Trends in Prevalence and Related Risk Factors of Overweight and Obesity among Women of Reproductive Age in Zimbabwe, 2005–2015
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data
2.2. Measurement of Outcome Variable
2.3. Independent Variable
2.4. Statistical Analysis
2.5. Ethical Considerations
3. Results
3.1. Distribution of Characteristics
3.2. Trends Over Time in the Prevalence of Overweight and Obesity
3.3. Logistic Regression
3.4. Relationship between Socioeconomic Status and Demographic Factors with Overweight and Obesity
3.5. Overweight and Obesity and Potential Modifiable Risk Factors
4. Discussion
Strengths and Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- WHO. Global Status Report on Noncommunicable Diseases 2014; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- WHO. Fact Sheet on Obesity and Overweight; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Lim, S.S.; Vos, T.; Flaxman, A.D.; Danaei, G.; Shibuya, P.K.; Adair-Rohani, H.; AlMazroa, M.A.; Amann, M.; Anderson, P.H.R.; Andrews, K.G.; et al. A comparative risk assessment of burden of disease and injury attributable to 67 risk factors and risk factor clusters in 21 regions, 1990–2010: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study, 2010. Lancet 2012, 380, 2224–2260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, G.A.; Singh, G.M.; Lu, Y.; Danaei, G.; Lin, J.K.; Finucane, M.M.; Bahalim, A.N.; McIntire, R.K.; Gutierrez, H.R.; Cowan, M.; et al. National, regional, and global trends in adult overweight and obesity prevalence. Popul. Health Metr. 2012, 10, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obesity and Overweight. Available online: http://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/obesity-and-overweight (accessed on 20 August 2018).
- Ng, M.; Fleming, T.; Thomson, B.; Robinson, M.; Graetz, N.; Margono, C.; Mullany, E.C.; Biryukov, S.; Abbafati, C.; Abera, S.F.; et al. Global, regional and national prevalence of overweight and obesity in children and adults 1980–2013: A systematic analysis. Lancet 2014, 384, 766–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abubakari, A.R.; Lauder, W.; Agyemang, C.; Kirk, A.; Bhopal, R.S. Prevalence and time trends in obesity among adult West African populations: A meta-analysis. Obes. Rev. 2008, 9, 297–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agmeyang, C.; Boatemaa, S.; Agyemang, F.G.; de-Graft, A.A. Metabolic Syndrome. In Metabolic Syndrome; Springer International Publishing: Basel, Switzerland, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Neupane, S.; Prakash, K.C.; Doku, D.T. Overweight and obesity among women: Analysis of demographic and health survey data from 32 Sub-Saharan African Countries. BMC Public Health 2016, 16, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sommer, I.; Gieber, U.; Mahlknecht, P.; Thaler, K.; Bouskill, K.; Gartlehner, G.; Mendis, S. Socioeconomic inequalities in non-communicable diseases and their risk factors: An overview of systematic reviews. BMC Public Health 2015, 15, 914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdhalah, K.Z.; Jean, C.F.; Rhoune, O. Overweight and obesity in urban Africa: A problem of the rich or the poor? BMC Public Health 2009, 9, 465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, T. Emerging disease burdens and the poor in cities of the developing world. J. Urban Health 2007, 84, 54–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sodjinou, R.; Agueh, V.; Fayomi, B. Obesity and cardio-metabolic risk factors in urban adults of Benin: Relationship with socio-economic status, urbanization, and lifestyle patterns. BMC Public Health 2008, 8, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tebekaw, Y.; Colon-Ramos, U.; Teller, C.H. Rising Overweight-Obesity and its socio-demographic correlates in Addis Ababa, Ethiopia, 2000–2011. In Proceedings of the Poster Session 7; Sheraton: New Orleans, LA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Roskam, A.J.R.; Kunst, A.E.; Van Oyen, H.; Demarest, S.; Klumbiene, J.; Regidor, E.; Helmert, U.; Jusot, F.; Dzurova, D.; Mackenbach, J.P.; et al. Comparative appraisal of educational inequalities in overweight and obesity among adults in 19 European countries. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2010, 39, 392–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLaren, L. Socioeconomic status and obesity. Epidemiol. Rev. 2007, 29, 29–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sartorius, B.; Veerman, L.J.; Manyema, M.; Chola, L.; Hofman, K. Determinants of Obesity and Associated Population Attributability, South Africa: Empirical Evidence from a National Panel Survey, 2008–2012. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0130218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ministry of Health & Child Care. National Health Strategy for Zimbabwe (2016–2020): Equity & Quality in Health—Leaving no One Behind; Government of Zimbabwe, Ministry of Health & Child Care: Harare, Zimbabwe, 2016.
- Kamadjeu, R.M.; Edwards, R.; Atanga, J.S.; Kiawi, E.C.; Unwin, N.; Mbanya, J.C. Anthropometry measures and prevalence of obesity in the urban adult population of Cameroon: An update from the Cameroon Burden of Diabetes Baseline Survey. BMC Public Health 2006, 6, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Popkin, B.M.; Doak, C.M. The obesity epidemic is a worldwide phenomenon. Nutr. Rev. 1998, 56, 106–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Omran, A.R. The epidemiologic transition theory: A preliminary update. J. Trop. Pediatr. 1983, 29, 305–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimbabwe National Statistics Agency and ICF International. Zimbabwe Demographic and Health Survey 2015: Final Report; Zimbabwe National Statistics Agency (ZIMSTAT) and ICF International: Rockville, MD, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Kelly, T.; Yang, W.; Chen, C.S.; Reynolds, K.; He, J. Global burden of obesity in 2005 and projections to 2030. Int. J. Obes. 2008, 32, 1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramanian, S.V.; Perkins, J.M.; Özaltin, E.; Davey Smith, G. Weight of nations: A socioeconomic analysis of women in low- to middle-income countries. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2011, 93, 413–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uthman, O.A. Patterns, distribution, and determinants of under- and overnutrition among women in Nigeria: A population-based analysis. J. Public Health 2009, 17, 289–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrha, S.; Shiferaw, S.; Ahmed, K.Y. Overweight and obesity and its socio-demographic correlates among urban Ethiopian women: Evidence from the 2011 EDHS. BMC Public Health 2016, 16, 636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alemu, E.; Atnafu, A.; Yitayal, M.; Yimam, K.; Alemu, E.; Atnafu, A.; Yitayal, M.; Yimam, K. Prevalence of Overweight and/or obesity and associated Factors among High School Adolescents in Arada Sub city, Addis Ababa, Ethiopia. J. Nutr. Food Sci. 2014, 4, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruger, H.S.; Venter, C.S.; Vorster, H.H.; Margetts, B.M. Physical inactivity is the major determinant of obesity in black women in the North West Province, South Africa: The THUSA study. Transition and Health During Urbanisation of South Africa. Nutrition 2002, 18, 422–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffiths, P.; Bentley, M. Women of higher socio-economic status are more likely to be overweight in Karnataka, India. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2005, 59, 1217–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, N.; Goel, K.; Shah, P.; Misra, A. Childhood obesity in developing countries: Epidemiology, determinants, and prevention. Endocr. Rev. 2012, 33, 48–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monda, K.L.; Adair, L.S.; Zhai, F.; Popkin, B.M. Longitudinal relationships between occupational and domestic physical activity patterns and body weight in China. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2008, 62, 1318–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strickland, J.R. Enhancing Workplace Wellness Efforts to Reduce Obesity: A Qualitative Study of Low-Wage Workers in St Louis, Missouri, 2013–2014. Prev. Chronic Dis. 2015, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United Nations Educational Scientific & Cultural Organizationn Adult Literacy Rate, Population 15+ Years (Both Sexes, Female, Male). Available online: http://data.uis.unesco.org/Index.aspx?DataSetCode=EDULIT_DS&popupcustomise=true&lang=en# (accessed on 20 August 2018).
- Kennedy, G.; Nantel, G.; Shetty, P. Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations Globalization of food systems in developing countries: Impact on food security and nutrition. FAO Food Nutr. Pap. 2004, 83, 1–300. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Popkin, B.M. The nutrition transition: An overview of world patterns of change. Nutr. Rev. 2004, 62, S140–S143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popkin, B.M.; Lu, B.; Zhai, F. Understanding the nutrition transition: Measuring rapid dietary changes in transitional countries. Public Health Nutr. 2002, 5, 947–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayon-Orea, C.; Martinez-Gonzalez, M.A.; Bes-Rastrollo, M. Alcohol consumption and body weight: A systematic review. Nutr. Rev. 2011, 69, 419–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traversy, G.; Chaput, J.P. Alcohol Consumption and Obesity: An Update. Curr. Obes. Rep. 2015, 4, 122–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, K.; Hargreaves, M.K.; Liu, J.; Schlundt, D.; Sanderson, M.; Matthews, C.E.; Dewey, C.M.; Kenerson, D.; Buchowski, M.S.; Blot, W.J. Relationship Between Smoking and Obesity Among Women. Am. J. Health Behav. 2011, 35, 627–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuovinen, E.L.; Saarni, S.E.; Männistö, S.; Borodulin, K.; Patja, K.; Kinnunen, T.H.; Kaprio, J.; Korhonen, T. Smoking status and abdominal obesity among normal- and overweight/obese adults: Population-based FINRISK study. Prev. Med. Rep. 2016, 4, 324–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Variables | 2005/2006 | 2010/2011 | 2015 |
|---|---|---|---|
| (n = 8158) | (n = 8448) | (n = 9066) | |
| N (%)/Percentile | N (%)/Percentile | N (%)/Percentile | |
| Body Mass Index (BMI) kg/m2 (Mean (± SD)) | 23.17 (5.20) | 26.89 (16.01) | 24.56 (5.53) |
| 5th percentile | 17.77 | 18.09 | 18.24 |
| 10th percentile | 18.66 | 18.91 | 19.21 |
| 75th percentile | 24.99 | 26.47 | 27.02 |
| 95th percentile | 31.22 | 40.17 | 34.49 |
| Age (Mean (± SD)) | 27.86 (9.54) | 28.32 (9.49) | 28.62 (9.39) |
| 15–19 | 1959 (24.10) | 1867 (22.10) | 1994 (21.99) |
| 20–24 | 1718 (21.06) | 1604 (18.99) | 1571 (17.33) |
| 25–29 | 1290 (15.81) | 1501 (17.77) | 1482 (16.35) |
| 30–34 | 1108 (13.58) | 1180 (13.97) | 1423 (15.70) |
| 35–39 | 793 (9.72) | 955 (11.30) | 1114 (12.29) |
| 40+ | 1290 (15.81) | 1341 (15.87) | 1482 (16.35) |
| Marital Status | |||
| Never married | 2369 (29.04) | 2292 (27.13) | 2540 (28.02) |
| Currently married | 4380 (53.69) | 4694 (55.56) | 5047 (55.67) |
| Living together | 120 (1.47) | 226 (2.68) | 268 (2.96) |
| Widowed | 636 (7.80) | 575 (6.81) | 409 (4.51) |
| Divorced/separated | 653 (8.00) | 661 (7.82) | 802 (8.85) |
| Parity | |||
| <2 | 3812 (46.73) | 3797 (44.95) | 3914 (43.17) |
| 2–3 | 2376 (29.12) | 2787 (32.99) | 3173 (35.00) |
| 4–5 | 1165 (14.28) | 1270 (15.03) | 1487 (16.40) |
| 6+ | 805 (9.87) | 594 (7.03) | 492 (5.43) |
| Place of residence | |||
| Urban | 2966 (36.36) | 3208 (37.97) | 4079 (44.99) |
| Rural | 5192 (63.64) | 5240 (62.03) | 4987 (55.01) |
| Educational Level | |||
| No education | 364 (4.46) | 212 (2.51) | 92 (1.01) |
| Primary | 2703 (33.13) | 2412 (28.55) | 2179 (24.03) |
| Secondary and higher | 5091 (62.41) | 5824 (68.94) | 6795 (74.95) |
| Employment Status | |||
| Not currently employed | 5142 (63.03) | 5439 (64.38) | 5317 (58.65) |
| Currently employed | 3016 (36.97) | 3009 (35.62) | 3749 (41.35) |
| Wealth (Index) | |||
| Poorest | 1472 (18.04) | 1550 (18.35) | 1359 (14.99) |
| Poorer | 1458 (17.87) | 1426 (16.88) | 1327 (14.64) |
| Middle | 3216 (39.42) | 3361 (39.78) | 3750 (41.36) |
| Richer | 2012 (24.66) | 2111 (24.99) | 2630 (29.01) |
| Region | |||
| Manicaland | 955 (11.71) | 921 (10.90) | 925 (10.20) |
| Mashonaland Central | 680 (8.34) | 824 (10.00) | 891 (9.83) |
| Mashonaland East | 638 (7.82) | 783 (9.27) | 825 (9.10) |
| Mashonaland West | 707 (8.67) | 889 (10.52) | 964 (10.63) |
| Matebeleland North | 632 (7.75) | 714 (8.45) | 795 (8.77) |
| Matebeleland South | 586 (7.18) | 779 (9.22) | 743 (8.20) |
| Midlands | 1021 (12.52) | 901 (10.67) | 967 (10.67) |
| Masvingo | 875 (10.73) | 723 (8.56) | 959 (10.58) |
| Harare | 1268 (15.54) | 1108 (13.12) | 1109 (12.23) |
| Bulawayo | 796 (9.76) | 806 (9.54) | 888 (9.79) |
| Currently Smoking | |||
| Yes | 77 (0.94) | 52 (0.62) | 49 (0.54) |
| No | 8081 (99.06) | 8396 (99.38) | 9017 (99.46) |
| Currently Drinking | |||
| Yes | - | 338 (3.73) | |
| No | - | 8728 (96.27) |
| Variables | 2005/2006 (n = 8158) | 2010/2011 (n = 8448) | 2015 (n = 9066) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Overweight and Obese (%) | Overweight and Obese (%) | Overweight and Obese (%) | |
| Age | |||
| 15–19 | 11.5 | 15.5 | 13.7 |
| 20–24 | 18.2 | 22.9 | 25.5 |
| 25–29 | 25.7 | 34.9 | 37.5 |
| 30–34 | 31.9 | 41.1 | 47.5 |
| 35–39 | 37.7 | 44.3 | 52.3 |
| 40+ | 39.7 | 52.2 | 52.3 |
| Marital Status | |||
| Never married | 15.4 | 20.2 | 19.3 |
| Currently married | 28.8 | 37.9 | 44.3 |
| Living together | 35.0 | 32.3 | 44.3 |
| Widowed | 32.9 | 41.4 | 46.0 |
| Divorced/separated | 24.7 | 35.7 | 40.3 |
| Parity | |||
| <2 | 17.34 | 23.70 | 23.94 |
| 2–3 | 29.63 | 38.39 | 45.89 |
| 4–5 | 34.76 | 43.78 | 46.20 |
| 6+ | 33.29 | 44.11 | 47.76 |
| Place of residence | |||
| Urban | 35.5 | 44.5 | 46.5 |
| Rural | 18.9 | 26.0 | 28.4 |
| Educational Level | |||
| No education | 26.9 | 36.3 | 32.6 |
| Primary | 21.9 | 30.3 | 29.7 |
| Secondary and higher | 26.4 | 34.0 | 29.7 |
| Employment Status | |||
| Not currently employed | 21.6 | 28.6 | 29.3 |
| Currently employed | 30.6 | 41.0 | 46.9 |
| Wealth (Index) | |||
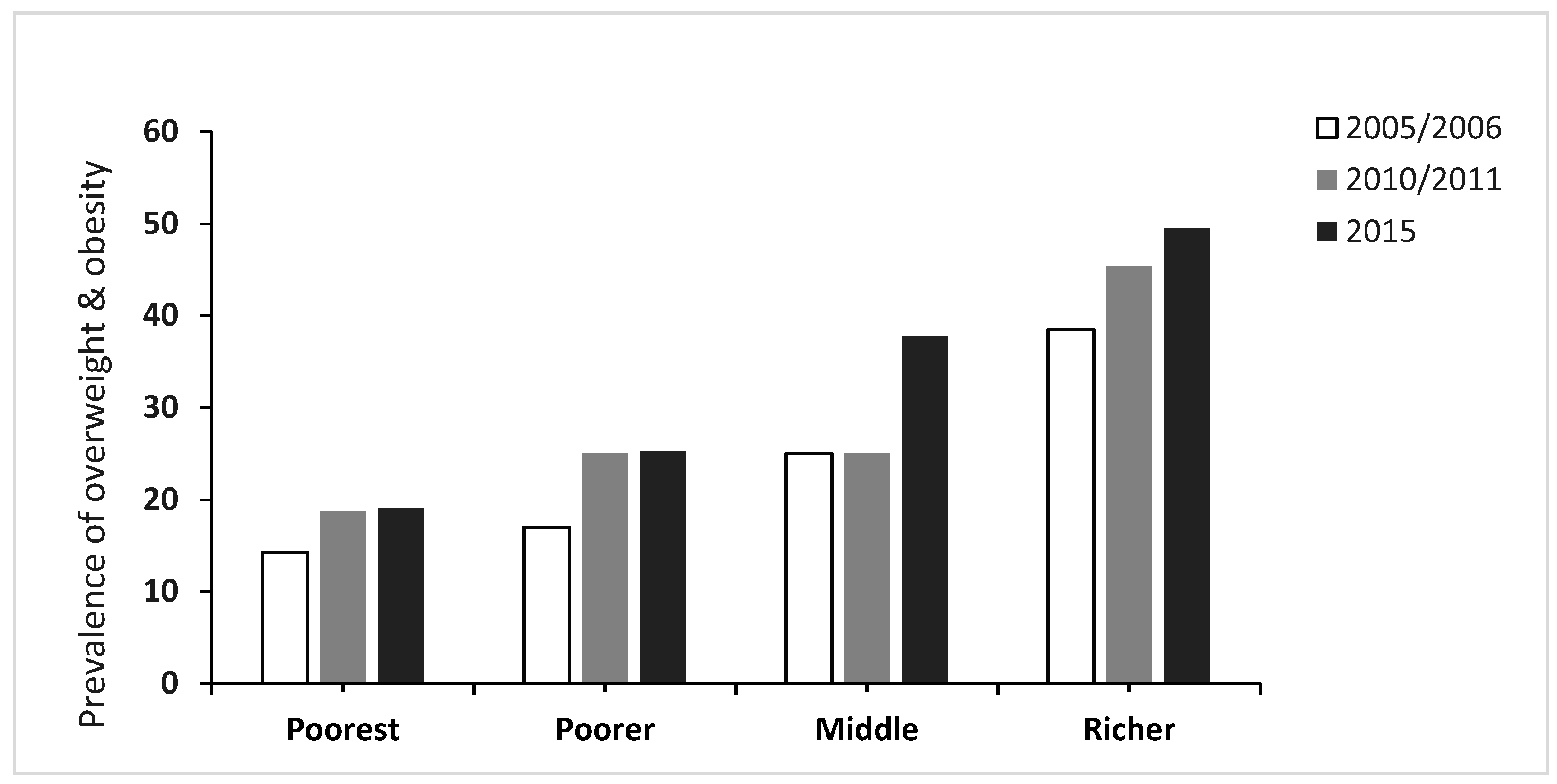
| Poorest | 14.3 | 18.7 | 19.1 |
| Poorer | 17.0 | 25.0 | 25.2 |
| Middle | 25.0 | 25.0 | 37.8 |
| Richer | 38.5 | 45.4 | 49.5 |
| Region | |||
| Manicaland | 26.9 | 34.3 | 35.8 |
| Mashonaland Central | 14.7 | 26.0 | 33.3 |
| Mashonaland East | 22.1 | 28.2 | 33.3 |
| Mashonaland West | 20.5 | 29.6 | 33.2 |
| Matebeleland North | 16.1 | 24.7 | 30.2 |
| Matebeleland South | 24.6 | 26.3 | 31.8 |
| Midlands | 21.3 | 32.5 | 34.2 |
| Masvingo | 20.9 | 31.0 | 35.1 |
| Harare | 36.2 | 47.0 | 47.7 |
| Bulawayo | 36.2 | 44.0 | 45.2 |
| Currently Smoking | |||
| Yes | 22.1 | 34.6 | 51.0 |
| No | 25.0 | 33.0 | 36.5 |
| Currently Drinking | |||
| Yes | - | - | 55.3 |
| No | - | - | 35.8 |
| Total | 25.0 a | 33.0 a | 36.6 a |
| Variables | 2005/2006 | 2010/2011 | 2015 |
|---|---|---|---|
| aOR (95% CI) | aOR (95% CI) | aOR (95% CI) | |
| Age | |||
| 15–19 (ref) | |||
| 20–24 | 1.38 (1.12–1.71) *** | 1.27 (1.04–1.54) ** | 1.47 (1.21–1.78) *** |
| 25–29 | 2.06 (1.61–2.63) *** | 2.19 (1.77–2.70) *** | 2.24 (1.81–2.77) *** |
| 30–34 | 2.72 (2.09–3.54) *** | 2.71 (2.15–3.41) *** | 3.21 (2.56–4.02) *** |
| 35–39 | 3.40 (2.57–4.51) *** | 3.23 (2.54–4.13) *** | 3.98 (3.13–5.06) *** |
| 40+ | 4.37 (3.28–5.83) *** | 4.70 (3.66–6.02) *** | 4.73 (3.73–6.01) *** |
| Marital Status | |||
| Never married (ref) | |||
| Currently married | 1.32 (1.08–1.61) *** | 1.44(1.21–1.71) *** | 1.72 (1.45–2.05) *** |
| Living together | 1.63 (1.05–2.53) ** | 1.14 (0.81–1.60) | 1.11 (0.81–1.53) |
| Widowed | 1.05 (0.80–1.37) | 1.02 (0.79–1.32) | 1.24 (0.94–1.63) * |
| Divorced/separated | 0.97 (0.75–1.26) | 1.24 (0.98–1.56) | 1.29 (1.04–1.60) ** |
| Parity | |||
| <2 (ref) | |||
| 2–3 | 1.21 (1.01–1.44) ** | 1.16 (1.01–1.35) * | 1.26 (1.09–1.47) ** |
| 4–5 | 1.37 (1.10–1.71) *** | 1.37 (1.14–1.68) *** | 1.21 (1.00–1.46) ** |
| 6+ | 1.34 (1.03–1.74) ** | 1.38 (1.14–1.68) ** | 1.53 (1.18–1.98) *** |
| Place of residence | |||
| Urban (ref) | |||
| Rural | 0.72 (0.58–0.88) ** | 0.63 (0.53–0.74) *** | 0.78 (0.68–0.90) *** |
| Educational Level | |||
| No education (ref) | |||
| Primary | 0.97 (0.74–1.27) | 1.02 (0.74–1.39) | 1.16 (0.72–1.87) |
| Secondary and higher | 1.16 (0.86–1.54) | 1.12 (0.82–1.54) | 1.39 (0.86–2.24) |
| Employment Status | |||
| Not currently employed (ref) | |||
| Currently employed | 1.27 (1.13–1.42) *** | 1.09 (0.98–1.22) | 1.19 (1.07–1.32) *** |
| Wealth (Index) | |||
| Poorest (ref) | |||
| Poorer | 1.25 (1.01–1.54) * | 1.57 (1.30–1.90) *** | 1.47 (1.20–1.78) *** |
| Middle | 1.80 (1.48–2.19) *** | 2.19 (1.84–2.61) *** | 2.40 (2.01–2.87) *** |
| Richer | 3.11 (2.40–4.01) *** | 3.06 (2.47–3.78) *** | 3.61 (2.89–4.51) *** |
| Region | |||
| Manicaland (ref) | |||
| Mashonaland Central | 0.49 (0.37–0.64) *** | 0.67 (0.54–0.84) *** | 0.93 (0.75–1.15) |
| Mashonaland East | 0.69 (0.53–0.88) ** | 0.72 (0.58–0.90) ** | 0.86 (0.70–1.07) |
| Mashonaland West | 0.61 (0.48–0.79) *** | 0.75 (0.60–0.92) ** | 0.81 (0.66–1.01) * |
| Matebeleland North | 0.69(0.51–0.91) ** | 0.84 (0.66–1.08) | 0.94 (0.75–1.17) |
| Matebeleland South | 0.97 (0.75–1.25) | 0.82 (0.65–1.03) | 0.86 (0.69–1.08) |
| Midlands | 0.64 (0.51–0.81) *** | 0.93 (0.75–1.15) | 0.91 (0.74–1.13) |
| Masvingo | 0.87 (0.69–1.09) | 1.01 (0.81–1.27) | 0.99 (0.80–1.22) |
| Harare | 0.86 (0.68–1.10) | 1.01(0.80–1.25) | 1.14 (0.93–1.39) |
| Bulawayo | 0.85 (0.65–1.10) | 0.96 (0.76–1.21) | 0.98 (0.78–1.21) |
| Currently Smoking | |||
| Yes (ref) | |||
| No | 1.69 (0.94–3.01) | 1.45 (0.78–2.68) | 0.83 (0.44–1.53) |
| Currently Drinking | |||
| Yes (ref) | - | - | |
| No | - | - | 0.48 (0.38–0.62) *** |
| Observations | 8158 | 8448 | 9066 |
| Pseudo R2 | 0.1129 | 0.1160 | 0.1422 |
| Log Likelihood | −4086.2314 | −4736.0011 | −5106.2441 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mukora-Mutseyekwa, F.; Zeeb, H.; Nengomasha, L.; Kofi Adjei, N. Trends in Prevalence and Related Risk Factors of Overweight and Obesity among Women of Reproductive Age in Zimbabwe, 2005–2015. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 2758. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16152758
Mukora-Mutseyekwa F, Zeeb H, Nengomasha L, Kofi Adjei N. Trends in Prevalence and Related Risk Factors of Overweight and Obesity among Women of Reproductive Age in Zimbabwe, 2005–2015. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2019; 16(15):2758. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16152758
Chicago/Turabian StyleMukora-Mutseyekwa, Fadzai, Hajo Zeeb, Lydia Nengomasha, and Nicholas Kofi Adjei. 2019. "Trends in Prevalence and Related Risk Factors of Overweight and Obesity among Women of Reproductive Age in Zimbabwe, 2005–2015" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 16, no. 15: 2758. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16152758
APA StyleMukora-Mutseyekwa, F., Zeeb, H., Nengomasha, L., & Kofi Adjei, N. (2019). Trends in Prevalence and Related Risk Factors of Overweight and Obesity among Women of Reproductive Age in Zimbabwe, 2005–2015. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 16(15), 2758. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16152758





