Children with Fetal Alcohol Syndrome (FAS): 3D-Analysis of Palatal Depth and 3D-Metric Facial Length
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design, Setting and Participants
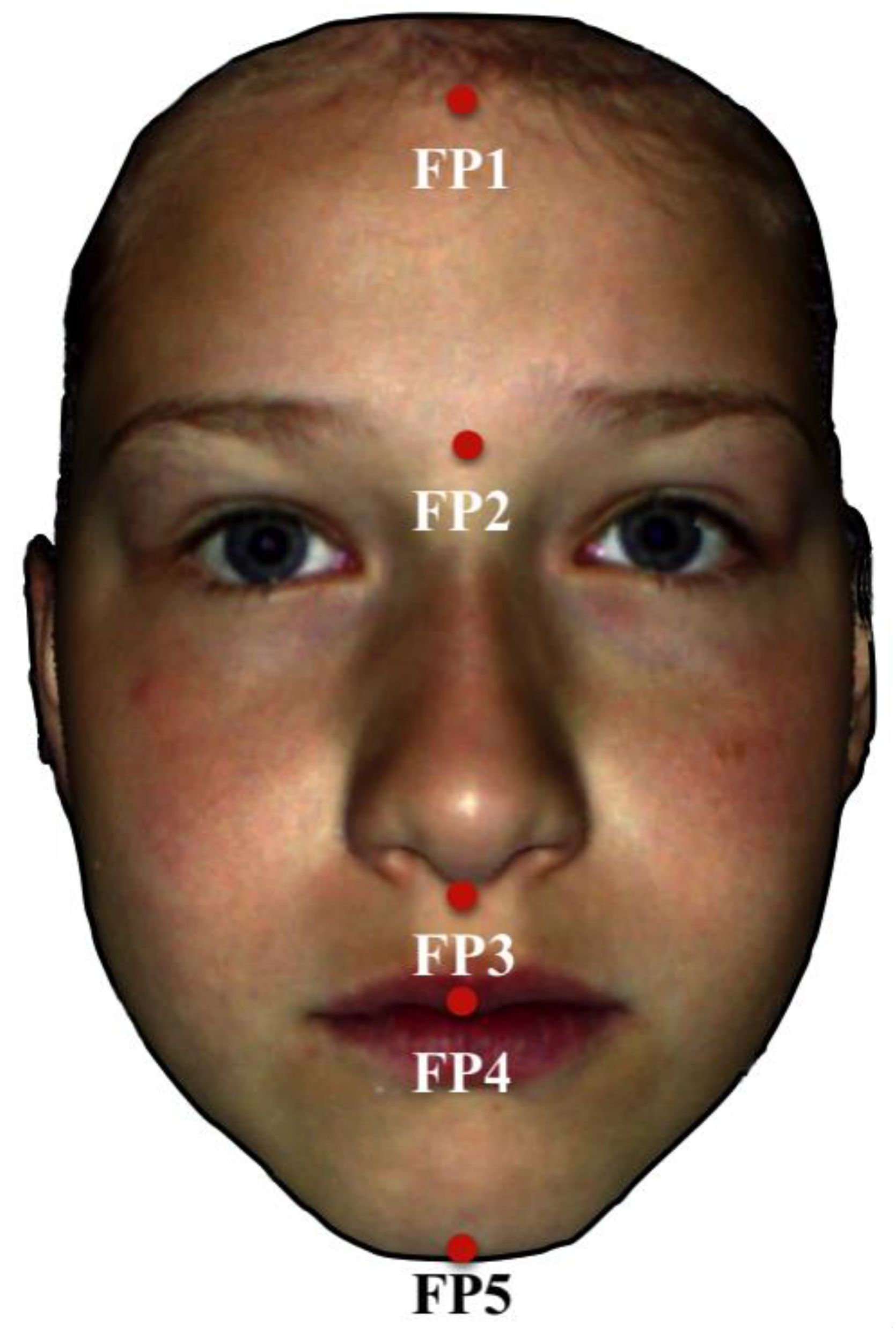
2.2. Variables and Data Sources/Management
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Study Participants
3.2. Main Results
4. Discussion
5. Strength and Limitations
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Landgraf, M.N.; Nothacker, M.; Heinen, F. Diagnosis of fetal alcohol syndrome (FAS): German guideline version 2013. Eur. J. Paediatr. Neurol. Off. J. Eur. Paediatr. Neurol. Soc. 2013, 17, 437–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenmyer, J.R.; Klug, M.G.; Kambeitz, C.; Popova, S.; Burd, L. A multicountry updated assessment of the economic impact of fetal alcohol spectrum disorder: Costs for children and adults. J. Addict. Med. 2018, 12, 466–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lupton, C.; Burd, L.; Harwood, R. Cost of fetal alcohol spectrum disorders. Am. J. Med. Genet. Part C Semin. Med. Genet. 2004, 127C, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Popova, S.; Lange, S.; Shield, K.; Mihic, A.; Chudley, A.E.; Mukherjee, R.A.; Bekmuradov, D.; Rehm, J. Comorbidity of fetal alcohol spectrum disorder: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet 2016, 387, 978–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lange, S.; Probst, C.; Gmel, G.; Rehm, J.; Burd, L.; Popova, S. Global prevalence of fetal alcohol spectrum disorder among children and youth: A systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Pediatr. 2017, 171, 948–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- May, P.A.; Gossage, J.P. Maternal risk factors for fetal alcohol spectrum disorders: Not as simple as it might seem. Alcohol Res. Health J. Natl. Inst. Alcohol Abus. Alcohol. 2011, 34, 15–26. [Google Scholar]
- Astley, S.J.; Magnuson, S.I.; Omnell, L.M.; Clarren, S.K. Fetal alcohol syndrome: Changes in craniofacial form with age, cognition, and timing of ethanol exposure in the macaque. Teratology 1999, 59, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, K.K.; Gupta, V.K.; Shirasaka, T. An update on fetal alcohol syndrome—Pathogenesis, risks, and treatment. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2016, 40, 1594–1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- May, P.A.; Baete, A.; Russo, J.; Elliott, A.J.; Blankenship, J.; Kalberg, W.O.; Buckley, D.; Brooks, M.; Hasken, J.; Abdul-Rahman, O.; et al. Prevalence and characteristics of fetal alcohol spectrum disorders. Pediatrics 2014, 134, 855–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popova, S.; Lange, S.; Probst, C.; Gmel, G.; Rehm, J. Estimation of national, regional, and global prevalence of alcohol use during pregnancy and fetal alcohol syndrome: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Glob. Health 2017, 5, e290–e299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astley, S.J.; Clarren, S.K. Diagnosing the full spectrum of fetal alcohol-exposed individuals: Introducing the 4-digit diagnostic code. Alcohol Alcohol. 2000, 35, 400–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoyme, H.E.; May, P.A.; Kalberg, W.O.; Kodituwakku, P.; Gossage, J.P.; Trujillo, P.M.; Buckley, D.G.; Miller, J.H.; Aragon, A.S.; Khaole, N.; et al. A practical clinical approach to diagnosis of fetal alcohol spectrum disorders: Clarification of the 1996 institute of medicine criteria. Pediatrics 2005, 115, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoyme, H.E.; Kalberg, W.O.; Elliott, A.J.; Blankenship, J.; Buckley, D.; Marais, A.S.; Manning, M.A.; Robinson, L.K.; Adam, M.P.; Abdul-Rahman, O.; et al. Updated clinical guidelines for diagnosing fetal alcohol spectrum disorders. Pediatrics 2016, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Modabber, A.; Peters, F.; Kniha, K.; Goloborodko, E.; Ghassemi, A.; Lethaus, B.; Holzle, F.; Mohlhenrich, S.C. Evaluation of the accuracy of a mobile and a stationary system for three-dimensional facial scanning. J. Cranio-Maxillo-Facial Surg. Off. Publ. Eur. Assoc. Cranio-Maxillo-Facial Surg. 2016, 44, 1719–1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lippold, C.; Liu, X.; Wangdo, K.; Drerup, B.; Schreiber, K.; Kirschneck, C.; Moiseenko, T.; Danesh, G. Facial landmark localization by curvature maps and profile analysis. Head Face Med. 2014, 10, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanck-Lubarsch, M.; Dirksen, D.; Feldmann, R.; Sauerland, C.; Kirschneck, C.; Hohoff, A. 3D analysis of philtrum depth in children with fetal alcohol syndrome. Alcohol Alcohol. 2019, 54, 152–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco de Sa Gomes, C.; Libdy, M.R.; Normando, D. Scan time, reliability and accuracy of craniofacial measurements using a 3D light scanner. J. Oral. Biol. Craniofac. Res. 2019, 9, 331–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sfondrini, M.F.; Gandini, P.; Malfatto, M.; Di Corato, F.; Trovati, F.; Scribante, A. Computerized casts for orthodontic purpose using powder-free intraoral scanners: Accuracy, execution time, and patient feedback. BioMed Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanck-Lubarsch, M.; Flieger, S.; Feldmann, R.; Kirschneck, C.; Sauerland, C.; Hohoff, A. Malocclusion can give additional hints for diagnosis of fetal alcohol spectrum disorder. Alcohol Alcohol. 2019, 54, 56–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanck-Lubarsch, M.; Dirksen, D.; Feldmann, R.; Sauerland, C.; Hohoff, A. 3D-analysis of mouth, nose and eye parameters in children with fetal alcohol syndrome (FAS). Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 2535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanck-Lubarsch, M.; Dirksen, D.; Feldmann, R.; Sauerland, C.; Hohoff, A. Tooth malformations, DMFT index, speech impairment and oral habits in patients with fetal alcohol syndrome. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 4401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blanck-Lubarsch, M.; Dirksen, D.; Feldmann, R.; Sauerland, C.; Kirschneck, C.; Hohoff, A. Asymmetry-index and orthodontic facial analysis of children with foetal alcohol syndrome using 3D-facial scans. Pediatr. Res. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korkhaus, G. Anatomische Vorbemerkungen. In Gebiss-, Kiefer- und Gesichtsorthopädie, 2nd ed.; Bruhn, C., Hofrath, H., Eds.; Bergmann: München, Germany, 1939; Volume 4, pp. 60–61. [Google Scholar]
- Gan, N.; Xiong, Y.; Jiao, T. Accuracy of intraoral digital impressions for whole upper jaws, including full dentitions and palatal soft tissues. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0158800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bischoff, G.; Borocz, Z.; Proll, C.; Kleinheinz, J.; von Bally, G.; Dirksen, D. Modular optical topometric sensor for 3D acquisition of human body surfaces and long-term monitoring of variations. Biomed. Tech. Biomed. Eng. 2007, 52, 284–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Berg, M.; Cheong, O.; van Kreveld, M.; Overmars, M. Computational Geometry: Algorithms and Applications; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Greenbaum, R.; Koren, G. Fetal alcohol spectrum disorder—New diagnostic initiatives. Paediatr. Child Health 2002, 7, 139–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Astley, S.J.; Clarren, S.K. A fetal alcohol syndrome screening tool. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 1995, 19, 1565–1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, I.T.; Hussain, K. Craniofacial and oral manifestations of fetal alcohol syndrome. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 1990, 85, 505–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, D.M.; Emanuele, B.; Savazzi, S. A new illusion of height and width: Taller people are perceived as thinner. Psychon. Bull. Rev. 2013, 20, 1154–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Chapanis, A.; Mankin, D.A. The vertical-horizontal illusion in a visually-rich environment. Percept. Psychophys. 1967, 2, 249–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eslami Amirabadi, G.; Golshah, A.; Derakhshan, S.; Khandan, S.; Saeidipour, M.; Nikkerdar, N. Palatal dimensions at different stages of dentition in 5 to 18-year-old Iranian children and adolescent with normal occlusion. BMC Oral Health 2018, 18, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zankl, A.; Eberle, L.; Molinari, L.; Schinzel, A. Growth charts for nose length, nasal protrusion, and philtrum length from birth to 97 years. Am. J. Med. Genet. 2002, 111, 388–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Investigated Parameters | Total | FAS Group | Control Group | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gender | 0.604 2 | |||
| Male | 33 | 15 | 18 | |
| Female | 27 | 15 | 12 | |
| Age at examination, years | 0.095 1 | |||
| Mean (SD) | 8.5 (1.6) | 8.8 (1.5) | 8.2 (1.8) | |
| Median (Range) | 8.3 (5.8–11.9) | 8.6 (6.6–11.2) | 7.6 (5.8–11.9) | |
| Palatal depth, mm | 0.708 1 | |||
| Mean (SD) | 12.6 (1.6) | 12.6 (1.5) | 12.5 (1.7) | |
| Median (Range) | 12.4 (9.3–16.8) | 12.6 (10.1–16.8) | 12.3 (9.3–16.2) | |
| Total facial length (FP1–FP5), mm | 0.737 1 | |||
| Mean (SD) | 151.5 (8.5) | 151.1 (9.0) | 151.8 (8.1) | |
| Median (Range) | 153.6 (127–168.4) | 153.5 (133.8–168.4) | 154.2 (127–163.9) | |
| FP1–FP2, mm | 0.042 1 | |||
| Mean (SD) | 52.1 (4.5) | 53.4 (4.5) | 50.8 (4.2) | |
| Median (Range) | 52 (42.75–63.2) | 54.2 (46.3–63.2) | 50.8 (42.8–57) | |
| FP2–FP3, mm | <0.001 1 | |||
| Mean (SD) | 46 (4.6) | 42.6 (3.6) | 49.1 (3.1) | |
| Median (Range) | 46.2 (36.2–54.3) | 41.5 (36.2–50.8) | 49.6 (41.2–54.3) | |
| FP3–FP4, mm | <0.001 1 | |||
| Mean (SD) | 18 (2.6) | 19.6 (2.3) | 16.5 (1.9) | |
| Median (Range) | 18 (12.4–24.9) | 19.8 (14.8–24.9) | 16.7 (12.4–18.9) | |
| FP3–FP5, mm | 0.007 1 | |||
| Mean (SD) | 53.4 (4.3) | 55.1 (4.4) | 51.9 (3.7) | |
| Median (Range) | 53.2 (43.1–65.9) | 56.2 (45.5–65.9) | 51.9 (43.1–60.2) | |
| FP4–FP5, mm | 0.701 1 | |||
| Mean (SD) | 35.6 (3) | 35.7 (3.1) | 35.5 (2.9) | |
| Median (Range) | 35.3 (29.8–42.3) | 36 (30.3–41.8) | 34.7 (29.8–42.3) |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Blanck-Lubarsch, M.; Dirksen, D.; Feldmann, R.; Sauerland, C.; Hohoff, A. Children with Fetal Alcohol Syndrome (FAS): 3D-Analysis of Palatal Depth and 3D-Metric Facial Length. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 95. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17010095
Blanck-Lubarsch M, Dirksen D, Feldmann R, Sauerland C, Hohoff A. Children with Fetal Alcohol Syndrome (FAS): 3D-Analysis of Palatal Depth and 3D-Metric Facial Length. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2020; 17(1):95. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17010095
Chicago/Turabian StyleBlanck-Lubarsch, Moritz, Dieter Dirksen, Reinhold Feldmann, Cristina Sauerland, and Ariane Hohoff. 2020. "Children with Fetal Alcohol Syndrome (FAS): 3D-Analysis of Palatal Depth and 3D-Metric Facial Length" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 17, no. 1: 95. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17010095
APA StyleBlanck-Lubarsch, M., Dirksen, D., Feldmann, R., Sauerland, C., & Hohoff, A. (2020). Children with Fetal Alcohol Syndrome (FAS): 3D-Analysis of Palatal Depth and 3D-Metric Facial Length. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 17(1), 95. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17010095





