Long-Term Effectiveness of Liraglutide for Weight Management and Glycemic Control in Type 2 Diabetes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Participants
2.2. Data Collection
2.3. Assessments
2.4. Outcome Measures
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Characteristics of the Study Cohort
3.2. Primary Outcome
3.3. Secondary Outcomes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization. Obesity and Overweight Fact Sheer. Available online: http://www.who.int/dietphysicalactivity/media/en/gsfs_obesity.pdf (accessed on 1 November 2019).
- Pinkney, J. Prevention and cure of type 2 diabetes. BMJ 2002, 325, 232–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilding, J.P.H. The importance of weight management in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Int. J. Clin. Pract. 2014, 68, 682–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Daousi, C.; Casson, I.F.; Gill, G.V.; MacFarlane, I.A.; Wilding, J.P.; Pinkney, J.H. Prevalence of obesity in type 2 diabetes in secondary care: Association with cardiovascular risk factors. Postgrad. Med. J. 2006, 82, 280–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wing, R.R.; Lang, W.; Wadden, T.A.; Safford, M.; Knowler, W.C.; Bertoni, A.G.; Hill, J.O.; Brancati, F.L.; Peters, A.; Wagenknecht, L. Look AHEAD Research Group. Benefits of modest weight loss in improving cardiovascular risk factors in overweight and obese individuals with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2011, 34, 1481–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dewan, S.; Wilding, J. Adult obesity: Metabolic syndrome, diabetes and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. In Clinical Obesity in Adults and Children, 2nd ed.; Blackwell Publishing: Oxford, UK, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Bray, G.A.; Ryan, D.H. Medical therapy for the patient with obesity. Circulation 2012, 125, 1695–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermansen, K.; Mortensen, L.S. Bodyweight changes associated with antihyperglycaemic agents in Type 2 diabetes mellitus. Drug Safes 2007, 30, 1127–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potts, J.E.; Gray, L.J.; Brady, E.M.; Khunti, K.; Davies, M.J.; Bodicoat, D.H. The effect of glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists on weight Loss in type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and mixed treatment comparison meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0126769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Davies, M.J.; D’Alessio, D.A.; Fradkin, J.; Kernan, W.N.; Mathieu, C.; Mingrone, G.; Rossing, P.; Tsapas, A.; Wexler, D.J.; Buse, J.B. Management of Hyperglycemia in Type 2 Diabetes, 2018. A Consensus Report by the American Diabetes Association (ADA) and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD). Diabetes Care 2018, 41, 2669–2701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nauck, M.A.; Vardarli, I.; Deacon, C.F.; Holst, J.J.; Meier, J.J. Secretion of glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) in type 2 diabetes: What is up, what is down? Diabetologia 2011, 54, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- van Bloemendaal, L.; IJzerman, R.G.; Ten Kulve, J.S.; Barkhof, F.; Konrad, R.J.; Drent, M.L.; Veltman, D.J.; Diamant, M. GLP-1 receptor activation modulates appetite- and reward-related brain areas in humans. Diabetes 2014, 63, 4186–4196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Buse, J.B.; Rosenstock, J.; Sesti, G.; Schmidt, W.E.; Montanya, E.; Brett, J.H.; Zychma, M.; Blonde, L. LEAD-6 Study Group. Liraglutide once a day versus exenatide twice a day for type 2 diabetes: A 26-week randomised, parallel-group, multinational, open-label trial (LEAD-6). Lancet 2009, 374, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garber, A.; Henry, R.; Ratner, R.; Garcia-Hernandez, P.A.; Rodriguez-Pattzi, H.; Olvera-Alvarez, I.; Hale, P.M.; Zdravkovic, M.; Bode, B. LEAD-3 (Mono) Study Group. Liraglutide versus glimepiride monotherapy for type 2 diabetes (LEAD-3 Mono): A randomised, 52-week, phase III, double-blind, parallel-treatment trial. Lancet 2009, 373, 473–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marre, M.; Shaw, J.; Brandle, M.; Bebakar, W.M.; Kamaruddin, N.A.; Strand, J.; Zdravkovic, M.; Le Thi, T.D.; Colagiuri, S. LEAD-1 SU study group. Liraglutide, a once-daily human GLP-1 analogue, added to a sulphonylurea over 26 weeks produces greater improvements in glycaemic and weight control compared with adding rosiglitazone or placebo in subjects with type 2 diabetes (LEAD-1 SU). Diabet. Med. 2009, 26, 268–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nauck, M.; Frid, A.; Hermansen, K.; Shah, N.S.; Tankova, T.; Mitha, I.H.; Zdravkovic, M.; Düring, M.; Matthews, D.R. LEAD-2 Study Group. Efficacy and safety comparison of liraglutide, glimepiride, and placebo, all in combination with metformin, in type 2 diabetes: The LEAD (liraglutide effect and action in diabetes)-2 study. Diabetes Care 2009, 32, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Russell-Jones, D.; Vaag, A.; Schmitz, O.; Sethi, B.K.; Lalic, N.; Antic, S.; Zdravkovic, M.; Ravn, G.M.; Simó, R. Liraglutide Effect and Action in Diabetes 5 (LEAD-5) met+SU Study Group. Liraglutide vs insulin glargine and placebo in combination with metformin and sulfonylurea therapy in type 2 diabetes mellitus (LEAD-5 met+SU): A randomised controlled trial. Diabetologia 2009, 52, 2046–2055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zinman, B.; Gerich, J.; Buse, J.B.; Lewin, A.; Schwartz, S.; Raskin, P.; Hale, P.M.; Zdravkovic, M.; Blonde, L. LEAD-4 Study Investigators. Efficacy and safety of the human glucagon-like peptide-1 analog liraglutide in combination with metformin and thiazolidinedione in patients with type 2 diabetes (LEAD-4 Met+TZD). Diabetes Care 2009, 32, 1224–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Davies, M.J.; Bergenstal, R.; Bode, B.; Kushner, R.F.; Lewin, A.; Skjøth, T.V.; Andreasen, A.H.; Jensen, C.B.; DeFronzo, R.A. NN8022-1922 Study Group. Efficacy of Liraglutide for Weight Loss Among Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. The SCALE Diabetes Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2015, 314, 687–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ostawal, A.; Mocevic, E.; Kragh, N.; Xu, W. Clinical effectiveness of liraglutide in type 2 diabetes treatment in the real-world setting: A systematic literature review. Diabetes Ther. 2016, 7, 411–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- American Diabetes Association. 9. Pharmacologic Approaches to Glycemic Treatment: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes—2019. Diabetes Care 2019, 42, S90–S102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stevens, R.J.; Kothari, V.; Adler, A.I.; Stratton, I.M. United Kingdom Prospective Diabetes Study (UKPDS) Group. The UKPDS risk engine: A model for the risk of coronary heart disease in type II diabetes (UKPDS 56). Clin. Sci. (Lond.) 2001, 101, 671–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zinman, B.; Schmidt, W.E.; Moses, A.; Lund, N.; Gough, S. Achieving a clinically relevant composite outcome of an HbA1c of <7% without weight gain or hypoglycaemia in type 2 diabetes: A meta-analysis of the liraglutide clinical trial programme. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2012, 14, 77–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, P.; Yu, D.M.; Chen, L.M.; Chang, B.C.; Ji, Q.D.; Li, S.Y.; Zhu, M.; Ding, S.H.; Zhang, B.Z.; Wang, S.L.; et al. Liraglutide reduces the body weight and waist circumference in Chinese overweight and obese type 2 diabetic patients. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2015, 36, 200–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lapolla, A.; Frison, V.; Bettio, M.; Dal Pos, M.; Rocchini, P.; Panebianco, G.; Tadiotto, F.; Da Tos, V.; D’Ambrosio, M.; Marangoni, A.; et al. Correlation between baseline characteristics and clinical outcomes in a large population of diabetes patients treated with liraglutide in a real-world setting in Italy. Clin. Ther. 2015, 37, 574–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiefari, E.; Capula, C.; Vero, A.; Oliverio, R.; Puccio, L.; Liguori, R.; Pullano, V.; Greco, M.; Foti, D.; Tirinato, D.; et al. Add-On Treatment with Liraglutide Improves Glycemic Control in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes on Metformin Therapy. Diabetes Technol. Ther. 2015, 17, 468–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilding, J.P.; Overgaard, R.V.; Jacobsen, L.V.; Jensen, C.B.; le Roux, C.W. Exposure-response analyses of liraglutide 3.0 mg for weight management. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2016, 18, 491–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Anichini, R.; Cosimi, S.; Di Carlo, A.; Orsini, P.; De Bellis, A.; Seghieri, G.; Franconi, F.; Baccetti, F. Gender difference in response predictors after 1-year exenatide therapy twice daily in type 2 diabetic patients: A real-world experience. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. 2013, 6, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Buysschaert, M.; Preumont, V.; Oriot, P.R.; Paris, I.; Ponchon, M.; Scarnière, D.; Selvais, P.; UCL Study Group for Exenatide. One-year metabolic outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes treated with exenatide in routine practice. Diabetes Metab. 2010, 36, 381–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franconi, F.; Campesi, I. Sex and gender influences on pharmacological response: An overview. Expert Rev. Clin. Pharmacol. 2014, 7, 469–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franconi, F.; Campesi, I.; Occhioni, S.; Tonolo, G. Sex-gender differences in diabetes vascular complications and treatment. Endocr. Metab. Immune Disord. Drug Targets 2012, 12, 179–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legato, M.J.; Gelzer, A.; Goland, R.; Ebner, S.A.; Rajan, S.; Villagra, V.; Kosowski, M. Writing Group for The Partnership for Gender-Specific Medicine. Gender-specific care of the patient with diabetes: Review and recommendations. Gend. Med. 2006, 3, 131–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manicardi, V.; Rossi, M.; Romeo, L.; Giandalia, A.; Calabrese, M.; Cimino, E.; Antenucci, D.; Bollati, P.; Li Volsi, P.; Maffettone, A.; et al. Gender differences in type 2 diabetes (Italy). Italy J. Gend.-Specif. Med. 2016, 2, 60–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frison, V.; Simioni, N.; Marangoni, A.; Balzano, S.; Vinci, C.; Zenari, L.; De Moliner, L.; Tadiotto, F.; D’Ambrosio, M.; Confortin, L.; et al. Clinical Impact of 5 Years of Liraglutide Treatment on Cardiovascular Risk Factors in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in a Real-Life Setting in Italy: An Observational Study. Diabetes Ther. 2018, 9, 2201–2208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Teslovich, T.M.; Musunuru, K.; Smith, A.V.; Edmondson, A.C.; Stylianou, I.M.; Koseki, M.; Pirruccello, J.P.; Ripatti, S.; Chasman, D.I.; Willer, C.J.; et al. Biological, clinical and population relevance of 95 loci for blood lipids. Nature 2010, 466, 707–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuchenbaecker, K.; Telkar, N.; Reiker, T.; Walters, R.G.; Lin, K.; Eriksson, A.; Gurdasani, D.; Gilly, A.; Southam, L.; Tsafantakis, E.; et al. Understanding Society Scientific Group. The transferability of lipid loci across African, Asian and European cohorts. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 4330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ramos-Lopez, O.; Riezu-Boj, J.I.; Milagro, F.I.; Goni, L.; Cuervo, M.; Martinez, J.A. Differential lipid metabolism outcomes associated with ADRB2 gene polymorphisms in response to two dietary interventions in overweight/obese subjects. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2018, 28, 165–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poduri, A.; Khullar, M.; Bahl, A.; Sehrawat, B.S.; Sharma, Y.; Talwar, K.K. Common variants of HMGCR, CETP, APOAI, ABCB1, CYP3A4, and CYP7A1 genes as predictors of lipid-lowering response to atorvastatin therapy. DNA Cell Biol. 2010, 29, 629–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertoluci, M.C.; Rocha, V.Z. Cardiovascular risk assessment in patients with diabetes. Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 2017, 9, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pencina, M.J.; Navar, A.M.; Wojdyla, D.; Sanchez, R.J.; Khan, I.; Elassal, J.; D’Agostino, R.B.; Peterson, E.D.; Sniderman, A.D. Quantifying Importance of Major Risk Factors for Coronary Heart Disease. Circulation 2019, 139, 1603–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farzadfar, F. Cardiovascular disease risk prediction models: Challenges and perspectives. Lancet Glob. Health 2019, 7, e1288–e1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Buse, J.B.; Sesti, G.; Schmidt, W.E.; Montanya, E.; Chang, C.T.; Xu, Y.; Blonde, L.; Rosenstock, J.; Liraglutide Effect Action in Diabetes-6 Study Group. Switching to once-daily liraglutide from twice-daily exenatide further improves glycemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes using oral agents. Diabetes Care 2010, 33, 1300–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Di Gaetano, C.; Voglino, F.; Guarrera, S.; Fiorito, G.; Rosa, F.; Di Blasio, A.M.; Manzini, P.; Dianzani, I.; Betti, M.; Cusi, D.; et al. An overview of the genetic structure within the Italian population from genome-wide data. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e43759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiefari, E.; Tanyolaç, S.; Iiritano, S.; Sciacqua, A.; Capula, C.; Arcidiacono, B.; Nocera, A.; Possidente, K.; Baudi, F.; Ventura, V.; et al. polymorphism of HMGA1 is associated with increased risk of metabolic syndrome and related components. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiefari, E.; Ventura, V.; Capula, C.; Randazzo, G.; Scorcia, V.; Fedele, M.; Arcidiacono, B.; Nevolo, M.T.; Bilotta, F.L.; Vitiello, M.; et al. A polymorphism of HMGA1 protects against proliferative diabetic retinopathy by impairing HMGA1-induced VEGFA expression. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 39429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Brunetti, A.; Chiefari, E.; Foti, D.P. Pharmacogenetics in type 2 diabetes: Still a conundrum in clinical practice. Expert Rev. Endocrinol. Metab. 2017, 12, 155–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mirabelli, M.; Chiefari, E.; Caroleo, P.; Vero, R.; Brunetti, F.S.; Corigliano, D.M.; Arcidiacono, B.; Foti, D.P.; Puccio, L.; Brunetti, A. Long-Term Effectiveness and Safety of SGLT-2 Inhibitors in an Italian Cohort of Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. J. Diabetes Res. 2019, 2019, 3971060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
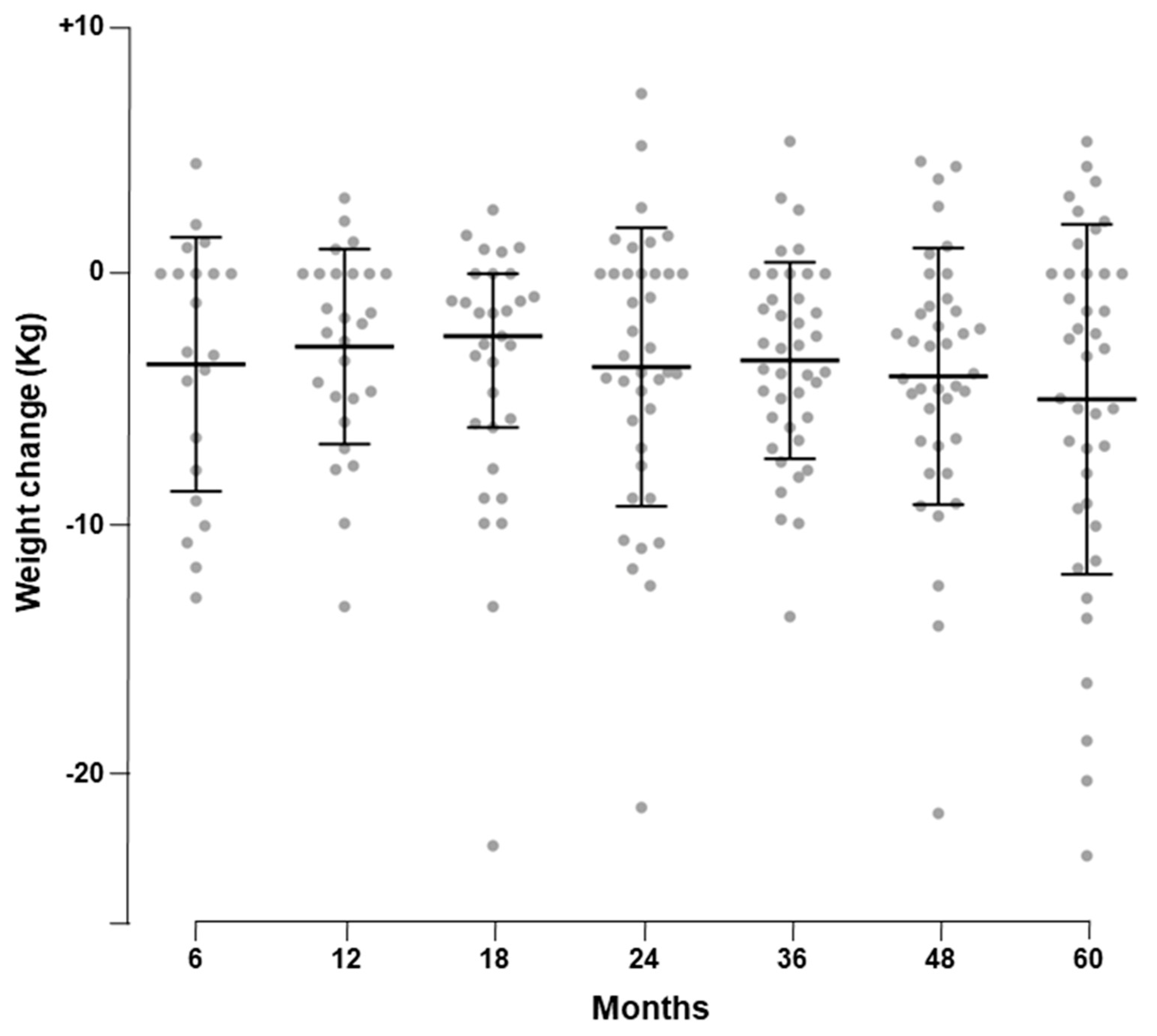

| Baseline Characteristics | |
|---|---|
| Female gender, n | 22 (55.0) |
| Ethnicity | Caucasian |
| Age, years | 57.5 ± 6.6 |
| Diabetes duration, years | 8.2 ± 5.6 |
| Diabetes duration ≥10 years, n | 13 (32.5) |
| Hypertension, n | 37 (92.5) |
| Dyslipidemia, n | 31 (77.5) |
| Weight, Kg | 92.1 ± 20.6 |
| BMI (Kg/m2) | 34.0 ± 6.8 |
| Overweight (BMI ≥ 25 Kg/m2), n | 14 (35.0) |
| Obesity (BMI ≥ 30 Kg/m2), n | 26 (65.0) |
| Coronary artery disease, n | 5 (12.5) |
| History of stroke/TIA, n | 1 (2.5) |
| Peripheral artery disease, n | 0 (0.0) |
| Diabetic microvascular complications, n | 12 (30.0) |
| Diabetic retinopathy, n | 6 (15.0) |
| Diabetic nephropathy, n | 5 (12.5) |
| Diabetic neuropathy (autonomic/peripheral), n | 1 (2.5) |
| Concomitant Medications | n (%) |
|---|---|
| Metformin | 39 (97.5) |
| Sulphonylureas | 6 (15.0) |
| Meglitinides | 3 (7.5) |
| Pioglitazone | 3 (7.5) |
| Acarbose | 2 (5.0) |
| Insulin | 0 (0.0) |
| Angiotensin-converting-enzyme inhibitors | 18 (46.2) |
| Angiotensin II receptor blockers | 14 (35.9) |
| Calcium channel blockers | 9 (23.1) |
| Beta–blockers | 11 (28.2) |
| Diuretics | 17 (43.6) |
| Loop diuretics | 1 (2.6) |
| Alpha-1-blockers | 3 (7.7) |
| Statins | 21 (53.8) |
| Ezetimibe | 5 (12.8) |
| Cardioaspirin | 6 (15.4) |
| B | Beta | T | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BMI | 0.387 | 0.380 | 2.533 | 0.016 |
| Female gender | 5.086 | 0.365 | 2.420 | 0.020 |
| * Female gender | 6.459 | 0.464 | 2.975 | 0.005 |
| Parameters | Baseline | 5 Years | Change | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HbA1c, % | 7.9 ± 0.9 | 7.0 ± 0.7 | −0.9 ± 0.9 | <0.001 |
| HbA1c < 7%, n | 7 (17.5) | 20 (50) | 13 | <0.001 |
| FPG, mg/dL) | 164.8 ± 32.8 | 140.8 ± 26.6 | −22.7 ± 33.0 | <0.001 |
| Creatinine, mg/dL | 0.8 ± 0.1 | 0.8 0.2 | −0.1 ± 0.2 | 0.174 * |
| eGFR, ml/min/m2 | 92.5 ± 20.3 | 87.5 ± 17.0 | −9.2 ± 17.3 | 0.787 |
| Total cholesterol, mg/dL | 180.5 ± 33.3 | 163.8 ± 36.8 | −13.9 ± 47.5 | 0.739 * |
| HDL-C, mg/dL | 46.6 ± 7.1 | 47.1 ± 8.9 | 1.6 ± 5.8 | 0.262 |
| Triglycerides, mg/dL | 178.3 ± 74.8 | 142.4 ± 58.5 | −24.1 ± 87.0 | 0.283 * |
| Systolic BP, mmHg | 132.9 ± 15.9 | 127.5 ± 18.9 | −4.6 ± 14.4 | 0.128 * |
| Diastolic BP, mmHg | 72.9 ± 9.2 | 72.2 ± 10.1 | 0.4 ± 11.4 | 0.983 * |
| UKPDS Score | Baseline | 5 Years | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Non-fatal CHD (5 years) | 5.0 ± 3.0 | 6.9 ± 5.8 | <0.001 |
| Fatal CHD (5 years) | 2.9 ± 2.3 | 4.6 ± 4.5 | <0.001 |
| Non-fatal stroke (5 years) | 1.9 ± 1.6 | 3.8 ± 3.6 | <0.001 |
| Fatal stroke (5 years) | 0.3 ± 0.2 | 0.5 ± 0.5 | <0.001 |
| Non-fatal CHD (10 years) | 11.7 ± 6.5 | 14.2 ± 9.2 | 0.004 |
| Fatal CHD (10 years) | 7.4 ± 5.3 | 10.1 ± 8.2 | <0.001 |
| Non-fatal stroke (10 years) | 5.4 ± 4.5 | 9.8 ± 7.9 | <0.001 |
| Fatal stroke (10 years) | 0.8 ± 0.7 | 1.3 ± 1.1 | <0.001 |
| Non-fatal CHD (5 years) | 5.0 ± 3.0 | 6.9 ± 5.8 | <0.001 |
| Fatal CHD (5 years) | 2.9 ± 2.3 | 4.6 ± 4.5 | <0.001 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mirabelli, M.; Chiefari, E.; Caroleo, P.; Arcidiacono, B.; Corigliano, D.M.; Giuliano, S.; Brunetti, F.S.; Tanyolaç, S.; Foti, D.P.; Puccio, L.; et al. Long-Term Effectiveness of Liraglutide for Weight Management and Glycemic Control in Type 2 Diabetes. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 207. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17010207
Mirabelli M, Chiefari E, Caroleo P, Arcidiacono B, Corigliano DM, Giuliano S, Brunetti FS, Tanyolaç S, Foti DP, Puccio L, et al. Long-Term Effectiveness of Liraglutide for Weight Management and Glycemic Control in Type 2 Diabetes. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2020; 17(1):207. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17010207
Chicago/Turabian StyleMirabelli, Maria, Eusebio Chiefari, Patrizia Caroleo, Biagio Arcidiacono, Domenica Maria Corigliano, Stefania Giuliano, Francesco Saverio Brunetti, Sinan Tanyolaç, Daniela Patrizia Foti, Luigi Puccio, and et al. 2020. "Long-Term Effectiveness of Liraglutide for Weight Management and Glycemic Control in Type 2 Diabetes" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 17, no. 1: 207. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17010207
APA StyleMirabelli, M., Chiefari, E., Caroleo, P., Arcidiacono, B., Corigliano, D. M., Giuliano, S., Brunetti, F. S., Tanyolaç, S., Foti, D. P., Puccio, L., & Brunetti, A. (2020). Long-Term Effectiveness of Liraglutide for Weight Management and Glycemic Control in Type 2 Diabetes. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 17(1), 207. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17010207











