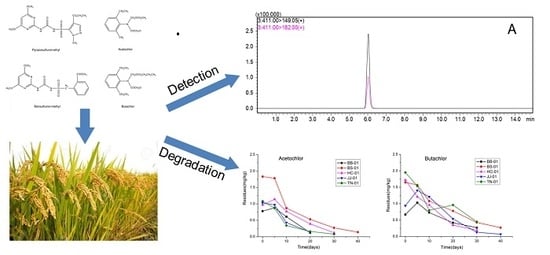
Dissipation Dynamics and Residue of Four Herbicides in Paddy Fields Using HPLC-MS/MS and GC-MS
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Equipment
2.2. Field Experiment Design
2.3. Analytical Procedure
2.3.1. Sample Preparation
2.3.2. HPLC-MS/MS Analysis
2.3.3. GC-MS Analysis
2.3.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Method Validation
3.2. Dissipation of Four Herbicides in a Rice Field Ecosystem
3.3. Final Residue of Four Herbicides
4. Discussion
4.1. Optimization of HPLC-MS/MS Method
4.2. Optimization of GC-MS Method
4.3. Four Herbicides’ Dissipation and Final Residue
4.4. Dietary Risk Assessment
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rao, G.S.; Deveshwar, P.; Sharma, M.; Kapoor, S.; Rao, K.V. Evolvement of transgenic male-sterility and fertility-restoration system in rice for production of hybrid varieties. Plant Mol. Biol. 2018, 96, 35–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Xu, P.; Li, J.; Wang, H. Dissipation and residue of pymetrozine in rice field ecosystem. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2015, 187, 78–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Shen, Y.; Yu, X.Y.; Liu, X.J. Dissipation of chlorpyrifos and residue analysis in rice, soil and water under paddy field conditions. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2012, 78, 276–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, F.; Wang, L.; Zhou, L.; Pan, C. Dissipation and residues of monosultap in rice plant and environment. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2012, 88, 362–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Fan, S.; Bai, A.; Li, X.; Pan, C. Dissipation and residues of bispyribac-sodium in rice and environment. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2013, 185, 9743–9749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosoya, K.; Sugiyama, S. Weed communities and their negative impact on rice yield in no-input paddy fields in the northern part of Japan. Biol. Agric. Hortic. 2017, 33, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Feng, Y.; Li, X.; Zeng, D. Analytical Confirmation of Various Herbicides in Drinking Water Resources in Sugarcane Production Regions of Guangxi, China. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2018, 100, 815–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Lu, A.; Wang, J.; Li, J.; Ping, H.; Luan, Y.; Chen, J.; Ha, X. Determination of five sulfonylurea herbicides in environmental waters and soil by ultra high performance liquid chromatography with tandem mass spectrometry after extraction using graphene. J. Sep. Sci. 2014, 37, 3714–3721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokley, R.A.; Mayer, L.C.; Huang, S.B.; Vargo, J.D. Analytical method for the determination of metolachlor, acetochlor, alachlor, dimethenamid, and their corresponding ethanesulfonic and oxanillic acid degradates in water using SPE and LC/ESI-MS/MS. Anal. Chem. 2002, 74, 3754–3759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.B.; Sharma, R.; Singh, N. Persistence of pyrazosulfuron in rice-field and laboratory soil under Indian tropical conditions. Pest Manag. Sci. 2012, 68, 828–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ok, J.; Doan, N.H.; Watanabe, H.; Thuyet, D.Q.; Boulange, J. Behavior of butachlor and pyrazosulfuron-ethyl in paddy water using micro paddy lysimeters under different temperature conditions in spring and summer. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2012, 89, 306–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, N.; Singh, S.B. Translocation and degradation of pyrazosulfuron-ethyl in rice soil. Pest Manag. Sci. 2011, 67, 1451–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cara, I.G.; Lipsa, F.D.; Cara, M.S.; Burtan, L.; Topa, D.; Jitareanu, G. Dissipation of Acetochlor and Residue Analysis in Maize and Soil under Field Conditions. Agrolife Sci. J. 2017, 6, 48–55. [Google Scholar]
- Rao, P.C.; Lakshmi, C.S.R.; Madhavi, M.; Swapna, G.; Sireesha, A. Butachlor dissipation in rice grown soil and its residues in grain. Indian J. Weed Sci. 2012, 44, 84–87. [Google Scholar]
- Chopra, N.K. Effect of doses and stages of application of pyrazosulfuron ethyl on weeds in transplanted rice. Indian J. Weed Sci. 2003, 35, 27–29. [Google Scholar]
- Akira, O.; Jong, Y.P.; Kozo, I.; Hiroshi, M. Selective mode of action of bensulfuron methyl among rice cultivates. J. Weed Sci. Technol. 1991, 36, 27–35. [Google Scholar]
- Rajkhowa, D.J.; Gogol, A.K.; Kandali, R.; Borua, I.C. Effect of dose and stage of application of acetochlor in transplanted rice. Indian J. Weed Sci. 2004, 36, 60–63. [Google Scholar]
- Narwal, S.; Singh, S.; Malik, R.K.; Panwar, K.S. Effect of acetochlorand ready mix of anilofos ethoxysulfuron on divergent weed flora in transplanted rice. Indian J. Weed Sci. 2002, 34, 28–31. [Google Scholar]
- Tomlin, C. The Pesticide Manual, 15th ed.; British Crop Production Council: Hampshire, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Janaki, P.; Nithya, C.; Kalaiyarasi, D.; Sakthivel, N.; Nk, P.; Chinnusamy, C. Residue of bensulfuron methyl in soil and rice following its pre- and post-emergence application. Plant Soil Environ. 2016, 62, 428–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kaur, P.; Randhawa, S.K.; Duhan, A.; Bhullar, M.S. Influence of Long Term Application of Butachlor on its Dissipation and Harvest Residues in Soil and Rice. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2017, 98, 874–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, T.S.; Moon, B.C.; Cho, J.R. An Overview of Resistant Weeds to Sulfonylurea Herbicides in Rice Field, Korea. Korean J. Weed Sci. 2005, 25, 67–74. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, I.Y.; Won, T.J.; Seo, Y.H.; Kim, E.J.; Yun, Y.T.; Cho, S.H.; Kwon, O.D.; Kim, S.K.; Chung, W.G.; Park, T.S.; et al. Occurrence Trends of SU-Herbicide Resistant Weeds in Paddy Fields in Korea. Weed Turfgrass Sci. 2013, 2, 318–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, Y.; Tominaga, T.; Ohsako, T. Microsatellite variability of sulfonylurea-resistant and susceptible populations of Schoenoplectus juncoides (Cyperaceae) in Kinki, Japan. Weed Res. 2013, 53, 429–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, S.Q. Herbicide-Resistant Weeds in Paddy Field and their Control. Pesticides 2001, 7, 43–48. [Google Scholar]
- Rebelo, A.M.; Dolzan, M.D.; Heller, M.; Deschamps, F.C.; Abate, G.; Micke, G.A.; Grassi, M.T. Simultaneous Determination of Herbicides in Rice by QuEChERS and LC-MS/MS Using Matrix-Matched Calibration. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2015, 27, 186–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, P.; Wang, J.J.; Liu, G.J.; Guan, J.Y. Determination of sulfonylurea herbicides in food crops by matrix solid-phase dispersion extraction coupled with high-performance liquid chromatography. Food Anal. Method 2014, 7, 1530–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, B.M.; Wolfe, N.L. Multiresidue determination of sulfonylurea herbicides by capillary electrophoresis for hydrolysis studies in water and sediments. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 1996, 356, 508–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.; Wang, G.; Gao, C.; Yan, Y.; Wen, B. Optimization of derivatization procedure and gas chromatography-mass spectrometry method for determination of bensulfuron-methyl herbicide residues in water. J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2015, 995–996, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyake, S.; Ishii, Y.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Ohde, K.; Motoki, M.; Kawata, M.; Ito, S.; Yuasa, Y.; Ohkawa, H. Simple Determination of Herbicides in Rice Paddy Water by Immunoassay. ACS Symp. Ser. 2003, 853, 124–138. [Google Scholar]
- Fenoll, J.; Hellin, P.; Sabater, P.; Flores, P.; Navarro, S. Trace analysis of sulfonylurea herbicides in water samples by solid-phase extraction and liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Talanta 2012, 101, 273–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yang, J.; Shi, R.; Su, Q.; Yao, L.; Li, P. Determination of acetanilide herbicides in cereal crops using accelerated solvent extraction, solid-phase extraction and gas chromatography-electron capture detector. J. Sep. Sci. 2011, 34, 1675–1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, R.S.; Diao, C.P.; Wang, X.; Jiang, T.; Yuan, J.P. Rapid determination of amide herbicides in environmental water samples with dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction prior to gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2008, 391, 2915–2921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rejczak, T.; Tuzimski, T. Recent Trends in Sample Preparation and Liquid Chromatography/Mass Spectrometry for Pesticide Residue Analysis in Food and Related Matrixes. J. AOAC Int. 2015, 98, 1143–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, M.F.; Chen, W.Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, D.Y.; Chen, A.; Liu, J.Y.; Luo, X.W.; Yan, Q.P. Determination of herbicide pyraclonil residue in rice, soil and water using high-performance liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry. Anal. Methods 2017, 9, 4790–4796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Institute for the Control of Agrochemicals, Ministry of Agriculture. Guidelines on Pesticide Residue Trials (NY/T 788-2004); Institute for the Control of Agrochemicals, Ministry of Agriculture: Beijing, China, 2004.
- Diao, J.; Lv, C.; Wang, X.; Dang, Z.; Zhu, W.; Zhou, Z. Influence of soil properties on the enantioselective dissipation of the herbicide lactofen in soils. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 5865–5871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diao, J.; Xu, P.; Wang, P.; Lu, Y.; Lu, D.; Zhou, Z. Environmental behavior of the chiral aryloxyphenoxypropionate herbicide diclofop-methyl and diclofop: Enantiomerization and enantioselective degradation in soil. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 2042–2047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diao, J.; Xu, P.; Wang, P.; Lu, D.; Lu, Y.; Zhou, Z. Enantioselective Degradation in Sediment and Aquatic Toxicity to Daphnia magna of the Herbicide Lactofen Enantiomers. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 2439–2445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Wang, P.; Lu, Y.; Zhou, G.; Diao, J.; Zhou, Z. Enantioselective bioaccumulation of soil-associated fipronil enantiomers in Tubifex tubifex. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 219–220, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, X.; Liang, L.; Liu, F. Dissipation and residues of clethodim and its oxidation metabolites in a rape-field ecosystem using QuEChERS and liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry. Food Chem. 2014, 143, 170–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roehrs, R.; Zanella, R.; Pizzuti, I.; Adaime, M.B.; Pareja, L.; Niell, S.; Cesio, M.V.; Heinzen, H. Liquid chromatographic-diode-array detection multiresidue determination of rice herbicides in drinking and paddy-field water. J. AOAC Int. 2009, 92, 1190–1195. [Google Scholar]
- Ayano, E.; Kanazawa, H.; Ando, M.; Nishimura, T. Determination and quantitation of sulfonylurea and urea herbicides in water samples using liquid chromatography with electrospray ionization mass spectrometric detection. Anal. Chim. Acta 2004, 507, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.B.; Li, C.; Peng, C.F.; Li, X.Q.; Xu, C.L. A Rapid Multi-Residue Determination Method of Herbicides in Grain by GC—MS-SIM. J. Chromatogr. Sci. 2008, 46, 424–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Yang, H.; Wang, L.; Han, B.; Wang, X.; Lee, S.C. Analysis of chloroacetanilide herbicides in water samples by solid-phase microextraction coupled with gas chromatography–mass spectrometry. Anal. Chim. Acta 2007, 591, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malhat, F.; Badawy, H.M.; Barakat, D.A.; Saber, A.N. Residues, dissipation and safety evaluation of chromafenozide in strawberry under open field conditions. Food Chem. 2014, 152, 18–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, S.; Hua, X.W.; Wei, W.; Gu, Y.C.; Liu, X.; Chen, J.; Chen, M.; Xie, Y.T.; Zhou, S.; Meng, X.D. Research on Controllable Degradation of Novel Sulfonylurea Herbicides in Acidic and Alkaline Soils. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 7661–7668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, S.B.; Neera, S. Degradation behaviour of pyrazosulfuron-ethyl in water as affected by pH. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part B Pestic. Food Contam. Agric. Wastes 2013, 48, 266–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, C. Environmental Behavior of the Herbicide Acetochlor in Soil. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2003, 71, 919–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, J.Y.; Zhen, Z.H.; Deng, Z.B. Simultaneous determination of acetochlor and propisochlor residues in corn and soil by solid phase extraction and gas chromatography with electron capture detection. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2011, 86, 95–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, R.S.; Koskinen, W.C.; Graff, C.D.; Anderson, J.L.; Mulla, D.J.; Nater, E.A.; Alonso, D.G. Acetochlor Persistence in Surface and Subsurface Soil Samples. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2013, 224, 1747–1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malhat, F.; Kamel, E.; Saber, A.; Hassan, E.; Youssef, A.; Almaz, M.; Hassan, A.; Fayz Ael, S. Residues and dissipation of kresoxim methyl in apple under field condition. Food Chem. 2013, 140, 371–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Sood, C.; Jaggi, S.; Ravindranath, S.D.; Bhardwaj, S.P.; Shanker, A. Dissipation behavior of propargite—An acaricide residues in soil, apple (Malus pumila) and tea (Camellia sinensis). Chemosphere 2005, 58, 837–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Food Safety Standard-Maximum Residue Limits for Pesticides in Food(GB2763-2016); Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs: Beijing, China, 2016; pp. 1–253.
- Ge, K.Y.; Jia, J.B.; Liu, H. Food-based dietary guidelines in China practices and problems. Ann. Nutr. Metab. 2007, 51, 26–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| No. | Experimental Plots | Location |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | BB-01 | 106.368, 29.747689 |
| 2 | BB-02 | 106.389278, 29.881666 |
| 3 | BS-01 | 106.11499, 29.534675 |
| 4 | BS-02 | 106.159433, 29.613598 |
| 5 | HC-01 | 106.397122, 30.125637 |
| 6 | HC-02 | 106.181094, 30.185661 |
| 7 | JJ-01 | 106.273947, 29.073062 |
| 8 | JJ-02 | 106.276326, 29.14402 |
| 9 | TN-01 | 105.809623, 30.20763 |
| 10 | TN-02 | 105.836951, 30.233446 |
| Herbicides | Retention Time (min) | Qualifying Ions (m/z) | Quantifying Ions (m/z) | Fragmentor (V) | Collision Energy (V) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pyrazosulfuron-ethyl | 7.08 | 436.9->178.1 | 436.9->178.1 | 135 | 15 |
| 436.9->281.9 | 20 | ||||
| Bensulfuron-methyl | 6.12 | 411.0->149.0 | 411.0->149.0 | 120 | 20 |
| 411.0->182.1 | 20 |
| Herbicides | Retention Time (min) | Qualifying Ions (m/z) | Quantifying Ions (m/z) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Acetochlor | 8.58 | 146.0, 162.0, 174.0 | 146.0 |
| Butachlor | 11.22 | 176.0, 160.0, 57.0 | 176.0 |
| Herbicides | Sample Matrix | Fortified Level (mg·kg−1) | Average Recovery (%) | RSD (%) | Calibration Curve | R2 | LOD (ng) | LOQ (mg·kg−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pyrazosulfuron-ethyl | Soil | 0.01 | 84.7 | 1.9 | y = 1.11E + 06x − 2358.2 | 0.9998 | 0.25 | 0.01 |
| 0.1 | 94.5 | 6.0 | ||||||
| 0.5 | 91.8 | 4.2 | ||||||
| Husked rice | 0.01 | 92.4 | 3.7 | y = 9.31E + 05x + 2447.4 | 0.9993 | 0.25 | 0.01 | |
| 0.1 | 102.8 | 1.5 | ||||||
| 0.5 | 102.1 | 2.6 | ||||||
| Rice hull | 0.01 | 106.4 | 3.7 | y = 1.00E + 06x − 3245.4 | 0.9998 | 0.10 | 0.01 | |
| 0.1 | 95.3 | 5.1 | ||||||
| 0.5 | 81.0 | 3.6 | ||||||
| Bensulfuron-methyl | Soil | 0.01 | 95.5 | 10.7 | y = 4.63E + 06x + 12105 | 0.9999 | 0.25 | 0.01 |
| 0.05 | 102.7 | 5.1 | ||||||
| 0.5 | 78.9 | 3.1 | ||||||
| Husked rice | 0.01 | 83.2 | 13.4 | y = 4.36E + 06x + 11910.5 | 0.9998 | 0.25 | 0.01 | |
| 0.05 | 90.5 | 14.9 | ||||||
| 0.5 | 80.0 | 9.8 | ||||||
| Rice hull | 0.01 | 94.2 | 4.6 | y = 5.00E + 06x + 9465.6 | 0.9999 | 0.10 | 0.01 | |
| 0.05 | 92.6 | 9.8 | ||||||
| 0.5 | 92.4 | 4.9 | ||||||
| Acetochlor | Soil | 0.1 | 96.3 | 2.5 | y =9.31E + 02x− 5.3453 | 0.9982 | 1.0 | 0.1 |
| 0.5 | 93.6 | 5.9 | ||||||
| 1 | 93.8 | 0.9 | ||||||
| Husked rice | 0.01 | 94.6 | 3.7 | y =9.75E + 02x − 6.546 | 0.9979 | 0.10 | 0.01 | |
| 0.05 | 99.5 | 1.2 | ||||||
| 0.5 | 97.6 | 3.8 | ||||||
| Rice hull | 0.01 | 87.4 | 9.7 | y =9.93E + 02x− 1.5344 | 0.9994 | 0.04 | 0.01 | |
| 0.05 | 90.8 | 5.8 | ||||||
| 0.5 | 93.7 | 7.2 | ||||||
| Butachlor | Soil | 0.1 | 108.0 | 9.2 | y =9.65E + 02x − 1.8882 | 0.9995 | 1.0 | 0.1 |
| 0.5 | 90.8 | 6.3 | ||||||
| 1 | 95.9 | 2.2 | ||||||
| Husked rice | 0.05 | 86.3 | 3.6 | y =9.09E + 02x + 7.9348 | 0.9988 | 0.50 | 0.05 | |
| 0.5 | 98.4 | 3.8 | ||||||
| 1 | 98.7 | 3.2 | ||||||
| Rice hull | 0.05 | 86.9 | 8.5 | y =9.23E + 02+ 3.8587 | 0.9992 | 0.20 | 0.05 | |
| 0.5 | 97.3 | 9.1 | ||||||
| 1 | 89.4 | 5.3 |
| Herbicides | Dosage (g a.i.ha−1) | Locality | Regression Equation | Determination Coefficient (R2) | Half-Life (Days) a |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pyrazosulfuron-ethyl | 22.5 | BB-01 | y = 0.8949e−0.126x | 0.907 | 5.5 |
| 22.5 | BB-02 | y = 0.8806e−0.129x | 0.976 | 5.4 | |
| 22.5 | BS-01 | y = 1.6411e−0.143x | 0.990 | 4.8 | |
| 22.5 | BS-02 | y = 1.1799e−0.122x | 0.921 | 5.7 | |
| 22.5 | HC-01 | y = 1.1129e−0.118x | 0.974 | 5.9 | |
| 22.5 | HC-02 | y = 1.0955e−0.124x | 0.906 | 5.6 | |
| 22.5 | JJ-01 | y = 0.8676e−0.078x | 0.759 | 8.9 | |
| 22.5 | JJ-02 | y = 1.1424e−0.109x | 0.982 | 6.4 | |
| 22.5 | TN-01 | y = 1.1852e−0.113x | 0.954 | 6.1 | |
| 22.5 | TN-02 | y = 1.0365e−0.115x | 0.968 | 6.0 | |
| Bensulfuron-methyl | 26.2 | BB-01 | y = 1.2314e−0.081x | 0.983 | 8.6 |
| 26.2 | BB-02 | y = 0.866e−0.06x | 0.841 | 11.6 | |
| 26.2 | BS-01 | y = 1.6713e−0.132x | 0.919 | 5.3 | |
| 26.2 | BS-02 | y = 1.0613e−0.1x | 0.852 | 6.9 | |
| 26.2 | HC-01 | y = 1.1017e−0.133x | 0.910 | 5.2 | |
| 26.2 | HC-02 | y = 0.8935e−0.189x | 0.995 | 3.7 | |
| 26.2 | JJ-01 | y = 0.9964e−0.059x | 0.722 | 11.7 | |
| 26.2 | JJ-02 | y = 1.1328e−0.097x | 0.931 | 7.1 | |
| 26.2 | TN-01 | y = 1.2326e−0.08x | 0.985 | 8.7 | |
| 26.2 | TN-02 | y = 0.7745e−0.135x | 0.908 | 5.1 | |
| Acetochlor | 52.5 | BB-01 | y = 0.5111e−0.082x | 0.651 | 8.5 |
| 52.5 | BB-02 | y = 0.731e−0.112x | 0.966 | 6.2 | |
| 52.5 | BS-01 | y = 1.112e−0.062x | 0.948 | 11.2 | |
| 52.5 | BS-02 | y = 0.7667e−0.073x | 0.917 | 9.5 | |
| 52.5 | HC-01 | y = 0.6889e−0.117x | 0.965 | 5.9 | |
| 52.5 | HC-02 | y = 0.7935e−0.051x | 0.867 | 13.6 | |
| 52.5 | JJ-01 | y = 0.5751e−0.091x | 0.862 | 7.6 | |
| 52.5 | JJ-02 | y = 0.7309e−0.093x | 0.984 | 7.5 | |
| 52.5 | TN-01 | y = 0.4187e−0.199x | 0.993 | 3.5 | |
| 52.5 | TN-02 | y = 0.54e−0.055x | 0.772 | 12.6 | |
| Butachlor | 112.4 | BB-01 | y = 0.6421e−0.053x | 0.766 | 13.1 |
| 112.4 | BB-02 | y = 1.1605e−0.07x | 0.953 | 9.9 | |
| 112.4 | BS-01 | y = 1.3721e−0.07x | 0.942 | 9.9 | |
| 112.4 | BS-02 | y = 1.1642e−0.061x | 0.869 | 11.4 | |
| 112.4 | HC-01 | y = 1.0269e−0.08x | 0.918 | 8.7 | |
| 112.4 | HC-02 | y = 1.5685e−0.068x | 0.951 | 10.2 | |
| 112.4 | JJ-01 | y = 0.7114e−0.141x | 0.960 | 4.9 | |
| 112.4 | JJ-02 | y = 0.997e−0.089x | 0.755 | 7.8 | |
| 112.4 | TN-01 | y = 0.6035e−0.123x | 0.455 | 5.6 | |
| 112.4 | TN-02 | y = 1.3817e−0.074x | 0.964 | 9.4 |
| Herbicides | Dosage (g a.i.ha−1) | Locality | Regression Equation | Determination Coefficient (R2) | Half-Life (Days) a |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pyrazosulfuron-ethyl | 45 | BB-01 | y = 1.4646e−0.106x | 0.915 | 6.5 |
| 45 | BB-02 | y = 1.5816e−0.132x | 0.932 | 5.3 | |
| 45 | BS-01 | y = 2.6684e−0.11x | 0.954 | 6.3 | |
| 45 | BS-02 | y = 1.515e−0.105x | 0.938 | 6.6 | |
| 45 | HC-01 | y = 1.4547e−0.089x | 0.980 | 7.8 | |
| 45 | HC-02 | y = 1.8413e−0.118x | 0.875 | 5.9 | |
| 45 | JJ-01 | y = 1.4889e−0.106x | 0.963 | 6.5 | |
| 45 | JJ-02 | y = 1.5209e−0.082x | 0.951 | 8.5 | |
| 45 | TN-01 | y = 1.4166e−0.093x | 0.990 | 7.5 | |
| 45 | TN-02 | y = 1.4806e−0.089x | 0.977 | 7.8 | |
| Bensulfuron-methyl | 52.4 | BB-01 | y = 2.2066e−0.064x | 0.774 | 10.8 |
| 52.4 | BB-02 | y = 1.217e−0.091x | 0.952 | 7.6 | |
| 52.4 | BS-01 | y = 2.6665e−0.088x | 0.983 | 7.9 | |
| 52.4 | BS-02 | y = 1.6514e−0.09x | 0.962 | 7.7 | |
| 52.4 | HC-01 | y = 1.1966e−0.078x | 0.664 | 8.9 | |
| 52.4 | HC-02 | y = 1.6466e−0.174x | 0.992 | 4.0 | |
| 52.4 | JJ-01 | y = 1.8788e−0.06x | 0.967 | 11.6 | |
| 52.4 | JJ-02 | y = 1.635e−0.079x | 0.988 | 8.8 | |
| 52.4 | TN-01 | y = 2.076e−0.096x | 0.912 | 7.2 | |
| 52.4 | TN-02 | y = 0.7745e−0.075x | 0.653 | 9.2 | |
| Acetochlor | 105 | BB-01 | y = 1.1331e−0.1x | 0.843 | 6.9 |
| 105 | BB-02 | y = 1.7331e−0.079x | 0.936 | 8.8 | |
| 105 | BS-01 | y = 1.9839e−0.066x | 0.985 | 10.5 | |
| 105 | BS-02 | y = 1.5256e−0.076x | 0.931 | 9.1 | |
| 105 | HC-01 | y = 1.3609e−0.073x | 0.918 | 9.5 | |
| 105 | HC-02 | y = 1.2829e−0.055x | 0.866 | 12.6 | |
| 105 | JJ-01 | y = 1.2586e−0.107x | 0.954 | 6.5 | |
| 105 | JJ-02 | y = 1.765e−0.121x | 0.962 | 5.7 | |
| 105 | TN-01 | y = 1.0778e−0.09x | 0.971 | 7.7 | |
| 105 | TN-02 | y = 1.5539e−0.115x | 0.896 | 6.0 | |
| Butachlor | 224.8 | BB-01 | y = 0.9324e−0.039x | 0.796 | 17.8 |
| 224.8 | BB-02 | y = 1.5805e−0.063x | 0.943 | 11.0 | |
| 224.8 | BS-01 | y = 1.8038e−0.047x | 0.988 | 14.7 | |
| 224.8 | BS-02 | y = 1.8759e−0.052x | 0.919 | 13.3 | |
| 224.8 | HC-01 | y = 1.7919e−0.076x | 0.990 | 9.1 | |
| 224.8 | HC-02 | y = 2.3666e−0.064x | 0.951 | 10.8 | |
| 224.8 | JJ-01 | y = 1.7142e−0.077x | 0.900 | 9.0 | |
| 224.8 | JJ-02 | y = 1.5782e−0.079x | 0.938 | 8.8 | |
| 224.8 | TN-01 | y = 1.7773e−0.044x | 0.837 | 15.8 | |
| 224.8 | TN-02 | y = 1.8878e−0.063x | 0.949 | 11.0 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yu, Q.; Zhang, P.; He, Y.; Xu, Z.; He, X.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, H.; He, L. Dissipation Dynamics and Residue of Four Herbicides in Paddy Fields Using HPLC-MS/MS and GC-MS. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 236. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16020236
Yu Q, Zhang P, He Y, Xu Z, He X, Hu Y, Zhang H, He L. Dissipation Dynamics and Residue of Four Herbicides in Paddy Fields Using HPLC-MS/MS and GC-MS. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2019; 16(2):236. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16020236
Chicago/Turabian StyleYu, Qian, Ping Zhang, Yuhan He, Zhifeng Xu, Xiulong He, Yuan Hu, Hongjun Zhang, and Lin He. 2019. "Dissipation Dynamics and Residue of Four Herbicides in Paddy Fields Using HPLC-MS/MS and GC-MS" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 16, no. 2: 236. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16020236
APA StyleYu, Q., Zhang, P., He, Y., Xu, Z., He, X., Hu, Y., Zhang, H., & He, L. (2019). Dissipation Dynamics and Residue of Four Herbicides in Paddy Fields Using HPLC-MS/MS and GC-MS. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 16(2), 236. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16020236