Familial Environment and Overweight/Obese Adolescents’ Physical Activity
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study design
2.2. Participants
2.3. Procedures
2.4. Measures
2.5. Data Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Roberts, K.C.; Shields, M.; de Groh, M.; Aziz, A.; Gilbert, J.A. Overweight and obesity in children and adolescents: Results from the 2009 to 2011 Canadian health measures survey. Health Rep. 2012, 23, 37–41. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shields, M. Overweight and obesity among children and youth. Health Rep. 2005, 17, 27–42. [Google Scholar]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Promoting Better Health for Young People Through Physical Activity and Sports 2000. Available online: http://www2.ed.gov/offices/OSDFS/physedrpt.pdf (accessed on 6 October 2014).
- Tremblay, M.S.; Leblanc, A.G.; Kho, M.E.; Saunders, T.J.; Larouche, R.; Colley, R.C.; Goldfield, G.; Connor, G.S. Systematic review of sedentary behaviour and health indicators in school-aged children and youth. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2011, 8, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ornelas, I.J.; Perreira, K.M.; Ayala, G.X. Parental influences on adolescent physical activity: A longitudinal study. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2007, 4, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schrempft, S.; van Jaarsveld, C.H.; Fisher, A.; Wardle, J. the obesogenic quality of the home environment: associations with diet, physical activity, TV viewing, and BMI in preschool children. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0134490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darling, N.; Steinberg, L. Parenting style as context: An integrative model. Psychol. Bull. 1993, 113, 487–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niemeier, B.S.; Hektner, J.M.; Enger, K.B. Parent participation in weight-related health interventions for children and adolescents: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Prev. Med. 2012, 55, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGuire, M.T.; Hannan, P.J.; Neumark-Sztainer, D.; Cossrow, N.H.; Story, M. Parental correlates of physical activity in a racially/ethnically diverse adolescent sample. J. Adolesc. Health 2002, 30, 253–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bungum, T.J.; Vincent, M.L. Determinants of physical activity among female adolescents. Am. J. Prev. Med. 1997, 13, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoefer, W.R.; McKenzie, T.L.; Sallis, J.F.; Marshall, S.J.; Conway, T.L. Parental provision of transportation for adolescent physical activity. Am. J. Prev. Med. 2001, 21, 48–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davison, K.K.; Cutting, T.M.; Birch, L.L. Parents’ activity-related parenting practices predict girls’ physical activity. Med. Sci. Sport Exerc. 2003, 35, 1589–1595. [Google Scholar]
- Gustafson, S.L.; Rhodes, R.E. Parental correlates of physical activity in children and early adolescents. Sports Med. 2006, 36, 79–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trost, S.G.; Loprinzi, P.D. Parental influences on physical activity behavior in children and adolescents: A brief review. Am. J. Lifestyle Med. 2011, 5, 171–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, A.W.; Watts, A.W.; Masse, L.C. Parent-adolescent patterns of physical activity, sedentary behaviors and sleep among a sample of overweight and obese adolescents. J. Phys. Act. Health 2015, 12, 1469–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colley, R.C.; Wong, S.L.; Garriguet, D.; Janssen, I.; Connor, G.S.; Tremblay, M.S. Physical activity, sedentary behaviour and sleep in Canadian children: Parent-report versus direct measures and relative associations with health risk. Health Rep. 2012, 23, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- De Vet, E.; de Ridder, D.T.; de Wit, J.B. Environmental correlates of physical activity and dietary behaviours among young people: A systematic review of reviews. Obes. Rev. 2011, 12, e130–e142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitzmann, K.M.; Dalton, W.T.; Buscemi, J. Beyond parenting practices: family context and the treatment of pediatric obesity. Fam. Relat. 2008, 57, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumrind, D. Current patterns of parental authority. Dev. Psychol. 1971, 4, 1–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumrind, D. Parental disciplinary patterns and social competence in children. Youth Soc. 1978, 9, 239–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zametkin, A.J.; Zoon, C.K.; Klein, H.W.; Munson, S. Psychiatric aspects of child and adolescent obesity: A review of the past 10 years. J. Am. Acad. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry 2004, 43, 134–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amed, S.; Dean, H.J.; Panagiotopoulos, C.; Sellers, E.A.; Hadjiyannakis, S.; Laubscher, T.A.; Dannenbaum, D.; Shah, B.R.; Booth, G.L.; Hamilton, J.K. Type 2 diabetes, medication-induced diabetes, and monogenic diabetes in Canadian children. Diabetes Care 2010, 33, 786–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patrick, H.; Hennessy, E.; McSpadden, K.; Oh, A. Parenting styles and practices in children's obesogenic behaviors: Scientific gaps and future research directions. Child Obes. 2013, 9 (Suppl. 1), S73–S86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rhee, K. Childhood overweight and the relationship between parent behaviors, parenting style, and family functioning. Ann. Am. Acad. Polit. Soc. Sci. 2008, 615, 11–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hennessy, E.; Hughes, S.O.; Goldberg, J.P.; Hyatt, R.R.; Economos, C.D. Parent-child interactions and objectively measured child physical activity: A cross-sectional study. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2010, 7, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bronfenbrenner, U. The Ecology of Human Development; Harvard University Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Larsen, J.K.; Hermans, R.C.; Sleddens, E.F.; Engels, R.C.; Fisher, J.O.; Kremers, S.P. How parental dietary behavior and food parenting practices affect children’s dietary behavior. Interacting sources of influence? Appetite 2015, 89, 246–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masse, L.C.; Watts, A.W.; Barr, S.I.; Tu, A.W.; Panagiotopoulos, C.; Geller, J.; Chanoine, J.P. Individual and household predictors of adolescents’ adherence to a web-based intervention. Ann. Behav. Med. 2014, 49, 371–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ihmels, M.A.; Welk, G.J.; Eisenmann, J.C.; Nusser, S.M. Development and preliminary validation of a family nutrition and physical activity (FNPA) screening tool. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2009, 6, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masse, L.C.; Watts, A.W. Stimulating innovations in the measurement of parenting constructs. Child Obes. 2013, 9 (Suppl. 1), S5–S13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cullen, K.W.; Baranowski, T.; Rittenberry, L.; Cosart, C.; Owens, E.; Hebert, D.; deMoor, C. Socioenvironmental influences on children’s fruit, juice and vegetable consumption as reported by parents: Reliability and validity of measures. Public Health Nutr. 2000, 3, 345–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olson, D. FACES IV and the circumplex model: Validation study. J. Marital Family Ther. 2011, 37, 64–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mâsse, L.C.; Fuemmeler, B.F.; Anderson, C.B.; Matthews, C.E.; Trost, S.G.; Catellier, D.J.; Treuth, M. Accelerometer data reduction: A comparison of four reduction algorithms on select outcome variables. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2005, 37 (Suppl. 11), S544–S554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Troiano, R.P.; Berrigan, D.; Dodd, K.W.; Mâsse, L.C.; Tilert, T.; McDowell, M. Physical activity in the United States measured by accelerometer. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2008, 40, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evenson, K.R.; Catellier, D.J.; Gill, K.; Ondrak, K.S.; McMurray, R.G. Calibration of two objective measures of physical activity for children. J. Sports Sci. 2008, 26, 1557–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trost, S.G.; Loprinzi, P.D.; Moore, R.; Pfeiffer, K.A. Comparison of accelerometer cut points for predicting activity intensity in youth. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2011, 43, 1360–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sallis, J.F.; Haskell, W.L.; Wood, P.D.; Fortmann, S.P.; Rogers, T.; Blair, S.N.; Paffenbarger, R.S., Jr. Physical activity assessment methodology in the five-city project. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1985, 121, 91–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridley, K.; Ainsworth, B.E.; Olds, T.S. Development of a compendium of energy expenditures for youth. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2008, 5, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mattocks, C.; Leary, S.; Ness, A.; Deere, K.; Saunders, J.; Tilling, K.; Kirkby, J.; Blair, S.N.; Riddoch, C. Calibration of an accelerometer during free-living activities in children. Int. J. Pediatr. Obes. 2007, 2, 218–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Treuth, M.S.; Schmitz, K.; Catellier, D.J.; McMurray, R.G.; Murray, D.M.; Almeida, M.J.; Going, S.; Norman, J.E.; Pate, R. Defining accelerometer thresholds for activity intensities in adolescent girls. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2004, 36, 1259–1266. [Google Scholar]
- Jago, R.; Davison, K.K.; Brockman, R.; Page, A.S.; Thompson, J.L.; Fox, K.R. Parenting styles, parenting practices, and physical activity in 10- to 11-year olds. Prev. Med. 2011, 52, 44–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fuemmeler, B.F.; Anderson, C.B.; Masse, L.C. Parent-child relationship of directly measured physical activity. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2011, 8, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trost, S.G.; Sallis, J.F.; Pate, R.R.; Freedson, P.S.; Taylor, W.C.; Dowda, M. Evaluating a model of parental influence on youth physical activity. Am. J. Prev. Med. 2003, 25, 277–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dempsey, J.M.; Kimiecik, J.C.; Horn, T.S. Parental influence on children’s moderate to vigorous physical activity participation: An expectancy-value approach. Pediatr. Exerc. Sci. 1993, 5, 151–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brustad, R.J. Attraction to physical activity in urban schoolchildren: Parental socialization and gender influences. Res. Q. Exerc. Sport 1996, 67, 316–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loth, K.; Wall, M.; Choi, C.W.; Bucchianeri, M.; Quick, V.; Larson, N.; Neumark-Sztainer, D. Family meals and disordered eating in adolescents: Are the benefits the same for everyone? Int. J. Eat. Disord. 2015, 48, 100–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maynard, P.E.; Olson, D.H. Circumplex model of family systems: A treatment tool in family counseling. J. Couns. Dev. 1987, 65, 502–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banis, H.T.; Varni, J.W.; Wallander, J.L.; Korsch, B.M.; Jay, S.M.; Adler, R.; Garciatemple, E.; Negrete, V. Psychological and social adjustment of obese children and their families. Child Care Health Dev. 1988, 14, 157–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langer, S.L.; Crain, A.L.; Senso, M.M.; Levy, R.L.; Sherwood, N.E. Predicting child physical activity and screen time: Parental support for physical activity and general parenting styles. J. Pediatr. Psychol. 2014, 39, 633–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ray, C.; Kalland, M.; Lehto, R.; Roos, E. Does parental warmth and responsiveness moderate the associations between parenting practices and children's health-related behaviors? J. Nutr. Educ. Behav. 2013, 45, 602–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prince, S.A.; Adamo, K.B.; Hamel, M.E.; Hardt, J.; Connor Gorber, S.; Tremblay, M. A comparison of direct versus self-report measures for assessing physical activity in adults: A systematic review. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2008, 5, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerr, M.; Stattin, H. What parents know, how they know it, and several forms of adolescent adjustment: Further support for a reinterpretation of monitoring. Dev. Psychol. 2000, 36, 366–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connor, T.G. Annotation: Theeffects’ of parenting reconsidered: Findings, challenges, and applications. J. Child Psychol. Psychiatry 2002, 43, 555–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sallis, J.F.; Saelens, B.E. Assessment of physical activity by self-report: Status, limitations, and future directions. Res. Q. Exerc. Sport 2000, 71 (Suppl. 2), S1–S14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sirard, J.R.; Pate, R.R. Physical activity assessment in children and adolescents. Sports Med. 2001, 31, 439–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maccoby, E.E.; Martin, J.A. Socialization in the context of the family: Parent-child interaction. In Handbook of Child Psychology: Socialization, Personality, and Social Development; Mussen, P.H., Hetherington, E.M., Eds.; Wiley & Sons, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1983; pp. 1–101. [Google Scholar]
- Farajian, P.; Panagiotakos, D.B.; Risvas, G.; Malisova, O.; Zampelas, A. Hierarchical analysis of dietary, lifestyle and family environment risk factors for childhood obesity: The GRECO study. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2014, 68, 1107–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Chen, H.J.; Liang, L.; Wang, Y. Parent-child resemblance in weight status and its correlates in the United States. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e65361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, J.E.; Helsel, B.; Griffin, S.F.; Liang, J. Associations between parental BMI and the family nutrition and physical activity environment in a community sample. J. Commun. Health 2017, 42, 1233–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Ratios | Scores (Use Percentiles) |
|---|---|
| Cohesion Ratio | Balanced Cohesion/ ((Enmeshed + Disengaged)/2) |
| Flexibility Ratio | Balanced Flexibility/ ((Chaotic + Rigid)/2) |
| % | Mean ± SD | Range | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Adolescent age, in years (n = 172) | 13.1 ± 1.8 | 11.0–16.0 | |
| Adolescent sex, female (n = 172) | 55.2 | ||
| Adolescent BMI z-score (n = 172) | 2.70 ± 0.83 | 1.1–6.0 | |
| Parent age, year (n = 172) | 45.7 ± 6.2 | 31–66 | |
| Parent sex, female (n = 172) | 84.3 | ||
| Parent BMI (n = 172) | 30.3 ± 7.3 | 18.3–69.0 | |
| Household income in CAD (n = 169) | |||
| $60,000 or less | 34.9 | -- | -- |
| $60, 000– $100,000 | 33.7 | -- | -- |
| $100, 001 or more | 31.4 | -- | -- |
| Parent education (n = 172) | |||
| High school or less | 17.4 | -- | -- |
| Trade certificate/diploma | 41.3 | -- | -- |
| Bachelor degree | 18.6 | -- | -- |
| More than bachelor degree | 22.7 | -- | -- |
| Parental marital status (n = 172) | |||
| Married or Common-law | 70.9 | -- | -- |
| Single/Widowed/Separated/Divorced | 29.1 | -- | -- |
| Ethnicity (n = 171) | |||
| White | 48.0 | -- | -- |
| East or Southeast Asian | 13.5 | -- | -- |
| South Asian | 12.3 | -- | -- |
| Aboriginal | 10.0 | -- | -- |
| Other ethnicity | 16.4 | -- | -- |
| n | Mean ± SD | Range | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Independent Variables | |||
| Parenting Practices | |||
| Physical activity | 160 | 2.4 ± 0.8 | 1–4 |
| Parental Modeling | |||
| Measured MVPA (min/day) | 155 | 29.3 ± 20.3 | 1.0–103.1 |
| Self-reported MVPA (min/day) | 170 | 68.9 ± 89.7 | 0.0–488.6 |
| Dependent Variables | |||
| Adolescent Health Behaviours | |||
| Measured MVPA (min/day) | 131 | 34.4 ± 20.9 | 2.8–119 |
| Self-reported MVPA (min/day) | 158 | 56.1 ± 47.7 | 0.0–272.1 |
| Moderators | |||
| Parenting Style | |||
| Authoritative | 160 | 34.8 ± 4.3 | 21–40 |
| Permissive | 170 | 6.0 ± 1.4 | 3–11 |
| Family Functioning | |||
| Cohesion ratio | 168 | 2.1 ± 0.63 | 0.88–4.4 |
| Flexibility ratio | 162 | 1.4 ± 0.35 | 0.68–3.1 |
| Accelerometer MVPA Time | Self-Reported MVPA Time | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model 1 | Final Model | Model 1 | Final Model | ||
| SC (SE) | SC (SE) | SC (SE) | SC (SE) | ||
| Independent Variable | PA Practices | 0.17 (0.09) p = 0.06 | 0.09 (0.11) p = 0.43 | 0.38 (0.08) p = 0.00 | 0.38 (0.08) p = 0.00 |
| Moderators | Authoritative Style | -- | −0.15 (0.09) p = 0.10 | -- | 0.01 (0.08) p = 0.85 |
| Permissive Style | -- | −0.07(0.09) p = 0.46 | -- | −0.06 (0.08) p = 0.41 | |
| Family Functioning | -- | −0.05 (0.09) p = 0.53 | -- | 0.12 (0.08) p = 0.15 | |
| Authoritative Style* PA Practices | -- | R | -- | R | |
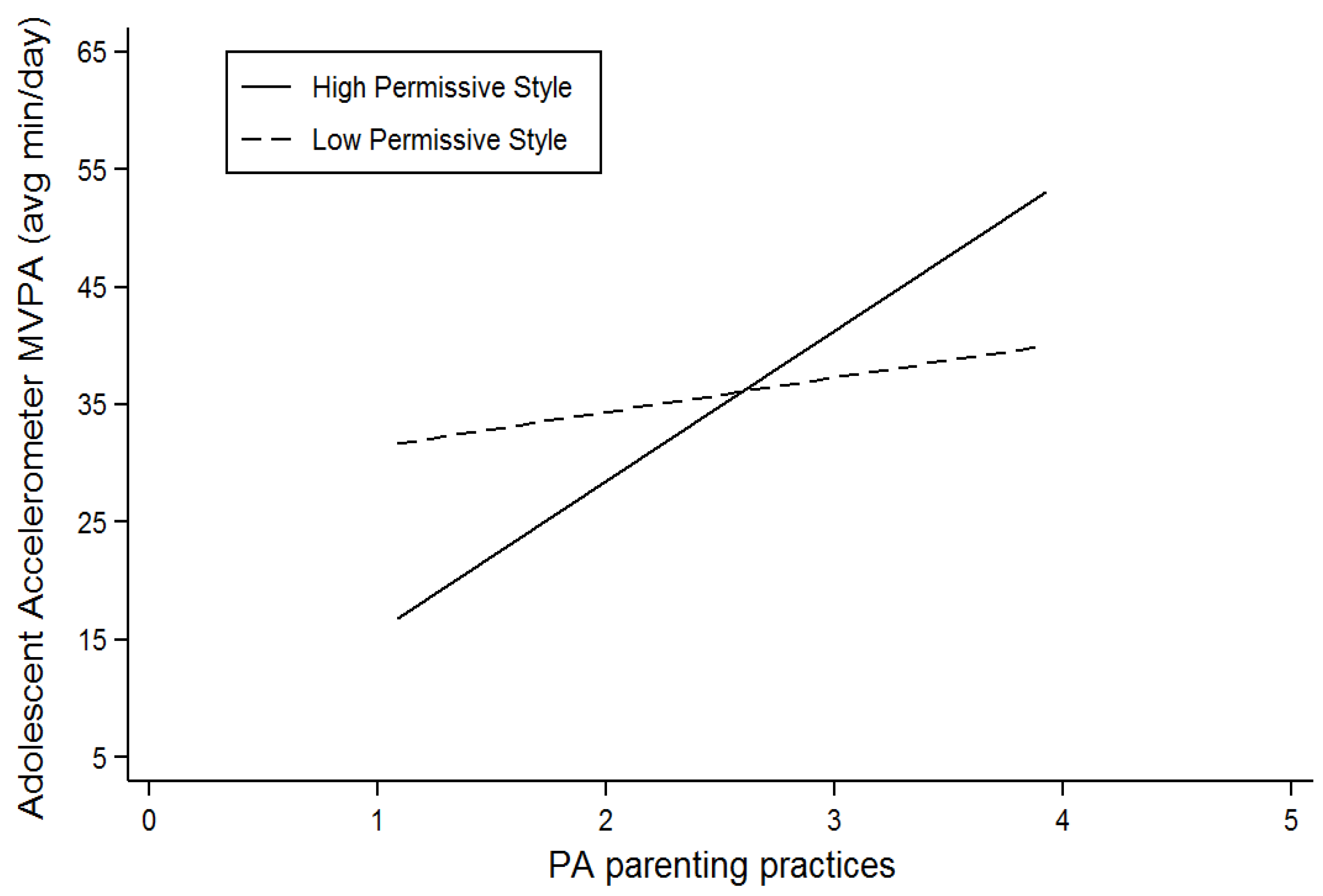
| Permissive Style* PA Practices | -- | 0.23 (0.11) p = 0.03 | -- | R | |
| Family Functioning* PA Practices | -- | R | -- | R | |
| Covariates | Adolescent sex | 0.22 (0.08) p = 0.01 | 0.21 (0.08) p = 0.01 | 0.17 (0.07) p = 0.02 | 0.18 (0.07) p = 0.02 |
| Adolescent age | 0.00 (0.09) p = 0.98 | −0.06 (0.09) p = 0.53 | 0.02 (0.08) p = 0.76 | 0.06 (0.08) p = 0.47 | |
| Parent income | −0.06 (0.09) p = 0.46 | −0.02 (0.09) p = 0.83 | 0.01 (0.08) p = 0.88 | −0.03 (0.08) p = 0.67 | |
| Accelerometer MVPA | Self-report MVPA | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model 1 | Final | Model 1 | Final | ||
| SC(SE) | SC(SE) | SC(SE) | SC(SE) | ||
| Independent Variable | Modeling (PA) | 0.22 (0.08) p = 0.00 | 0.21 (0.08) p = 0.01 | 0.29 (0.08) p = 0.00 | 0.30 (0.07) p = 0.00 |
| Moderators | Authoritative Style | -- | −0.06 (0.09) p = 0.54 | -- | 0.09 (0.08) p = 0.27 |
| Permissive Style | -- | −0.02 (0.09) p = 0.83 | -- | −0.07 (0.08) p = 0.38 | |
| Family Functioning | -- | 0.00 (0.10) p = 0.99 | -- | 0.12 (0.09) p = 0.18 | |
| Authoritative Style* Parental Modeling PA | -- | R | -- | R | |
| Permissive Style* Parental Modeling PA | -- | R | -- | R | |
| Family Functioning* Parental Modeling PA | -- | R | -- | R | |
| Covariates | Adolescent sex | 0.19 (0.08) p = 0.02 | 0.23 (0.08) p = 0.00 | 0.23 (0.07) p = 0.00 | 0.23 (0.07) p = 0.00 |
| Adolescent age | −0.04 (0.09) p = 0.63 | −0.05 (0.09) p = 0.57 | −0.07 (0.08) p = 0.35 | −0.02 (0.08) p = 0.78 | |
| Parent income | −0.05 (0.09) p = 0.60 | −0.06 (0.09) p = 0.54 | 0.08 (0.08) p = 0.33 | 0.02 (0.08) p = 0.80 | |
| Accelerometer PA | Self-Report PA | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model 1 | Final Model | Model 1 | Final Model | ||
| SC (SE) | SC (SE) | SC (SE) | SC (SE) | ||
| Independent Variables | PA Practices | 0.12 (0.09) p = 0.19 | 0.04 (0.11) p = 0.75 | 0.33 (0.08) p = 0.00 | 0.33 (0.08) p = 0.00 |
| Modeling (PA) | 0.19 (0.08) p = 0.02 | 0.16 (0.09) p = 0.07 | 0.22 (0.08) p = 0.00 | 0.23 (0.07) p = 0.00 | |
| Moderators | Authoritative Style | -- | −0.12 (0.09) p = 0.20 | -- | 0.03 (0.08) p = 0.71 |
| Permissive Style | -- | −0.04 (0.09) p = 0.64 | -- | −0.09 (0.08) p = 0.22 | |
| Family Functioning | -- | −0.01 (0.10) p = 0.91 | -- | 0.12 (0.08) p = 0.15 | |
| Authoritative Style* PA Practices | -- | R | -- | R | |
| Permissive Style* PA Practices | -- | 0.23 (0.11) p = 0.03 | -- | R | |
| Family Functioning* PA Practices | -- | R | -- | R | |
| Authoritative Style* Modeling (PA) | -- | R | -- | R | |
| Permissive Style* Modeling (PA) | -- | R | -- | R | |
| Family Functioning* Modeling (PA) | -- | R | -- | R | |
| Covariates | Adolescent sex | 0.22 (0.01) p = 0.01 | 0.21(0.08) p = 0.00 | 0.18 (0.07) p = 0.01 | 0.19 (0.07) p = 0.00 |
| Adolescent age | −0.01 (0.09) p = 0.89 | −0.05 (0.09) p = 0.53 | 0.00 (0.08) p = 0.90 | 0.05 (0.08) p = 0.53 | |
| Parent income | −0.06 (0.09) p = 0.48 | −0.03 (0.09) p = 0.75 | 0.05 (0.07) p = 0.55 | −0.01 (0.08) p = 0.92 | |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Carbert, N.S.; Brussoni, M.; Geller, J.; Mâsse, L.C. Familial Environment and Overweight/Obese Adolescents’ Physical Activity. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 2558. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16142558
Carbert NS, Brussoni M, Geller J, Mâsse LC. Familial Environment and Overweight/Obese Adolescents’ Physical Activity. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2019; 16(14):2558. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16142558
Chicago/Turabian StyleCarbert, Nicole S., Mariana Brussoni, Josie Geller, and Louise C. Mâsse. 2019. "Familial Environment and Overweight/Obese Adolescents’ Physical Activity" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 16, no. 14: 2558. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16142558
APA StyleCarbert, N. S., Brussoni, M., Geller, J., & Mâsse, L. C. (2019). Familial Environment and Overweight/Obese Adolescents’ Physical Activity. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 16(14), 2558. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16142558





