Pneumoproteins in Offshore Drill Floor Workers
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Participants
2.2. Examinations
2.3. Laboratory Analysis
2.4. Nicotine and Cotinine in Serum
2.5. Air Sampling and Measurements
2.6. Statistics
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- OGP/IPIECA Drilling Fluid Task Force. Drilling Fluid and Health Risk Management; Report No. 396; International Association of Oil & Gas Producers/International Petroleum Industry Environmental Conservation Association: London, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Davidson, R.G.; Evans, M.J.; Hamlin, J.W.; Saunders, K.J. Occupational hygiene aspects of the use of oil-based drilling fluids. Ann. Occup. Hyg. 1988, 32, 325–332. [Google Scholar]
- Eide, I. A review of exposure conditions and possible health effects associated with aerosol and vapour from low-aromatic oil-based drilling fluids. Ann. Occup. Hyg. 1990, 34, 149–157. [Google Scholar]
- James, R.W.; Schei, T.; Navestad, P.; Geddes, A.; Nelson, M.G.; Webster, D. Improving the working environment and drilling economics through drilling fluid chemistry. SPE Drill. Complet. 2000, 15, 254–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardner, R. Overview and characteristics of some occupational exposures and health risks on offshore oil and gas installation. Ann. Occup. Hyg. 2003, 47, 201–210. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bråtveit, M.; Steinsvåg, K.; Lie, S.; Moen, B.E. Modeling of oil mist and oil vapor concentration in the shale shaker area on offshore drilling installations. J. Occup. Environ. Hyg. 2009, 6, 679–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galea, K.S.; Sanchez-Jimenez, A.; Steinsvag, K.; Searl, A.; Cherrie, J.W.; Krüger, K.; Peikli, V.; van Tongeren, M. Characteristics of Oil Mist and Vapours from Drilling Fluids Emitted from a Shale Shaker at an Onshore Test Facility; Research Report TM/10/01; Institute of Occupational Medicine: Edinburgh, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Steinsvåg, K.; Bråtveit, M.; Moen, B.E. Exposure to oil mist and oil vapour during offshore drilling in Norway, 1979–2004. Ann. Occup. Hyg. 2006, 50, 109–122. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hansen, A.B.; Larsen, E.; Hansen, L.V.; Lyngsaae, M.; Kunze, H. Elemental composition of airborne dust in the Shale Shaker House during an offshore drilling operation. Ann. Occup. Hyg. 1991, 35, 651–657. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kirkhus, N.E.; Thomassen, Y.; Ulvestad, B.; Woldbæk, T.; Ellingsen, D.G. Occupational exposure to airborne contaminants during offshore oil drilling. Environ. Sci. Process Impacts 2015, 17, 1257–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirkhus, N.E.; Skare, Ø.; Ulvestad, B.; Aaløkken, T.M.; Günther, A.; Olsen, R.; Thomassen, Y.; Lund, M.B.; Ellingsen, D.G. Pulmonary function and high-resolution computed tomography examinations among offshore drill floor workers. Int. Arch. Occup. Environ. Health 2018, 91, 317–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogino, S.; Nishihara, R.; VanderWeele, T.J.; Wang, M.; Nishi, A.; Lochhead, P.; Qian, Z.R.; Zhang, X.; Wu, K.; Nan, H.; et al. The role of molecular pathological epidemiology in the study of neoplastic and non-neoplastic diseases in the era of precision medicine. Epidemiology 2016, 27, 602–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermans, C.; Bernard, A. Lung epithelium–specific proteins. Characteristics and potential applications as markers. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1999, 159, 646–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.-S.; Chen, P.-W.; Tsai, P.-J.; Su, S.-H.; Liao, P.-C. Proteomics analysis revealed changes in rat bronchoalveolar lavage fluid proteins associated with oil mist exposure. Proteomics 2006, 6, 2236–2250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broeckaert, F.; Bernard, A. Clara cell secretory protein (CC16): Characteristics and perspectives as lung peripheral biomarker. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2000, 30, 469–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lakind, J.S.; Holgate, S.T.; Ownby, D.R.; Mansur, A.H.; Helms, P.J.; Pyatt, D.; Hays, S.M. A critical review of the use of Clara cell secretory protein (CC16) as a biomarker of acute or chronic pulmonary effects. Biomarkers 2007, 12, 445–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sorensen, G.L.; Husby, S.; Holmskov, U. Surfactant protein A and surfactant protein D variation in pulmonary disease. Immunobiology 2007, 212, 381–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaw, J.E.; Sin, D.D. Unifying thoracic biomarkers: Surfactant protein-D and beyond. Expert Rev. Respir. Med. 2012, 6, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartl, D.; Griese, M. Surfactant protein D in human lung diseases. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2006, 36, 423–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bowler, R.P. Surfactant protein as a biomarker for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. COPD J. Chronic Obs. Pulm. Dis. 2012, 9, 651–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wert, S.E.; Yoshida, M.; LeVine, A.M.; Ikegami, M.; Jones, T.; Ross, G.F.; Fisher, J.H.; Korfhagen, T.R.; Whitsett, J.A. Increased metalloproteinase activity, oxidant production and emphysema in surfactant protein D gene-inactivated mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 5972–5977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Rittenhouse-Olson, K.; Scheider, W.L.; Mu, L. Effect of particulate matter air pollution on C-reactive protein: A review of epidemiologic studies. Rev. Environ. Health 2012, 27, 133–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiraiwa, K.; van Eeden, S.F. Contribution of lung macrophages to the inflammatory responses induced by exposure to air pollutants. Mediat. Inflamm. 2013, 619523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kongerud, J.; Vale, J.R.; Aalen, O.O. Questionnaire reliability and validity for aluminum potroom workers. Scand. J. Work Environ. Health 1989, 15, 364–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellingsen, D.G.; Bast-Pettersen, R.; Efskind, J.; Gjølstad, M.; Olsen, R.; Thomassen, Y.; Molander, P. Hand tremor related to smoking habits and the consumption of caffeine in male industrial workers. Neurotoxicology 2006, 27, 525–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saeed, W.R.; Distante, S.; Holmes, J.D.; Kohle, P.S. Skin injuries afflicting three oil workers following contact with calcium bromide and/or calcium chloride. Burns 1997, 23, 634–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helleday, R.; Segerstedt, B.; Forsberg, B.; Mudway, I.; Nordberg, G.; Bernard, A. Blomberg, A. Exploring the time dependence of serum clara cell protein as a biomarker of pulmonary injury in humans. Chest 2006, 130, 672–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stockfelt, L.; Sällsten, G.; Olin, A.-C.; Almerud, P.; Samuelsson, L.; Johannesson, S.; Molnar, P.; Strandberg, B.; Almstrand, A.-C.; Bergemalm-Rynell, K.; et al. Effects on airways of short-term exposure to two kinds of wood smoke in a chamber study of healthy humans. Inhal. Toxicol. 2012, 24, 47–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freberg, B.I.; Olsen, R.; Thorud, S.; Daae, H.L.; Hersson, M.; Molander, P.; Barregard, L.; Ellingsen, D.G. Pulmonary function and serum pneumoproteins in professional ski waxers. Inhal. Toxicol. 2016, 28, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robin, M.; Dong, P.; Hermans, C.; Bernard, A.; Bertsen, A.D.; Doyle, I.R. Serum levels of CC-16, SP-A and SP-B reflect tobacco-smoke exposure in asymptomatic subjects. Eur. Respir. J. 2002, 20, 1152–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berthoin, K.; Broeckaert, F.; Robin, M.; Haufroid, V.; De Burbure, C.; Bernard, A. Serum pneumoproteins and biomarkers of exposure to urban air pollution: A cross-sectional comparison of policemen and foresters. Biomarkers 2004, 9, 341–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutti, A.; Corradi, M.; Goldoni, M.; Vettori, M.V.; Bernard, A.; Apostoli, P. Exhaled metallic elements and serum pneumoproteins in asymptomatic smokers and patients with COPD or asthma. Chest 2006, 129, 1288–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madsen, C.; Durand, K.L.; Nafstad, P.; Schwarze, P.E.; Rønningen, K.S.; Håheim, L.L. Associations between environmental exposures and serum concentrations of Clara cell protein among elderly men in Oslo, Norway. Environ. Res. 2008, 108, 354–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellingsen, D.G.; Ulvestad, B.; Andersson, L.; Barregard, L. Pneumoproteins and inflammatory biomarkers in asphalt pavers. Biomarkers 2010, 15, 498–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernard, A.; Marchandise, F.X.; Depelchin, S.; Lawerys, R.; Sibille, Y. Clara cell protein in serum and bronchoalveolar lavage. Eur. Respir. J. 1992, 5, 1231–1238. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lesur, O.; Bernard, A.M.; Begin, R.O. Clara cell protein (CC16) and surfactant-associated protein A (SP-A) in asbestos-exposed workers. Chest 1996, 109, 467–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shijubo, N.; Honda, Y.; Itoh, Y.; Yamaguchi, T.; Kuroki, Y.; Akino, T.; Kawai, T.; Abe, S. BAL surfactant protein A and Clara cell 10-kDa protein levels in healthy subjects. Lung 1998, 176, 257–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, J.-P.; Chi, C.-H.; Li, H.-C.; Tang, X.-Y. Effects of N-acetylcysteine on Clara cells in rats with cigarette smoke exposure. Chin. Med. J. 2010, 123, 412–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laucho-Contreras, M.E.; Polverino, F.; Tesfaigzi, Y.; Pilon, A.; Celli, B.R.; Owen, C.A. Club cell protein 16 (CC16) augmentation: A potential disease-modifying approach for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2016, 20, 869–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guerra, S.; Halonen, M.; Vasquez, M.M.; Spangenberg, A.; Stern, D.A.; Morgan, W.J.; Wright, A.L.; Lavi, I.; Tarès, L.; Carsin, A.-E.; et al. Relation between circulating CC16 concentrations, lung function and development of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease across the lifespan: A prospective study. Lancet Respir. Med. 2015, 3, 613–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boswell, C.; Curwall, M.; Elswick, R.K., Jr.; Leyden, D. Modelling nicotine intake in smokers and snuff users using biological fluid nicotine metabolites. Biomarkers 2000, 5, 341–354. [Google Scholar]
- Doyle, I.R.; Hermans, C.; Bernard, A.; Nicholas, T.E.; Bersten, A.D. Clearance of Clara cell secretory protein 16 (CC16) and surfactant proteins A and B from blood in acute respiratory failure. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1998, 158, 1528–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorensen, G.L.; Hjelmborg, J.V.; Kyvik, K.O.; Fenger, M.; Høj, A.; Bendixen, C.; Sørensen, T.I.; Holmskov, U. Genetic and environmental influences of surfactant protein D serum levels. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2006, 290, 1010–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Characteristics | Drill Floor Workers AM † (Min–Max) | Referents AM (Min–Max) |
|---|---|---|
| Age (years) a | 30 (19–59) | 46 (30–69) |
| Height (cm) | 180.7 (169–196) | 181.5 (169–196) |
| Weight (kg) | 85.0 (60–126) | 87.4 (67–123) |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 26.1 (20.7–39.3) | 26.6 (20.2–36.8) |
| Years of work offshore a | 5.8 (0.5–32) | 14 (0–35) |
| Current smokers (%) | 31 | 23 |
| Current snuff users (%) | 39 | 15 |
| Oil mist (mg/m3) ‡,# | 0.18 (<DL–6.0) | - |
| Oil vapour (mg/m3) ‡,# | 14 (<DL–120) | - |
| MUDFe (mg/m3) ‡,☼ | 0.14 (<DL–2.4) | - |
| Biomarkers | Drill Floor Workers | Referents | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AM † | Min–Max | AM | Min–Max | p | |
| CRP ‡ (mg/L) | 0.9 (1.0) | 0.1–12 | 1.4 (1.3) | 0.2–16 | 0.02 |
| CC-16 (µg/L) | 4.5 (4.6) | 1.0–9.1 | 4.4 (4.3) | 1.0–12 | 0.62 |
| SPD ‡ (µg/L) | 166 (167) | 70–886 | 176 (174) | 59–448 | 0.45 |
| Current smokers (n) | 20 | - | 15 | - | - |
| S-nicotine (µg/L) | 14.0 | <DL–53 | 20.4 | <DL–54 | 0.18 |
| S-cotinine (µg/L) | 205 | <DL–382 | 236 | 4.3–438 | 0.50 |
| Current snuff-users (n) | 24 | - | 9 | - | - |
| S-nicotine (µg/L) | 14.8 | <DL–54 | 19.2 | <DL–39 | 0.40 |
| S-cotinine (µg/L) | 315 | <DL–1275 | 340 | 123–500 | 0.79 |
| Biomarkers | Drill Floor Workers (n = 65/51) a | Referents (n = 64/55) a,b | Drill Floor Workers vs. Referents | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bio-Marker | Esti-Mate | Lower | Upper | p | Esti-Mate | Lower | Upper | p | Esti-Mate | Lower | Upper | p | |
| Not adjusted for time of day | CRP c | –0.12 | −0.23 | 0.00 | 0.045 | −0.07 | −0.18 | 0.05 | 0.25 | −0.05 | −0.21 | 0.11 | 0.53 |
| SPD c | −0.02 | −0.05 | 0.01 | 0.12 | −0.03 | −0.06 | −0.01 | 0.017 | 0.01 | −0.03 | 0.05 | 0.56 | |
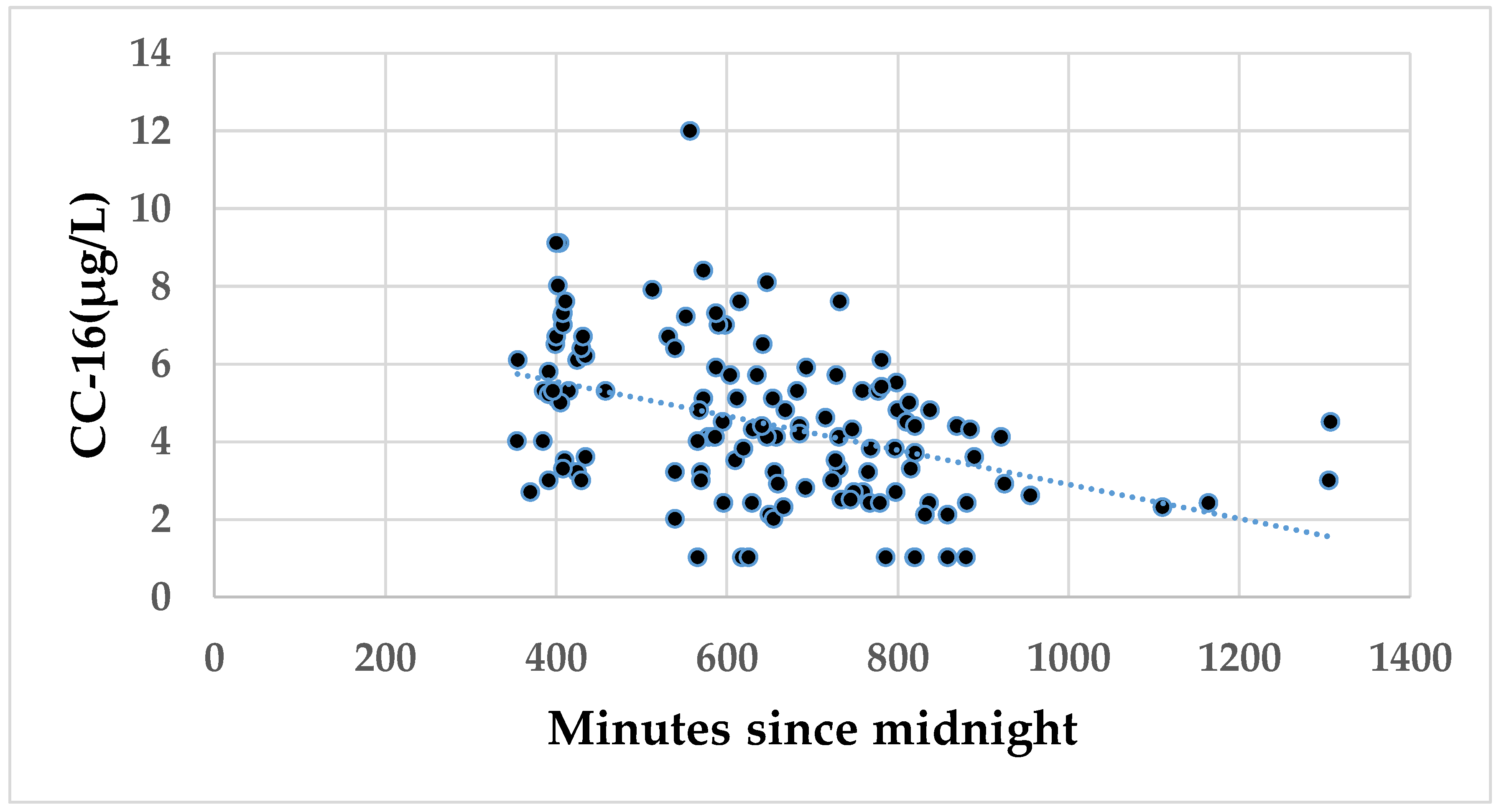
| CC16 | −0.71 | −1.06 | −0.36 | 0.0001 | −0.59 | −0.93 | −0.24 | 0.001 | −0.12 | −0.62 | 0.37 | 0.62 | |
| Adjusted for time of day | CRP c | −0.14 | −0.27 | −0.01 | 0.038 | −0.09 | −0.23 | 0.05 | 0.19 | −0.04 | −0.21 | 0.12 | 0.58 |
| SPD c | −0.01 | −0.05 | 0.02 | 0.36 | −0.02 | −0.06 | 0.01 | 0.2 | 0.01 | −0.03 | 0.05 | 0.64 | |
| CC16 | −0.35 | −0.77 | 0.07 | 0.1 | −0.12 | −0.57 | 0.33 | 0.61 | −0.23 | −0.73 | 0.26 | 0.36 | |
| Biomarkers | Expo | Age | BMI | Smoking | Sampling Time | Infection | Mult. r |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CRP (mg/L) † | - | 0.008 * | 0.04 *** | - | - | 0.28 ** | 0.45 *** |
| SP-D (µg/L) † | - | - | - | - | - | - | No model |
| CC-16 (µg/L) | - | - | - | −0.73 * | −0.004 *** | - | 0.45 *** |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kirkhus, N.E.; Ulvestad, B.; Barregard, L.; Skare, Ø.; Olsen, R.; Thomassen, Y.; Ellingsen, D.G. Pneumoproteins in Offshore Drill Floor Workers. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 300. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16030300
Kirkhus NE, Ulvestad B, Barregard L, Skare Ø, Olsen R, Thomassen Y, Ellingsen DG. Pneumoproteins in Offshore Drill Floor Workers. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2019; 16(3):300. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16030300
Chicago/Turabian StyleKirkhus, Niels E., Bente Ulvestad, Lars Barregard, Øivind Skare, Raymond Olsen, Yngvar Thomassen, and Dag G. Ellingsen. 2019. "Pneumoproteins in Offshore Drill Floor Workers" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 16, no. 3: 300. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16030300
APA StyleKirkhus, N. E., Ulvestad, B., Barregard, L., Skare, Ø., Olsen, R., Thomassen, Y., & Ellingsen, D. G. (2019). Pneumoproteins in Offshore Drill Floor Workers. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 16(3), 300. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16030300





