Energy System Contributions and Physical Activity in Specific Age Groups during Exergames
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Study Design
2.3. Exergames Procedures
2.4. Physiological Measurements
2.5. Calculating Energy System Contributions
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Physiological Parameters
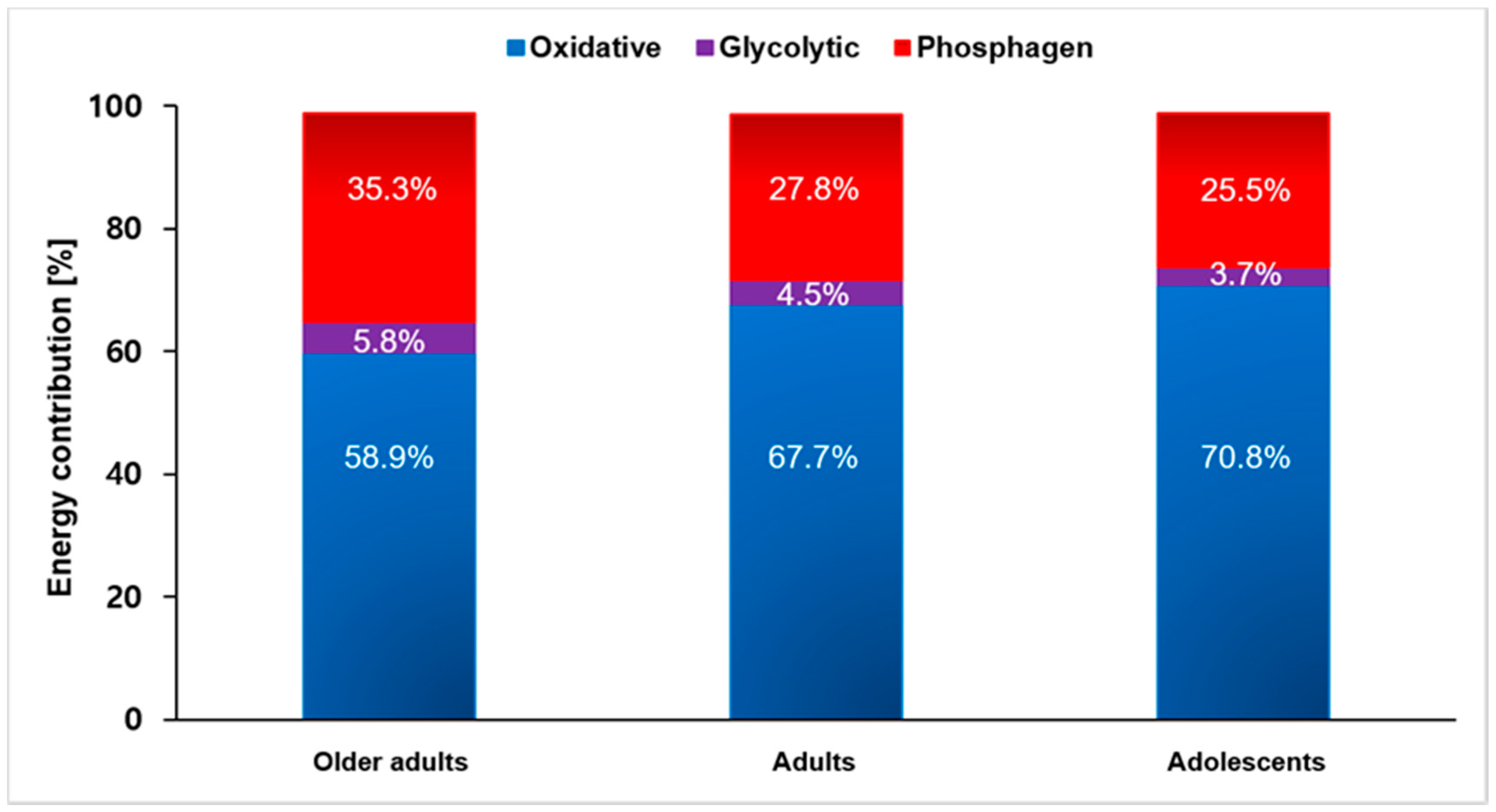
3.2. Energy System Contributions
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kruger, R. Proteomics insights on how physical inactivity can influence cardiovascular health. Eur. J. Prev. Cardiol. 2019, 26, 1862–1864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilmot, E.G.; Edwardson, C.L.; Achana, F.A.; Davies, M.J.; Gorely, T.; Gray, L.J.; Khunti, K.; Yates, T.; Biddle, S.J. Sedentary time in adults and the association with diabetes, cardiovascular disease and death: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabetologia 2012, 55, 2895–2905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunstan, D.W.; Barr, E.L.; Healy, G.N.; Salmon, J.; Shaw, J.E.; Balkau, B.; Magliano, D.J.; Cameron, A.J.; Zimmet, P.Z.; Owen, N. Television viewing time and mortality: The Australian Diabetes, Obesity and Lifestyle Study (AusDiab). Circulation 2010, 121, 384–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, S.W.; Kim, S.H.; Kang, S.H.; Kim, H.J.; Yoon, C.H.; Youn, T.J.; Chae, I.H. Mortality reduction with physical activity in patients with and without cardiovascular disease. Eur. Heart J. 2019, 40, 3547–3555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kabir, M.; Dhruba, Q.F.F.; Mahmud, H.; Hasan, M.K.; Zaman, A.R. Gaming Insight: Conversion of Popular Sedentary Games into Motion-Based Form. Int. J. Hum. Comput. Int. 2020, 36, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, W.; Lin, J.H.; Crouse, J. Is playing exergames really exercising? A meta-analysis of energy expenditure in active video games. Cyberpsychol. Behav. Soc. Netw. 2011, 14, 681–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, W.; Crouse, J.C.; Lin, J.H. Using active video games for physical activity promotion: A systematic review of the current state of research. Health Educ. Behav. 2013, 40, 171–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Best, J.R. Exergaming in Youth: Effects on Physical and Cognitive Health. Z. Psychol. 2013, 221, 72–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, L.M.; Kerse, N.; Frakking, T.; Maddison, R. Active Video Games for Improving Physical Performance Measures in Older People: A Meta-analysis. J. Geriatr. Phys. Ther. 2018, 41, 108–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaput, J.P.; Genin, P.M.; Le Moel, B.; Pereira, B.; Boirie, Y.; Duclos, M.; Thivel, D. Lean adolescents achieve higher intensities but not higher energy expenditure while playing active video games compared with obese ones. Pediatr. Obes. 2016, 11, 102–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owen, N.; Healy, G.H.; Matthews, C.E.; Dunstan, D.W. Too Much Sitting: The Population-Health Science of Sedentary Behavior. Exerc. Sport Sci. Rev. 2010, 38, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tremblay, M.S.; Colley, R.C.; Saunders, T.J.; Healy, G.N.; Owen, N. Physiological and health implications of a sedentary lifestyle. Appl. Physiol. Nutr. Metab. 2010, 35, 725–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Z.; Chen, S.; Pasco, D.; Pope, Z. A meta-analysis of active video games on health outcomes among children and adolescents. Obes. Rev. 2015, 16, 783–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monedero, J.; McDonnell, A.C.; Keoghan, M.; O’Gorman, D.J. Modified Active Videogame Play Results in Moderate-Intensity Exercise. Games Health J. 2014, 3, 234–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graves, L.E.; Ridgers, N.D.; Williams, K.; Stratton, G.; Atkinson, G.; Cable, N.T. The physiological cost and enjoyment of Wii Fit in adolescents, young adults, and older adults. J. Phys. Act. Health 2010, 7, 393–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, F.A.; Bertuzzi, R.; Dourado, A.C.; Santos, V.G.; Franchini, E. Energy demands in taekwondo athletes during combat simulation. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2012, 112, 1221–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Campos Mello, F.; de Moraes Bertuzzi, R.C.; Grangeiro, P.M.; Franchini, E. Energy systems contributions in 2,000 m race simulation: A comparison among rowing ergometers and water. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2009, 107, 615–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- di Prampero, P.E.; Ferretti, G. The energetics of anaerobic muscle metabolism: A reappraisal of older and recent concepts. Respir. Physiol. 1999, 118, 103–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gastin, P.B. Energy system interaction and relative contribution during maximal exercise. Sports Med. 2001, 31, 725–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomczak, M.; Tomczak, E. The need to report effect size estimates revisited. An overview of some recommended measures of effect size. Trends Sport Sci. 2014, 1, 19–25. [Google Scholar]
- Yigit, S.; Mendes, M. Which Effect Size Measure is Appropriate for One-Way and Two-Way ANOVA Models? A Monte Carlo Simulation Study. Stat. J. 2018, 16, 295–313. [Google Scholar]
- Brooks, G.A. The lactate shuttle during exercise and recovery. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 1986, 18, 360–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brooks, G.A. The Science and Translation of Lactate Shuttle Theory. Cell Metab. 2018, 27, 757–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClelland, G.B.; Khanna, S.; González, G.F.; Butz, C.E.; Brooks, G.A. Peroxisomal membrane monocarboxylate transporters: Evidence for a redox shuttle system? Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2003, 304, 130–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monedero, J.; Murphy, E.E.; O’Gorman, D.J. Energy expenditure and affect responses to different types of active video game and exercise. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0176213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Older Adults (n = 26) | Adults (n = 24) | Adolescents (n = 24) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 75.4 ± 4.4 | 27.8 ± 3.3 | 14 ± 0.8 |
| Body mass (kg) | 59.4 ± 8.7 | 73.4 ± 17.8 | 71.3 ± 11.5 |
| Height (cm) | 157.2 ± 8.6 | 170.9 ± 11.9 | 173.3 ± 5.2 |
| HRmean (beats·min−1) | 105.3 ± 18.8 | 122.8 ± 15.9 a,*** | 119.7 ± 13.4 a,** |
| HRpeak (beats·min−1) | 115.1 ± 19.6 | 132.4 ± 18.4 a,* | 126.3 ± 12.9 |
| VO2mean (mL·kg−1·min−1) | 14.1 ± 3.7 | 16.3 ± 3.1 | 16.9 ± 3.1 a * |
| VO2peak (mL·kg−1·min−1) | 19.2 ± 4.9 | 19.9 ± 3.8 | 20.6 ± 4.1 |
| Peak La− (mmol·L−1) | 2.3 ± 1.3 | 2.0 ± 0.9 | 1.6 ± 0.4 a * |
| ∆La− (mmol·L−1) | 1.0 ± 1.1 | 0.7 ± 6.0 | 0.6 ± 0.3 |
| WPCR (kJ) | 20.0 ± 10.9 | 20.7 ± 11.5 | 20.9 ± 22.7 |
| WPCR (%) | 35.3 ± 7.7 | 27.8 ± 7.5 | 25.5 ± 14.5 a *** |
| WLa− (kJ) | 3.7 ± 4.1 | 3.5 ± 3.6 | 2.5 ± 1.4 |
| WLa− (%) | 5.8 ± 4.3 | 4.5 ± 2.7 | 3.7 ± 2.1 |
| WAER (kJ) | 31.7 ± 10.7 | 47.9 ± 15.6 a *** | 46.9 ± 8.2 a *** |
| WAER (%) | 58.9 ± 9.7 | 67.7 ± 7.5 | 70.8 ± 14.4 a *** |
| WTOTAL (kJ) | 55.4 ± 23.2 | 72.1 ± 28 a * | 70.3 ± 24.1 a * |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Park, S.-B.; Kim, M.; Lee, E.; Lee, D.; Son, S.J.; Hong, J.; Yang, W.-H. Energy System Contributions and Physical Activity in Specific Age Groups during Exergames. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 4905. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17134905
Park S-B, Kim M, Lee E, Lee D, Son SJ, Hong J, Yang W-H. Energy System Contributions and Physical Activity in Specific Age Groups during Exergames. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2020; 17(13):4905. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17134905
Chicago/Turabian StylePark, Seung-Bo, Minjun Kim, Eunseok Lee, Doowon Lee, Seong Jun Son, Junggi Hong, and Woo-Hwi Yang. 2020. "Energy System Contributions and Physical Activity in Specific Age Groups during Exergames" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 17, no. 13: 4905. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17134905
APA StylePark, S.-B., Kim, M., Lee, E., Lee, D., Son, S. J., Hong, J., & Yang, W.-H. (2020). Energy System Contributions and Physical Activity in Specific Age Groups during Exergames. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 17(13), 4905. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17134905









