Memory Function, Neurological, and Immunological Biomarkers in Allergic Asthmatic Mice Intratracheally Exposed to Bisphenol A
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Novel Object Recognition Test
2.4. Quantification of mRNA Expression Levels
2.5. Immunohistochemical Analyses
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Body Weight and Brain Weight
3.2. Effect of Bisphenol A (BPA) Exposure on Novel Object Recognition Test
3.3. Effect of BPA Exposure on the mRNA Expressions of N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) Receptor Subunits in the Hippocampus
3.4. Effect of BPA Exposure on the mRNA Expressions of Inflammatory Cytokines in the Hypothalamus
3.5. Effect of BPA Exposure on the mRNA Expressions of Inflammatory and Microglia Markers in the Hypothalamus
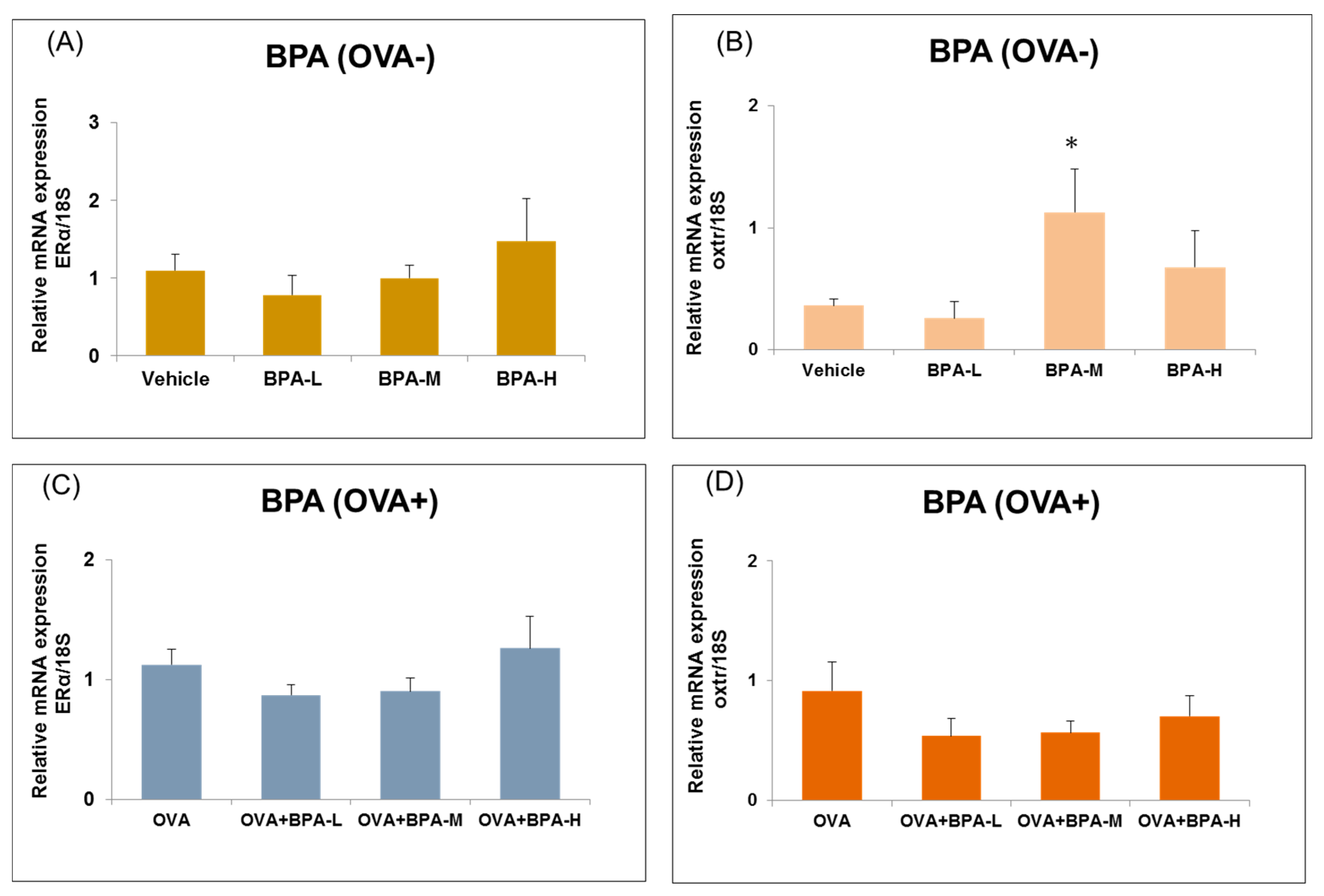
3.6. Effect of BPA Exposure on the mRNA Expressions of Estrogen Receptor and Oxytocin Receptor in the Hypothalamus
3.7. Immunohistochemical Analyses
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ABI | Applied Biosystems |
| BPA | Bisphenol A |
| CNS | central nervous system |
| COX2 | cyclooxygenase-2 |
| DEHP | di-(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate |
| DI | discrimination index |
| ER | estrogen receptor |
| HPA | hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal |
| Iba1 | ionized calcium binding adapter molecule 1 |
| IL | interleukin |
| NGF | nerve growth factor |
| NMDA | N-methyl-D-aspartate |
| OVA | ovalbumin |
| oxtr | oxytocin receptor |
| PBS | phosphate buffered saline |
| RT-PCR | reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction |
| S.E. | standard error |
| TNF | tumor necrosis factor |
| TrkA | tropomyosin receptor kinase A |
References
- Negishi, T.; Kawasaki, K.; Takatori, A.; Ishii, Y.; Kyuwa, S.; Kuroda, Y.; Yoshikawa, Y. Effects of perinatal exposure to bisphenol A on the behavior of offspring in F344 rats. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2003, 14, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohoni, P.; Sumpter, J.P. Several environmental oestrogens are also anti-androgens. J. Endocrinol. 1998, 158, 327–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kwak, E.S.; Just, A.; Whyatt, R.; Miller, R.L. Phthalates, Pesticides, and Bisphenol-A Exposure and the Development of Nonoccupational Asthma and Allergies: How Valid Are the Links? Open Allergy J. 2009, 2, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bauer, S.M.; Roy, A.; Emo, J.; Chapman, T.J.; Georas, S.N.; Lawrence, B.P. The effects of maternal exposure to bisphenol A on allergic lung inflammation into adulthood. Toxicol. Sci. 2012, 130, 82–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patisaul, H.B.; Bateman, H.L. Neonatal exposure to endocrine active compounds or an ER beta agonist increases adult anxiety and aggression in gonadally intact male rats. Horm. Behav. 2008, 53, 580–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patisaul, H.B.; Fortino, A.E.; Polston, E.K. Neonatal genistein or bisphenol-A exposure alters sexual differentiation of the AVPV. Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 2006, 28, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubin, B.S.; Lenkowski, J.R.; Schaeberle, C.M.; Vandenberg, L.N.; Ronsheim, P.M.; Soto, A.M. Evidence of altered brain sexual differentiation in mice exposed perinatally to low, environmentally relevant levels of bisphenol A. Endocrinology 2006, 147, 3681–3691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bornehag, C.G.; Sundell, J.; Weschler, C.J.; Sigsgaard, T.; Lundgren, B.; Hasselgren, M.; Hägerhed-Engman, L. The association between Asthma and allergic symptoms in children and phthalates in house dust: A nested case-control study. Environ. Health Perspect. 2004, 112, 1393–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaakkola, J.J.; Oie, L.; Nafstad, P.; Botten, G.; Samuelsen, S.O.; Magnus, P. Interior surface materials in the home and the development of bronchial obstruction in young children in Oslo, Norway. Am. J. Public Health 1999, 89, 188–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaakkola, J.J.; Ieromnimon, A.; Jaakkola, M.S. Interior surface materials and Asthma in adults: A population-based incident case-control study. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2006, 164, 742–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Win-Shwe, T.T.; Yamamoto, S.; Nakajima, D.; Furuyama, A.; Fukushima, A.; Ahmed, S.; Goto, S.; Fujimaki, H. Modulation of neurological related allergic reaction in mice exposed to low-level. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2007, 222, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujimaki, H.; Win-Shwe, T.T.; Yamamoto, S.; Nakajima, D.; Goto, S. The expression of nerve growth factor in mice lung following low-level toluene exposure. Toxicol. Lett. 2009, 191, 240–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Migliarini, B.; Piccinetti, C.C.; Martella, A.; Maradonna, F.; Gioacchini, G.; Carnevali, O. Perspectives on endocrine disruptor effects on metabolic sensors. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2011, 170, 416–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leonard, B.E.; Schwarz, M.; Myint, A.M. The metabolic syndrome in schizophrenia: Is inflammation a contributing cause? J. Psychopharmacol. 2012, 26, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dietert, R.R.; Dietert, J.M. Potential for early-life immune insult including developmental immunotoxicity in autism and autism spectrum disorders: Focus on critical windows of immune vulnerability. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health B Crit. Rev. 2008, 11, 660–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hertz-Picciotto, I.; Park, H.Y.; Dostal, M.; Kocan, A.; Trnovec, T.; Sram, R. Prenatal exposures to persistent and non-persistent organic compounds and effects on immune system development. Basic Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2008, 102, 146–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, T.C.; Lee, C.T.; Lai, T.J.; Lee, C.T.; Lee, K.Y.; Chen, V.C.; Stewart, R. Association of Asthma and bipolar disorder: A nationwide population-based study in Taiwan. J. Affect. Disord. 2014, 168, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.K.; Wang, H.Y.; Chen, Y.W.; Lin, P.Y.; Wu, C.K.; Tseng, P.T. Significantly higher prevalence rate of Asthma and bipolar disorder co-morbidity: A meta-analysis and review under PRISMA guidelines. Medicine 2016, 95, e3217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.; Wang, L.; Tang, S.; Yuan, L.; Wu, S.; Du, X.; Xiang, Y.; Qu, X.; Liu, H.; Luo, H.; et al. ITGB4 deficiency in bronchial epithelial cells directs airway inflammation and bipolar disorder-related behavior. J. Neuroinflamm. 2018, 15, 246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koike, E.; Yanagisawa, R.; Win-Shwe, T.T.; Takano, H. Exposure to low-dose bisphenol A during the juvenile period of development disrupts the immune system and aggravates allergic airway inflammation in mice. Int. J. Immunopathol. Pharmacol. 2018, 32, 2058738418774897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inagaki, T.; Frankfurt, M.; Luine, V. Estrogen-induced memory enhancements are blocked by acute bisphenol A in adult female rats: Role of dendritic spines. Endocrinology 2012, 153, 3357–3367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gada, E.; Khan, D.A.; DeFina, L.F.; Brown, E.S. The relationship between Asthma and self-reported anxiety in a predominantly healthy adult population. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2014, 112, 329–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodwin, R.D.; Scheckne, R.B.; Pena, L.; Feldman, J.M.; Taha, F.; Lipsitz, J.D. A 10-year prospective study of respiratory disease and depression and anxiety in adulthood. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2014, 113, 565–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trojan, T.D.; Khan, D.A.; Defina, L.F.; Akpotaire, O.; Goodwin, R.D.; Brown, E.S. Asthma and depression: The Cooper Center Longitudinal Study. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2014, 112, 432–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caldera-Alvarado, G.; Khan, D.A.; Defina, L.F.; Pieper, A.; Brown, E.S. Relationship between Asthma and cognition: The Cooper Center Longitudinal Study. Allergy 2013, 68, 545–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, J.; Wolansky, L.J.; Khatry, D.; Geba, G.P.; Molfino, N.A. Brain magnetic resonance imaging in adults with Asthma. Contemp. Clin. Trials 2011, 32, 86–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlson, S.M.; Kim, J.; Khan, D.A.; King, K.; Lucarelli, R.T.; McColl, R.; Peshock, R.; Brown, E.S. Hippocampal volume in patients with Asthma: Results from the Dallas Heart Study. J. Asthma 2017, 54, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, D.R.; O’Connor, J.C.; Hartman, M.E.; Tapping, R.I.; Freund, G.G. Acute hypoxia activates the neuroimmune system, which diabetes exacerbates. J. Neurosci. 2007, 27, 1161–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klausen, T.; Olsen, N.V.; Poulsen, T.D.; Richalet, J.P.; Pedersen, B.K. Hypoxemia increases serum interleukin-6 in humans. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. Occup. Physiol. 1997, 76, 480–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montplaisir, J.; Bédard, M.A.; Richer, F.; Rouleau, I. Neurobehavioral manifestations in obstructive sleep apnea syndrome before and after treatment with continuous positive airway pressure. Sleep 1992, 15, S17–S19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cory-Slechta, D.A.; Merchant-Borna, K.; Allen, J.L.; Liu, S.; Weston, D.; Conrad, K. Variations in the nature of behavioral experience can differentially alter the consequences of developmental exposures to lead, prenatal stress, and the combination. Toxicol. Sci. 2013, 131, 194–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cory-Slechta, D.A.; O’Mara, D.J.; Brockel, B.J. Nucleus accumbens dopaminergic medication of fixed interval schedule-controlled behavior and its modulation by low-level lead exposure. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1998, 286, 794–805. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rossi-George, A.; Virgolini, M.B.; Weston, D.; Thiruchelvam, M.; Cory-Slechta, D.A. Interactions of lifetime lead exposure and stress: Behavioral, neurochemical and HPA axis effects. Neurotoxicology 2011, 32, 83–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Win-Shwe, T.T.; Yanagisawa, R.; Koike, E.; Nitta, H.; Takano, H. Expression levels of neuroimmune biomarkers in hypothalamus of allergic mice after phthalate exposure. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2013, 33, 1070–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sobolewski, M.; Conrad, K.; Marvin, E.; Allen, J.L.; Cory-Slechta, D.A. Endocrine active metals, prenatal stress and enhanced neurobehavioral disruption. Horm. Behav. 2018, 101, 36–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ministry of the Environment of Japan. Environmental Risk Assessment of Chemicals vol. 3 [15] Bisphenol, A. Available online: http://www.env.go.jp/chemi/report/h16-01/index.html (accessed on 7 August 2017). (In Japanese)
- Ennaceur, A.; Delacour, J. A new one-trial test for neurobiological studies of memory in rats. 1: Behavioral data. Behav. Brain Res. 1988, 31, 47–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Win-Shwe, T.T.; Nakajima, D.; Ahmed, S.; Fujimaki, H. Impairment of novel object recognition in adulthood after neonatal exposure to diazinon. Arch. Toxicol. 2013, 87, 753–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dix, S.L.; Aggleton, J.P. Extending the spontaneous preference test of recognition: Evidence of object-location and object-context recognition. Behav. Brain Res. 1999, 99, 191–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Win-Shwe, T.T.; Fujitani, Y.; Kyi-Tha-Thu, C.; Furuyama, A.; Michikawa, T.; Tsukahara, S.; Nitta, H.; Hirano, S. Effects of diesel engine exhaust origin secondary organic aerosols on novel object recognition ability and maternal behavior in BALB/c mice. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2014, 11, 11286–11307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Win-Shwe, T.T.; Nway, N.C.; Imai, M.; Lwin, T.T.; Mar, O.; Watanabe, H. Social behavior, neuroimmune markers and glutamic acid decarboxylase levels in a rat model of valproic acid-induced autism. J. Toxicol. Sci. 2018, 43, 631–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Iwamura, E.; Yamada, K.; Ichitani, Y. Involvement of hippocampal NMDA receptors in retrieval of spontaneous object recognition memory in rats. Behav. Brain Res. 2016, 307, 92–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gouw, A.M.; Efe, G.; Barakat, R.; Preecha, A.; Mehdizadeh, M.; Garan, S.A.; Brooks, G.A. Roles of estrogen receptor-alpha in mediating life span: The hypothalamic deregulation hypothesis. Physiol. Genom. 2017, 49, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perera, F.; Vishnevetsky, J.; Herbstman, J.B.; Calafat, A.M.; Xiong, W.; Rauh, V.; Wang, S. Prenatal bisphenol A exposure and child behavior in an inner-city cohort. Environ. Health Perspect. 2012, 120, 1190–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perera, F.; Nolte, E.L.; Wang, Y.; Margolis, A.E.; Calafat, A.M.; Wang, S.; Garcia, W.; Hoepner, L.A.; Peterson, B.S.; Rauh, V.; et al. Bisphenol A exposure and symptoms of anxiety and depression among inner city children at 10–12 years of age. Environ. Res. 2016, 151, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roen, E.L.; Wang, Y.; Calafat, A.M.; Wang, S.; Margolis, A.; Herbstman, J.; Hoepner, L.A.; Rauh, V.; Perera, F.P. Bisphenol A exposure and behavioral problems among inner city children at 7–9 years of age. Environ. Res. 2015, 142, 739–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elsworth, J.D.; Jentsch, J.D.; Groman, S.M.; Roth, R.H.; Redmond, E.D., Jr.; Leranth, C. Low circulating levels of bisphenol—A induce cognitive deficits and loss of asymmetric spine synapses in dorsolateral prefrontal cortex and hippocampus of adult male monkeys. J. Comp. Neurol. 2015, 523, 1248–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aloe, L.; Alleva, E.; Fiore, M. Stress and nerve growth factor: Findings in animal models and humans. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2002, 73, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giedd, J.N.; Blumenthal, J.; Jeffries, N.O.; Castellanos, F.X.; Liu, H.; Zijdenbos, A.; Paus, T.; Evans, A.C.; Rapoport, J.L. Rapoport, Brain development during childhood and adolescence: A longitudinal MRI study. Nat. Neurosci. 1999, 2, 861–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barker, G.R.; Warburto, E.C. When Is the Hippocampus Involved in Recognition Memory? J. Neurosci. 2011, 31, 10721–10731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Blair, J.A.; McGee, H.; Bhatta, S.; Palm, R.; Casadesus, G. Hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal axis involvement in learning and memory and Alzheimer’s disease: More than “just” estrogen. Front. Endocrinol. 2015, 6, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, G.; Yan, J.; Zhang, Y.; Li, B.; Cai, D. Metabolic learning and memory formation by the brain influence systemic metabolic homeostasis. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 6704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franzen, R.; Bouhy, D.; Schoenen, J. Nervous system injury: Focus on the inflammatory cytokine ’granulocyte-macrophage colony stimulating factor. Neurosci. Lett. 2004, 361, 76–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cacquevel, M.; Lebeurrier, N.; Chéenne, S.; Vivien, D. Cytokines in neuroinflammation and Alzheimer’s disease. Curr. Drug Targets 2004, 5, 529–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Win-Shwe, T.T.; Yamamoto, S.; Ahmed, S.; Kakeyama, M.; Kobayashi, T.; Fujimaki, H. Brain cytokine and chemokine mRNA expression in mice induced by intranasal instillation with ultrafine carbon black. Toxicol. Lett. 2006, 163, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Win-Shwe, T.T.; Mitsushima, D.; Yamamoto, S.; Fukushima, A.; Funabashi, T.; Kobayashi, T.; Fujimaki, H. Changes in neurotransmitter levels and proinflammatory cytokine mRNA expressions in the mice olfactory bulb following nanoparticle exposure. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2008, 226, 192–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Win-Shwe, T.T.; Yamamoto, S.; Fujitani, Y.; Hirano, S.; Fujimaki, H. Spatial learning and memory function-related gene expression in the hippocampus of mouse exposed to nanoparticle-rich diesel exhaust. Neurotoxicology 2008, 29, 940–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Win-Shwe, T.T.; Tsukahara, S.; Yamamoto, S.; Fukushima, A.; Kunugita, N.; Arashidani, K.; Fujimaki, H. Up-regulation of neurotrophin-related gene expression in mouse hippocampus following low-level toluene exposure. Neurotoxicology 2010, 31, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Win-Shwe, T.T.; Fujimaki, H.; Fujitani, Y.; Hirano, S. Novel object recognition ability in female mice following exposure to nanoparticle-rich diesel exhaust. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2012, 262, 355–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, R.; Hou, G.; Li, D.; Yuan, T.F. A possible change process of inflammatory cytokines in the prolonged chronic stress and its ultimate implications for health. Sci. World J. 2014, 2014, 780616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giulian, D. Microglia and disease of the nervous system. Curr. Top. Neurol. 1992, 12, 23–54. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, J.; Patisaul, H.B. Sexually dimorphic expression of hypothalamic estrogen receptors alpha and beta and Kiss1 in neonatal male and female rats. J. Comp. Neurol. 2011, 519, 2954–2977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furuta, M.; Numakawa, T.; Chiba, S.; Ninomiya, M.; Kajiyama, Y.; Adachi, N.; Akema, T.; Kunugi, H. Estrogen, predominantly via estrogen receptor alpha, attenuates postpartum-induced anxiety- and depression-like behaviors in female rats. Endocrinology 2013, 154, 3807–3816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gabor, C.S.; Phan, A.; Clipperton-Allen, A.E.; Kavaliers, M.; Choleris, E. Interplay of oxytocin, vasopressin, and sex hormones in the regulation of social recognition. Behav. Neurosci. 2012, 126, 97–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donaldson, Z.R.; Young, L.J. Oxytocin, vasopressin, and the neurogenetics of sociality. Science 2008, 322, 900–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCarthy, M.M.; Altemus, M. Central nervous system actions of oxytocin and modulation of behavior in humans. Mol. Med. Today 1997, 3, 269–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolstenholme, J.T.; Edwards, M.; Shetty, S.R.; Gatewood, J.D.; Taylor, J.A. Gestational Exposure to Bisphenol A Produces Transgenerational Changes in Behaviors and Gene Expression. Endocrinology 2012, 153, 3828–3838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]







| Exposure Groups | Body Weight (g) | Brain Weight (mg) |
|---|---|---|
| Vehicle | 27.78 ± 0.59 | 450.30 ± 5.83 |
| BPA-L | 27.47 ± 1.30 | 436.77 ± 12.65 |
| BPA-M | 28.98 ± 0.57 | 426.82 ± 4.86 |
| BPA-H | 28.33 ± 0.30 | 434.38 ± 2.69 |
| OVA | 29.32 ± 0.71 | 441.55 ± 4.28 |
| OVA + BPA-L | 27.54 ± 0.79 | 450.84 ± 5.44 |
| OVA + BPA-M | 29.22 ± 0.78 | 438.76 ± 6.00 |
| OVA + BPA-H | 28.34 ± 0.48 | 440.00 ± 6.67 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Win-Shwe, T.-T.; Yanagisawa, R.; Koike, E.; Takano, H. Memory Function, Neurological, and Immunological Biomarkers in Allergic Asthmatic Mice Intratracheally Exposed to Bisphenol A. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 3770. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16193770
Win-Shwe T-T, Yanagisawa R, Koike E, Takano H. Memory Function, Neurological, and Immunological Biomarkers in Allergic Asthmatic Mice Intratracheally Exposed to Bisphenol A. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2019; 16(19):3770. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16193770
Chicago/Turabian StyleWin-Shwe, Tin-Tin, Rie Yanagisawa, Eiko Koike, and Hirohisa Takano. 2019. "Memory Function, Neurological, and Immunological Biomarkers in Allergic Asthmatic Mice Intratracheally Exposed to Bisphenol A" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 16, no. 19: 3770. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16193770
APA StyleWin-Shwe, T.-T., Yanagisawa, R., Koike, E., & Takano, H. (2019). Memory Function, Neurological, and Immunological Biomarkers in Allergic Asthmatic Mice Intratracheally Exposed to Bisphenol A. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 16(19), 3770. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16193770





