Investigation and Source Apportionment of Air Pollutants in a Large Oceangoing Ship during Voyage
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sampling Site
2.2. Sampling Method
- V0—sample volume under the standard state, L;
- Vi—sampling volume, i.e., the product of sampling flow and sampling time, L;
- T—sampling point temperature, °C;
- T0—absolute temperature at the standard state, 273 K;
- P—atmospheric pressure at the sampling point, kPa;
- P0—atmospheric pressure at the standard state, 101.3 kPa.
2.3. Detection Method
2.4. Statistical Analysis
2.4.1. Factor Analysis
- zji—the standardized score of variable j;
- a—factor loading;
- f—factor score;
- m—number of common factors used for variables;
- e—remainder of the error;
- i—sample quantity;
- j—number of variables.
2.4.2. Multivariate Linear Regression
- k—number of explanatory variables;
- βK—partial regression coefficient;
- β0—constant;
- X—independent variable;
- µ—random error.
2.4.3. Cluster Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Level of Pollutants at Ship Sampling Sites
3.2. Pollution Source Apportionment at the Sampling Sites
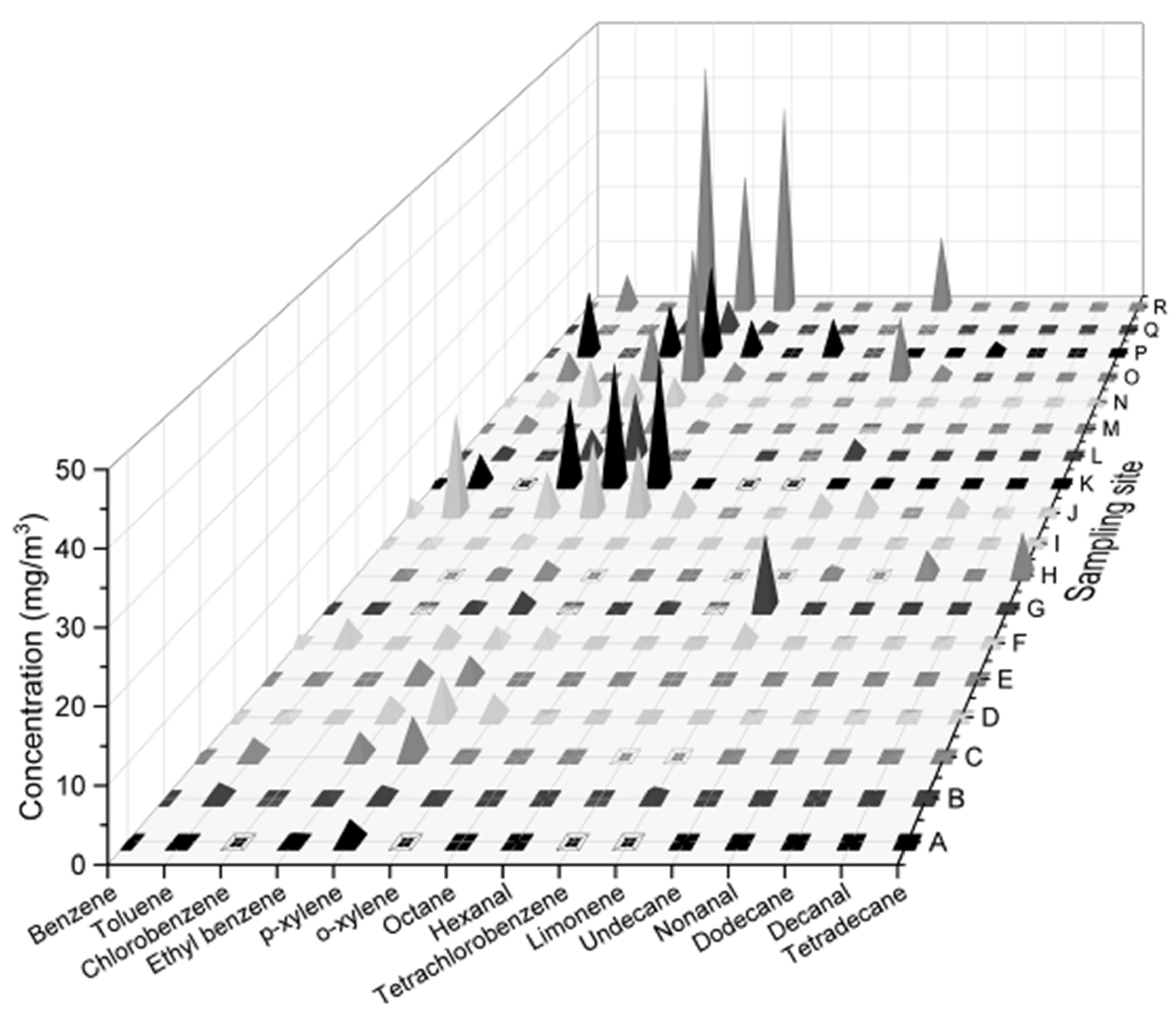
3.3. Distribution of Sampling Site Pollution
3.4. Contribution Rates of Sampling Site Pollution Source
3.5. Classification of Sampling Site Pollution Levels
4. Conclusions
Limitations and Future Research
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fang, J.; He, Y.; Xu, L.; Pan, H.; Xu, X. Analysis of volatile compounds in the closed ship cabins. Ship. Sci. Technol. 2013, 35, 90–95. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, Z.; Wang, X.; Li, H.; Huang, J.; Mo, F.; Shen, H. Investigation of subjective evaluation to cabin air quality in vessels. Occup. Health. 2016, 32, 104–105. [Google Scholar]
- Elskus, A.A.; Ingersoll, C.G.; Kemble, N.E.; Echols, K.R.; Brumbaugh, W.G.; Henquinet, J.W.; Watten, B.J. Real-time analysis of organic compounds in ship engine aerosol emissions using resonance-enhanced multiphoton ionisation and proton transfer mass spectrometry. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2015, 407, 5939–5951. [Google Scholar]
- Oeder, S.; Kanashova, T.; Sippula, O.; Sapcariu, S.C.; Streibel, T.; Arteaga-Salas, J.M.; Passig, J.; Dilger, M.; Paur, H.R.; Schlager, C.; et al. Particulate matter from both heavy fuel oil and diesel fuel shipping emissions show strong biological effects on human lung cells at realistic and comparable in vitro exposure conditions. PLoS. ONE 2015, 10, e0126536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Streibel, T.; Schnelle-Kreis, J.; Czech, H.; Harndorf, H.; Jakobi, G.; Jokiniemi, J.; Karg, E.; Lintelmann, J.; Matuschek, G.; Michalke, B.; et al. Aerosol emissions of a ship diesel engine operated with diesel fuel or heavy fuel oil. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2017, 24, 10976–10991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, D.; Yu, T.; Chen, L.; Zhou, A.; Shen, X. Advances on the evaluation methods of ship nonmetallic material emission property and measurement. Chin. J. Ship. Research. 2015, 10, 113–120. [Google Scholar]
- NRC. Submarine Air Quality; National Academy Press: Washington, DC, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Mccarrick, A. Measurements of monoethanolamine near a US navy carbon dioxide scrubber. In Proceedings of the 40th International Conference on Environmental Systems, Barcelona, Spain, 11–15 July 2010; ARC: Reston, VA, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sampson, H. International Seafarers and Transnationalism in the Twenty First Century; Manchester University Press: Manchester, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Gordon, G.E. Receptor models. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1980, 14, 792–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Xu, X.; Ding, Z.; Chen, Y.; Lian, H.Z. In vitro inhalation/ingestion bioaccessibility, health risks, and source appointment of airborne particle-bound elements trapped in room air conditioner filters. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2018, 25, 26059–26068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Li, J.; Zhang, Q. Water quality assessment in the rivers along the water conveyance system of the Middle Route of the South to North Water Transfer Project (China) using multivariate statistical techniques and receptor modeling. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 195, 306–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, K.P.; Malik, A.; Mohan, D.; Sinha, S. Multivariate statistical techniques for the evaluation of spatial and temporal variations in water quality of Gomti River (India)—A case study. Water. Res. 2004, 38, 3980–3992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otto, M. Multivariate Methods. In Analytical Chemistry; Kellner, R., Mermet, J.M., Otto, M., Widmer, H.M., Eds.; Wiley: Weinheim, Germany, 1998; p. 916. [Google Scholar]
- Material Safety Data Sheets. Available online: http://cheman.chemnet.com/en-msds.html (accessed on 10 December 2018).[Green Version]
- Gustafson, D.L.; Long, M.E.; Thomas, R.S.; Benjamin, S.A.; Yang, R.S. Comparative hepatocarcinogenicity of hexachlorobenzene, pentachlorobenzene, 1,2,4,5-tetrachlorobenzene, and 1,4-dichlorobenzene: application of a medium-term liver focus bioassay and molecular and cellular indices. Toxicol. Sci. 2000, 53, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaghef, H.; Hellman, B. Demonstration of chlorobenzene-induced DNA damage in mouse lymphocytes using the single cell gel electrophoresis assay. Toxicology 1995, 96, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saghir, S.A.; Zhang, F.; Rick, D.L.; Kan, L.; Bus, J.S.; Bartels, M.J. In vitro metabolism and covalent binding of ethylbenzene to microsomal protein as a possible mechanism of ethylbenzene-induced mouse lung tumorigenesis. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2010, 57, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaiser, H.F. The varimax criterion for analytic rotation in factor analysis. Psychometrika 1958, 32, 443–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.W.; Lin, K.H.; Kuo, Y.M. Application of factor analysis in the assessment of ground water quality in a Blackfoot disease area in Taiwan. Sci. Total. Environ. 2003, 313, 77–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Yang, X.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Z. Determination of benzene series compounds in oil paints by Internal Standard Method using GC/MS. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 34, 135–138. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, J.; Wang, X.; Cao, H.; Mao, Y.; Zhou, G. Benzene series in oil paint thinners determined by gas chromatography. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 30, 19–21. [Google Scholar]
- Schweitzer, P.A. Paintings and Coatings: Applications and Corrosion Resistance; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Heibati, B.; Godri; Pollitt, K.J.; Charati, J.Y.; Ducatman, A.; Shokrzadeh, M.; Karimi, A.; Mohammadyan, M. Biomonitoring-based exposure assessment of benzene, toluene, ethylbenzene and xylene among workers at petroleum distribution facilities. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 149, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Wang, Y.; Tian, S. Relationship between gasoline composition and calculated octane number distribution according to boiling range. Acta. Petrolei. Sinica. 2017, 33, 138–143. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, S.H.; Bai, Y.H.; Zhang, G.S.; Ma, J. Study on the characteristics of VOCs source profiles of vehicle exhaust and gasoline emission. Acta. Scientiarum. Naturalium. Universitatis. Pekinensis. 2003, 39, 507–511. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.T.; Yang, G.F.; Wang, G.; Xu, C.M.; Shen, B.J.; Gao, J.S. Effect of reaction temperature on the catalytic pyrolysis of gasoline for the favored production of light olefins. Modern. Chemical. Industry. 2009, 29, 74–77. [Google Scholar]
- Sinha, S.N.; Kulkarni, P.K.; Shah, S.H.; Desai, N.M.; Patel, G.M.; Mansuri, M.M.; Saiyed, H.N. Environmental monitoring of benzene and toluene produced in indoor air due to combustion of solid biomass fuels. Sci. Total Environ. 2006, 357, 280–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klein, F.; Platt, S.M.; Farren, N.J.; Detournay, A.; Bruns, E.A.; Bozzetti, C.; Daellenbach, K.R.; Kilic, D.; Kumar, N.K.; Pieber, S.M.; et al. Characterization of Gas-Phase Organics Using Proton Transfer Reaction Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry: Cooking Emissions. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 1243–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Förster, M.; Bolzinger, M.A.; Ach, D.; Montagnac, G.; Briançon, S. Ingredients tracking of cosmetic formulations in the skin: A confocal Raman microscopy investigation. Pharm. Res. 2011, 28, 858–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, R.; An, D.; Lu, W.; Shi, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, P.; Qi, H.; Wang, Q. Impacts of a flash flood on drinking water quality: Case study of areas most affected by the 2012 Beijing flood. Heliyon 2016, 2, e00071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Cai, Q.; Ye, L.; Qu, X. Evaluation of spatial and temporal variation in stream water quality by multivariate statistical techniques: A case study of the Xiangxi River basin, China. Quatern. Int. 2012, 282, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, S.; Zhang, Q. Response of dissolved trace metals to land use/land cover and their source apportionment using a receptor model in a subtropic river, China. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 190, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Sampling Site | Location | Sampling Site | Location | Sampling Site | Location |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | Wheel house | G | Pastry room | M | Engine control room |
| B | Compartment 1 | H | Incineration room | N | Shower room |
| C | Dining room | I | Switching room | O | Compartment 2 |
| D | Alley way 1 | J | Lavatory | P | Galley |
| E | Engine room | K | Store room | Q | Pump room |
| F | Cabin | L | Alley way 2 | R | Fuel oil tank |
| Kaiser–Meyer–Olkin measure of sampling adequacy | 0.307 | |
| Bartlett’s test of sphericity | Approx. Chi-square | 342.816 |
| df | 105 | |
| Sig. | 0.000 | |
| Component | Initial Eigenvalues | Extraction Sums of Squared Loadings | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | % Of Variance | Cumulative % | Total | % of Variance | Cumulative % | |
| 1 | 5.497 | 36.649 | 36.649 | 5.497 | 36.649 | 36.649 |
| 2 | 3.355 | 22.367 | 59.015 | 3.355 | 22.367 | 59.015 |
| 3 | 1.915 | 12.763 | 71.779 | 1.915 | 12.763 | 71.779 |
| 4 | 1.576 | 10.508 | 82.287 | 1.576 | 10.508 | 82.287 |
| 5 | 1.021 | 6.805 | 89.092 | 1.021 | 6.805 | 89.092 |
| 6 | 0.659 | 4.395 | 93.487 | |||
| 7 | 0.553 | 3.686 | 97.173 | |||
| 8 | 0.236 | 1.572 | 98.745 | |||
| 9 | 0.091 | 0.605 | 99.350 | |||
| 10 | 0.042 | 0.283 | 99.633 | |||
| 11 | 0.024 | 0.162 | 99.795 | |||
| 12 | 0.018 | 0.118 | 99.913 | |||
| 13 | 0.011 | 0.071 | 99.985 | |||
| 14 | 0.002 | 0.014 | 99.998 | |||
| 15 | 0.000 | 0.002 | 100.000 | |||
| Variables | Component | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |
| Benzene | 0.804 | −0.417 | 0.219 | −0.237 | 0.023 |
| Toluene | 0.804 | 0.223 | 0.527 | 0.003 | −0.010 |
| Chlorobenzene | −0.125 | −0.025 | 0.093 | −0.141 | 0.948 |
| Ethylbenzene | 0.457 | 0.752 | −0.412 | 0.035 | 0.133 |
| p-xylene | 0.515 | 0.698 | −0.109 | 0.080 | −0.076 |
| o-xylene | 0.561 | 0.647 | −0.360 | −0.001 | 0.102 |
| Octane | 0.862 | −0.307 | 0.266 | −0.205 | −0.003 |
| Hexanal | −0.085 | 0.562 | 0.709 | 0.390 | −0.030 |
| Tetrachlorobenzene | 0.870 | −0.133 | 0.164 | −0.282 | −0.003 |
| Limonene | 0.368 | 0.518 | −0.377 | −0.078 | −0.174 |
| Undecane | 0.845 | −0.217 | 0.228 | 0.165 | −0.080 |
| Nonanal | −0.131 | 0.748 | 0.496 | 0.227 | 0.122 |
| Dodecane | 0.613 | −0.475 | −0.155 | 0.601 | 0.087 |
| Decanal | 0.791 | −0.059 | −0.399 | −0.024 | 0.144 |
| Tetradecane | 0.159 | −0.356 | −0.211 | 0.879 | 0.084 |
| Model | Non-Standardized Coefficient | Standardized Coefficient | |
|---|---|---|---|
| B | Standard Error | Beta | |
| Constant | 5.805 × 10−7 | 0.000 | |
| F1 | 0.366 | 0.000 | 0.788 |
| F2 | 0.224 | 0.000 | 0.481 |
| F3 | 0.128 | 0.000 | 0.274 |
| F4 | 0.105 | 0.000 | 0.226 |
| F5 | 0.068 | 0.000 | 0.146 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Q.; An, D.; Sun, R.; Su, M. Investigation and Source Apportionment of Air Pollutants in a Large Oceangoing Ship during Voyage. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 389. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16030389
Wang Q, An D, Sun R, Su M. Investigation and Source Apportionment of Air Pollutants in a Large Oceangoing Ship during Voyage. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2019; 16(3):389. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16030389
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Qiang, Daizhi An, Rubao Sun, and Mingxing Su. 2019. "Investigation and Source Apportionment of Air Pollutants in a Large Oceangoing Ship during Voyage" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 16, no. 3: 389. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16030389
APA StyleWang, Q., An, D., Sun, R., & Su, M. (2019). Investigation and Source Apportionment of Air Pollutants in a Large Oceangoing Ship during Voyage. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 16(3), 389. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16030389






