A Study of Using Natural Sorbent to Reduce Iron Cations from Aqueous Solutions
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Trends in the Use of Sorbents for the Removal of Iron Ions from Aqueous Solutions
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Natural Zeolite-Clinoptilolite
3.2. Monitoring Kinetic Properties
4. Results
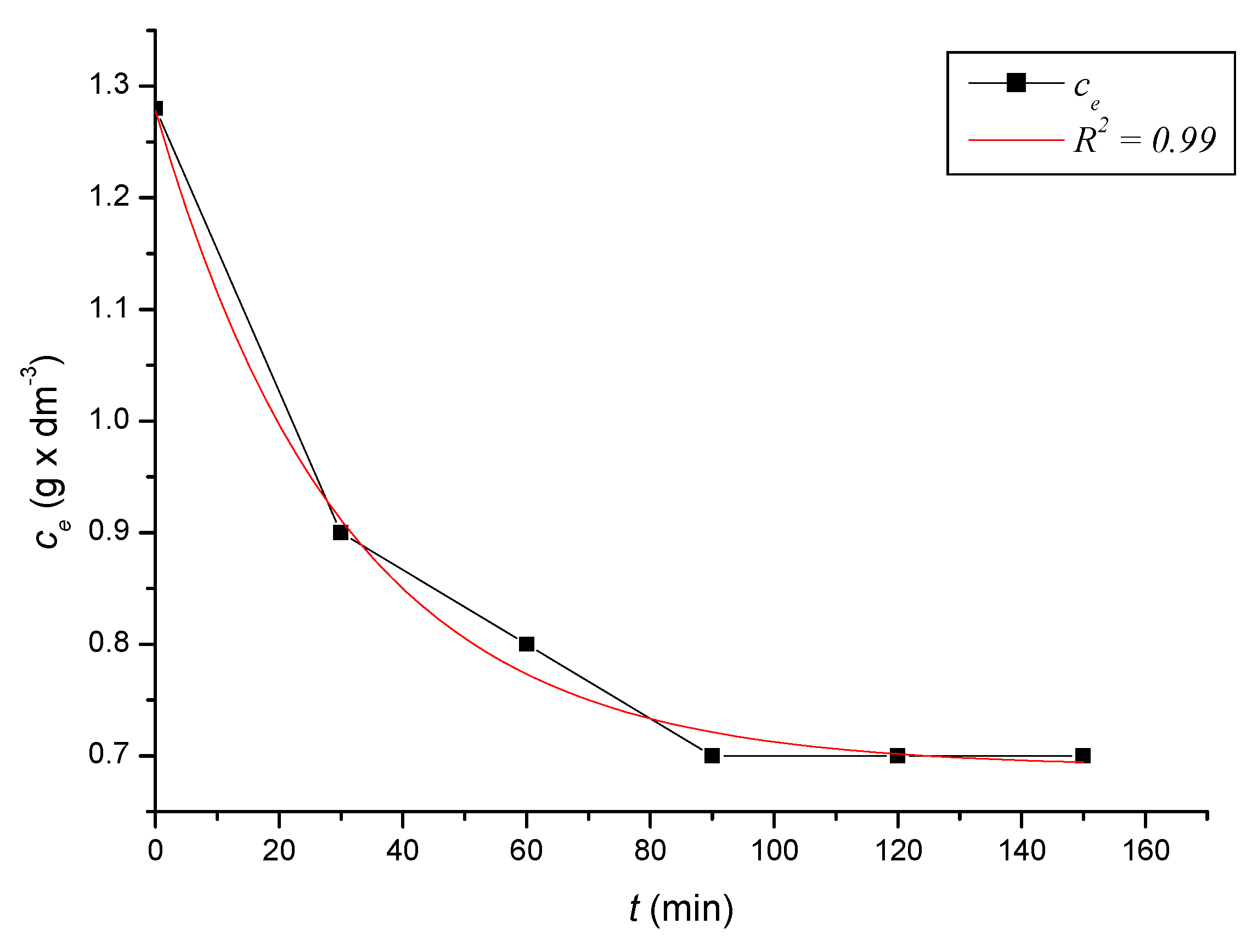
4.1. Defining Equilibrium in the System
4.2. The Freundlich Sorption Isotherm and the Actual Prediction Model
5. Discussion
5.1. Comparison, Verification, and Interpretation of Obtained Data
5.2. Calculation of the Standard Deviation
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bolisetty, S.; Peydayesh, M.; Mezzenga, R. Sustainable technologies for water purification from heavy metals: Review and analysis. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2019, 48, 463–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pyrzyńska, K.; Bystrzejewski, M. Comparative study of heavy metal ions sorption onto activated carbon, carbon nanotubes, and carbon-encapsulated magnetic nanoparticles. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2010, 362, 102–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trivedi, P.; Axe, L. Modeling Cd and Zn Sorption to Hydrous Metal Oxides. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2000, 34, 2215–2223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.-H.; Wang, S.; Wei, J.; Zhang, X.; Xu, C.; Luan, Z.; Wu, D.; Wei, B. Lead adsorption on carbon nanotubes. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2002, 357, 263–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.; Chiu, H. Adsorption of zinc(II) from water with purified carbon nanotubes. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2006, 61, 1138–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lloyd-Jones, P.; Rangel-Mendez, J.R.; Streat, M. Mercury Sorption from Aqueous Solution by Chelating Ion Exchange Resins, Activated Carbon and a Biosorbent. Process. Saf. Environ. Prot. 2004, 82, 301–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, L.; Yu, J. Applications of Zeolites in Sustainable Chemistry. Chem 2017, 3, 928–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ostroski, I.C.; De Barros, M.A.S.D.; Da Silva, C.; Dantas, J.H.; Arroyo, P.A.; Lima, O.C.M. The Removal of Fe(III) Ions by Adsorption onto Zeolite Columns. Adsorpt. Sci. Technol. 2007, 25, 757–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Castello, E.; Alcaraz, N.; Gras, M.L.; Mayor, L.; Argüelles, A.; Vidal-Brotóns, D. Pectinesterase Extraction from Orange Juice Solid Wastes. In Proceedings of the International Conference of Food Innovation, Bangna, Thailand, 25 October 2010. [Google Scholar]
- El-Sherif, I.Y.; Fathy, N.A.; Hanna, A.A. Removal of Mn (II) and Fe (II) ions from aqueous solution using precipitation and dsorption methods. J. Appl. Sci. Res. 2013, 9, 233–239. [Google Scholar]
- Robinson-Lora, M.A.; Brennan, R.A. Efficient metal removal and neutralization of acid mine drainage by crab-shell chitin under batch and continuous-flow conditions. Bioresour. Technol. 2009, 100, 5063–5071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khin, M.M.; Nair, A.S.; Babu, V.J.; Murugan, R.; Ramakrishna, S. A review on nanomaterials for environmental remediation. Energy Environ. Sci. 2012, 5, 8075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cama, J.; Ayora, C.; Querol, X.; Ganor, J. Dissolution Kinetics of Synthetic Zeolite NaP1 and Its Implication to Zeolite Treatment of Contaminated Waters. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 4871–4877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, T.C.; Loganathan, P.; Nguyen, T.V.; Vigneswaran, S.; Kandasamy, J.; Naidu, R. Simultaneous adsorption of Cd, Cr, Cu, Pb, and Zn by an iron-coated Australian zeolite in batch and fixed-bed column studies. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 270, 393–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, Y.S. Review of second-order models for adsorption systems. J. Hazard. Mater. 2006, 136, 681–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barloková, D.; Ilavský, J. Natural Zeolites with a Surface MnO2 Layer in Water Treatment. Chem. Listy. 2014, 108, 1153–1157. [Google Scholar]
- Reháková, M.; Čuvanová, S.; Gavaľová, Z.; Rimár, J. Application of Natural Zeolite of the Clinoptilolite Type in Agrochemistry and Agriculture. Chem. Listy. 2003, 97, 260–264. [Google Scholar]
- Sabová, L.; Chmielewská, E.; Gáplovská, K. Development and Exploitation of Combined Zeolite Adsorbents for Removing Oxyanions from Water. Chem. Listy. 2010, 104, 243–250. [Google Scholar]
- Weckhuysen, B.M.; Yu, J. Recent advances in zeolite chemistry and catalysis. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 7022–7024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanchard, G.; Maunaye, M.; Martin, G. Removal of heavy metals from waters by means of natural zeolites. Water Res. 1984, 18, 1501–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chmielewská, E. Biomimetics-Synergy of PHysiological Processes from Nature and Current Biomolecular Engineering in Development of Environmental Adsorbents. Chem. Listy. 2016, 110, 563–569. (In Czech) [Google Scholar]
- Pandová, I.; Panda, A.; Jurko, J. Clinoptilolite Testing as Sorbent Nitrogen Oxides from Combustion Engines Gases. Chem. Listy. 2011, 105, 609–611. [Google Scholar]
- Pandová, I.; Panda, A.; Valíček, J.; Harničárová, M.; Kušnerová, M.; Palkova, Z. Use of Sorption of Copper Cations by Clinoptilolite for Wastewater Treatment. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Heal. 2018, 15, 1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Főldesová, M.; Hudec, P. Study of Surface Characteristics of Slovak Natural Zeolite-Clinoptilolite by Physical Adsorption of Nitrogen. Pet. Coal. 2007, 49, 34–40. [Google Scholar]
- Milonjić, S.; Čupić, S.D.; Čerović, L. Sorption of Ferric and Ferrous Ions on Silica. Mater. Sci. Forum 2006, 518, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ackley, M.W. Application of natural zeolites in the purification and separation of gases. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2003, 61, 25–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moshoeshoe, M.; Nadiye-Tabbiruka, M.S.; Obuseng, V. A review of the chemistry, structure, properties and applications of zeolites. Am. J. Mater. Sci. 2017, 7, 196–221. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Yan, C.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, H.; Zhou, S.; Wu, L. Synthesis of zeolite P1 from fly ash under solvent-free conditions for ammonium removal from water. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 202, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thirugnanasambandham, K.; Sivakumar, V. Enzymatic catalysis treatment method of meat industry wastewater using lacasse. J. Environ. Heal. Sci. Eng. 2015, 13, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tapia, J.M.; Muňoz, J.A.; González, F.; Blázquez, M.L.; Ballester, A. Mechanism of adsorption of ferric iron by extracellularpolymeric substances (EPS) from a bacterium Acidiphilium sp. Water. Sci. Technol. 2011, 64, 1716–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, X.; Li, M.; Zhang, Z.; Feng, C.; Bai, W.; Sugiura, N. Electrochemical regeneration of zeolites and the removal of ammonia. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 169, 746–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Q.; Liu, S.; Cao, Z.; Wang, Y. Amonia removal from aqueous solution using natural Chinese clinoptilolite. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2005, 44, 229–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, J.; Chung, Y.-C.; Shin, H.-S.; Son, D.-H. Enhanced ammonia nitrogen removal using consistent biological regeneration and ammonium exchange of zeolite in modified SBR process. Water Res. 2004, 38, 347–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, D.; Ho, Y.; Tang, X. Comparative sorption kinetic studies of ammonium onto zeolite. J. Hazard. Mater. 2006, 133, 252–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]












| c0 (g × dm−3) | ce (g × dm−3) | q (mg × g−1) |
|---|---|---|
| 0.46 | 0.20 | 1.60 |
| 0.56 | 0.30 | 1.90 |
| 0.82 | 0.40 | 2.63 |
| 1.12 | 0.60 | 3.01 |
| 1.28 | 0.70 | 3.60 |
| 1.40 | 0.80 | 3.70 |
| c0 (g × dm−3) | ce (g × dm−3) | E (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 0.46 | 0.20 | 56.00 |
| 0.56 | 0.30 | 43.00 |
| 0.82 | 0.40 | 51.21 |
| 1.12 | 0.60 | 46.40 |
| 1.28 | 0.70 | 45.31 |
| 1.40 | 0.80 | 42.60 |
| ce (mg × dm−3) | q MD (mg × g−1) | q (10) (mg × g−1) | q (15) (mg × g−1) | ∆ |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 200 | 1.6 | 1.668 | 1.534 | −0.134 |
| 300 | 2 | 2.212 | 2.054 | −0.159 |
| 400 | 2.5 | 2.611 | 2.526 | −0.085 |
| 600 | 3.1 | 3.116 | 3.380 | 0.264 |
| 700 | 3.6 | 3.273 | 3.777 | 0.504 |
| 800 | 3.7 | 3.387 | 4.157 | 0.770 |
| Ø 2.371 | Ø 2.324 | Ø 2.490 | Ø 0.166 |
| cei (mg × dm−3) | qi (mg × g−1) | qv (mg × g−1) | (qi − qv)2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 200 | 1.60 | 1.53 | 0.0049 |
| 300 | 1.90 | 2.05 | 0.0225 |
| 400 | 2.63 | 2.52 | 0.0121 |
| 600 | 3.01 | 3.38 | 0.1369 |
| 700 | 3.60 | 3.78 | 0.0324 |
| 800 | 3.70 | 4.16 | 0.2116 |
| pH (−) | Efficiency (%) |
|---|---|
| 3.8 | 44 |
| 4.2 | 47 |
| 4.5 | 50 |
| 4.8 | 53 |
| 5.0 | 56 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pandová, I.; Rimár, M.; Panda, A.; Valíček, J.; Kušnerová, M.; Harničárová, M. A Study of Using Natural Sorbent to Reduce Iron Cations from Aqueous Solutions. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 3686. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17103686
Pandová I, Rimár M, Panda A, Valíček J, Kušnerová M, Harničárová M. A Study of Using Natural Sorbent to Reduce Iron Cations from Aqueous Solutions. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2020; 17(10):3686. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17103686
Chicago/Turabian StylePandová, Iveta, Miroslav Rimár, Anton Panda, Jan Valíček, Milena Kušnerová, and Marta Harničárová. 2020. "A Study of Using Natural Sorbent to Reduce Iron Cations from Aqueous Solutions" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 17, no. 10: 3686. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17103686
APA StylePandová, I., Rimár, M., Panda, A., Valíček, J., Kušnerová, M., & Harničárová, M. (2020). A Study of Using Natural Sorbent to Reduce Iron Cations from Aqueous Solutions. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 17(10), 3686. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17103686








