Key Risk Factors Affecting Farmers’ Mental Health: A Systematic Review
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Identification
2.2. Screening Questions
- Are farmers included as a general study population? (y/n)
- Are any kind of “mental disorders” part of the study? (y/n)
2.3. Eligibility Assessment
- Does the study clearly mention which risk factors/stressors affect farmers’ mental health (y/n)?
- Does the study detail the direction on farmers’ mental health (+/−/0)?
2.4. Assessment of the Quality of the Studies and Detection of Possible Bias
3. Systematic Review Results
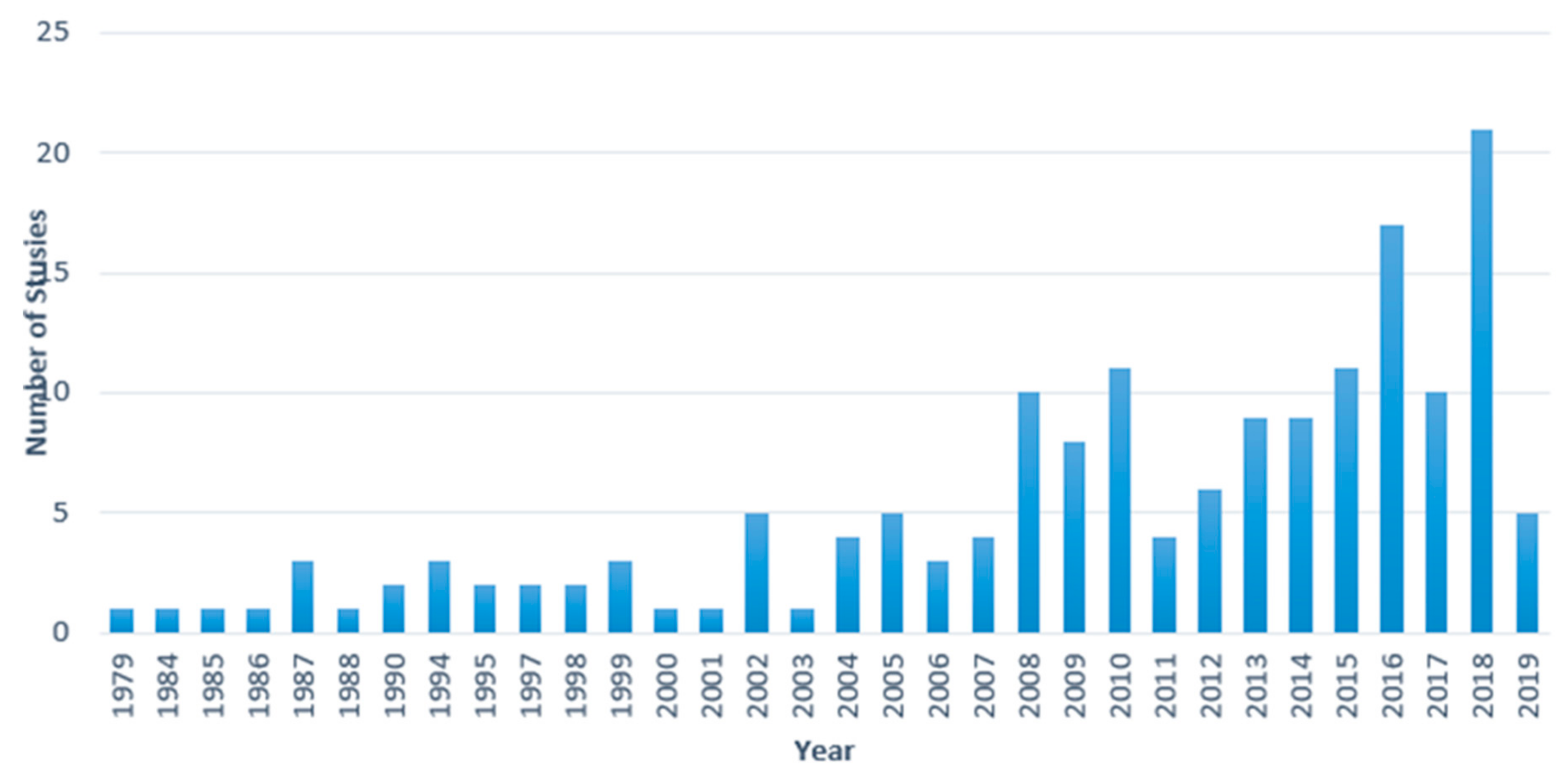
3.1. Geographic Focus
3.2. Measures and Methods of Farmer Mental Health and Assessment of Quality
3.3. Mental Disorders among Farmers Versus Non-Farmers
3.4. Farm Risk Factors
3.4.1. Pesticide Exposure
3.4.2. Financial Pressures
3.4.3. Climate Variability
3.4.4. Poor Physical Health/Past Injury
3.4.5. Other Risk Factors
3.5. Socio-Demographic and Farm Characteristics Associated with Mental Health
3.6. Barriers to Help-Seeking Behaviour
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Risk of Bias Assessment Questions
References
- Gregoire, A. The mental health of farmers. Occup. Med. 2002, 52, 471–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fraser, C.E.; Smith, K.B.; Judd, F.; Humphreys, J.S.; Fragar, L.J.; Henderson, A. Farming and mental health problems and mental illness. Int. J. Soc. Psychiatry 2005, 51, 340–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, P.; Tremblay, G.; Oliffe, J.L.; Jbilou, J.; Robertson, S. Male farmers with mental health disorders: A scoping review. Aust. J. Rural Health 2013, 21, 3–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Price, L.; Evans, N. From stress to distress: Conceptualizing the British family farming patriarchal way of life. J. Rural Stud. 2009, 25, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, J.L.; Walker, L.S.; MacLennan, P.M. An informal look at farm stress. Psychol. Rep. 1986, 59, 427–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raine, G. Causes and effects of stress on farmers: A qualitative study. Health Educ. J. 1999, 58, 259–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McShane, C.J.; Quirk, F.; Swinbourne, A. Development and validation of a work stressor scale for Australian farming families. Aust. J. Rural Health 2016, 24, 238–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vega, W.; Warheit, G.; Palacio, R. Psychiatric symptomatology among Mexican American farmworkers. Soc. Sci. Med. 1985, 20, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staniford, A.K.; Dollard, M.F.; Guerin, B. Stress and help-seeking for drought-stricken citrus growers in the Riverland of South Australia. Aust. J. Rural Health 2009, 17, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firth, H.M.; Williams, S.M.; Herbison, G.P.; McGee, R.O. Stress in New Zealand farmers. Stress Health J. Int. Soc. Investig. Stress 2007, 23, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mora, D.C.; Quandt, S.A.; Chen, H.; Arcury, T.A. Associations of Poor Housing with Mental Health Among North Carolina Latino Migrant Farmworkers. J. Agromedicine 2016, 21, 327–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hovey, J.D.; Magaña, C.G. Exploring the Mental Health of Mexican Migrant Farm Workers in the Midwest: Psychosocial Predictors of Psychological Distress and Suggestions for Prevention and Treatment. J. Psychol. 2002, 136, 493–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Logstein, B. Farm-Related Concerns and Mental Health Status Among Norwegian Farmers. J. Agromedicine 2016, 21, 316–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanklang, S.; Kaewboonchoo, O.; Morioka, I.; Plernpit, S.-A. Gender Differences in Depression Symptoms Among Rice Farmers in Thailand. Asia Pac. J. Public Health 2016, 28, 83–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, R.T. The on-going farm crisis: Extension leadership in rural communities. J. Ext. 1996, 34, 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Hedlund, D.; Berkowitz, A. The incidence of socialpsychologicl stress in farm families. Int. J. Sociol. Fam. 1979, 9, 233–243. [Google Scholar]
- Hossain, D.; Eley, R.; Coutts, J.; Gorman, D. Mental health of farmers in Southern Queensland: Issues and support. Aust. J. Rural Health 2008, 16, 343–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiott, A.E.; Grzywacz, J.G.; Davis, S.W.; Quandt, S.A.; Arcury, T.A. Migrant Farmworker Stress: Mental Health Implications. J. Rural Health 2008, 24, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hovey, J.D.; Magaña, C.G. Psychosocial Predictors of Anxiety Among Immigrant Mexican Migrant Farmworkers: Implications for Prevention and Treatment. Cult. Divers. Ethn. Minority Psychol. 2002, 8, 274–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, A.; Su, D.; Lander, L.; Rivera, R. Stress Factors Contributing to Depression Among Latino Migrant Farmworkers in Nebraska. J. Immigr. Minority Health 2015, 17, 1627–1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deary, I.J.; Willock, J.; McGregor, M. Stress In Farming. Stress Med. 1997, 13, 131–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grzywacz, J.G.; Quandt, S.A.; Chen, H.; Isom, S.; Kiang, L.; Vallejos, Q.; Arcury, T.A. Depressive Symptoms Among Latino Farmworkers Across the Agricultural Season: Structural and Situational Influences. Cult. Divers. Ethn. Minority Psychol. 2010, 16, 335–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bin, H.; Lamm, F.; Tipples, R. The Impact of Stressors on the Psychological Wellbeing of New Zealand Farmers and The Development of an Explanatory Conceptual Model. Policy Pract. Health Saf. 2008, 6, 79–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simkin, S.; Hawton, K.; Fagg, J.; Malmberg, A. Stress in farmers: A survey of farmers in England and Wales. Occup. Environ. Med. 1998, 55, 729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carvajal, S.; Kibor, C.; McClelland, D.; Ingram, M.; Zapien, J.; Torres, E.; Redondo, F.; Rodriguez, K.; Rubio-Goldsmith, R.; Meister, J.; et al. Stress and Sociocultural Factors Related to Health Status Among US–Mexico Border Farmworkers. J. Immigr. Minority Health 2014, 16, 1176–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wheeler, S.A.; Zuo, A.; Loch, A. Water torture: Unravelling the psychological distress of irrigators in Australia. J. Rural Stud. 2018, 62, 183–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lunner Kolstrup, C.; Kallioniemi, M.; Lundqvist, P.; Kymäläinen, H.-R.; Stallones, L.; Brumby, S. International Perspectives on Psychosocial Working Conditions, Mental Health, and Stress of Dairy Farm Operators. J. Agromedicine 2013, 18, 244–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kearney, G.D.; Rafferty, A.P.; Hendricks, L.R.; Allen, D.L.; Tutor-Marcom, R. A cross-sectional study of stressors among farmers in eastern North Carolina. N. C. Med. J. 2014, 75, 384–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, R. The ongoing farm crisis: Health, mental health and safety issues in Wisconsin. Rural Ment. Health 2001, 26, 15–17. [Google Scholar]
- Walker, L.S.; Walker, J.L. Stressors and symptoms predictive of distress in farmers. Fam. Relat. 1987, 36, 374–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simsek, Z.; Ersin, F.; Kirmizitoprak, E. Development of the Seasonal Migrant Agricultural Worker Stress Scale in Sanliurfa, Southeast Turkey. J. Agromedicine 2015, 21, 56–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Connor, K.; Stoecklin-Marois, M.; Schenker, M.B. Examining nervios among immigrant male farmworkers in the MICASA study: Sociodemographics, housing conditions and psychosocial factors. J. Immigr. Minority Health 2015, 17, 198–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terrazas, S.R.; McCormick, A. Coping Strategies That Mitigate Against Symptoms of Depression Among Latino Farmworkers. Hisp. J. Behav. Sci. 2018, 40, 57–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.-P.; Qin, P.; Liu, Y.-Y.; Yuan, L.; Gu, L.-X.; Jia, C.-X. Mental disorders and suicide attempt in rural China. Psychiatry Res. 2018, 261, 190–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glasscock, D.J.; Rasmussen, K.; Carstensen, O.; Hansen, O.N. Psychosocial factors and safety behaviour as predictors of accidental work injuries in farming. Work Stress 2006, 20, 173–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olowogbon, T.S.; Yoder, A.M.; Fakayode, S.B.; Falola, A.O. Agricultural stressors: Identification, causes and perceived effects among Nigerian crop farmers. J. Agromedicine 2019, 24, 46–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kallioniemi, M.K.; Simola, A.; Kaseva, J.; Kymäläinen, H.-R. Stress and Burnout Among Finnish Dairy Farmers. J. Agromedicine 2016, 21, 259–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, A.N.; Fragar, L.J. Suicide in Australian farming. Aust. N. Z. Psychiatry 2002, 36, 81–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, A. Farmers’ Suicide in India: Implications for Public Mental Health. Int. J. Soc. Psychiatry 2011, 57, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunde, L.; Kõlves, K.; Kelly, B.; Reddy, P.; De Leo, D. Pathways to suicide in Australian farmers: A life chart analysis. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Perceval, M.; Kõlves, K.; Reddy, P.; De Leo, D. Farmer suicides: A qualitative study from Australia. Occup. Med. 2017, 67, 383–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- World Health Organization. Mental Health: Strengthening Mental Health Promotion; Fact Sheet No 220; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. Depression and Other Common Mental Disorders: Global Health Estimates; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. Promoting Mental Health: Concepts, Emerging Evidence, Practice: Summary Report; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Department of Health and Ageing. National Mental Health Report 2013: Tracking Progress of Mental Health Reform in Australia 1993–2011; Commonwealth of Australia: Canberra, Australia.
- Moher, D.; Liberati, A.; Tetzlaff, J.; Altman, D.G. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: The PRISMA statement. Ann. Intern. Med. 2009, 151, 264–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Handbook for Conducting a Literature-Based Health Assessment Using OHAT Approach for Systematic Review and Evidence Integration; Office of Health Assessment and Translation, Division of National Toxicology Program, National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences; U.S. Department of Health and Human Services: Washington, DC, USA. Available online: https://ntp.niehs.nih.gov/ntp/ohat/pubs/handbookjan2015_508.pdf (accessed on 7 November 2019).
- Berkowitz, A.; Wesley Perkins, H. Stress among farm women: Work and family as interacting systems. J. Marriage Fam. 1984, 46, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega, S.T.; Johnson, D.R.; Beeson, P.G.; Craft, B.J. The farm crisis and mental health: A longitudinal study of the 1980s. Rural Sociol. 1994, 59, 598–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kallioniemi, M.K.; Simola, A.J.K.; Kymäläinen, H.-R.; Vesala, H.T.; Louhelainen, J.K. Mental symptoms among Finnish farm entrepreneurs. Ann. Agric. Environ. Med. 2009, 16, 159–168. [Google Scholar]
- Beseler, C.; Stallones, L.; Hoppin, J.A.; Alavanja, M.C.; Blair, A.; Keefe, T.; Kamel, F. Depression and pesticide exposures in female spouses of licensed pesticide applicators in the agricultural health study cohort. J. Occup. Environ. Med. 2006, 48, 1005–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onwuameze, O.E.; Paradiso, S.; Peek-Asa, C.; Donham, K.J.; Rautiainen, R.H. Modifiable risk factors for depressed mood among farmers. Ann. Clin. Psychiatry 2013, 25, 83–90. [Google Scholar]
- Fennell, K.M.; Jarrett, C.E.; Kettler, L.J.; Dollman, J.; Turnbull, D.A. “Watching the bank balance build up then blow away and the rain clouds do the same”: A thematic analysis of South Australian farmers’ sources of stress during drought. J. Rural Stud. 2016, 46, 102–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zwerling, C.; Sprince, N.; Wallace, R.; Davis, C.; Whitten, P.; Heeringa, S. Occupational injuries among agricultural workers 51 to 61 years old: A national study. J. Agric. Saf. Health 1995, 4, 237–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otsuka, K.; Kato, S. Relationship between Diagnostic Subtypes of Depression and Occupation in Japan. Psychopathology 2000, 33, 324–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weisskopf, M.G.; Moisan, F.; Tzourio, C.; Rathouz, P.J.; Elbaz, A. Pesticide Exposure and Depression Among Agricultural Workers in France. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2013, 178, 1051–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Garnefski, N.; Baan, N.; Kraaij, V. Psychological distress and cognitive emotion regulation strategies among farmers who fell victim to the foot-and-mouth crisis. Personal. Individ. Differ. 2005, 38, 1317–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brew, B.; Inder, K.; Allen, J.; Thomas, M.; Kelly, B. The health and wellbeing of Australian farmers: A longitudinal cohort study. BMC Public Health 2016, 16, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Poletto, Â.R.; Gontijo, L.A. Family farming workers mental health in a microrregion in southern Brazil. Work 2012, 41, 4987–4994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wesseling, C.; van Wendel de Joode, B.; Keifer, M.; London, L.; Mergler, D.; Stallones, L. Symptoms of psychological distress and suicidal ideation among banana workers with a history of poisoning by organophosphate or n-methyl carbamate pesticides. Occup. Environ. Med. 2010, 67, 778–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Olff, M.; Koeter, M.W.J.; Van Haaften, E.H.; Kersten, P.H.; Gersons, B.P.R. Impact of a foot and mouth disease crisis on post-traumatic stress symptoms in farmers. Br. J. Psychiatry 2005, 186, 165–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Walker, J.L.; Walker, L.J.S. Self-reported stress symptoms in farmers. J. Clin. Psychol. 1988, 44, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McShane, C.J.; Quirk, F. Mediating and moderating effects of work–home interference upon farm stresses and psychological distress. Aust. J. Rural Health 2009, 17, 244–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Ko, Y.; Lee, W.J. Depressive symptoms and severity of acute occupational pesticide poisoning among male farmers. Occup. Environ. Med. 2013, 70, 303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Z.-R.; Hong, S.-Y.; Han, M.-J.; Lee, H.-S.; Gil, H.-O.; Yang, J.-O.; Lee, E.-Y.; Hong, S.-Y. Clinical observation of 12 farmers who believe themselves to have suffered from chronic pesticide intoxication. Korean J. Intern. Med. 2008, 23, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çakmur, H. Health Risks Faced by Turkish Agricultural Workers. Sci. World J. 2014, 2014, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Alpass, F.; Flett, R.; Humphries, S.; Massey, C.; Morriss, S.; Long, N. Stress in Dairy Farming and the Adoption of New Technology. Int. J. Stress Manag. 2004, 11, 270–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albrecht, G.; Sartore, G.-M.; Connor, L.; Higginbotham, N.; Freeman, S.; Kelly, B.; Stain, H.; Tonna, A.; Pollard, G. Solastalgia: The Distress Caused by Environmental Change. Aust. N. Z. Psychiatry 2007, 15, S95–S98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peel, D.; Berry, H.L.; Schirmer, J. Perceived profitability and well-being in Australian dryland farmers and irrigators. Aust. J. Rural Health 2015, 23, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atreya, K.; Kumar Sitaula, B.; Overgaard, H.; Man Bajracharya, R.; Sharma, S. Knowledge, attitude and practices of pesticide use and acetylcholinesterase depression among farm workers in Nepal. Int. J. Environ. Health Res. 2012, 22, 401–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mackenzie Ross, S.J.; Brewin, C.R.; Curran, H.V.; Furlong, C.E.; Abraham-Smith, K.M.; Harrison, V. Neuropsychological and psychiatric functioning in sheep farmers exposed to low levels of organophosphate pesticides. Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 2010, 32, 452–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hong, S.-Y.; Jeong, D.-S.; Gil, H.-W.; Yang, J.-O.; Lee, E.-Y.; Hong, S.-Y. The estimation of pesticide exposure in depression scores: In case of Korean orchard farmers. J. Pest Sci. 2009, 82, 261–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tribble, A.G.; Summers, P.; Chen, H.; Quandt, S.A.; Arcury, T.A. Musculoskeletal pain, depression, and stress among Latino manual laborers in North Carolina. Arch. Environ. Occup. Health 2016, 71, 309–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayrami, M.; Hashemi, T.; Malekirad, A.A.; Ashayeri, H.; Faraji, F.; Abdollahi, M. Electroencephalogram, cognitive state, psychological disorders, clinical symptom, and oxidative stress in horticulture farmers exposed to organophosphate pesticides. Toxicol. Ind. Health 2012, 28, 90–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillien, A.; Laurent, L.; Soumagne, T.; Puyraveau, M.; Laplante, J.-J.; Andujar, P.; Annesi-Maesano, I.; Roche, N.; Degano, B.; Dalphin, J.-C. Anxiety and depression among dairy farmers: The impact of COPD. Int. J. Chron. Obs. Pulm. Dis. 2018, 13, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- King, D.; Lane, A.; MacDougall, C.; Greenhill, J. The Resilience and Mental Health and Wellbeing of Farm Families Experiencing Climate Variation in South Australia; National Institute of Labour Studies Incorporated: Adelaide, Australia, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Booth, N.J.; Lloyd, K. Stress in farmers. Int. J. Soc. Psychiatry 2000, 46, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rostamabadi, A.; Mazloumi, A.; Rahimi Foroushani, A. Work Ability Index (WAI) and its health-related determinants among Iranian farmers working in small farm enterprises. J. Occup. Health 2014, 56, 478–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eberhardt, B.J.; Pooyan, A. Development of the Farm Stress Survey: Factorial Structure, Reliability, and Validity. Educ. Psychol. Meas. 1990, 50, 393–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hannay, D.; Jones, R. The effects of foot-and-mouth on the health of those involved in farming and tourism in Dumfries and Galloway. Eur. J. Gen. Pract. 2002, 8, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, S.-B.; Kim, T.H.; Min, S.; Lee, K.; Kang, D.R.; Choi, J.R. Exposure to pesticide as a risk factor for depression: A population-based longitudinal study in Korea. Neurotoxicology 2017, 62, 181–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saxena, S.; Rp, V.; Soman, B. Exposure to firearm: Impact on psychological health in central India. Indian J. Community Health 2013, 25, 413–421. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Gu, S.; Duan, S.; Wu, Y.; Ye, C.; Wang, J.; Dong, H. Comparative Study on Health-Related Quality of Life of Farmers and Workers. Value Health Reg. Issues 2017, 12, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L. Stress and mental health of farmer-workers. Chin. J. Ind. Hyg. Occup. Dis. 2005, 23, 418–423. [Google Scholar]
- Jessie, G.; Deborah De, M.; Mathijn, W.; Christophe, V. What’s up with the self-employed? A cross-national perspective on the self-employed’s work-related mental well-being. SSM Popul. Health 2018, 4, 317–326. [Google Scholar]
- Stallones, L.; Beseler, C. Safety practices and depression among farm residents. Ann. Epidemiol. 2004, 14, 571–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syson-Nibbs, L.; Saul, C.; Cox, P. Tideswell health survey: A population survey of the health needs and service utilization of a farming community. Public Health 2006, 120, 221–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elliott, M.; Heaney, C.A.; Wilkins, J.R., III; Mitchell, G.L.; Bean, T. Depression and Perceived Stress Among Cash Grain Farmers in Ohio. J. Agric. Saf. Health 1995, 1, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bean, T.L.; Nolan, J.A. Recognize and manage the stress of farm life. In Agriculture National Resources; Ohio State University: Columbus, OH, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Kolstrup, C.; Lundqvist, P.; Pinzke, S. Psychosocial Work Environment Among Employed Swedish Dairy and Pig Farmworkers. J. Agromedicine 2008, 13, 23–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanne, B.; Mykletun, A.; Moen, B.E.; Dahl, A.A.; Tell, G.S. Farmers are at risk for anxiety and depression: The Hordaland Health Study. Occup. Med. 2004, 54, 92–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wallis, A.; Dollard, M.F. Local and global factors in work stress—the Australian dairy farming examplar. Scand. J. Work Environ. Health 2008, 66–74. [Google Scholar]
- Arcury, T.A.; Sandberg, J.C.; Talton, J.W.; Laurienti, P.J.; Daniel, S.S.; Quandt, S.A. Mental Health Among Latina Farmworkers and Other Employed Latinas in North Carolina. J. Rural Ment. Health 2018, 42, 89–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohidon, C.; Santin, G.; Imbernon, E.; Goldberg, M. Working conditions and depressive symptoms in the 2003 decennial health survey: The role of the occupational category. Soc. Psychiatry Psychiatr. Epidemiol. 2010, 45, 1135–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hounsome, B.; Edwards, R.; Hounsome, N.; Edwards-Jones, G. Psychological Morbidity of Farmers and Non-farming Population: Results from a UK Survey. Community Ment. Health J. 2012, 48, 503–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konstantinos, D.; Eleni, S.; Eleni, J.; Nikolaos, C.; John, E.; Michalis, L. Does Farming Have an Effect on Health Status? A Comparison Study in West Greece. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2013, 10, 776–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rayens, M.K.; Reed, D.B. Predictors of Depressive Symptoms in Older Rural Couples: The Impact of Work, Stress and Health. J. Rural Health 2014, 30, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thelin, A.G. Working environment conditions in rural areas according to psychosocial indices. Ann. Agric. Environ. Med. 1998, 5, 139. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Torske, M.O.; Hilt, B.; Glasscock, D.; Lundqvist, P.; Krokstad, S. Anxiety and depression symptoms among farmers. The HUNT Study, Norway. J. Agromedicine 2015, 21, 24–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Torske, M.O.; Hilt, B.; Bjørngaard, J.H.; Glasscock, D.; Krokstad, S. Disability pension and symptoms of anxiety and depression: A prospective comparison of farmers and other occupational groups. The HUNT Study, Norway. BMJ Open 2015, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yin, H.; Xu, G.; Tian, H.; Yang, G.; Wardenaar, K.J.; Schoevers, R.A. The prevalence, age-of-onset and the correlates of DSM-IV psychiatric disorders in the Tianjin Mental Health Survey (TJMHS). Psychol. Med. 2018, 48, 473–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ulrich, A.; Molina, Y.; Briant, K.J.; Onstad, L.E.; Copeland, W.; Holte, S.E.; Thompson, B. Stress Among Latinos: Does it Vary by Occupation and Agricultural Season? J. Occup. Environ. Med. 2018, 60, 810–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Judd, F.; Jackson, H.; Fraser, C.; Murray, G.; Robins, G.; Komiti, A. Understanding suicide in Australian farmers. Soc. Psychiatry Psychiatr. Epidemiol. 2006, 41, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, H.V.; Lewis, G.; Thomas, D.R.; Salmon, R.L.; Chalmers, R.M.; Coleman, T.J.; Kench, S.M.; Morgan-Capner, P.; Meadows, D.; Sillis, M.; et al. Mental health of British farmers. Occup. Environ. Med. 2003, 60, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Feng, D.; Ji, L.; Xu, L. Effect of subjective economic status on psychological distress among farmers and non-farmers of rural China. Aust. J. Rural Health 2015, 23, 215–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomasson, K.; Gudmundsson, G. Mental health and wellbeing in Icelandic farmers. Laeknabladid 2009, 95, 763–769. [Google Scholar]
- Stain, H.; Kelly, B.; Lewin, T.; Higginbotham, N.; Beard, J.; Hourihan, F. Social networks and mental health among a farming population. Soc. Psychiatry Psychiatr. Epidemiol. 2008, 43, 843–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malekirad, A.A.; Faghih, M.; Mirabdollahi, M.; Kiani, M.; Fathi, A.; Abdollahi, M. Neurocognitive, mental health, and glucose disorders in farmers exposed to Organophosphorus pesticides.(Report). Arch. Hyg. Toksikol. 2013, 64, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jamal, G.A.; Hansen, S.; Pilkington, A.; Buchanan, D.; Gillham, R.A.; Abdel-Azis, M.; Julu, P.O.O.; Al-Rawas, S.F.; Hurley, F.; Ballantyne, J.P. A clinical neurological, neurophysiological, and neuropsychological study of sheep farmers and dippers exposed to organophosphate pesticides. Occup. Environ. Med. 2002, 59, 434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Aiwerasia, V.F.N.; David, N.M.; Timo, J.P.; Michael, P.S.; Godson, M. Acute health effects of organophosphorus pesticides on Tanzanian small-scale coffee growers. J. Exp. Anal. Environ. Epidemiol. 2001, 11, 335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Steenland, K.; Jenkins, B.; Ames, R.G.; O’Malley, M.; Chrislip, D.; Russo, J. Chronic neurological sequelae to organophosphate pesticide poisoning. Am. J. Public Health 1994, 84, 731–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Corral, S.A.; de Angel, V.; Salas, N.; Zúñiga-Venegas, L.; Gaspar, P.A.; Pancetti, F. Cognitive impairment in agricultural workers and nearby residents exposed to pesticides in the Coquimbo Region of Chile. Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 2017, 62, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muñoz-Quezada, M.T.; Lucero, B.; Iglesias, V.; Levy, K.; Muñoz, M.P.; Achú, E.; Cornejo, C.; Concha, C.; Brito, A.M.; Villalobos, M. Exposure to organophosphate (OP) pesticides and health conditions in agricultural and non-agricultural workers from Maule, Chile. Int. J. Environ. Health Res. 2017, 27, 82–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, V.; Mackenzie Ross, S. Anxiety and depression following cumulative low-level exposure to organophosphate pesticides. Environ. Res. 2016, 151, 528–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quandt, S.A.; Chen, H.; Grzywacz, J.G.; Vallejos, Q.M.; Galvan, L.; Arcury, T.A. Cholinesterase depression and its association with pesticide exposure across the agricultural season among Latino farmworkers in North Carolina. Environ. Health Perspect. 2010, 118, 635–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Beseler, C. Diagnosed Depression and Low, Intermediate, and High Pesticide Exposures in Iowa and North Carolina Farm Applicators and Their Spouses Enrolled in the Agricultural Health Study. Ph.D. Thesis, Colorado State University, Fort Collins, CO, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Da Silva, V.d.S.P.; de Mello, M.S.C.; Otero, U.B. Exposure to pesticides and mental disorders in a rural population of Southern Brazil. Neurotoxicology 2016, 56, 7–16. [Google Scholar]
- Siegel, M.; Starks, S.; Sanderson, W.; Kamel, F.; Hoppin, J.; Gerr, F. Organic solvent exposure and depressive symptoms among licensed pesticide applicators in the Agricultural Health Study. Int. Arch. Occup. Environ. Health 2017, 90, 849–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Povey, A.C.; McNamee, R.; Alhamwi, H.; Stocks, S.J.; Watkins, G.; Burns, A.; Agius, R. Pesticide exposure and screen-positive neuropsychiatric disease in British sheep farmers. Environ. Res. 2014, 135, 262–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Wu, M.; Yao, H.; Yang, Y.; Cui, M.; Tu, Z.; Stallones, L.; Xiang, H. Pesticide poisoning and neurobehavioral function among farm workers in Jiangsu, People’s Republic of China. Cortex 2016, 74, 396–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fariba, T.; Gholamhassan, V.; Mohammad, A.; Ali Akbar, M. A Comparative Study of the Quality of Life, Depression, Anxiety and Stress in Farmers Exposed to Organophosphate Pesticides with those in a Control Group. J. Chem. Health Risks 2016, 6, 143–151. [Google Scholar]
- Conti, C.L.; Barbosa, W.M.; Simão, J.B.P.; Álvares-da-Silva, A.M. Pesticide exposure, tobacco use, poor self-perceived health and presence of chronic disease are determinants of depressive symptoms among coffee growers from Southeast Brazil. Psychiatry Res. 2018, 260, 187–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suten Geofrey, M.; Ezra Jonathan, M.; Aiwerasia Vera, N.; Simon, M. Health Symptoms Associated with Pesticides Exposure among Flower and Onion Pesticide Applicators in Arusha Region. Ann. Glob. Health 2018, 84, 369–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mearns, J.; Dunn, J.; Lees-Haley, P.R. Psychological effects of organophosphate pesticides: A review and call for research by psychologists. J. Clin. Psychol. 1994, 50, 286–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beshwari, M.M.M.; Bener, A.; Ameen, A.; Al-Mehdi, A.M.; Ouda, H.Z.; Pasha, M.A.H. Pesticide-related health problems and diseases among farmers in the United Arab Emirates. Int. J. Environ. Health Res. 1999, 9, 213–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrano-Medina, A.; Ugalde-Lizárraga, A.; Bojorquez-Cuevas, M.S.; Garnica-Ruiz, J.; González-Corral, M.A.; García-Ledezma, A.; Pineda-García, G.; Cornejo-Bravo, J.M. Neuropsychiatric Disorders in Farmers Associated with Organophosphorus Pesticide Exposure in a Rural Village of Northwest México. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kannuri, N.K.; Jadhav, S. Generating toxic landscapes: Impact on well-being of cotton farmers in Telangana, India. Anthropol. Med. 2018, 25, 121–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bryant, L.; Garnham, B. Economies, ethics and emotions: Farmer distress within the moral economy of agribusiness. J. Rural Stud. 2014, 34, 304–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulgar, C.; Trejo, G.; Suerken, C.; Ip, E.; Arcury, T.; Quandt, S. Economic Hardship and Depression Among Women in Latino Farmworker Families. J. Immigr. Minority Health 2016, 18, 497–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Truchot, D.; Andela, M. Burnout and hopelessness among farmers: The Farmers Stressors Inventory. Soc. Psychiatry Psychiatr. Epidemiol. 2018, 5, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kureshi, J.S.; Somsundaram, K. Assessment of occupational stress among farmers in Aurangabad district, Maharashtra. Int. J. Community Med. Public Health 2018, 5, 1434–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Belyea, M.J.; Lobao, L.M. Psychosocial Consequences of Agricultural Transformation: The Farm Crisis and Depression. Rural Sociol. 1990, 55, 58–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bultena, G.; Lasley, P.; Geller, J. The farm crisis: Patterns and impacts of financial distress among Iowa farm families. Rural Sociol. 1986, 51, 436. [Google Scholar]
- Bryant, L.; Garnham, B. Beyond discourses of drought: The micro-politics of the wine industry and farmer distress. J. Rural Stud. 2013, 32, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welke, C. Farm/Ranch Stressors and the Distress and Job Satisfaction of Farm Family Members: The Buffering Effects of Perceived Social Support. Ph.D. Thesis, University of South Dakota, Vermillion, SD, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Lawrence, P.; Maxwell, B.; Rew, L.; Ellis, C.; Bekkerman, A. Vulnerability of dryland agricultural regimes to economic and climatic change. Ecol. Soc. 2018, 23, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dai, A. Increasing drought under global warming in observations and models. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2013, 3, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vins, H.; Bell, J.; Saha, S.; Hess, J.J. The mental health outcomes of drought: A systematic review and causal process diagram. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2015, 12, 13251–13275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ellis, N.R.; Albrecht, G.A. Climate change threats to family farmers’ sense of place and mental wellbeing: A case study from the Western Australian Wheatbelt. Soc. Sci. Med. 2017, 175, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Berry, H.L.; Kelly, B.J.; Hanigan, I.C.; Coates, J.H.; McMichael, A.J.; Welsh, J.A.; Kjellstrom, T. Rural mental health impacts of climate change. In Commissioned Report for the Garnaut Climate Change Review; The Australian National University: Canberra, Australia, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Stain, H.J.; Kelly, B.; Carr, V.J.; Lewin, T.J.; Fitzgerald, M.; Fragar, L. The psychological impact of chronic environmental adversity: Responding to prolonged drought. Soc. Sci. Med. 2011, 73, 1593–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sartore, G.-M.; Kelly, B.; Stain, H.J. Drought and its effect on mental health: How GPs can help. Aust. Fam. Physician 2007, 36, 990–993. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Edwards, B.; Gray, M.; Hunter, B. A sunburnt country: The economic and financial impact of drought on rural and regional families in Australia in an era of climate change. Aust. J. Lab. Econ. 2009, 12, 109–131. [Google Scholar]
- Acharibasam, J.W.; Anuga, S.W. Psychological distance of climate change and mental health risks assessment of smallholder farmers in Northern Ghana: Is habituation a threat to climate change? Clim. Risk Manag. 2018, 21, 16–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, B.; Gray, M.; Hunter, B. The impact of drought on mental health in rural and regional Australia. Soc. Indic. Res. 2015, 121, 177–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Austin, E.K.; Handley, T.; Kiem, A.S.; Rich, J.L.; Lewin, T.J.; Askland, H.H.; Askarimarnani, S.S.; Perkins, D.A.; Kelly, B.J. Drought-related stress among farmers: Findings from the Australian Rural Mental Health Study. Med. J. Aust. 2018, 209, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanigan, I.C.; Schirmer, J.; Niyonsenga, T. Drought and Distress in Southeastern Australia. EcoHealth 2018, 15, 642–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Hanna, E.G.; Kjellstrom, T. Working in Australia’s heat: Health promotion concerns for health and productivity. Health Promot. Int. 2013, 30, 239–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berry, H.L.; Waite, T.D.; Dear, K.B.; Capon, A.G.; Murray, V. The case for systems thinking about climate change and mental health. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2018, 8, 282–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linn, J.G.; Husaini, B.A. Determinants of psychological depression and coping behaviors of Tennessee farm residents. J. Community Psychol. 1987, 15, 503–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, J.; Welch, N. Researching the Rural–Metropolitan Health Differential Using the ‘Social Determinants of Health’. Aust. J. Rural Health 2000, 8, 254–260. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Carruth, A.; Logan, C. Depressive Symptoms in Farm Women: Effects of Health Status and Farming Lifestyle Characteristics, Behaviors, and Beliefs. Publ. Health Promot. Dis. Prev. 2002, 27, 213–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brumby, S.; Chandrasekara, A.; McCoombe, S.; Kremer, P.; Lewandowski, P. Cardiovascular risk factors and psychological distress in Australian farming communities. Aust. J. Rural Health 2012, 20, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schulz, P.S.; Zimmerman, L.; Johansson, P. Seasonal Work and Cardiovascular Risk Factors in Farmers. J. Cardiovasc. Nurs. 2018, 33, E35–E39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hawes, N.J.; Wiggins, A.T.; Reed, D.B.; Hardin-Fanning, F. Poor sleep quality is associated with obesity and depression in farmers. Public Health Nurs. 2019, 36, 270–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, F.G.; de Souza, C.M.; Hidalgo, M.P.L. Work routines moderate the association between eveningness and poor psychological well-being. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzoni, S.E.; Boiko, P.E.; Katon, W.J.; Russo, J. Depression and disability in seasonal and migrant Hispanic agricultural workers. Gen. Hosp. Psychiatry 2007, 29, 450–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stieglitz, J.; Schniter, E.; von Rueden, C.; Kaplan, H.; Gurven, M. Functional Disability and Social Conflict Increase Risk of Depression in Older Adulthood Among Bolivian Forager-Farmers. J. Gerontol. Ser. B Psychol. Sci. Soc. Sci. 2015, 70, 948–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- DeArmond, S.; Stallones, L.; Chen, P.; Sintek, E. Depression and somatic symptoms within the farming community. J. Agric. Saf. Health 2006, 12, 5–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crandall, C.S.; Fullerton, L.; Olson, L.; Sklar, D.P.; Zumwalt, R. Farm-related injury mortality in New Mexico, 1980–1991. Accid. Anal. Prev. 1997, 29, 257–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rostamabadi, A.; Jahangiri, M.; Naderi Mansourabadi, B.; Javid, M.; Ghorbani, M.; Banaee, S. Prevalence of chronic diseases and occupational injuries and their influence on the health-related quality of life among farmers working in small-farm enterprises. J. Agromedicine 2019, 24, 248–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scarth, R.D.; Zwerling, C.; Lewis, M.Q.; Burmeister, L.F. Depression and risk factors among Iowa farmers. J. Agromedicine 1997, 3, 207–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Logstein, B. Predictors of mental complaints among Norwegian male farmers. Occup. Med. 2016, 66, 332–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Peck, D.F.; Grant, S.; McArthur, W.; Godden, D. Psychological impact of foot-and-mouth disease on farmers. J. Ment. Health 2002, 11, 523–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huth, N.; Cocks, B.; Dalgliesh, N.; Poulton, P.; Marinoni, O.; Garcia, J. Farmers’ perceptions of coexistence between agriculture and a large scale coal seam gas development. Agric. Hum. Values 2018, 35, 99–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, M.I.; Hine, D.W.; Bhullar, N.; Dunstan, D.A.; Bartik, W. Fracked: Coal seam gas extraction and farmers’ mental health. J. Environ. Psychol. 2016, 47, 22–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisner, C.S.; Neal, R.D.; Scaife, B. The effect of the 1996 ‘beef crisis’ on depression and anxiety in farmers and non-farming controls. Br. J. Psychiatry 1999, 49, 385–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eddy, P.; Wertheim, E.H.; Hale, M.W.; Wright, B.J. Trait Mindfulness Helps Explain the Relationships Between Job Stress, Physiological Reactivity, and Self-Perceived Health. J. Occup. Environ. Med. 2019, 61, e12–e18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulder, P.L.; Kenkel, M.; Shellenberger, S.; Constantine, M.; Streiegel, R.; Sears, S.; Jumper-Thurman, P.; Kalodner, M.; Danda, C.; Hager, A. The Behavioral Health Care Needs of Rural Women; American Psychological Association, Committee on Rural Health: Washington, DC, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, H.; Cho, S.-Y.; Kim, J.-S.; Yoon, S.-Y.; Kim, B.-I.; An, J.-M.; Kim, K.-B. Difference in health status of Korean farmers according to gender. Ann. Occup. Environ. Med. 2019, 31, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weigel, R.R.; Weigel, D.J. Identifying stressors and coping strategies in two-generation farm families. Fam. Relat. 1987, 36, 379–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunn, K. Farmers’ Stress and Coping in a Time of Drought. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Adelaide, Adelaide, Australia, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Berkowitz, A.D.; Perkins, H.W. Correlates of Psychosomatic Stress Symptoms among Farm Women: A Research Note on Farm and Family Functioning. J. Hum. Stress 1985, 11, 76–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zapata Roblyer, M.I.; Grzywacz, J.G.; Suerken, C.K.; Trejo, G.; Ip, E.H.; Arcury, T.A.; Quandt, S.A. Interpersonal and social correlates of depressive symptoms among Latinas in farmworker families living in North Carolina. Women Health 2015, 56, 177–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Millondaga, K.J. Mothers, wives, and farmers: Stories of women ‘gone mad’. Asian J. Women’s Stud. 2018, 24, 396–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alston, M.; Clarke, J.; Whittenbury, K. Contemporary Feminist Analysis of Australian Farm Women in the Context of Climate Changes. Soc. Sci. 2018, 7, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pattnaik, I.; Lahiri-Dutt, K.; Lockie, S.; Pritchard, B. The feminization of agriculture or the feminization of agrarian distress? Tracking the trajectory of women in agriculture in India. Asia Pac. Econ. 2018, 23, 138–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.L. Assessment of Pesticide-Related Pollution and Occupational Health of Vegetable Farmers in Benguet Province, Philippines. J. Health Pollut. 2017, 7, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Ma, J.; Tan, L.; Chen, Y.; Li, X.; Tian, X.; Zhou, X.; Liu, X. Epidemiology of severe mental illness in Hunan province in central China during 2014-2015: A multistage cross-sectional study. PLoS ONE 2017, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McClure, H.; Josh Snodgrass, J.; Martinez, C.; Squires, E.; Jiménez, R.; Isiordia, L.; Eddy, J.; McDade, T.; Small, J. Stress, Place, and Allostatic Load Among Mexican Immigrant Farmworkers in Oregon. J. Immigr. Minority Health 2015, 17, 1518–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polain, J.D.; Berry, H.L.; Hoskin, J.O. Rapid change, climate adversity and the next ‘big dry’: Older farmers’ mental health. Aust. J. Rural Health 2011, 19, 239–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daghagh Yazd, S.; Wheeler, S.A.; Zuo, A. Exploring the Drivers of Irrigator Mental Health in the Murray–Darling Basin, Australia. Sustainability 2019, 11, 6097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cross, P.; Edwards, R.T.; Hounsome, B.; Edwards-Jones, G. Comparative assessment of migrant farm worker health in conventional and organic horticultural systems in the United Kingdom. Sci. Total Environ. 2008, 391, 55–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, K.M.; Baidya, R.; Aryal, A.; Farmer, J.R.; Valliant, J. Neurological and mental health outcomes among conventional and organic farmers in Indiana, USA. Ann. Agric. Environ. Med. 2018, 25, 244–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brigance, C.; Soto Mas, F.; Sanchez, V.; Handal, A.J. The Mental Health of the Organic Farmer: Psychosocial and Contextual Actors. Workplace Health Saf. 2018, 66, 606–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soto Mas, F.; Handal, A.J.; Rohrer, R.E.; Tomalá Viteri, E. Health and safety in organic farming: A qualitative study. J. Agromedicine 2018, 23, 92–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornally, N.; McCarthy, G. Help-seeking behaviour: A concept analysis. Int. J. Nurs. Pract. 2011, 17, 280–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alston, M.; Kent, J. The Big Dry: The link between rural masculinities and poor health outcomes for farming men. J. Sociol. 2008, 44, 133–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beseler, C.L.; Stallones, L. A Cohort Study of Pesticide Poisoning and Depression in Colorado Farm Residents. Ann. Epidemiol. 2008, 18, 768–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wheeler, S.A.; Zuo, A.; Xu, Y.; Grafton, Q.; Daghagh Yazd, S. Emergency Drought Relief Package—Health and Resilience Services: An Evidence Check; Sax Institute: Sydney, Australia, 2019; Available online: https://www.saxinstitute.org.au/wp-content/uploads/19.04.09_Evidence-Check_Emergency-Drought-Relief-Package-Health-and-Resilience-Services.pdf (accessed on 7 May 2019).
- Daghagh Yazd, S.; Wheeler, S.A.; Zuo, A. Understanding the impacts of water scarcity and socio-economic demographics on farmer mental health in the Murray-Darling Basin. Ecol. Econ. 2020, 169, 106564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henderson, C.; Evans-Lacko, S.; Thornicroft, G. Mental illness stigma, help seeking, and public health programs. Am. J. Public Health 2013, 103, 777–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modenese, A.; Korpinen, L.; Gobba, F. Solar radiation exposure and outdoor work: An underestimated occupational risk. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 2063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roberts, L.; Jones, G.; Brooks, R. Why Do You Ride?: A Characterization of Mountain Bikers, Their Engagement Methods, and Perceived Links to Mental Health and Well-Being. Front. Psychol. 2018, 9, 1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rafie, C.; Ning, Y.; Wang, A.; Gao, X.; Houlihan, R. Impact of physical activity and sleep quality on quality of life of rural residents with and without a history of cancer: Findings of the Day and night study. Cancer Manag. Res. 2018, 10, 5525–5535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]


| Geographical Location | Number of Studies | Percent of Total |
|---|---|---|
| US | 45 | 27% |
| Australia | 29 | 17% |
| UK | 13 | 8% |
| Mexico | 10 | 6% |
| China | 5 | 3% |
| South Korea | 6 | 3% |
| Norway | 5 | 3% |
| Iran | 6 | 3% |
| India | 5 | 3% |
| France | 4 | 2% |
| Brazil | 5 | 2% |
| Canada | 3 | 2% |
| New Zealand | 3 | 2% |
| Chile | 2 | 1% |
| Sweden | 2 | 1% |
| Turkey | 2 | 1% |
| Finland | 2 | 1% |
| Netherlands | 2 | 1% |
| Tanzania | 2 | |
| Philippines | 2 | |
| Other countries (Iceland, Nepal, Egypt, Pakistan, United Arab Emirates, Costa Rica, Greece, Japan, Malaysia, Thailand, Bolivia, Ghana, Nigeria, Europe countries) | 14 | Less than 1% each |
| Scale | Count | Percent of Total |
|---|---|---|
| Centre for Epidemiologic Studies-Depression (CES-D) [33] | 29 | 18% |
| Questionnaires based on the Midtown Manhattan study [48]/the Warheit study [49]/the Raitasalo study [50]/the Karasek and Theorells study/asked questions such as: “has a DOCTOR ever told you that you had been diagnosed with depression requiring medication?” [51]/ “how would you rate your level of depression in the last quarter?” [52]/ “the most stressful situation you had experienced in the past month” [53]/ “have you had any injuries at work that required medical attention or treatment?” [54]/ “had any treatments or hospitalization for depression?” [55]/ “do you currently feel the defined type of stress?” [37]/ “have you had previous hospitalization for depression, by exposure to different pesticides?” [56]/21 item questionnaire [5]/Cognitive Emotion Regulation Questionnaire [57]/Copenhagen Psychosocial Questionnaire [57]/Patient Health Questionnaire (PHQ-9) [58]/Self-Reporting Questionnaire (SRQ-20) [59] | 28 | 17% |
| In-depth interviews [9], focus groups [17] * | 18 | 11% |
| Brief Symptom Inventory Scale [60]/15-item impact of Event Scale [61]/19 item Inventory Scale [62]/48 item Stress Scale [31]/Depression-Anxiety-Stress Scale [63]/Geriatric Depression Screening Scale [64]/Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale [65]/Farming Family Stressor scale [7]/Beck Depression Scale (BDS) [66]/12-item Stress Scale [67]/Border Community and Immigration Stress Scale [25]/Environmental Distress Scale (EDS) [68] | 16 | 9% |
| (Kessler 10) K10 [69] | 12 | 7% |
| Clinical Test [70]/Medical Symptom Validity Test [71]/Mini International Neuropsychiatric Interview Diagnostic Test (MINI) [19] | 12 | 7% |
| Farm Stressor Inventory [30]/Personality Assessment Inventory (PAI) [19]/Edinburgh Farming Stress Inventory (EFSI) [21]/Beck Depression Inventory (BDI) [72]/Welke’s Farm Ranch Stress Inventory [28]/Migrant Farmworker Stress Inventory [73] | 11 | 6% |
| Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE) [74] | 9 | 5% |
| Hospital Anxiety and Depression (HAD) [75] | 8 | 5% |
| General Health Questionnaire-12 (GHQ-12) [76]/General Health Questionnaire-28 (GHQ-28) [77] | 7 | 4% |
| SF-36 [78] | 4 | 2% |
| Health Option Survey (HOS) [8]/Farm Stress Survey (FSS) [79] | 2 | 1% |
| Other methods (COOP/WONCA charts [80]/short-form Geriatric Depression [81]/psychological domain score of WHOQOLBREF [82]/(EQ-5D-3L) [83]/(SCL-25) [13]/(SCL-90) [84]/(ICD-9)/EuroQOL (EQ-5D)/Five-item Well-being Index (WHO-5) [85] | 11 | 6% |
| Key Risk Factors | Total Number (and %) of Studies Naming This Stress | Developed Countries (No. and %) | Developing Countries (No. and %) | USA (No. and %) | Australia (No. and %) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pesticide exposure | 43 (19%) | 25 (15%) | 18 (34%) | 11 (16%) | 1 (2%) |
| Finances in general (input prices/income/profit/market condition) | 39 (18%) | 31 (18%) | 8 (18%) | 14 (21%) | 6 (15%) |
| Weather uncertainty (incl. drought and climate change) | 25 (11%) | 22 (13%) | 3 (5%) | 5 (7%) | 16 (40%) |
| Poor physical health/past injury | 23 (10%) | 18 (10%) | 5 (7%) | 9 (13%) | 1 (2%) |
| Farming in general/heavy workload/stress/hazards in farming | 17 (8%) | 12 (7%) | 5 (11%) | 7 (10%) | 2 (5%) |
| Government policies and regulations/paper-work | 14 (6%) | 13 (8%) | 1 (2%) | 5 (7%) | 2 (5%) |
| Isolation/loneliness/lack of social relationships | 14 (6%) | 11 (7%) | 3 (7%) | 4 (6%) | 2 (5%) |
| Concern about the future of the farm/animal disease/machinery breakdown | 12 (5%) | 12 (7%) | 0 (0%) | 3 (4%) | 2 (5%) |
| Working with family (role conflict) | 12 (5%) | 11 (7%) | 1 (2%) | 5 (7%) | 2 (5%) |
| Time pressure | 9 (4%) | 7 (4%) | 2 (5%) | 2 (3%) | 2 (5%) |
| Other issues—no theme identified (e.g., paddy glut/firearm exposure/media criticism/coal seam gas/electricity irrigation costs development/leaving family for work/community characteristics/work ability/lack of skilled labour/living condition/poor housing)/poor access to market information/levels of mindfulness | 14 (6%) | 10 (5%) | 5 (9%) | 4 (6%) | 5 (12%) |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Daghagh Yazd, S.; Wheeler, S.A.; Zuo, A. Key Risk Factors Affecting Farmers’ Mental Health: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 4849. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16234849
Daghagh Yazd S, Wheeler SA, Zuo A. Key Risk Factors Affecting Farmers’ Mental Health: A Systematic Review. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2019; 16(23):4849. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16234849
Chicago/Turabian StyleDaghagh Yazd, Sahar, Sarah Ann Wheeler, and Alec Zuo. 2019. "Key Risk Factors Affecting Farmers’ Mental Health: A Systematic Review" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 16, no. 23: 4849. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16234849
APA StyleDaghagh Yazd, S., Wheeler, S. A., & Zuo, A. (2019). Key Risk Factors Affecting Farmers’ Mental Health: A Systematic Review. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 16(23), 4849. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16234849





