Inspiratory Muscle Training in Intermittent Sports Modalities: A Systematic Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
2.3. Search Strategy—Data Sources
2.4. Methodological Quality of the Studies
2.5. Data Collection and Extraction
3. Results
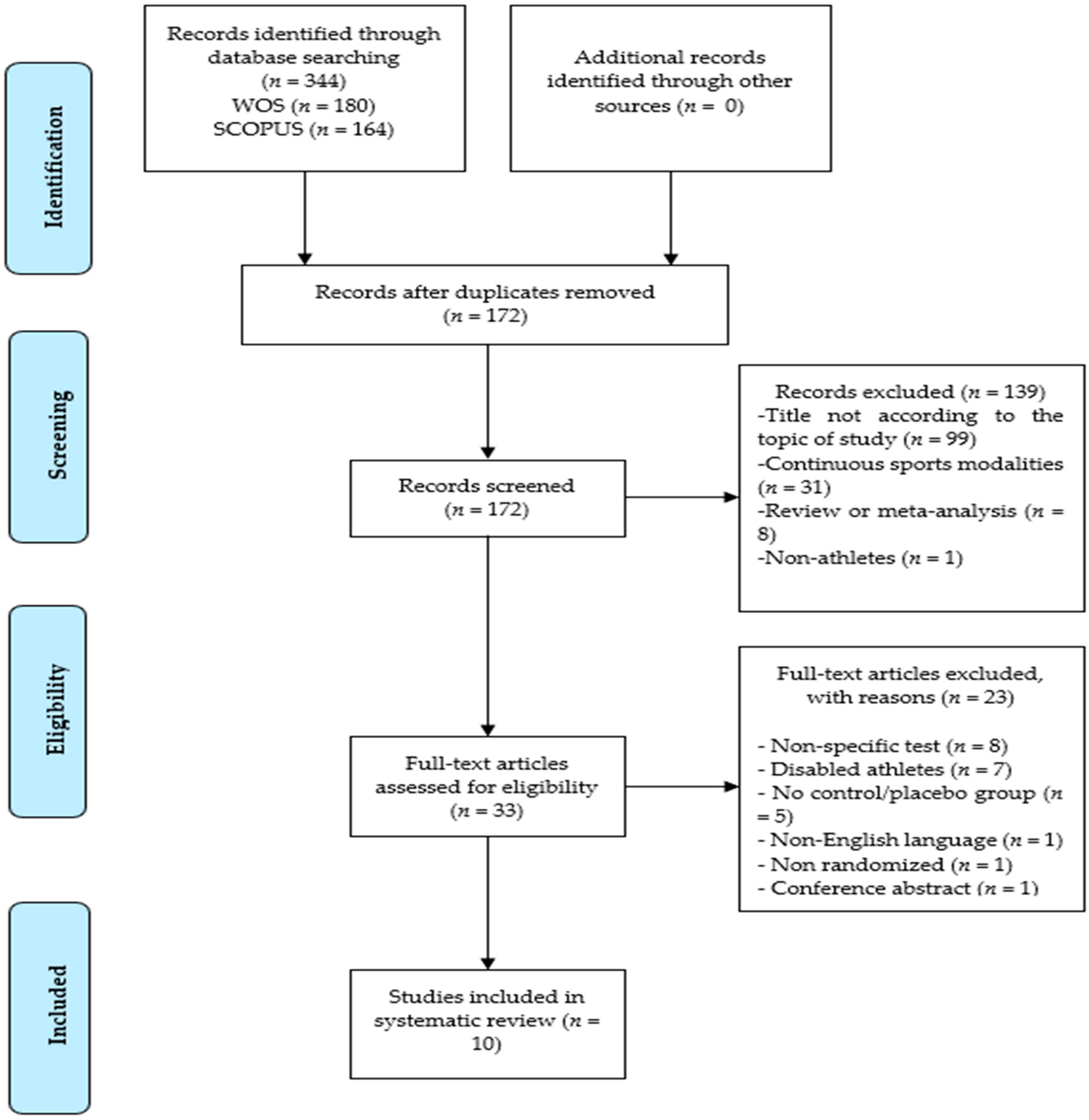
3.1. Study Selection
3.2. Characteristics of the Participants
3.3. Description of the Interventions and the Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Protocol and Intervention
4.1.1. Chronic Treatment
4.1.2. Acute Treatment
4.1.3. Combination of Acute and Chronic Treatment
4.2. Sports Practiced and Sports Level
4.3. Study Limitations
5. Conclusions
6. Practical Applications
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sales, A.T.D.N.; Fregonezi, G.A.D.F.; Ramsook, A.H.; Guenette, J.A.; Lima, I.N.D.F.; Reid, W.D. Respiratory Muscle Endurance after Training in Athletes and Non-Athletes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Phys. Ther. Sport 2016, 17, 76–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mackała, K.; Kurzaj, M.; Okrzymowska, P.; Stodółka, J.; Coh, M.; Rożek-Piechura, K. The Effect of Respiratory Muscle Training on the Pulmonary Function, Lung Ventilation, and Endurance Performance of Young Soccer Players. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 17, 234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Talavera, I.; Lobato, S.D.; Bolado, P.R.; Villasante, C. Músculos Respiratorios. Arch. Bronconeumol. 1992, 28, 239–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roussos, C.; Macklem, P. The Respiratory Muscles. N. Engl. J. Med. 1982, 307, 786–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- HajGhanbari, B.; Yamabayashi, C.; Buna, T.; Coelho, J.; Freedman, K.; Morton, T.; Palmer, S.; Toy, M.; Walsh, C.; Sheel, A.; et al. Effects of Respiratory Muscle Training on Performance in Athletes. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2012, 27, 1643–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Illi, S.K.; Held, U.; Frank, I.; Spengler, C.M. Effect of Respiratory Muscle Training on Exercise Performance in Healthy Individuals. Sports Med. 2012, 42, 707–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheel, A. Respiratory Muscle Training in Healthy Individuals. Sports Med. 2002, 32, 567–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lötters, F.; Tol, B.; Kwakkel, G.; Gosselink, R. Effects of Controlled Inspiratory Muscle Training in Patients with COPD: A Meta-Analysis. Eur. Respir. J. Off. J. Eur. Soc. Clin. Respir. Physiol. 2002, 20, 570–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williamson, E.; Pederson, N.; Rawson, H.; Daniel, T. The Effect of Inspiratory Muscle Training on Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy: A Meta-Analysis. Pediatr. Phys. Ther. 2019, 31, 323–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chicharro, J.L.; Mulas, A.L. El sistema pulmonar como limitante del rendimiento en ejercicios de resistencia. In Fisiología del Ejercicio, 3rd ed.; Chicharro, J.L., Vaquero, A.F., Eds.; Médica Panamericana: México, Mexico, 2006; pp. 386–394. [Google Scholar]
- Aaron, E.A.; Seow, K.C.; Johnson, B.D.; Dempsey, J.A. Oxygen Cost of Exercise Hyperpnea: Implications for Performance. J. Appl. Physiol. 1992, 72, 1818–1825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harms, C.A.; Wetter, T.J.; McClaran, S.R.; Pegelow, D.F.; Nickele, G.A.; Nelson, W.B.; Hanson, P.; Dempsey, J.A. Effects of Respiratory Muscle Work on Cardiac Output and Its Distribution during Maximal Exercise. J. Appl. Physiol. 1998, 85, 609–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katayama, K.; Itoh, Y.; Saito, M.; Koike, T.; Ishida, K. Sympathetic Vasomotor Outflow and Blood Pressure Increase during Exercise with Expiratory Resistance. Physiol. Rep. 2015, 3, e12421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romer, L.M.; Polkey, M.I. Exercise-Induced Respiratory Muscle Fatigue: Implications for Performance. J. Appl. Physiol. 2008, 104, 879–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harms, C.A.; Babcock, M.A.; McClaran, S.R.; Pegelow, D.F.; Nickele, G.A.; Nelson, W.B.; Dempsey, J.A. Respiratory Muscle Work Compromises Leg Blood Flow during Maximal Exercise. J. Appl. Physiol. 1997, 82, 1573–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harms, C.; Wetter, T.; Croix, C.; Pegelow, D.; Dempsey, J. Effects of Respiratory Muscle Work on Exercise Performance. J. Appl. Physiol. 2000, 89, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romer, L.; Lovering, A.; Haverkamp, H.; Pegelow, D.; Dempsey, J. Effect of Inspiratory Muscle Work on Peripheral Fatigue of Locomotor Muscles in Healthy Humans. J. Physiol. 2006, 571, 425–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, B.; Aaron, E.; Babcock, M.; Dempsey, J. Respiratory Muscle Fatigue during Exercise: Implications for Performance. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 1996, 28, 1129–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wells, G.; Norris, S. Assessment of Physiological Capacities of Elite Athletes & Respiratory Limitations to Exercise Performance. Paediatr. Respir. Rev. 2009, 10, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ker, J.A.; Schultz, C. Respiratory Muscle Fatigue after an Ultra-Marathon Measured as Inspiratory Task Failure. Int. J. Sports Med. 1996, 17, 493–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loke, J.; Mahler, D.A.; Virgulto, J. Respiratory Muscle Fatigue after Marathon Running. J. Appl. Physiol. 1982, 52, 821–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lomax, M.E.; McConnell, A.K. Inspiratory Muscle Fatigue in Swimmers after a Single 200 m Swim. J. Sports Sci. 2003, 21, 659–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babcock, M.A.; Pegelow, D.F.; Harms, C.A.; Dempsey, J.A. Effects of Respiratory Muscle Unloading on Exercise-Induced Diaphragm Fatigue. J. Appl. Physiol. 2002, 93, 201–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nava, S.; Zanotti, E.; Rampulla, C.; Rossi, A. Respiratory Muscle Fatigue Does Not Limit Exercise Performance during Moderate Endurance Run. J. Sports Med. Phys. Fit. 1992, 32, 39–44. [Google Scholar]
- Mcconnell, A.K.; Lomax, M. The Influence of Inspiratory Muscle Work History and Specific Inspiratory Muscle Training upon Human Limb Muscle Fatigue. J. Physiol. 2006, 577, 445–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Witt, J.; Guenette, J.; Rupert, J.; Mckenzie, D.; Sheel, A. Inspiratory Muscle Training Attenuates the Human Respiratory Muscle Metaboreflex. J. Physiol. 2007, 584, 1019–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McConnell, A.K. Respiratory Muscle Training as an Ergogenic Aid. J. Exerc. Sci. Fit. 2009, 7, S18–S27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romer, L.; McConnell, A.; Jones, D. Inspiratory Muscle Fatigue in Trained Cyclists: Effects of Inspiratory Muscle Training. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2002, 34, 785–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verges, S.; Lenherr, O.; Haner, A.; Schulz, C.; Spengler, C. Increased Fatigue Resistance of Respiratory Muscles during Exercise after Respiratory Muscle Endurance Training. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2007, 292, R1246–R1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavalcante Silva, R.L.; Hall, E.; Maior, A.S. Inspiratory Muscle Training Improves Performance of a Repeated Sprints Ability Test in Professional Soccer Players. J. Bodyw. Mov. Ther. 2019, 23, 452–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, P.; Sharpe, G.; Johnson, M. Inspiratory Muscle Training Reduces Blood Lactate Concentration during Volitional Hyperpnoea. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2008, 104, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guy, J.; Edwards, A.; Deakin, G. Inspiratory Muscle Training Improves Exercise Tolerance in Recreational Soccer Players Without Concomitant Gain in Soccer-Specific Fitness. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2013, 28, 483–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McConnell, A.K.; Sharpe, G.R. The Effect of Inspiratory Muscle Training upon Maximum Lactate Steady-State and Blood Lactate Concentration. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2005, 94, 277–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spengler, C.M.; Roos, M.; Laube, S.M.; Boutellier, U. Decreased Exercise Blood Lactate Concentrations after Respiratory Endurance Training in Humans. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. Occup. Physiol. 1999, 79, 299–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, S.; Sato, M.; Okubo, T. Expiratory Muscle Training and Sensation of Respiratory Effort during Exercise in Normal Subjects. Thorax 1995, 50, 366–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volianitis, S.; McConnell, A.K.; Koutedakis, Y.; McNaughton, L.; Backx, K.; Jones, D.A. Inspiratory Muscle Training Improves Rowing Performance. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2001, 33, 803–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Najafi, A.; Ebrahim, K.; Ahmadizad, S.; Jahani Ghaeh Ghashlagh, G.R.; Javidi, M.; Hackett, D. Improvements in Soccer-Specific Fitness and Exercise Tolerance Following 8 Weeks of Inspiratory Muscle Training in Adolescent Males. J. Sports Med. Phys. Fit. 2019, 59, 1975–1984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, T.K.; Fu, F.H.; Chung, P.K.; Eston, R.; Lu, K.; Quach, B.; Nie, J.; So, R. The Effect of Inspiratory Muscle Training on High-Intensity, Intermittent Running Performance to Exhaustion. Appl. Physiol. Nutr. Metab. 2008, 33, 671–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holm, P.; Sattler, A.; Fregosi, R. Endurance Training of Respiratory Muscles Improves Cycling Performance in Fit Young Cyclists. BMC Physiol. 2004, 4, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, D.; Kohrt, W.; Bates, B.; Skinner, J. Effects of Respiratory Muscle Endurance Training on Ventilatory and Endurance Performance of Moderately Trained Cyclists*. Int. J. Sports Med. 1987, 8, 88–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wylegala, J.; Pendergast, D.; Gosselin, L.; Warkander, D.; Lundgren, C. Respiratory Muscle Training Improves Swimming Endurance in Divers. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2007, 99, 393–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, M.; Sharpe, G.; Brown, P. Inspiratory Muscle Training Improves Cycling Time-Trial Performance and Anaerobic Work Capacity but Not Critical Power. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2007, 101, 761–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kilding, A.; Brown, S.; McConnell, A. Inspiratory Muscle Training Improves 100 and 200 m Swimming Performance. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2009, 108, 505–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verges, S.; Renggli, A.; Notter, D.; Spengler, C. Effects of Different Respiratory Muscle Training Regimes on Fatigue-Related Variables during Volitional Hyperpnoea. Respir. Physiol. Neurobiol. 2009, 169, 282–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McConnell, A.K.; Romer, L.M. Respiratory Muscle Training in Healthy Humans: Resolving the Controversy. Int. J. Sports Med. 2004, 25, 284–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, H.; Tong, T.K.; Huang, C.; Nie, J.; Lu, K.; Quach, B. Specific Inspiratory Muscle Warm-up Enhances Badminton Footwork Performance. Appl. Physiol. Nutr. Metab. 2007, 32, 1082–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, T.K.; Fu, F.H. Effect of Specific Inspiratory Muscle Warm-up on Intense Intermittent Run to Exhaustion. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2006, 97, 673–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Archiza, B.; Andaku, D.K.; Caruso, F.C.R.; Bonjorno, J.C.; Oliveira, C.R.D.; Ricci, P.A.; Amaral, A.C.D.; Mattiello, S.M.; Libardi, C.A.; Phillips, S.A.; et al. Effects of Inspiratory Muscle Training in Professional Women Football Players: A Randomized Sham-Controlled Trial. J. Sports Sci. 2018, 36, 771–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lomax, M.; Grant, I.; Corbett, J. Inspiratory Muscle Warm-up and Inspiratory Muscle Training: Separate and Combined Effects on Intermittent Running to Exhaustion. J. Sports Sci. 2011, 29, 563–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, T.K.; Fu, F.H.; Eston, R.; Chung, P.K.; Quach, B.; Lu, K. Chronic and Acute Inspiratory Muscle Loading Augment the Effect of a 6-Week Interval Program on Tolerance of High-Intensity Intermittent Bouts of Running. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2010, 24, 3041–3048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leddy, J.; Limprasertkul, A.; Patel, S.; Modlich, F.; Buyea, C.; Pendergast, D.; Lundgren, C. Isocapnic Hyperpnea Training Improves Performance in Competitive Male Runners. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2007, 99, 665–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mickleborough, T.; Nichols, T.; Lindley, M.; Chatham, K.; Ionescu, A. Inspiratory Flow Resistive Loading Improves Respiratory Muscle Function and Endurance Capacity in Recreational Runners. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2009, 20, 458–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gething, A.D.; Williams, M.; Davies, B. Inspiratory Resistive Loading Improves Cycling Capacity: A Placebo-Controlled Trial. Br. J. Sports Med. 2004, 38, 730–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markov, G.; Spengler, C.M.; Knöpfli-Lenzin, C.; Stuessi, C.; Boutellier, U. Respiratory Muscle Training Increases Cycling Endurance without Affecting Cardiovascular Responses to Exercise. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2001, 85, 233–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urrútia, G.; Bonfill, X. PRISMA Declaration: A Proposal to Improve the Publication of Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses. Med. Clin. 2010, 135, 507–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maher, C.; Sherrington, C.; Herbert, R.; Moseley, A.; Elkins, M. Reliability of the PEDro Scale for Rating Quality of Randomized Controlled Trials. Phys. Ther. 2003, 83, 713–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Physiotherapy Evidence Database. Available online: https://www.pedro.org.au/english/downloads/pedro-scale/ (accessed on 15 March 2020).
- Romer, L.M.; McConnell, A.K.; Jones, D.A. Effects of Inspiratory Muscle Training upon Recovery Time during High Intensity, Repetitive Sprint Activity. Int. J. Sports Med. 2002, 23, 353–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicks, C.R.; Morgan, D.W.; Fuller, D.K.; Caputo, J.L. The Influence of Respiratory Muscle Training upon Intermittent Exercise Performance. Int. J. Sports Med. 2009, 30, 16–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes Júnior, A.D.O.; Donzeli, M.A.; Shimano, S.G.N.; de Oliveira, N.M.L.; Ruas, G.; Bertoncello, D. Effects of High-Intensity Inspiratory Muscle Training in Rugby Players. Rev. Bras. Med. do Esporte 2018, 24, 216–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faghy, M.; Brown, P. Whole Body Active Warm-up and Inspiratory Muscle Warm-up Do Not Improve Running Performance When Carrying Thoracic Loads. Appl. Physiol. Nutr. Metab. 2017, 42, 810–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, M.A.; Gregson, I.R.; Mills, D.E.; Gonzalez, J.T.; Sharpe, G.R. Inspiratory Muscle Warm-up Does Not Improve Cycling Time-Trial Performance. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2014, 114, 1821–1830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurić, I.; Labor, S.; Plavec, D.; Labor, M. Inspiratory Muscle Strength Affects Anaerobic Endurance in Professional Athletes. Arh. Hig. Rada Toksikol. 2019, 70, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sperlich, B.; Fricke, H.; de Marées, M.; Linville, J.W.; Mester, J. Does Respiratory Muscle Training Increase Physical Performance? Mil. Med. 2009, 174, 977–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartz, C.S.; Sindorf, M.A.G.; Lopes, C.R.; Batista, J.; Moreno, M.A. Effect of Inspiratory Muscle Training on Performance of Handball Athletes. J. Hum. Kinet. 2018, 63, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chuanye, H.; Hua, L. The Effect of Dyspnea on Badminton Players’ Performance. J. Jilin Inst. Phys. Educ. 2010, 6, 23. [Google Scholar]
- Tranchita, E.; Minganti, C.; Musumeci, L.; Squeo, M.R.; Parisi, A. Inspiratory Muscles Training in Young Basketball Players: Preliminary Evaluation. Med. Dello Sport 2014, 67, 411–422. [Google Scholar]
- Ozmen, T.; Gunes, G.Y.; Ucar, I.; Dogan, H.; Gafuroglu, T.U. Effects of Respiratory Muscle Training on Pulmonary Function and Aerobic Endurance in Soccer Players. J. Sports Med. Phys. Fit. 2017, 57, 507–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romer, L.; McConnell, A. Specificity and Reversibility of Inspiratory Muscle Training. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2003, 35, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| P (Population) | I (Intervention) | C (Comparison) | O (Outcomes) | S (Study Design) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Subjects who practice intermittent sports modalities | Use of RMT and/or IMT | Same conditions with placebo and/or control groups | Increase in performance | Randomized controlled trial (RCT) |
| First Author, Year | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | Total | Quality |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Romer, 2002 [58] | Yes | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 9 | Excellent | |
| Tong, 2006 [47] | Yes | 1 | - | - | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 5 | Fair | |||
| Lin, 2007 [46] | Yes | 1 | - | - | - | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 5 | Fair | ||
| Tong, 2008 [38] | Yes | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 7 | Good | |||
| Nicks, 2009 [59] | Yes | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 6 | Good | ||||
| Tong, 2010 [50] | Yes | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 6 | Good | ||||
| Guy, 2014 [32] | Yes | 1 | - | 1 | 1 | - | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 7 | Good | |
| Archiza, 2017 [48] | Yes | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 8 | Good | ||
| Nunes Júnior, 2018 [60] | Yes | 1 | 1 | 1 | - | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 8 | Good | ||
| Najafi, 2019 [37] | Yes | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 6 | Good |
| First Author, Year | M/F | Age in Years (SD) | VO2max (mL/kg/min) | Sport | Competitive Level |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Romer, 2002 [58] | 24/0 | E = 21.3 (1.1) P = 20.2 (0.7) | E = 56.3 (0.9) P = 55.8 (1.7) | Football, rugby, field hockey, and basketball | Recreational and semi-professional |
| Tong, 2006 [47] | 10/0 | T = 21.3 (1.2) | T = 62.9 (4.2) | Football and rugby | Recreational |
| Lin, 2007 [46] | 10/0 | T = 23.0 (2.0) | T = 51.0 (6.0) | Badminton | Recreational |
| Tong, 2008 [38] | 30/0 | E = 21.3 (0.9) P = 21.5 (2.1) C = 22.0 (1.9) | E = 60.8 (4.7) P = 55.8 (7.9) C = 59.1 (5.2) | Football and rugby | Recreational |
| Nicks, 2009 [59] | 20/7 | E = 19.8 (0.9) C = 19.9 (1.3) | Not reported | Football | Professional |
| Tong, 2010 [50] | 18/0 | E = 21.1 (1.1) C = 22.3 (1.0) | E = 59.0 (6.3) C = 58.1 (4.5) | Football and rugby | Recreational |
| Guy, 2014 [32] | 31/0 | E = 26.6 (8.2) P = 23.9 (6.7) C = 21.3 (4.9) | E = 44.0 (6.7) P = 42.9 (8.7) C = 46.3 (6.2) | Football | Recreational |
| Archiza, 2017 [48] | 0/18 | E = 22.0 (3.9) P = 20.1 (2.0) | E = 41.2 (4.0) P = 41.7 (3.8) | Football | Professional |
| Nunes Júnior, 2018 [60] | 20/0 | E = 22.0 (4.0) C = 23.0 (2.0) | Not reported | Rugby | Recreational |
| Najafi, 2019 [37] | 30/0 | E1 = 16.5 (0.7) E2 = 16.7 (0.5) P = 16.7 (0.8) | Not reported | Football | Semi-professional |
| First Author, Year | Type of Training | Starting Intensity | Progression of Training Intensity | Number of Sessions per Week | Number of Weeks | Duration of Exercise | Supervision | Control/Placebo | Specific Test | Main Results of the Analyzed Variables |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Romer, 2002 [58] | POWERbreathe (threshold) | 50% MIP | Progressive increase, until they can only do 30 repetitions | 2 sessions daily, 7 days per week | 6 weeks | 30 inspirations | Supervised | Placebo: 1 session of 60 inspirations at 15% MIP | RSA | ↑ PIF (≈20%) ↑ MIP (≈33%) ↑ Performance (≈7%) |
| Tong, 2006 [47] | POWERbreathe (threshold) | 40% MIP | No progression | 2 pre-test sessions | Only 1 test | 30 inspirations | Supervised | Placebo: same protocol, but at 15% MIP Control: no intervention | Yo-Yo intermittent recovery test | ↑ MIP (≈9%) ↑ Vmax (≈5%) ↑ WImax (≈21%) ↑ Popt (≈16%) ↑ MRPD (≈13%) ↓ RPB/4i (≈22%) ↑ Performance (≈19%) |
| Lin, 2007 [46] | POWERbreathe (threshold) | 40% MIP | No progression | 2 pre-test sessions | Only 1 test | 30 inspirations | Supervised | Placebo: same protocol, but at 15% MIP Control: no intervention | Badminton-footwork test | ↑ P0 (≈8%) ↑ MRPD (≈9%) ↓ RPB/min (≈7%) ↑ Performance (≈7%) |
| Tong, 2008 [38] | POWERbreathe (threshold) | 50% MIP | Increase of 10 or 15 cmH2O when 30 repetitions are performed without stopping | 2 sessions daily, 6 days per week | 6 weeks | 30 inspirations | Supervised | Placebo: same protocol, but at 15% MIP Control: no intervention | Yo-Yo intermittent recovery test | ↑ P0 (≈32%) ↑ WImax (≈40%) ↑ Popt (≈38%) ↑ MRPD (≈39%) ↓ RPE/4i (≈11%) ↓ RPB/4i (≈12%) ↓ 20 m VE (≈10%) ↓ 20 m VT/ti (≈8%) ↑ Performance (≈16%) |
| Nicks, 2009 [59] | PowerLung (threshold) | 50% MIP | Progressive increase once or twice a week, until they can only do 30 repetitions | 2 sessions daily, 5 days per week | 5 weeks | 30 inspirations | Normally supervised, when not, participants submitted training logs | Control: no intervention | RSA | ↑ MIP (≈20%) ↑ Performance (≈17%) |
| Tong, 2010 [50] | POWERbreathe (threshold) | EIMT = 50% MIP EWU = 40% MIP | Increase of 10 or 15 cm H2O when 30 repetitions are performed without stopping | EIMT = 2 sessions daily, 6 days per week EWU = 2 pre-test sessions | EIMT = 4 weeks EWU = 6 weeks | 30 inspirations | Not reported | Control: no intervention | Yo-Yo intermittent recovery test | ↑ P0 (≈20%) ↓ RPE (≈8%) ↓ RPB (≈16%) ↓ 20 m VE (≈10%) ↓ 20 m VE/VO2 (≈8%) ↓ 20 m VT/Ti (≈10%) ↓ 10 s VE (≈10%) ↓ 10 s VE/VO2 (≈5%) ↑ Performance1 (≈31%) ↑ Performance2 (200 m, ≈ 25%; 600 m, ≈ 53%; 800 m, ≈ 36%) |
| Guy, 2014 [32] | POWERbreathe (threshold) | 55% MIP | No progression | 2 sessions daily, 2 days per week | 6 weeks | 30 inspirations | Not reported | Placebo: same protocol, but at 15% MIP Control: no intervention | SSFT | ↑ MIP (≈13%) ↓ Blood lactate (≈32%) |
| Archiza, 2017 [48] | POWERbreathe (threshold) | 50% MIP | Progressive increase every week | 2 sessions daily, 5 days per week | 6 weeks | 30 inspirations | Supervised | Placebo: same protocol, but at 15% MIP | RSA | ↑ MIP (≈22%) ↓ RSABEST (≈4%) ↓ RSAMEAN (≈6%) ↓ RSADEC (≈30%) |
| Nunes Júnior, 2018 [60] | Breather Plus IMT Power (threshold) | 80% MIP | Progressive increase from the fourth training session | 3 sessions per week | 12 weeks | 30 inspirations | Supervised | Control: same protocol but without resistance | Yo-Yo intermittent recovery test | ↑ MVV (22%) ↑ MIP (≈29%) ↑ MEP (≈32%) ↑ Performance (≈14%) |
| Najafi, 2019 [37] | POWERbreathe (threshold) | E1 = 55% MIP E2 = 45% MIP | Progressive increase once a week | 2 sessions daily, 5 days per week | 8 weeks | E1 = 25–35 inspirations E2 = 45–55 inspirations | Supervised | Placebo: 30 inspirations at 15% MIP | Yo-Yo intermittent recovery test | ↑ MIP (E1: 27.2%; E2: 30.6%) ↓ RPE (E1: 26.9%; E2: 28.9%) ↓ RPB (E1: 62.1%; E2: 56.3%) ↓ Lactate (E1: 29.4%; E2: 27.5) ↓ Fatigue index (E1: 34.4%; E2: 40.6%) ↑ Performance (E1: 8.9%; E2: 8.1%) |
| Monday | Tuesday | Wednesday | Thursday | Friday | Saturday | Sunday |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chronic IMT, performing one session in the morning and another at night | Chronic IMT, performing one session in the morning and another at night | Chronic IMT, performing one session in the morning and another at night | Acute IMT, performing both sessions in the locker room, before going out to train | Chronic IMT, performing one session in the morning and another at night | Chronic IMT, performing one session in the morning and another at night | Acute IMT, performing both sessions in the locker room, before going out to pre-game warm-up |
| Training | Rest | Training | Training | Training | Activation | Match |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lorca-Santiago, J.; Jiménez, S.L.; Pareja-Galeano, H.; Lorenzo, A. Inspiratory Muscle Training in Intermittent Sports Modalities: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 4448. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17124448
Lorca-Santiago J, Jiménez SL, Pareja-Galeano H, Lorenzo A. Inspiratory Muscle Training in Intermittent Sports Modalities: A Systematic Review. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2020; 17(12):4448. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17124448
Chicago/Turabian StyleLorca-Santiago, Juan, Sergio L. Jiménez, Helios Pareja-Galeano, and Alberto Lorenzo. 2020. "Inspiratory Muscle Training in Intermittent Sports Modalities: A Systematic Review" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 17, no. 12: 4448. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17124448
APA StyleLorca-Santiago, J., Jiménez, S. L., Pareja-Galeano, H., & Lorenzo, A. (2020). Inspiratory Muscle Training in Intermittent Sports Modalities: A Systematic Review. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 17(12), 4448. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17124448








