Radiation Dose to the Eye Lens through Radiological Imaging Procedures at the Surgical Workplace during Trauma Surgery
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
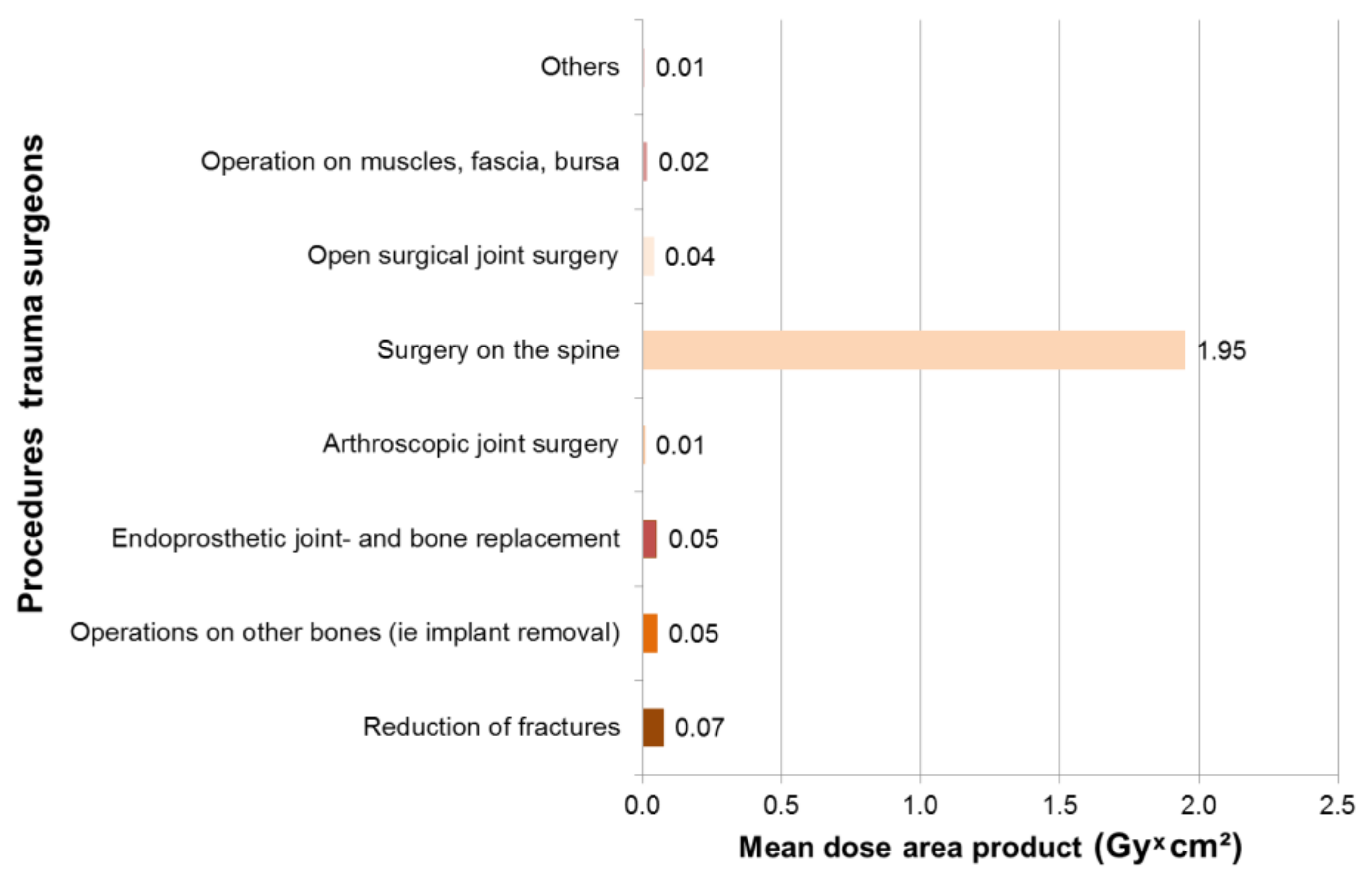
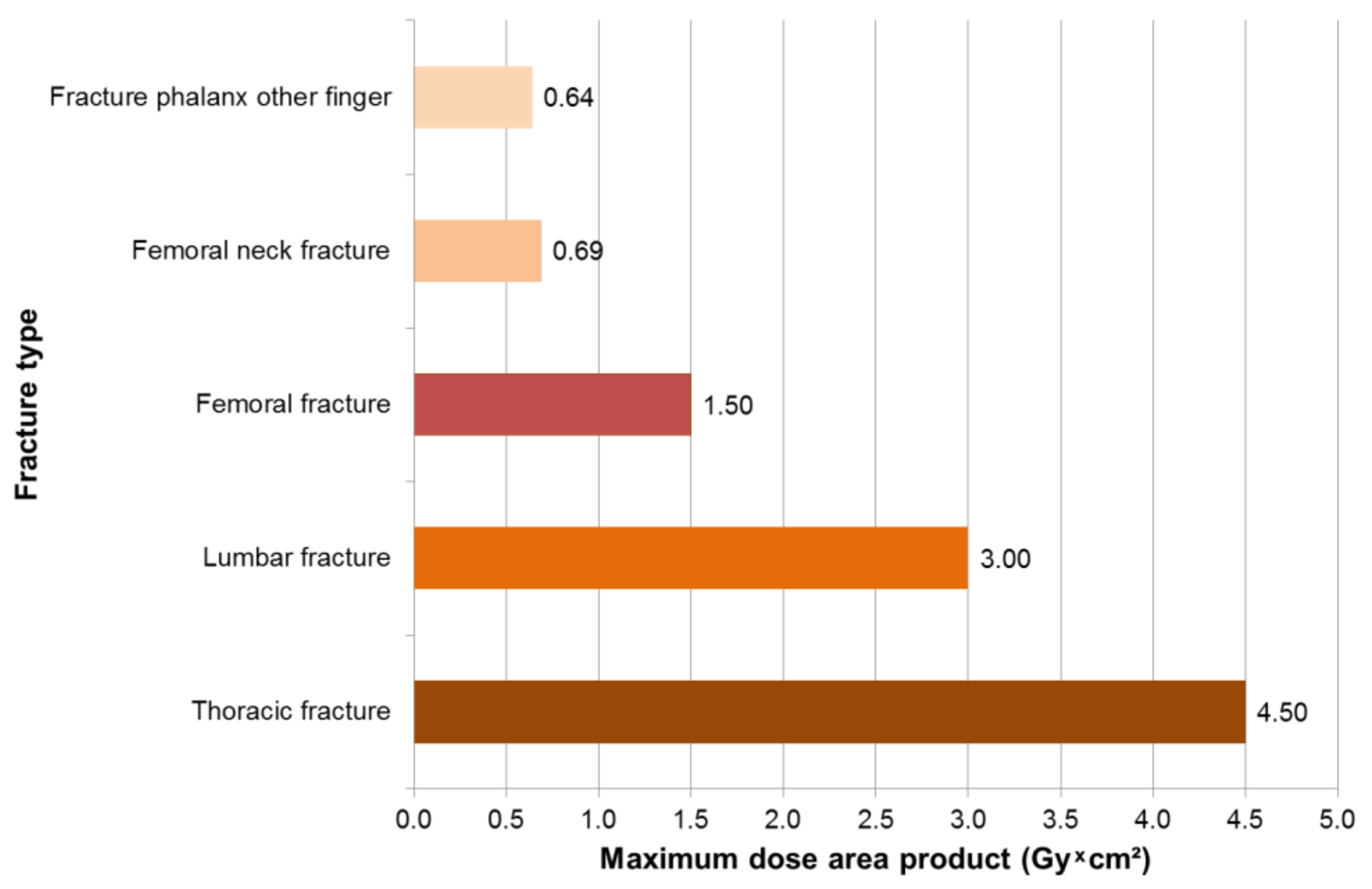
3.1. Results—Trauma Surgeons
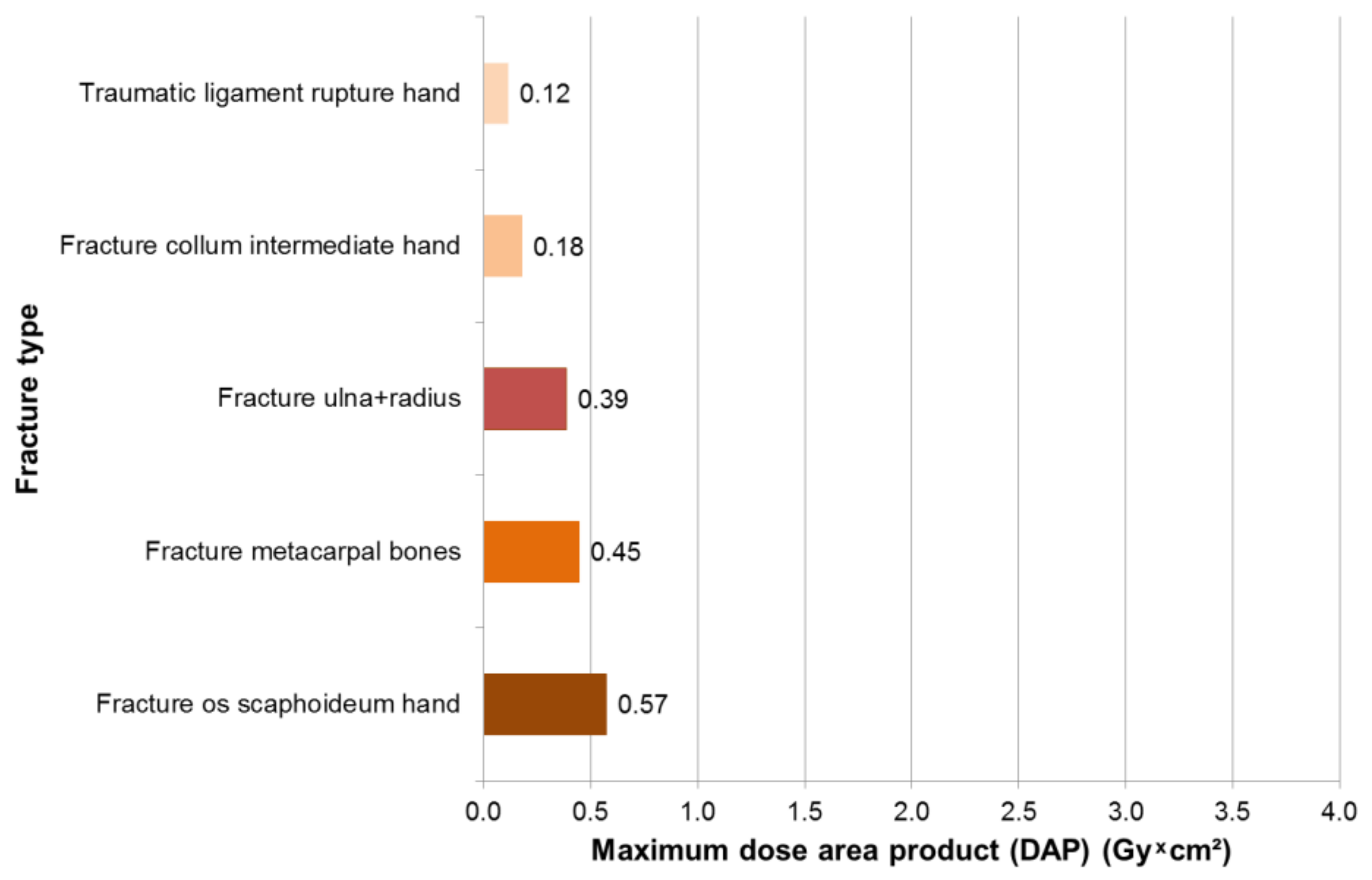
3.2. Results—Hand Surgeons
3.3. Results Surgical Assistants
3.4. Comparison of Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Council Directive 2013/59/Euratom of 5 December 2013 Laying Down Basic Safety Standards for Protection Against the Dangers Arising from Exposure to Ionising Radiation, And Repealing Directives 89/618/Euratom, 90/641/Euratom, 96/29/Euratom, 97/43/Euratom and 2003/122/Euratom. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/ALL/?uri=CELEX%3A32013L0059 (accessed on 19 August 2019).
- Strahlenschutzgesetz vom 27. Juni 2017 (BGBl. I S. 1966), Das Durch Artikel 2 des Gesetzes Vom 27. Juni 2017 (BGBl. I S. 1966) Geändert Worden Ist. Available online: http://www.gesetze-im-internet.de/strlschg/StrlSchG.pdf (accessed on 19 August 2019).
- Strahlenschutzverordnung Vom 29. November 2018 (BGBl. I S. 2034, 2036). Available online: http://www.gesetze-im-internet.de/strlschv_2018/StrlSchV.pdf (accessed on 19 August 2019).
- Stewart, F.A.; Akleyev, A.V.; Hauer-Jensen, M.; Hendry, J.H.; Kleiman, N.J.; MacVittie, T.J.; Aleman, B.M.; Edgar, A.B.; Mabuchi, K.; Muirhead, C.R.; et al. International Commission on Radiological Protection (ICRP). ICRP Statement on Tissue Reactions / Early and Late Effects of Radiation in Normal Tissues and Organs—Threshold Doses for Tissue Reactions in a Radiation Protection Context. ICRP Publication 118. Ann. ICRP 2012, 41, 1–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Commission on Radiological Protection (ICRP). The 2007 Recommendations of the International Commission on Radiological Protection. ICRP Publication 103. Ann. ICRP. 2007. Available online: http://www.icrp.org/publication.asp?id=ICRP%20Publication%20103 (accessed on 19 August 2019).
- Little, M.P.; Kitahara, C.M.; Cahoon, E.K.; Bernier, M.-O.; Velazquez-Kronen, R.; Doody, M.M.; Borrego, D.; Miller, J.S.; Alexander, B.H.; Simon, S.L.; et al. Occupational radiation exposure and risk of cataract incidence in a cohort of US radiologic technologists. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 2018, 33, 1179–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.P.; Miller, D.L.; De Gonzalez, A.B.; Balter, S.; Kleinerman, R.A.; Ostroumova, E.; Simon, S.L.; Linet, M.S. Occupational radiation doses to operators performing fluoroscopically-guided procedures. Health Phys. 2012, 103, 80–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahl, H.G.; Ewen, K. 138. Strahlenbelastung bei unfallchirurgischen Operationen. Langenbeck’s Arch. Surg. 1977, 345, 607–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuchs, M.; Schmid, A.; Eiteljörge, T.; Modler, H.; Stürmer, K.M. Strahlenbelastung des Chirurgen durch intraoperatives Röntgen: Risiken und Dosismanagement im OP. In Vielfalt und Einheit der Chirurgie Humanität und Wissenschaft; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1998; pp. 1111–1113. [Google Scholar]
- Fuchs, M.; Schmid, A.; Eiteljörge, T.; Modler, M.; Stürmer, K.M. Exposure of the surgeon to radiation during surgery. Int. Orthop. 1998, 22, 153–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fuchs, M.; Modler, H.; Schmid, A.; Dumont, C.; Modler, H.; Stürmer, K.M. Messung der intraoperativen Strahlenexposition des Unfallchirurgen. Unfallchirurg 1999, 102, 371–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- König, B.; Freude, T.; Müller, B.; Renker, F.; Figel, M.; Stöckle, U. Lokalisations-Bezogene Strahlenbelastung für Unfallchirurgen im OP—Prospektive Auswertung Separater Einzelmessungen für Augen, Hände und Streustrahlung. Available online: https://www.egms.de/static/en/meetings/dkou2010/10dkou291.shtml (accessed on 19 August 2019).
- Mariscalco, M.W.; Yamashita, T.; Steinmetz, M.P.; Krishnaney, A.A.; Lieberman, I.H.; Mroz, T.E. Radiation exposure to the surgeon during open lumbar microdiscectomy and minimally invasive microdiscectomy, a prospective; controlled trial. Spine 2011, 36, 255–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kesavachandran, C.N.; Haamann, F.; Nienhaus, A. Radiation exposure of eyes, thyroid gland and hands in orthopaedic staff: a systematic review. Eur. J. Med. Res. 2012, 17, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lonjon, N.; Le Corre, M.; Le Roy, J.; Greffier, J.; Fuentes, S.; Tonetti, J.; Charles, Y.P.; Blondel, B.; Kouyoumdjïan, P. Surgeon’s and Patient’s Radiation Exposure Through Vertebral Body Cement Augmentation Procedures: A Prospective Multicentric Study of 49 Cases. World Neurosurg. 2016, 93, 371–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romanova, K.; Vassileva, J.; Alyakov, M. Radiation exposure to the eye lens of orthopaedic surgeons during various orthopaedic procedures. Radiat. Prot. Dosim. 2015, 165, 310–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schütz, U.; Beer, M.; Wild, A.; Oehler, S.; Kraus, M. Radiation protection during C-arm based spine interventions in orthopedics and traumatology. OUP 2016, 4, 224–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bera, G.; Gellie, G.; Jamet, E.; Entine, F.; Michel, X. Eye lens radiation exposure of workers during medical interventional procedures and surgery. Radiat. Prot. Dosim. 2018, 182, 323–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coppeta, L.; Pietroiusti, A.; Neri, A.; Spataro, A.; De Angelis, E.; Perrone, S.; Magrini, A. Risk of radiation-induced lens opacities among surgeons and interventional medical staff. Radiol. Phys. Technol. 2019, 12, 26–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, M.E.; Davis, M.L.; MacClean, C.R.; Davis, J.G.; Smith, B.L.; Humphries, J.R. Radiation exposure and associated risks to operating-room personnel during use of fluoroscopic guidance for selected orthopaedic surgical procedures. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. Vol. 1983, 65, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harstall, R.; Heini, P.F.; Mini, R.L.; Orler, R. Radiation exposure to the surgeon during fluoroscopically assisted percutaneous vertebroplasty: A prospective study. Spine 2005, 30, 1893–1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muzaffar, T.S.T.; Imran, Y.; Iskandar, M.A.; Zakaria, A. Radiation exposure to the surgeon during femoral interlocking nailing under fluoroscopic imaging. Med. J. Malays. 2005, 60, 26–29. [Google Scholar]
- Strohmaier, J.; Naber, C. Untersuchungen zur Strahlenexposition der Augenlinse von beruflich Strahlenexponiertem Personal. Available online: https://www.bmu.de/fileadmin/Daten_BMU/Pools/Forschungsdatenbank/fkz_3613_s_40011_strahlenexposition_augenlinse_bf.pdf (accessed on 19 August 2019).
- Pugliese, M.; Amatiello, A.; Correra, M.; Stoia, V.; Cerciello, V.; Roca, V.; Loffredo, F.; Fiore, F.; La Verde, G. Evaluation of the current status of the eye lens radiation exposure in an Interventional Radiology department. Med. Lav. 2018, 109, 471–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowak, M.; Sans-Merce, M.; Lemesre, C.; Elmiger, R.; Damet, J. Eye lens monitoring programme for medical staff involved in fluoroscopy guided interventional procedures in Switzerland. Phys. Medica 2019, 57, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouffler, S.; Peters, S.; Gilvin, P.; Slack, K.; Markiewicz, E.; Quinlan, R.; Gillan, J.; Coster, M.; Barnard, S.; Rothkamm, K.; et al. The lens of the eye: exposures in the UK medical sector and mechanistic studies of radiation effects. Ann. ICRP 2015, 44, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carinou, E.; Ferrari, P.; Bjelac, O.C.; Gingaume, M.; Merce, M.S.; O’Connor, U. Eye lens monitoring for interventional radiology personnel: Dosemeters, calibration and practical aspects ofHp(3) monitoring. A 2015 review. J. Radiol. Prot. 2015, 35, R17–R34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Covens, P.; Dabin, J.; De Troyer, O.; Dragusin, O.; Maushagen, J.; Struelens, L. Track, calculate and optimise eye lens doses of interventional cardiologists using mEyeDose and mEyeDose_X. J. Radiol. Prot. 2018, 38, 678–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoder, R.C.; Dauer, L.T.; Balter, S.; Boice, J.D.; Grogan, H.A.; Mumma, M.T.; Passmore, C.N.; Rothenberg, L.N.; Vetter, R.J.; Yoder, R.C. Dosimetry for the study of medical radiation workers with a focus on the mean absorbed dose to the lung, brain and other organs. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 2018, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cretti, F. Assessment of occupational radiation dose in interventional settings. Med. Lav. 2018, 109, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Domienik-Andrzejewska, J.K.; Ciraj-Bjelac, O.; Askounis, P.; Covens, P.; Dragusin, O.; Jacob, S.; Farah, J.; Gianicolo, E.; Padovani, R.; Teles, P.M.P.; et al. Past and present work practices of European interventional cardiologists in the context of radiation protection of the eye lens—Results of the EURALOC study. J. Radiol. Prot. 2018, 38, 934–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alejo, L.; Koren, C.; Corredoira, E.; Sánchez, F.; Bayón, J.; Serrada, A.; Guibelalde, E. Eye lens dose correlations with personal dose equivalent and patient exposure in paediatric interventional cardiology performed with a fluoroscopic biplane system. Phys. Medica 2017, 36, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bahruddin, N.A.; Hashim, S.; Karim, M.K.A.; Sabarudin, A.; Ang, W.C.; Salehhon, N.; Bakar, K.A. Radiation dose to physicians’ eye lens during interventional radiology. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2016, 694, 12035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behrens, R.; Hupe, O.; Busch, F.; Denk, J.; Engelhardt, J.; Günther, K.; Hödlmoser, H.; Jordan, M.; Strohmaier, J. Intercomparison of eye lens dosemeters. Radiat. Prot. Dosim. 2017, 174, 6–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Häusler, U.; Czarwinski, R.; Brix, G. Radiation exposure of medical staff from interventional x-ray procedures: A multicentre study. Eur. Radiol. 2009, 19, 2000–2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartmann, J.; Distler, F.A.; Baumüller, M.; Guni, E.; Pahernik, S.; Wucherer, M.; Baumueller, M.; A Pahernik, S. Risk of Radiation-Induced Cataracts: Investigation of Radiation Exposure to the Eye Lens During Endourologic Procedures. J. Endourol. 2018, 32, 897–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, D.Z.; Lacasse, M.C.; Khan, R.; Murphy, K.J. Radiation Cataractogenesis: The Progression of Our Understanding and Its Clinical Consequences. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2017, 28, 412–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krisanachinda, A.; Srimahachota, S.; Matsubara, K. The current status of eye lens dose measurement in interventional cardiology personnel in Thailand. Radiol. Phys. Technol. 2017, 10, 142–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsubara, K.; Lertsuwunseri, V.; Srimahachota, S.; Krisanachinda, A.; Tulvatana, W.; Khambhiphant, B.; Sudchai, W.; Rehani, M. Eye lens dosimetry and the study on radiation cataract in interventional cardiologists. Phys. Medica 2017, 44, 232–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendelsohn, D.; Strelzow, J.; Dea, N.; Ford, N.L.; Batke, J.; Pennington, A.; Yang, K.; Ailon, T.; Boyd, M.; Dvorak, M.; et al. Patient and surgeon radiation exposure during spinal instrumentation using intraoperative computed tomography-based navigation. Spine J. 2016, 16, 343–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piwowarska-Bilska, H.; Supinska, A.; Iwanowski, J.; Birkenfeld, B. Should Personnel of Nuclear Medicine Departments Use Personal Dosimeters for Eye Lens Dose Monitoring? Radiat. Prot. Dosim. 2018, 183, 393–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rathmann, N.; Kostrzewa, M.; Kara, K.; Bartling, S.; Haubenreisser, H.; O Schoenberg, S.; Diehl, S.J. Radiation exposure of the interventional radiologist during percutaneous biopsy using a multiaxis interventional C-arm CT system with 3D laser guidance: A phantom study. Br. J. Radiol. 2015, 88, 20150151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seals, K.F.; Lee, E.W.; Cagnon, C.H.; Al-Hakim, R.A.; Kee, S.T. Radiation-induced cataractogenesis, a critical literature review for the interventional radiologist. Cardiovasc. Intervent. Radiol. 2016, 39, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, E.H.; Struelens, L.; Covens, P.; Ueno, S.; Koguchi, Y.; Vanhavere, F.; Buls, N. Optimization of a radiophotoluminescent glass dosimeter for occupational eye lens dosimetry in interventional radiology/cardiology. Radiat. Prot. Dosim. 2018, 182, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Struelens, L.; Dabin, J.; Carinou, E.; Askounis, P.; Ciraj-Bjelac, O.; Domienik-Andrzejewska, J.; Berus, D.; Padovani, R.; Farah, J.; Convens, P. Radiation-Induced Lens Opacities among Interventional Cardiologists, Retrospective Assessment of Cumulative Eye Lens Doses. Radiat. Res. 2018, 189, 399–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, A.; Matsubara, K.; Sasa, Y. Measurement of radiation doses to the eye lens during orthopaedic surgery using an C-arm X-ray system. Radiat. Prot. Dosim. 2018, 179, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamashita, K.; Higashino, K.; Wada, K.; Morimoto, M.; Abe, M.; Takata, Y.; Sakai, T.; Fukui, Y.; Sairyo, K. Radiation Exposure to the Surgeon and Patient During a Fluoroscopic Procedure: How High Is the Exposure Dose? A Cadaveric Study. Spine 1976, 41, 1254–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rampersaud, Y.R.; Foley, K.T.; Shen, A.C.; Williams, S.; Solomito, M. Radiation exposure to the spine surgeon during fluoroscopically assisted pedicle screw insertion. Spine 2000, 25, 2637–2645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| Surgeries with Intraoperative X-Rays | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Statistical Characteristics | Trauma Surgeons (n = 249) | Hand Surgeons (n = 169) | Surgical Assistants (n = 237) |
| Duration of radioscopy (Sec) | |||
| Median | 8 | 29 | 11 |
| Quartil 1 | 3 | 9 | 4 |
| Quartil 3 | 21 | 63 | 36 |
| Minimum | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Maximum | 230 | 305 | 407 |
| Dose area product (Gy × cm2) | |||
| Median | 0.02 | 0.03 | 0.02 |
| Quartil 1 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 |
| Quartil 3 | 0.04 | 0.08 | 0.08 |
| Minimum | <0.00 | <0.00 | <0.00 |
| Maximum | 4.6 | 0.57 | 4.47 |
| Duration of the surgery (Min) | |||
| Median | 59 | 70 | 69 |
| Quartil 1 | 38 | 42 | 42 |
| Quartil 3 | 81 | 119 | 102 |
| Minimum | 10 | 5 | 10 |
| Maximum | 229 | 512 | 638 |
| Hand Surgeons | Trauma Surgeons | Surgical Assistants | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Statistical Characteristics | Participants (mSv) n = 4 | Reference (mSv) n = 5 | Participants (mSv) n = 5 | Reference (mSv) n = 5 | Participants (mSv) n = 4 | Reference (mSv) n = 5 |
| Mean | 1.20 | 1.06 | 1.22 | 1.29 | 1.22 | 0.84 |
| Standard deviation | 0.10 | 0.26 | 0.16 | 0.08 | 0.04 | 0.04 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Apelmann, C.; Kowald, B.; Weinrich, N.; Dischinger, J.; Nienhaus, A.; Seide, K.; Martens, H.; Jürgens, C. Radiation Dose to the Eye Lens through Radiological Imaging Procedures at the Surgical Workplace during Trauma Surgery. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 3850. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16203850
Apelmann C, Kowald B, Weinrich N, Dischinger J, Nienhaus A, Seide K, Martens H, Jürgens C. Radiation Dose to the Eye Lens through Radiological Imaging Procedures at the Surgical Workplace during Trauma Surgery. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2019; 16(20):3850. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16203850
Chicago/Turabian StyleApelmann, Christian, Birgitt Kowald, Nils Weinrich, Jens Dischinger, Albert Nienhaus, Klaus Seide, Heiko Martens, and Christian Jürgens. 2019. "Radiation Dose to the Eye Lens through Radiological Imaging Procedures at the Surgical Workplace during Trauma Surgery" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 16, no. 20: 3850. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16203850
APA StyleApelmann, C., Kowald, B., Weinrich, N., Dischinger, J., Nienhaus, A., Seide, K., Martens, H., & Jürgens, C. (2019). Radiation Dose to the Eye Lens through Radiological Imaging Procedures at the Surgical Workplace during Trauma Surgery. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 16(20), 3850. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16203850





