Magnesium Alginate in Gastro-Esophageal Reflux: A Randomized Multicenter Cross-Over Study in Infants
Abstract
1. Background
2. Methods
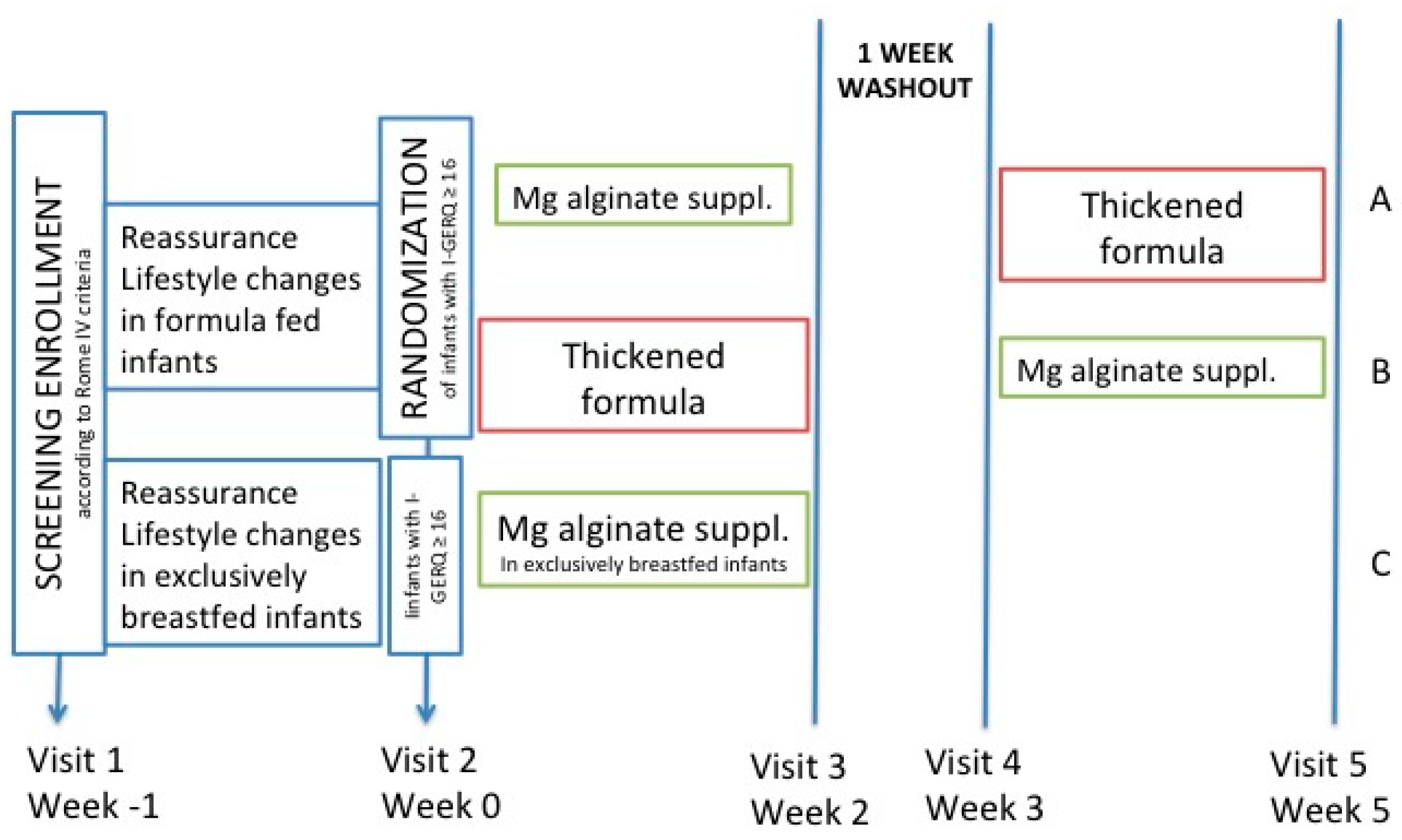
Study Design and Patients
3. Statistical Analysis
4. Results
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Funding
Abbreviations
| ESPGHAN | European Society for Paediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition |
| FIGDs | Functional Gastrointestinal Diseases |
| GER | Gastroesophageal Reflux |
| I-GERQ-R | Infant Gastroesophageal Reflux Questionnaire Revised |
| NASPGHAN | North American Society for Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition |
| NICE | National Institute for Health and Care Excellence |
| PPI | Proton Pump Inhibitor |
Appendix A. ROME IV Diagnostic Criteria for Infant Regurgitation
- Regurgitation two or more times per day for three or more weeks.
- No retching, hematemesis, aspiration, apnea, failure to thrive, feeding or swallowing difficulties, or abnormal posturing.
References
- Ferreira-Maia, A.P.; Matijasevich, A.; Wang, Y.P. Epidemiology of functional gastrointestinal disorders in infants and toddlers: A systematic review. World J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 22, 6547–6558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iacono, G.; Merolla, R.; D’Amico, D.; Bonci, E.; Cavataio, F.; Di Prima, L.; Scalici, C.; Indinnimeo, L.; Averna, M.R.; Carroccio, A.; et al. Gastrointestinal symptoms in infancy: A population-based prospective study. Dig. Liver Dis. 2005, 37, 432–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campanozzi, A.; Boccia, G.; Pensabene, L.; Panetta, F.; Marsgelia, A.; Strisciuglio, P.; Barbera, C.; Magazzu, G.; Pettoelo-Mantovani, M.; Stajano, A. Prevalence and natural history of gastroesophageal reflux: Pediatric prospective survey. Pediatrics 2009, 123, 779–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandenplas, Y.; Abkari, A.; Bellaiche, M.; Benninga, M.; Chouraqui, J.P.; Cokura, F.; Harb, T.; Hegar, B.; Lifshcitz, C.; Ludwig, T.; et al. Prevalence and Health Outcomes of Functional Gastrointestinal Symptoms in Infants from Birth to 12 Months of Age. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2015, 61, 531–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvatore, S.; Baldassarre, M.E.; Di Mauro, A.; Laforgia, N.; Tafuri, S.; Bianchi, F.P.; Datolli, E.; Morando, L.; Pensabene, L.; Meneghin, F.; et al. Neonatal Antibiotics and Prematurity Are Associated with an Increased Risk of Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders in the First Year of Life. J. Pediatr. 2019, 212, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahon, J.; Lifschitz, C.; Ludwig, T.; Thapar, N.; Glanville, J.; Miqdady, M.; Saps, M.; Hock Qaurk, S.; Lenoir Wijnkoop, I.; Edwards, M.; et al. The costs of functional gastrointestinal disorders and related signs and symptoms in infants: A systematic literature review and cost calculation for England. BMJ Open 2017, 7, e015594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Indrio, F.; Di Mauro, A.; Riezzo, G.; Cavallo, L.; Francavilla, R. Infantile colic, regurgitation, and constipation: An early traumatic insult in the development of functional gastrointestinal disorders in children? Eur. J. Pediatr. 2015, 174, 841–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvatore, S.; Abkari, A.; Cai, W.; Catto-Smith, A.; Cruchet, S.; Gottrand, F.; Hegar, B.; Lifschitz, C.; Ludwig, T.; Shah, N.; et al. Review shows that parental reassurance and nutritional advice help to optimize the management of functional gastrointestinal disorders in infants. Acta Paediatr. 2018, 107, 1512–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvatore, S.; Barberi, S.; Borrelli, O.; Castellazzi, A.; Di Mauro, D.; Di Mauro, G.; Doria, M.; Francavilla, R.; Landi, M.; Martelli, A.; et al. Pharmacological interventions on early functional gastrointestinal disorders. Ital. J. Pediatr. 2016, 42, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvatore, S.; Savino, F.; Singendonk, M.; Tabbers, M.; Benninga, M.A.; Staiano, A.; Vandenplas, Y. Thickened infant formula: What to know. Nutrition 2018, 49, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianchetti, M. Emerging from gastroesophageal reflux (EMERGE): An Italian survey—II the viewpoint of the patient. J. Biol. Regul. Homeost. Agents. 2018, 32, 983–988. [Google Scholar]
- Bianchetti, M.; Peralta, S.; Nicita, R.; Aragona, S.E.; Ciprandi, G.; Arrigoni, A.; Artuso, D.; Astegiano, M.; Azzinnari, C.; Battaglia, E.; et al. Emerging from gastroesophageal reflux (EMERGE): An Italian survey—I the viewpoint of the gastroenterologist. J. Biol. Regul. Homeost. Agents 2018, 32, 973–981. [Google Scholar]
- Tighe, M.; Afzal, N.A.; Bevan, A.; Hayen, A.; Munro, A.; Beattie, R.M. Pharmacological treatment of children with gastro-oesophageal reflux. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2014, 11, CD008550. [Google Scholar]
- Zeevenhooven, J.; Koppen, I.; Benninga, M. The New Rome IV Criteria for Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders in Infants and Toddlers. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. Nutr. 2017, 20, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosen, R.; Vandenplas, Y.; Singendonk, M.; Cabana, M.; DiLorenzo, C.; Gottrand, F.; Gupta, S.; Langendam, M.; Staiano, A.; Thapar, N.; et al. Pediatric gastroe-sophageal reflux clinical practice guidelines: Joint recommendations of the north american society for pediatric gastroenterology, hepatology, and nutrition and the European society for pediatric gastroenterology, hepatology, and nutrition. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2018, 66, 516–554. [Google Scholar]
- National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE). Gastro-Oesophageal Reflux Disease: Recognition, Diagnosis and Management in Children and Young People; National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE): London, UK, 2015.
- Kleinman, L.; Rothman, M.; Strauss, R.; Orenstein, S.R.; Nelson, S.; Vandenplas, Y.; Cucchiara, S.; Revicki, D.A. The infant gastroesophageal reflux questionnaire revised: Development and validation as an evaluative instrument. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2006, 4, 588–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvatore, S.; Hauser, B.; Vandemaele, K.; Novario, R.; Vandenplas, Y. Gastroesophageal reflux disease in infants: How much is predictable with questionnaires, pH-metry, endoscopy and histology? J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2005, 40, 210–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvatore, S.; Ripepi, A.; Huysentruyt, K.; van de Maele, K.; Nosetti, L.; Agosti, M.; Salvatoni, A.; Vandenplas, Y. The Effect of Alginate in Gastroesophageal Reflux in Infants. Paediatr. Drugs 2018, 20, 575–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ummarino, D.; Miele, E.; Martinelli, M.; Scarpato, E.; Crocetto, F.; Sciorio, E.; Staiano, A. Effect of magnesium-alginate plus simethicone on gastroesophageal reflux in infants. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2015, 60, 230–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buts, J.P.; Barudi, C.; Otte, J.B. Double-blind controller study on the efficacy of sodium alginate (Gaviscon) in reducing gastroesophageal reflux assessed by 24 h continuous pH monitoring in infants and children. Eur. J. Pediatr. 1986, 146, 156–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corvaglia, L.; Aceti, A.; Mariani, E.; de Giorgi, M.; Carpetti, M.G.; Faldella, G. The efficacy of sodium alginate (Gaviscon) for treatment of gastroesophageal reflux in preterm infants. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2011, 33, 466–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gawarammana, I.B.; Cobum, J.; Greene, S.; Dargan, P.I. Severe hypokalemic metabolic alkalosis following ingestion of Gaviscon. Clin. Toxicol. 2007, 45, 176–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorbie, A.L.; Symon, D.N.; Stockdale, E.J. Gaviscon bezoars. Arch. Dis. Child. 1984, 59, 905–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mir, N.A. Gastro-oesophageal reflux. Issues in clinical practice. BMJ 2010, 341, c5158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinsen, T.C.; Bergh, K.; Waldum, H.L. Gastric juice: A barrier against infectious diseases. Basic Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2005, 96, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fidler Mis, N.; Braegger, C.; Bronsky, J.; Campoy, C.; Domellof, M.; Embelton, N.; Hojsak, I.; Hulst, J.; Indiro, F.; Lapillonne, A.; et al. Sugar in Infants, Children and Adolescents: A Position Paper of the European Society for Paediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition Committee on Nutrition. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2017, 65, 681–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magnuson, B.A.; Roberts, A.; Nestmann, E.R. Critical review of the current literature on the safety of sucralose. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2017, 106, 324–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quitadamo, P.; Papadopoulou, A.; Wenzl, T.; Urbonas, V.; Kneepkens, C.M.F.; Roman, E.; Orel, R.; Pavkov, D.J.; Dias, J.A.; Vandenplas, Y.; et al. European pediatrician’s approach to children with GER symptoms: Survey of the implementation of 2009 NASPGHAN-ESPGHAN guidelines. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2014, 58, 505–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, H.C.; Vandenplas, Y. Effect of cereal-thickened formula and upright positioning on regurgitation, gastric emptying, and weight gain in infants with regurgitation. Nutrition 2007, 23, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Group A Magnesium-Alginate—Thickened Formula (n = 27) | Group B Thickened Formula—Magnesium-Alginate (n = 26) | Group C Magnesium Alginate in Exclusively Breast-Fed Infants (n = 19) | F | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gestational age at birth, mean ± SD, weeks | 37.3 ± 3.3 | 36.8 ± 4.0 | 38.7 ± 1.9 | 1.882 | 0.16 |
| Age at enrolment, mean ± SD, days | 51.8 ± 41.1 | 84.4 ± 57.2 | 60.6 ± 29.6 | 3.327 | 0.042 |
| I-GERQ-R at enrolment, mean ± SD | 21.2 ± 4.1 | 22.9 ± 4.8 | 20.8 ± 4.1 | 1.455 | 0.24 |
| Magnesium Alginate Cumulative Effects in Formula-Fed Infants | Thickened Formula Cumulative Effects in Formula-Fed Infants | Magnesium Alginate in Exclusively Breast-Fed Infants | |
|---|---|---|---|
| I-GERQ-R mean reduction | −8.96 (6.93) t = 8.77 p < 0.0001 | −9.74 (7.66) t = 8.63 p < 0.0001 | −10.95 (3.37) t = 14.14 p < 0.0001 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Baldassarre, M.E.; Di Mauro, A.; Pignatelli, M.C.; Fanelli, M.; Salvatore, S.; Di Nardo, G.; Chiaro, A.; Pensabene, L.; Laforgia, N. Magnesium Alginate in Gastro-Esophageal Reflux: A Randomized Multicenter Cross-Over Study in Infants. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 83. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17010083
Baldassarre ME, Di Mauro A, Pignatelli MC, Fanelli M, Salvatore S, Di Nardo G, Chiaro A, Pensabene L, Laforgia N. Magnesium Alginate in Gastro-Esophageal Reflux: A Randomized Multicenter Cross-Over Study in Infants. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2020; 17(1):83. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17010083
Chicago/Turabian StyleBaldassarre, Maria Elisabetta, Antonio Di Mauro, Maria Cristina Pignatelli, Margherita Fanelli, Silvia Salvatore, Giovanni Di Nardo, Andrea Chiaro, Licia Pensabene, and Nicola Laforgia. 2020. "Magnesium Alginate in Gastro-Esophageal Reflux: A Randomized Multicenter Cross-Over Study in Infants" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 17, no. 1: 83. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17010083
APA StyleBaldassarre, M. E., Di Mauro, A., Pignatelli, M. C., Fanelli, M., Salvatore, S., Di Nardo, G., Chiaro, A., Pensabene, L., & Laforgia, N. (2020). Magnesium Alginate in Gastro-Esophageal Reflux: A Randomized Multicenter Cross-Over Study in Infants. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 17(1), 83. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17010083











