Measurement of Dioxin Emissions from a Small-Scale Waste Incinerator in the Absence of Air Pollution Controls
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Basic Information on the Basic SWI
2.2. Waste Characterization
2.3. Sampling and Analytical Methodologies
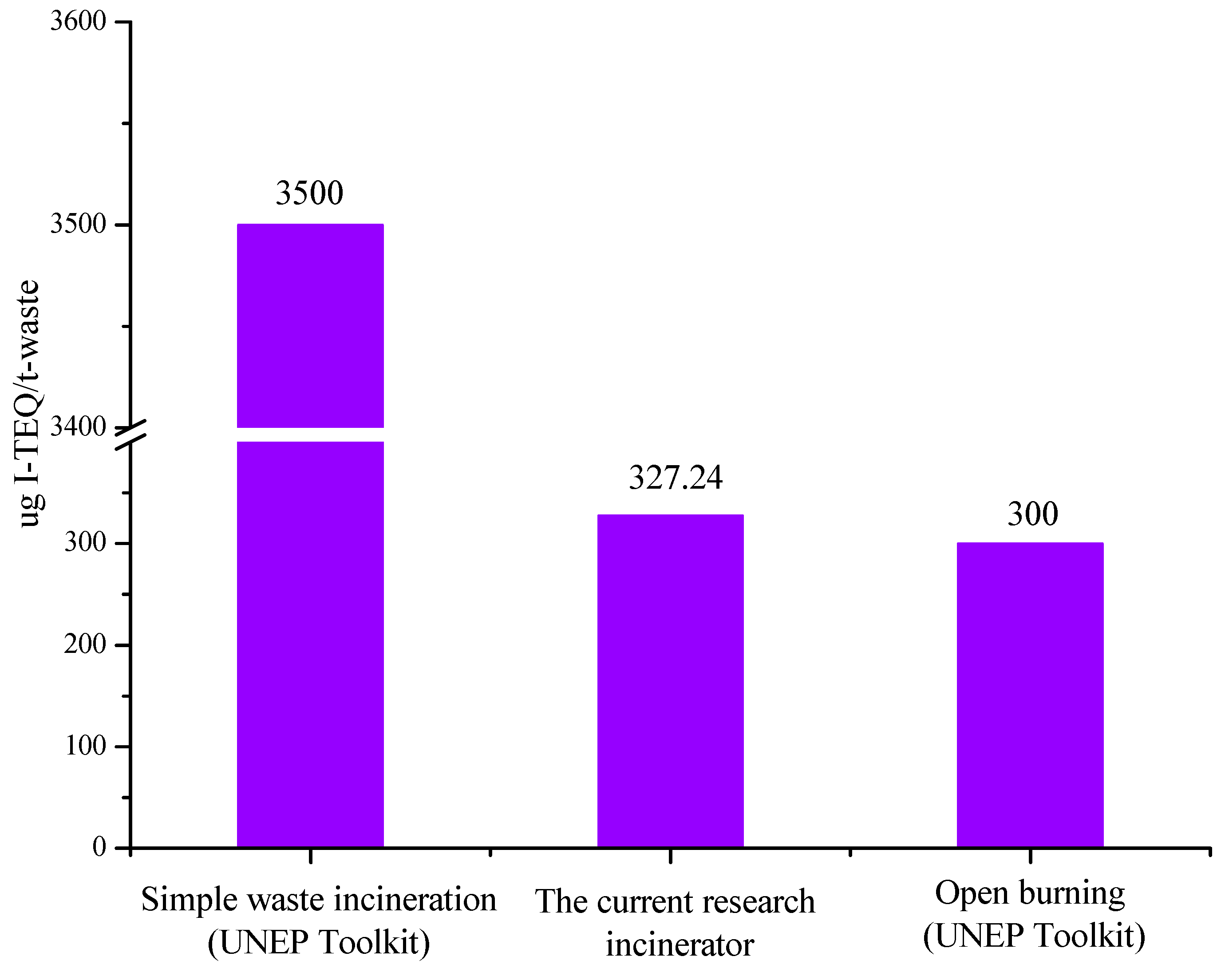
3. Results and Discussion
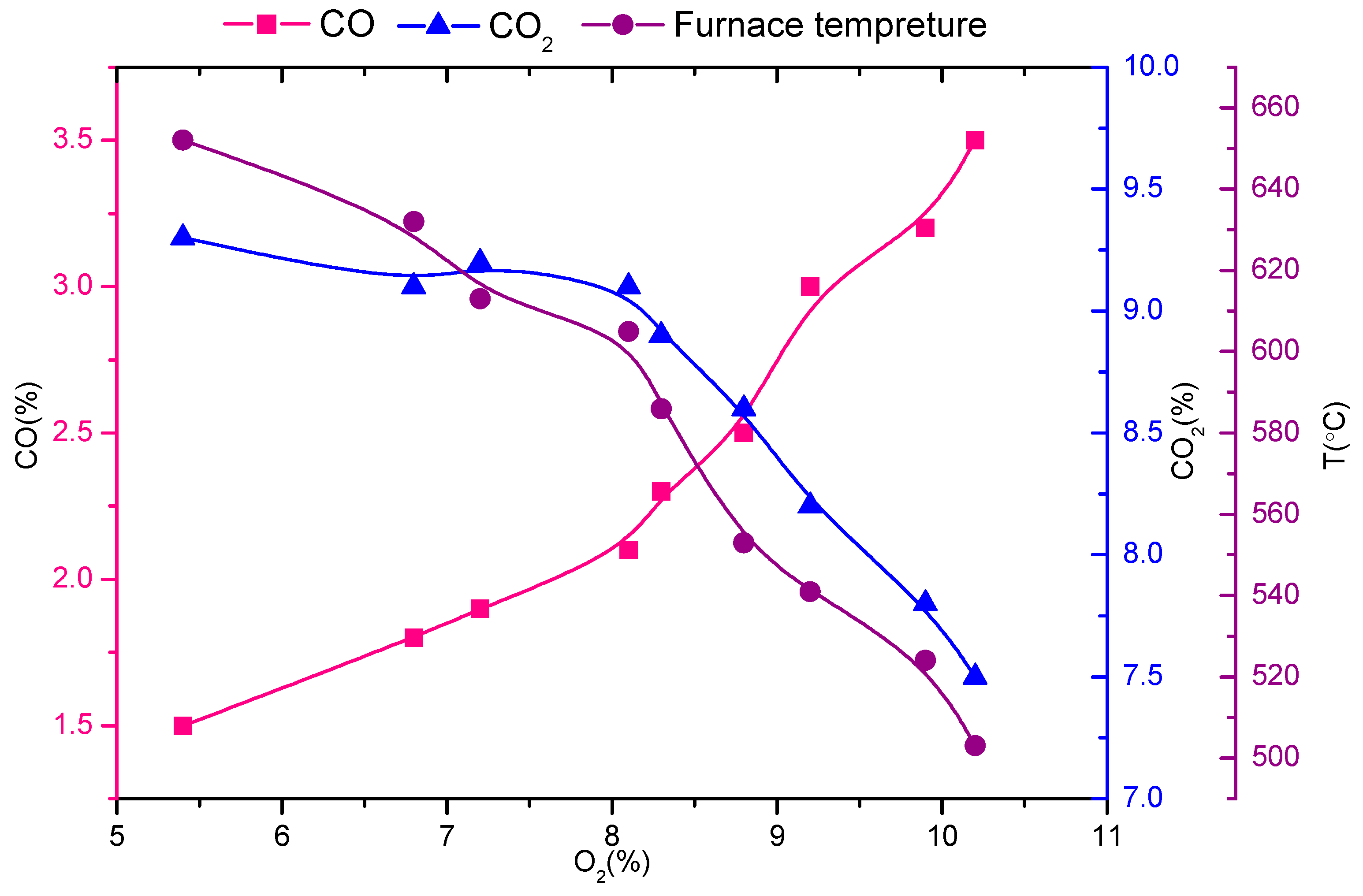
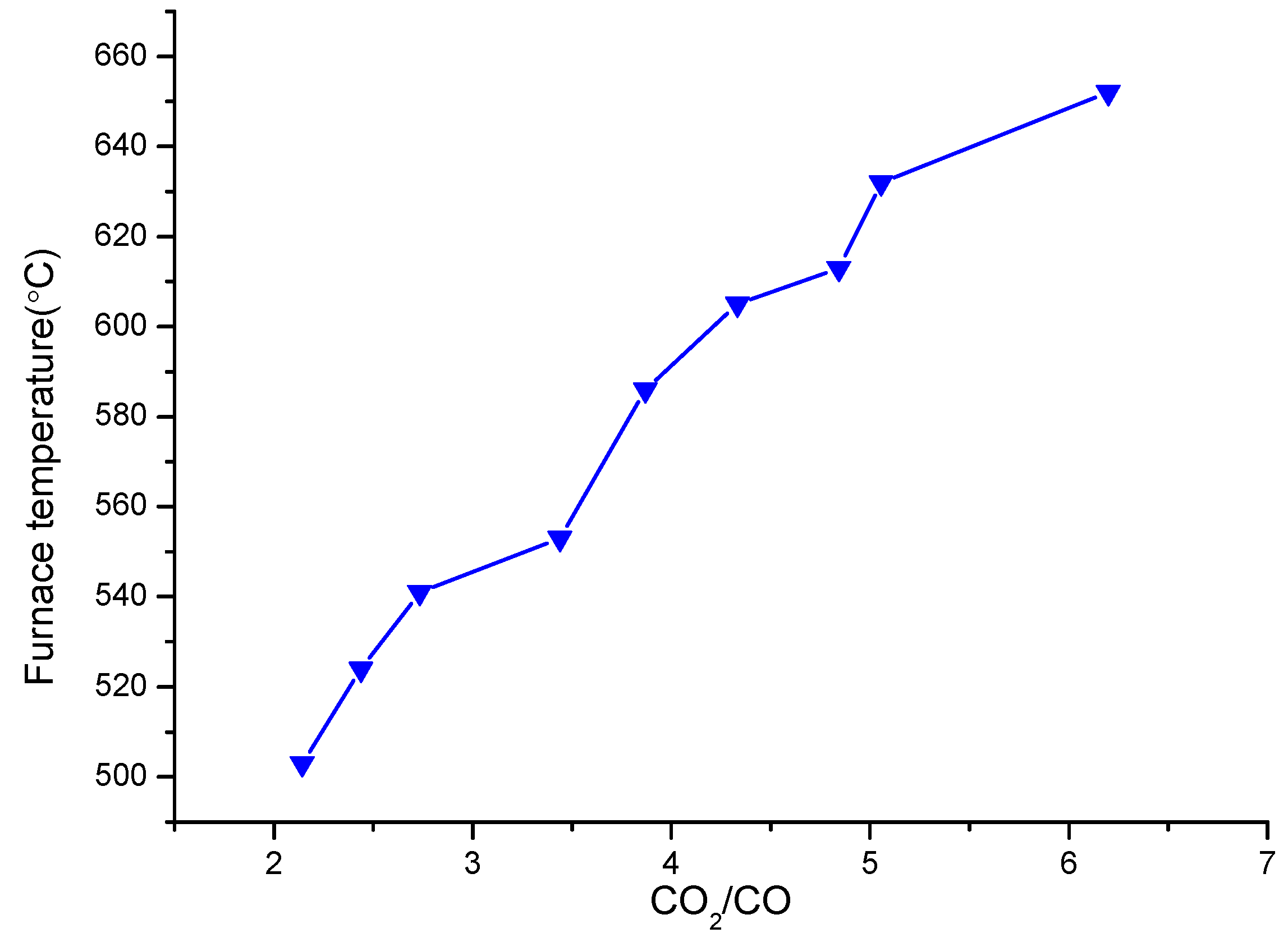
3.1. Evaluation of Combustion Conditions from the Basic SWI in the Absence of APCs
3.2. Content and Formation of PCDD/Fss from the Basic SWI in the Absence of APCs
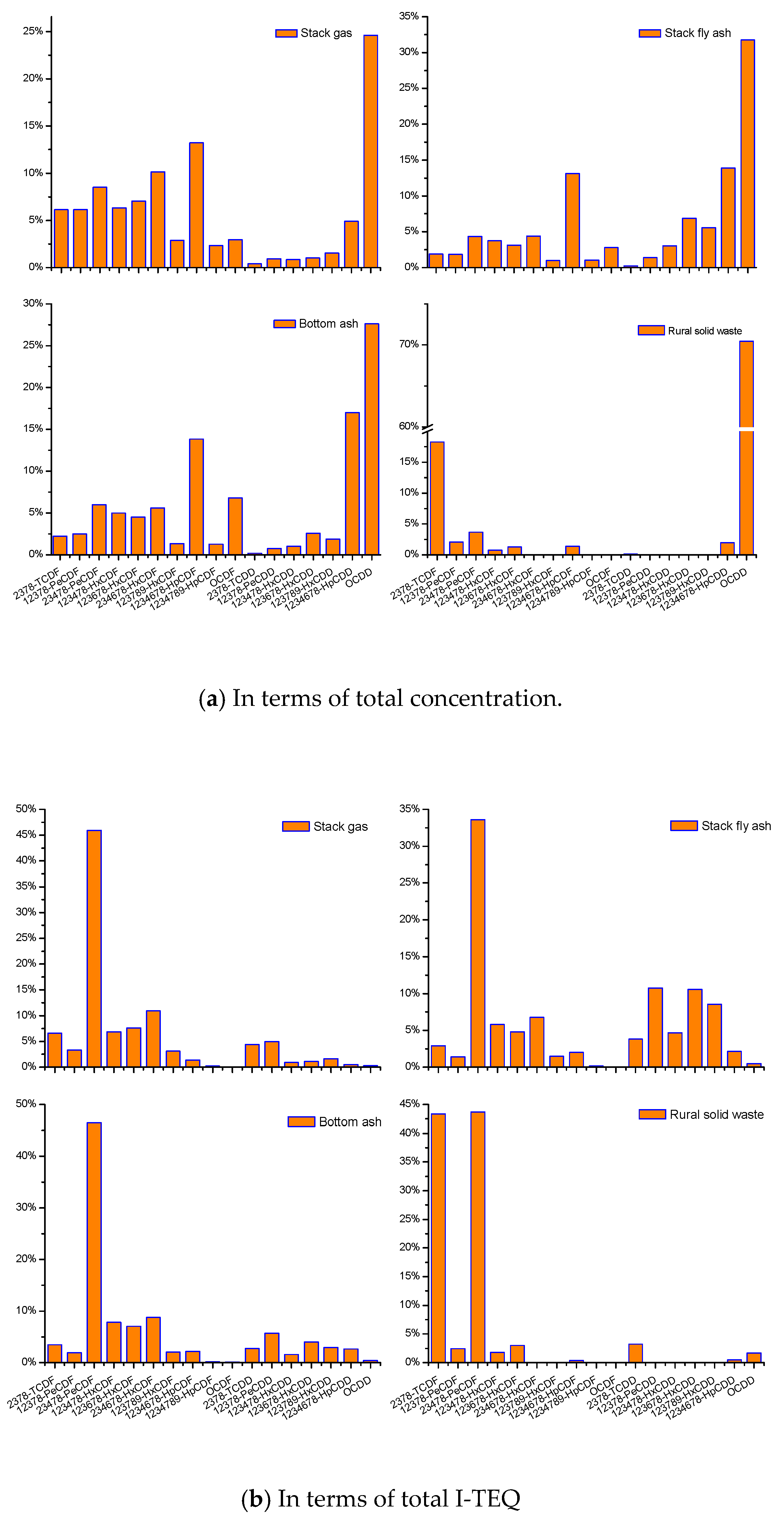
3.3. Congener Distribution and Fingerprint Analysis of PCDD/Fs from the Basic SWI
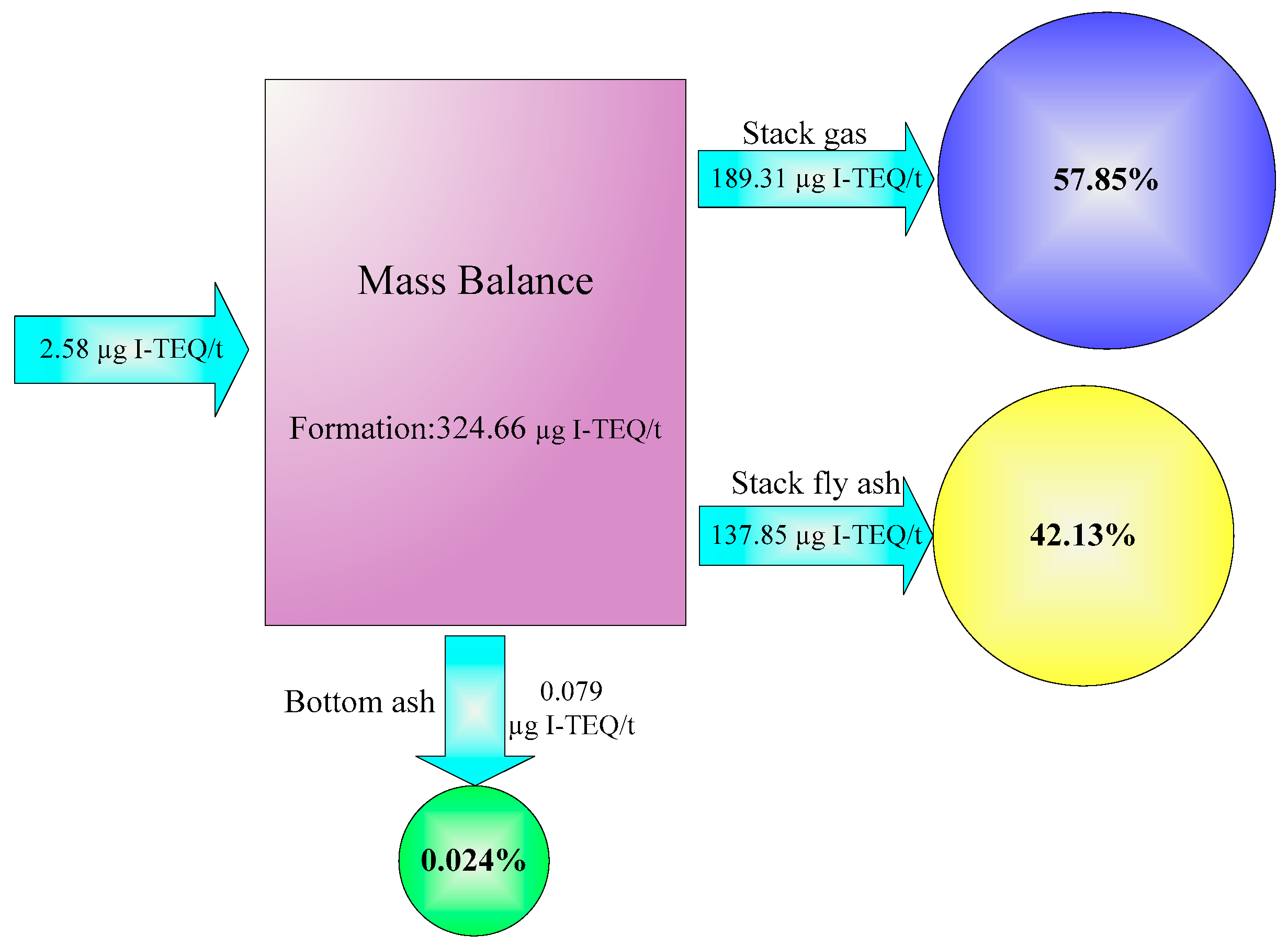
3.4. Emission Factor, Mass Balance, and Individual Exposure Assessment of PCDD/Fs from the Basic SWI
3.5. Comparison of Emissions to Those from the Refitted SWI Equipped with APCs
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, W.Y.; Wu, J.H.; Lin, S.C.; Chang, J.E. Bioremediation of polychlorinated-p-dioxins/dibenzofurans contaminated soil using simulated compost-amended landfill reactors under hypoxic conditions. J. Hazard Mater. 2016, 312, 159–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Buekens, A.; Li, X. Brominated flame retardants and the formation of dioxins and furans in fires and combustion. J. Hazard Mater. 2016, 304, 26–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, F.; Li, X.; Lu, J.W.; Hai, J.; Zhang, J.; Xie, B.; Hong, C. Emission characteristics of PCDD/Fs in stack gas from municipal solid waste incineration plants in Northern China. Chemosphere 2018, 200, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Y.; Liu, W.; Pan, W.; Wang, P.; Tian, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, M.; Chen, X.; Liao, X.; Zheng, M. Formation Pathways of Mono- to Octa-Chlorinated Dibenzo-p-dioxins and Dibenzofurans in Main Organochemical Industries. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 10945–10950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Liu, W.; Hou, M.; Li, Q.; Han, Y.; Li, H.; Yan, N.; Zheng, M. Mono- to Octachlorinated Polychlorinated Dibenzo-p-dioxin and Dibenzofuran Emissions from Sintering Plants Synergistically Controlled by the Desulfurization Process. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 5207–5215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ei, M.; Hai, J.; Cheng, J.; Lu, J.W.; Ren, M.Z.; Zhang, S.K.; Zhu, F. Emission characteristics of dioxins and heavy metals from small·scale thermal treatment furnaces for disposing domestic solid waste. J. Environ. Sci. (China) 2017, 37, 3836–3844. [Google Scholar]
- Guan, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, D.; Huang, X.; Li, H. Rural domestic waste management in Zhejiang Province, China: Characteristics, current practices, and an improved strategy. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2015, 65, 721–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Han, Z.; Liu, D.; Lei, Y.; Wu, J.; Li, S. Characteristics and management of domestic waste in the rural area of Southwest China. Waste Manag. Res. 2015, 33, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, M.; Hai, J.; Cheng, J.; Gui, L.; Lu, J.; Ren, M.Z.; Zhu, F.; Yang, Z.H. Emission characteristics of toxic pollutants from an updraft fixed bed gasifier for disposing rural domestic solid waste. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2017, 24, 19807–19815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.M. The emission inventory of PCDD/PCDF in Taiwan. Chemosphere 2004, 54, 1413–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, K.I.; Lee, S.H.; Lee, D.H. Emissions of PCDDs/DFs and dioxin-like PCBs from small waste incinerators in Korea. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 940–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, J.I.; Kim, K.H.; Jang, H.N.; Seo, Y.C.; Seok, K.S.; Hong, J.H.; Jang, M. Emission characteristics of particulate matter and heavy metals from small incinerators and boilers. Atmos. Environ. 2002, 36, 5057–5066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakao, T.; Aozasa, O.; Ohta, S.; Miyata, H. Formation of toxic chemicals including dioxin-related compounds by combustion from a small home waste incinerator. Chemosphere 2006, 62, 459–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNEP Chemicals. Standardized Toolkit for the Identification and Quantification of Dioin and Furan Releases. In United Nations Environment Program (UNEP) Chenicals, 2nd ed.; IOMC: Geneva, Switzerland, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Everaert, K.; Baeyens, J. Removal of PCDD/F from flue gases in fixed or moving bed adsorbers. Waste Manag. 2004, 24, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Everaert, K.; Baeyens, J. Catalytic combustion of volatile organic compounds. J. Hazard. Mater. 2004, 109, 113–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Everaert, K.; Baeyens, J.; Degrève, J. Entrained phase adsorption of PCDD/F from incinerator flue gases. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2003, 37, 1219–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Bourtsalas, A.C.; Themelis, N.J. Inventory of dioxin emissions of China. In Proceedings of the Conference of the Global WTERT Council, New York, NY, USA, 6–7 October 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, J.H.; Chen, T.; Li, X.D.; Zhang, J.; Lu, S.Y.; Ni, M.J.; Cen, K.F. Evaluation of PCDD/Fs emission from fluidized bed incinerators co-firing MSW with coal in China. J. Hazard Mater. 2006, 135, 47–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Tian, Z.; Li, H.; Xie, H.; Xiao, K.; Li, C.; Tang, C.; Zheng, M. Mono- to Octa-Chlorinated PCDD/Fs in Stack Gas from Typical Waste Incinerators and Their Implications on Emission. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 9774–9780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Larebeke, N.; Hens, L.; Schepens, P.; Covaci, A.; Baeyens, J.; Everaet, K.; Bernheim, J.L.; Vlietinck, R.; De Poorter, G. The Belgian PCB and dioxin incident of January-June 1999: Exposure data and potential impact on health. Environ. Health Perspect. 2001, 109, 265–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Hai, J.; Cheng, J. Characterization and mass balance of dioxin from a large-scale municipal solid waste incinerator in China. Waste Manag. 2012, 32, 1156–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Guo, X.; Fu, X.; Shao, Y.; Xu, Y.; Hai, J.; Ren, M.; Zhang, S. Emission characteristics of PCDD/Fs from a small waste incinerator in China. Organohalogen Compd. 2015, 77, 137–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Hai, J.; Ren, M.; Zhang, S.; Cheng, J.; Yang, Z. Emission, mass balance, and distribution characteristics of PCDD/Fs and heavy metals during cocombustion of swage sludge and coal in power plants. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 2123–2130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Hai, J.; Cheng, J.; Cai, Z.; Ren, M.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, J. Evaluation of PCDD/Fs and metals emission from a circulating fluidized bed incinerator co-combusting sewage sludge with coal. J. Environ. Sci. 2013, 25, 231–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bie, R.; Li, S.; Wang, H. Characterization of PCDD/Fs and heavy metals from MSW incineration plant in Harbin. Waste Manag. 2007, 27, 1860–1869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abad, E.; Adrados, M.A.; Caixach, J.; Fabrellas, B.; Rivera, J. Dioxin mass balance in a municipal waste incinerator. Chemosphere 2000, 40, 1143–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makoto, S.; Yoji, S.; Yasuhiro, I.; Toru, K. Reduction of total dioxin emissions from MSW incinerators. Organhalogen Compd. 1998, 36, 325–328. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, D.; Xu, X.; Zheng, M.; Chiu, C.H. Effect of copper chloride on the emissions of PCDD/Fs and PAHs from PVC combustion. Chemosphere 2002, 48, 857–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Altarawneh, M.; Dlugogorski, B.Z.; Kennedy, E.M.; Mackie, J.C. Catalytic effect of CuO and other transition metal oxides in formation of dioxins: Theoretical investigation of reaction between 2,4,5-trichlorophenol and CuO. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 5708–5715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Chen, Z.; Lu, S.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, M.; Li, X.; Yan, J. Emission characteristics of polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and dibenzofurans from the Co-combustion of municipal colid waste in a lab-scale drop-tube furnace. Energy Fuels 2018, 32, 5396–5404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin, Y.T.; Lin, C.; Chang-Chien, G.P.; Wang, Y.M. PCDD/F formation catalyzed by the metal chlorides and chlorinated aromatic compounds in fly ash. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2012, 12, 228–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuzuhara, S.; Sato, H.; Kasai, E.; Nakamura, T. Influence of Metallic Chlorides on the Formation of PCDD/Fs during Low-Temperature Oxidation of Carbon. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2003, 37, 2431–2435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Lin, X.; Lu, S.; Li, X.; Yan, J. Suppressing formation pathway of PCDD/Fs by S-N-containing compound in full-scale municipal solid waste incinerators. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 359, 1391–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, Y.; Zhang, H.; Fan, S.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, J. Emissions of PCDD/Fs from municipal solid waste incinerators in China. Chemosphere 2009, 75, 1153–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Everaert, K.; Baeyens, J. The formation and emission of dioxins in large scale thermal processes. Chemosphere 2002, 46, 439–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Everaert, K.; Baeyens, J. Correlation of PCDD/F emissions with operating parameters of municipal solid waste incinerators. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2001, 51, 718–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conesa, J.A.; Font, R.; Fullana, A.; Martin-Gullon, I.; Aracil, I.; Galvez, A.; Molto, J.; Gomez-Rico, M.F. Comparison between emissions from the pyrolysis and combustion of different wastes. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2009, 84, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, M.; Buekens, A.; Li, X. Open burning as a source of dioxins. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 47, 543–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Proximate Analysis | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Moisture content (wt. %) | 61.57 | Ash (wt. %) | 8.91 |
| Volatile matter (wt. %) | 26.38 | Fixed carbon (wt. %) | 3.14 |
| Low calorific value (kJ/kg) | 4278 | Low calorific value (dry basis, kJ/kg) | 10,153 |
| Physical composition analysis (wt. %) | |||
| Kitchen waste | 40.25 | Grass and wood | 3.88 |
| Plastic | 21.93 | Glass | 6.12 |
| Paper | 18.54 | Metal | 0.27 |
| Textile | 6.88 | Sandy soil | 2.13 |
| Elemental analysis on dry basis (wt. %) | |||
| C | 35.9 | H | 4.54 |
| O | 25.73 | N | 0.44 |
| S | 0.12 | Cl | 0.11 |
| Heavy metals on dry basis (mg/kg) | |||
| Pb | 20.81 | Cr | 298.13 |
| Hg | 1.74 | As | N.D. |
| Cd | N.D. | Cu | 35.34 |
| Output/Input | PCDD | PCDF | Total PCDD/F | Total I-TEQ PCDD/F |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Output: | ||||
| Stack gas (ng/Nm3) (n = 3) | 13.33 ± 0.20 | 25.57 ± 0.68 | 38.90 ± 0.88 | 3.60 ± 0.18 |
| Stack fly ash (ng/g) (n = 3) | 66.51 ± 3.00 | 39.52 ± 0.39 | 106.02 ± 3.40 | 6.89 ± 0.62 |
| Bottom ash (ng/kg) (n = 3) | 2.92 ± 0.29 | 2.81 ± 0.19 | 5.73 ± 0.48 | 0.37 ± 0.05 |
| Input: | ||||
| RSW (ng/kg) (n = 3) | 44.33 ± 2.96 | 16.78 ± 0.93 | 61.11 ± 3.89 | 2.58 ± 0.06 |
| Comparison between Individual Exposure | Dioxin Exposure Data from the Chinese Basic SWIs or Open Burning | Exposure Data from the Belgian Dioxin Incident [21] |
|---|---|---|
| Total amount | 3000 g I-TEQ | 1 g I-TEQ |
| Average intake | 150 pg I-TEQ/kg body weight based on 1000 million Chinese | 500 pg I-TEQ/kg body weight based on 10 million Belgians |
| Intake per day over 70 years | 0.006 pg I-TEQ/kg per day | 0.02 pg I-TEQ/kg per day |
| Rate of increase based on mean dioxin body burden | 2.2% | 7% |
| Cancer risk assessment | 10 additional cancer deaths/10 million Chinese | 32 additional cancer deaths/10 million Belgians |
| Comparison with PCDD/F Emissions | PCDD | PCDF | Total PCDD/F | I-TEQ Total PCDD/F |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stack gas from the basic SWI (ng/Nm3) (n = 3) | 13.33 ± 0.20 | 25.57 ± 0.68 | 38.90 ± 0.88 | 3.60 ± 0.18 |
| Flue gas at the ACI+BG inlet from the refitted SWI (ng/Nm3) (n = 3) | 16.71 ± 1.51 | 19.0 2±2 .50 | 35.73 ± 4.01 | 4.83 ± 0.56 |
| Flue gas at the ACI+BG outlet from the refitted SWI (ng/Nm3) (n = 3) | 0.299 ± 0.035 | 0.304 ±0 .013 | 0.604 ± 0.022 | 0.042 ± 0.005 |
| PCDD/Fs removal efficiency by ACI+BG (%) | 98.24% | 99.13% |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, G.; Huang, X.; Liao, W.; Kang, S.; Ren, M.; Hai, J. Measurement of Dioxin Emissions from a Small-Scale Waste Incinerator in the Absence of Air Pollution Controls. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 1267. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16071267
Zhang G, Huang X, Liao W, Kang S, Ren M, Hai J. Measurement of Dioxin Emissions from a Small-Scale Waste Incinerator in the Absence of Air Pollution Controls. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2019; 16(7):1267. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16071267
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Gang, Xiangxuan Huang, Wenbo Liao, Shimin Kang, Mingzhong Ren, and Jing Hai. 2019. "Measurement of Dioxin Emissions from a Small-Scale Waste Incinerator in the Absence of Air Pollution Controls" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 16, no. 7: 1267. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16071267
APA StyleZhang, G., Huang, X., Liao, W., Kang, S., Ren, M., & Hai, J. (2019). Measurement of Dioxin Emissions from a Small-Scale Waste Incinerator in the Absence of Air Pollution Controls. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 16(7), 1267. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16071267




