Informing Behaviour Change: What Sedentary Behaviours Do Families Perform at Home and How Can They Be Targeted?
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample
2.2. Measures
2.3. Data Management and Analysis
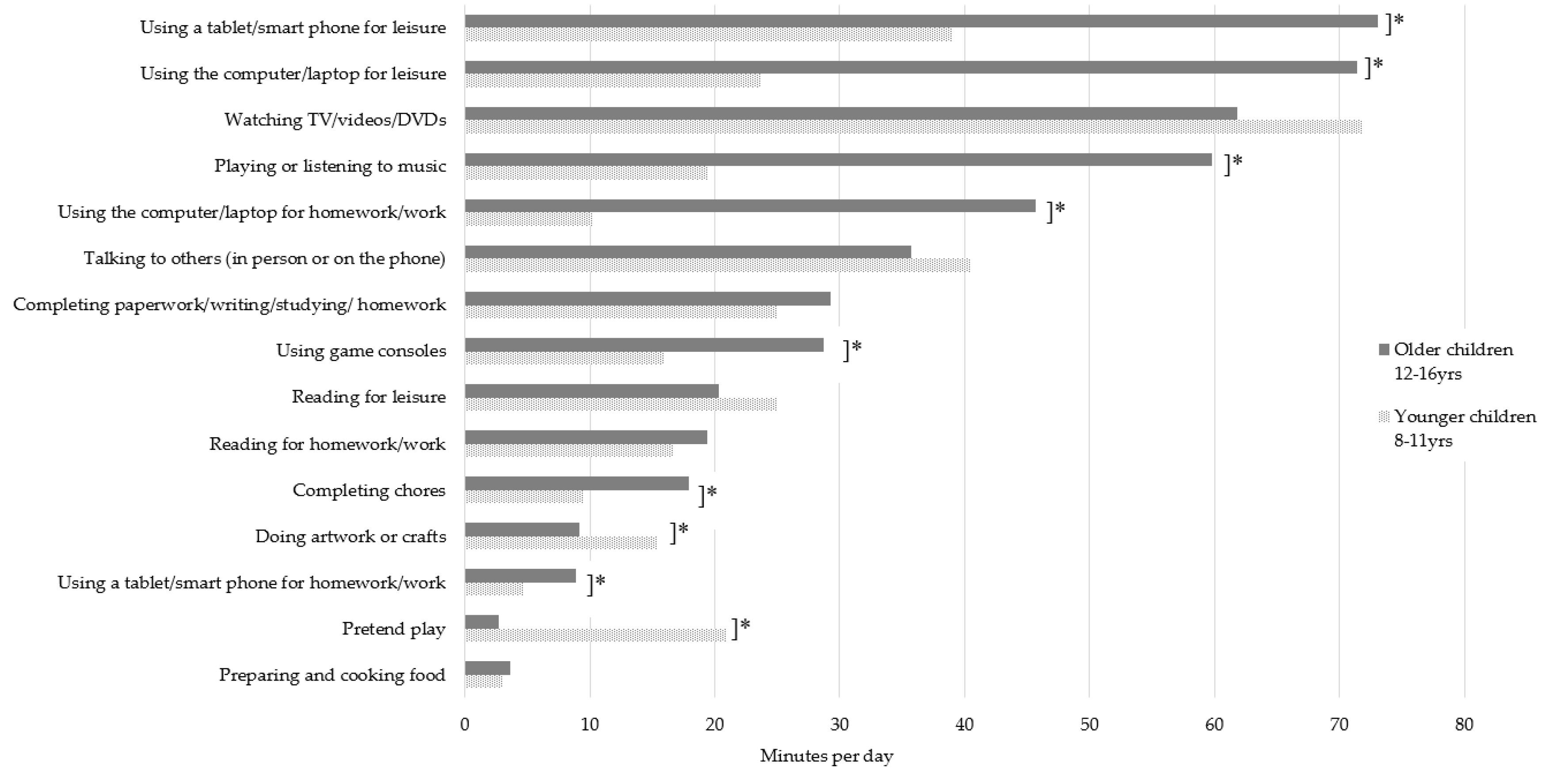
3. Results
3.1. Prevalence of Parent and Child Home-Based Sitting Behaviours
3.2. Sedentary Behaviours Children and Parents Could Change
3.3. Impacts of Sedentary Behaviour on Child Health
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tremblay, M.S.; Participants, O.B.O.S.T.C.P.; Aubert, S.; Barnes, J.D.; Saunders, T.J.; Carson, V.; Latimer-Cheung, A.E.; Chastin, S.F.; Altenburg, T.M.; Chinapaw, M.J.; et al. Sedentary Behavior Research Network (SBRN)—Terminology Consensus Project process and outcome. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2017, 14, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tremblay, M.S.; Leblanc, A.G.; Kho, M.E.; Saunders, T.J.; Larouche, R.; Colley, R.C.; Goldfield, G.; Gorber, S.C. Systematic review of sedentary behaviour and health indicators in school-aged children and youth. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2011, 8, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chastin, S.F.M.; De Craemer, M.; Lien, N.; Bernaards, C.; Buck, C.; Oppert, J.-M.; Nazare, J.-A.; Lakerveld, J.; O’Donoghue, G.; Holdsworth, M.; et al. The SOS-framework (Systems of Sedentary behaviours): An international transdisciplinary consensus framework for the study of determinants, research priorities and policy on sedentary behaviour across the life course: A DEDIPAC-study. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2016, 13, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aubert, S.; Barnes, J.D.; Abdeta, C.; Nader, P.A.; Adeniyi, A.F.; Aguilar-Farias, N.; Tenesaca, D.S.A.; Bhawra, J.; Brazo-Sayavera, J.; Cardon, G.; et al. Global Matrix 3.0 Physical Activity Report Card Grades for Children and Youth: Results and Analysis From 49 Countries. J. Phys. Act. Health 2018, 15, S251–S273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Active Healthy Kids Australia. Muscular Fitness: It’s Time for a Jump Start. The 2018 Active Healthy Kids Australia Report Card on Physical Activity for Children and Young People; Active Healthy Kids Australia: Adelaide, South Australia, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Marsh, S.; Foley, L.S.; Wilks, D.C.; Maddison, R. Family-based interventions for reducing sedentary time in youth: A systematic review of randomized controlled trials. Obes. Rev. 2014, 15, 117–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biddle, S.J.H.; Petrolini, I.; Pearson, N. Interventions designed to reduce sedentary behaviours in young people: A review of reviews. Br. J. Sports Med. 2014, 48, 182–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altenburg, T.M.; Holthe, J.K.-V.; Chinapaw, M.J.M. Effectiveness of intervention strategies exclusively targeting reductions in children’s sedentary time: A systematic review of the literature. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2016, 13, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavelka, J.; Husarova, D.; Sevcikova, A.; Geckova, A.M. Country, age, and gender differences in the prevalence of screen-based behaviour and family-related factors among school-aged children. Acta Gymnica 2016, 46, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bucksch, J.; Sigmundova, D.; Hamrik, Z.; Troped, P.J.; Melkevik, O.; Ahluwalia, N.; Borraccino, A.; Tynjälä, J.; Kalman, M.; Inchley, J. International Trends in Adolescent Screen-Time Behaviors From 2002 to 2010. J. Adolesc. Health 2016, 58, 417–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, S.; Kim, H.; Kang, M.; Pedisic, Z.; Loprinzi, P.D. Secular Trends in Sedentary Behavior Among High School Students in the United States, 2003 to 2015. Am. J. Health Promot. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Australian Bureau of Statistics. Children’s Participation in Cultural and Leisure Activities; Commonwealth of Australia: Canberra, Australia, 2012.
- Arundell, L.; Fletcher, E.; Salmon, J.; Veitch, J.; Hinkley, T. A systematic review of the prevalence of sedentary behavior during the after-school period among children aged 5–18 years. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2016, 13, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klitsie, T.; Corder, K.; Visscher, T.L.; Atkin, A.J.; Jones, A.P.; Van Sluijs, E.M. Children’s sedentary behaviour: Descriptive epidemiology and associations with objectively-measured sedentary time. BMC Public Health 2013, 13, 1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Australian Government Department of Health. Australia’s Physical Activity & Sedentary Behaviour Guidelines for Children (5–12 Years); Australian Government: Canberra, Australia, 2014.
- Canadian Society for Exercise Physiology (CSEP). Canadian 24-Hour Movement Guidelines for Children and Youth (Ages 5–17 Years); Australian Government: Canberra, Australia, 2016.
- Ball, K.; Cleland, V.; Dollman, J.; Turrell, G. Action Area 7: Disadvantaged Populations. In Blueprint for an Active Australia, 2nd ed.; National Heart Foundation of Australia: Melbourne, Australia, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Cornwall, A.; Jewkes, R. What is participatory research? Soc. Sci. Med. 1995, 41, 1667–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauman, A.E.; Petersen, C.B.; Blond, K.; Rangul, V.; Hardy, L.L. The Descriptive Epidemiology of Sedentary Behaviour. In Sedentary Behaviour Epidemiology; Leitzmann, M.F., Jochem, C., Schmid, D., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 73–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjelland, M.; Soenens, B.; Bere, E.; Kovacs, E.; Lien, N.; Maes, L.; Manios, Y.; Moschonis, G.; Velde, S.J.T. Associations between parental rules, style of communication and children’s screen time. BMC Public Health 2015, 15, 1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMinn, A.M.; Griffin, S.J.; Jones, A.P.; van Sluijs, E.M.F. Family and home influences on children’s after-school and weekend physical activity. Eur. J. Public Health 2012, 23, 805–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garriguet, D.; Colley, R.; Bushnik, T. Parent-Child association in physical activity and sedentary behaviour. Health Rep. 2017, 28, 3–11. [Google Scholar]
- Totland, T.H.; Bjelland, M.; Lien, N.; Bergh, I.H.; Gebremariam, M.K.; Grydeland, M.; Ommundsen, Y.; Andersen, L.F. Adolescents’ prospective screen time by gender and parental education, the mediation of parental influences. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2013, 10, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanders, W.; Parent, J.; Forehand, R.; Breslend, N.L.; Lafko, N. The roles of general and technology-related parenting in managing youth screen time. J. Fam. Psychol. 2016, 30, 641–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauricella, A.R.; Wartella, E.; Rideout, V.J. Young children’s screen time: The complex role of parent and child factors. J. Appl. Dev. Psychol. 2015, 36, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carson, V.; Cliff, D.P.; Janssen, X.; Okely, A.D. Longitudinal levels and bouts of sedentary time among adolescent girls. BMC Pediatr. 2013, 13, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fletcher, E.A.; Salmon, J.; McNaughton, S.A.; Orellana, L.; Wadley, G.D.; Bruce, C.; Dempsey, P.C.; Lacy, K.E.; Dunstan, D.W. Effects of breaking up sitting on adolescents’ postprandial glucose after consuming meals varying in energy: A cross-over randomised trial. J. Sci. Med. Sport 2018, 21, 280–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Healy, G.N.; Matthews, C.E.; Dunstan, D.W.; Winkler, E.A.; Owen, N. Sedentary time and cardio-metabolic biomarkers in US adults: NHANES 2003–06. Eur. Hear. J. 2011, 32, 590–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stierlin, A.S.; De Lepeleere, S.; Cardon, G.; Dargent-Molina, P.; Hoffmann, B.; Murphy, M.H.; Kennedy, A.; O’Donoghue, G.; Chastin, S.F.M.; De Craemer, M.; et al. A systematic review of determinants of sedentary behaviour in youth: A DEDIPAC-study. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2015, 12, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dietz, W.H.; Gortmaker, S.L. Preventing Obesity in Children and Adolescents 1. Annu. Rev. Public Health 2001, 22, 337–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campbell, K.J.; Lioret, S.; McNaughton, S.A.; Crawford, D.A.; Salmon, J.; Ball, K.; McCallum, Z.; Gerner, B.E.; Spence, A.; Cameron, A.; et al. A Parent-Focused Intervention to Reduce Infant Obesity Risk Behaviors: A Randomized Trial. Pediatrics 2013, 131, 652–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]

| Children | Parents | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | Mean mins/day (±SD) | n | Mean mins/day (±SD) | |
| Watching TV/videos/DVDs | 430 | 67.5 (±59.3) | 397 | 62.5 (±64.9) |
| Using a tablet/smart phone for leisure | 424 | 53.6 (±70.3) | 425 | 80.8 (±104.2) |
| Using the computer/laptop for leisure | 434 | 42.7 (±72.0) | 432 | 38.3 (±63.7) |
| Talking to others (in person or on the phone) | 397 | 39.3 (±72.4) | 410 | 47.4 (±79.1) |
| Playing or listening to music | 400 | 35.9 (±69.9) | 418 | 27.7 (±88.5) |
| Completing paperwork/writing/studying/homework | 364 | 26.7 (±65.2) | 403 | 13.4 (±42.4) |
| Using the computer/laptop for homework/work | 456 | 24.5 (±57.7) | 426 | 47.2 (±91.7) |
| Reading for leisure | 386 | 23.2 (±32.8) | 405 | 25.9 (±49.2) |
| Using game consoles | 404 | 21.1 (±50.0) | 426 | 1.5 (±12.7) |
| Reading for homework/work | 355 | 17.7 (±49.8) | 414 | 9.1 (±35.1) |
| Pretend play | 379 | 13.6 (±26.7) | 415 | 3.1 (±29.6) |
| Doing artwork or crafts | 369 | 13.0 (±24.3) | 414 | 7.4 (±28.3) |
| Completing chores | 395 | 13.0 (±35.0) | 416 | 52.8 (±99.6) |
| Using a tablet/smart phone for homework/work | 404 | 3.7 (±19.7) | 414 | 11.9 (±30.1) |
| Preparing and cooking food | 387 | 3.2 (±7.8) | 427 | 25.5 (±65.2) |
| Total sedentary behaviours | 192 | 427.3 (±264.3) | 250 | 485.2 (±530.3) |
| Total screen-based sedentary behaviours | 290 | 218.0 (±165.1) | 324 | 250.7 (±233.2) |
| Total non-screen-based sedentary behaviours | 217 | 197.7 (±164.1) | 290 | 218.2 (±337.2) |
| Children | Parents | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| If Trying to Reduce Home-Based Sitting, Could You/Your Child Reduce Time Spent… | Yes, Definitely Could Reduce (%) | Maybe Could Reduce (%) | Yes, Definitely Could Reduce (%) | Maybe Could Reduce (%) |
| Using a tablet/smart phone for leisure | 58.9 | 31.8 | 64.5 | 26.3 |
| Using game consoles | 52.6 | 28.2 | 38.5 | 23.9 |
| Watching TV/videos/DVDs | 50.2 | 37.7 | 52.2 | 30.5 |
| Using the computer/laptop for leisure | 50.5 | 35.3 | 53.2 | 28.6 |
| Using a tablet/smart phone for homework/work | 20.1 | 23.2 | 35.4 | 25.1 |
| Using the computer/laptop for homework/work | 15.9 | 24.1 | 32.7 | 21.9 |
| Playing or listening to music | 7.4 | 29.6 | 22.2 | 27.1 |
| Talking to others (in person or on the phone) | 6.9 | 24.1 | 27.9 | 31.9 |
| Pretend play | 6.9 | 19.9 | 26.1 | 17.9 |
| Completing paperwork/writing/studying/homework | 5.4 | 20.7 | 19.7 | 24.9 |
| Doing artwork or crafts | 4.5 | 20.7 | 23.9 | 23.0 |
| Completing chores | 6.6 | 14.5 | 23.0 | 20.1 |
| Reading for leisure | 3.8 | 16.7 | 17.1 | 24.0 |
| Preparing and cooking food | 5.5 | 15.0 | 19.8 | 13.6 |
| Reading for homework/work | 3.5 | 14.3 | 18.9 | 23.3 |
| Statement: Would You Try to Reduce Your Child’s Sitting at Home If Told Sitting Too Much Could… | % Parents Likely to Try to Reduce Child’s Sitting |
|---|---|
| Increase their risk for poor mental health | 85.2 |
| Adversely impact future health as an adult | 85.1 |
| Increase their risk for poor muscle and bone health | 82.7 |
| Increase their risk factors for diabetes and cardiovascular disease risk | 81.4 |
| Increase their risk for overweight and obesity | 79.1 |
| Adversely impact academic outcomes | 79.1 |
| Adversely impact their social skills | 78.5 |
| Adversely impact their level of resilience | 77.6 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Arundell, L.; Parker, K.; Salmon, J.; Veitch, J.; Timperio, A. Informing Behaviour Change: What Sedentary Behaviours Do Families Perform at Home and How Can They Be Targeted? Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 4565. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16224565
Arundell L, Parker K, Salmon J, Veitch J, Timperio A. Informing Behaviour Change: What Sedentary Behaviours Do Families Perform at Home and How Can They Be Targeted? International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2019; 16(22):4565. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16224565
Chicago/Turabian StyleArundell, Lauren, Kate Parker, Jo Salmon, Jenny Veitch, and Anna Timperio. 2019. "Informing Behaviour Change: What Sedentary Behaviours Do Families Perform at Home and How Can They Be Targeted?" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 16, no. 22: 4565. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16224565
APA StyleArundell, L., Parker, K., Salmon, J., Veitch, J., & Timperio, A. (2019). Informing Behaviour Change: What Sedentary Behaviours Do Families Perform at Home and How Can They Be Targeted? International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 16(22), 4565. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16224565






