Bisphenol A, Tobacco Smoke, and Age as Predictors of Oxidative Stress in Children and Adolescents
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Selection of Subjects
2.2. Questionnaire
2.3. Urine
2.3.1. BPA
2.3.2. Cotinine
2.3.3. 15.F2t-Isoprostane (15F2t-IsoP)
2.3.4. Creatinine
2.4. Statistical Analysis
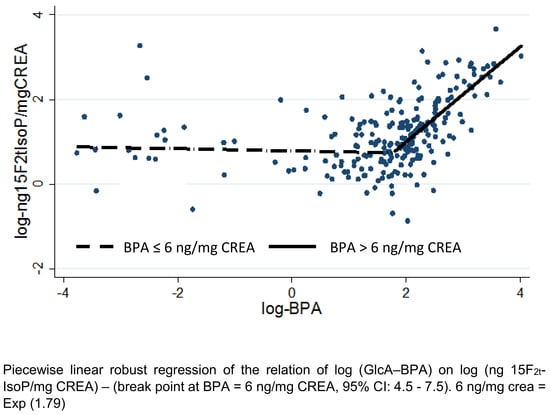
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Limitations and Future Purposes
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Srivastava, S.; Gupta, P.; Chandolia, A.; Alam, I. Bisphenol A: A threat to human health? J. Environ. Health 2015, 77, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mielke, H.; Gundert-Remy, U. Bisphenol A levels in blood depend on age and exposure. Toxicol. Lett. 2009, 190, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lakind, J.S.; Naiman, D.Q. Daily intake of bisphenol A and potential sources of exposure: 2005–2006 National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. J. Exp. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2011, 21, 272–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talsness, C.E.; Andrade, A.J.M.; Kuriyama, S.N.; Taylor, J.A.; vom Saal, F.S. Components of plastic: Experimental studies in animals and relevance for human health. Philos. Trans. R Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2009, 364, 2079–2096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodman, J.E.; McConnell, E.E.; Sipes, I.G.; Witorsch, R.J.; Slayton, T.M.; Yu, C.J.; Lewis, A.S.; Rhomberg, L.R. An updated weight of the evidence evaluation of reproductive and developmental effects of low doses of bisphenol A. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 2006, 36, 387–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richter, C.A.; Birnbaum, L.S.; Farabollini, F.; Newbold, R.R.; Rubin, B.S.; Talsness, C.E.; Vandenbergh, J.G.; Walser-Kuntz, D.R.; vom Saal, F.S. In vivo effects of bisphenol A in laboratory rodent studies. Reprod. Toxicol. 2007, 24, 199–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimizu, M.; Ohta, K.; Matsumoto, Y.; Fukuoka, M.; Ohno, Y.; Ozawa, S. Sulfation of bisphenol A abolished its estrogenicity based on proliferation and gene expression in human breast cancer MCF-7 cells. Toxicol. In Vitro 2002, 16, 549–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukata, H.; Miyagawa, H.; Yamazaki, N.; Mori, C. Comparison of Elisa-and LC-MS-Based Methodologies for the Exposure Assessment of Bisphenol, A. Toxicol. Mech. Methods 2006, 16, 427–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsukioka, T.; Terasawa, J.; Sato, S.; Hatayama, Y.; Makino, T.; Nakazawa, H. Development of analytical method for determining trace amounts of BPA in urine samples and estimation of exposure to BPA. J. Environ. Chem. 2014, 14, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Rang, O.; Liu, F.; Xia, W.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, S.; Xu, S. A systematic review of metabolomics biomarkers for Bisphenol A exposure. Metabolomics 2018, 14, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gassman, N.R. Induction of oxidative stress by bisphenol A and its pleiotropic effects. Environ. Mol. Mutagen. 2017, 58, 60–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.-X.; Liu, C.; Shen, Y.; Wang, Q.; Pan, A.; Yang, P.; Chen, Y.-J.; Deng, Y.-L.; Lu, Q.; Cheng, L.-M.; et al. Urinary levels of bisphenol A, F and S and markers of oxidative stress among healthy adult men: Variability and association analysis. Environ. Int. 2019, 123, 301–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, W.; Chen, J.; Li, Y.; Chen, Z.; Jiang, L.; Yang, M.; Wu, M. Oxidative stress and immune disturbance after long-term exposure to bisphenol A in juvenile common carp (Cyprinus carpio). Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2016, 130, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geens, T.; Roosens, L.; Neels, H.; Covaci, A. Assessment of human exposure to Bisphenol-A, Triclosan and Tetrabromobisphenol-A through indoor dust intake in Belgium. Chemosphere 2009, 76, 755–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vandenberg, L.N.; Gerona, R.R.; Kannan, K.; Taylor, J.A.; van Breemen, R.B.; Dickenson, C.A.; Liao, C.; Yuan, Y.; Newbold, R.R.; Padmanabhan, V.; et al. A round robin approach to the analysis of bisphenol a (BPA) in human blood samples. Environ. Health 2014, 13, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, N.; Chuang, J.; Morgan, M.K.; Lordo, R.A.; Sheldon, L.S. An observational study of the potential exposures of preschool children to pentachlorophenol, bisphenol-A, and nonylphenol at home and daycare. Environ. Res. 2007, 103, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pirard, C.; Sagot, C.; Deville, M.; Dubois, N.; Charlier, C. Urinary levels of bisphenol A, triclosan and 4-nonylphenol in a general Belgian population. Environ. Int. 2012, 48, 78–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dekant, W.; Völkel, W. Human exposure to bisphenol A by biomonitoring: Methods, results and assessment of environmental exposures. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2008, 228, 114–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Mun, G.-I.; Choi, E.; Kim, M.; Jeong, J.S.; Kang, K.W.; Jee, S.; Lim, K.-M.; Lee, Y.-S. Submicromolar bisphenol A induces proliferation and DNA damage in human hepatocyte cell lines in vitro and in juvenile rats in vivo. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2018, 111, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bono, R.; Romanazzi, V.; Munnia, A.; Piro, S.; Allione, A.; Ricceri, F.; Guarrera, S.; Pignata, C.; Matullo, G.; Wang, P.; et al. Malondialdehyde-deoxyguanosine adduct formation in workers of pathology wards: The role of air formaldehyde exposure. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2010, 23, 1342–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bono, R.; Romanazzi, V. Isoprostanes as Biomarkers of Disease and Early Biological Effect. In General Methods in Biomarker Research and Their Applications; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 383–404. [Google Scholar]
- Calafat, A.M.; Ye, X.; Wong, L.-Y.; Reidy, J.A.; Needham, L.L. Exposure of the U.S. population to bisphenol A and 4-tertiary-octylphenol: 2003–2004. Environ. Health Perspect. 2008, 116, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Preuss, R.; Angerer, J.; Drexler, H. Naphthalene? An environmental and occupational toxicant. Int. Arch. Occup. Environ. Health 2003, 76, 556–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edginton, A.N.; Ritter, L. Predicting plasma concentrations of bisphenol A in children younger than 2 years of age after typical feeding schedules, using a physiologically based toxicokinetic model. Environ. Health Perspect. 2009, 117, 645–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- EFSA. Report on the Two-Phase Public Consultation on the Draft EFSA Scientific Opinion on Bisphenol A (BPA); EFSA Supporting Publications; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2015; Volume 12. [Google Scholar]
- Watkins, D.J.; Ferguson, K.K.; Anzalota Del Toro, L.V.; Alshawabkeh, A.N.; Cordero, J.F.; Meeker, J.D. Associations between urinary phenol and paraben concentrations and markers of oxidative stress and inflammation among pregnant women in Puerto Rico. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2014, 218, 212–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, Y.-C.; Park, E.-Y.; Park, M.-S.; Ko, J.A.; Oh, S.-Y.; Kim, H.; Lee, K.-H.; Leem, J.-H.; Ha, E.-H. Community level exposure to chemicals and oxidative stress in adult population. Toxicol. Lett. 2009, 184, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asimakopoulos, A.G.; Xue, J.; De Carvalho, B.P.; Iyer, A.; Abualnaja, K.O.; Yaghmoor, S.S.; Kumosani, T.A.; Kannan, K. Urinary biomarkers of exposure to 57 xenobiotics and its association with oxidative stress in a population in Jeddah, Saudi Arabia. Environ. Res. 2016, 150, 573–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munakata, S.; Ishimori, K.; Kitamura, N.; Ishikawa, S.; Takanami, Y.; Ito, S. Oxidative stress responses in human bronchial epithelial cells exposed to cigarette smoke and vapor from tobacco- and nicotine-containing products. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2018, 99, 122–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, M.-R.; Cooke, M.S.; Kuo, C.-Y.; Pan, C.-H.; Liu, H.-H.; Yang, H.-J.; Chen, S.-C.; Chiang, Y.-C.; Hu, C.-W. Children are particularly vulnerable to environmental tobacco smoke exposure: Evidence from biomarkers of tobacco-specific nitrosamines, and oxidative stress. Environ. Int. 2018, 120, 238–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcon, A.; Pesce, G.; Calciano, L.; Bellisario, V.; Dharmage, S.C.; Garcia-Aymerich, J.; Gislasson, T.; Heinrich, J.; Holm, M.; Janson, C.; et al. Trends in smoking initiation in Europe over 40 years: A retrospective cohort study. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0201881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romanazzi, V.; Pirro, V.; Bellisario, V.; Mengozzi, G.; Peluso, M.; Pazzi, M.; Bugiani, M.; Verlato, G.; Bono, R. 15-F2t isoprostane as biomarker of oxidative stress induced by tobacco smoke and occupational exposure to formaldehyde in workers of plastic. Sci. Total Environ. Total Environ. 2013, 442, 20–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Migliore, E.; Piccioni, P.; Garrone, G.; Ciccone, G.; Borraccino, A.; Bugiani, M. Changing prevalence of asthma in Turin school children between 1994 and 1999. Monaldi Arch. Chest Dis. 2005, 63, 74–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Bono, R.; Bellisario, V.; Romanazzi, V.; Pirro, V.; Piccioni, P.; Pazzi, M.; Bugiani, M.; Vincenti, M. Oxidative stress in adolescent passive smokers living in urban and rural environments. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2014, 217, 287–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bacon, D.W.; Watts, D.G. Estimating the Transition between Two Intersecting Straight Lines. Biometrika 1971, 58, 525–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, L.J.; Morrow, J.D. Measurement of F(2)-isoprostanes as an index of oxidative stress in vivo. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2000, 28, 505–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacob, K.D.; Noren Hooten, N.; Trzeciak, A.R.; Evans, M.K. Markers of oxidant stress that are clinically relevant in aging and age-related disease. Mech. Ageing Dev. 2013, 134, 139–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bono, R.; Tassinari, R.; Bellisario, V.; Gilli, G.; Pazzi, M.; Pirro, V.; Mengozzi, G.; Bugiani, M.; Piccioni, P. Urban air and tobacco smoke as conditions that increase the risk of oxidative stress and respiratory response in youth. Environ. Res. 2015, 137, 141–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouzid, M.A.; Hammouda, O.; Matran, R.; Robin, S.; Fabre, C. Changes in oxidative stress markers and biological markers of muscle injury with aging at rest and in response to an exhaustive exercise. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, 904–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heid, J.; Cencioni, C.; Ripa, R.; Baumgart, M.; Atlante, S.; Milano, G.; Scopece, A.; Kuenne, C.; Guenther, S.; Azzimato, V.; et al. Age-dependent increase of oxidative stress regulates microRNA-29 family preserving cardiac health. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Squillacioti, G.; Bellisario, V.; Grignani, E.; Mengozzi, G.; Bardaglio, G.; Dalmasso, P.; Bono, R. The Asti Study: The Induction of Oxidative Stress in A Population of Children According to Their Body Composition and Passive Tobacco Smoking Exposure. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Characteristics of Students | Primary School (7–10 Years) | Secondary School (11–14 Years) | High School (15–19 Years) | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N. | 87 | 34 | 102 | 223 |
| Gender N. (%) | Male 47 (54.0%) Female 40 | Male 15 (44.1%) Female 19 | Male 57 (55.8%) Female 45 | Male 119 (53.4%) Female 104 |
| Age (years) Mean ± s.d. | 8.87 ± 1.0 | 11.7 ± 0.8 | 16.6 ± 1.71 | 12.8 ± 3.8 |
| Height (m) Mean ± s.d. | 1.39 ± 0.08 | 1.54 ± 0.1 | 1.71 ± 0.08 | 1.56 ± 0.17 |
| Weight (kg) Mean ± s.d. | 35.6 ± 9.8 | 45.0 ± 7.5 | 64.5 ± 12.4 | 50.2 ± 17.2 |
| Smoking habits N (%) | Active 0 Passive 26 (30%) Not exposed 61 (70%) | Active 0 Passive 5 (14.7%) Not exposed 29 (85.3%) | Active 18 (17.6%) Passive 21 (20.5%) Not exposed 63 (61.9%) | Active 18 (8%) Passive 52 (23.3%) Not exposed 153 (68.7%) |
| Educational Level | Cotinine [ng/mg CREA] | 15F2t-IsoP [ng/mg CREA] | Total BPA Inactivated [ng/mg CREA] |
|---|---|---|---|
| g-Mean (±s.d.) Min–Max | g-Mean (±s.d.) Min–Max | g-Mean (±sd) Min–Max | |
| Primary school (7–10) | 11.2 (±8.1) 1.06–382.9 | 3.3 (±2.2) 0.6–38.8 | 2.3 (±6.8) 0.02–38.7 |
| Secondary school (11–14) | 2.81 (±13.4) 0.1–372.3 | 2.5 (±2.1) 0.5–17.1 | 5.4 (±2.5) 0.9–34.4 |
| High school (15–19) | 26.3 (±16.8) 0.1–1730.9 | 3.9 (±2.4) 0.4–23.2 | 8.4 (±2.2) 0.3–55.4 |
| Total g-mean (±s.d.) min–max | 9.8 (±13.9) 0.03–1730 | 3.2 (±2.8) 0.41–38.8 | 4.9 (±4.2) 0.02–55.4 |
| log 15F2t-IsoP | Coef. | 95% CI Lower limit–Upper Limit | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| breakpoint | 1.79 | 1.56 | 2.02 | 0.00 |
| breakpoint | 1.79 | 1.56 | 2.02 | 0.00 |
| Log (total inactive BPA) < breakpoint | −0.01 | −0.10 | 0.08 | 0.82 |
| ≥ breakpoint | 1.11 | 0.87 | 1.34 | 0.00 |
| Log Cotinine (ng/mg CREA) | 0.03 | 0.00 | 0.06 | 0.05 |
| <10 | 0 | |||
| Age class 11–14 | −0.20 | −0.41 | 0.00 | 0.05 |
| ≥ 15 | −0.07 | −0.27 | 0.14 | 0.53 |
| Constant | 0.73 | 0.59 | 0.87 | 0.00 |
| Age Classes | Means | 95%c CI Lower Limit–Upper Limit | p < | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years old) | <10 | 1.19 | 1.02–1.36 | NS |
| 11–14 | 0.91 | 0.71–1.11 | <0.05 | |
| ≥15 | 1.37 | 1.37–1.18 | NS | |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bono, R.; Bellisario, V.; Tassinari, R.; Squillacioti, G.; Manetta, T.; Bugiani, M.; Migliore, E.; Piccioni, P. Bisphenol A, Tobacco Smoke, and Age as Predictors of Oxidative Stress in Children and Adolescents. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 2025. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16112025
Bono R, Bellisario V, Tassinari R, Squillacioti G, Manetta T, Bugiani M, Migliore E, Piccioni P. Bisphenol A, Tobacco Smoke, and Age as Predictors of Oxidative Stress in Children and Adolescents. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2019; 16(11):2025. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16112025
Chicago/Turabian StyleBono, Roberto, Valeria Bellisario, Roberta Tassinari, Giulia Squillacioti, Tilde Manetta, Massimiliano Bugiani, Enrica Migliore, and Pavilio Piccioni. 2019. "Bisphenol A, Tobacco Smoke, and Age as Predictors of Oxidative Stress in Children and Adolescents" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 16, no. 11: 2025. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16112025
APA StyleBono, R., Bellisario, V., Tassinari, R., Squillacioti, G., Manetta, T., Bugiani, M., Migliore, E., & Piccioni, P. (2019). Bisphenol A, Tobacco Smoke, and Age as Predictors of Oxidative Stress in Children and Adolescents. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 16(11), 2025. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16112025