Mind–Body Exercise for Anxiety and Depression in COPD Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Method
2.1. Search Strategy
2.2. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
2.3. Study Selection and Data Extraction
2.4. Quality Assessment of Each Eligible Study
2.5. Study Analysis Method
3. Results
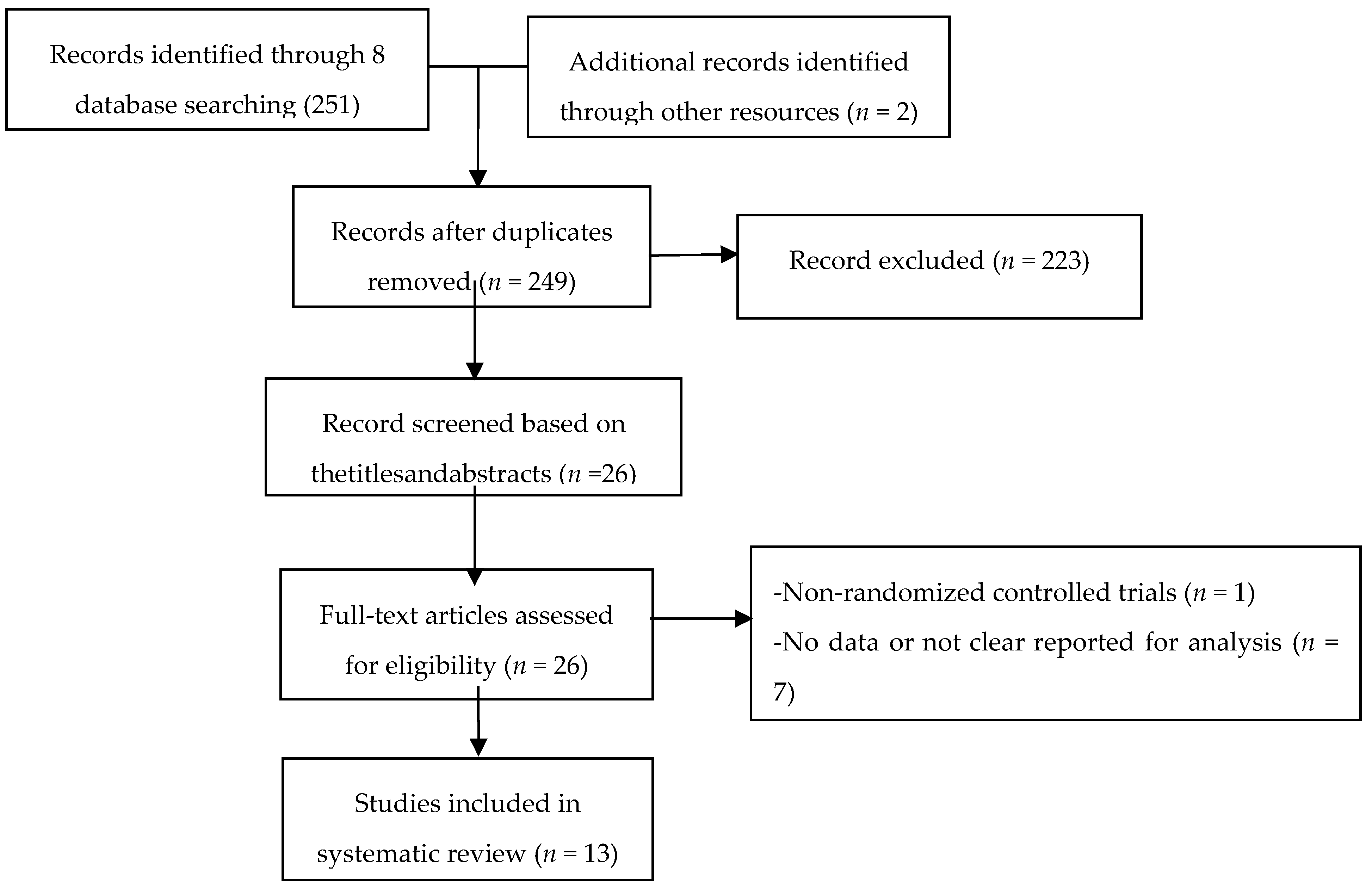
3.1. Studies Selection
3.2. Characteristics of Eligible Studies
3.3. Methodological Quality Assessment
3.4. Meta-Analysis of Outcome Indicators
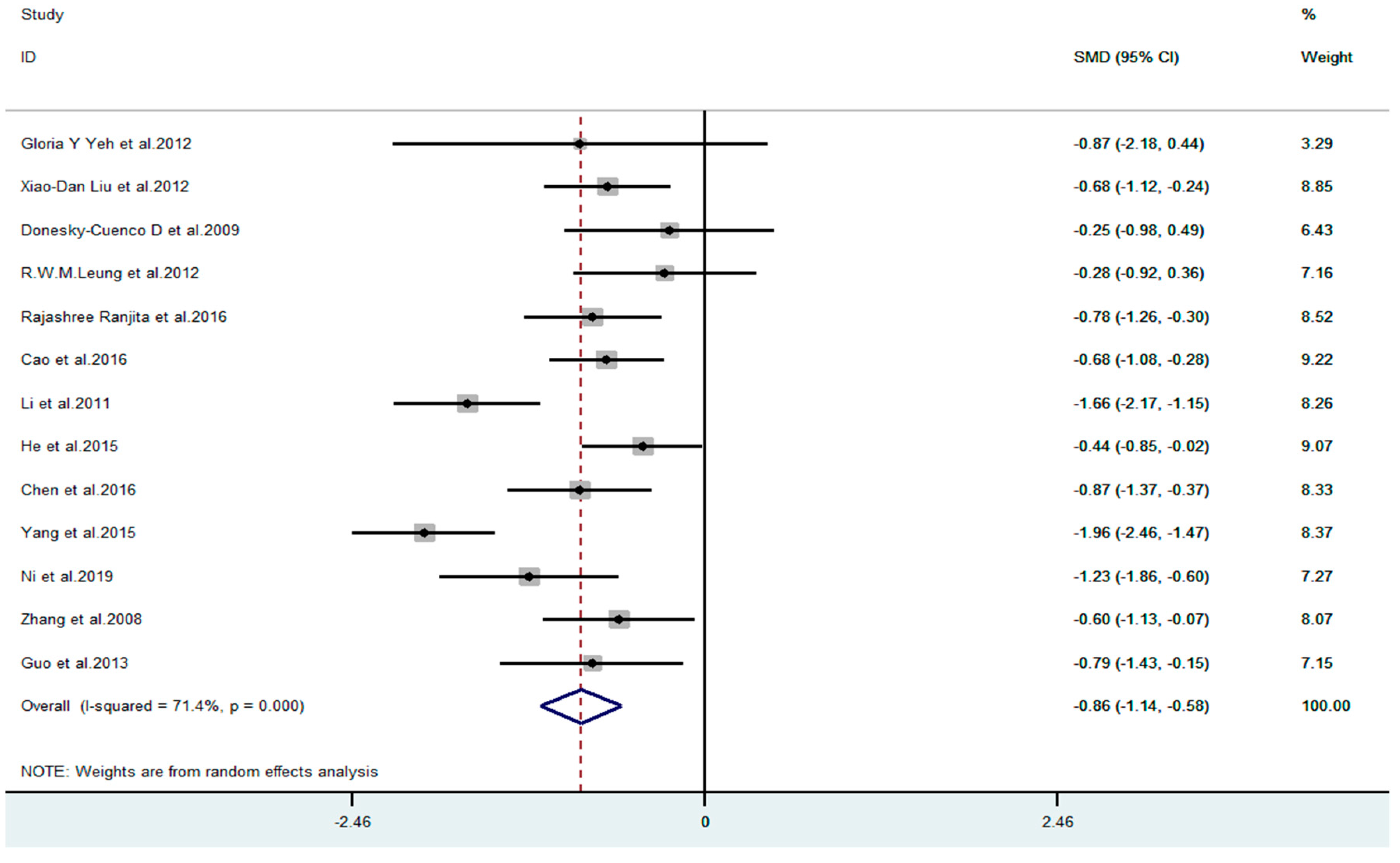
3.4.1. Effect of Mind–Body Exercise on COPD Patients with Anxiety
3.4.2. Regression Analysis
3.4.3. Sub-Group Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Limitations
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease: Global Strategy for the Diagnosis, Management, and Prevention of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Available online: http://www.goldcopd.org/ (accessed on 21 December 2015).
- COPD of Respiratory branch of CMA. Guidelines for diagnosis and treatment of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (2013 Revision). Chin. J. Med. Front. 2014, 6, 67–80. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, C.Y. Strategy and practice of traditional Chinese medicine in the treatment of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Electron. J. Integr. Chin. West. Med. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2016, 4, 31–33. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, Z.P.; Chen, L. Research Progress of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease with Anxiety and Depression. Chin. J. Respir. Crit. Care 2019, 18, 491–494. [Google Scholar]
- Tselebis, A.; Pachi, A.; Ilias, I.; Kosmas, E.; Bratis, D.; Moussas, G.; Tzanakis, N. Strategies to improve anxiety and depression in patients with COPD: A mental health perspective. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2016, 12, 297–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yohannes, A.M.; Kaplan, A.; Hanania, N.A. Anxiety and depression in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: Recognition and management. Clev. Clin. J. Med. 2018, 85, S11–S18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soriano, J.B.; Abajobir, A.A.; Abate, K.H.; Abera, S.F.; Agrawal, A.; Ahmed, M.B. Global, regional, and national deaths, prevalence, disability-adjusted life years, and years lived with disability for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and asthma, 1990–2015: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015. Lancet Respir. Med. 2017, 5, 691–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Minino, A.M.; Xu, J.; Kochanek, K.D. Deaths: Preliminary data for 2008. Natl. Vital. Stat. Rep. 2010, 59, 1–52. [Google Scholar]
- Lopez, A.D.; Shibuya, K.; Rao, C.; Mathers, C.D.; Hansell, A.L.; Held, L.S.; Schmid, V.; Buist, S. Chronicobstructive pulmonary disease: Current burden and future projections. Eur. Respir. J. 2006, 27, 397–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, F.L.; Yeh, M.L.; Lai, Y.H.; Lin, K.C.; Yu, C.J.; Chang, J.S. Two-month breathing-based walking improves anxiety, depression, dyspnoea and quality of life in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: A randomised controlled study. J. Clin. Nurs. 2019, 28, 3632–3640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, C.M.D.; Neto, M.G.; Saquetto, M.B.; da Conceicao, C.S.; Souza-Machado, A. Effects of upper limb resistance exercise on aerobic capacity, muscle strength, and quality of life in COPD patients: A randomized controlled trial. Clin. Rehabil. 2018, 32, 1636–1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.J.; Loprinzi, P.D.; Yang, L.; Liu, J.; Liu, S.J.; Zou, L.Y. The Beneficial Effects of Traditional Chinese Exercises for Adults with Low Back Pain: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Med. Lith. 2019, 55, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zou, L.Y.; Zhang, Y.J.; Yang, L.; Loprinzi, P.D.; Yeung, A.S.; Kong, J.; Chen, K.W.; Song, K.; Xiao, T.; Li, H. Are Mindful Exercises Safe and Beneficial for Treating Chronic Lower Back Pain? A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, K.; Liu, S.J.; Kong, Z.W.; Zhang, Y.J.; Liu, J. Mind-Body Exercise (Wuqinxi) for Patients with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Int. J. Environ. Res. 2019, 16, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zou, L.Y.; Han, J.; Li, X.C.; Yeung, A.; Hui, S.C.; Tsang, W.N.; Ren, Z.B.; Wang, L. The Effects of Tai Chi on Lower Limb Proprioception in Adults Aged Over 55: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2019, 100, 1102–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, L.Y.; Zhang, Y.J.; Liu, Y.; Tian, X.P.; Xiao, T.; Liu, X.L.; Yeung, A.S.; Liu, J.; Wang, X.Q.; Yang, Q. The Effects of Tai Chi Chuan Versus Core Stability Training on Lower-Limb Neuromuscular Function in Aging Individuals with Non-Specific Chronic Lower Back Pain. Med. Linthuania 2019, 55, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zou, L.Y.; Loprinzi, P.D.; Yeung, A.S.; Zeng, N.; Huang, T. The Beneficial Effects of Mind-Body Exercises for People with Mild Cognitive Impairment: A Systematic Review with Meta-analysis. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2019, 100, 1556–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.W.; Zhang, Y.J.; Kong, Z.W.; Loprinzi, P.D.; Hu, Y.; Ye, J.J.; Liu, S.J.; Yu, J.J.; Zou, L.Y. The Effects of Tai Chi on Markers of Atherosclerosis, Lower-limb Physical Function, and Cognitive Ability in Adults Aged Over 60: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, J.; Xie, H.H.; Liu, M.; Wang, Z.B.; Zou, L.Y.; Yeung, A.S.; Hui, S.S.C.; Yang, Q. The Effects of Tai Chi on Heart Rate Variability in Older Chinese Individuals with Depression. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 2771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zou, L.Y.; Sasaki, J.E.; Wei, G.X.; Huang, T.; Yeung, A.S.; Neto, O.B.; Chen, K.W.; Hui, S.S.C. Effects of Mind–Body Exercises (Tai Chi/Yoga) on Heart Rate Variability Parameters and Perceived Stress: A Systematic Review with Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. J. Clin. Med. 2018, 7, 404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, S.J.; Ren, Z.B.; Wang, L.; Wei, G.X.; Zou, L.Y. Mind-Body (Baduanjin) Exercise Prescription for Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: A Systematic Review with Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 1830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tanaka, H.; Suksom, D. Mind-body exercises. Am. J. Lifestyle Med. 2015, 9, 459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, A.S.; Sze, S.L.; Siu, N.Y.; Lau, E.M.; Cheung, M.C. A Chinese mind-body exercise improves self- control of children with autism: A randomized controlled trial. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e68184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zou, L.Y.; Yeung, A.S.; Li, C.X.; Wei, G.X.; Chen, K.W.; Kinser, P.A.; Chan, J.S.M.; Ren, Z.B. Effects of Meditative Movements on Major Depressive Disorder: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. J. Clin. Med. 2018, 7, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zou, L.Y.; Yeung, A.S.; Zeng, N.; Wang, C.Y.; Sun, L.; Tomas, G.A.; Wang, H.R. Effects of Mind-Body Exercises for Mood and Functional Capabilities in Patients with Stroke: An Analytical Review of Randomized Controlled Trials. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zou, L.Y.; Yeung, A.; Quan, X.F.; Hui, S.S.C.; Hu, X.Y.; Chan, J.S.M.; Wang, C.Y.; Boyden, S.D.; Sun, L.; Wang, H.R. Mindfulness-based Baduanjin exercise for depression and anxiety in people with physical or mental illnesses: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, S.; Zou, L.Y.; Chen, L.Z.; Yao, Y.; Loprinzi, P.D.; Siu, P.M.; Wei, G.X. The Effect of Tai Chi Chuan on Negative Emotions in Non-Clinical Populations: A Meta-Analysis and Systematic Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 3033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, J.; Pei, J.; Sun, K.X.; Li, H.H.; Zhou, C.X.; Wu, J.; Huang, M.; Ji, L. Interactive dynamic scalp acupuncture combined with occupational therapy for upper limb motor impairment in stroke:a randomized controlled trial. Chin. Acupunct. Moxibustion 2015, 35, 983–985. [Google Scholar]
- Gautam, S.; Tolahunase, M.; Kumar, U.; Data, R. Impact of yoga based mind-body intervention on systemic inflammatory markers and co-morbid depression in active Rheumatoid arthritis patients: A randomized controlled trial. Restor. Neurol. Neurosci. 2019, 37, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manchanda, S.C.; Madan, K. Yoga and meditation in cardiovascular disease. Clin. Res. Cardiol. 2014, 103, 675–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.L.; Chai, Y.; Pan, X.J.; Shen, H.; Wei, X.; Xie, Y.M. Taichi for treating osteopenia and primary osteoporosis: A meta-analysis and trial sequential analysis. Clin. Interv. Aging 2019, 14, 91–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zou, L.; Albert, Y.; Quan, X.; Wang, H. A Systematic review and Meta-Analysis of Mindfulness-based (Baduanjin) exercise for alleviating musculoskeletal pain and improving sleep quality in people with chronic diseases. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jiang, H.; Tan, C.; Yuan, S. Baduanjin exercise for insomnia: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Behav. Sleep Med. 2017, 4, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Love, M.F.; Sharrief, A.; Chaoul, A.; Savitz, S.; Beauchamp, J.E.S. Mind-Body Interventions, Psychological Stressors, and Quality of Life in Stroke Survivors: A Systematic Review. Stroke 2019, 50, 434–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bridle, C.; Spanjers, K.; Patel, S. Effect of exercise on depression severity in older people: Systematic review and meta-analysisofrandomised controlled trials. Br. J. Psychiatry J. Ment. Sci. 2012, 201, 180–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gloria, Y.Y.; David, H.R.; Peter, M.W.; Roger, B.D.; Mary, T.Q.; Russell, S.P. Tai Chi Exercise for Patients With Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: A Pilot Study. Respir. Car 2012, 55, 1475–1482. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.D.; Jin, H.Z.; Bobby, H.P.N.; Gu, Y.H.; Wu, Y.C.; Lu, G. Therapeutic Effects of Qigong in Patients withCOPD: A Randomized Controlled Trial. HongKong J. Occup. Ther. 2012, 22, 38–46. [Google Scholar]
- DorAnne, D.C.; Huong, Q.N.; Steven, P.; Virginia, C.K. Yoga Therapy Decreases Dyspnea-Related Distress and Improves Functional Performance in People with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: A Pilot Study. J. Altern. Complementary Med. 2009, 15, 225–234. [Google Scholar]
- Regina, W.M.L.; Zoe, J.M.; Matthew, J.P.; Jennifer, A.A. Short-form Sun-style Tai Chi as an exercise training modality in people with COPD Corresponding. Eur. Respir. J. 2013, 41, 1051–1057. [Google Scholar]
- Rajashree, R.; Badhai, S.; Hankey, A.; Nagendra, H.R. A randomized controlled study on assessment of health status, depression, and anxiety in coal miners with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease following yoga training. Int. J. Yoga 2016, 9, 137–144. [Google Scholar]
- He, R.; Cheng, Y.F.; Wei, S.S. To observe the clinical curative effect of the traditional Hua TuoWuqinxi in improving patients’ living quality with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. J. Clin. Chin. Med. 2015, 27, 966–968. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.Y.; Peng, L.; Fan, B.H.; Lu, J.H. Clinical Research of the Effects of "Six-Character Formula" of Physical Exercise Combined with Method of Benefiting Qi and Activating Blood on the Lung Rehabilitation in COPD in Stable Phase. Henan Chin. Med. 2016, 23, 835–837. [Google Scholar]
- Ni, X.M.; Zhang, X.A.; Ge, L.N. Effect of Health Qigong Five-animal Boxing on Anxiety, Depression and Quality of Life of the COPD Patients. MedInnov. China 2019, 16, 166–169. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, M.R. Clinical Observation of the Prescription of Health Qigong Raise Lung on Remission GradeⅠChronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. J. Emerg. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2012, 22, 1312–1313. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.; Lu, C.H.; Zhang, L.L.; Zhang, J.; Hu, M.; Fan, S.X. Effect of self-invented yoga breathing exercises on pulmonary rehabilitation and depression in COPD patients. J. Nurs. Sci. 2015, 30, 18–21. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, C.; Guo, X.J.; Chen, N.; Yan, X.; Zhang, H.L. Research of Effects of Eight-section Brocade of TCM on Treating Anxiety and Depression in the Elderly Patients with Lung-spleen Qi Deficiency in Stable Period of COPD. J. Liaoning Univ. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2016, 18, 120–123. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.D. Clinical Effect of Taijiquan Exercise on Depression and Anxiety of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Chin. J. Aesthetic Med. 2011, 20, 129–130. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.; Chen, W.H.; Jin, X.Q.; Wu, W.Q.; Yang, R.; Yu, Y.Y. The effects of collective kinesio therapy on anxiety and depression in COPD patients at stable stage. Chin. J. Rehabil. Med. 2008, 23, 732–734. [Google Scholar]
- Yohannes, A.M.; Junkes-Cunha, M.; Smith, J. Management of Dyspnea and Anxiety in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: A Critical Review. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2017, 18, 1096-e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Liu, J.M.; Cui, H.S.; Sun, B.; Jiang, L.D. Systematic evaluation of the influence of traditional qigong therapy on depression and anxiety scores in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. World J. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2018, 13, 1006–1012. [Google Scholar]
- Trivedi, M.H.; Greer, T.L.; Grannemann, B.D. Exercise asan augmentation strategy for treatment of major depression. J. Psychiatr. Pract. 2006, 12, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, H.; Liu, P. A Meta-Analysis of the Effect of Physical Exercise as a Treatment on Depression. J. Tianjin Univ. Sports 2018, 33, 500–507. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, J.P.; Bai, J.W. Research progress of COPD combined with anxiety/depression. J. Tongji Univ. (Med. Ed.) 2017, 38, 113–116+122. [Google Scholar]
- Stavrou, N.; Debevec, T.; Eiken, O. Hypoxia exacerbates negative emotional state during inactivity: The effect of 21 days hypoxic bed rest and confinement. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hynninen, M.J.; Pallesen, S.; Nordhus, I.H. Factors affecting health status in COPD patients with co-morbid anxiety or depression. Int. J. Chron. Obs. Pulmon. Dis. 2007, 2, 323–328. [Google Scholar]
- Spalletta, G.; Bossù, P.; Ciaramella, A. The etiology of post-stroke depression: A review of the literature and a new hypothesis involving inflammatory cytokines. Mol. Psychiatry 2006, 11, 984–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, X.D.; Hong, W.; Qian, W. Psychological intervention in the treatment of essential hypertension with anxiety. Asia-Pac. Tradit. Med. 2009, 5, 139–141. [Google Scholar]
- Lecheler, L.; Richter, M.; Franzen, D.P. The frequent and under recognised co-occurrence of acute exacerbated COPD and depression warrants screening: A systematic review. Eur. Respir. Rev. 2017, 26, 170026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, Q.; Li, F.L. Investigation and analysis of anxiety and depression in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Modernhospital 2019, 19, 933–936. [Google Scholar]
- Rong, X.J.; Li, C.Z.; Liang, D. Effects of tai chi on cardiopulmonary function in middle-aged and elderly people. Chin. J. Rehabil. Med. 2009, 24, 345–347. [Google Scholar]
- D’ascola, A.; Bruschetta, G.; Zanghì, G. Changes in plasma 5-HT levels and equine leukocyte SERT expression in response to treadmill exercise. Res. Vet. Sci. 2018, 118, 184–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wegner, M.; Helmich, I.; Machado, S.; ENardi, A.; Arias-Carrión, O.; Budde, H. Effects of exercise on anxiety and depression disorders: Review of meta- analyses and neuro-biological mechanisms. CNS Neurol. Disord. Drug Targets 2014, 13, 1002–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, P.J.; Duan, C.Z.; Cai, B.; Xu, H.W. Changes of Glucocorticoid Receptor During Physical Training. J. Shanghai Phys. Educ. Inst. 2002, 1, 33–37+42. [Google Scholar]
- Berchtold, N.C.; Kesslak, J.P.; Cotman, C.W. Hippocampal brain-derived neurotrophic factor gene regulation by exercise and the medial septum. J. Neurosci. Res. 2002, 68, 511–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olson, A.K.; Eadie, B.D.; Ernst, C.; Christie, B.R. Environmental enrichment and voluntary exercise massively increase neurogenesis in the adult hippocampus via dissociable pathways. Hippocampus 2006, 16, 250–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gendron, L.M.; Nyberg, A.; Saey, D. Active mind-body movement therapies as an adjunct to or in comparison with pulmonary rehabilitation for people with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2018, 10, CD012290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.B.; Liu, X.D.; Wang, L.B.; Wang, Z.W.; Hu, J.; Yan, J.T. Effects of Tai Chi on exercise capacity and health-related quality of life in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Chronic Obstr. Pulm. Dis. 2014, 9, 1253–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Luo, X.T.; Zhang, J.F.; Castelberg, R.; Wu, T.; Yu, P.M.; He, C.Q.; Wang, P. The Effects of Traditional Chinese Exercise in Patients with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: A Meta-Analysis. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0161564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borge, C.R.; Hagen, K.B.; Mengshole, A.M.; Omenaas, E.; Moum, T.; Wahl, A.K. Effects of controlled breathing exercises and respiratory muscle training in people with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: Results from evaluating the quality of evidence in systematic reviews. BMC Pulm. Med. 2014, 14, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.Y.; Li, W.Y.; Cao, H.J.; Klupp, N.; Liu, J.P.; Bensoussan, A.; Kiat, H.; Chang, D. Does Tai Chi improve psychological well-being and quality of life in patients with cardiovascular disease and/or cardiovascular risk factors? A systematic review protocol. BMJ Open 2017, 7, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PEDro-Scale. Available online: https: //www.pedro.org.au/simplified-chinese/pedro-scale/ (accessed on 4 August 2010).

| Reference | Location (Language) | Participant Characteristics | Intervention Program | Training | Outcome Measured | Follow-Up | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample Size (AttritionRate) | Disease Course | Mean Ageor Age Range | Frequency (Weekly) | Time (Min) | Duration (Week) | |||||
| Gloria Y et al. [36] | Boston, USA | 10 | T = 2.4 ± 0.5 | T = 65 ± 6 | T = tai chi + usual care | 2 | 60 | 12 | CESD | no |
| (English) | 0% | C = 2.6 ± 0.5 | C = 66 ± 6 | C = usual care | no | |||||
| Liu et al. [37] | Nanjing, China | 132 | T = 7.54 (2.73) | T = 61.82 (7.69) | T = yijinjing, wuqinxi, liuzijue, baduanjin, | 3 | 60 | 24 | QoL | yes |
| (English) | 8.90% | C = 7.57 (2.97) | C = 62.2 (6.34) | C = health education | yes | |||||
| Doranne D et al. [38] | San Francisco, USA | 41 | NR | T = 72.2 ±6.5 | T = yoga + usual care control | 2 | 60 | 12 | CESD | no |
| (English) | 7.10% | NR | C = 67.7 ±11.5 | C = usual care control + education pamphlet | SSAI | no | ||||
| Regina W et al. [39] | Sydney Australia | 42 | T = 8 | T = 75(83−67) | T = sun-style tai chi | 5 | 30 | 12 | HADS | yes |
| (English) | 9% | C = 8 | C = 75(83−67) | C = usual medical care | yes | |||||
| Rajashree R et al. [40] | Karnataka, India | 81 | T = 9.92 ± 3.25 | T = 53.69 ± 5.66 | T = yoga | 6 | 90 | 12 | BDI STAI | no |
| (English) | 8.90% | C = 10.69 ± 2.54 | C = 54.36 ± 5.40 | C = conventional therapy | no | |||||
| Cao et al. [46] | Nanjing, China | 103 | T = 13.33 ± 9.39 | T = 70.83 ± 6.22 | T = usual care + Baduanjin | 4 | 30 | 24 | SAS SDS | no |
| (Chinese) | 9.90% | C = 14.54 ± 7.61 | C = 70.14 ± 5.71 | C = usual + walking | no | |||||
| Li et al. [47] | Chengdu, China | 80 | T = 10.56 ± 5.7 | T = 64.56 ± 4.73 | T = usual care + taijiquan | 5 | 30 | 12 | SAS SDS | no |
| (Chinese) | 0% | C = 9.80 ± 6.12 | C = 62.68 ± 5.76 | C = usual care | no | |||||
| He et al. [41] | Bozhou, China | 100 | T = 14.52 ± 5.96 | T = 58.66 ± 7.56 | T = usual care + wuqinxi | 4 | 30-60 | 24 | QoL | no |
| (Chinese) | 9.30% | NR | C = 58.64 ± 7.52 | C = usual care | no | |||||
| Chen et al. [42] | Qidong, China | 70 | NR | T = 68.75 ± 8.67 | T = usual care + rehabilitation method + liuzijue | 7 | 60 | 24 | HADS | no |
| (Chinese) | 9.57% | NR | C = 69.31 ± 7.54 | C = usual care + rehabilitation method | no | |||||
| Yang et al. [45] | Wuhan, China | 98 | T = 17.19 ± 8.20 | T = 63.70 ± 5.69 | T = usual care + yoga breathing exercise | 7 | 48 | 48 | SDS | yes |
| (Chinese) | 9.18% | C = 15.50 ± 5.89 | C = 64.49 ± 6.10 | C = usual care | yes | |||||
| Ni et al. [43] | Shenyang, China | 50 | T = 8.09 ± 3.23 | T = 51.78 ± 4.02 | T = usual care + wuqinxi | 5 | 60 | 12 | HAMA HAMD | no |
| (Chinese) | 9.40% | C = 7.92 ± 3.41 | C = 51.08 ± 4.49 | C = usual care | no | |||||
| Zhang et al. [48] | Shanghai, China | 57 | NR | T = 69.9 ± 4.73 | T = usual care + relaxing exercise + baduanjin | 3 | 30 | 8 | SAS SDS | no |
| (Chinese) | 0% | NR | C = 69.68 ± 8.66 | C = usual care | no | |||||
| Guo et al. [44] | Nanjing, China | 42 | T = 6.52 ± 2.43 | T = 56.68 ± 6.42 | T = daily life + health qigong | NR | NR | 24 | QoL | no |
| (Chinese) | 0% | C = 6.82 ± 2.43 | C = 58.94 ± 5.96 | C = daily life | no | |||||
| Author [Reference] | Item 1 | Item 2 | Item 3 | Item 4 | Item 5 | Item 6 | Item 7 | Item 8 | Item 9 | Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gloria Y et al. [36] | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 7 |
| Liu et al. [37] | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 8 |
| Doranne D et al. [38] | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 5 |
| Regina W et al. [39] | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 9 |
| Rajashree R et al. [40] | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 8 |
| He et al. [41] | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 6 |
| Chen et al. [42] | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 5 |
| Ni et al. [43] | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 6 |
| Guo et al. [44] | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 6 |
| Yang et al. [45] | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 6 |
| Cao et al. [46] | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 6 |
| Li et al. [47] | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 6 |
| Zhang et al. [48] | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 4 |
| _ES | Coef. | Std.err. | t | P > t | (95% Conf. Interval) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| age | 0.046262 | 0.020389 | 2.27 | 0.064 | −0.0036268 | 0.0961507 |
| disease course | 0.028787 | 0.027162 | 1.06 | 0.33 | −0.0376763 | 0.095201 |
| frequency | −0.18836 | 0.080357 | −2.34 | 0.058 | −0.3849857 | 0.0082662 |
| time | 0.009947 | 0.007121 | 1.4 | 0.212 | −0.0074775 | 0.0273719 |
| duration | −0.019 | 0.012111 | −1.57 | 0.168 | −0.0486287 | 0.0106379 |
| event | 0.159324 | 0.144056 | 1.11 | 0.311 | −0.1931674 | 0.5118153 |
| _cons | −3.66007 | 1.646477 | −2.22 | 0.068 | −7.688854 | 0.3687162 |
| _ES | Coef. | Std.err. | t | P > t | (95% Conf. Interval) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| age | 0.031596 | 0.084411 | 0.37 | 0.721 | −0.174951 | 0.238143 |
| disease course | 0.027794 | 0.026581 | 1.05 | 0.336 | −0.0372465 | 0.0928345 |
| frequency | −0.18264 | 0.17994 | −1.02 | 0.349 | −0.6229385 | 0.2576581 |
| time | 0.008767 | 0.015687 | 0.56 | 0.596 | −0.029616 | 0.0471513 |
| duration | −0.01785 | 0.021621 | −0.83 | 0.441 | −0.0707587 | 0.0350514 |
| event | 0.043127 | 0.37444 | 0.12 | 0.912 | −0.873095 | 0.959349 |
| _cons | −2.24179 | 2.063563 | −1.09 | 0.319 | −7.291147 | −2.807567 |
| Group | Sub-Group | N | SMD | 95% CI | p | I2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| event | tai chi | 2 | −1.02 | −1.41, −0.64 | 0.145 | 53% |
| health qigong | 7 | −0.77 | −0.96, −0.59 | 0.076 | 47.50% | |
| yoga | 2 | −0.42 | −0.82, −0.03 | 0.356 | 0.0% | |
| disease course (year) | less than 10 years | 5 | −0.79 | −1.03, −0.54 | 0.033 | 61.9% |
| more than 10 years | 3 | −0.90 | −1.15, −0.65 | 0.224 | 33.2% | |
| year | 50–59.9 | 4 | −0.86 | −1.12, −0.59 | 0.028 | 67% |
| 60–69.9 | 4 | −0.72 | −0.96, −0.48 | 0.11 | 50.3% | |
| more than 70 | 3 | −0.68 | −1.00, −0.37 | 0.216 | 34.80% | |
| frequency (time/week) | 2–3 times/week | 3 | −0.5 | −0.8, −0.19 | 0.548 | 0.0% |
| 4–5 times/week | 5 | −0.96 | −1.18, −0.74 | 0.063 | 55.1% | |
| 6–7 times/week | 2 | −0.52 | −0.86, −0.18 | 0.889 | 0.0% | |
| time (min) | 30 ≤ min < 60 | 5 | −0.83 | −1.04, −0.61 | 0.372 | 6.1% |
| 60 ≤ min ≤ 90 | 5 | −0.63 | −0.87, −0.4 | 0.016 | 67.3% | |
| duration (week) | 8–12 weeks | 6 | −0.82 | −1.06, −0.59 | 0.01 | 67% |
| 24 weeks | 5 | −0.71 | −0.91, −0.5 | 0.511 | 0.0% |
| Group | Sub-Group | N | SMD | 95% CI | p | I2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| event | tai chi | 3 | −0.96 | −1.97,0.05 | 0.004 | 81.9% |
| health qigong | 7 | −0.71 | −0.89, −0.52 | 0.55 | 0.0% | |
| yoga | 3 | −1.02 | −2.00, −0.04 | 0.000 | 89.1% | |
| disease course (year) | less than 10 years | 6 | −0.75 | −0.99, −0.51 | 0.483 | 0.0% |
| more than 10 years | 4 | −1.17 | −1.89, −0.46 | 0.000 | 90% | |
| year | 50–59.9 | 3 | −0.77 | −1.19, −0.34 | 0.111 | 54.4% |
| 60–69.9 | 7 | −1.08 | −1.52, −0.64 | 0.000 | 75.9% | |
| more than 70 | 3 | −0.51 | −0.82, −0.21 | 0.424 | 0.0% | |
| frequency (time/week) | 2–3 times/week | 4 | −0.59 | −0.89, −0.29 | 0.758 | 0.0% |
| 4–5 times/week | 5 | −0.85 | −1.34, −0.37 | 0.001 | 78.4% | |
| 6–7 times/week | 3 | −1.2 | −1.95, −0.46 | 0.001 | 85.3% | |
| time (min) | 30 ≤ min < 60 | 6 | −0.78 | −1.02, −0.55 | 0.496 | 0.0% |
| 60 ≤ min ≤ 90 | 6 | −0.94 | −1.48, −0.40 | 0.000 | 86.4% | |
| duration (week) | 8–12 weeks | 7 | −0.83 | −1.24, −0.42 | 0.007 | 66.0% |
| 24 weeks | 5 | −0.90 | −1.32, −0.47 | 0.000 | 79.4% | |
| 48weeks | 1 | −1.96 | −2.46, −1.47 | −− | −− |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Z.; Liu, S.; Wang, L.; Smith, L. Mind–Body Exercise for Anxiety and Depression in COPD Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 22. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17010022
Li Z, Liu S, Wang L, Smith L. Mind–Body Exercise for Anxiety and Depression in COPD Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2020; 17(1):22. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17010022
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Zaimin, Shijie Liu, Lin Wang, and Lee Smith. 2020. "Mind–Body Exercise for Anxiety and Depression in COPD Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 17, no. 1: 22. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17010022
APA StyleLi, Z., Liu, S., Wang, L., & Smith, L. (2020). Mind–Body Exercise for Anxiety and Depression in COPD Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 17(1), 22. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17010022






