Characterization and Source Identification of Polybrominated Diphenyl Ethers (PBDEs) in Air in Xi’an: Based on a Five-Year Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection and Preparation
2.2. Instrumental Analysis
2.3. Quality Assurance/Quality Control
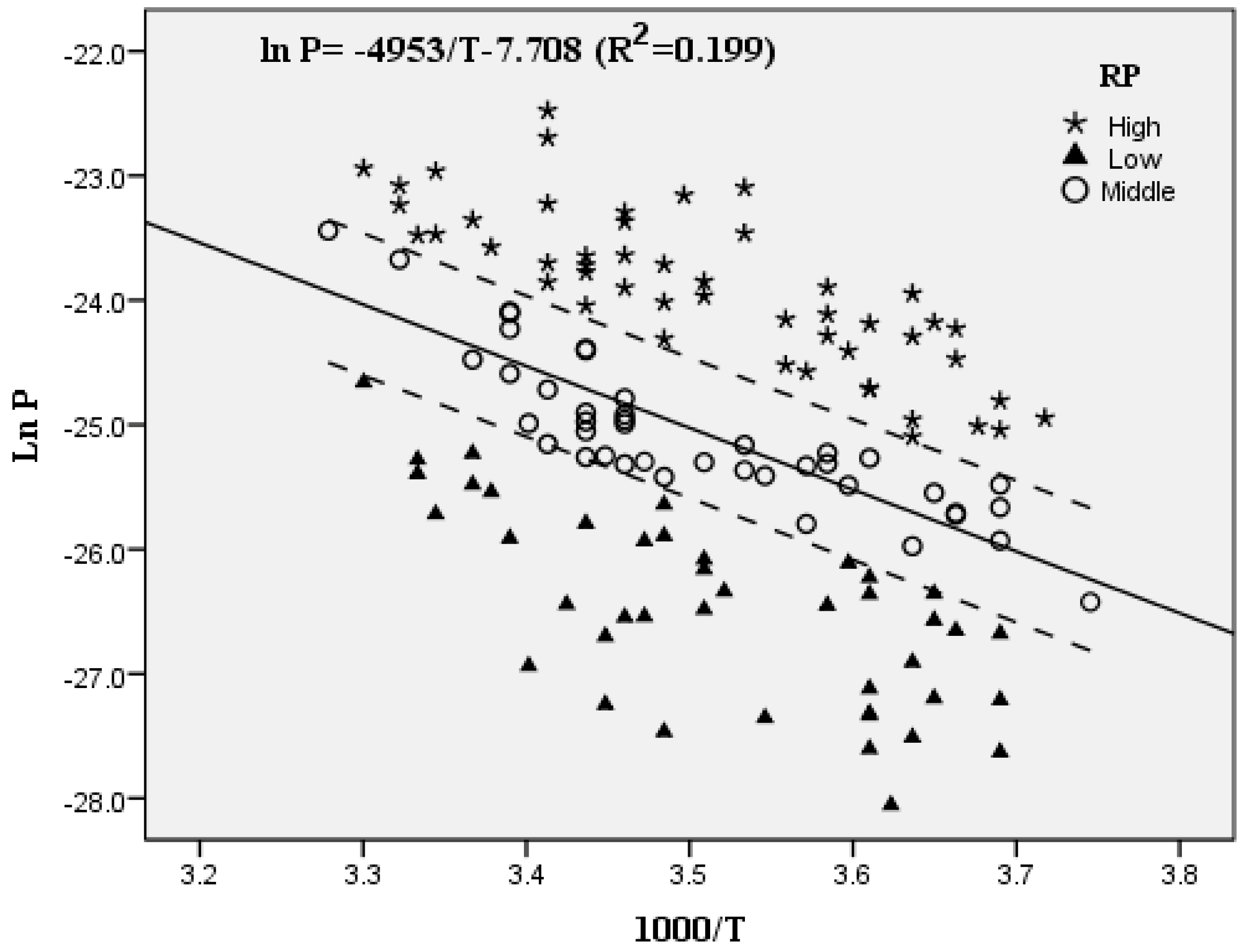
2.4. Clausius–Clapeyron Equation
2.5. Hybrid Single-Particle Lagrangian Integrated Trajectory (HYSPLIT) Model
2.6. Cluster Analysis
2.7. The Concentration Weighted Trajectory (CWT)
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Concentration and Congener Profiles
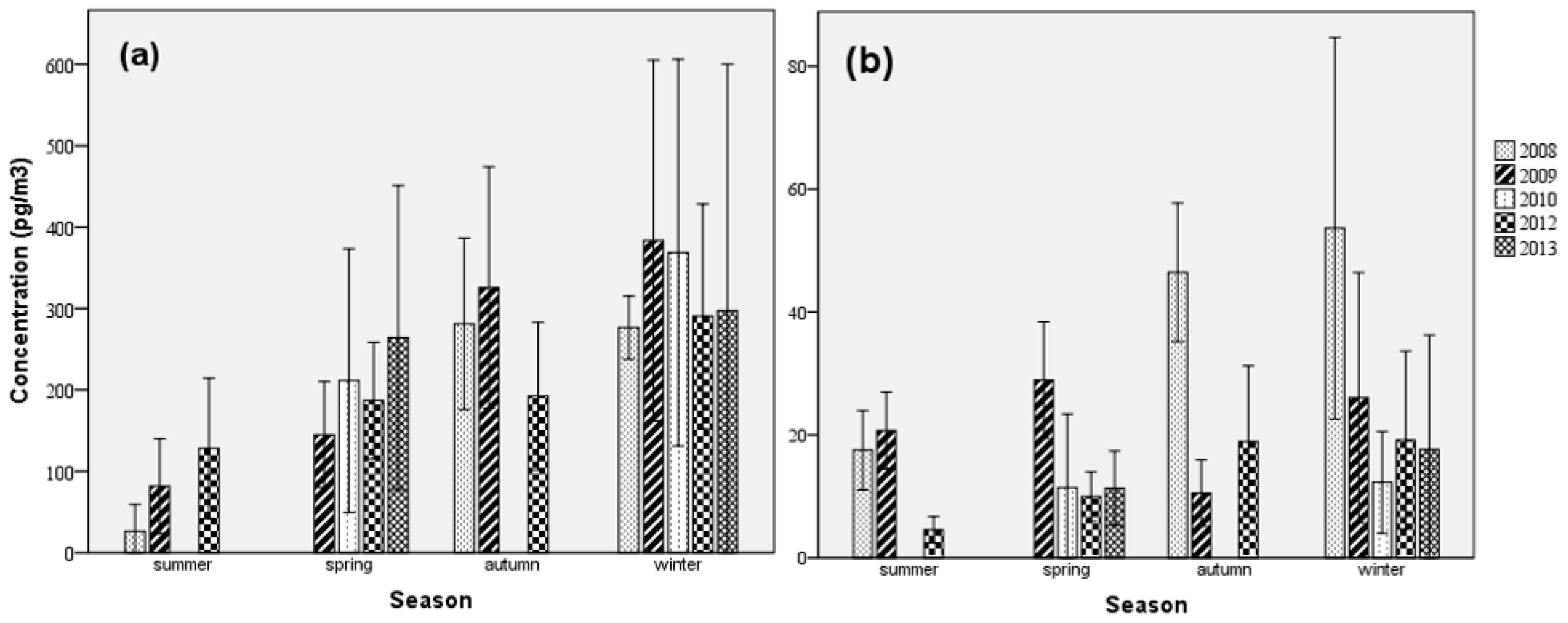
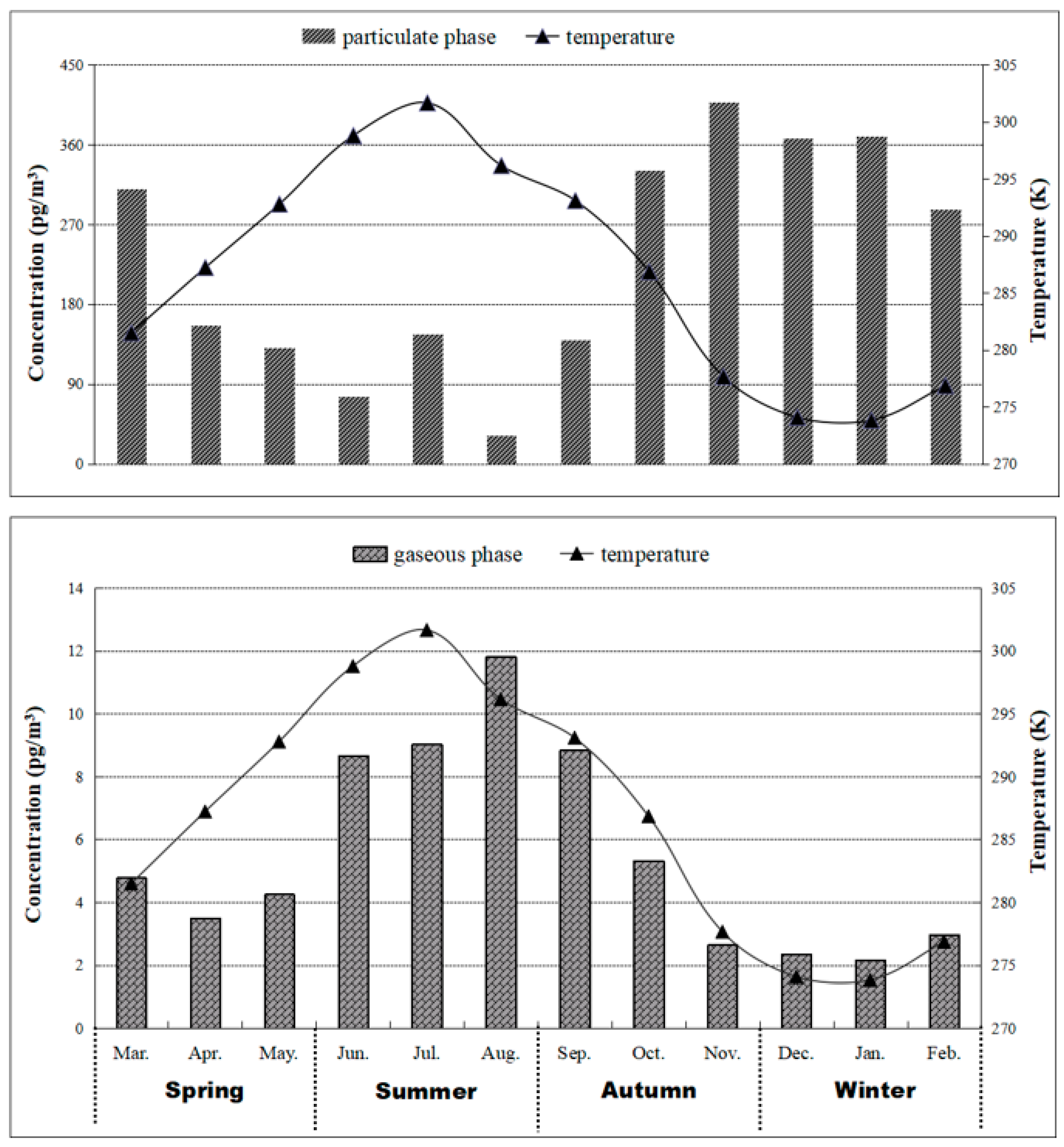
3.1.1. Residue Levels
3.1.2. Congener Profiles
3.2. Temperature Dependence and Cluster Analysis
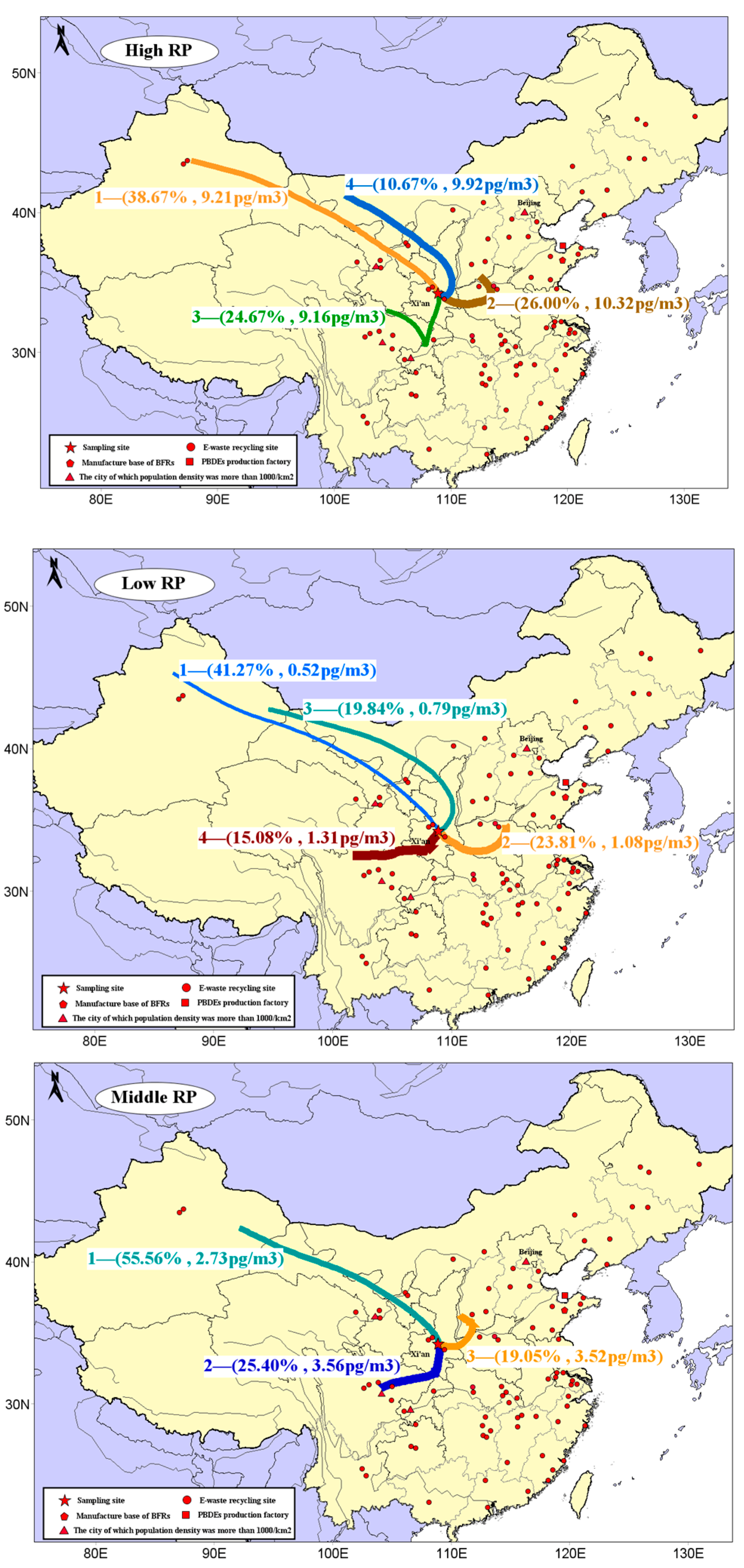
3.3. Potential Source Identification
3.3.1. Principal Component Analysis (PCA)
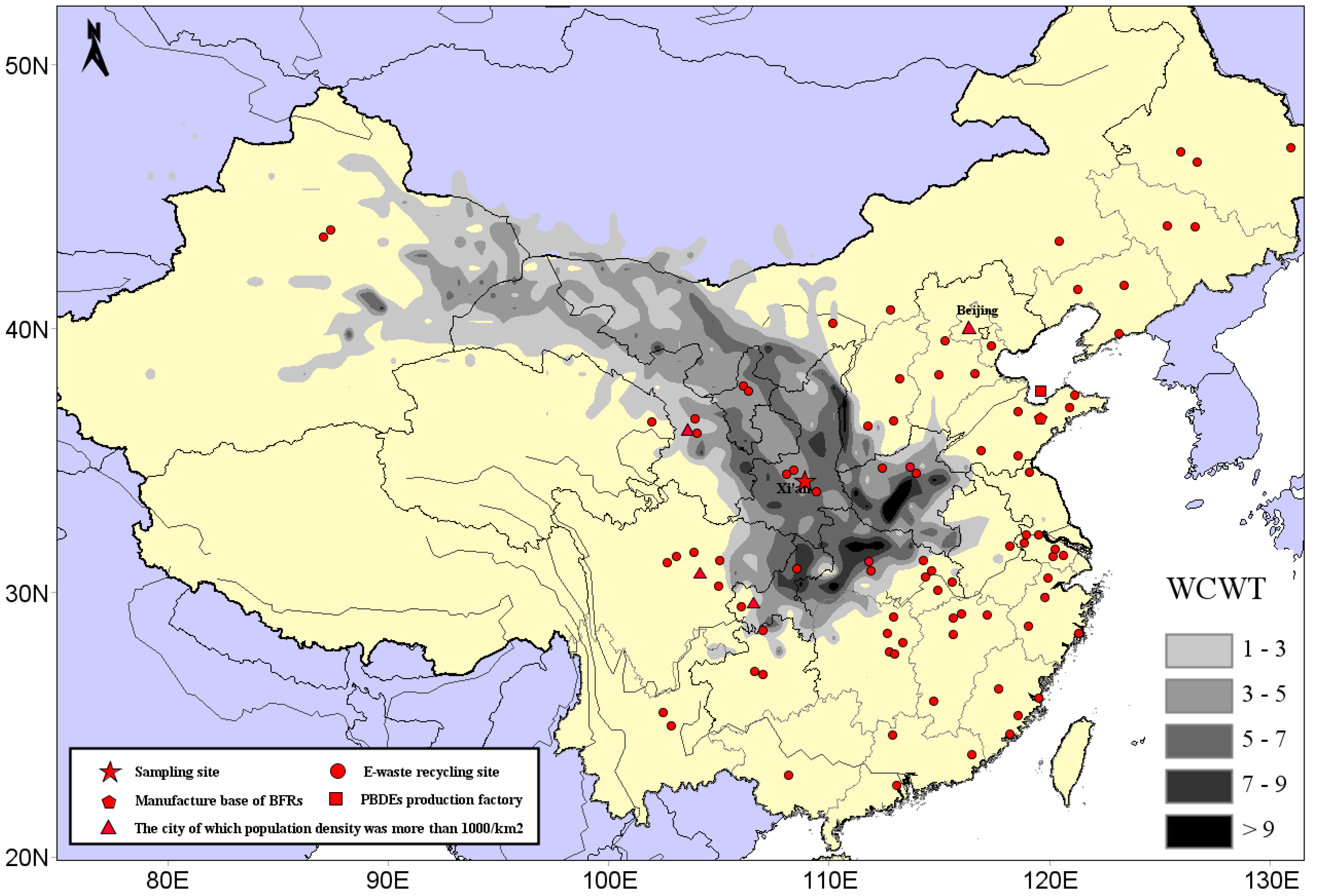
3.3.2. CWT Modeling
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mehran, A.; Pedro, A.; Andreas, S.D.; Ake, B. An overview of commercially used brominated flame retardants, their applications, their use patterns in different countries/regions and possible modes of release. Environ. Int. 2004, 29, 683–689. [Google Scholar]
- Osako, M.; Kim, Y.J.; Sakai, S.I. Leaching of brominated flame retardants in leachate from landfills in Japan. Chemosphere 2004, 57, 1571–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Decarlo, V.J. Studies on brominated chemicals in the environment. Ann. Ny. Acad. Sci. 1979, 320, 678–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andersson, Ö.; Blomkvist, G. Polybrominated aromatic pollutants found in fish in Sweden. Chemosphere 1981, 10, 1051–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, G.; Bu, Q.; Cao, Z.; Du, X.; Xia, J.; Wu, M.; Huang, J. Brominated flame retardants (BFRs): A review on environmental contamination in China. Chemosphere 2016, 150, 479–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bo, J.; Asplund, L.; Olsson, M. Brominated flame retardants—Ubiquitous environmental pollutants? Chemosphere 1987, 16, 2343–2349. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, J.; Qiu, X.; Zhang, J.; Duan, X.; Zhu, T. State of polybrominated diphenyl ethers in China: An overview. Chemosphere 2012, 88, 769–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willett, K.L.; Ulrich, E.M.; Hites, R.A. Differential toxicity and environmental fates of hexachlorocyclohexane isomers. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1998, 32, 2197–2207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ter Schure, A.F.H.; Larson, P.; Agrell, C.; Boon, J.P. Atmospheric transport of polybrominated diphenyl ethers and polychlorinated biphenyls to the Baltic Sea. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2004, 38, 1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eriksson, P.; Jakobsson, E.; Fredriksson, A. Brominated flame retardants: A novel class of developmental neurotoxicants in our environment? Environ. Health Persp. 2001, 109, 903–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viberg, H.; Fredriksson, A.; Eriksson, P. Neonatal exposure to the brominated flame retardant 2,2′,4,4′,5-pentabromodiphenyl ether causes altered susceptibility in the cholinergic transmitter system in the adult mouse. Toxicol. Sci. 2002, 67, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, T.; Taylor, M.M.; Devito, M.J.; Crofton, K.M. Developmental exposure to brominated diphenyl ethers Results in thyroid hormone disruption. Toxicol. Sci. 2002, 66, 105–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Renner, R. Government Watch: In U.S., flame retardants will be voluntarily phased out. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2003, 38, 14A. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- COPs. Available online: http://chm.pops.int/ (accessed on 7 February 2019).
- Cortes, D.R.; Basu, I.; Sweet, C.W.; Brice, K.A.; Hoff, R.M.; Hites, R.A. Temporal trends in gas-phase concentrations of chlorinated pesticides measured at the shores of the great lakes. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1998, 32, 1920–1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.L.; Zhang, C.Z.; Ma, W.L.; Yany, M.; Zhou, B.H.; Liu, L.Z.; Li, Y.F. Pollution characterization and source apportionment of polybrominated diphenyl ethers in autumn air of Xi’an. Environ. Sci. 2011, 32, 2226–2230. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, B.H.; Zhang, C.Z.; Jiang, J.L.; Ma, W.L.; Li, Y.F.; Yang, M.; Liu, L.Y.; Yang, Z.L. Seasonal variations and human exposure assessment of polybrominated diphenyl ethers in air of Xi’an. China Environ. Sci. 2012, 9, 1591–1596. [Google Scholar]
- De Winter-Sorkina, R.; Bakker, M.I.; Wolterink, G.; Zeijlmaker, M.J. Brominated Flame Retardants: Occurrence, Dietary Intake and RIsk Assessment; Rijksinstituut Voor Volksgezondheid En Milieu Rivm: Bilthoven, The Netherlands, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, M.; Qi, H.; Jia, H.; Ren, N.; Ding, Y.; Ma, W.; Liu, L.; Hung, H.; Sverkov, E.; Li, Y. Polybrominated diphenyl ethers in air across china: Levels, compositions, and gas-particle partitioning. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 8978–8984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, W.J.; Zheng, J.S.; Bi, X.H.; Fu, J.M.; Wong, M.H. Distribution of PBDEs in air particles from an electronic waste recycling site compared with Guangzhou and Hong Kong, South China. Environ. Int. 2007, 33, 1063–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillery, B.R.; Basu, I.; Sweet, C.W.; Hites, R.A. Temporal and spatial trends in a long-term study of gas-phase PCB concentrations near the great lakes. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1997, 31, 1811–1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortes, D.R.; Hoff, R.M.; Brice, K.A.; Hites, R.A. Evidence of current pesticide use from temporal and Clausius-Clapeyron plots: A case study from the integrated atmospheric deposition network. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1999, 33, 511–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.D.; Pagano, J.J.; Milligan, M.S.; Hopke, P.K.; Skubis, S.; Holsen, T.M. Polychlorinated biphenyls (PCB) and dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane (DDE) air concentrations in the Lake Ontario region: Trends and potential sources. Atmos. Environ. 2010, 44, 3173–3178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NOAA. Available online: http://www.arl.noaa.gov/HYSPLIT_info.php (accessed on 7 February 2019).
- Weather Underground. Available online: https://www.wunderground.com/weather/cn/xi’an (accessed on 7 February 2019).
- Zhao, H.; Wang, T.J.; Jiang, F.; Xie, M. Investigation into the source of air pollutants to Hong Kong by using backward trajectory method during the TRACE-P campaign. J. Trop. Meteorol. 2009, 2, 181–186. [Google Scholar]
- Borge, R.; Lumbreras, J.; Vardoulakis, S.; Kassomenos, P.; Rodríguez, E. Analysis of long-range transport influences on urban PM using two-stage atmospheric trajectory clusters. Atmos. Environ. 2007, 41, 4434–4450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirois, A.; Bottenheim, J.W. Use of backward trajectories to interpret the 5-year record of PAN and O3 ambient air concentrations at Kejimkujik National Park, Nova Scotia. J. Geophys. Res. 1995, 100, 2867–2881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seibert, P.; Kromp-Kolb, H.; Baltensperger, U.; Jost, D.T.; Schwikowski, M. Trajectory analysis of high-alpine air pollution data. Springer 1994, 694, 253–269. [Google Scholar]
- Eunha, H.; Hites, R.A. Brominated flame retardants in the atmosphere of the East-Central United States. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 7794–7802. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.G.; Mai, B.X.; Bi, X.H.; Chen, S.Y.; Wang, X.M.; Ran, Y.; Luo, X.J.; Sheng, G.Y.; Fu, J.M.; Zeng, E.Y. Concentration levels, compositional profiles, and gas-particle partitioning of polybrominated diphenyl ethers in the atmosphere of an urban city in South China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 1190–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banu, C.; Mustafa, O. Atmospheric concentrations and phase partitioning of polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) in Izmir, Turkey. Chemosphere 2008, 71, 1067–1078. [Google Scholar]
- Duohong, C.; Xinhui, B.; Jinping, Z.; Chen, L.; Tan, L.; Mai, B.; Sheng, G.; Fu, J.; Wong, M. Pollution characterization and diurnal variation of PBDEs in the atmosphere of an E-waste dismantling region. Environ. Pollut. 2009, 157, 1051–1057. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, Z.; Liao, R.E.; Li, H.; Mo, L.; Zeng, X.; Sheng, G.; Fu, J. Particle-bound dechlorane plus and polybrominated diphenyl ethers in ambient air around Shanghai, China. Environ. Pollut. 2011, 159, 2982–2988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenliang, H.; Jialiang, F.; Zeping, G.; Chen, D.; Wu, M.; Fu, J. Polybrominated diphenyl ethers in the atmosphere of Taizhou, a major e-waste dismantling area in China. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2009, 83, 783–788. [Google Scholar]
- Manolis, M.; Athanasios, B.; Stephanou, E.G. Particle-size distribution and gas/particle partitioning of atmospheric polybrominated diphenyl ethers in urban areas of Greece. Environ. Pollut. 2009, 157, 1227–1233. [Google Scholar]
- Shuangxin, S.; Yeru, H.; Kuiyuan, W.; Liang, D.; Yongliang, Y. Levels and seasonal variations of polybrominated diphenyl ethers in the urban atmosphere of Beijing, China. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2013, 90, 296–301. [Google Scholar]
- He, W.; Qin, N.; He, Q.S.; Kong, X.Z.; Liu, W.X.; Wang, Q.M.; Yaang, C.; Jiang, Y.J.; Yang, B.; Bai, Z.L.; et al. Atmospheric PBDEs at rural and urban sites in central China from 2010 to 2013: Residual levels, potential sources and human exposure. Environ. Pollut. 2014, 192, 232–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Jin, J.; Wang, Y.; Li, M.Y.; He, S.J.; Xu, M.; Sun, Y.M. Comparative study of the level and distribution of polybrominated diphenyl ethers and new brominated flame retardants in the atmosphere of typical urban. Environ. Sci. 2014, 35, 1230–1237. [Google Scholar]
- Ge, H.B.; Guo, L.; Li, A.M.; Zhang, Y.; Tang, C.; He, X.M.; Li, H.X. Study of the level and distribution of polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) in the atmosphere of Wuhan. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 41, 77–82. [Google Scholar]
- De Wit, C.A. An overview of brominated flame retardants in the environment. Chemosphere 2002, 46, 583–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.H.; Li, L.P.; Bi, X.H.; Zhao, J.P.; Sheng, G.Y.; Fu, J.M. PBDEs pollution in the atmosphere of a typical e-waste dismantling region. Huan Jing Ke Xue 2008, 29, 2105–2110. [Google Scholar]
- U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. Polybrominated Diphenyl Ethers (PBDEs) Project Plan, Technical U.S.; Environment Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2006.
- Li, Y.F.; Zhu, N.Z.; Liu, L.Y.; Qi, H.; Ma, W.L.; Song, W.W.; Li, W.L. Air pollution characteristic of polybrominated diphenyl ethers in Heilongjiang province. J. Nat. Sci. HeiLongjiang Univ. 2014, 31, 228–232. [Google Scholar]
- MEPSSC. Available online: http://weee.mepscc.cn/Index.do?method=flow (accessed on 7 February 2019).
| Classify | Congener | Detection Frequencies | Concentration (pg/m3) | Proportion | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gaseous Phase | Particulate Phase | Gaseous Phase | Particulate Phase | Total | |||
| tri-BDE | BDE-17 | 98.51% | 88.06% | 1.14 ± 1.15 | 0.50 ± 1.08 | 1.64 ± 1.68 | 9.70% ± 6.10% |
| BDE-28 | 83.58% | 70.90% | 1.05 ± 1.54 | 0.48 ± 1.26 | 1.53 ± 2.16 | 5.90% ± 5.70% | |
| tetra-BDE | BDE-47 | 40.30% | 47.76% | 1.20 ± 1.94 | 1.43 ± 2.57 | 2.63 ± 3.50 | 9.50% ± 10.40% |
| BDE-66 | 59.70% | 73.88% | 0.20 ± 0.31 | 0.60 ± 0.66 | 0.80 ± 0.68 | 5.70% ± 4.50% | |
| penta-BDE | BDE-85 | 70.90% | 65.67% | 0.19 ± 0.21 | 0.46 ± 1.36 | 0.65 ± 1.40 | 5.20% ± 6.10% |
| BDE-99 | 76.87% | 97.76% | 0.44 ± 0.86 | 3.51 ± 4.80 | 3.95 ± 5.03 | 17.20% ± 7.70% | |
| BDE-100 | 76.12% | 96.27% | 0.17 ± 0.31 | 1.61 ± 2.42 | 1.79 ± 2.55 | 11.80% ± 12.90% | |
| hexa-BDE | BDE-138 | 35.82% | 51.49% | 0.12 ± 0.62 | 1.28 ± 3.19 | 1.40 ± 3.32 | 6.30% ± 9.90% |
| BDE-153 | 54.48% | 82.84% | 0.12 ± 0.25 | 3.16 ± 3.92 | 3.28 ± 3.90 | 15.00% ± 9.20% | |
| BDE-154 | 58.96% | 95.52% | 0.11 ± 0.20 | 1.22 ± 2.34 | 1.32 ± 2.33 | 7.30% ± 4.80% | |
| hepta-BDE | BDE-183 | 36.57% | 90.30% | 0.05 ± 0.12 | 1.23 ± 1.80 | 1.28 ± 1.81 | 6.40% ± 3.90% |
| deca-BDE | BDE-209 | 0.00% | 100.00% | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 232.6 ± 193.0 | 232.6 ± 193.0 | - |
| 1 Σ12PBDEs | - | - | 4.79 ± 5.59 | 248.4 ± 199.0 | 253.2 ± 198.4 | - | |
| 2 Σ11PBDEs | - | - | 4.79 ± 5.59 | 15.8 ± 17.7 | 20.6 ± 19.7 | - | |
| Sampling Site | Year | Arithmetic Mean Concentration | Concentration Range | N a | References | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ΣPBDEs b | BDE-209 | ΣPBDEs b | BDE-209 | ||||
| Chicago, USA | 2002–2003 | 31.6 | 68.4 | 9.6–68 | 2.6–956 | 19 | [30] |
| Guangzhou, China | 2004 | 1024 | 1423 | 88.8–3673 | 263.8–4200 | 11 | [31] |
| Izmir, Turkey | 2004–2005 | 31.4 | 30.7 | - | - | 7 | [32] |
| Guiyu, China | 2005 | 9579 | 2164 | - | - | 11 | [33] |
| Shanghai, China | 2006 | 104 ± 54 | 640 ± 143 | - | - | 20 | [34] |
| Taizhou, China | 2006–2007 | 79.4 | 210.5 | 17–165 | 86–439 | 13 | [35] |
| Athens, Greece | 2006–2007 | 13 | - | 21–30 | - | 12 | [36] |
| Beijing, China | 2009–2010 | 6.2 | 164 | nd c–23.6 | 30.7–454 | 8 | [37] |
| Lake Chaohu, China | 2010–2013 | 15.4 | 233.9 | 2.2–72.0 | nd–233.9 | 14 | [38] |
| Weifang, China | 2011–2012 | 228 | 1.4 × 105 | - | 1.5 × 104~2.4 × 105 | 8 | [39] |
| Nanning, China | 2011–2012 | 8.4 | 314.4 | - | 27.1~783.0 | 8 | [39] |
| Wuhan, China | 2015–2016 | 14.5 | - | 5.99–45.4 | - | 9 | [40] |
| Xi’an, China | 2008–2010 | 24.8 | 241.2 | 2.26–85.94 | 0–1041 | 12 | This study |
| 2012–2013 | 14.28 | 219.4 | 2.39–85.15 | 50.6–764.5 | 12 | This study | |
| Meteorological Factor | Relative PBDEs Partial Pressure | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low (42) | Middle (42) | High (50) | |||
| Temperature | High (68) | 50.75% | 45.24% | 52.38% | 54.00%↑ |
| Low (66) | 49.25% | 54.76%↑ | 47.62% | 46.00% | |
| Precipitation | Yes (27) | 20.15% | 19.05% | 23.81%↑ | 18.00% |
| No (107) | 79.85% | 80.95% | 76.19% | 82.00%↑ | |
| Wind Speed | Fast (62) | 46.27% | 54.76%↑ | 38.10% | 46.00% |
| Slow (72) | 53.73% | 45.24% | 61.90%↑ | 54.00% | |
| Wind Direction | Northwest (82) | 61.19% | 66.67% | 61.90% | 58.00% |
| Southeast (52) | 38.81% | 33.33% | 38.10% | 42.00%↑ | |
| Principal Component | Eigenvalue | Percentage Variance (%) | Cumulative Percentage (%) | PBDEs Congeners with Higher Load |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 3.929 | 32.74 | 32.74 | BDE-17, -28, -47, -99, -153 |
| 2 | 2.527 | 21.06 | 53.80 | BDE-66, -100, -154, -183 |
| 3 | 2.124 | 17.70 | 71.50 | BDE-85, -138 |
| 4 | 1.546 | 12.88 | 84.38 | BDE-209 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ye, L.; Zhang, C.; Han, D.; Ji, Z. Characterization and Source Identification of Polybrominated Diphenyl Ethers (PBDEs) in Air in Xi’an: Based on a Five-Year Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 520. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16030520
Ye L, Zhang C, Han D, Ji Z. Characterization and Source Identification of Polybrominated Diphenyl Ethers (PBDEs) in Air in Xi’an: Based on a Five-Year Study. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2019; 16(3):520. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16030520
Chicago/Turabian StyleYe, Lei, Chengzhong Zhang, Deming Han, and Zheng Ji. 2019. "Characterization and Source Identification of Polybrominated Diphenyl Ethers (PBDEs) in Air in Xi’an: Based on a Five-Year Study" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 16, no. 3: 520. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16030520
APA StyleYe, L., Zhang, C., Han, D., & Ji, Z. (2019). Characterization and Source Identification of Polybrominated Diphenyl Ethers (PBDEs) in Air in Xi’an: Based on a Five-Year Study. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 16(3), 520. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16030520





