Effects of Soil Aggregate Stability on Soil Organic Carbon and Nitrogen under Land Use Change in an Erodible Region in Southwest China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
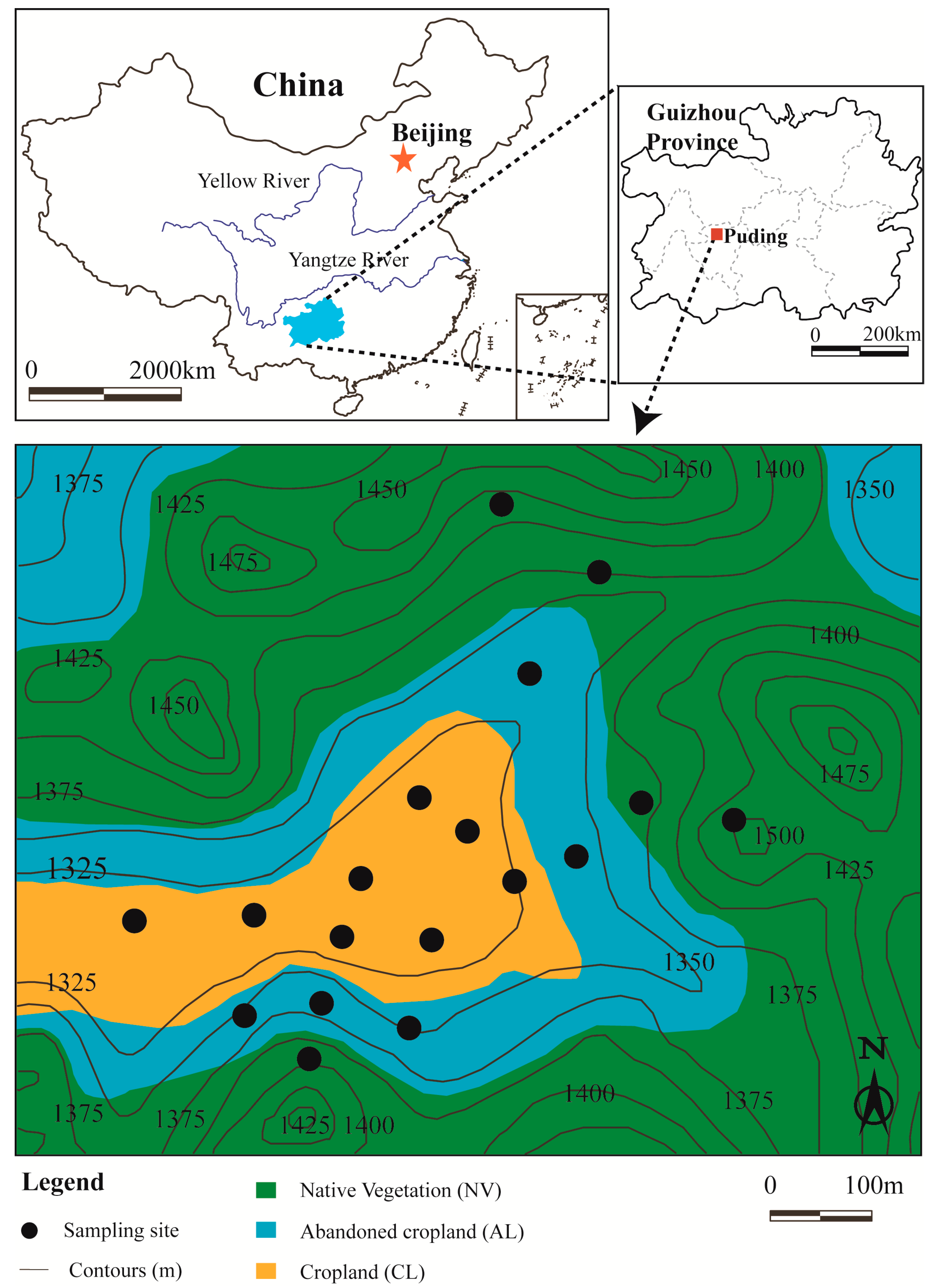
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Soil Sampling
2.3. Soil Analysis
2.4. Parameter Estimation
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Soil Particle Distribution, Soil pH, and Aggregate Distribution under Different Land Uses
3.2. Effects of Land Use Change and Soil Depth on SOC, SON, Aggregate Stability, and K Factor
3.3. Effects of Aggregate Stability on SOC and SON in an Erodible Region
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Deng, L.; Liu, G.B.; Shangguan, Z.P. Land-use conversion and changing soil carbon stocks in China’s ’Grain-for-Green’ Program: A synthesis. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2014, 20, 3544–3556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Niu, S.; Luo, Y. Global patterns of the dynamics of soil carbon and nitrogen stocks following afforestation: A meta-analysis. New Phytol. 2012, 195, 172–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Wen, L.; Yang, L.; Luo, P.; Xiao, K.; Chen, H.; Zhang, W.; He, X.; Chen, H.; Wang, K. Dynamics of soil organic carbon and nitrogen following agricultural abandonment in a karst region. J. Geophys. Res. 2017, 122, 230–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavalieri, K.M.V.; Silva, A.P.D.; Tormena, C.A.; Leão, T.P.; Dexter, A.R.; Håkansson, I. Long-term effects of no-tillage on dynamic soil physical properties in a Rhodic Ferrasol in Paraná, Brazil. Soil Tillage Res. 2009, 103, 158–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dungait, J.A.J.; Hopkins, D.W.; Gregory, A.S.; Whitmore, A.P. Soil organic matter turnover is governed by accessibility not recalcitrance. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2012, 18, 1781–1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Zhang, X.; Green, S.M.; Dungait, J.A.J.; Wen, X.; Tang, Y.; Guo, Z.; Yang, Y.; Sun, X.; Quine, T.A. Nitrogen functional gene activity in soil profiles under progressive vegetative recovery after abandonment of agriculture at the Puding Karst Critical Zone Observatory, SW China. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2018, 125, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chavarria, D.N.; Pérez-Brandan, C.; Serri, D.L.; Meriles, J.M.; Restovich, S.B.; Andriulo, A.E.; Jacquelin, L.; Vargas-Gil, S. Response of soil microbial communities to agroecological versus conventional systems of extensive agriculture. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2018, 264, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhao, H.; Zhang, T.; Zhao, X.; Drake, S. Community succession along a chronosequence of vegetation restoration on sand dunes in Horqin Sandy Land. J. Arid Environ. 2005, 62, 555–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynch, J.; Bragg, E. Microorganisms and soil aggregate stability. In Advances in Soil Science; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Choudhury, S.G.; Srivastava, S.; Singh, R.; Chaudhari, S.K.; Sharma, D.K.; Singh, S.K.; Sarkar, D. Tillage and residue management effects on soil aggregation, organic carbon dynamics and yield attribute in rice-wheat cropping system under reclaimed sodic soil. Soil Tillage Res. 2014, 136, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Six, J.; Bossuyt, H.; Degryze, S.; Denef, K. A history of research on the link between (micro)aggregates, soil biota, and soil organic matter dynamics. Soil Tillage Res. 2004, 79, 7–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tisdall, J.M.; Oades, J.M. Organic matter and water-stable aggregates in soils. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 1982, 33, 141–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annabi, M.; Raclot, D.; Bahri, H.; Bailly, J.S.; Gomez, C.; Bissonnais, Y.L. Spatial variability of soil aggregate stability at the scale of an agricultural region in Tunisia. Catena 2017, 153, 157–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Six, J.; Elliott, E.; Paustian, K. Aggregate and soil organic matter dynamics under conventional and no-tillage systems. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1999, 63, 1350–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Six, J.; Elliott, E.T.; Paustian, K.; Doran, J.W. Aggregation and Soil Organic Matter Accumulation in Cultivated and Native Grassland Soils. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1998, 62, 1367–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garland, G.; Bünemann, E.K.; Oberson, A.; Frossard, E.; Six, J. Plant-mediated rhizospheric interactions in maize-pigeon pea intercropping enhance soil aggregation and organic phosphorus storage. Plant Soil 2017, 415, 37–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M.; Wang, X.; Liusui, Y.; Chao, H.; Zhao, C.; Hua, L. Variation of soil aggregation and intra-aggregate carbon by long-term fertilization with aggregate formation in a grey desert soil. Catena 2017, 149, 437–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharyya, R.; Prakash, V.; Kundu, S.; Srivastva, A.K.; Gupta, H.S.; Mitra, S. Long term effects of fertilization on carbon and nitrogen sequestration and aggregate associated carbon and nitrogen in the Indian sub-Himalayas. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 2010, 86, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villasica, L.J.; Lina, S.; Asio, V. Aggregate stability affects carbon sequestration potential of different tropical soils. Ann. Trop. Res. 2018, 40, 71–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Xie, S.; Zhu, L.; Tian, Y.; Jia, Y. Evaluation of soil erosion risk in Karst regions of Chongqing, China. SPIE 2008, 7083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, J.; Yue, F.J.; Wang, Z.J.; Wu, Q.; Qin, C.Q.; Li, S.L. Quantifying depression trapping effect on rainwater chemical composition during the rainy season in karst agricultural area, southwestern China. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 218, 116998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, L.; Zhang, Z.; Shangguan, Z. Long-term fencing effects on plant diversity and soil properties in China. Soil Tillage Res. 2014, 137, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Zheng, F.; Römkens, M.J.M.; Darboux, F. Soil erodibility for water erosion: A perspective and Chinese experiences. Geomorphology 2013, 187, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Zheng, F.; Guan, Y. Improved USLE-K factor prediction: A case study on water erosion areas in China. Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 2016, 4, 168–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Yu, Y.; Dong, J.; Yang, Q.; Xu, X. Adapting & testing use of USLE K factor for agricultural soils in China. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2019, 269, 148–155. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, L.; Tan, W.; Fang, L.; Ji, L.; Deng, H. Spatial analysis of soil aggregate stability in a small catchment of the Loess Plateau, China: I. Spatial variability. Soil Tillage Res. 2018, 179, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, C.; Wang, S.; Bai, X.; Li, Y.; Tian, Y.; Li, Y.; Wu, L.; Luo, G. Soil erosion evolution and spatial correlation analysis in a typical karst geomorphology, using RUSLE with GIS. Solid Earth 2017, 8, 721–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, G.; Deng, L.; Shangguan, Z. Effects of soil aggregate stability on soil N following land use changes under erodible environment. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2018, 262, 18–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Zeng, C.; Liu, Z.H.; Wang, S.J. Effect of different land use/land cover on karst hydrogeochemistry: A paired catchment study of Chenqi and Dengzhanhe, Puding, Guizhou, SW China. J. Hydrol. 2010, 388, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Han, G.; Liu, M.; Wang, L. Geochemical Characteristics of Rare Earth Elements in Soils from Puding Karst Critical Zone Observatory, Southwest China. Sustainability 2019, 11, 4963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Han, G.; Li, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Song, Z. Soil organic carbon sequestration in soil aggregates in the karst Critical Zone Observatory, Southwest China. Plant Soil Environ. 2019, 65, 253–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Han, G.; Zhang, Q.; Song, Z. Variations and Indications of δ13CSOC and δ15NSON in Soil Profiles in Karst Critical Zone Observatory (CZO), Southwest China. Sustainability 2019, 11, 2144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Han, G.; Liu, M.; Liang, T. Spatial distribution and controlling factors of heavy metals in soils from Puding Karst Critical Zone Observatory, southwest China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2019, 78, 279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staff, S.S. Keys to Soil Taxonomy; USDA Natural Resources Conservation Service: Washington, DC, USA, 2010.
- Wang, S.J.; Liu, Q.M.; Zhang, D.F. Karst rocky desertification in southwestern China: Geomorphology, landuse, impact and rehabilitation. Land Degrad. Dev. 2004, 15, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Gao, P.; Niu, X.; Sun, J. Policy-driven China’s Grain to Green Program: Implications for ecosystem services. Ecosyst. Serv. 2017, 27, 38–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blois, J.L.; Williams, J.W.; Fitzpatrick, M.C.; Jackson, S.T.; Ferrier, S. Space can substitute for time in predicting climate-change effects on biodiversity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 9374–9379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, G.S.; Jiang, N.H.; Zhang, L.D.; Liu, Z.L. Soil Physical and Chemical Analysis and Description of Soil Profiles; China Standard Methods Press: Beijing, China, 1996; pp. 24–25. [Google Scholar]
- Midwood, A.J.; Boutton, T.W. Soil carbonate decomposition by acid has little effect on δ13C of organic matter. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1998, 30, 1301–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, L.; Ding, W.; Cai, Z. Long-term application of organic manure and nitrogen fertilizer on N2O emissions, soil quality and crop production in a sandy loam soil. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2005, 37, 2037–2045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharpley, A.N.; Williams, J.R. EPIC-erosion/productivity impact calculator: 1. Model determination. USDA Technol. Bull. 1990, 1759, 235. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, K.L.; Shu, A.P.; Xu, X.L.; Yang, Q.K.; Yu, B. Soil erodibility and its estimation for agricultural soils in China. J. Arid Environ. 2008, 72, 1002–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, G.; Song, Z.; Tang, Y. Geochemistry of rare earth elements in soils under different land uses in a typical karst area, Guizhou Province, Southwest China. Can. J. Soil Sci. 2017, 97, 606–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, G.; Li, F.; Tang, Y. Variations in soil organic carbon contents and isotopic compositions under different land uses in a typical karst area in Southwest China. Geochem. J. 2015, 49, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franzluebbers, A.J.; Arshad, M.A. Soil Microbial Biomass and Mineralizable Carbon of Water-Stable Aggregates. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1997, 61, 1090–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Six, J.; Elliott, E.T.; Paustian, K. Soil macroaggregate turnover and microaggregate formation: A mechanism for C sequestration under no-tillage agriculture. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2000, 32, 2099–2103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Han, G.L.; Li, Z.C.; Liu, T.Z.; Yang, X.M.; Wu, Y.T.; Song, Z.L. Effects of slope position and land use on the stability of aggregate-associated organic carbon in calcareous soils. Acta Geochim. 2017, 36, 456–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, J.; Luo, D.H.; Xia, J.; Zhang, Z.H.; Hu, G. Vegetation in karst terrain of southwestern China allocates more biomass to roots. Solid Earth 2015, 6, 1209–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlesinger, W.H. Carbon balance in terresterial detritus. Ann. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 1977, 8, 51–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houben, D.; Faucon, M.P.; Mercadal, A.M. Response of Organic Matter Decomposition to No-Tillage Adoption Evaluated by the Tea Bag Technique. Soil Syst. 2018, 2, 2030042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aiken, G.R.; Mcknight, D.M.; Wershaw, R.L.; Maccarthy, P. Humic Substances in Soil, Sediment, and Water: Geochemistry, Isolation and Characterization; Wiley Intersciences: New York, NY, USA, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Stevenson, F.J. Organic matter-micronutrient reactions in soil. In Micronutrients in Agriculture, 2nd ed.; Soil Science Society of America, Inc.: Madison, WI, USA, 1991; pp. 145–186. [Google Scholar]
- Oades, J.M.; Waters, A.G. Aggregate hierarchy in soils. Aust. J. Soil Res. 1991, 29, 815–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oades, J.M. Soil organic matter and structural stability: Mechanisms and implications for management. Plant Soil 1984, 76, 319–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, B.; Li, Z.; Li, P.; Liu, G.; Xue, S. Soil erodibility, microbial biomass, and physical–chemical property changes during long-term natural vegetation restoration: A case study in the Loess Plateau, China. Ecol. Res. 2010, 25, 531–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez Rodríguez, A.; Arbelo, C.D.; Guerra, J.A.; Mora, J.L.; Notario, J.S.; Armas, C.M. Organic carbon stocks and soil erodibility in Canary Islands Andosols. Catena 2006, 66, 228–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spohn, M.; Giani, L. Impacts of land use change on soil aggregation and aggregate stabilizing compounds as dependent on time. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2011, 43, 1081–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Q.; Darboux, F.; Man, C.; Zhu, Z.; An, S. Soil aggregate stability under different rain conditions for three vegetation types on the Loess Plateau (China). Catena 2018, 167, 276–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haynes, R.J.; Swift, R.S.; Stephen, R.C. Influence of mixed cropping rotations (pasture-arable) on organic matter content, water stable aggregation and clod porosity in a group of soils. Soil.Tillage Res. 1991, 19, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shepherd, T.G.; Saggar, S.; Newman, R.H.; Ross, C.W.; Dando, J.L. Tillage-induced changes to soil structure and organic carbon fractions in New Zealand soils. Aust. J. Soil Res. 2001, 39, 465–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Soil Depth (cm) | Clay Content (%) | Silt Content (%) | Sand Content (%) | Soil pH | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NV | AL | CL | NV | AL | CL | NV | AL | CL | NV | AL | CL | |
| 0–10 | 18 (3) | 18 (2) | 20 (3) | 81 (4) | 81 (2) | 80 (3) | 1 (2) | – | – | 7.2 (0.6) | 7.0 (0.3) | 6.9 (0.5) |
| 10–20 | 17 (2) | 19 (1) | 20 (3) | 83 (2) | 81 (1) | 80 (3) | – | – | – | 7.3 (0.4) | 7.1 (0.4) | 7.1 (0.5) |
| 20–30 | 18 (2) | 19 (2) | 18 (2) | 82 (2) | 81 (2) | 82 (2) | – | – | – | 7.4 (0.4) | 7.2 (0.4) | 7.2 (0.4) |
| 30–50 | 17 (3) | 19 (2) | 19 (2) | 83 (3) | 81 (2) | 81 (2) | – | – | – | 7.4 (0.2) | 7.2 (0.6) | 7.2 (0.2) |
| 50–90 | 19 (4) | 19 (4) | 19 (5) | 81 (4) | 81 (4) | 81 (5) | – | – | – | 7.5 (0.1) | 7.2 (0.6) | 7.4 (0.1) |
| Soil Depth (cm) | Macro-Aggregate (%) | Micro-Aggregate (%) | Silt + Clay-Sized Fraction (%) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NV | AL | CL | NV | AL | CL | NV | AL | CL | |
| 0–10 | 82 (7) a | 79 (4) a | 63 (8) b | 8 (2) b | 9 (2) b | 15 (3) a | 10 (5) b | 12 (2) b | 22 (7) a |
| 10–20 | 83 (4) a | 79 (3) ab | 66 (16) b | 8 (2) b | 9 (3) ab | 15 (6) a | 10 (3) a | 12 (2) a | 19 (11) a |
| 20–30 | 81 (7) a | 76 (4) a | 62 (19) a | 7 (2) b | 10 (1) ab | 15 (5) a | 11 (6) a | 14 (3) a | 23 (17) a |
| 30–50 | 77 (17) a | 75 (6) a | 71 (19) a | 9 (2) a | 10 (1) a | 12 (5) a | 15 (13) a | 16 (5) a | 16 (14) a |
| 50–90 | 68 (3) a | 64 (18) a | 67 (16) a | 13 (2) a | 12 (3) a | 16 (8) a | 19 (4) a | 24 (18) a | 16 (9) a |
| Factor | Variable | df | F | Sig. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Soil depth | SOC | 4 | 12.038 | 0 |
| SON | 4 | 14.186 | 0 | |
| K factor | 4 | 11.845 | 0 | |
| MWD | 4 | 1.198 | 0.32 ns | |
| Land use change | SOC | 2 | 2.296 | 0.108 |
| SON | 2 | 3.523 | 0.035 | |
| K factor | 2 | 0.199 | 0.82 ns | |
| MWD | 2 | 6.17 | 0.003 | |
| Soil depth × land use change | SOC | 8 | 1.058 | 0.403 ns |
| SON | 8 | 1.103 | 0.372 ns | |
| K factor | 8 | 0.543 | 0.82 ns | |
| MWD | 8 | 0.709 | 0.682 ns |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, M.; Han, G.; Zhang, Q. Effects of Soil Aggregate Stability on Soil Organic Carbon and Nitrogen under Land Use Change in an Erodible Region in Southwest China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 3809. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16203809
Liu M, Han G, Zhang Q. Effects of Soil Aggregate Stability on Soil Organic Carbon and Nitrogen under Land Use Change in an Erodible Region in Southwest China. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2019; 16(20):3809. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16203809
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Man, Guilin Han, and Qian Zhang. 2019. "Effects of Soil Aggregate Stability on Soil Organic Carbon and Nitrogen under Land Use Change in an Erodible Region in Southwest China" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 16, no. 20: 3809. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16203809
APA StyleLiu, M., Han, G., & Zhang, Q. (2019). Effects of Soil Aggregate Stability on Soil Organic Carbon and Nitrogen under Land Use Change in an Erodible Region in Southwest China. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 16(20), 3809. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16203809






