Significant Cellular Viability Dependence on Time Exposition at ELF-EMF and RF-EMF In Vitro Studies
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Lines and Cell Culture
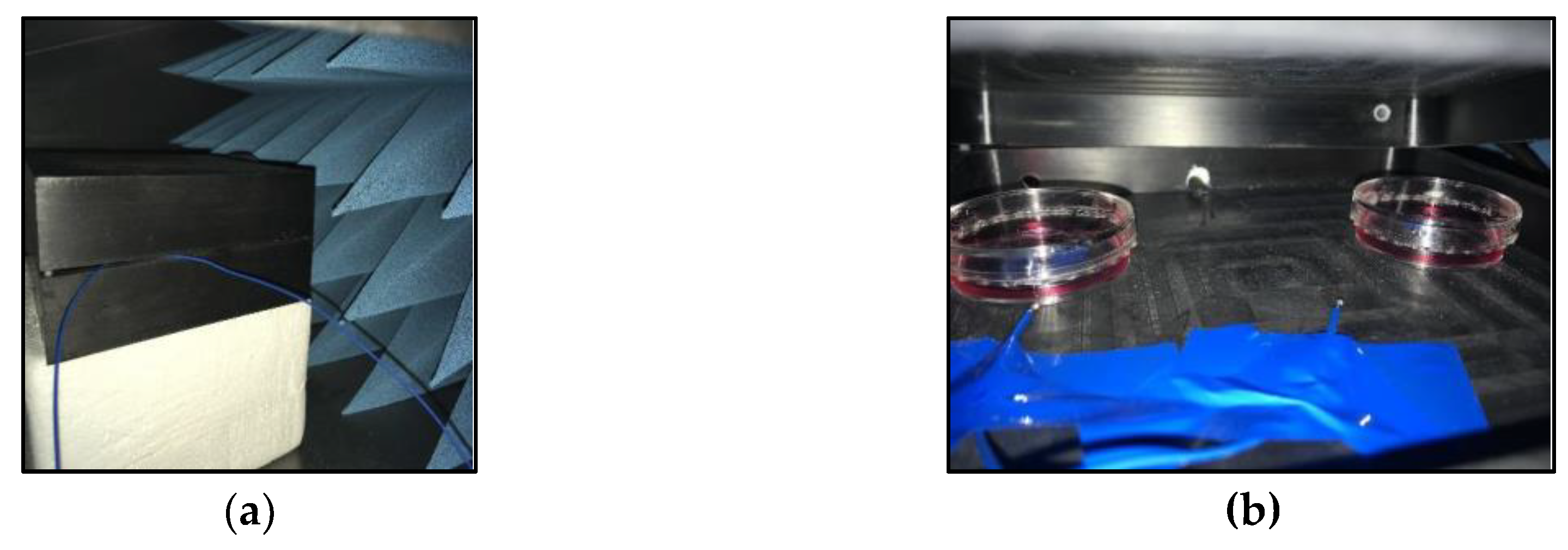
2.2. Exposure to Electromagnetic Fields with Extreme Low Frequencies Between 20 Hz and 50 Hz
2.3. Exposure to Electromagnetic Fields with Extreme High Frequencies
2.4. Cell Viability
2.5. Trypan Blue Assay
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Time and Frequency Results
3.1.1. Time and Frequency Effects of a 100 µT ELF-EMF on Cell Viability
3.1.2. Time-Dependent Effect of an EHF-EMF on Cell Viability
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Seze, R.; Lahitte, A.; Moreau, J.M.; Veyret, B. Generation of extremely-low frequency magnetic fields with standard available commercial equipment: Implications for experimental bioelectromagnetics work. Bioelectrochem. Bioenerg. 1994, 35, 127–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adlkofer, F.; Tauber, R.W.; Rüdiger, H.G.; Wobus, A.M.; Trillo, A.; Leszczynski, D.; Kolb, H.A.; Bersani, F.; Lagroye, I.; Kuster, N.; et al. Risk Evaluation of Potential Environmental Hazards from Low Energy Electromagnetic Field Exposure Using Sensitive in vitro Methods. In Bioelectromagnetics Current Concepts; Final Report of a Project Funded by the European Union under the Programme Quality of Life and Management of Living Resources; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2004; Available online: https://itis.swiss/assets/Downloads/Papers-Reports/Reports/REFLEXFinal-Report171104.pdf (accessed on 12 May 2019).
- Koziorowska, A.; Romerowicz-Misielak, M.; Sołek, P.; Koziorowski, M. Extremely low frequency variable electromagnetic fields affect cancer and noncancerous cells in vitro differently: Preliminary study. Electromagn. Biol. Med. 2018, 37, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.; Im, W.S.; Kang, L.; Lee, S.T.; Chu, K.; Kim, B.I. The application of magnets directs the orientation of neurite outgrowth in cultured human neuronal cells. J. Neurosci. Methods 2008, 174, 91–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akbarnejad, Z.; Eskandary, H.; Vergallo, C.; Nematollahi-Mahani, S.N.; Dini, L.; Darvishzadeh-Mahani, F.; Ahmadi, M. Effects of extremely low-frequency pulsed electromagnetic fields (ELF-PEMFs) on glioblastoma cells (U87). Electromagn. Biol. Med. 2017, 36, 238–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez-Castejón, C.; Pérez-Bruzón, R.N.; Llorente, M.; Pes, N.; Lacasa, C.; Figols, T.; Lahoz, M.; Maestú, C.; Vera-Gil, A.; Del Moral, A.; et al. Exposure to ELF-pulse modulated X band microwaves increases in vitro human astrocytoma cell proliferation. Histol. Histopathol. 2009, 24, 1551–1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, T.Y.; Zou, S.P.; Knapp, P.E. Exposure to cell phone radiation up-regulates apoptosis genes in primary cultures of neurons and astrocytes. Neurosci. Lett. 2007, 412, 34–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markovà, E.; Malmgren, L.O.G.; Belyaev, I.Y. Microwaves from Mobile Phones Inhibit 53BP1 Focus Formation in Human Stem Cells More Strongly Than in Differentiated Cells: Possible Mechanistic Link to Cancer Risk. Environ. Health Perspect. 2010, 118, 394–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sunkari, V.G.; Aranovitch, B.; Portwood, N.; Nikoshkov, A. Effects of a low-intensity electromagnetic field on fibroblast migration and proliferation. Electromagn. Biol. Med. 2011, 30, 80–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Council Recommendation 1999/519/EC. Council Recommendation of 12 July 1999 on the Limitation of Exposure of the General Public to Electromagnetic Fields (0 Hz to 300 GHz). Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/LexUriServ/LexUriServ.do?uri=OJ:L:1999:199:0059:0070:EN:PDF (accessed on 11 June 2019).
- Akbarnejad, Z.; Eskandary, H.; Dini, L.; Vergallo, C.; Nematollahi-Mahani, S.N.; Farsinejad, A.; Abadi, M.F.S.; Ahmadi, M. Cytotoxicity of temozolomide on human glioblastoma cells is enhanced by the concomitant exposure to an extremely low-frequency electromagnetic field (100 Hz, 100 G). Biomed. Pharm. 2017, 92, 254–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falone, S.; Santini, S.; Cordone, V.; Cesare, P.; Bonfigli, A.; Grannonico, M.; Di Emidio, G.; Tatone, C.; Cacchio, M.; Amicarelli, F. Power frequency magnetic field promotes a more malignant phenotype in neuroblastoma cells via redox-related mechanisms. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 11470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.C.; Hong, M.N.; Jung, S.H.; Kim, B.C.; Suh, Y.J.; Ko, Y.G.; Lee, Y.S.; Lee, B.Y.; Cho, Y.G.; Myung, S.H.; et al. Effect of extremely low frequency magnetic fields on cell proliferation and gene expression. Bioelectromagnetics 2015, 36, 506–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahbazi-GahroueI, D.; Hashemi-Beni, B.; Ahmadi, Z. Effects of RF-EMF Exposure from GSM Mobile Phones on Proliferation Rate of Human Adipose-derived Stem Cells: An In-vitro Study. J. Biomed. Phys. Eng. 2016, 6, 243–252. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Duan, W.; Xu, S.; Chen, C.; He, M.; Zhang, L.; Yu, Z.; Zhou, Z. Exposure to 1800 MHz radiofrequency electromagnetic radiation induces oxidative DNA base damage in a mouse spermatocyte-derived cell line. Toxicol. Lett. 2013, 218, 2–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falzone, N.; Huyser, C.; Fourie, F.; Toivo, T.; Leszczynski, D.; Franken, D. In vitro effect of pulsed 900 MHz GSM radiation on mitochondrial membrane potential and motility of human spermatozoa. Bioelectromagnetics 2008, 29, 268–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wyde, M.E.; Horn, T.L.; Capstick, M.H.; Ladbury, J.M.; Koepke, G.; Wilson, P.F.; Kissling, G.E.; Stout, M.D.; Kuster, N.; Melnick, R.L.; et al. Effect of Cell Phone Radiofrequency Radiation on Body Temperature in Rodents: Pilot Studies of the National Toxicology Program’s Reverberation Chamber Exposure System. Bioelectromagnetics 2018, 39, 190–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| 20 Hz | p Value |
|---|---|
| 24 h | 0.435 |
| 48 h | 0.005 |
| 72 h | 0.207 |
| 30 Hz | p Value |
|---|---|
| 24 h | 0.007 |
| 48 h | 0.002 |
| 72 h | 0.001 |
| 50 Hz | p Value |
|---|---|
| 24 h | 0.009 |
| 48 h | 0.299 |
| 72 h | 0.002 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
García-Minguillán López, O.; Jiménez Valbuena, A.; Maestú Unturbe, C. Significant Cellular Viability Dependence on Time Exposition at ELF-EMF and RF-EMF In Vitro Studies. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 2085. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16122085
García-Minguillán López O, Jiménez Valbuena A, Maestú Unturbe C. Significant Cellular Viability Dependence on Time Exposition at ELF-EMF and RF-EMF In Vitro Studies. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2019; 16(12):2085. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16122085
Chicago/Turabian StyleGarcía-Minguillán López, Olga, Ana Jiménez Valbuena, and Ceferino Maestú Unturbe. 2019. "Significant Cellular Viability Dependence on Time Exposition at ELF-EMF and RF-EMF In Vitro Studies" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 16, no. 12: 2085. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16122085
APA StyleGarcía-Minguillán López, O., Jiménez Valbuena, A., & Maestú Unturbe, C. (2019). Significant Cellular Viability Dependence on Time Exposition at ELF-EMF and RF-EMF In Vitro Studies. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 16(12), 2085. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16122085




