Synergistic Effects of Climate Change and Marine Pollution: An Overlooked Interaction in Coastal and Estuarine Areas
Abstract
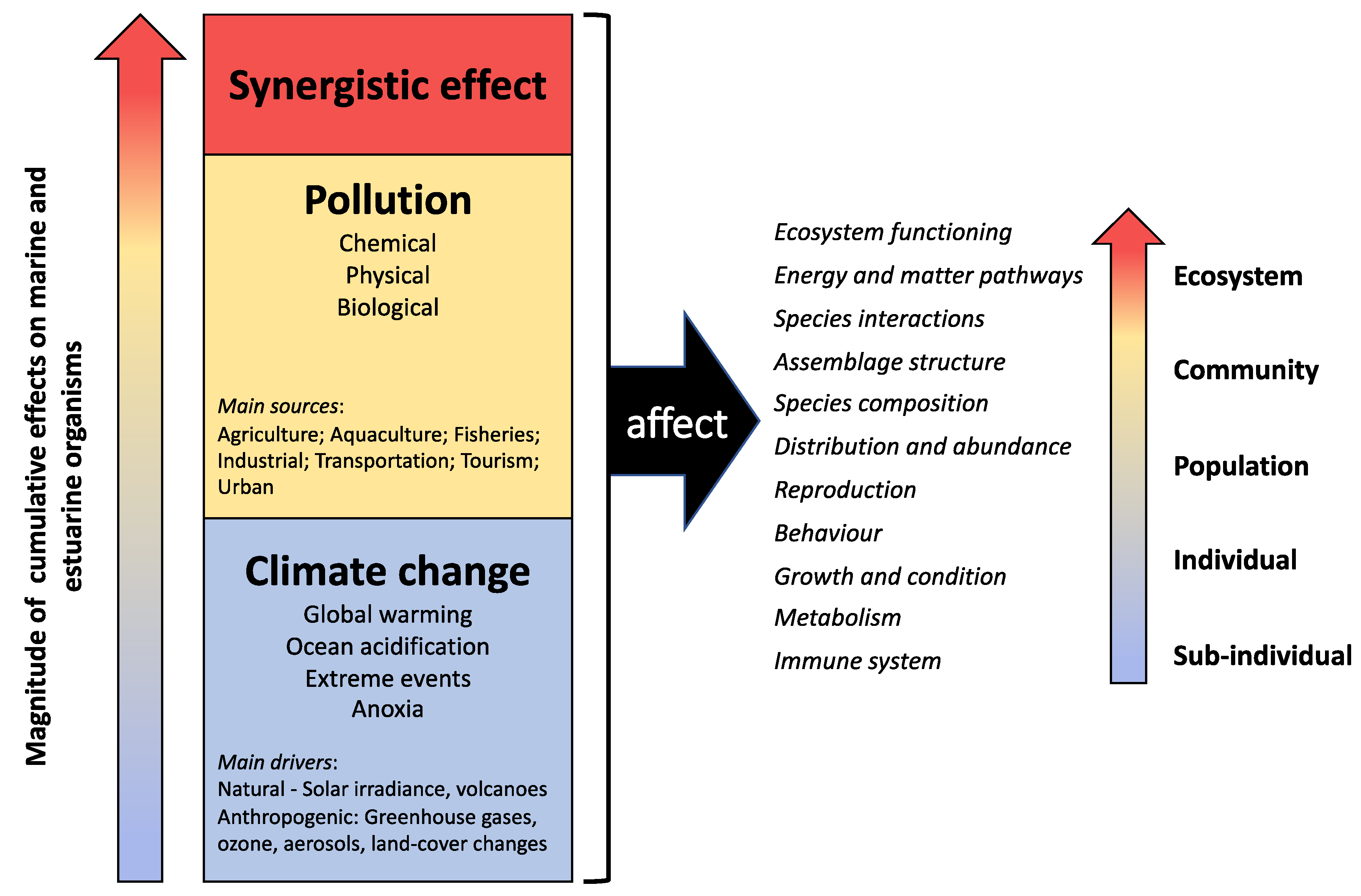
:1. Introduction
2. Marine Pollutants in Coastal Areas
2.1. Eutrophication
2.2. Metals
2.3. Organic Compounds
2.4. Emerging Contaminants
3. Climate Change Drivers and Their Impacts on Pollutants
4. Upscaling Synergistic Effects of Pollution and Climate Change at Different Biological Levels
5. Methodological Approaches to Address Synergistic Effects
6. Knowledge Gaps and Future Prospects
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Barbier, E.B.; Hacker, S.D.; Kennedy, C.; Koch, E.W.; Stier, A.C.; Silliman, B.R. The value of estuarine and coastal ecosystem services. Ecol. Monogr. 2011, 81, 169–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costanza, R.; d’Arge, R.; de Groot, R.; Farber, S.; Grasso, M.; Hannon, B.; Limburg, K.; Naeem, S.; O’Neill, R.V.; Paruelo, J.; et al. The value of the world’s ecosystem services and natural capital. Nature 1997, 387, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halpern, B.S.; Walbridge, S.; Selkoe, K.A.; Kappel, C.V.; Micheli, F.; D’Agrosa, C.; Bruno, J.F.; Casey, K.S.; Ebert, C.; Fox, H.E.; et al. A global map of human impact on marine ecosystems. Science 2008, 319, 948–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Díaz, S.; Settele, J.; Brondízio, E.; Ngo, H.T.; Guèze, M.; Agard, J.; Arneth, A.; Balvanera, P.; KBrauman, K.; Butchart, S.; et al. Summary for Policymakers of the Global Assessment Report on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services of the Intergovernmental Science-Policy Platform on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services; Global assessment: Bonn, Germany, 2019; p. 39. [Google Scholar]
- IPCC. Climate Change 2013: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of the Working Group I to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; IPCC: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2013; p. 1535. ISBN 978-92-9169-138-8. [Google Scholar]
- Robins, P.E.; Skov, M.W.; Lewis, M.J.; Giménez, L.; Davies, A.G.; Malham, S.K.; Neill, S.P.; McDonald, J.E.; Whitton, T.A.; Jackson, S.E.; et al. Impact of climate change on UK estuaries: A review of past trends and potential projections. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2016, 169, 119–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hallett, C.S.; Hobday, A.J.; Tweedley, J.R.; Thompson, P.A.; McMahon, K.; Valesini, F.J. Observed and predicted impacts of climate change on the estuaries of south-western Australia, a Mediterranean climate region. Reg. Environ. Chang. 2017, 18, 1357–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowe, J.A.; Howard, T.P.; Pardaens, A.; Tinker, J.; Holt, J.; Wakelin, S.; Milne, G.; Leake, J.; Wolf, J.; Horsburgh, K.; et al. UK Climate Projections Science Report: Marine and Coastal Projections; Met Office Hadley Centre: Exeter, UK, 2009; p. 95. ISBN 978-1-906360-03-0.
- Caldeira, K.; Wickett, M.E. Oceanography: Anthropogenic carbon and ocean pH. Nature 2003, 425, 365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- FAO. The State of World Fisheries and Aquaculture: Meeting the Sustainable Development Goals; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2018; p. 210. [Google Scholar]
- Palomares, M.-L.D.; Pauly, D. Coastal Fisheries: The Past, Present, and Possible Futures. In Coasts and Estuaries; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 569–576. [Google Scholar]
- Jennings, S.; Kaiser, M.J. The Effects of Fishing on Marine Ecosystems; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1998; pp. 201–352. [Google Scholar]
- Allendorf, F.W.; England, P.R.; Luikart, G.; Ritchie, P.A.; Ryman, N. Genetic effects of harvest on wild animal populations. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2008, 23, 327–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, S.M.; Kolding, J.; Rice, J.; Rochet, M.J.; Zhou, S.; Arimoto, T.; Beyer, J.E.; Borges, L.; Bundy, A.; Dunn, D.; et al. Conservation. Reconsidering the consequences of selective fisheries. Science 2012, 335, 1045–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heino, M.; Godø, O.R. Fisheries-Induced Selection Pressures in the Context of Sustainable Fisheries. Bull. Mar. Sci. 2002, 70, 639–656. [Google Scholar]
- Ortuño Crespo, G.; Dunn, D.C.; Travers-Trolet, M. A review of the impacts of fisheries on open-ocean ecosystems. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2017, 74, 2283–2297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pauly, D.; Watson, R.; Alder, J. Global trends in world fisheries: Impacts on marine ecosystems and food security. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2005, 360, 5–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barange, M.; Merino, G.; Blanchard, J.L.; Scholtens, J.; Harle, J.; Allison, E.H.; Allen, J.I.; Holt, J.; Jennings, S. Impacts of climate change on marine ecosystem production in societies dependent on fisheries. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2014, 4, 211–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, W.W.L.; Lam, V.W.Y.; Sarmiento, J.L.; Kearney, K.; Watson, R.E.G.; Zeller, D.; Pauly, D. Large-scale redistribution of maximum fisheries catch potential in the global ocean under climate change. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2010, 16, 24–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beiras, R. Basic Concepts. In Marine Pollution; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 3–20. [Google Scholar]
- Wilhelmsson, D.; Thompson, R.C.; Holmström, K.; Lindén, O.; Eriksson-Hägg, H. Marine Pollution. In Managing Ocean Environments in a Changing Climate: Sustainability and Economic Perspectives; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013; pp. 127–169. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, A.; Hedman, J.E.; Nyberg, E.; Haglund, P.; Cousins, I.T.; Wiberg, K.; Bignert, A. Temporal trends in dioxins (polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxin and dibenzofurans) and dioxin-like polychlorinated biphenyls in Baltic herring (Clupea harengus). Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2013, 73, 220–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNEP. Improving the Management of Agricultural Pesticides in Colombia, Costa Rica and Nicaragua Experiences of the Gef-Reducing Pesticide Run-Off to the Caribbean Sea Project; United Nations Environment Programme: Kingston, Jamaica, 2011; p. 77. [Google Scholar]
- UN. The First Global Integrated Marine Assessment. World Ocean Assessment I. Chapter 20. Coastal, Riverine and Atmospheric Inputs from Land; UN: New York, NY, USA, 2016; p. 93. [Google Scholar]
- Crain, C.M.; Kroeker, K.; Halpern, B.S. Interactive and cumulative effects of multiple human stressors in marine systems. Ecol. Lett. 2008, 11, 1304–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sala, E.; Knowlton, N. Global marine biodiversity trends. Annu. Rev. Environ. Resour. 2006, 31, 93–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GESAMP. Pollution in the Opean Ocean: A Review of Assessments and Related Studies; International Maritime Organization: London, UK, 2009; p. 64. [Google Scholar]
- Howarth, R.W. Coastal nitrogen pollution: A review of sources and trends globally and regionally. Harmful Algae 2008, 8, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NRC. Clean Coastal Waters; National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Boesch, D.F. Challenges and opportunities for science in reducing nutrient over-enrichment of coastal ecosystems. Estuaries 2002, 25, 886–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Yuan, J.; Lu, X.; Su, C.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, C.; Cao, X.; Li, Q.; Su, J.; Ittekkot, V.; et al. Major threats of pollution and climate change to global coastal ecosystems and enhanced management for sustainability. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 239, 670–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Diaz, R.J.; Rosenberg, R. Spreading dead zones and consequences for marine ecosystems. Science 2008, 321, 926–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duffus, J.H. Heavy metals-A meaningless term. Pure Appl. Chem. 2002, 74, 793–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridgway, J.; Shimmield, G. Estuaries as repositories of historical contamination and their impact on shelf seas. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2002, 55, 903–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adiele, R.C.; Stevens, D.E.; Kamunde, C. Cadmium-and calcium-mediated toxicity in rainbow trout Oncorhynchus mykiss in vivo: Interactions on fitness and mitochondrial endpoints. Chemosphere 2011, 85, 1604–1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonseca, V.; Serafim, A.; Company, R.; Bebianno, M.J.; Cabral, H. Effect of copper exposure on growth, condition indices and biomarker response in juvenile sole Solea senegalensis. Sci. Mar. 2009, 73, 51–58. [Google Scholar]
- Coteur, G.; Gillan, D.; Pernet, P.; Dubois, P. Alteration of cellular immune responses in the seastar Asteria rubens following dietary exposure to cadmium. Aquat. Toxicol. 2005, 73, 418–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jezierska, B.; Lugowska, K.; Witeska, M. The effects of heavy metals on embryonic development of fish (a review). Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2009, 35, 625–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rainbow, P.S. Trace metal concentrations in aquatic invertebrates: Why and so what? Environ. Pollut. 2002, 120, 497–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batley, G.E.; Apte, S.C.; Stauber, J.L. Speciation and Bioavailability of Trace Metals in Water: Progress Since 1982. Aust. J. Chem. 2004, 57, 903–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vareda, J.; Valente, A.J.; Durães, L. Assessment of heavy metal pollution from anthropogenic activites and remediation strategies: A review. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 246, 101–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonseca, V.; França, S.; Duarte, B.; Caçador, I.; Cabral, H.N.; Mieiro, C.L.; Coelho, J.P.; Pereira, E.; Reis-Santos, P. Spatial variation in mercury bioaccumulation and magnificaion in a temperate estuarine food web. Front. Mar. Sci. 2019, 6, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karagas, M.R.; Choi, A.L.; Oken, E.; Horvat, M.; Schoeny, R.; Kamai, E.; Cowell, W.; Grandjean, P.; Korrick, S. Evidence on the human health effects of low-level methylmercury exposure. Environ. Health Perspect. 2012, 120, 799–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Depew, D.C.; Basu, N.; Burgess, N.M.; Campbell, L.M.; Devlin, E.W.; Drevnick, P.E.; Hammerschmidt, C.R.; Murphy, C.A.; Sandheinrich, M.K.; Wiener, J.G. Toxicity of dietary methylmercury to fish: Derivation of ecologically meaningful threshold concentrations. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2012, 31, 1536–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pacyna, E.G.; Pacyna, J.M.; Pirrone, M. European emissions of atmospheric mercury from anthropogenic sources in 1995. Atmos. Environ. 2001, 35, 2987–2996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dachs, J.; Méjanelle, L. Organic Pollutants in Coastal Waters, Sediments, and Biota: A Relevant Driver for Ecosystems During the Anthropocene? Estuaries Coasts 2010, 33, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muir, D.C.G.; Howard, P.H. Are There Other Persistent Organic Pollutants? A Challenge for Environmental Chemists†. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 7157–7166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, D.; Currell, M.J. Persistent organic pollutants in China’s surface water systems. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 580, 602–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casey, J.M.; Baird, A.H.; Brandl, S.J.; Hoogenboom, M.O.; Rizzari, J.R.; Frisch, A.J.; Mirbach, C.E.; Connolly, S.R. A test of trophic cascade theory: Fish and benthic assemblages across a predator density gradient on coral reefs. Oecologia 2017, 183, 161–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clements, W.H.; Rohr, J.R. Community responses to contaminants: Using basic ecological principles to predict ecotoxicological effects. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2009, 28, 1789–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.K.; Yoon, J. Chronological trends of emission, environmental level and human exposure of POPs over the last 10 years (1999–2010) in Korea: Implication to science and policy. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 470–471, 1346–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kummerer, K. The presence of pharmaceuticals in the environment due to human use—Present knowledge and future challenges. J. Environ. Manag. 2009, 90, 2354–2366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunnarsson, L.; Jauhiainen, A.; Kristiansson, E.; Nerman, O.; Larsson, D.G.J. Evolutionary Conservation of Human Drug Targets in Organisms used for Environmental Risk Assessments. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 5807–5813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daughton, C.G. Pharmaceuticals and the Environment (PiE): Evolution and impact of the 739 published literature revealed by bibliometric analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 562, 391–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteiro, S.C.; Boxall, A.B.A. Occurrence and Fate of Human Pharmaceuticals in the Environment. In Reviews of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2010; pp. 53–154. [Google Scholar]
- Arnold, K.E.; Brown, A.R.; Ankley, G.T.; Sumpter, J.P. Medicating the environment: Assessing risks of pharmaceuticals to wildlife and ecosystems. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2014, 369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjorlenius, B.; Ripszam, M.; Haglund, P.; Lindberg, R.H.; Tysklind, M.; Fick, J. Pharmaceutical residues are widespread in Baltic Sea coastal and offshore waters-Screening for pharmaceuticals and modelling of environmental concentrations of carbamazepine. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 633, 1496–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis-Santos, P.; Pais, M.; Duarte, B.; Cacador, I.; Freitas, A.; Vila Pouca, A.S.; Barbosa, J.; Leston, S.; Rosa, J.; Ramos, F.; et al. Screening of human and veterinary pharmaceuticals in estuarine waters: A baseline assessment for the Tejo estuary. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 135, 1079–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez-Munoz, D.; Rodriguez-Mozaz, S.; Maulvault, A.L.; Tediosi, A.; Fernandez-Tejedor, M.; Van den Heuvel, F.; Kotterman, M.; Marques, A.; Barcelo, D. Occurrence of pharmaceuticals and endocrine disrupting compounds in macroalgaes, bivalves, and fish from coastal areas in Europe. Environ. Res. 2015, 143, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- aus der Beek, T.; Weber, F.A.; Bergmann, A.; Hickmann, S.; Ebert, I.; Hein, A.; Kuster, A. Pharmaceuticals in the environment--Global occurrences and perspectives. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2016, 35, 823–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guoa, X.; Wanga, J. The chemical behaviors of microplastics in marine environment: A review. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 142, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saidani, B.; Sellami, B.; Khazri, A.; Mezni, A.; Dellali, M.; Joubert, O.; Sheehan, D.; Beyrem, H. Metal accumulation, biochemical and behavioral responses on the Mediterranean clams Ruditapes decussatus exposed to two photocatalyst nanocomposites (TiO2 NPs and AuTiO2 NPs). Aquat. Toxicol. 2019, 208, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noyes, P.D.; Lema, S.C. Forecasting the impacts of chemical pollution and climate change interactions on the health of wildlife. Curr. Zool. 2015, 61, 669–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alava, J.J.; Cheung, W.W.L.; Ross, P.S.; Sumaila, U.R. Climate change-contaminant interactions in marine food webs: Toward a conceptual framework. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2017, 23, 3984–4001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Hung, H.; Macdonald, R.W. The influence of global climate change on the environmental fate of persistent organic pollutants: A review with emphasis on the Northern Hemisphere and the Arctic as a receptor. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2016, 146, 89–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, X.; Sun, D.; Yao, T. Climate change and global cycling of persistent organic pollutants: A critical review. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2016, 59, 1899–1911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maulvault, A.L.; Camacho, C.; Barbosa, V.; Alves, R.; Anacleto, P.; Fogaca, F.; Kwadijk, C.; Kotterman, M.; Cunha, S.C.; Fernandes, J.O.; et al. Assessing the effects of seawater temperature and pH on the bioaccumulation of emerging chemical contaminants in marine bivalves. Environ. Res. 2018, 161, 236–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alava, J.J.; Cisneros-Montemayor, A.M.; Sumaila, R.; Cheung, W.W.L. Projected amplification of food web bioaccumulation of MeHg and PCBs under climate change in the Northeastern Pacific. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nardi, A.; Mincarelli, L.F.; Benedetti, M.; Fattorini, D.; d’Errico, G.; Regoli, F. Indirect effects of climate changes on cadmium bioavailability and biological effects in the Mediterranean mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis. Chemosphere 2017, 169, 493–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomiero, A.; Viarengo, A. Effects of elevated temperature on the toxicity of copper and oxytetracycline in the marine model, Euplotes crassus: A climate change perspective. Environ. Pollut. 2014, 194, 262–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folt, C.L.; Chen, C.Y.; Moore, M.V.; Burnaford, J. Synergism and antagonism among multiple stressors. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1999, 44, 864–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Przeslawski, R.; Byrne, M.; Mellin, C. A review and meta-analysis of the effects of multiple abiotic stressors on marine embryos and larvae. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2015, 21, 2122–2140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellis, J.I.; Clark, D.; Atalah, J.; Jiang, W.; Taiapa, C.; Patterson, M.; Sinner, J.; Hewitt, J. Multiple stressor effects on marine infauna: Responses of estuarine taxa and functional traits to sedimentation, nutrient and metal loading. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 12013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, R.B.; Baumann, H.; Grear, J.S.; Aller, R.C.; Gobler, C.J. Coastal ocean acidification: The other eutrophication problem. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2014, 148, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bijma, J.; Portner, H.O.; Yesson, C.; Rogers, A.D. Climate change and the oceans--what does the future hold? Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2013, 74, 495–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, X.; Chen, X.; Zhuang, J. The positive relationship between ocean acidification and pollution. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 91, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez-Delgado, E.A. The emerging threats of climate change on tropical coastal ecosystem services, public health, local economies and livelihood sustainability of small islands: Cumulative impacts and synergies. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 101, 5–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nikinmaa, M. Climate change and ocean acidification-interactions with aquatic toxicology. Aquat. Toxicol. 2013, 126, 365–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falkenberg, L.J.; Connell, S.D.; Russell, B.D.; Frid, C. Disrupting the effects of synergies between stressors: Improved water quality dampens the effects of future CO2 on a marine habitat. J. Appl. Ecol. 2013, 50, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanina, A.V.; Sokolova, I.M. Interactive effects of metal pollution and ocean acidification on physiology of marine organisms. Curr. Zool. 2015, 61, 653–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, R.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Q.; Dong, Z.; Yang, D.; Liu, H.; Ran, W.; Qu, Y.; Zhao, J. Seawater acidification aggravated cadmium toxicity in the oyster Crassostrea gigas: Metal bioaccumulation, subcellular distribution and multiple physiological responses. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 642, 809–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coelho, F.J.; Santos, A.L.; Coimbra, J.; Almeida, A.; Cunha, A.; Cleary, D.F.; Calado, R.; Gomes, N.C. Interactive effects of global climate change and pollution on marine microbes: The way ahead. Ecol. Evol. 2013, 3, 1808–1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galic, N.; Grimm, V.; Forbes, V.E. Impaired ecosystem process despite little effects on populations: Modeling combined effects of warming and toxicants. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2017, 23, 2973–2989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokolova, I.M.; Lannig, G. Interactive effects of metal pollution and temperature on metabolism in aquatic ectotherms: Implications of global climate change. Clim. Res. 2008, 37, 181–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, R.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Yang, D.; Liu, H.; Qu, Y.; Zhao, J. The impact of ocean acidification and cadmium on the immune responses of Pacific oyster, Crassostrea gigas. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2018, 81, 456–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, W.; Zha, S.; Wang, Y.; Shi, W.; Xiao, G.; Chai, X.; Wu, H.; Liu, G. Benzo[a]pyrene exposure under future ocean acidification scenarios weakens the immune responses of blood clam, Tegillarca granosa. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2017, 63, 465–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorey, N.; Maboloc, E.; Chan, K.Y.K. Development of the sea urchin Heliocidaris crassispina from Hong Kong is robust to ocean acidification and copper contamination. Aquat. Toxicol. 2018, 205, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boukadida, K.; Banni, M.; Gourves, P.Y.; Cachot, J. High sensitivity of embryo-larval stage of the Mediterranean mussel, Mytilus galloprovincialis to metal pollution in combination with temperature increase. Mar. Environ. Res. 2016, 122, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faggio, C.; Tsarpali, V.; Dailianis, S. Mussel digestive gland as a model tissue for assessing xenobiotics: An overview. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 636, 220–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nardi, A.; Benedetti, M.; d’Errico, G.; Fattorini, D.; Regoli, F. Effects of ocean warming and acidification on accumulation and cellular responsiveness to cadmium in mussels Mytilus galloprovincialis: Importance of the seasonal status. Aquat. Toxicol. 2018, 204, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humanes, A.; Noonan, S.H.; Willis, B.L.; Fabricius, K.E.; Negri, A.P. Cumulative Effects of Nutrient Enrichment and Elevated Temperature Compromise the Early Life History Stages of the Coral Acropora tenuis. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0161616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, B.D.; Thompson, J.-A.I.; Falkenberg, L.J.; Connell, S.D. Synergistic effects of climate change and local stressors: CO2 and nutrient-driven change in subtidal rocky habitats. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2009, 15, 2153–2162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gouvêa, L.P.; Schubert, N.; Martins, C.D.L.; Sissini, M.; Ramlov, F.; Rodrigues, E.R.d.O.; Bastos, E.O.; Freire, V.C.; Maraschin, M.; Carlos Simonassi, J.; et al. Interactive effects of marine heatwaves and eutrophication on the ecophysiology of a widespread and ecologically important macroalga. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2017, 62, 2056–2075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warwick, R.M.; Tweedley, J.R.; Potter, I.C. Microtidal estuaries warrant special management measures that recognise their critical vulnerability to pollution and climate change. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 135, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Wang, J.; Fan, J.; Gao, D.; Ju, H. Effects of rainfall on microbial water quality on Qingdao No. 1 Bathing Beach, China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2013, 66, 185–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corbari, C.; Lassini, F.; Macini, M. Effect of intense short rainfall events on coastal water quality parameters from remote sensing data. Cont. Shelf Res. 2016, 123, 18–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debecker, S.; Dinh, K.V.; Stoks, R. Strong Delayed Interactive Effects of Metal Exposure and Warming: Latitude-Dependent Synergisms Persist Across Metamorphosis. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 2409–2417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- White, L.; Donohue, I.; Emmerson, M.C.; O’Connor, N.E. Combined effects of warming and nutrients on marine communities are moderated by predators and vary across functional groups. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2018, 24, 5853–5866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Christensen, V.; Walters, C.J. Ecopath with Ecosim: Methods, capabilities and limitations. Ecol. Model. 2004, 172, 109–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrne, M. Global change ecotoxicology: Identification of early life history bottlenecks in marine invertebrates, variable species responses and variable experimental approaches. Mar. Environ. Res. 2012, 76, 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dijkstra, J.A.; Buckman, K.L.; Ward, D.; Evans, D.W.; Dionne, M.; Chen, C.Y. Experimental and natural warming elevates mercury concentrations in estuarine fish. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e58401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, R.I.A.; Dossena, M.; Bohan, D.A.; Jeppesen, E.; Kordas, R.L.; Ledger, M.E.; Meerhoff, M.; Moss, B.; Mulder, C.; Shurin, J.B.; et al. Mesocosm Experiments as a Tool for Ecological Climate-Change Research. In Global Change in Multispecies Systems: Part 3; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2013; pp. 71–181. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Teichert, N.; Borja, A.; Chust, G.; Uriarte, A.; Lepage, M. Restoring fish ecological quality in estuaries: Implication of interactive and cumulative effects among anthropogenic stressors. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 542, 383–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tam, J.C.; Link, J.S.; Large, S.I.; Andrews, K.; Friedland, K.D.; Gove, J.; Hazen, E.; Holsman, K.; Karnauskas, M.; Samhouri, J.F.; et al. Comparing Apples to Oranges: Common Trends and Thresholds in Anthropogenic and Environmental Pressures across Multiple Marine Ecosystems. Front. Mar. Sci. 2017, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Levin, P.S.; Fogarty, M.J.; Murawski, S.A.; Fluharty, D. Integrated ecosystem assessments: Developing the scientific basis for ecosystem-based management of the ocean. PLoS Biol. 2009, 7, e1000014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Booth, S.; Zeller, D. Mercury, Food Webs, and Marine Mammals: Implications of Diet and Climate Change for Human Health. Environ. Health Perspect. 2005, 113, 521–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa, T.; Domingos, T.; Poggiale, J.C.; Kooijman, S.A. Dynamic energy budget theory restores coherence in biology. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2010, 365, 3413–3428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kooijman, S.A. Dynamic Energy Budget Theory for Metabolic Organization; Cambridge University Press: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2010; p. 509. [Google Scholar]
- Sousa, T.; Domingos, T.; Kooijman, S.A. From empirical patterns to theory: A formal metabolic theory of life. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B 2009, 363, 2453–2464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nisbet, R.M.; Muller, E.B.; Lika, K.; Kooijman, S.A.L.M. From molecules to ecosystems through dynamic energy budget models. J. Anim. Ecol. 2008, 69, 913–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, G.M.; Augustine, S.; Lika, K.; Pecquerie, L.; Domingos, T.; Kooijman, S.A.L.M. The AmP project: Comparing species on the basis of dynamic energy budget parameters. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2018, 14, e1006100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashauer, R.; Jager, T. Physiological modes of action across species and toxicants: The key to predictive ecotoxicology. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2018, 20, 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jager, T.; Barsi, A.; Hamda, N.T.; Martin, B.T.; Zimmer, E.I.; Ducrot, V. Dynamic energy budgets in population ecotoxicology: Applications and outlook. Ecol. Model. 2014, 280, 140–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baas, J.; Augustine, S.; Marques, G.M.; Dorne, J.-L. Dynamic energy budget models in ecological risk assessment: From principles to applications. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 628, 249–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, B.T.; Jager, T.; Nisbet, R.M.; Preuss, T.G.; Hammers-Wirtz, M.; Grimm, V. Extrapolating ecotoxicological effects from individuals to populations: A generic approach based on Dynamic Energy Budget theory and individual-based modeling. Ecotoxicology 2013, 22, 574–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niinemets, Ü.; Kahru, A.; Nõges, P.; Tuvikene, A.; Vasemägi, A.; Mander, Ü.; Nõges, T. Environmental feedbacks in temperate aquatic ecosystems under global change: Why do we need to consider chemical stressors? Reg. Environ. Chang. 2017, 17, 2079–2096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cabral, H.; Fonseca, V.; Sousa, T.; Costa Leal, M. Synergistic Effects of Climate Change and Marine Pollution: An Overlooked Interaction in Coastal and Estuarine Areas. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 2737. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16152737
Cabral H, Fonseca V, Sousa T, Costa Leal M. Synergistic Effects of Climate Change and Marine Pollution: An Overlooked Interaction in Coastal and Estuarine Areas. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2019; 16(15):2737. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16152737
Chicago/Turabian StyleCabral, Henrique, Vanessa Fonseca, Tânia Sousa, and Miguel Costa Leal. 2019. "Synergistic Effects of Climate Change and Marine Pollution: An Overlooked Interaction in Coastal and Estuarine Areas" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 16, no. 15: 2737. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16152737
APA StyleCabral, H., Fonseca, V., Sousa, T., & Costa Leal, M. (2019). Synergistic Effects of Climate Change and Marine Pollution: An Overlooked Interaction in Coastal and Estuarine Areas. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 16(15), 2737. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16152737





