 0.13 |
| Indexes | Exposed Group (n = 140) | Control Group (n = 140) | t | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FVC (liter) | 3.41 ± 0.99 | 3.65 ± 1.22 | −1.807 | 0.072 |
| FVC% | 90.17 ± 16.70 | 91.98 ± 24.06 | −0.731 | 0.465 |
| FEV1.0 (liter) | 3.28 ± 0.95 | 3.54 ± 1.13 | −2.084 | 0.038 |
| FEV1.0% | 100.21 ± 17.89 | 103.61 ± 26.38 | −1.262 | 0.208 |
| MMEF (liter/second) | 5.69 ± 2.14 | 6.28 ± 1.90 | −2.439 | 0.035 |
| PEFR (liter/second) | 8.97 ± 3.27 | 9.93 ± 3.02 | −2.552 | 0.011 |
| PEFR% | 104.04 ± 27.80 | 110.89 ± 26.73 | −2.102 | 0.036 |
| FEF75 (liter/second) | 4.21 ± 1.78 | 4.63 ± 1.67 | −2.036 | 0.043 |
| FEF75% | 206.14 ± 81.03 | 235.57 ± 85.31 | −2.960 | 0.003 |
| FEF50 (liter/second) | 6.90 ± 2.63 | 7.45 ± 2.32 | −1.856 | 0.065 |
| FEF50% | 151.81 ± 49.70 | 164.54 ± 47.60 | −2.189 | 0.029 |
| FEF25 (liter/second) | 8.76 ± 3.28 | 9.54 ± 3.03 | −2.067 | 0.040 |
| FEF25% | 122.82 ± 36.47 | 131.43 ± 34.31 | −2.035 | 0.043 |
| FEF50/FEF25 | 80.44 ± 15.82 | 79.50 ± 14.17 | 0.524 | 0.601 |
| FEV1.0/FVC% | 111.64 ± 0.09 | 113.10 ± 0.07 | −151.511 | <0.001 |
| MVV | 135.42 ± 35.57 | 144.02 ± 45.45 | −1.763 | 0.079 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, Y.; Bao, M.; Xiao, J.; Qiu, Z.; Wu, K. Effects of PM2.5 on Cardio-Pulmonary Function Injury in Open Manganese Mine Workers. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 2017. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16112017
Huang Y, Bao M, Xiao J, Qiu Z, Wu K. Effects of PM2.5 on Cardio-Pulmonary Function Injury in Open Manganese Mine Workers. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2019; 16(11):2017. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16112017
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Yuanni, Mian Bao, Jiefeng Xiao, Zhaolong Qiu, and Kusheng Wu. 2019. "Effects of PM2.5 on Cardio-Pulmonary Function Injury in Open Manganese Mine Workers" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 16, no. 11: 2017. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16112017
APA StyleHuang, Y., Bao, M., Xiao, J., Qiu, Z., & Wu, K. (2019). Effects of PM2.5 on Cardio-Pulmonary Function Injury in Open Manganese Mine Workers. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 16(11), 2017. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16112017






