Spatial Statistics and Influencing Factors of the COVID-19 Epidemic at Both Prefecture and County Levels in Hubei Province, China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
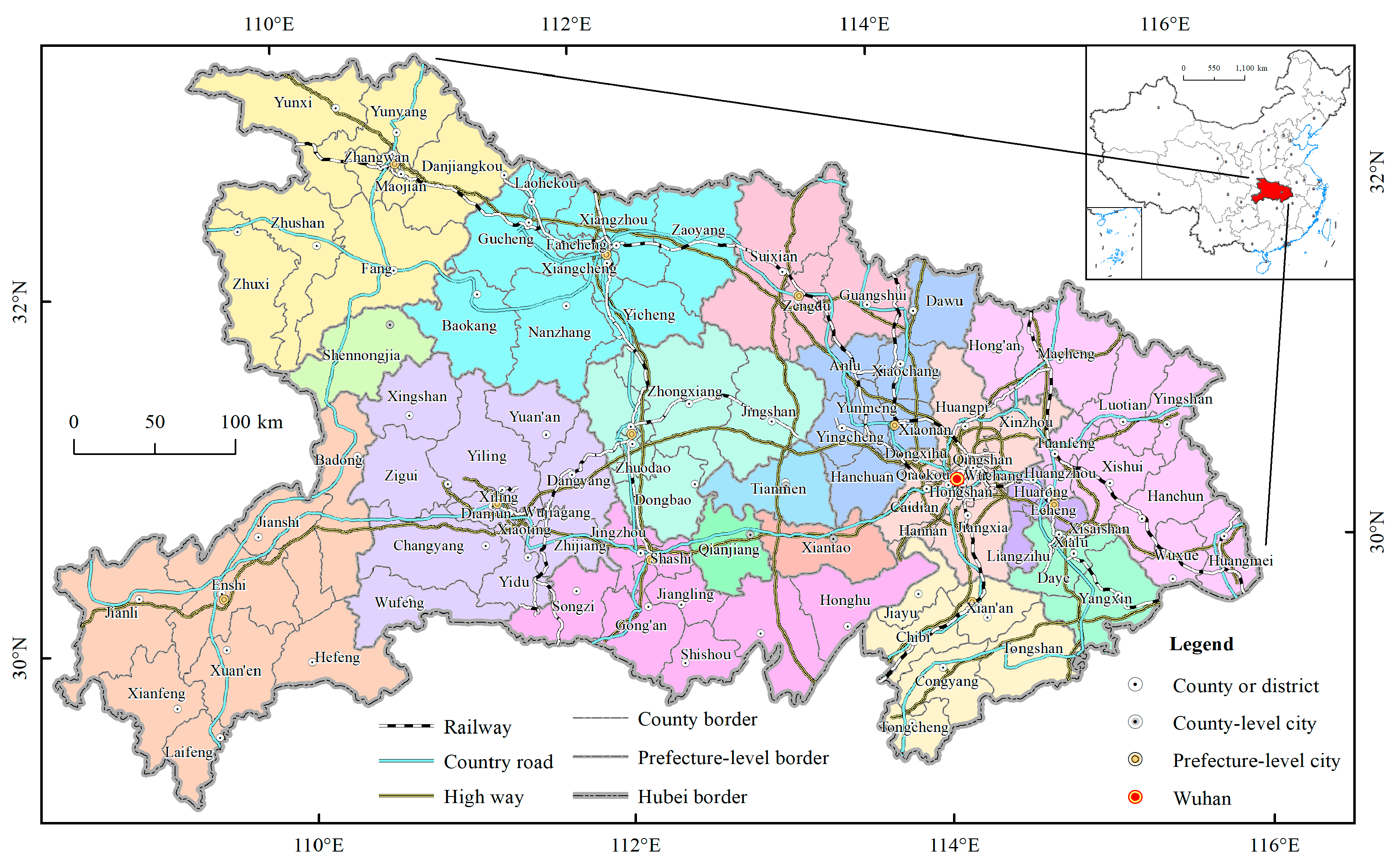
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Sources
2.3. Research Methods
3. Results
3.1. Spatial Statistics of the COVID-19 Epidemic
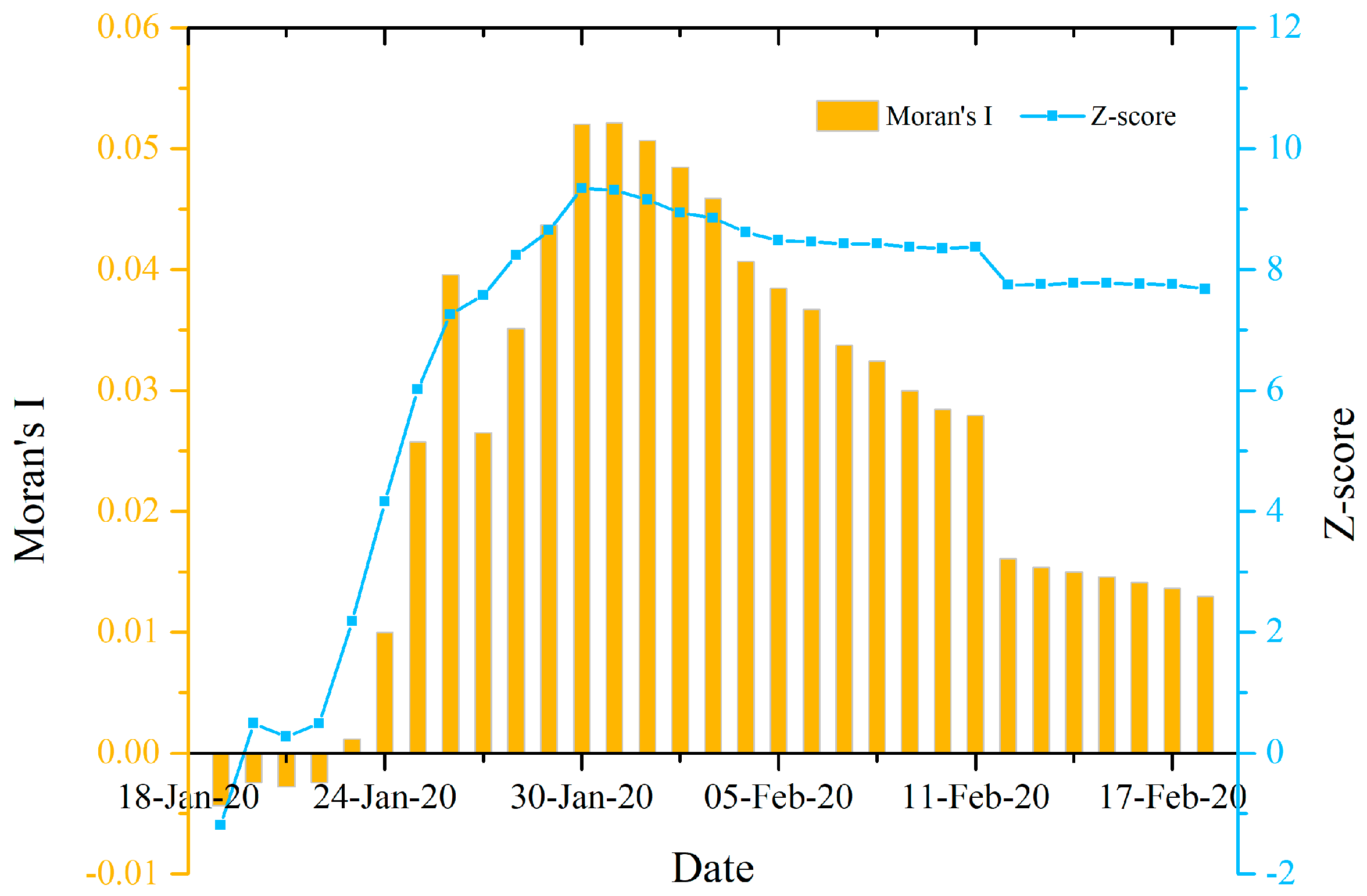
3.1.1. Spatial Autocorrelations of the Provincial COVID-19 Outbreaks Nationwide
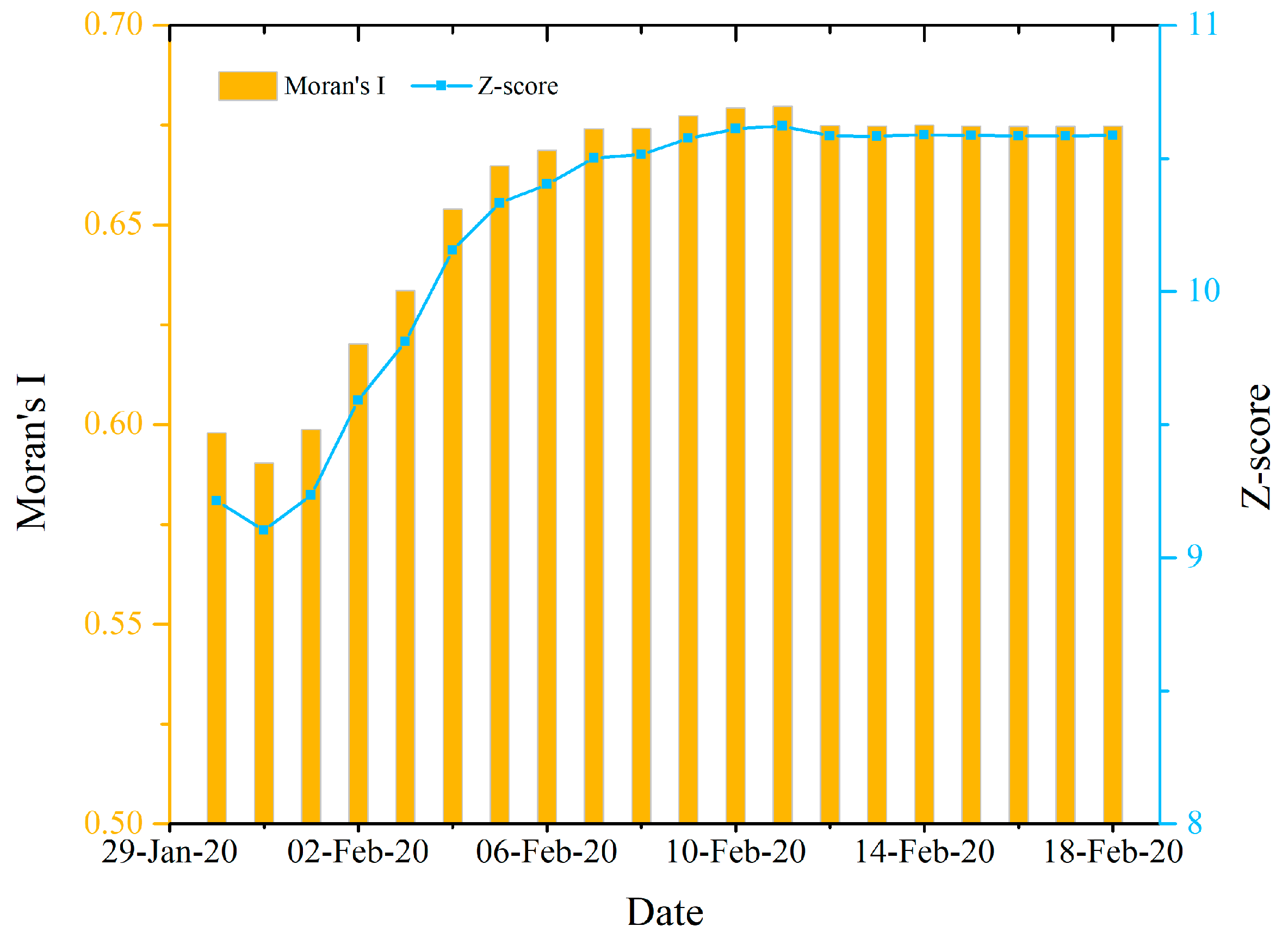
3.1.2. Spatial Autocorrelations of the Prefecture Level COVID-19 Outbreaks Nationwide
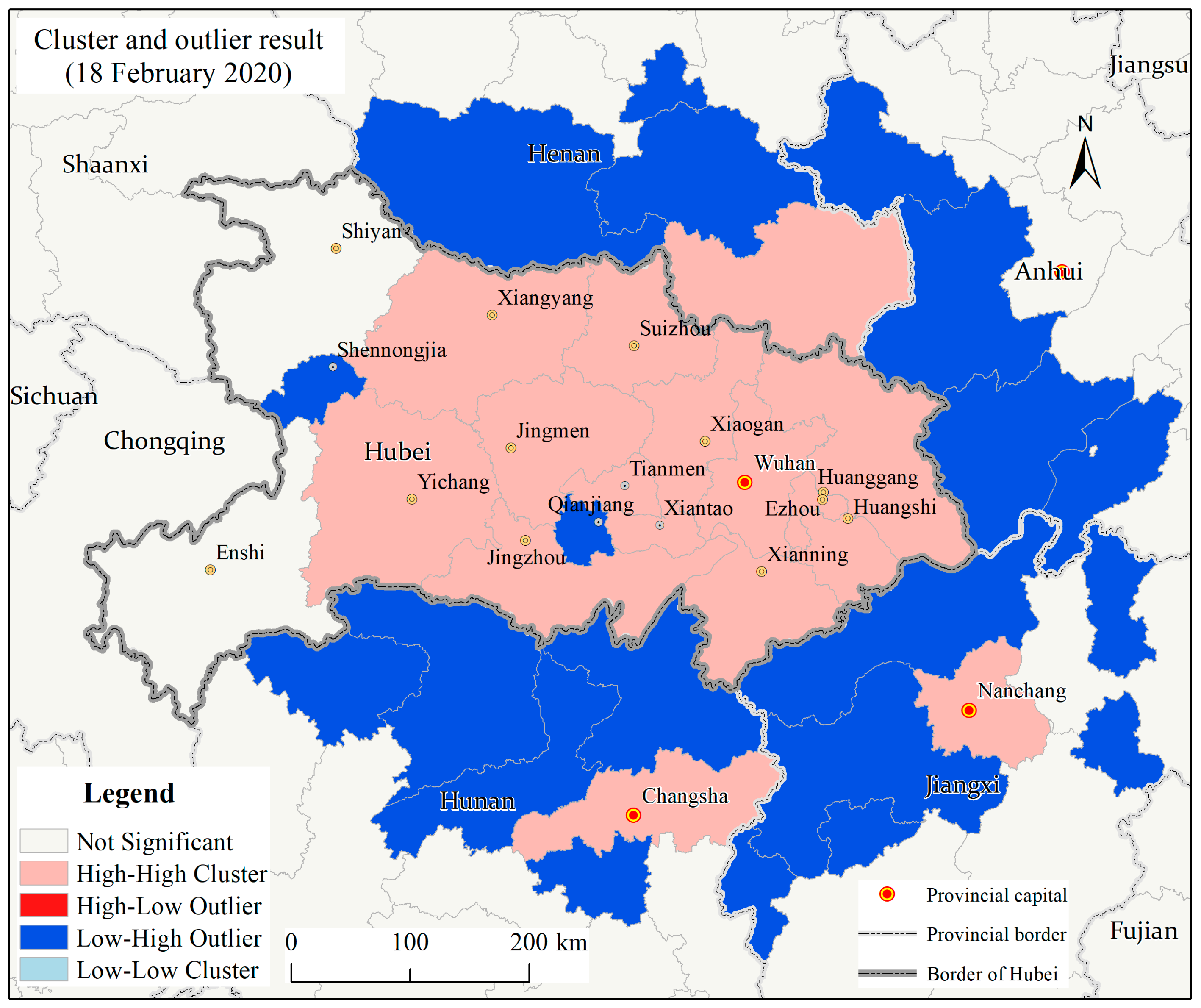
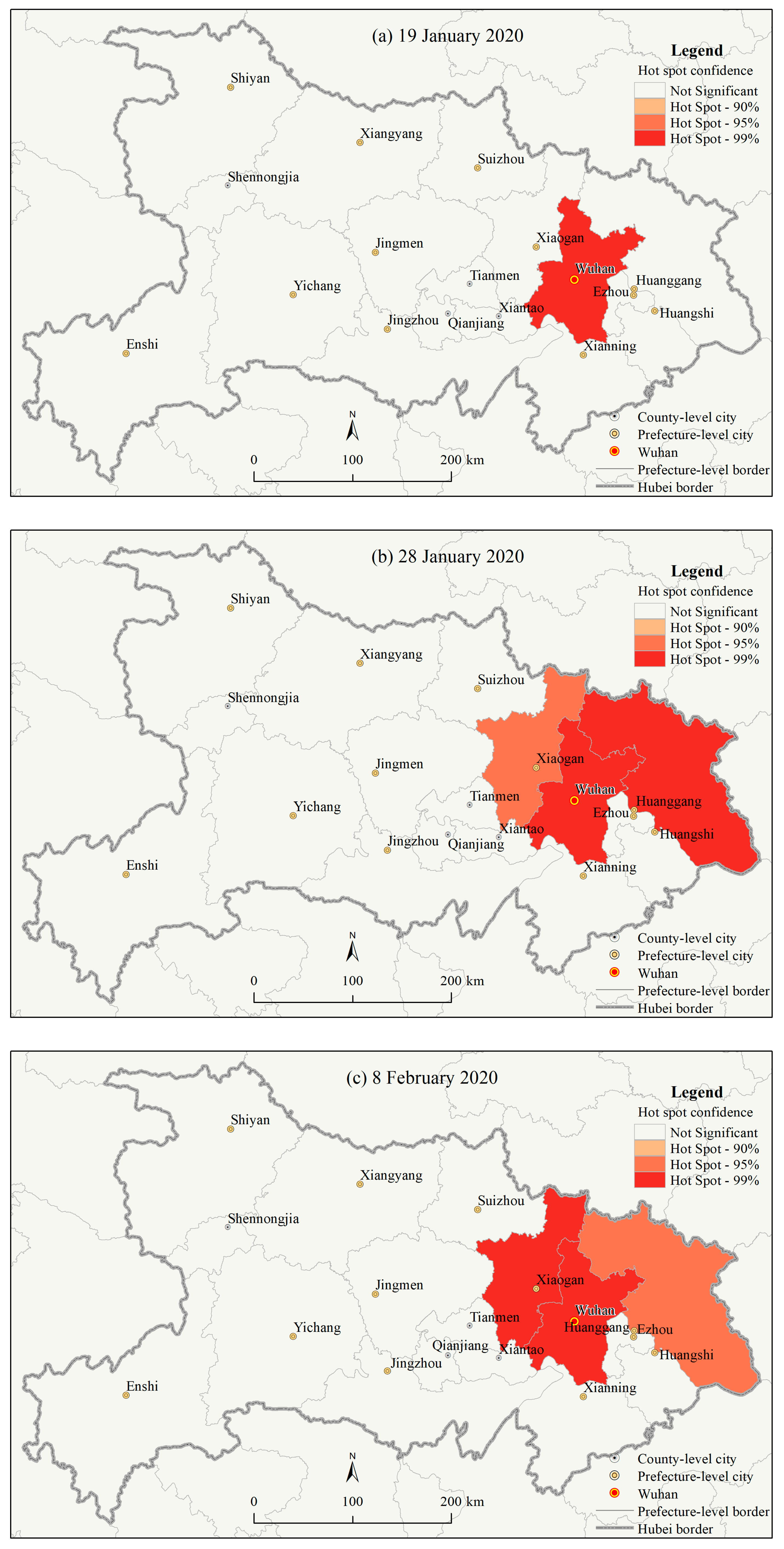
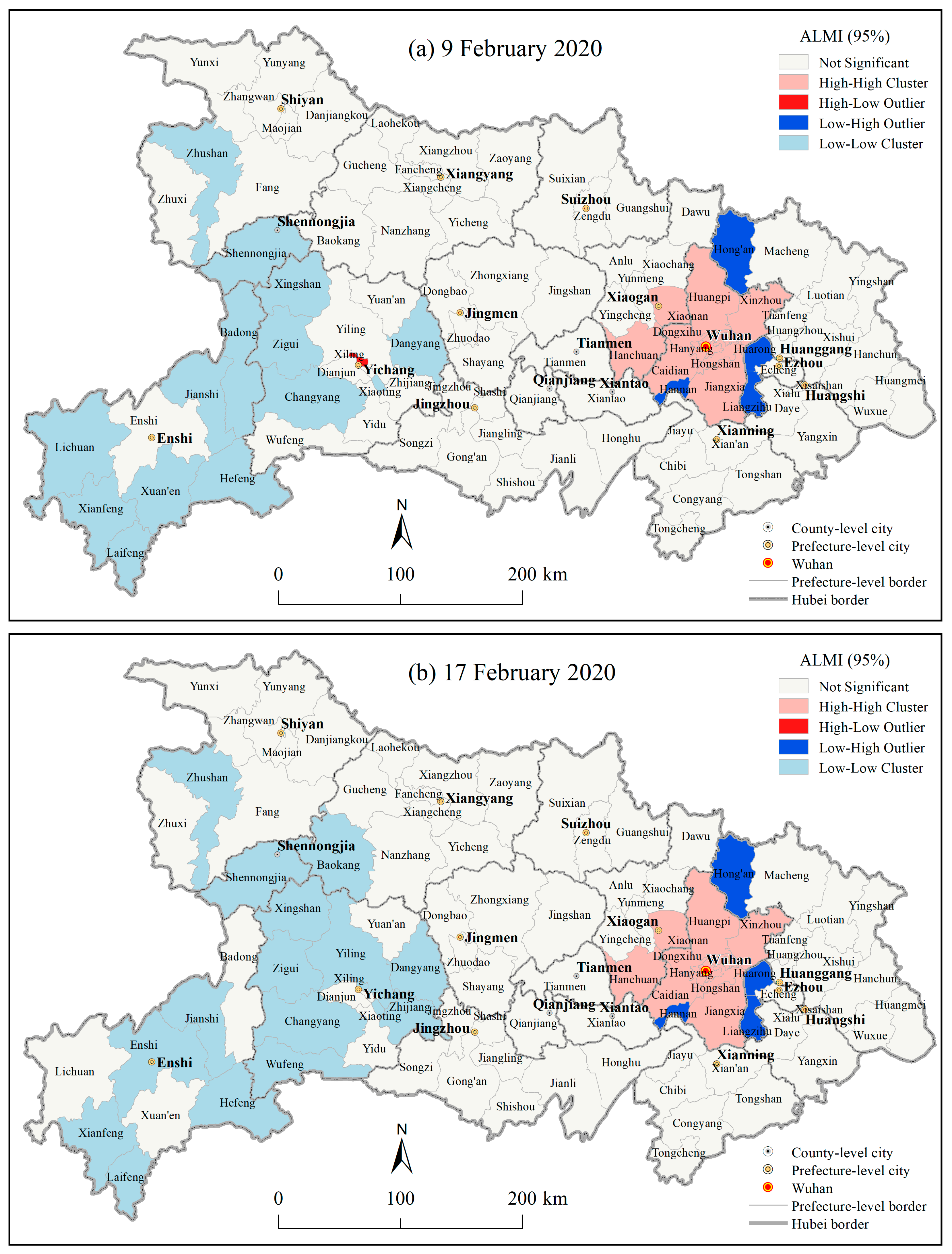
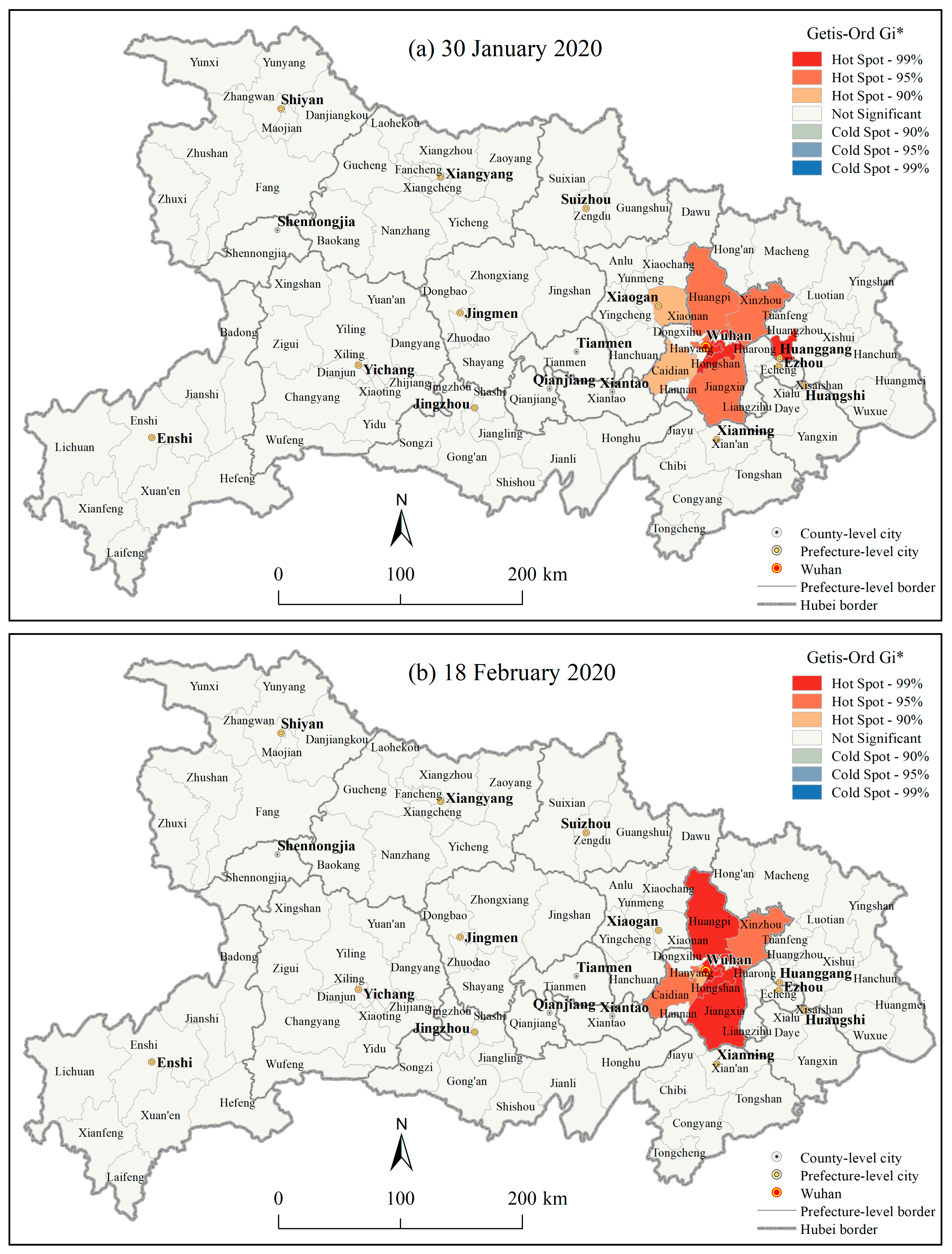
3.1.3. Spatial Autocorrelations of the County Level COVID-19 Outbreaks in Hubei Province
3.2. Influencing Factors of the COVID-19 Epidemic
3.2.1. Influencing Factors of the Prefecture Level COVID-19 Outbreaks in Hubei Province
3.2.2. Influencing Factors of the County Level COVID-19 Outbreaks in Hubei Province
4. Discussion
4.1. Geographic Risk Identification Based on the Spatial Statistics of the COVID-19 Epidemic
4.2. Potential Risk Factors of the COVID-19 Spread
4.3. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| SARS | severe acute respiratory syndrome |
| SARS-CoV-2 | 2019 novel coronavirus |
| COVID-19 | novel coronavirus pneumonia 2019 (coronavirus disease 2019) |
| CCC | cumulative confirmed COVID-19 cases |
| DCC | daily new confirmed COVID-19 cases |
| LISA | Local Indicators of Spatial Association |
| ALMI | Anselin Local Moran’s I |
| LA | land area |
| PD | population density |
| RGP | registered population |
| RSP | resident population |
| BMI | Baidu migration index |
| GDP | gross domestic production |
| TRS | total retail sales of consumer goods |
| DEM | digital elevation model |
| MAXE | maximum elevation |
| MINE | minimum elevation |
| MNE | mean elevation |
| RAE | range of elevation |
References
- Guan, W.; Ni, Z.; Hu, Y.; Liang, W.; Ou, C.; He, J.; Liu, L.; Shan, H.; Lei, C.; Hui, D.S.C.; et al. Clinical Characteristics of Coronavirus Disease 2019 in China. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 1708–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Horby, P.W.; Hayden, F.G.; Gao, G.F. A novel coronavirus outbreak of global health concern. Lancet 2020, 395, 470–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- National Health Commission of the People’s Republic of China. Update on the novel coronavirus pneumonia situation in China as of 24:00 2 April 2020. Available online: http://www.nhc.gov.cn/xcs/yqtb/202004/4786774c1fd84e16b29d872f95241561.shtml (accessed on 3 April 2020).
- Johns Hopkins University. The Johns Hopkins COVID-19 Map Dashboard. Available online: https://coronavirus.jhu.edu/map.html (accessed on 3 April 2020).
- Editorial. Communication, collaboration, and cooperation can stop the 2019 coronavirus. Nat. Med. 2020, 26, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, X.; Wang, B.; Kang, Y. Novel coronavirus infection during the 2019–2020 epidemic: Preparing intensive care units—the experience in Sichuan Province, China. Intens. Care Med. 2020, 46, 357–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhao, S.; Lin, Q.; Ran, J.; Musa, S.S.; Yang, G.; Wang, W.; Lou, Y.; Gao, D.; Yang, L.; He, D.; et al. Preliminary estimation of the basic reproduction number of novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) in China, from 2019 to 2020: A data-driven analysis in the early phase of the outbreak. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 92, 214–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Forna, A.; Dorigatti, I.; Nouvellet, P.; Donnelly, C.A. Spatiotemporal variability in case fatality ratios for 2013–2016 Ebola epidemic in West Africa. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 93, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.W.; Tambyah, P.A.; Hui, D.S.C. Emergence of a novel coronavirus causing respiratory illness from Wuhan, China. J. Infection 2020, 80, 350–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J. Pathogenicity and transmissibility of 2019-nCoV—A quick overview and comparison with other emerging viruses. Microbes Infect. 2020, 22, 69–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, P.; Yang, X.; Wang, X.; Hu, B.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, W.; Si, H.; Zhu, Y.; Li, B.; Huang, C.; et al. A pneumonia outbreak associated with a new coronavirus of probable bat origin. Nature 2020, 549, 270–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, N.; Zhang, D.; Wang, W.; Li, X.; Yang, B.; Song, J.; Zhao, X.; Huang, B.; Shi, W.; Lu, R.; et al. A novel coronavirus from patients with pneumonia in China, 2019. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 727–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Chen, P.; Wang, J.; Feng, J.; Zhou, H.; Li, X.; Zhong, W.; Hao, P. Evolution of the novel coronavirus from the ongoing Wuhan outbreak and modeling of its spike protein for risk of human transmission. Sci. China Life Sci. 2020, 63, 457–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huang, C.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Ren, L.; Zhao, J.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Fan, G.; Xu, J.; Gu, X.; et al. Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China. Lancet 2020, 395, 497–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, N.; Zhou, M.; Dong, X.; Qu, J.; Gong, F.; Han, Y.; Qiu, Y.; Wang, J.; Liu, Y.; Wei, Y.; et al. Epidemiological and clinical characteristics of 99 cases of 2019 novel coronavirus pneumonia in Wuhan, China: A descriptive study. Lancet 2020, 395, 507–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chan, J.F.; Yuan, S.; Kok, K.; To, K.K.; Chu, H.; Yang, J.; Xing, F.; Liu, J.; Yip, C.C.; Poon, R.W.; et al. A familial cluster of pneumonia associated with the 2019 novel coronavirus indicating person-to-person transmission: A study of a family cluster. Lancet 2020, 395, 514–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, R.; Zhao, X.; Li, J.; Niu, P.; Yang, B.; Wu, H.; Wang, W.; Song, H.; Huang, B.; Zhu, N.; et al. Genomic characterisation and epidemiology of 2019 novel coronavirus: Implications for virus origins and receptor binding. Lancet 2020, 395, 565–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, Y.; Liu, Q.; Guo, D. Emerging coronaviruses: Genome structure, replication, and pathogenesis. J. Med. Virol. 2020, 92, 418–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Huang, F.; Wang, F.; Yuan, J.; Wang, Z.; Li, J.; Li, J.; Feng, C.; et al. Clinical and biochemical indexes from 2019-nCoV infected patients linked to viral loads and lung injury. Sci. China Life Sci. 2020, 63, 364–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qin, L.; Sun, Q.; Wang, Y.; Wu, K.; Chen, M.; Shia, B.; Wu, S. Prediction of Number of Cases of 2019 Novel Coronavirus (COVID-19) Using Social Media Search Index. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 2365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, J.T.; Leung, K.; Leung, G.M. Nowcasting and forecasting the potential domestic and international spread of the 2019-nCoV outbreak originating in Wuhan, China: A modelling study. Lancet 2020, 395, 689–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mollalo, A.; Vahedi, B.; Rivera, K.M. GIS-based spatial modeling of COVID-19 incidence rate in the continental United States. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 728, 138884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinazzi, M.; Davis, J.T.; Ajelli, M.; Gioannini, C.; Litvinova, M.; Merler, S.; Pastore Y Piontti, A.; Mu, K.; Rossi, L.; Sun, K.; et al. The effect of travel restrictions on the spread of the 2019 novel coronavirus (COVID-19) outbreak. Science 2020, 368, 395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hu, B.; Gong, J.; Sun, J.; Zhou, J. Exploring the epidemic transmission network of SARS in-out flow in mainland China. China Sci. Bull. 2013, 58, 452–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, J.; Wang, J.; Meng, B.; Liu, X. Spatial association analysis on epidemic of SARS in Beijing, 2003. J. Zhejiang Univ. (Agric. Life Sci.) 2005, 31, 97–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Ying, L. An exploratory spatial data analysis of SARS epidemic in China. Adv. Earth Sci. 2005, 20, 282–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Z.; Wang, J.; Gao, Y.; Han, W.; Feng, X.; Zeng, G. Risk factors and autocorrelation characteristics on severe acute respiratory syndrome in Guangzhou. Acta Geogr. Sinica 2008, 63, 981–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, C.; Chen, W.; Zheng, S.; Zhao, J.; Wang, J.; Cao, W. Analysis of Spatiotemporal Characteristics of Pandemic SARS Spread in Mainland China. BioMed Res. Int. 2016, 2016, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cao, Z.; Zeng, D.; Zheng, X.; Wang, Q.; Wang, F.; Wang, J.; Wang, X. Spatio-temporal evolution of Beijing 2003 SARS epidemic. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2010, 40, 776–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, D.; Choi, H.; Kim, J.; Choi, J. Spatial epidemic dynamics of the COVID-19 outbreak in China. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 96–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, B.; Gong, J.; Zhou, J.; Sun, J.; Yang, L.; Xia, Y.; Ibrahim, A.N. Spatial-temporal characteristics of epidemic spread in-out flow—Using SARS epidemic in Beijing as a case study. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2013, 56, 1380–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Thilakavathy, K.; Kumar, S.S.; He, G.; Liu, S.V. Potential Factors Influencing Repeated SARS Outbreaks in China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pirouz, B.; Haghshenas, S.S.; Haghshenas, S.S.; Piro, P. Investigating a Serious Challenge in the Sustainable Development Process: Analysis of Confirmed cases of COVID-19 (New Type of Coronavirus) Through a Binary Classification Using Artificial Intelligence and Regression Analysis. Sustainability 2020, 12, 2427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, J.; Zhou, J.; Yao, J.; Zhang, X.; Li, L.; Xu, X.; He, X.; Wang, B.; Fu, S.; Niu, T.; et al. Impact of meteorological factors on the COVID-19 transmission: A multi-city study in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 726, 138513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tosepu, R.; Gunawan, J.; Effendy, D.S.; Ahmad, L.O.A.I.; Lestari, H.; Bahar, H.; Asfian, P. Correlation between weather and Covid-19 pandemic in Jakarta, Indonesia. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 725, 138436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- You, H.; Wu, X.; Guo, X. Distribution of COVID-19 Morbidity Rate in Association with Social and Economic Factors in Wuhan, China: Implications for Urban Development. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 3417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Sha, D.; Liu, W.; Houser, P.; Zhang, L.; Hou, R.; Lan, H.; Flynn, C.; Lu, M.; Hu, T.; et al. Spatiotemporal Patterns of COVID-19 Impact on Human Activities and Environment in Mainland China Using Nighttime Light and Air Quality Data. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Yang, X.; Shi, R. Spatial Distribution of the Population in Shandong Province at Multi-Scales. Prog. Geogr. 2012, 31, 176–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Wang, D. The spatial sprawl and driving mechanism of the floating population in Beijing metropolitan areas. Sci. Geogr. Sin. 2019, 39, 1729–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Li, N.; Wu, W.; Wu, J. Evolution of spatial-temporal pattern of county economic development in China during 1982–2010. Prog. Geogr. 2014, 33, 102–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, T.; Lin, N.H.; Lin, C.; King, C.; Su, M. Spatial mapping of temporal risk characteristics to improve environmental health risk identification: A case study of a dengue epidemic in Taiwan. Sci. Total Environ. 2006, 367, 631–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Huang, H. Analysis on the characteristics of gathering and spreading of major infectious diseases. Chinese J. Public Health 2010, 26, 1186–1188. [Google Scholar]
- Ge, L.; Zhao, Y.; Zhou, K.; Mu, X.; Yu, H.; Wang, Y.; Wang, N.; Fan, H.; Guo, L.; Huo, X. Spatio-Temporal Pattern and Influencing Factors of Hemorrhagic Fever with Renal Syndrome (HFRS) in Hubei Province (China) between 2005 and 2014. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0167836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ge, R.; Wang, J.; Zhang, L.; Tian, G.; Feng, Y. Impacts of urbanization on the urban thermal environment in Beijing. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2016, 36, 6040–6049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moran, P.A.P. Notes on Continuous Stochastic Phenomena. Biometrika 1950, 37, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anselin, L. Local Indicators of Spatial Association—LISA. Geogr. Anal. 1995, 27, 93–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ord, K.; Getis, A. Local spatial autocorrelation statistics: Distributional issues and an application. Geogr. Anal. 2010, 27, 286–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, C.; Rosentreter, J.; Voltersen, M.; Baumgart, C.; Schmullius, C.; Hese, S. Spatio-temporal analysis of the relationship between 2D/3D urban site characteristics and land surface temperature. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 193, 225–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Lv, J.; Tan, Y.; Guo, M.; Gu, Y.; Xu, S.; Zhou, Y. Temporospatial variations and Spearman correlation analysis of ozone concentrations to nitrogen dioxide, sulfur dioxide, particulate matters and carbon monoxide in ambient air, China. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2019, 10, 1203–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hafeez, S.; Amin, M.; Munir, B.A. Spatial mapping of temporal risk to improve prevention measures: A case study of dengue epidemic in Lahore. Spat. Spat. Temp. Epidemiol. 2017, 21, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Liu, X.; Huang, Y.; Ma, Z.; Bi, J. Epidemic transition of environmental health risk during China’s urbanization. Sci. Bull. 2017, 62, 92–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, P.; Wang, J.; Atkinson, P.M. Identifying the spatio-temporal risk variability of avian influenza A H7N9 in China. Ecol. Model. 2019, 414, 108807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Tong, Y.; Hu, S.; Ke, Y. Measurement of Intercity Interaction among Wuhan urban clusters. Urban Probl. 2017, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, S.; Chen, M. Study on Urban Economic Relations and Regional Economic Development in Hubei Province. Stat. Decis. 2018, 34, 127–130. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, J.; Li, J.; Zhou, H.; Huang, J. Dynamic development of Wuhan metropolitan area based on urban connection. Planners 2017, 33, 85–92. [Google Scholar]
- Heymann, D.L. Data sharing and outbreaks: Best practice exemplified. Lancet 2020, 395, 469–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, B.; Kraemer, M.U.G.; Xu, B.; Gutierrez, B.; Mekaru, S.; Sewalk, K.; Loskill, A.; Wang, L.; Cohn, E.; Hill, S.; et al. Open access epidemiological data from the COVID-19 outbreak. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2020, 20, 534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]


| Indicator | MINE | MAXE | MNE | RAE | LA | PD | RGP | RSP | TRS | GDP | BMI | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CCC0123 | −0.508 * | −0.084 | −0.185 | −0.097 | 0.218 | 0.231 | 0.640 ** | 0.647 ** | 0.555 * | 0.608 ** | 0.579 * | |||||||||
| CCC0124 | −0.321 | 0.021 | −0.067 | 0.018 | 0.328 | 0.123 | 0.650 ** | 0.605 * | 0.411 | 0.418 | 0.460 | |||||||||
| CCC0125 | −0.568 * | 0.082 | 0.039 | 0.076 | 0.375 | 0.158 | 0.712 ** | 0.702 ** | 0.622 ** | 0.654 ** | 0.586 * | |||||||||
| CCC0126 | −0.515 * | 0.113 | 0.075 | 0.104 | 0.417 | 0.169 | 0.757 ** | 0.765 ** | 0.689 ** | 0.737 ** | 0.602 * | |||||||||
| CCC0127 | −0.531 * | 0.045 | −0.006 | 0.037 | 0.347 | 0.254 | 0.753 ** | 0.764 ** | 0.699 ** | 0.766 ** | 0.704 ** | |||||||||
| CCC0128 | −0.451 | 0.088 | 0.049 | 0.074 | 0.373 | 0.238 | 0.755 ** | 0.782 ** | 0.725 ** | 0.784 ** | 0.607 * | |||||||||
| CCC0129 | −0.468 | 0.047 | −0.005 | 0.034 | 0.355 | 0.267 | 0.772 ** | 0.797 ** | 0.750 ** | 0.819 ** | 0.679 ** | |||||||||
| CCC0130 | −0.473 | −0.025 | −0.061 | −0.044 | 0.248 | 0.368 | 0.711 ** | 0.745 ** | 0.748 ** | 0.811 ** | 0.654 ** | |||||||||
| CCC0131 | −0.468 | 0.022 | −0.017 | −0.002 | 0.316 | 0.319 | 0.765 ** | 0.799 ** | 0.811 ** | 0.865 ** | 0.668 ** | |||||||||
| CCC0201 | −0.456 | 0.042 | 0.002 | 0.015 | 0.324 | 0.304 | 0.755 ** | 0.794 ** | 0.814 ** | 0.868 ** | 0.650 ** | |||||||||
| CCC0202 | −0.527 * | −0.012 | −0.054 | −0.032 | 0.304 | 0.350 | 0.779 ** | 0.816 ** | 0.831 ** | 0.882 ** | 0.682 ** | |||||||||
| CCC0203 | −0.505 * | 0.034 | 0.005 | 0.010 | 0.326 | 0.304 | 0.767 ** | 0.794 ** | 0.806 ** | 0.850 ** | 0.661 ** | |||||||||
| CCC0204 | −0.551 * | 0.015 | −0.022 | 0.000 | 0.324 | 0.348 | 0.799 ** | 0.824 ** | 0.838 ** | 0.875 ** | 0.725 ** | |||||||||
| CCC0205 | −0.522 * | −0.027 | −0.051 | −0.051 | 0.265 | 0.370 | 0.738 ** | 0.760 ** | 0.782 ** | 0.824 ** | 0.675 ** | |||||||||
| CCC0206 | −0.534 * | −0.059 | −0.083 | −0.086 | 0.233 | 0.395 | 0.721 ** | 0.748 ** | 0.770 ** | 0.816 ** | 0.657 ** | |||||||||
| CCC0207 | −0.534 * | −0.059 | −0.083 | −0.086 | 0.233 | 0.395 | 0.721 ** | 0.748 ** | 0.770 ** | 0.816 ** | 0.657 ** | |||||||||
| CCC0208 | −0.561 * | −0.074 | −0.108 | −0.096 | 0.228 | 0.439 | 0.750 ** | 0.775 ** | 0.804 ** | 0.843 ** | 0.732 ** | |||||||||
| CCC0209 | −0.529 * | −0.071 | −0.096 | −0.100 | 0.208 | 0.419 | 0.708 ** | 0.733 ** | 0.760 ** | 0.804 ** | 0.675 ** | |||||||||
| CCC0210 | −0.527 * | −0.096 | −0.120 | −0.125 | 0.174 | 0.449 | 0.689 ** | 0.711 ** | 0.735 ** | 0.782 ** | 0.686 ** | |||||||||
| CCC0211 | −0.498 * | −0.086 | −0.110 | −0.115 | 0.189 | 0.436 | 0.691 ** | 0.718 ** | 0.745 ** | 0.787 ** | 0.657 ** | |||||||||
| CCC0212 | −0.529 * | −0.120 | −0.154 | −0.145 | 0.172 | 0.451 | 0.696 ** | 0.718 ** | 0.725 ** | 0.787 ** | 0.704 ** | |||||||||
| CCC0213 | −0.554 * | −0.147 | −0.179 | −0.172 | 0.127 | 0.490 * | 0.667 ** | 0.684 ** | 0.701 ** | 0.757 ** | 0.725 ** | |||||||||
| CCC0214 | −0.551 * | −0.135 | −0.167 | −0.162 | 0.137 | 0.485 * | 0.674 ** | 0.691 ** | 0.716 ** | 0.767 ** | 0.732 ** | |||||||||
| CCC0215 | −0.554 * | −0.147 | −0.179 | −0.172 | 0.127 | 0.490 * | 0.667 ** | 0.684 ** | 0.701 ** | 0.757 ** | 0.725 ** | |||||||||
| CCC0216 | −0.569 * | −0.162 | −0.199 | −0.184 | 0.108 | 0.517 * | 0.659 ** | 0.676 ** | 0.699 ** | 0.755 ** | 0.754 ** | |||||||||
| CCC0217 | −0.566 * | −0.150 | −0.186 | −0.174 | 0.118 | 0.512 * | 0.667 ** | 0.684 ** | 0.713 ** | 0.765 ** | 0.761 ** | |||||||||
| CCC0218 | −0.566 * | −0.150 | −0.186 | −0.174 | 0.118 | 0.512 * | 0.667 ** | 0.684 ** | 0.713 ** | 0.765 ** | 0.761 ** | |||||||||
| tMean | −0.539 * | −0.113 | −0.145 | −0.140 | 0.169 | 0.466 | 0.701 ** | 0.721 ** | 0.743 ** | 0.792 ** | 0.725 ** | |||||||||
| N5 | NES | NS | NM | NW | None | PW | PM | PS | PES | P5 | ||||||||||
| p < 0.05 | −1~−0.8 | −0.8~−0.6 | −0.6~−0.4 | −0.4~−0.2 | −0.2~0.2 | 0.2~0.4 | 0.4~0.6 | 0.6~0.8 | 0.8~1 | p < 0.05 | ||||||||||
| Indicator | MINE | MAXE | MNE | RAE | LA | PD | RGP | RSP | TRS | GDP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CCC0126 | −0.314 * | −0.477 ** | −0.513 ** | −0.478 ** | −0.289 * | 0.482 ** | 0.257 * | 0.286 * | 0.449 ** | 0.290 * |
| CCC0127 | −0.287 * | −0.537 ** | −0.523 ** | −0.529 ** | −0.150 | 0.424 ** | 0.344 ** | 0.386 ** | 0.470 ** | 0.331 ** |
| CCC0128 | −0.321 ** | −0.483 ** | −0.484 ** | −0.482 ** | −0.179 | 0.499 ** | 0.466 ** | 0.508 ** | 0.591 ** | 0.488 ** |
| CCC0129 | −0.326 ** | −0.491 ** | −0.494 ** | −0.489 ** | −0.145 | 0.526 ** | 0.529 ** | 0.575 ** | 0.648 ** | 0.538 ** |
| CCC0130 | −0.354 ** | −0.537 ** | −0.534 ** | −0.535 ** | −0.221 * | 0.583 ** | 0.499 ** | 0.583 ** | 0.705 ** | 0.633 ** |
| CCC0131 | −0.372 ** | −0.557 ** | −0.544 ** | −0.556 ** | −0.266 * | 0.613 ** | 0.465 ** | 0.552 ** | 0.704 ** | 0.622 ** |
| CCC0201 | −0.406 ** | −0.532 ** | −0.552 ** | −0.526 ** | −0.254 * | 0.618 ** | 0.494 ** | 0.578 ** | 0.705 ** | 0.609 ** |
| CCC0202 | −0.456 ** | −0.570 ** | −0.601 ** | −0.561 ** | −0.276 ** | 0.657 ** | 0.530 ** | 0.613 ** | 0.706 ** | 0.597 ** |
| CCC0203 | −0.488 ** | −0.589 ** | −0.628 ** | −0.577 ** | −0.277 ** | 0.664 ** | 0.547 ** | 0.630 ** | 0.712 ** | 0.606 ** |
| CCC0204 | −0.502 ** | −0.603 ** | −0.640 ** | −0.590 ** | −0.305 ** | 0.691 ** | 0.545 ** | 0.626 ** | 0.699 ** | 0.586 ** |
| CCC0205 | −0.509 ** | −0.611 ** | −0.649 ** | −0.598 ** | −0.311 ** | 0.695 ** | 0.543 ** | 0.624 ** | 0.696 ** | 0.589 ** |
| CCC0206 | −0.511 ** | −0.614 ** | −0.651 ** | −0.600 ** | −0.293 ** | 0.689 ** | 0.553 ** | 0.634 ** | 0.694 ** | 0.584 ** |
| CCC0207 | −0.517 ** | −0.624 ** | −0.665 ** | −0.610 ** | −0.297 ** | 0.696 ** | 0.553 ** | 0.635 ** | 0.703 ** | 0.584 ** |
| CCC0208 | −0.519 ** | −0.631 ** | −0.669 ** | −0.617 ** | −0.299 ** | 0.700 ** | 0.554 ** | 0.638 ** | 0.705 ** | 0.584 ** |
| CCC0209 | −0.520 ** | −0.632 ** | −0.668 ** | −0.619 ** | −0.299 ** | 0.703 ** | 0.554 ** | 0.636 ** | 0.696 ** | 0.571 ** |
| CCC0210 | −0.518 ** | −0.633 ** | −0.668 ** | −0.619 ** | −0.295 ** | 0.700 ** | 0.551 ** | 0.632 ** | 0.697 ** | 0.566 ** |
| CCC0211 | −0.522 ** | −0.642 ** | −0.679 ** | −0.629 ** | −0.292 ** | 0.706 ** | 0.561 ** | 0.642 ** | 0.705 ** | 0.570 ** |
| CCC0212 | −0.525 ** | −0.646 ** | −0.680 ** | −0.634 ** | −0.269 * | 0.689 ** | 0.570 ** | 0.650 ** | 0.705 ** | 0.577 ** |
| CCC0213 | −0.528 ** | −0.632 ** | −0.677 ** | −0.620 ** | −0.284 ** | 0.694 ** | 0.575 ** | 0.648 ** | 0.694 ** | 0.560 ** |
| CCC0214 | −0.533 ** | −0.635 ** | −0.683 ** | −0.622 ** | −0.283 ** | 0.690 ** | 0.570 ** | 0.642 ** | 0.696 ** | 0.559 ** |
| CCC0215 | −0.534 ** | −0.640 ** | −0.687 ** | −0.627 ** | −0.277 ** | 0.689 ** | 0.580 ** | 0.653 ** | 0.704 ** | 0.567 ** |
| CCC0216 | −0.532 ** | −0.646 ** | −0.690 ** | −0.632 ** | −0.277 ** | 0.690 ** | 0.579 ** | 0.651 ** | 0.704 ** | 0.569 ** |
| CCC0217 | −0.530 ** | −0.650 ** | −0.693 ** | −0.636 ** | −0.276 ** | 0.690 ** | 0.580 ** | 0.652 ** | 0.710 ** | 0.574 ** |
| CCC0218 | −0.525 ** | −0.650 ** | −0.690 ** | −0.638 ** | −0.275 ** | 0.688 ** | 0.574 ** | 0.649 ** | 0.708 ** | 0.572 ** |
| tMean | −0.515 ** | −0.638 ** | −0.677 ** | −0.626 ** | −0.290 ** | 0.702 ** | 0.562 ** | 0.645 ** | 0.720 ** | 0.587 ** |
| N5 | NES | NS | NM | NW | None | PW | PM | PS | PES | P5 |
| p < 0.05 | −1~−0.8 | −0.8~−0.6 | −0.6~−0.4 | −0.4~−0.2 | −0.2~0.2 | 0.2~0.4 | 0.4~0.6 | 0.6~0.8 | 0.8~1 | p < 0.05 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xiong, Y.; Wang, Y.; Chen, F.; Zhu, M. Spatial Statistics and Influencing Factors of the COVID-19 Epidemic at Both Prefecture and County Levels in Hubei Province, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 3903. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17113903
Xiong Y, Wang Y, Chen F, Zhu M. Spatial Statistics and Influencing Factors of the COVID-19 Epidemic at Both Prefecture and County Levels in Hubei Province, China. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2020; 17(11):3903. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17113903
Chicago/Turabian StyleXiong, Yongzhu, Yunpeng Wang, Feng Chen, and Mingyong Zhu. 2020. "Spatial Statistics and Influencing Factors of the COVID-19 Epidemic at Both Prefecture and County Levels in Hubei Province, China" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 17, no. 11: 3903. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17113903
APA StyleXiong, Y., Wang, Y., Chen, F., & Zhu, M. (2020). Spatial Statistics and Influencing Factors of the COVID-19 Epidemic at Both Prefecture and County Levels in Hubei Province, China. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 17(11), 3903. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17113903






