Grazing and Cultivated Grasslands Cause Different Spatial Redistributions of Soil Particles
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Sites
2.2. Experimental Design and Soil Sampling
2.3. Particle Size Analysis
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
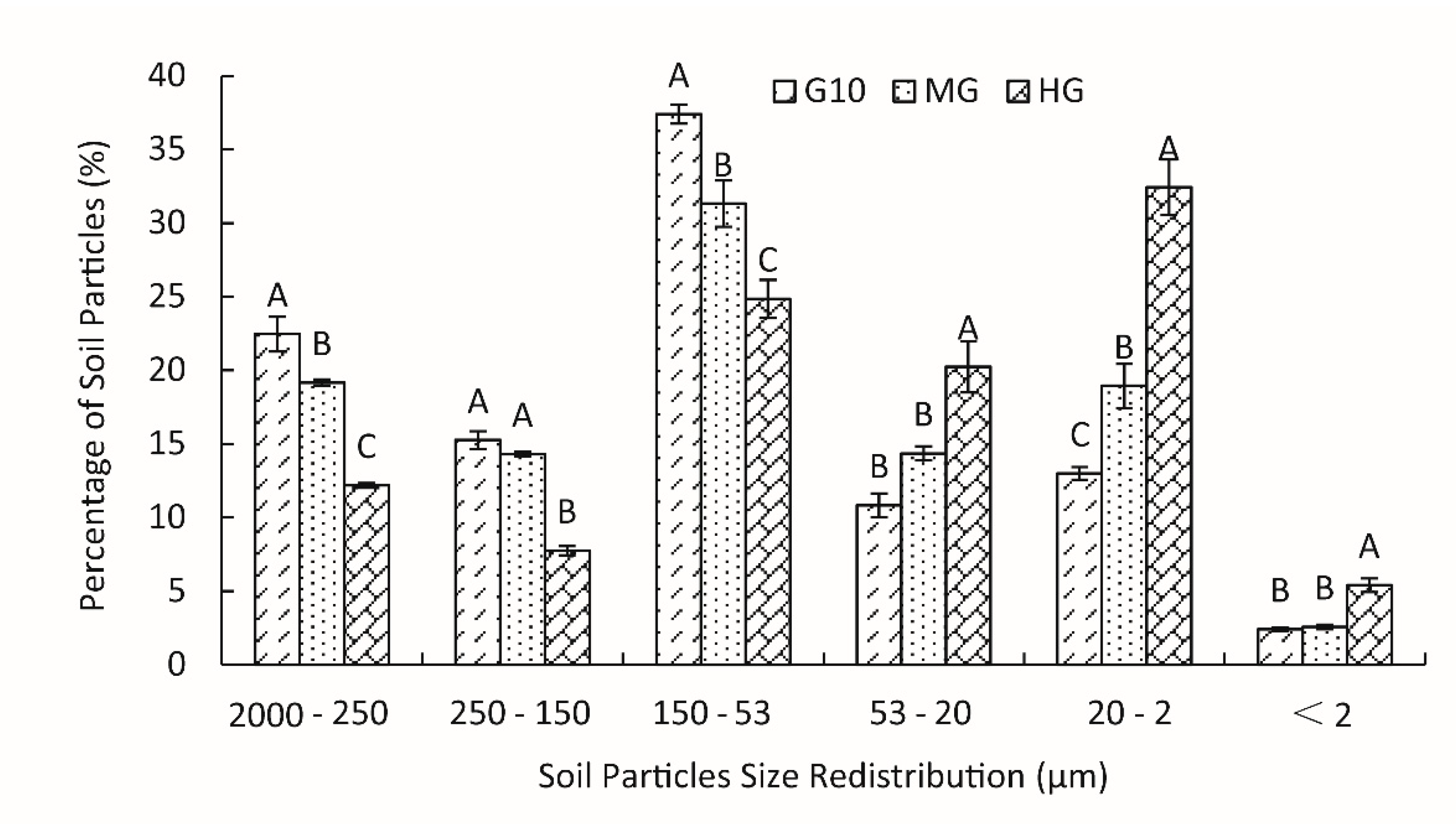
3.1. Effects of Grazing Intensity on the Redistribution of Soil Particle Sizes
3.2. Effects of Cultivation Age on the Redistribution of Soil Particle Sizes
4. Discussion
4.1. Effects of Grazing Intensity on the Redistribution of Soil Particle Sizes
4.2. Effects of Cultivation Age on the Redistribution of Soil Particle Sizes
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kang, L.; Han, X.; Zhang, Z.; Sun, O.J. Grassland ecosystems in china: Review of current knowledge and research advancement. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. 2007, 362, 997–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, Y.; Wang, X.; Guo, Z.; Chen, J.; Xin, X.; Xu, D.; Yan, R.; Chen, B.; Xu, L. Influence of wind erosion on dry aggregate size distribution and nutrients in three steppe soils in northern China. Catena 2018, 170, 159–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cameron, K.; Di, H.; Moir, J. Nitrogen losses from the soil/plant system: A review. Ann. Appl. Boil. 2013, 162, 145–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.J.; Gong, Z.T. Assessment and analysis of soil quality changes after eleven years of reclamation in subtropical china. Geoderma 1998, 81, 339–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halvorson, A.D.; Reule, C.A.; Anderson, R.L. Evaluation of management practices for converting grassland back to cropland. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2000, 55, 57–62. [Google Scholar]
- Islam, K.; Weil, R. Land use effects on soil quality in a tropical forest ecosystem of Bangladesh. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2000, 79, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelliher, F.; Curtin, D.; Condron, L. Soil carbon stocks in particle-size fractions under seasonally irrigated, grazed pasture. N. Z. J. Agric. Res. 2013, 56, 239–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Tian, F.Q.; Hu, H.P.; Hu, H.C. Soil particle size distribution and its relationship with soil water and salt under mulched drip irrigation in xinjiang of china. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 2011, 54, 1568–1574. [Google Scholar]
- Katsalirou, E.; Deng, S.; Nofziger, D.L.; Gerakis, A.; Fuhlendorf, S.D. Spatial structure of microbial biomass and activity in prairie soil ecosystems. Eur. J. Soil Boil. 2010, 46, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Wu, L.; Lin, Q.; Yuan, M.; Xu, D.; Yu, H.; Hu, Y.; Duan, J.; Li, X.; He, Z.; et al. Responses of the functional structure of soil microbial community to livestock grazing in the tibetan alpine grassland. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2013, 19, 637–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Six, J.; Elliott, E.; Paustian, K. Soil macroaggregate turnover and microaggregate formation: A mechanism for C sequestration under no-tillage agriculture. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2000, 32, 2099–2103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Are, K.; Oshunsanya, S.; Oluwatosin, G. Changes in soil physical health indicators of an eroded land as influenced by integrated use of narrow grass strips and mulch. Soil Tillage Res. 2018, 184, 269–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.-Z.; Zhao, H.-L.; Zhang, T.-H.; Zhao, X.-Y. Soil properties following cultivation and non-grazing of a semi-arid sandy grassland in northern China. Soil Tillage Res. 2004, 75, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Ding, G.D.; Yu, M.H.; Gao, G.L.; Zhao, Y.Y.; Wu, G.H.; Wang, L. Effect of Straw Checkerboards on Wind Proofing, Sand Fixation, and Ecological Restoration in Shifting Sandy Land. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 2184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, G.; Xiang, N.; Lv, S.Q.; Zhang, G.C. Fractal characterization of soil particle-size distribution under different land-use patterns in the Yellow River Delta Wetland in China. J. Soils Sediments 2014, 14, 1116–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, J.; Zhao, X.; Zuo, X.; Wang, S.; Wang, X.; Luo, Y. Land cover changes and the effects of cultivation on soil properties in shelihu wetland, horqin sandy land, northern china. J. Arid Land 2013, 5, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tai, H.; Pang, J.L.; Wen, Q.; Yan, S. Fractal characteristics of particle size distribution in soils different in land use. J. Ecol. Rural Environ. 2008, 24, 41–44. [Google Scholar]
- Zhai, X.; Li, S.; Huang, D.; Tang, S.; Wang, K. The effect of different ecosystems on groundwater consumption in an agro-pastoral ecotone of northern China from an innovative perspective. Sustain. Water Resour. Manag. 2017, 4, 667–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nan, L.; Kan, H.; Yang, G.; Zhang, Y. Changes in plant, soil, and microbes in a typical steppe from simulated grazing: Explaining potential change in soil C. Ecol. Monogr. 2016, 85, 269–286. [Google Scholar]
- Ghorbani, N.; Raiesi, F.; Ghorbani, S. Bulk soil and particle size-associated C and N under grazed and ungrazed regimes in Mountainous arid and semi-arid rangelands. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 2012, 93, 15–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, N.; Wu, L.; Wang, Y.; Han, X. Changes in carbon and nitrogen in soil particle-size fractions along a grassland restoration chronosequence in northern China. Geoderma 2009, 150, 302–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, M.; Hab, G.; Zhao, M.; Suo, P.; Pan, L. Grazing intensity effects on the soil property of range sites in hunshandake sand land. Pratacult. Sci. 2004, 21, 108–111. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, H.; Wang, Y.R.; Wu, C.X.; Ta, L. Effects of grazing on soil physical and chemical properties of alxa desert grassland. J. Desert Res. 2002, 22, 339–343. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, H.L.; Ren, J.Z. Integrated influence of experimental trampling and simulated precipitation on fractal dimension of soil particle size distributions in the steppes of huanxian county in eastern gansu province, china. Acta Pratacult. Sin. 2009, 18, 202–209. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, A.X.; LI, Y.H.; Lei, R. The soil fractal dimension characteristics in desertification process on the edge of wetland in ganjiahu. Arid Environ. Monit. 2011, 25, 219–223. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, G.; Liu, G.; Wang, G.; Wang, Y. Effects of vegetation cover and rainfall intensity on sediment-bound nutrient loss, size composition and volume fractal dimension of sediment particles. J. Arid Land 2011, 21, 676–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hewins, D.B.; Lyseng, M.P.; Schoderbek, D.F.; Alexander, M.; Willms, W.D.; Carlyle, C.N.; Chang, S.X.; Bork, E.W. Grazing and climate effects on soil organic carbon concentration and particle-size association in northern grasslands. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montero, E. Rényi dimensions analysis of soil particle-size distributions. Ecol. Model. 2005, 182, 305–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noiret, R.; Glaude, M. Comparison of soil organic carbon content, hydraulic conductivity, and particle size fractions between a grassland and a nearby black pine plantation of 40 years in two surface depths. Environ. Geol. 2009, 56, 1563–1575. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Zhao, W.; Wang, L.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Feng, Q. Relationship between soil water content and soil particle size on typical slopes of the Loess Plateau during a drought year. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 648, 943–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Six, J.; Elliott, E.; Paustian, K.; Doran, J.W. Aggregation and Soil Organic Matter Accumulation in Cultivated and Native Grassland Soils. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1998, 62, 1367–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliott, E.; Cambardella, C. Physical separation of soil organic matter. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 1991, 34, 407–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y. Fractal dimension of soil particle size distributionunder different land use/land coverage. Acta Pedol. Sin. 2005, 42, 336–339. [Google Scholar]
- Sheehy, J.; Regina, K.; Alakukku, L.; Six, J. Impact of no-till and reduced tillage on aggregation and aggregate-associated carbon in Northern European agroecosystems. Soil Tillage Res. 2015, 150, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, T.T.; Wang, X.; Sun, X.T.; Qiu, Y.; Li, D.L. Characterization of soil physical properties under different land use types. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2014, 28, 123–126. [Google Scholar]

| Grazing Intensity | Soil Depth | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0~10 cm | 10~20 cm | 20~40 cm | 40~60 cm | |
| 2000~250 μm | ||||
| G10 | 17.12 aA * | 13.89 aB | 13.25 aB | 12.66 aB |
| MG | 11.68 bB | 12.99 aAB | 14.61 aA | 14.14 aA |
| HG | 5.56 cAB | 7.80 bA | 6.36 bA | 3.32 bB |
| 250~150 μm | ||||
| G10 | 15.83 aA | 14.00 aA | 13.30 aA | 15.41 aA |
| MG | 10.28 bB | 9.15 bB | 11.30 abAB | 13.64 aA |
| HG | 7.59 bA | 7.87 bA | 6.87 bA | 4.54 bA |
| 150~53 μm | ||||
| G10 | 34.73 aA | 35.39 aA | 35.17 aA | 36.47 aA |
| MG | 33.62 aA | 28.80 bB | 32.64 abA | 34.60 aA |
| HG | 30.26 aA | 27.43 bA | 29.14 bA | 28.52 bA |
| 53~20 μm | ||||
| G10 | 13.09 bA | 14.17 bA | 15.22 aA | 11.44 bA |
| MG | 19.94 aA | 19.77 aA | 15.75 aB | 12.57 bB |
| HG | 20.97 aAB | 18.22 abAB | 17.66 aB | 21.41 aA |
| 20~2 μm | ||||
| G10 | 16.78 cA | 19.65 bA | 19.74 bA | 20.39 bA |
| MG | 22.27 bB | 26.05 aA | 22.23 bB | 21.83 bB |
| HG | 31.29 aA | 34.84 aA | 33.67 aA | 37.26 aA |
| <2 μm | ||||
| G10 | 2.44 bA | 2.91 aA | 3.32 bA | 3.63 aA |
| MG | 2.22 bA | 3.24 aA | 3.47 bA | 3.22 aA |
| HG | 4.32 aA | 3.86 aA | 6.29 aA | 4.93 aA |
| Cultivation Age | Soil Depth | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0~10 cm | 10~20 cm | 20~40 cm | 40~60 cm | |
| 2000~250 μm | ||||
| C5 | 11.42 bA * | 8.51 bA | 12.00 bA | 11.49 bA |
| C10 | 17.65 aA | 20.15 aA | 18.90 abA | 18.82 abA |
| C15 | 15.25 abC | 17.84 aBC | 26.77 aA | 23.52 aAB |
| 250~150 μm | ||||
| C5 | 7.25 cAB | 5.15 bB | 7.10 bAB | 8.43 bA |
| C10 | 13.14 bA | 14.54 aA | 14.51 aA | 13.64 aA |
| C15 | 16.96 aA | 16.19 aAB | 14.52 aAB | 13.38 aB |
| 150~53 μm | ||||
| C5 | 28.77 bA | 22.58 cB | 22.43 bB | 25.62 bAB |
| C10 | 31.44 bA | 30.36 bA | 30.99 aA | 32.45 abA |
| C15 | 39.78 aA | 38.74 aA | 35.66 aA | 35.40 aA |
| 53~20 μm | ||||
| C5 | 21.44 aAB | 23.13 aA | 18.66 aB | 17.70 aB |
| C10 | 16.10 bA | 14.23 bAB | 14.27 bAB | 12.83 bB |
| C15 | 11.99 cA | 11.19 bAB | 9.33 cC | 10.78 bB |
| 20~2 μm | ||||
| C5 | 26.86 aB | 34.78 aA | 33.60 aAB | 31.43 aAB |
| C10 | 19.06 bA | 18.25 bA | 18.92 bA | 19.50 bA |
| C15 | 13.65 cA | 13.52 cAB | 11.70 cB | 14.27 bA |
| <2 μm | ||||
| C5 | 4.26 aB | 5.85 aA | 6.20 aA | 5.33 aA |
| C10 | 2.60 bA | 2.47 bA | 2.41 bA | 2.77 bA |
| C15 | 2.38 bA | 2.53 bA | 2.03 bA | 2.65 bA |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, J.; Shang, J.; Huang, D.; Tang, S.; Zhao, T.; Yang, X.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, K.; Shao, X. Grazing and Cultivated Grasslands Cause Different Spatial Redistributions of Soil Particles. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 2639. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16152639
Li J, Shang J, Huang D, Tang S, Zhao T, Yang X, Zhang Q, Liu K, Shao X. Grazing and Cultivated Grasslands Cause Different Spatial Redistributions of Soil Particles. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2019; 16(15):2639. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16152639
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Jinsheng, Jianying Shang, Ding Huang, Shiming Tang, Tianci Zhao, Xiaomeng Yang, Qian Zhang, Kesi Liu, and Xinqing Shao. 2019. "Grazing and Cultivated Grasslands Cause Different Spatial Redistributions of Soil Particles" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 16, no. 15: 2639. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16152639
APA StyleLi, J., Shang, J., Huang, D., Tang, S., Zhao, T., Yang, X., Zhang, Q., Liu, K., & Shao, X. (2019). Grazing and Cultivated Grasslands Cause Different Spatial Redistributions of Soil Particles. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 16(15), 2639. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16152639






