Metal (Pb, Cu, Cd, and Zn) Transfer along Food Chain and Health Risk Assessment through Raw Milk Consumption from Free-Range Cows
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sampling
2.2. Sample Preparation and Analysis
2.3. Transfer Factors
2.4. Health Risk Assessment
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Quality Assurance Data
3.2. Metal Contents in Soil, Water, Forage, and Milk Samples
3.3. Transfer Factors from Soil to Forage and from Forage to Milk
3.4. Health Risk Assessment through Milk Consumption
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Roman, S.; Sanchez-Siles, L.M.; Siegrist, M. The importance of food naturalness for consumers: Results of a systematic review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 67, 44–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todea, D.; Cadar, O.; Simedru, D.; Roman, C.; Tanaselia, C.; Suatean, I.; Naghiu, A. Determination of major-to-trace minerals and polyphenols in different apple cultivars. Not. Bot. Horti. Agrobot. 2014, 42, 523–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cadar, O.; Miclean, M.; Cadar, S.; Tanaselia, C.; Senila, L.; Senila, M. Assessment of heavy metals in cow’s milk in Rodnei mountains area, Romania. Environ. Eng. Manag. J. 2015, 14, 2523–2528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucey, J.A. Raw Milk Consumption: Risks and Benefits. Nutr. Today 2015, 50, 189–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magdas, D.A.; Dehelean, A.; Feher, I.; Cristea, G.; Puscas, R.; Dan, S.D.; Cordea, D.V. Discrimination markers for the geographical and species origin of raw milk within Romania. Int. Dairy J. 2016, 61, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miclean, M.; Cadar, O.; Roman, C.; Tanaselia, C.; Stefanescu, L.; Groza, I.S. The influence of environmental contamination on heavy metals and organochlorine compounds levels in milk. Environ. Eng. Manag. J. 2011, 10, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miclean, M.; Cadar, O.; Levei, E.A.; Todea, D.A. Human health risk assessment of organochlorine compounds associated with raw milk consumption in a Romanian industrial area. Ital. J. Food Sci. 2018, 30, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Mantovani, A.; Frazzoli, C. Risk assessment of toxic contaminants in animal feed. CAB Rev. Persp. Agric. Vet. Sci. Nutr. Nat. Res. 2010, 5, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meshref, A.M.S.; Moselhy, W.A.; Hassan, N.H.Y. Heavy metals and trace elements levels in milk and milk products. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2014, 8, 381–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thornton, I.; Abrahams, P. Soil ingestion—A major pathway of heavy metals into livestock grazing contaminated land. Sci. Total Environ. 1983, 28, 287–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miclean, M.; Cadar, O.; Levei, L.; Senila, L.; Ozunu, A. Metal contents and potential health risk assessment of crops grown in a former mining district (Romania). J. Environ. Sci. Health B 2018, 53, 595–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacLachlan, D.J. Estimating the transfer of contaminants in animal feedstuffs to livestock tissues, milk and eggs: A review. Anim. Prod. Sci. 2011, 51, 1067–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adipah, S. Introduction of human health associated with risk assessment. J. Environ. Sci. Health A 2018, 2, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoaghia, M.A.; Cadar, O.; Hognogi, G.G.; Levei, E.; Moisa, C.; Roman, C. Quality and human health risk assessment of metals and nitrogen compounds in drinking water from an urban area near a former non-ferrous ore smelter. Anal. Lett. 2019, 52, 1268–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miclean, M.; Levei, E.; Cadar, O.; Senila, M.; Groza, I.S. Comparison of two empirical models for soil to ryegrass transfer of metals in Baia Mare mining area. Carpath. J. Earth Environ. 2013, 8, 93–100. [Google Scholar]
- Soares, V.A.; Kus, M.; Peixoto, A.L.C.; Carrocci, J.S.; Salazar, R.F.S.; Izario-Filho, H.J. Determination of nutritional and toxic elements in pasteurized bovine milk from Vale do Paraiba region (Brazil). Food Contr. 2010, 21, 45–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanova-Petropulos, V.; Balabanova, B.; Bogeva, E.; Frentiu, T.; Ponta, M.; Senila, M.; Gulaboski, R.; Irimie, F.D. Rapid determination of trace elements in macedonian grape brandies for their characterization and safety evaluation. Food Anal. Methods 2017, 10, 459–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senila, M.; Drolc, A.; Pintar, A.; Senila, L.; Levei, E. Validation and measurement uncertainty evaluation of the ICP-OES method for the multi-elemental determination of essential and nonessential elements from medicinal plants and their aqueous extracts. J. Anal. Sci. Technol. 2014, 5, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kabata-Pendias, A. Soil-plant transfer of trace elements-an environmental issue. Geoderma 2004, 122, 143–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leeman, W.R.; Van Den Berg, K.J.; Houben, G.F. Transfer of chemicals from feed to animal products: The use of transfer factors in risk assessment. Food Addit. Contam. A 2007, 24, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Environmental Protection Agency. Integrated Risk Information System. Available online: www.epa.gov/iris (accessed on 5 August 2019).
- ILSI. Summary of Evaluations Performed by the Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives (JECFA 1956–2003); First through Sixty First Meetings; ILSI Press International Life Sciences Institute: Geneva, Switzerland, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. Evaluation of certain contaminants in food. In Seventy-Second Report of the Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives in the WHO Technical Report Series; World Health Organization: Rome, Italy, 2011; p. 959. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, N.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, X.; Zheng, D.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, S. Population health risk due to dietary intake of heavy metals in the industrial area of Huludao city, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2007, 387, 96–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christophoridis, C.; Kosma, A.; Evgenakis, E.; Bourliva, A.; Fytianos, K. Determination of heavy metals and health risk assessment of cheese products consumed in Greece. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2019, 82, 103238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sipter, E.; Rozsa, E.; Gruiz, K.; Tatrai, E.; Morvai, V. Site-specific risk assessment in contaminated vegetable gardens. Chemosphere 2008, 71, 1301–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamunda, C.; Mathuthu, M.; Madhuku, M. Health risk assessment of heavy metals in soils from Witwatersrand Gold Mining Basin, South Africa. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2016, 13, 663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avigliano, E.; Lozano, C.; Pla, R.R.; Volpedo, A.V. Toxic element determination in fish from Paraná River Delta (Argentina) by neutron activation analysis: Tissue distribution and accumulation and health risk assessment by direct consumption. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2016, 54, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farokhneshat, F.; Mahvi, A.H.; Jamali, Y. Carcinogenic and Non-Carcinogenic Risk Assessment of Chromium in Drinking Water Sources: Birjand. Iran. Res. J. Environ. Toxicol. 2016, 10, 166–171. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, F.; Wei, W.; Li, M.; Huang, R.; Yang, F.; Duan, Y. Heavy metal contamination in rice-producing soils of Hunan Province, China and potential health risks. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2015, 12, 15584–15593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levei, E.; Frentiu, T.; Ponta, M.; Senila, M.; Miclean, M.; Roman, C.; Cordos, E. Characterization of soil quality and mobility of Cd, Cu, Pb and Zn in the Baia Mare area Northwest Romania following the historical pollution. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2009, 89, 635–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Order 756 (1997). Order of the Ministry of Water, Forestry and Environmental Protection for the Approval of the Regulation Regarding the Assessment of Environmental Pollution, No. 756 of November 3, 1997, Published in the Official Gazette No. 303 bis of November 6, 1997. (In Romanian)
- Law no. 311 of June 28, 2004 for Amending and Supplementing Law no. 458/2002 Regarding the Quality of Drinking Water, Published in the Official Gazette, Part I no. 582 of 6/30/2004. (In Romanian)
- Directive 2002/32/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 7 May 2002 on Undesirable Substances in Animal Feed, OJ L 140, 30.5.2002. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/LexUriServ/LexUriServ.do?uri=CONSLEG:2002L0032:20061020:EN:PDF (accessed on 23 March 2019).
- EC 1881/2006. Commission Regulation (EC) No 1881/2006 of 19 December 2006 setting maximum levels for certain contaminants in foodstuffs, 20.12.2006. Off. J. Eur. Union 2006, 364, 365–324. [Google Scholar]
- Caggiano, R.; Sabia, S.; D’Emilio, M.; Macchiato, M.; Anastasio, A.; Ragosta, M.; Paino, S. Metal levels in fodder, milk, dairy products, and tissues sampled in ovine farms of Southern Italy. Environ. Res. 2005, 99, 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coni, E.; Bocca, A.; Coppolelli, P.; Caroli, S.; Cavallucci, C.; Marinucci, M.T. Minor and trace element content in sheep and goat milk and dairy products. Food Chem. 1996, 57, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solis, C.; Isaac-Olive, K.; Mireles, A.; Vidal-Hernandez, M. Determination of trace metals in cow’s milk from waste water irrigated areas in Central Mexico by chemical treatment coupled to PIXE. Microchem. J. 2009, 91, 9–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ataro, A.; McCrindle, R.I.; Botha, B.M.; McCrindle, C.M.E.; Ndibewu, P.P. Quantification of trace elements in raw cow’s milk by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS). Food Chem. 2008, 111, 243–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilandzic, N.; Sedak, M.; Calopek, B.; Luburic, D.B.; Solomun Kolanovic, B.; Varenina, I.; Dokic, M.; Kmetic, I.; Murati, T. Lead concentrations in raw cow and goat milk collected in rural areas of Croatia from 2010 to 2014. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2016, 96, 645–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Qu, X.; Zheng, N.; Su, C.; Wang, J.; Soyeurt, H. Large scale study of the within and between spatial variability of lead, arsenic, and cadmium contamination of cow milk in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 650, 3054–3061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez-Bermudez, R.; Lopez-Alonso, M.; Miranda, M.; Fouz, R.; Orjales, I.; Herrero-Latorre, C. Chemometric authentication of the organic status of milk on the basis of trace element content. Food Chem. 2018, 240, 686–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, H.; Yang, W.T.; Zhou, X.; Liu, L.; Gu, J.F.; Wang, W.L.; Zhou, J.L.; Tian, T.; Peng, P.Q.; Liao, B.H. Accumulation of heavy metals in vegetable species planted in contaminated soils and the health risk assessment. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2016, 13, 289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kloke, A.; Sauerbeck, D.R.; Vetter, H. The contamination of plants and soils with heavy metals and the transport of metals in terrestrial food-chains. In Changing Metacycles and Human Health; Niragu, J., Ed.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1984; pp. 113–114. [Google Scholar]
- Thornton, I.; Farago, M.E. Geochemistry of Arsenic. In Arsenic, Exposure and Health Effects; Abernathy, C.O., Calderon, R.L., Chappell, W.R., Eds.; Chapman & Hall: London, UK, 1977; p. 27. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, X.; Zhang, F.; Zeng, C.; Zhang, M.; Devkota, L.P.; Yao, T. Relationship between heavy metal concentrations in soils and grasses of toadside farmland in Nepal. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2012, 9, 3209–3226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karunakara, N.; Ujwal, P.; Yashodhara, I.; Rao, C.; Sudeep, K.K.; Dileep, B.N.; Ravic, P.M. Studies on soil to grass transfer factor (Fv) and grass to milk transfer coefficient (Fm) for cesium in Kaiga region. J. Environ. Radioactiv. 2013, 124, 101–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harmanescu, M.; Alda, L.M.; Bordean, B.M.; Gogoasa, I.; Gergen, I. Heavy metals health risk assessment for population via consumption of vegetables grown in old mining area; a case study: Banat County, Romania. Chem. Cent. J. 2011, 5, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Rico, L.; Leyva-Perez, J.; Jara-Marini, M.E. Content and daily intake of copper, zinc, lead, cadmium, and mercury from dietary supplements in Mexico. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2007, 45, 1599–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sobhanardakani, S. Human health risk assessment of Cd, Cu, Pb and Zn through consumption of raw and pasteurized cow’s milk. Iran. J. Public Health 2018, 47, 1172–1180. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Islam, S.; Ahmed, K.; Al-Mamun, H.; Masunaga, S. Assessment of trace metals in foodstuffs grown around the vicinity of industries in Bangladesh. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2015, 42, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Analyte | Matrix | LOD | LOQ | U (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pb | Soil (mg kg−1) | 0.33 | 1.00 | 9.2 |
| Water (mg L−1) | 0.30 | 0.90 | 7.5 | |
| Forage (mg kg−1) | 0.006 | 0.018 | 9.0 | |
| Milk (mg kg−1) | 0.003 | 0.009 | 9.8 | |
| Cd | Soil (mg kg−1) | 0.11 | 0.33 | 11.2 |
| Water (mg L−1) | 0.10 | 0.30 | 6.4 | |
| Forage (mg kg−1) | 0.002 | 0.006 | 9.6 | |
| Milk (mg kg−1) | 0.001 | 0.003 | 10.1 | |
| Cu | Soil (mg kg−1) | 0.22 | 0.66 | 8.7 |
| Water (mg L−1) | 0.20 | 0.60 | 6.3 | |
| Forage (mg kg−1) | 0.004 | 0.012 | 10.1 | |
| Milk (mg kg−1) | 0.002 | 0.006 | 10.5 | |
| Zn | Soil (mg kg−1) | 0.11 | 0.33 | 10.3 |
| Water (mg L−1) | 0.33 | 1.00 | 3.2 | |
| Forage (mg kg−1) | 0.007 | 0.020 | 9.3 | |
| Milk (mg kg−1) | 0.003 | 0.010 | 9.9 |
| Concentration (n = 10) | Pb | Cd | Cu | Zn | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Soil | Range | 12.4–479 | 0.75–8.36 | 38.3–211 | 117–590 |
| Mean ± SD | 205 ± 164 | 4.34 ± 2.54 | 95.9 ± 55.2 | 283 ± 160 | |
| Median | 187 | 3.78 | 77.3 | 220 | |
| LV 1 | 50/100 | 3/5 | 100/200 | 300/600 | |
| n > LV | 70%/60% | 60%/40% | 30%/10% | 30%/0% | |
| Water | Range | 2.70–11.7 | 0.340–2.80 | 24.8–85.2 | 673–1570 |
| Mean ± SD | 5.20 ± 2.51 | 0.816 ± 0.761 | 51.7 ± 19.5 | 1041 ± 320 | |
| Median | 4.82 | 0.535 | 49.9 | 891 | |
| LV 2 | 10 | 5 | 100 | 5000 | |
| n > LV | 10% | 0% | 0% | 0% | |
| Forage | Range | 0.15–2.24 | 0.10–1.44 | 3.43–10.8 | 13.4–53.9 |
| Mean ± SD | 0.80 ± 0.66 | 0.41 ± 0.42 | 6.37 ± 2.20 | 28.4 ± 13.8 | |
| Median | 0.59 | 0.26 | 6.33 | 28.9 | |
| LV 3 | 30 | 1.0 | - | - | |
| n > LV | 0% | 10% | - | - | |
| Milk | Range | 0.010–0.048 | 0.003–0.011 | 0.095–0.446 | 2.38–4.38 |
| Mean ± SD | 0.024 ± 0.015 | 0.007 ± 0.003 | 0.265 ± 0.111 | 3.18 ± 0.665 | |
| Median | 0.018 | 0.007 | 0.286 | 2.94 | |
| LV 4 | 0.02 | - | - | - | |
| n > LV | 50% | - | - | - | |
| Pb | Cd | Cu | Zn | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TFsf | Range | 0.002–0.012 | 0.035–0.187 | 0.039–0.122 | 0.068–0.208 |
| Mean ± SD | 0.005 ± 0.003 | 0.094 ± 0.057 | 0.076 ± 0.025 | 0.107 ± 0.041 | |
| Median | 0.005 | 0.060 | 0.070 | 0.092 | |
| TFfm | Range | 0.015–0.075 | 0.006–0.067 | 0.022–0.071 | 0.075–0.247 |
| Mean ± SD | 0.040 ± 0.021 | 0.028 ± 0.021 | 0.042 ± 0.015 | 0.133 ± 0.061 | |
| Median | 0.037 | 0.021 | 0.040 | 0.117 | |
| Metal | EDI, µg·day−1 | EWI, µg·week−1 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Female | Male | Children | Female | Male | Children | |
| Pb | 4.82 | 7.24 | 12.1 | 33.8 | 50.6 | 84.4 |
| Cd | 1.35 | 2.03 | 3.38 | 9.45 | 14.2 | 23.6 |
| Cu | 53.0 | 79.5 | 132 | 371 | 556 | 927 |
| Zn | 636 | 953 | 1589 | 4449 | 6674 | 11123 |
| HQ/HI | n = 10 | Male | Female | Children |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HQPb | Range | 0.007–0.034 | 0.005–0.026 | 0.010–0.049 |
| Mean ± SD | 0.017 ± 0.011 | 0.013 ± 0.008 | 0.025 ± 0.015 | |
| Median | 0.013 | 0.010 | 0.019 | |
| HQCd | Range | 0.008–0.032 | 0.006–0.025 | 0.011–0.047 |
| Mean ± SD | 0.019 ± 0.009 | 0.015 ± 0.007 | 0.028 ± 0.013 | |
| Median | 0.019 | 0.014 | 0.027 | |
| HQCu | Range | 0.007–0.032 | 0.005–0.024 | 0.010–0.046 |
| Mean ± SD | 0.019 ± 0.008 | 0.015 ± 0.006 | 0.027 ± 0.011 | |
| Median | 0.020 | 0.016 | 0.029 | |
| HQZn | Range | 0.023–0.042 | 0.017–0.032 | 0.033–0.060 |
| Mean ± SD | 0.030 ± 0.006 | 0.023 ± 0.005 | 0.044 ± 0.009 | |
| Median | 0.028 | 0.021 | 0.040 | |
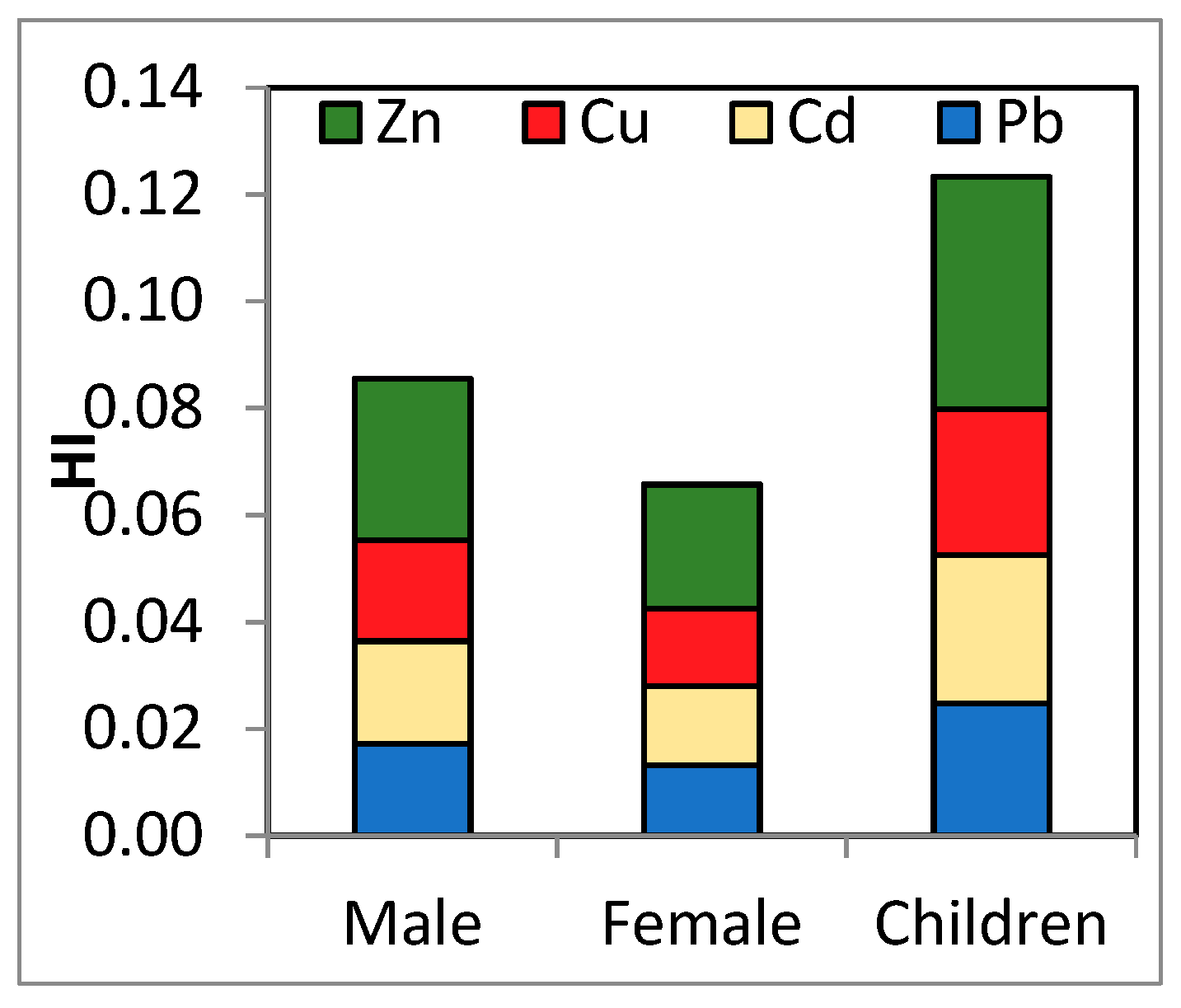
| HI | Range | 0.050–0.131 | 0.038–0.101 | 0.072–0.189 |
| Mean ± SD | 0.085 ± 0.030 | 0.066 ± 0.023 | 0.123 ± 0.044 | |
| Median | 0.080 | 0.062 | 0.116 |
| CR/TCR | n = 10 | Male | Female | Children |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CRPb | Range | 2.4 10−7–1.2 10−6 | 1.8 10−7–9.0 10−7 | 3.4 10−6–1.7 10−5 |
| Mean ± SD | 5.8 10−7 ± 3.6 10−7 | 4.5 10−7 ± 2.8 10−7 | 8.4 10−6 ± 5.2 10−6 | |
| Median | 4.4 10−7 | 3.4 10−7 | 6.4 10−6 | |
| CRCd | Range | 1.2 10−4–4.9 10−4 | 9.2 10−5–3.7 10−4 | 1.7 10−4–7.0 10−4 |
| Mean ± SD | 2.9 10−4 ± 1.4 10−4 | 2.2 10−4 ± 1.0 10−4 | 4.2 10−4 ± 2.0 10−4 | |
| Median | 2.8 10−4 | 2.2 10−4 | 4.1 10−4 | |
| TCR | Range | 1.2 10−4–4.9 10−4 | 9.2 10−5–3.8 10−4 | 1.8 10−5–7.2 10−4 |
| Mean ± SD | 2.9 10−4 ± 1.4 10−4 | 2.2 10−4 ± 1.0 10−4 | 4.2 10−4 ± 2.0 10−4 | |
| Median | 2.8 10−4 | 2.2 10−4 | 4.1 10−4 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Miclean, M.; Cadar, O.; Levei, E.A.; Roman, R.; Ozunu, A.; Levei, L. Metal (Pb, Cu, Cd, and Zn) Transfer along Food Chain and Health Risk Assessment through Raw Milk Consumption from Free-Range Cows. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 4064. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16214064
Miclean M, Cadar O, Levei EA, Roman R, Ozunu A, Levei L. Metal (Pb, Cu, Cd, and Zn) Transfer along Food Chain and Health Risk Assessment through Raw Milk Consumption from Free-Range Cows. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2019; 16(21):4064. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16214064
Chicago/Turabian StyleMiclean, Mirela, Oana Cadar, Erika Andrea Levei, Radu Roman, Alexandru Ozunu, and Levente Levei. 2019. "Metal (Pb, Cu, Cd, and Zn) Transfer along Food Chain and Health Risk Assessment through Raw Milk Consumption from Free-Range Cows" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 16, no. 21: 4064. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16214064
APA StyleMiclean, M., Cadar, O., Levei, E. A., Roman, R., Ozunu, A., & Levei, L. (2019). Metal (Pb, Cu, Cd, and Zn) Transfer along Food Chain and Health Risk Assessment through Raw Milk Consumption from Free-Range Cows. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 16(21), 4064. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16214064







